
- Matplotlib 基礎
- Matplotlib - 首頁
- Matplotlib - 簡介
- Matplotlib - 與Seaborn的比較
- Matplotlib - 環境搭建
- Matplotlib - Anaconda發行版
- Matplotlib - Jupyter Notebook
- Matplotlib - Pyplot API
- Matplotlib - 簡單繪圖
- Matplotlib - 儲存圖形
- Matplotlib - 標記
- Matplotlib - 圖形
- Matplotlib - 樣式
- Matplotlib - 圖例
- Matplotlib - 顏色
- Matplotlib - 顏色圖
- Matplotlib - 顏色圖歸一化
- Matplotlib - 選擇顏色圖
- Matplotlib - 顏色條
- Matplotlib - 文字
- Matplotlib - 文字屬性
- Matplotlib - 子圖示題
- Matplotlib - 圖片
- Matplotlib - 圖片蒙版
- Matplotlib - 註釋
- Matplotlib - 箭頭
- Matplotlib - 字型
- Matplotlib - 什麼是字型?
- 全域性設定字型屬性
- Matplotlib - 字型索引
- Matplotlib - 字型屬性
- Matplotlib - 比例尺
- Matplotlib - 線性與對數比例尺
- Matplotlib - 對稱對數與Logit比例尺
- Matplotlib - LaTeX
- Matplotlib - 什麼是LaTeX?
- Matplotlib - 用於數學表示式的LaTeX
- Matplotlib - 註釋中的LaTeX文字格式
- Matplotlib - PostScript
- 啟用註釋中的LaTeX渲染
- Matplotlib - 數學表示式
- Matplotlib - 動畫
- Matplotlib - 繪圖元素
- Matplotlib - 使用Cycler進行樣式設定
- Matplotlib - 路徑
- Matplotlib - 路徑效果
- Matplotlib - 變換
- Matplotlib - 刻度和刻度標籤
- Matplotlib - 弧度刻度
- Matplotlib - 日期刻度
- Matplotlib - 刻度格式化器
- Matplotlib - 刻度定位器
- Matplotlib - 基本單位
- Matplotlib - 自動縮放
- Matplotlib - 反轉座標軸
- Matplotlib - 對數座標軸
- Matplotlib - Symlog
- Matplotlib - 單位處理
- Matplotlib - 帶單位的橢圓
- Matplotlib - 脊柱
- Matplotlib - 座標軸範圍
- Matplotlib - 座標軸比例尺
- Matplotlib - 座標軸刻度
- Matplotlib - 座標軸格式化
- Matplotlib - Axes 類
- Matplotlib - 雙座標軸
- Matplotlib - Figure 類
- Matplotlib - 多圖
- Matplotlib - 網格
- Matplotlib - 面向物件介面
- Matplotlib - PyLab 模組
- Matplotlib - subplots() 函式
- Matplotlib - subplot2grid() 函式
- Matplotlib - 固定位置的繪圖元素
- Matplotlib - 手動等高線
- Matplotlib - 座標報告
- Matplotlib - AGG 過濾器
- Matplotlib - 飄帶框
- Matplotlib - 填充螺旋線
- Matplotlib - findobj 演示
- Matplotlib - 超連結
- Matplotlib - 圖片縮圖
- Matplotlib - 使用關鍵字繪圖
- Matplotlib - 建立Logo
- Matplotlib - 多頁PDF
- Matplotlib - 多程序
- Matplotlib - 列印標準輸出
- Matplotlib - 複合路徑
- Matplotlib - Sankey 類
- Matplotlib - MRI 與 EEG
- Matplotlib - 樣式表
- Matplotlib - 背景顏色
- Matplotlib - Basemap
- Matplotlib 事件處理
- Matplotlib - 事件處理
- Matplotlib - 關閉事件
- Matplotlib - 滑鼠移動
- Matplotlib - 點選事件
- Matplotlib - 滾動事件
- Matplotlib - 按鍵事件
- Matplotlib - 選擇事件
- Matplotlib - 視鏡
- Matplotlib - 路徑編輯器
- Matplotlib - 多邊形編輯器
- Matplotlib - 定時器
- Matplotlib - 視窗限制
- Matplotlib - 縮放視窗
- Matplotlib 視窗部件
- Matplotlib - 游標視窗部件
- Matplotlib - 帶註釋的游標
- Matplotlib - 按鈕視窗部件
- Matplotlib - 複選框
- Matplotlib - 套索選擇器
- Matplotlib - 選單視窗部件
- Matplotlib - 滑鼠游標
- Matplotlib - 多游標
- Matplotlib - 多邊形選擇器
- Matplotlib - 單選按鈕
- Matplotlib - 範圍滑塊
- Matplotlib - 矩形選擇器
- Matplotlib - 橢圓選擇器
- Matplotlib - 滑塊視窗部件
- Matplotlib - 區間選擇器
- Matplotlib - 文字框
- Matplotlib 繪圖
- Matplotlib - 條形圖
- Matplotlib - 直方圖
- Matplotlib - 餅圖
- Matplotlib - 散點圖
- Matplotlib - 箱線圖
- Matplotlib - 小提琴圖
- Matplotlib - 等高線圖
- Matplotlib - 3D 繪圖
- Matplotlib - 3D 等高線
- Matplotlib - 3D 線框圖
- Matplotlib - 3D 表面圖
- Matplotlib - 矢羽圖
- Matplotlib 有用資源
- Matplotlib - 快速指南
- Matplotlib - 有用資源
- Matplotlib - 討論
Matplotlib - 視窗限制
Viewlims 或 視窗限制 指的是沿 x 軸和 y 軸在繪圖中顯示的資料範圍。視窗限制對於互動式資料視覺化非常有用,因為它允許使用者動態調整資料的顯示。
Matplotlib 提供了各種方法和工具來互動式地設定和更新視窗限制,使使用者能夠有效地探索和分析資料。一般情況下,在 matplotlib 繪圖中,視窗限制會根據正在繪製的資料自動確定。
本教程將逐步實現如何在 Matplotlib 繪圖中使用視窗限制建立互動式縮放功能,以建立與使用者互動相對應的動態視覺化。
建立互動式縮放繪圖
建立一個類,當我們放大時重新生成分形集(曼德布羅集是數學中著名的分形),允許我們觀察越來越多的細節。此外,我們將在左側面板中顯示一個框,以顯示我們縮放到的區域。
此類定義了compute_image方法,根據提供的邊界計算曼德布羅集。而axes_update方法根據當前視窗限制更新繪圖。它確保每當視窗限制更改時,都會重新計算和重繪曼德布羅集。
class InteractiveFractal:
def __init__(self, h=500, w=500, niter=50, radius=2., power=2):
self.height = h
self.width = w
self.niter = niter
self.radius = radius
self.power = power
def compute_image(self, xstart, xend, ystart, yend):
self.x = np.linspace(xstart, xend, self.width)
self.y = np.linspace(ystart, yend, self.height).reshape(-1, 1)
c = self.x + 1.0j * self.y
threshold_time = np.zeros((self.height, self.width))
z = np.zeros(threshold_time.shape, dtype=complex)
mask = np.ones(threshold_time.shape, dtype=bool)
for i in range(self.niter):
z[mask] = z[mask]**self.power + c[mask]
mask = (np.abs(z) < self.radius)
threshold_time += mask
return threshold_time
def axes_update(self, ax):
ax.set_autoscale_on(False)
self.width, self.height = \
np.round(ax.patch.get_window_extent().size).astype(int)
vl = ax.viewLim
extent = vl.x0, vl.x1, vl.y0, vl.y1
im = ax.images[-1]
im.set_data(self.compute_image(*extent))
im.set_extent(extent)
ax.figure.canvas.draw_idle()
更新視窗限制
我們將建立一個類UpdateRectangle來建立一個矩形,該矩形代表我們在曼德布羅集中縮放到的區域。此類擴充套件了Rectangle類,並用於在視窗限制更改時更新表示縮放區域的矩形。當我們在左側面板放大時,矩形將更新其形狀以匹配座標軸的邊界。
class UpdateRectangle(Rectangle):
def __call__(self, ax):
self.set_bounds(*ax.viewLim.bounds)
ax.figure.canvas.draw_idle()
連接回調函式
回撥函式連線到第二個子圖 (ax2) 的xlim_changed 和ylim_changed 事件。每當視窗限制更改時,這些回撥函式都會觸發矩形和曼德布羅集的更新。
# Connect for changing the view limits
ax2.callbacks.connect('xlim_changed', rect)
ax2.callbacks.connect('ylim_changed', rect)
ax2.callbacks.connect('xlim_changed', md.ax_update)
ax2.callbacks.connect('ylim_changed', md.ax_update)
以下是完整程式碼
曼德布羅集最初繪製在兩個子圖 (ax1 和 ax2) 中。表示縮放區域的矩形新增到 ax1,並且回撥函式連線到 ax2 以處理視窗限制更改。
示例
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.patches import Rectangle
class UpdateRectangle(Rectangle):
def __call__(self, ax):
self.set_bounds(*ax.viewLim.bounds)
ax.figure.canvas.draw_idle()
class InteractiveFractal:
def __init__(self, h=500, w=500, niter=50, radius=2., power=2):
self.height = h
self.width = w
self.niter = niter
self.radius = radius
self.power = power
def compute_image(self, xstart, xend, ystart, yend):
self.x = np.linspace(xstart, xend, self.width)
self.y = np.linspace(ystart, yend, self.height).reshape(-1, 1)
c = self.x + 1.0j * self.y
threshold_time = np.zeros((self.height, self.width))
z = np.zeros(threshold_time.shape, dtype=complex)
mask = np.ones(threshold_time.shape, dtype=bool)
for i in range(self.niter):
z[mask] = z[mask]**self.power + c[mask]
mask = (np.abs(z) < self.radius)
threshold_time += mask
return threshold_time
def axes_update(self, ax):
ax.set_autoscale_on(False)
self.width, self.height = \
np.round(ax.patch.get_window_extent().size).astype(int)
vl = ax.viewLim
extent = vl.x0, vl.x1, vl.y0, vl.y1
im = ax.images[-1]
im.set_data(self.compute_image(*extent))
im.set_extent(extent)
ax.figure.canvas.draw_idle()
md = InteractiveFractal()
Z = md.compute_image(-2., 0.5, -1.25, 1.25)
fig1, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(7, 4))
ax1.imshow(Z, origin='lower',
extent=(md.x.min(), md.x.max(), md.y.min(), md.y.max()))
ax2.imshow(Z, origin='lower',
extent=(md.x.min(), md.x.max(), md.y.min(), md.y.max()))
rect = UpdateRectangle(
[0, 0], 0, 0, facecolor='none', edgecolor='black', linewidth=1.0)
rect.set_bounds(*ax2.viewLim.bounds)
ax1.add_patch(rect)
# Connect for changing the view limits
ax2.callbacks.connect('xlim_changed', rect)
ax2.callbacks.connect('ylim_changed', rect)
ax2.callbacks.connect('xlim_changed', md.axes_update)
ax2.callbacks.connect('ylim_changed', md.axes_update)
ax2.set_title("Zoom here")
plt.show()
輸出
執行上述程式後,您將得到以下輸出:
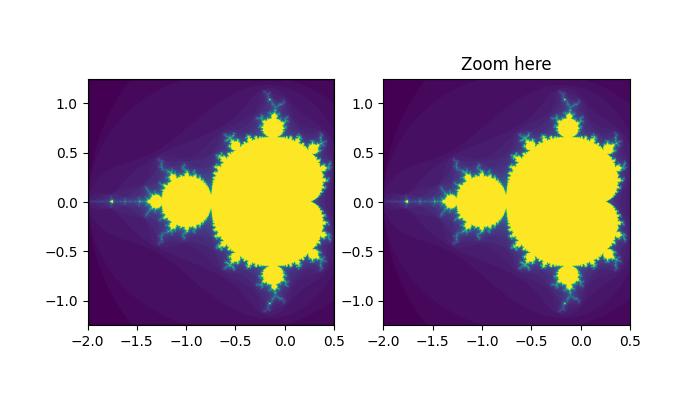 觀看下面的影片以瞭解視窗限制在此處的運作方式:
觀看下面的影片以瞭解視窗限制在此處的運作方式:
廣告