
- Matplotlib 基礎
- Matplotlib - 首頁
- Matplotlib - 簡介
- Matplotlib - 與 Seaborn 的比較
- Matplotlib - 環境設定
- Matplotlib - Anaconda 發行版
- Matplotlib - Jupyter Notebook
- Matplotlib - Pyplot API
- Matplotlib - 簡單繪圖
- Matplotlib - 儲存圖形
- Matplotlib - 標記
- Matplotlib - 圖形
- Matplotlib - 樣式
- Matplotlib - 圖例
- Matplotlib - 顏色
- Matplotlib - 色圖
- Matplotlib - 色圖歸一化
- Matplotlib - 選擇色圖
- Matplotlib - 色標
- Matplotlib - 文字
- Matplotlib - 文字屬性
- Matplotlib - 子圖示題
- Matplotlib - 影像
- Matplotlib - 影像蒙版
- Matplotlib - 註釋
- Matplotlib - 箭頭
- Matplotlib - 字型
- Matplotlib - 什麼是字型?
- 全域性設定字型屬性
- Matplotlib - 字型索引
- Matplotlib - 字型屬性
- Matplotlib - 刻度
- Matplotlib - 線性與對數刻度
- Matplotlib - 對稱對數與 Logit 刻度
- Matplotlib - LaTeX
- Matplotlib - 什麼是 LaTeX?
- Matplotlib - LaTeX 用於數學表示式
- Matplotlib - LaTeX 在註釋中的文字格式化
- Matplotlib - PostScript
- 在註釋中啟用 LaTeX 渲染
- Matplotlib - 數學表示式
- Matplotlib - 動畫
- Matplotlib - 圖形物件
- Matplotlib - 使用 Cycler 進行樣式設定
- Matplotlib - 路徑
- Matplotlib - 路徑效果
- Matplotlib - 座標變換
- Matplotlib - 刻度和刻度標籤
- Matplotlib - 弧度刻度
- Matplotlib - 日期刻度
- Matplotlib - 刻度格式化器
- Matplotlib - 刻度定位器
- Matplotlib - 基本單位
- Matplotlib - 自動縮放
- Matplotlib - 反轉軸
- Matplotlib - 對數軸
- Matplotlib - Symlog
- Matplotlib - 單位處理
- Matplotlib - 帶單位的橢圓
- Matplotlib - 脊柱
- Matplotlib - 軸範圍
- Matplotlib - 軸刻度
- Matplotlib - 軸刻度
- Matplotlib - 格式化軸
- Matplotlib - Axes 類
- Matplotlib - 雙軸
- Matplotlib - Figure 類
- Matplotlib - 多圖
- Matplotlib - 網格
- Matplotlib - 面向物件介面
- Matplotlib - PyLab 模組
- Matplotlib - Subplots() 函式
- Matplotlib - Subplot2grid() 函式
- Matplotlib - 錨定圖形物件
- Matplotlib - 手動等值線
- Matplotlib - 座標報告
- Matplotlib - AGG 過濾器
- Matplotlib - 帶狀框
- Matplotlib - 填充螺旋線
- Matplotlib - Findobj 演示
- Matplotlib - 超連結
- Matplotlib - 影像縮圖
- Matplotlib - 使用關鍵字繪圖
- Matplotlib - 建立 Logo
- Matplotlib - 多頁 PDF
- Matplotlib - 多程序
- Matplotlib - 列印標準輸出
- Matplotlib - 複合路徑
- Matplotlib - Sankey 類
- Matplotlib - MRI 與 EEG
- Matplotlib - 樣式表
- Matplotlib - 背景顏色
- Matplotlib - Basemap
- Matplotlib 事件處理
- Matplotlib - 事件處理
- Matplotlib - 關閉事件
- Matplotlib - 滑鼠移動
- Matplotlib - 點選事件
- Matplotlib - 滾動事件
- Matplotlib - 按鍵事件
- Matplotlib - 選擇事件
- Matplotlib - 透鏡
- Matplotlib - 路徑編輯器
- Matplotlib - 多邊形編輯器
- Matplotlib - 定時器
- Matplotlib - Viewlims
- Matplotlib - 縮放視窗
- Matplotlib 小部件
- Matplotlib - 游標小部件
- Matplotlib - 帶註釋的游標
- Matplotlib - 按鈕小部件
- Matplotlib - 複選框
- Matplotlib - 套索選擇器
- Matplotlib - 選單小部件
- Matplotlib - 滑鼠游標
- Matplotlib - 多游標
- Matplotlib - 多邊形選擇器
- Matplotlib - 單選按鈕
- Matplotlib - 範圍滑塊
- Matplotlib - 矩形選擇器
- Matplotlib - 橢圓選擇器
- Matplotlib - 滑塊小部件
- Matplotlib - 跨度選擇器
- Matplotlib - 文字框
- Matplotlib 繪圖
- Matplotlib - 條形圖
- Matplotlib - 直方圖
- Matplotlib - 餅圖
- Matplotlib - 散點圖
- Matplotlib - 箱線圖
- Matplotlib - 小提琴圖
- Matplotlib - 等值線圖
- Matplotlib - 3D 繪圖
- Matplotlib - 3D 等值線
- Matplotlib - 3D 線框圖
- Matplotlib - 3D 曲面圖
- Matplotlib - 矢羽圖
- Matplotlib 有用資源
- Matplotlib - 快速指南
- Matplotlib - 有用資源
- Matplotlib - 討論
Matplotlib - 滑鼠移動
在一般的計算機程式設計和軟體設計中,術語滑鼠移動指的是將計算機滑鼠裝置在表面上移動以在螢幕上建立相應的滑鼠游標或指標移動的動作。
Matplotlib 中的滑鼠移動
Matplotlib 中的滑鼠移動事件允許使用者捕獲游標在繪製圖形上的位置。此功能能夠建立互動式功能,例如在游標位置顯示資訊或根據游標的移動即時更新視覺化。
在本教程中,我們將探討如何在 Matplotlib 中使用滑鼠移動事件來增強互動式繪圖。這是透過連線到motion_notify_event來完成的,您可以捕獲游標的位置並實現各種操作,為使用者提供一種直觀的方式來探索和分析繪製的資料。
示例
讓我們從一個簡單的示例開始,該示例在滑鼠移動到輸出圖形上時列印資料和畫素座標。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Input data for ploting a circle
angs = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 10**6)
rs = np.zeros_like(angs) + 1
xs = rs * np.cos(angs)
ys = rs * np.sin(angs)
# Create a figure
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 4))
# Plot the data
plt.plot(xs, ys)
# Function to handle the event
def on_move(event):
if event.inaxes:
print(f'data coords {event.xdata}, {event.ydata},',
f'pixel coords {event.x}, {event.y}')
# connect the event with the callable function
binding_id = plt.connect('motion_notify_event', on_move)
# Display the plot
plt.show()
輸出
執行上述程式後,您將獲得以下輸出:
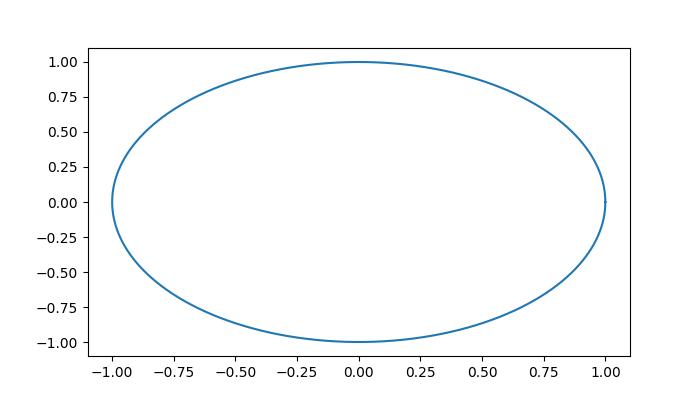
從上圖中,您可以連續讀取滑鼠移動時的座標:
data coords 0.22000000000192466, 0.8999999999988899, pixel coords 413, 324 data coords 0.21188940092360364, 0.9071428571417381, pixel coords 411, 325 data coords 0.20377880184528263, 0.9142857142845864, pixel coords 409, 326 data coords 0.19972350230612212, 0.9214285714274346, pixel coords 408, 327 data coords 0.1916129032278011, 0.9214285714274346, pixel coords 406, 327 data coords 0.1916129032278011, 0.9285714285702829, pixel coords 406, 328 data coords 0.18755760368864083, 0.9285714285702829, pixel coords 405, 328 data coords 0.18350230414948032, 0.9357142857131315, pixel coords 404, 329 data coords 0.17944700461031982, 0.9357142857131315, pixel coords 403, 329 data coords 0.1753917050711593, 0.9357142857131315, pixel coords 402, 329 data coords 0.1753917050711593, 0.9428571428559798, pixel coords 402, 330 data coords 0.1713364055319988, 0.9428571428559798, pixel coords 401, 330 data coords 0.1672811059928383, 0.949999999998828, pixel coords 400, 331 data coords 0.1632258064536778, 0.949999999998828, pixel coords 399, 331
觀看下面的影片以觀察滑鼠移動事件功能在此處的工作方式。

滑鼠移動的即時繪圖
可以透過在 matplotlib 中使用 motion_notify_event 來實現滑鼠移動的近乎即時繪圖。此事件允許您捕獲滑鼠游標的動態移動,從而能夠建立互動式和響應式視覺化。
示例
以下示例演示瞭如何使用 Matplotlib 即時繪製滑鼠路徑。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Create the plot
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(7, 4))
# Set the limits of the plot
ax.set_xlim(0, 1920-1)
ax.set_ylim(0, 1080-1)
# Initialize lists to store mouse coordinates
x,y = [0], [0]
# create empty plot
points, = ax.plot([], [], '-', color='green')
# cache the background
background = fig.canvas.copy_from_bbox(ax.bbox)
def on_move(event):
# Append the current mouse coordinates
x.append(event.xdata)
y.append(event.ydata)
# Update the plot data
points.set_data(x,y)
# Restore the background
fig.canvas.restore_region(background)
# Redraw the points
ax.draw_artist(points)
# Fill in the axes rectangle
fig.canvas.blit(ax.bbox)
# Connect the on_move function to the motion_notify_event
fig.canvas.mpl_connect("motion_notify_event", on_move)
# Display the plot
plt.show()
輸出
執行上述程式後,您將獲得以下輸出:
觀看下面的影片以觀察滑鼠移動事件功能在此處的工作方式。

使用 TriFinder 高亮三角形
使用matplotlib.tri模組中的TriFinder類來識別三角剖分內的三角形。透過將其與motion_notify_event結合使用,您可以動態突出顯示滑鼠移動到三角剖分圖上的三角形。
示例
此示例演示了在 Matplotlib 中使用 TriFinder 物件。當滑鼠在三角剖分上移動時,游標下的三角形會突出顯示,並且三角形的索引會顯示在繪圖示題中。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.patches import Polygon
from matplotlib.tri import Triangulation
def update_highlighted_triangle(triangle_index):
if triangle_index == -1:
points = [0, 0, 0]
else:
points = triangulation.triangles[triangle_index]
xs = triangulation.x[points]
ys = triangulation.y[points]
highlighted_polygon.set_xy(np.column_stack([xs, ys]))
def on_mouse_move(event):
if event.inaxes is None:
triangle_index = -1
else:
triangle_index = tri_finder(event.xdata, event.ydata)
update_highlighted_triangle(triangle_index)
ax.set_title(f'In triangle {triangle_index}')
event.canvas.draw()
# Create a Triangulation.
num_angles = 16
num_radii = 5
min_radius = 0.25
radii = np.linspace(min_radius, 0.95, num_radii)
angles = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, num_angles, endpoint=False)
angles = np.repeat(angles[..., np.newaxis], num_radii, axis=1)
angles[:, 1::2] += np.pi / num_angles
x_values = (radii*np.cos(angles)).flatten()
y_values = (radii*np.sin(angles)).flatten()
triangulation = Triangulation(x_values, y_values)
triangulation.set_mask(np.hypot(x_values[triangulation.triangles].mean(axis=1),
y_values[triangulation.triangles].mean(axis=1))
< min_radius)
# Use the triangulation's default TriFinder object.
tri_finder = triangulation.get_trifinder()
# Setup plot and callbacks.
fig, ax = plt.subplots(subplot_kw={'aspect': 'equal'}, figsize=(7, 4))
ax.triplot(triangulation, 'bo-')
highlighted_polygon = Polygon([[0, 0], [0, 0]], facecolor='y') # dummy data for (xs, ys)
update_highlighted_triangle(-1)
ax.add_patch(highlighted_polygon)
fig.canvas.mpl_connect('motion_notify_event', on_mouse_move)
plt.show()
輸出
執行上述程式後,您將獲得以下輸出:
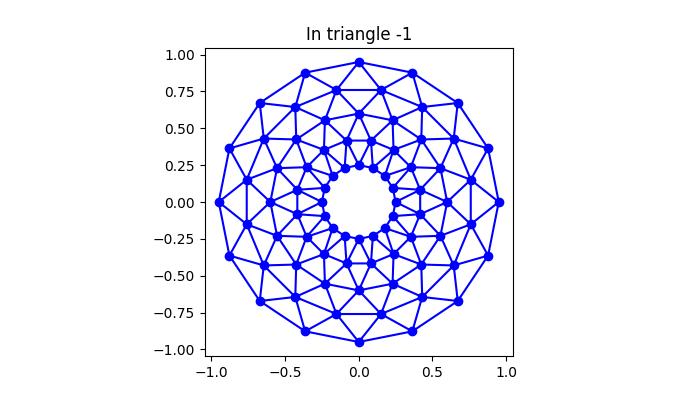
觀看下面的影片以觀察滑鼠移動事件功能在此處的工作方式。
