
- JavaFX 教程
- JavaFX - 首頁
- JavaFX - 概述
- JavaFX 安裝和架構
- JavaFX - 環境
- JavaFX - 使用 Netbeans 安裝
- JavaFX - 使用 Eclipse 安裝
- JavaFX - 使用 Visual Studio Code 安裝
- JavaFX - 架構
- JavaFX - 應用程式
- JavaFX 2D 形狀
- JavaFX - 2D 形狀
- JavaFX - 繪製直線
- JavaFX - 繪製矩形
- JavaFX - 繪製圓角矩形
- JavaFX - 繪製圓形
- JavaFX - 繪製橢圓
- JavaFX - 繪製多邊形
- JavaFX - 繪製折線
- JavaFX - 繪製三次貝塞爾曲線
- JavaFX - 繪製二次貝塞爾曲線
- JavaFX - 繪製弧形
- JavaFX - 繪製 SVGPath
- JavaFX 2D 物件的屬性
- JavaFX - 描邊型別屬性
- JavaFX - 描邊寬度屬性
- JavaFX - 描邊填充屬性
- JavaFX - 描邊屬性
- JavaFX - 描邊連線屬性
- JavaFX - 描邊斜接限制屬性
- JavaFX - 描邊端點屬性
- JavaFX - 平滑屬性
- JavaFX 路徑物件
- JavaFX - 路徑物件
- JavaFX - LineTo 路徑物件
- JavaFX - HLineTo 路徑物件
- JavaFX - VLineTo 路徑物件
- JavaFX - QuadCurveTo 路徑物件
- JavaFX - CubicCurveTo 路徑物件
- JavaFX - ArcTo 路徑物件
- JavaFX 顏色和紋理
- JavaFX - 顏色
- JavaFX - 線性漸變圖案
- JavaFX - 徑向漸變圖案
- JavaFX 文字
- JavaFX - 文字
- JavaFX 效果
- JavaFX - 效果
- JavaFX - 顏色調整效果
- JavaFX - 顏色輸入效果
- JavaFX - 影像輸入效果
- JavaFX - 混合效果
- JavaFX - 輝光效果
- JavaFX - 泛光效果
- JavaFX - 方框模糊效果
- JavaFX - 高斯模糊效果
- JavaFX - 運動模糊效果
- JavaFX - 反射效果
- JavaFX - 棕褐色效果
- JavaFX - 陰影效果
- JavaFX - 投影效果
- JavaFX - 內陰影效果
- JavaFX - 照明效果
- JavaFX - Light.Distant 效果
- JavaFX - Light.Spot 效果
- JavaFX - Point.Spot 效果
- JavaFX - 位移對映
- JavaFX - 透視變換
- JavaFX 動畫
- JavaFX - 動畫
- JavaFX - 旋轉過渡
- JavaFX - 縮放過渡
- JavaFX - 平移過渡
- JavaFX - 淡入淡出過渡
- JavaFX - 填充過渡
- JavaFX - 描邊過渡
- JavaFX - 順序過渡
- JavaFX - 並行過渡
- JavaFX - 暫停過渡
- JavaFX - 路徑過渡
- JavaFX 影像
- JavaFX - 影像
- JavaFX 3D 形狀
- JavaFX - 3D 形狀
- JavaFX - 建立立方體
- JavaFX - 建立圓柱體
- JavaFX - 建立球體
- 3D 物件的屬性
- JavaFX - 剔除面屬性
- JavaFX - 繪製模式屬性
- JavaFX - 材質屬性
- JavaFX 事件處理
- JavaFX - 事件處理
- JavaFX - 使用便捷方法
- JavaFX - 事件過濾器
- JavaFX - 事件處理程式
- JavaFX UI 控制元件
- JavaFX - UI 控制元件
- JavaFX - 列表檢視
- JavaFX - 手風琴
- JavaFX - 按鈕欄
- JavaFX - 選擇框
- JavaFX - HTML 編輯器
- JavaFX - 選單欄
- JavaFX - 分頁
- JavaFX - 進度指示器
- JavaFX - 滾動窗格
- JavaFX - 分隔符
- JavaFX - 滑塊
- JavaFX - 微調器
- JavaFX - 分割窗格
- JavaFX - 表格檢視
- JavaFX - 選項卡窗格
- JavaFX - 工具欄
- JavaFX - 樹檢視
- JavaFX - 標籤
- JavaFX - 複選框
- JavaFX - 單選按鈕
- JavaFX - 文字欄位
- JavaFX - 密碼欄位
- JavaFX - 檔案選擇器
- JavaFX - 超連結
- JavaFX - 工具提示
- JavaFX - 警報
- JavaFX - 日期選擇器
- JavaFX - 文字區域
- JavaFX 圖表
- JavaFX - 圖表
- JavaFX - 建立餅圖
- JavaFX - 建立折線圖
- JavaFX - 建立面積圖
- JavaFX - 建立條形圖
- JavaFX - 建立氣泡圖
- JavaFX - 建立散點圖
- JavaFX - 建立堆疊面積圖
- JavaFX - 建立堆疊條形圖
- JavaFX 佈局窗格
- JavaFX - 佈局窗格
- JavaFX - HBox 佈局
- JavaFX - VBox 佈局
- JavaFX - BorderPane 佈局
- JavaFX - StackPane 佈局
- JavaFX - TextFlow 佈局
- JavaFX - AnchorPane 佈局
- JavaFX - TilePane 佈局
- JavaFX - GridPane 佈局
- JavaFX - FlowPane 佈局
- JavaFX CSS
- JavaFX - CSS
- JavaFX 中的媒體
- JavaFX - 處理媒體
- JavaFX - 播放影片
- JavaFX 有用資源
- JavaFX - 快速指南
- JavaFX - 有用資源
- JavaFX - 討論
JavaFX - 快速指南
JavaFX - 概述
富網際網路應用程式是指那些提供與桌面應用程式類似功能和體驗的 Web 應用程式。與普通的 Web 應用程式相比,它們為使用者提供了更好的視覺體驗。這些應用程式作為瀏覽器外掛或虛擬機器交付,用於將傳統的靜態應用程式轉換為更增強、流暢、動畫和引人入勝的應用程式。
與傳統的桌面應用程式不同,RIA 不需要任何額外的軟體即可執行。作為替代方案,您應該安裝諸如 ActiveX、Java、Flash 等軟體,具體取決於應用程式。
在 RIA 中,圖形呈現由客戶端處理,因為它具有提供豐富圖形支援的外掛。簡而言之,RIA 中的資料操作在伺服器端進行,而相關的物件操作在客戶端進行。
我們有三種主要技術可用於開發 RIA。這些包括以下內容 -
- Adobe Flash
- Microsoft Silverlight
- JavaFX
Adobe Flash
此軟體平臺由 Adobe Systems 開發,用於建立富網際網路應用程式。除此之外,您還可以構建其他應用程式,例如向量、動畫、瀏覽器遊戲、桌面應用程式、移動應用程式和遊戲等。
這是最常用的開發和執行 RIA 的平臺,桌面瀏覽器滲透率為 96%。
Microsoft Silverlight
就像 Adobe flash 一樣,Microsoft Silverlight 也是一個用於開發和執行富網際網路應用程式的軟體應用程式框架。最初,此框架用於流媒體。當前版本也支援多媒體、圖形和動畫。
此平臺很少使用,桌面瀏覽器滲透率為 66%。
JavaFX
JavaFX 是一個 Java 庫,您可以使用它來開發富網際網路應用程式。透過使用 Java 技術,這些應用程式的瀏覽器滲透率為 76%。
什麼是 JavaFX?
JavaFX 是一個用於構建富網際網路應用程式的 Java 庫。使用此庫編寫的應用程式可以在多個平臺上始終如一地執行。使用 JavaFX 開發的應用程式可以在各種裝置上執行,例如臺式計算機、手機、電視、平板電腦等。
為了使用 Java 程式語言開發GUI 應用程式,程式設計師依賴於高階視窗工具包和Swing等庫。在 JavaFX 出現後,這些 Java 程式設計師現在可以使用豐富的內容更有效地開發 GUI 應用程式。
JavaFX 的需求
為了開發具有豐富功能的客戶端應用程式,程式設計師過去常常依賴各種庫來新增諸如媒體、UI 控制元件、Web、2D 和 3D 等功能。JavaFX 將所有這些功能包含在一個庫中。除了這些之外,開發人員還可以訪問現有 Java 庫(例如Swing)的功能。
JavaFX 提供了一套豐富的圖形和媒體 API,並透過硬體加速圖形利用了現代圖形處理單元。JavaFX 還提供介面,開發人員可以使用這些介面來組合圖形動畫和 UI 控制元件。
可以將 JavaFX 與基於 JVM 的技術(如 Java、Groovy 和 JRuby)一起使用。如果開發人員選擇 JavaFX,則無需學習其他技術,因為之前對上述任何技術的瞭解都足以使用 JavaFX 開發 RIA。
JavaFX 的特性
以下是 JavaFX 的一些重要特性 -
用 Java 編寫 - JavaFX 庫是用 Java 編寫的,可用於可以在 JVM 上執行的語言,包括 - Java、Groovy 和 JRuby。這些 JavaFX 應用程式也是平臺無關的。
FXML - JavaFX 提供了一種稱為 FXML 的語言,它是一種類似 HTML 的宣告性標記語言。此語言的唯一目的是定義使用者介面。
場景構建器 - JavaFX 提供了一個名為 Scene Builder 的應用程式。透過將此應用程式整合到 Eclipse 和 NetBeans 等 IDE 中,使用者可以訪問一個拖放設計介面,該介面用於開發 FXML 應用程式(就像 Swing 拖放和 DreamWeaver 應用程式一樣)。
Swing 互操作性 - 在 JavaFX 應用程式中,您可以使用Swing Node類嵌入 Swing 內容。同樣,您可以使用 JavaFX 功能(如嵌入式 Web 內容和豐富的圖形媒體)更新現有的 Swing 應用程式。
內建 UI 控制元件 - JavaFX 庫提供 UI 控制元件,我們可以使用這些控制元件開發功能齊全的應用程式。
類似 CSS 的樣式 - JavaFX 提供了類似 CSS 的樣式。透過使用它,您可以透過簡單的 CSS 知識來改進應用程式的設計。
畫布和列印 API - JavaFX 提供了 Canvas,這是一種即時模式的渲染 API。在javafx.scene.canvas包中,它包含一組用於畫布的類,我們可以使用這些類直接在 JavaFX 場景的區域內繪製。JavaFX 還提供了用於列印目的的類,位於javafx.print包中。
豐富的 API 集 - JavaFX 庫提供了一套豐富的 API 來開發 GUI 應用程式、2D 和 3D 圖形等。這套 API 還包括 Java 平臺的功能。因此,使用此 API,您可以訪問 Java 語言的功能,例如泛型、註釋、多執行緒和 Lambda 表示式。傳統的 Java 集合庫得到了增強,並且其中包含了可觀察列表和對映等概念。使用這些,使用者可以觀察資料模型中的變化。
整合的圖形庫 - JavaFX 提供了用於2d和3d圖形的類。
圖形管道 - JavaFX 支援基於稱為 Prism 的硬體加速圖形管道的圖形。當與支援的顯示卡或 GPU 一起使用時,它提供了流暢的圖形。如果系統不支援顯示卡,則 Prism 預設使用軟體渲染堆疊。
JavaFX 的歷史
JavaFX 最初由Chris Oliver開發,當時他在一家名為See Beyond Technology Corporation的公司工作,該公司於 2005 年被Sun Microsystems收購。
以下幾點提供了更多關於此專案的資訊 -
最初,這個專案名為 F3(形式服從功能),其開發目的是為了提供更豐富的介面來開發 GUI 應用程式。
Sun Microsystems於 2005 年 6 月收購了 See Beyond 公司,它將 F3 專案改名為JavaFX。
2007 年,JavaFX 在Java One上正式釋出,這是一個每年舉行的全球性網路會議。
2008 年,**NetBeans** 整合 JavaFX 可用。同年,JavaFX 1.0 的 Java **標準開發工具包** (Standard Development Kit) 釋出。
2009 年,甲骨文公司 (Oracle Corporation) 收購了 Sun Microsystems,同年也釋出了 JavaFX 的下一個版本 (1.2)。
2010 年,JavaFX 1.3 釋出,2011 年釋出了 JavaFX 2.0。
最新版本 JavaFX8 於 2014 年 3 月 18 日作為 Java 的一部分發布。
JavaFX - 環境
從 Java8 開始,JDK **(Java 開發工具包)** 中包含 **JavaFX** 庫。因此,要執行 JavaFX 應用程式,您只需在系統中安裝 Java8 或更高版本即可。
此外,Eclipse 和 NetBeans 等 IDE 也提供了對 JavaFX 的支援。本章將教你如何透過各種方式設定執行 JavaFX 應用程式的環境。
安裝 Java8
首先,您需要透過開啟命令提示符並在其中鍵入命令“Java”來驗證系統中是否已安裝 Java。
如果您的系統中沒有安裝 Java,命令提示符將顯示以下螢幕截圖中所示的訊息。
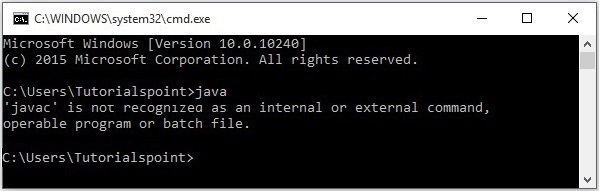
然後按照以下步驟安裝 Java。
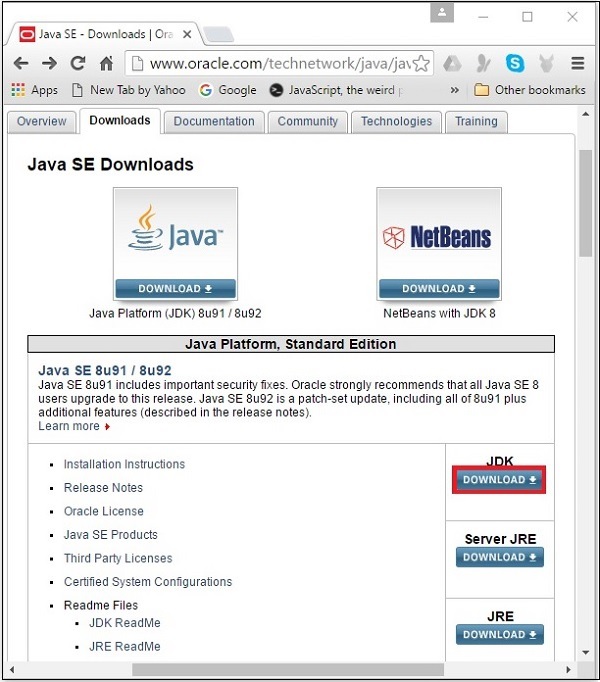
**步驟 1** − 訪問 JavaSE 下載 頁面,點選 JDK **下載** 按鈕,如下面的螢幕截圖中突出顯示的那樣。
**步驟 2** − 點選下載按鈕後,您將被重定向到 **Java SE 開發工具包 8 下載** 頁面。此頁面為您提供了適用於各種平臺的 JDK 連結。
接受許可協議,並透過點選相應的連結下載所需的軟體。
例如,如果您在 Windows 64 位作業系統上工作,則需要下載以下螢幕截圖中突出顯示的 JDK 版本。
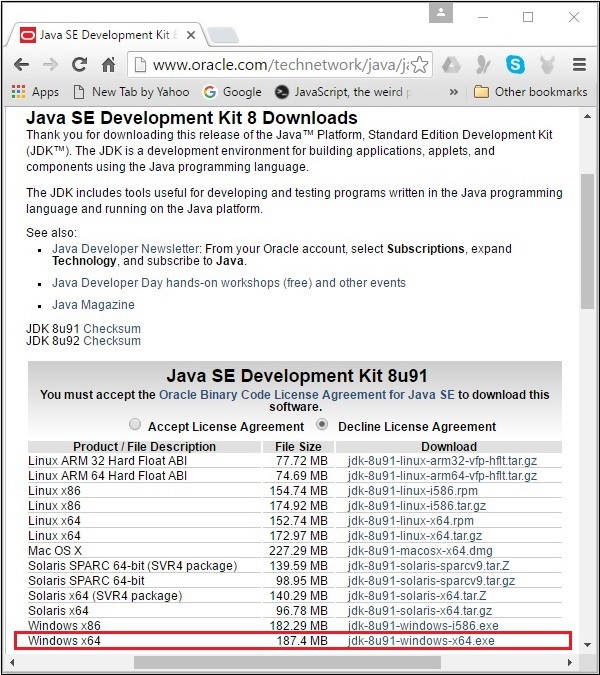
點選突出顯示的連結後,適用於 Windows 64 位作業系統的 Java8 開發工具包將下載到您的系統中。
**步驟 3** − 執行下載的二進位制可執行檔案以開始安裝 JDK8。
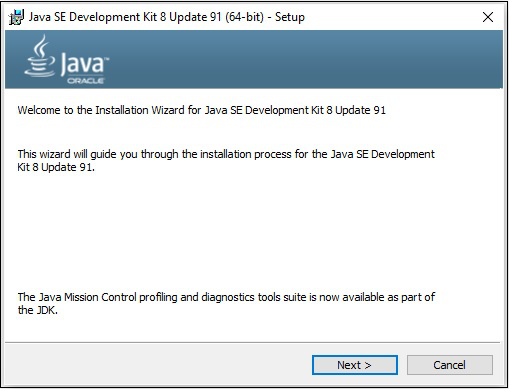
**步驟 4** − 選擇安裝目錄。
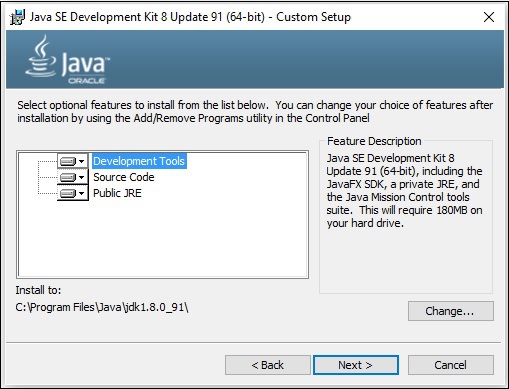
**步驟 5** − 選擇目標資料夾並點選“下一步”後,JavaFX 安裝過程將開始顯示進度條,如下面的螢幕截圖所示。
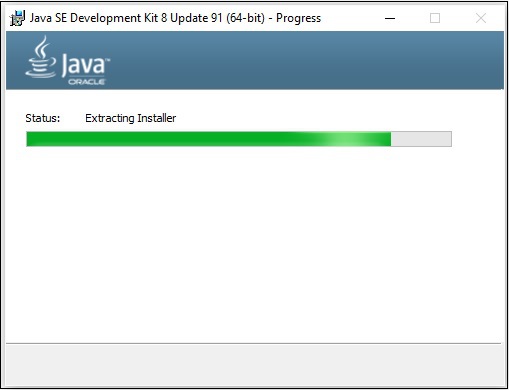
**步驟 6** − 根據需要更改安裝目錄,否則保留預設目錄並繼續。
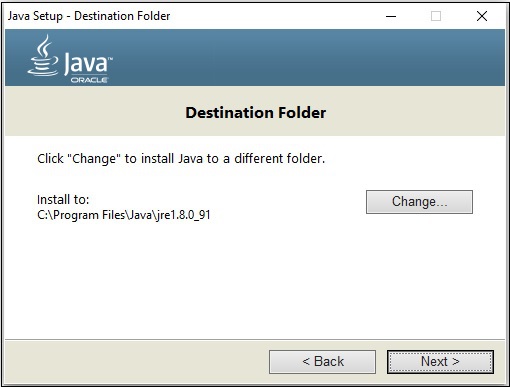
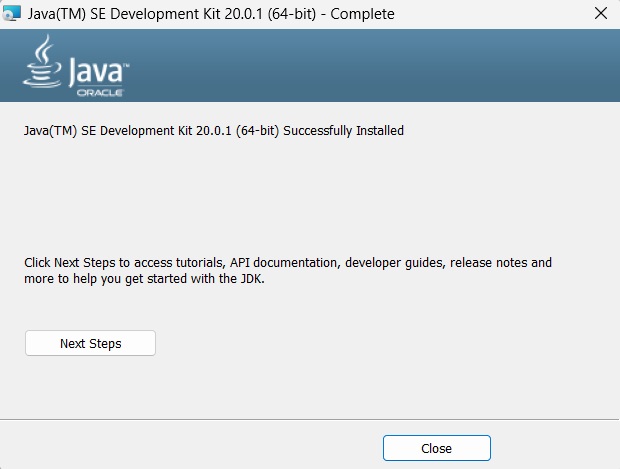
**步驟 7** − 透過點選“關閉”按鈕完成安裝過程,如下面的螢幕截圖所示。
設定 Windows 的路徑
安裝 Java 後,您需要設定路徑變數。假設您已將 Java 安裝在 **C:\Program Files\java\jdk1.8.0_91** 目錄中。
現在您可以按照以下步驟操作 −
右鍵點選“我的電腦”,然後選擇“屬性”。
在“高階”選項卡下點選“環境變數”按鈕。
現在,修改“Path”變數,使其也包含 Java 可執行檔案的路徑。例如,如果路徑當前設定為“C:\WINDOWS\SYSTEM32”,則將路徑更改為“C:\WINDOWS\SYSTEM32; C:\Program Files\java\ jdk1.8.0_91\bin”。
設定 NetBeans 的 JavaFX 環境
**NetBeans8** 內建支援 JavaFX。安裝後,您可以建立 JavaFX 應用程式,無需任何額外的外掛或 JAR 檔案。要設定 NetBeans 環境,您需要按照以下步驟操作。
**步驟 1** − 訪問 NetBeans 網站,然後點選“下載”按鈕下載 NetBeans 軟體。
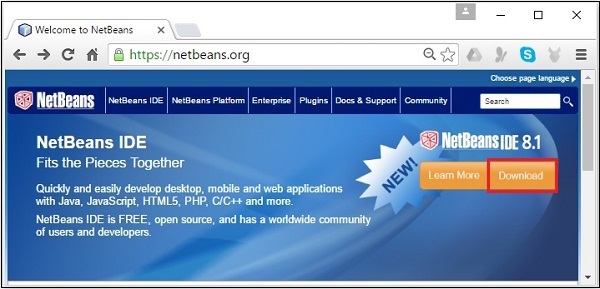
**步驟 2** − 點選“下載”後,您將進入 NetBeans 軟體的下載頁面,該頁面提供了適用於各種 Java 應用程式的 NetBeans 包。下載適用於 **JavaSE** 的 NetBeans 軟體,如下面的螢幕截圖所示。

**步驟 3** − 點選此按鈕後,檔案“netbeans-8.0-windows.exe”將下載到您的系統中。執行此檔案以安裝它。執行此檔案後,將啟動 NetBeans 安裝程式,如下面的螢幕截圖所示。
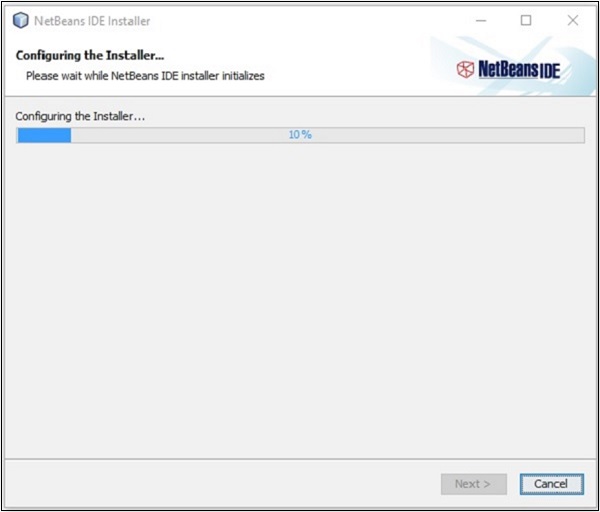
配置完成後,您將看到安裝程式的 **歡迎頁面**。
**步驟 4** − 點選“下一步”按鈕繼續安裝。

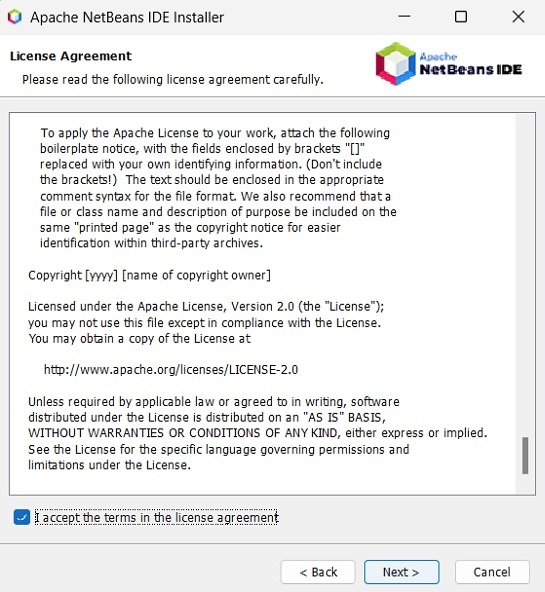
**步驟 5** − 下一個視窗包含 **NETBEANS IDE 8.0 許可協議**。仔細閱讀並透過選中“我接受許可協議中的條款”複選框接受協議,然後點選“下一步”按鈕。
**步驟 6** − 在下一個視窗中,您將遇到 **Junit** 的許可協議,透過選中“我接受許可協議中的條款,安裝 JUnit”單選按鈕接受它,然後點選“下一步”。
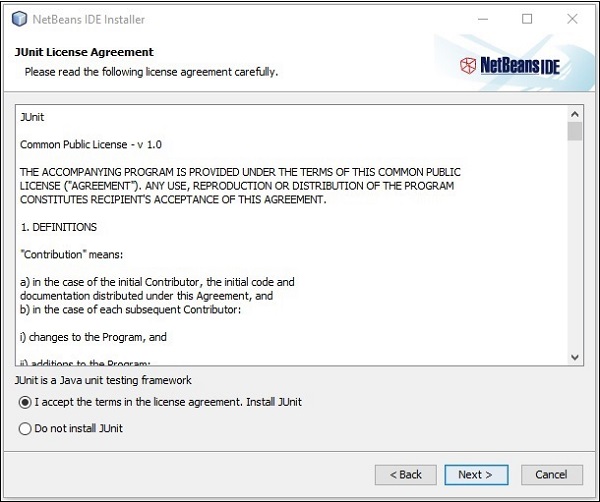
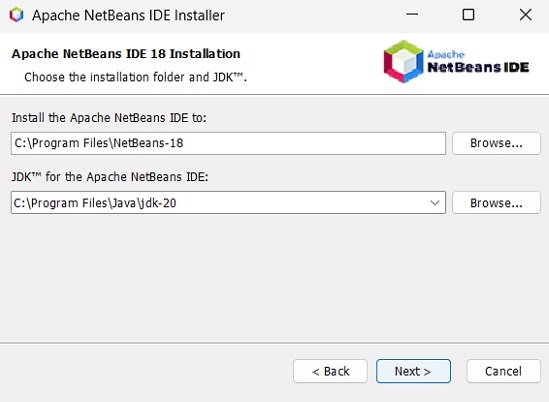
**步驟 7** − 選擇您需要安裝 Netbeans 8.0 的目標目錄。此外,您還可以瀏覽系統中安裝 **Java 開發工具包** 的目錄,然後點選“下一步”按鈕。
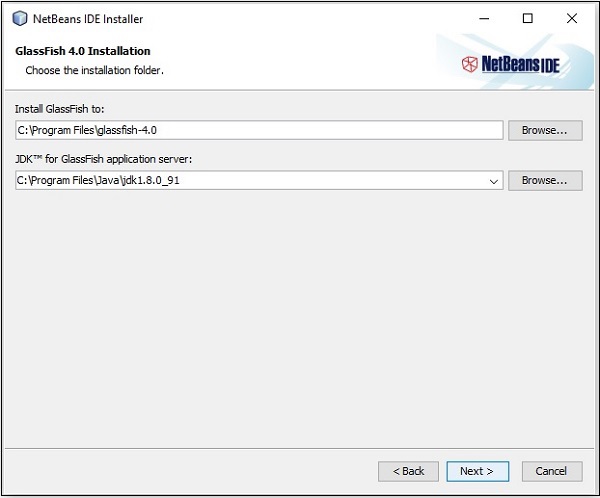
**步驟 8** − 同樣,選擇 **Glassfish 伺服器** 安裝的目標目錄。瀏覽 Java 開發工具包目錄(現在用於 Glassfish 參考),然後點選“下一步”。
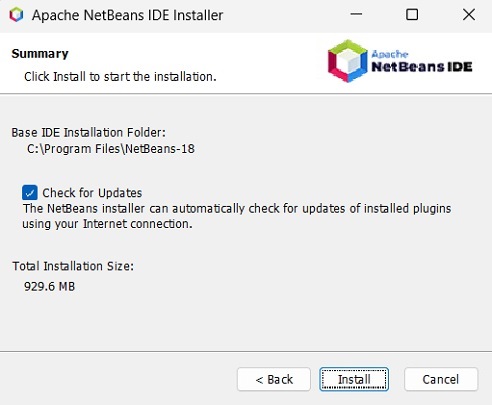
**步驟 9** − 選中“檢查更新”框以進行自動更新,然後點選“安裝”按鈕開始安裝。
**步驟 10** − 此步驟將開始安裝 NetBeans IDE 8.0,可能需要一段時間。
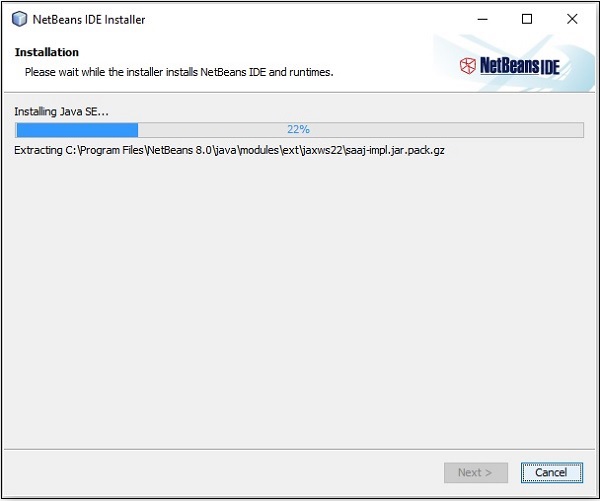
**步驟 11** − 過程完成後,點選“完成”按鈕完成安裝。
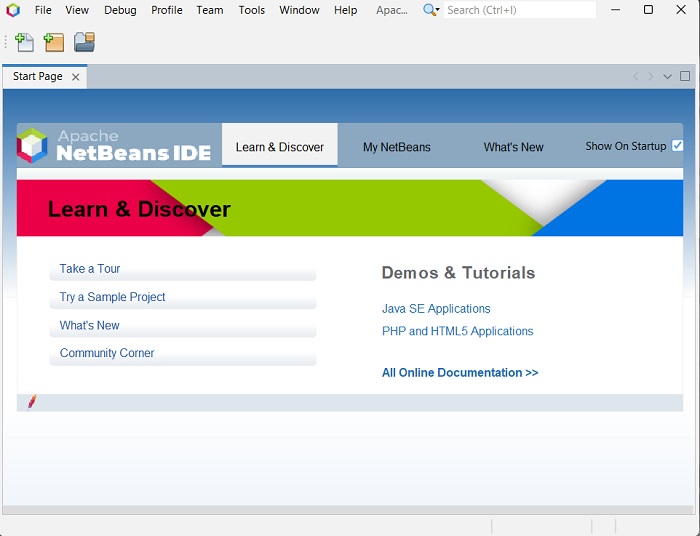
**步驟 12** − 啟動 NetBeans IDE 後,您將看到如下面的螢幕截圖所示的啟動頁面。
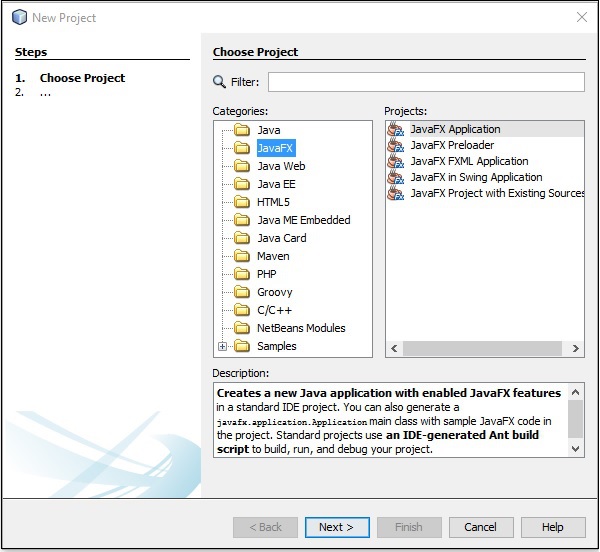
**步驟 13** − 在檔案選單中,選擇“新建專案”... 以開啟“新建專案”嚮導,如下面的螢幕截圖所示。

**步驟 14** − 在“新建專案”嚮導中,選擇 **JavaFX** 並點選“下一步”。它將開始為您建立一個新的 JavaFX 應用程式。
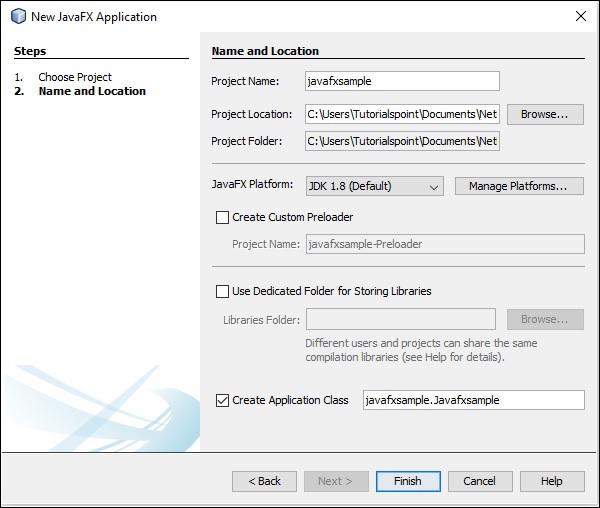
**步驟 15** − 在“新建 JavaFX 應用程式”視窗中選擇專案的名稱和位置,然後點選“完成”。它將建立一個名稱為給定名稱的示例應用程式。
在本例中,將建立一個名為 **javafxsample** 的應用程式。在此應用程式中,NetBeans IDE 將生成一個名為 **Javafxsample.java** 的 Java 程式。如下面的螢幕截圖所示,此程式將在 NetBeans 源包 **→ javafxsample** 中建立。
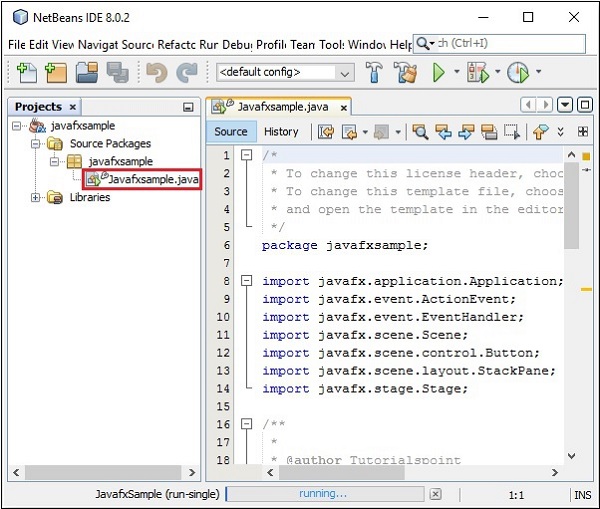
**步驟 16** − 右鍵點選該檔案,然後選擇“執行檔案”以執行此程式碼,如下面的螢幕截圖所示。
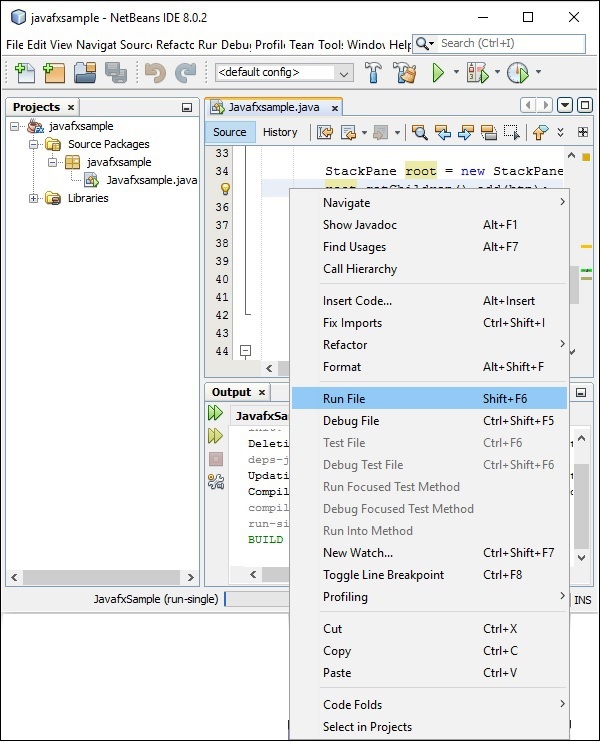
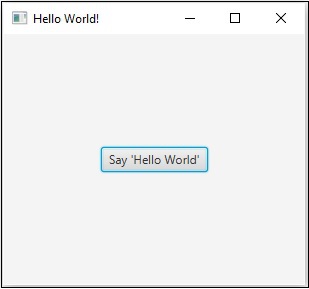
此自動生成的程式包含生成一個簡單的 JavaFX 視窗的程式碼,該視窗包含一個標籤為 **“Say ‘Hello World’”** 的按鈕。每次點選此按鈕時,字串 **“Hello World”** 將顯示在控制檯中,如下所示。
在 Eclipse 中安裝 JavaFX
JavaFX 中也提供了一個名為 **e(fx)clipse** 的外掛。您可以使用以下步驟在 Eclipse 中設定 JavaFX。首先,確保您的系統中已安裝 Eclipse。如果沒有,請下載並在您的系統中安裝 Eclipse。
安裝 Eclipse 後,請按照以下步驟在您的系統中安裝 **e(fx)clipse**。
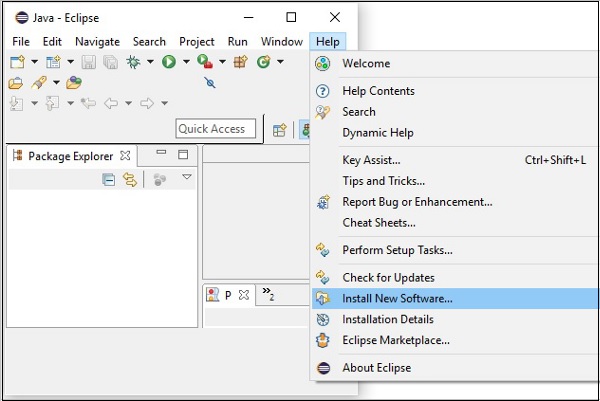
**步驟 1** − 在 Eclipse 的“幫助”選單中開啟 Eclipse,然後選擇“安裝新軟體”... 選項,如下所示。
點選後,它將顯示“可用軟體”視窗,如下面的螢幕截圖所示。
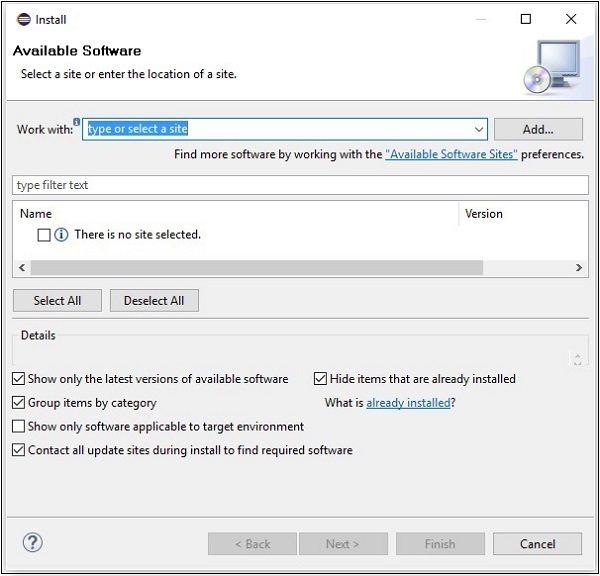
在此視窗的“使用”文字框中,您需要提供所需軟體的外掛連結。
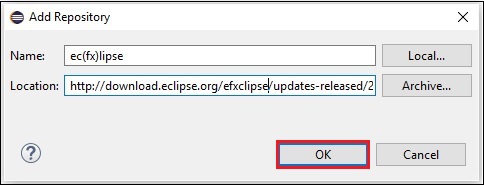
**步驟 2** − 點選“新增”... 按鈕。將外掛的名稱提供為 **e(fx)clipse**。接下來,提供以下連結作為位置:http://download.eclipse.org/efxclipse/updates-released/2.3.0/site/
**步驟 3** − 指定外掛的名稱和位置後,點選“確定”按鈕,如下面的螢幕截圖中突出顯示的那樣。
**步驟 4** − 新增外掛後不久,您將找到兩個複選框,分別為 **e(fx)clipse – install** 和 **e(fx)clipse – single components**。選中這兩個複選框,然後點選“新增”... 按鈕,如下面的螢幕截圖所示。
clipse_single_components.jpg)
**步驟 5** − 接下來,開啟 Eclipse IDE。點選“檔案”選單,然後選擇“專案”,如下面的螢幕截圖所示。
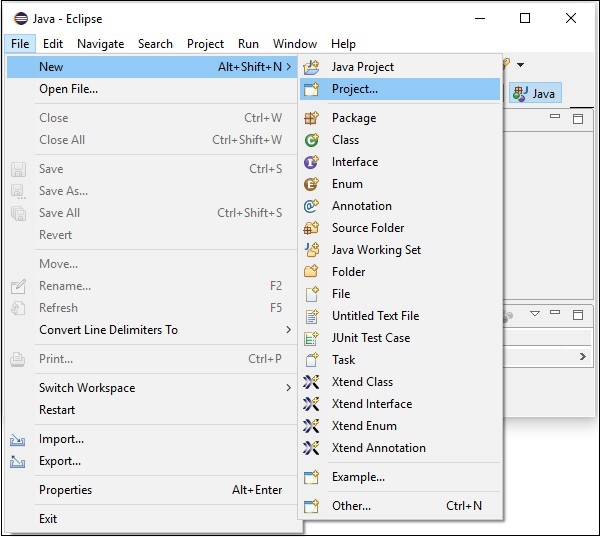
**步驟 6** − 然後,您將看到一個視窗,其中您可以看到 Eclipse 提供的用於建立專案的嚮導列表。展開 **JavaFX** 嚮導,選擇 **JavaFX 專案**,然後點選“下一步”按鈕,如下面的螢幕截圖所示。
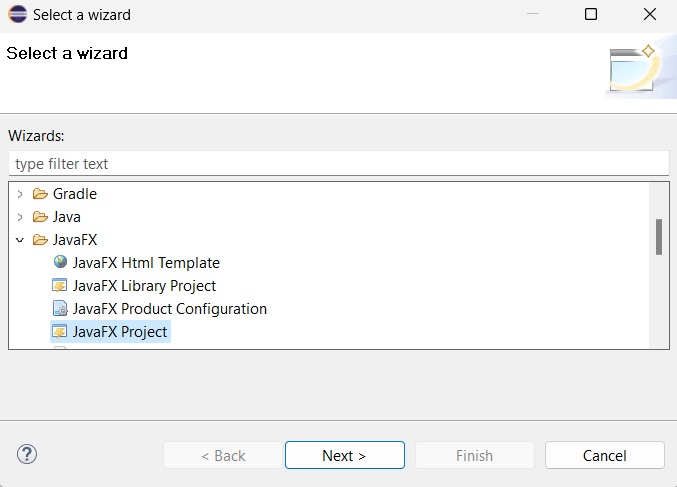
**步驟 7** − 點選“下一步”後,將開啟“新建專案”嚮導。在這裡,您可以鍵入所需的專案名稱,然後點選“完成”。
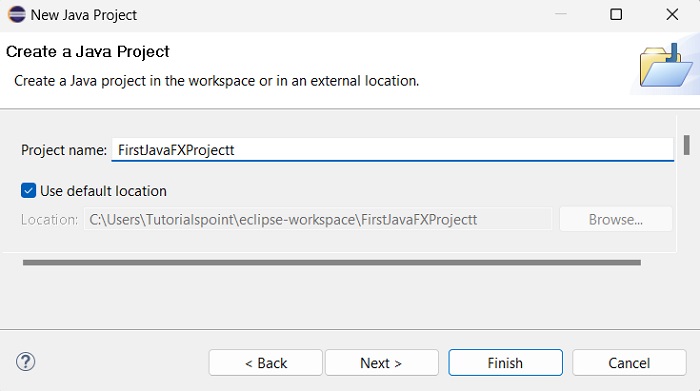
**步驟 8** − 點選“完成”後,將建立一個名稱為給定名稱(sample)的應用程式。在名為 **application** 的子包中,將生成一個名為 **Main.java** 的程式,如下所示。
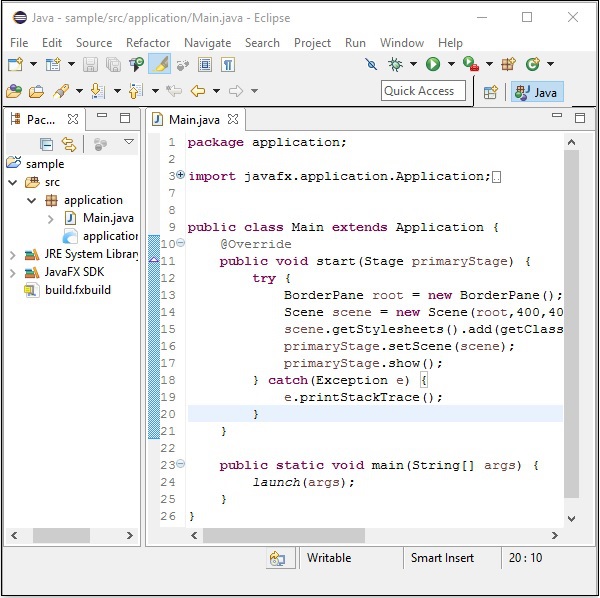
**步驟 9** − 此自動生成的程式包含生成一個空 JavaFX 視窗的程式碼。右鍵點選此檔案,選擇“以 Java 應用程式方式執行”,如下面的螢幕截圖所示。
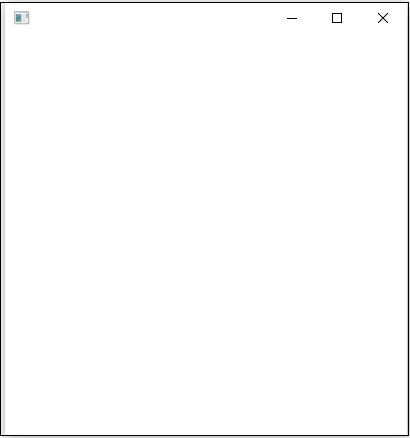
執行此應用程式後,它將為您提供一個空的 JavaFX 視窗,如下所示。
**注意** − 我們將在後面的章節中詳細討論程式碼。
JavaFX - 架構
JavaFX 提供了一個完整的 API,其中包含豐富的類和介面,用於構建具有豐富圖形的 GUI 應用程式。此 API 的重要包如下 −
**javafx.animation** − 包含用於向 JavaFX 節點新增基於轉換的動畫(如填充、淡入淡出、旋轉、縮放和平移)的類。
**javafx.application** − 包含一組負責 JavaFX 應用程式生命週期的類。
**javafx.css** − 包含用於向 JavaFX GUI 應用程式新增類似 CSS 的樣式的類。
**javafx.event** − 包含用於傳遞和處理 JavaFX 事件的類和介面。
**javafx.geometry** − 包含用於定義 2D 物件並在其上執行操作的類。
**javafx.stage** − 此包包含 JavaFX 應用程式的頂級容器類。
**javafx.scene** − 此包提供用於支援場景圖的類和介面。此外,它還提供諸如 canvas、chart、control、effect、image、input、layout、media、paint、shape、text、transform、web 等子包。有幾個元件支援 JavaFX 的這個豐富的 API。
下圖展示了 JavaFX API 的架構。在這裡您可以看到支援 JavaFX API 的元件。

場景圖 (Scene Graph)
在 JavaFX 中,GUI 應用程式使用場景圖進行編碼。場景圖是構建 GUI 應用程式的起點。它包含被稱為節點的(GUI)應用程式基元。
節點是一個視覺/圖形物件,它可能包含:
**幾何(圖形)物件** - (2D 和 3D),例如圓形、矩形、多邊形等。
**UI 控制元件** - 例如按鈕、複選框、選擇框、文字區域等。
**容器** - (佈局窗格),例如邊框窗格、網格窗格、流窗格等。
**媒體元素** - 例如音訊、影片和影像物件。
通常,節點的集合構成一個場景圖。所有這些節點都以分層順序排列,如下所示。
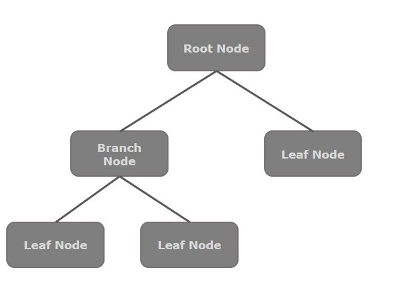
場景圖中的每個節點都有一個父節點,不包含任何父節點的節點稱為**根節點**。
同樣,每個節點都有一個或多個子節點,沒有子節點的節點稱為**葉子節點**;有子節點的節點稱為**分支節點**。
節點例項只能新增到場景圖一次。場景圖的節點可以具有效果、不透明度、變換、事件處理程式、應用程式特定狀態。
Prism
Prism 是一個**高效能硬體加速圖形管道**,用於渲染 JavaFX 中的圖形。它可以渲染 2D 和 3D 圖形。
為了渲染圖形,Prism 使用:
- Windows XP 和 Vista 上的 DirectX 9。
- Windows 7 上的 DirectX 11。
- Mac 和 Linux、嵌入式系統上的 OpenGL。
如果系統上圖形的硬體支援不足,則 Prism 使用軟體渲染路徑來處理圖形。
當與支援的顯示卡或 GPU 一起使用時,它可以提供更流暢的圖形。如果系統不支援顯示卡,則 Prism 預設使用軟體渲染堆疊(上述兩者之一)。
GWT(Glass Windowing Toolkit)
顧名思義,GWT 提供了管理視窗、計時器、表面和事件佇列的服務。GWT 將 JavaFX 平臺連線到本地作業系統。
Quantum Toolkit
它是在 Prism、Glass、媒體引擎和 Web 引擎的低階元件上的抽象層。它將 Prism 和 GWT 聯絡起來,並使它們可供 JavaFX 使用。
WebView
使用 JavaFX,您還可以將 HTML 內容嵌入到場景圖中。WebView 是 JavaFX 的一個元件,用於處理此內容。它使用一項名為**Web Kit**的技術,這是一種內部開源的 Web 瀏覽器引擎。此元件支援不同的 Web 技術,如 HTML5、CSS、JavaScript、DOM 和 SVG。
使用 WebView,您可以:
- 渲染來自本地或遠端 URL 的 HTML 內容。
- 支援歷史記錄並提供前進和後退導航。
- 重新載入內容。
- 將效果應用於 Web 元件。
- 編輯 HTML 內容。
- 執行 JavaScript 命令。
- 處理事件。
通常,使用 WebView,您可以從 Java 控制 Web 內容。
媒體引擎 (Media Engine)
**JavaFX 媒體引擎**基於一個稱為**Streamer**的開源引擎。此媒體引擎支援影片和音訊內容的播放。
JavaFX 媒體引擎為以下檔案格式提供音訊支援:
| 音訊 |
|
|---|---|
| 影片 |
|
**javafx.scene.media** 包包含用於在 JavaFX 中提供媒體功能的類和介面。它以三個元件的形式提供,它們是:
**媒體物件** - 表示媒體檔案
**媒體播放器** - 用於播放媒體內容。
**媒體檢視** - 用於顯示媒體。
JavaFX - 應用程式
在本章中,我們將詳細討論 JavaFX 應用程式的結構,並學習透過示例建立 JavaFX 應用程式。
JavaFX 應用程式結構
通常,JavaFX 應用程式將具有三個主要元件,即**舞臺 (Stage)**、**場景 (Scene)** 和**節點 (Nodes)**,如下面的圖所示。

舞臺 (Stage)
舞臺(視窗)包含 JavaFX 應用程式的所有物件。它由**javafx.stage** 包的**Stage** 類表示。主舞臺由平臺本身建立。建立的舞臺物件作為引數傳遞給**Application** 類的**start()** 方法(下一節將解釋)。
舞臺有兩個引數決定其位置,即**寬度 (Width)** 和**高度 (Height)**。它分為內容區域和裝飾(標題欄和邊框)。
有五種型別的舞臺可用:
- 帶裝飾 (Decorated)
- 無裝飾 (Undecorated)
- 透明 (Transparent)
- 統一 (Unified)
- 實用程式 (Utility)
您必須呼叫**show()** 方法來顯示舞臺的內容。
場景 (Scene)
場景表示 JavaFX 應用程式的物理內容。它包含場景圖的所有內容。**javafx.scene** 包的**Scene** 類表示場景物件。在任何例項中,場景物件都只能新增到一個舞臺。
您可以透過例項化 Scene 類來建立一個場景。您可以透過將其尺寸(高度和寬度)以及**根節點**傳遞給其建構函式來選擇場景的大小。
場景圖和節點 (Scene Graph and Nodes)
**場景圖**是一種樹狀資料結構(分層),表示場景的內容。相比之下,**節點**是場景圖的視覺/圖形物件。
節點可能包含:
幾何(圖形)物件(2D 和 3D),例如:圓形、矩形、多邊形等。
UI 控制元件,例如:按鈕、複選框、選擇框、文字區域等。
容器(佈局窗格),例如:邊框窗格、網格窗格、流窗格等。
媒體元素,例如:音訊、影片和影像物件。
**javafx.scene** 包的**Node** 類表示 JavaFX 中的一個節點,此類是所有節點的超類。
如前所述,節點有三種類型:
**根節點 (Root Node)** - 第一個場景圖被稱為根節點。
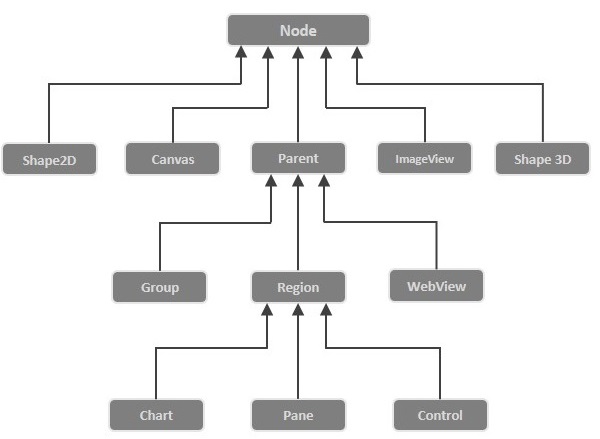
**分支節點/父節點 (Branch Node/Parent Node)** - 具有子節點的節點稱為分支/父節點。名為**Parent**的抽象類屬於**javafx.scene** 包,它是所有父節點的基類,這些父節點將屬於以下型別:
**組 (Group)** - 組節點是一個集合節點,包含子節點列表。每當渲染組節點時,都會按順序渲染其所有子節點。應用於組的任何變換、效果狀態都將應用於所有子節點。
**區域 (Region)** - 它是所有基於 JavaFX 節點的 UI 控制元件(如圖表、窗格和控制元件)的基類。
**WebView** - 此節點管理 Web 引擎並顯示其內容。
**葉子節點 (Leaf Node)** - 沒有子節點的節點稱為葉子節點。例如,矩形、橢圓、框、ImageView、MediaView 是葉子節點的示例。
必須將根節點傳遞給場景圖。如果將 Group 作為根傳遞,則所有節點都將被剪下到場景,並且場景大小的任何更改都不會影響場景的佈局。
建立 JavaFX 應用程式
要建立 JavaFX 應用程式,您需要例項化 Application 類並實現其抽象方法**start()**。在此方法中,我們將編寫 JavaFX 應用程式的程式碼。
Application 類
**javafx.application** 包的**Application** 類是 JavaFX 中應用程式的入口點。要建立 JavaFX 應用程式,您需要繼承此類並實現其抽象方法**start()**。在此方法中,您需要編寫 JavaFX 圖形的所有程式碼。
在**main** 方法中,您必須使用**launch()** 方法啟動應用程式。此方法在內部呼叫 Application 類的**start()** 方法,如下面的程式所示。
public class JavafxSample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception {
/*
Code for JavaFX application.
(Stage, scene, scene graph)
*/
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}
在**start()** 方法中,為了建立一個典型的 JavaFX 應用程式,您需要按照以下步驟操作:
使用所需的節點準備一個場景圖。
使用所需的尺寸準備一個場景,並將場景圖(場景圖的根節點)新增到其中。
準備一個舞臺,將場景新增到舞臺,並顯示舞臺的內容。
準備場景圖 (Preparing the Scene Graph)
根據您的應用程式,您需要使用所需的節點準備一個場景圖。由於根節點是第一個節點,因此您需要建立一個根節點。作為根節點,您可以從**Group、Region 或 WebView** 中選擇。
**Group** - 名為**Group**的類表示 Group 節點,它屬於**javafx.scene** 包,您可以透過例項化此類來建立一個 Group 節點,如下所示。
Group root = new Group();
**Group** 類的**getChildren()** 方法為您提供了一個**ObservableList** 類的物件,該物件儲存節點。我們可以檢索此物件並將節點新增到其中,如下所示。
//Retrieving the observable list object
ObservableList list = root.getChildren();
//Setting the text object as a node
list.add(NodeObject);
我們還可以將 Node 物件新增到組中,只需在例項化時將其傳遞給**Group** 類及其建構函式,如下所示。
Group root = new Group(NodeObject);
**Region** - 它是所有基於 JavaFX 節點的 UI 控制元件的基類,例如:
**Chart** - 此類是所有圖表的基類,它屬於**javafx.scene.chart** 包。
此類有兩個子類,分別是:**PieChart** 和**XYChart**。這兩個類又分別有子類,如**AreaChart、BarChart、BubbleChart** 等,用於在 JavaFX 中繪製不同型別的 XY 平面圖表。
您可以使用這些類將圖表嵌入到您的應用程式中。
**Pane** - Pane 是所有佈局窗格(如**AnchorPane、BorderPane、DialogPane** 等)的基類。此類屬於一個名為**javafx.scene.layout** 的包。
您可以使用這些類在應用程式中插入預定義的佈局。
控制元件 − 它是使用者介面控制元件(如手風琴、工具欄、選擇框、組合框基類、HTML編輯器等)的基類。此類屬於包 **javafx.scene.control**。
您可以使用這些類在應用程式中插入各種 UI 元素。
在組中,您可以例項化上述任何類並將其用作根節點,如下面的程式所示。
//Creating a Stack Pane
StackPane pane = new StackPane();
//Adding text area to the pane
ObservableList list = pane.getChildren();
list.add(NodeObject);
**WebView** - 此節點管理 Web 引擎並顯示其內容。
以下是 JavaFX 節點類層次結構的示意圖。
準備場景
JavaFX 場景由包 **javafx.scene** 中的 **Scene** 類表示。您可以透過例項化此類來建立場景,如下面的程式碼塊所示。
在例項化時,必須將根物件傳遞給場景類的建構函式。
Scene scene = new Scene(root);
您還可以傳遞兩個雙精度型別的引數,分別表示場景的高度和寬度,如下所示。
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 300);
準備舞臺
這是任何 JavaFX 應用程式的容器,它為應用程式提供了一個視窗。它由包 **javafx.stage** 中的 **Stage** 類表示。此類的物件作為 **Application** 類的 **start()** 方法的引數傳遞。
使用此物件,您可以在舞臺上執行各種操作。主要可以執行以下操作:−
使用 **setTitle()** 方法設定舞臺的標題。
使用 **setScene()** 方法將場景物件附加到舞臺。
使用 **show()** 方法顯示場景的內容,如下所示。
//Setting the title to Stage.
primaryStage.setTitle("Sample application");
//Setting the scene to Stage
primaryStage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the stage
primaryStage.show();
JavaFX 應用程式的生命週期
JavaFX Application 類有三個生命週期方法,它們是:−
start() − 入口點方法,其中需要編寫 JavaFX 圖形程式碼。
stop() − 一個空方法,可以重寫,在這裡您可以編寫停止應用程式的邏輯。
init() − 一個空方法,可以重寫,但不能在此方法中建立舞臺或場景。
除此之外,它還提供了一個名為 **launch()** 的靜態方法來啟動 JavaFX 應用程式。
由於 **launch()** 方法是靜態的,因此您需要從靜態上下文(通常為主函式)呼叫它。每當啟動 JavaFX 應用程式時,將執行以下操作(按相同的順序)。
建立應用程式類的例項。
呼叫 **init()** 方法。
呼叫 **start()** 方法。
啟動器等待應用程式完成並呼叫 **stop()** 方法。
終止 JavaFX 應用程式
當應用程式的最後一個視窗關閉時,JavaFX 應用程式將隱式終止。您可以透過將布林值“False”傳遞給靜態方法 **setImplicitExit()** 來關閉此行為(應從靜態上下文中呼叫)。
您可以使用 **Platform.exit()** 或 **System.exit**(int) 方法顯式終止 JavaFX 應用程式。
示例 1 – 建立一個空視窗
本節將教您如何建立一個顯示空視窗的 JavaFX 示例應用程式。以下是步驟:−
步驟 1:建立類
建立一個 Java 類並繼承包 **javafx.application** 中的 **Application** 類,並實現此類的 start() 方法,如下所示。
public class JavafxSample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception {
}
}
步驟 2:建立組物件
在 **start()** 方法中,透過例項化名為 Group 的類(屬於包 **javafx.scene**)來建立一個組物件,如下所示。
Group root = new Group();
步驟 3:建立場景物件
透過例項化名為 **Scene** 的類(屬於包 **javafx.scene**)來建立一個場景。在此類中,傳遞上一步中建立的 Group 物件 **(root)**。
除了根物件之外,您還可以傳遞兩個雙精度型別的引數,分別表示螢幕的高度和寬度,以及 Group 類的物件,如下所示。
Scene scene = new Scene(root,600, 300);
步驟 4:設定舞臺的標題
您可以使用 **Stage** 類的 **setTitle()** 方法設定舞臺的標題。**primaryStage** 是一個 Stage 物件,作為引數傳遞給場景類的 start 方法。
使用 **primaryStage** 物件,將場景的標題設定為 **示例應用程式**,如下所示。
primaryStage.setTitle("Sample Application");
步驟 5:將場景新增到舞臺
您可以使用名為 **Stage** 的類的 **setScene()** 方法將場景物件新增到舞臺。使用此方法新增上一步中準備的場景物件,如下所示。
primaryStage.setScene(scene);
步驟 6:顯示舞臺的內容
使用名為 **Stage** 類的 **show()** 方法顯示場景的內容,如下所示。
primaryStage.show();
步驟 7:啟動應用程式
透過從主方法呼叫 **Application** 類的靜態方法 **launch()** 來啟動 JavaFX 應用程式,如下所示。
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
示例
以下程式生成一個空的 JavaFX 視窗。將此程式碼儲存在名為 **JavafxSample.java** 的檔案中。
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class JavafxSample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception {
//creating a Group object
Group group = new Group();
//Creating a Scene by passing the group object, height and width
Scene scene = new Scene(group ,600, 300);
//setting color to the scene
scene.setFill(Color.BROWN);
//Setting the title to Stage.
primaryStage.setTitle("Sample Application");
//Adding the scene to Stage
primaryStage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
primaryStage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的 java 檔案。
javac JavafxSample.java java JavafxSample
執行後,上述程式將生成一個 JavaFX 視窗,如下所示。

示例 2 – 繪製直線
在前面的示例中,我們已經看到了如何建立一個空的舞臺,現在在這個示例中,讓我們嘗試使用 JavaFX 庫繪製一條直線。
以下是步驟:−
步驟 1:建立類
建立一個 Java 類並繼承包 **javafx.application** 中的 **Application** 類,並實現此類的 **start()** 方法,如下所示。
public class DrawingLine extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception {
}
}
步驟 2:建立線條
您可以透過例項化名為 **Line** 的類(屬於包 **javafx.scene.shape**)在 JavaFX 中建立線條,例項化此類,如下所示。
//Creating a line object Line line = new Line();
步驟 3:設定線條的屬性
透過設定屬性 **startX、startY、endX** 和 **endY**,使用其各自的 setter 方法指定在 X-Y 平面繪製線條的座標,如下面的程式碼塊所示。
line.setStartX(100.0); line.setStartY(150.0); line.setEndX(500.0); line.setEndY(150.0);
步驟 4:建立組物件
在 start() 方法中,透過例項化名為 Group 的類(屬於包 javafx.scene)來建立一個組物件。
將上一步中建立的 Line(節點)物件作為引數傳遞給 Group 類的建構函式,以便將其新增到組中,如下所示:−
Group root = new Group(line);
步驟 5:建立場景物件
透過例項化名為 **Scene** 的類(屬於包 **javafx.scene**)來建立一個場景。在此類中,傳遞上一步中建立的 Group 物件 **(root)**。
除了根物件之外,您還可以傳遞兩個雙精度型別的引數,分別表示螢幕的高度和寬度,以及 Group 類的物件,如下所示。
Scene scene = new Scene(group ,600, 300);
步驟 6:設定舞臺的標題
您可以使用 **Stage** 類的 **setTitle()** 方法設定舞臺的標題。**primaryStage** 是一個 Stage 物件,作為引數傳遞給場景類的 start 方法。
使用 **primaryStage** 物件,將場景的標題設定為 **示例應用程式**,如下所示。
primaryStage.setTitle("Sample Application");
步驟 7:將場景新增到舞臺
您可以使用名為 **Stage** 的類的 **setScene()** 方法將場景物件新增到舞臺。使用此方法新增上一步中準備的場景物件,如下所示。
primaryStage.setScene(scene);
步驟 8:顯示舞臺的內容
使用名為 **Stage** 類的 **show()** 方法顯示場景的內容,如下所示。
primaryStage.show();
步驟 9:啟動應用程式
透過從主方法呼叫 **Application** 類的靜態方法 **launch()** 來啟動 JavaFX 應用程式,如下所示。
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
示例
以下程式顯示瞭如何使用 JavaFX 生成直線。將此程式碼儲存在名為 **JavafxSample.java** 的檔案中。
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.shape.Line;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class DrawingLine extends Application{
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
//Creating a line object
Line line = new Line();
//Setting the properties to a line
line.setStartX(100.0);
line.setStartY(150.0);
line.setEndX(500.0);
line.setEndY(150.0);
//Creating a Group
Group root = new Group(line);
//Creating a Scene
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 300);
//Setting title to the scene
stage.setTitle("Sample application");
//Adding the scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of a scene
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的 java 檔案。
javac DrawingLine.java java DrawingLine
執行後,上述程式將生成一個 JavaFX 視窗,顯示一條直線,如下所示。

示例 3 – 顯示文字
我們也可以在 JavaFX 場景中嵌入文字。此示例演示如何在 JavaFX 中嵌入文字。
以下是步驟:−
步驟 1:建立類
建立一個 Java 類並繼承包 **javafx.application** 中的 **Application** 類,並實現此類的 **start()** 方法,如下所示。
public class DrawingLine extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage primaryStage) throws Exception {
}
}
步驟 2:嵌入文字
您可以透過例項化名為 **Text** 的類(屬於包 **javafx.scene.shape**)將文字嵌入到 JavaFX 場景中,例項化此類。
您可以透過將要嵌入的文字(以字串格式)傳遞給此類的建構函式來例項化它,或者可以使用預設建構函式建立文字物件,如下所示。
//Creating a Text object Text text = new Text();
步驟 3:設定字型
您可以使用 **Text** 類的 **setFont()** 方法設定文字的字型。此方法接受字型物件作為引數。將給定文字的字型設定為 45,如下所示。
//Setting font to the text text.setFont(new Font(45));
步驟 4:設定文字的位置
您可以透過使用各自的 setter 方法 **setX()** 和 **setY()** 設定 X、Y 座標,在 X-Y 平面設定文字的位置,如下所示。
//setting the position of the text text.setX(50); text.setY(150);
步驟 5:設定要新增的文字
您可以使用 Text 類的 setText() 方法設定要新增的文字。此方法接受一個字串引數,表示要新增的文字。
text.setText("Welcome to Tutorialspoint");
步驟 6:建立組物件
在 **start()** 方法中,透過例項化名為 Group 的類(屬於包 **javafx.scene**)來建立一個組物件。
將上一步中建立的 Text(節點)物件作為引數傳遞給 Group 類的建構函式,以便將其新增到組中,如下所示:−
Group root = new Group(text)
步驟 7:建立場景物件
透過例項化名為 **Scene** 的類(屬於包 **javafx.scene**)來建立一個場景。在此類中,傳遞上一步中建立的 Group 物件 **(root)**。
除了根物件之外,您還可以傳遞兩個雙精度型別的引數,分別表示螢幕的高度和寬度,以及 Group 類的物件,如下所示。
Scene scene = new Scene(group ,600, 300);
步驟 8:設定舞臺的標題
您可以使用 **Stage** 類的 **setTitle()** 方法設定舞臺的標題。**primaryStage** 是一個 Stage 物件,作為引數傳遞給場景類的 start 方法。
使用 **primaryStage** 物件,將場景的標題設定為 **示例應用程式**,如下所示。
primaryStage.setTitle("Sample Application");
步驟 9:將場景新增到舞臺
您可以使用名為 **Stage** 的類的 **setScene()** 方法將場景物件新增到舞臺。使用此方法新增上一步中準備的場景物件,如下所示。
primaryStage.setScene(scene);
步驟 10:顯示舞臺的內容
使用名為 **Stage** 類的 **show()** 方法顯示場景的內容,如下所示。
primaryStage.show();
步驟 11:啟動應用程式
透過從主方法呼叫 **Application** 類的靜態方法 **launch()** 來啟動 JavaFX 應用程式,如下所示。
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
示例
以下是使用 JavaFX 顯示文字的程式。將此程式碼儲存在名為 **DisplayingText.java** 的檔案中。
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.collections.ObservableList;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.scene.text.Font;
import javafx.scene.text.Text;
public class DisplayingText extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
//Creating a Text object
Text text = new Text();
//Setting font to the text
text.setFont(new Font(45));
//setting the position of the text
text.setX(50);
text.setY(150);
//Setting the text to be added.
text.setText("Welcome to Tutorialspoint");
//Creating a Group object
Group root = new Group();
//Retrieving the observable list object
ObservableList list = root.getChildren();
//Setting the text object as a node to the group object
list.add(text);
//Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 300);
//Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("Sample Application");
//Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的 java 檔案。
javac DisplayingText.java java DisplayingText
執行後,上述程式將生成一個 JavaFX 視窗,顯示文字,如下所示。

JavaFX - 2D 形狀
在上一章中,我們已經看到了 JavaFX 的基本應用,學習瞭如何建立空視窗以及如何在 JavaFX 的 XY 平面上繪製線條。除了線條之外,我們還可以繪製其他一些二維圖形。
二維圖形
通常,二維圖形是在 XY 平面上繪製的幾何圖形,包括線條、矩形、圓形等。
使用 JavaFX 庫,您可以繪製:−
預定義形狀,如線條、矩形、圓形、橢圓形、多邊形、折線、三次曲線、二次曲線、弧形。
路徑元素,如 MoveTO 路徑元素、線條、水平線、垂直線、三次曲線、二次曲線、弧形。
除此之外,您還可以透過解析 SVG 路徑繪製二維圖形。
上述每個二維圖形都由一個類表示,所有這些類都屬於包 **javafx.scene.shape**。名為 **Shape** 的類是 JavaFX 中所有二維圖形的基類。
建立二維圖形
要建立圖表,您需要:−
- 例項化所需形狀的相應類。
- 設定形狀的屬性。
- 將形狀物件新增到組中。
例項化相應類
要建立二維圖形,首先需要例項化其相應的類。
例如,如果您想建立一條線,則需要例項化名為 Line 的類,如下所示:−
Line line = new Line();
設定形狀的屬性
例項化類後,需要使用 setter 方法設定形狀的屬性。
例如,要繪製一條線,您需要傳遞線的起點和終點的 x 和 y 座標。您可以使用它們各自的 setter 方法指定這些值,如下所示:
//Setting the Properties of the Line line.setStartX(150.0f); line.setStartY(140.0f); line.setEndX(450.0f); line.setEndY(140.0f);
將形狀物件新增到組
最後,您需要將形狀的物件作為建構函式的引數傳遞給組,如下所示。
//Creating a Group object Group root = new Group(line);
下表提供了 JavaFX 提供的各種形狀(類)的列表。
| 序號 | 形狀和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
線
線是連線兩點的幾何結構。Line 類屬於 javafx.scene.shape 包,表示 XY 平面上的線。 |
| 2 |
矩形
通常,矩形是一個四邊形,它有兩對平行且共線的邊,所有內角都是直角。在 JavaFX 中,矩形由名為 Rectangle 的類表示。此類屬於 javafx.scene.shape 包。 |
| 3 |
圓角矩形
在 JavaFX 中,您可以繪製具有銳邊或圓弧邊的矩形,具有圓弧邊的矩形稱為圓角矩形。 |
| 4 |
圓形
圓形是形成閉合環路的線,環路上的每個點到中心點的距離都固定。在 JavaFX 中,圓形由名為 Circle 的類表示。此類屬於 javafx.scene.shape 包。 |
| 5 |
橢圓
橢圓由兩個點定義,每個點稱為焦點。如果取橢圓上的任意一點,則到焦點點的距離之和為常數。橢圓的大小由這兩個距離之和確定。 在 JavaFX 中,橢圓由名為 Ellipse 的類表示。此類屬於 javafx.scene.shape 包。 |
| 6 |
多邊形
由多個共面的線段首尾相連形成的閉合圖形。在 JavaFX 中,多邊形由名為 Polygon 的類表示。此類屬於 javafx.scene.shape 包。 |
| 7 |
折線
折線與多邊形相同,只是折線末端不閉合。或者,由一個或多個線段組成的連續線。在 JavaFX 中,折線由名為 Polygon 的類表示。此類屬於 javafx.scene.shape 包。 |
| 8 |
三次貝塞爾曲線
三次貝塞爾曲線是 XY 平面上的貝塞爾引數曲線,是 3 次曲線。在 JavaFX 中,三次貝塞爾曲線由名為 CubicCurve 的類表示。此類屬於 javafx.scene.shape 包。 |
| 9 |
二次貝塞爾曲線
二次貝塞爾曲線是 XY 平面上的貝塞爾引數曲線,是 2 次曲線。在 JavaFX 中,二次貝塞爾曲線由名為 QuadCurve 的類表示。此類屬於 javafx.scene.shape 包。 |
| 10 |
弧
弧是曲線的一部分。在 JavaFX 中,弧由名為 Arc 的類表示。此類屬於 javafx.scene.shape 包。 弧的型別除此之外,我們還可以繪製三種類型的弧:開放、弦、圓。 |
| 11 |
SVGPath
在 JavaFX 中,我們可以透過解析 SVG 路徑來構建影像。此類形狀由名為 SVGPath 的類表示。此類屬於 javafx.scene.shape 包。此類具有名為 content 的字串型別屬性。它表示 SVG 路徑編碼字串,影像應從此字串繪製。 |
透過 Path 類繪製更多形狀
在上一節中,我們已經瞭解瞭如何透過例項化類和設定相應引數來繪製一些簡單的預定義形狀。
但是,僅這些預定義形狀不足以構建比 javafx.shape 包提供的基本形狀更復雜的形狀。
例如,如果您想繪製如下所示的圖形元素,則不能依賴這些簡單的形狀。
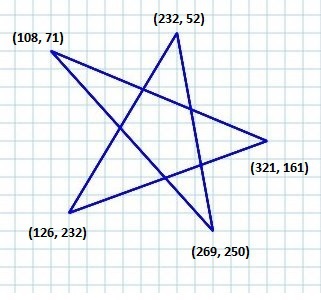
Path 類
為了繪製這種複雜的結構,JavaFX 提供了一個名為 Path 的類。此類表示形狀的幾何輪廓。
它附加到一個可觀察列表,該列表儲存各種 路徑元素,例如 moveTo、LineTo、HlineTo、VlineTo、ArcTo、QuadCurveTo、CubicCurveTo。
例項化時,此類將根據給定的路徑元素構造路徑。
您可以在例項化此類時將路徑元素傳遞給它,如下所示:
Path myshape = new Path(pathElement1, pathElement2, pathElement3);
或者,您可以獲取可觀察列表並使用 addAll() 方法新增所有路徑元素,如下所示:
Path myshape = new Path(); myshape.getElements().addAll(pathElement1, pathElement2, pathElement3);
您還可以使用 add() 方法逐個新增元素,如下所示:
Path myshape = new Path(); myshape.getElements().add(pathElement1);
MoveTo 路徑元素
路徑元素 MoveTo 用於將路徑的當前位置移動到指定點。它通常用於設定使用路徑元素繪製的形狀的起點。
它由 javafx.scene.shape 包中的名為 LineTo 的類表示。它有兩個雙精度資料型別屬性:
X - 從當前位置到要繪製線的點的 x 座標。
Y - 從當前位置到要繪製線的點的 y 座標。
您可以透過例項化 MoveTo 類並將新點的 x、y 座標作為引數傳遞來建立移動到路徑元素,如下所示:
MoveTo moveTo = new MoveTo(x, y);
如果您不向建構函式傳遞任何值,則新點將設定為 (0,0)。
您還可以使用它們各自的 setter 方法(如下所示)為 x、y 座標設定值:
setX(value); setY(value);
示例 - 繪製複雜路徑
在此示例中,我們將展示如何使用 Path、MoveTo 和 Line 類繪製以下形狀。
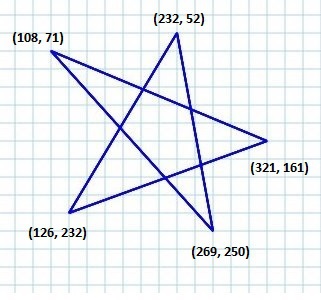
將此程式碼儲存在名為 ComplexShape.java 的檔案中。
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.scene.shape.LineTo;
import javafx.scene.shape.MoveTo;
import javafx.scene.shape.Path;
public class ComplexShape extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
//Creating a Path
Path path = new Path();
//Moving to the starting point
MoveTo moveTo = new MoveTo(108, 71);
//Creating 1st line
LineTo line1 = new LineTo(321, 161);
//Creating 2nd line
LineTo line2 = new LineTo(126,232);
//Creating 3rd line
LineTo line3 = new LineTo(232,52);
//Creating 4th line
LineTo line4 = new LineTo(269, 250);
//Creating 4th line
LineTo line5 = new LineTo(108, 71);
//Adding all the elements to the path
path.getElements().add(moveTo);
path.getElements().addAll(line1, line2, line3, line4, line5);
//Creating a Group object
Group root = new Group(path);
//Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 300);
//Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("Drawing an arc through a path");
//Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的 java 檔案。
javac ComplexShape.java java ComplexShape
執行後,上述程式生成一個 JavaFX 視窗,顯示從當前位置到指定點繪製的弧,如下所示。
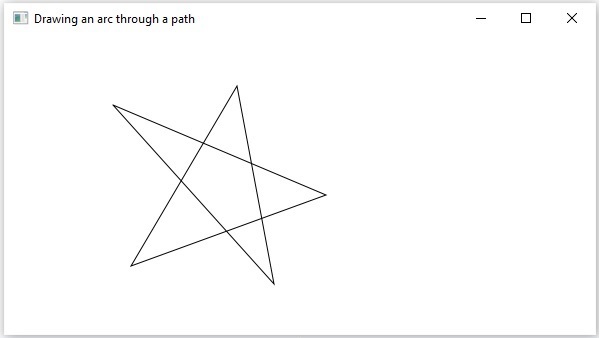
以下是 JavaFX 提供的各種路徑元素(類)。這些類存在於 javafx.shape 包中。所有這些類都繼承 PathElement 類。
| 序號 | 形狀和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
LineTo
路徑元素 line 用於從當前位置到指定座標中的點繪製一條直線。它由名為 LineTo 的類表示。此類屬於 javafx.scene.shape 包。 |
| 2 |
HlineTo
路徑元素 HLineTo 用於從當前位置到指定座標中的點繪製一條水平線。它由名為 HLineTo 的類表示。此類屬於 javafx.scene.shape 包。 |
| 3 |
VLineTo
路徑元素 垂直線 用於從當前位置到指定座標中的點繪製一條垂直線。它由名為 VLineTo 的類表示。此類屬於 javafx.scene.shape 包。 |
| 4 |
QuadCurveTo
路徑元素二次曲線用於從當前位置到指定座標中的點繪製一條 二次曲線。它由名為 QuadraticCurveTo 的類表示。此類屬於 javafx.scene.shape 包。 |
| 5 |
CubicCurveTo
路徑元素 三次曲線 用於從當前位置到指定座標中的點繪製一條三次曲線。它由名為 CubicCurveTo 的類表示。此類屬於 javafx.scene.shape 包。 |
| 6 |
ArcTo
路徑元素 Arc 用於從當前位置到指定座標中的點繪製一條弧。它由名為 ArcTo 的類表示。此類屬於 javafx.scene.shape 包。 |
二維物件的屬性
對於所有二維物件,您可以設定各種屬性,如填充、描邊、StrokeType 等。以下部分討論二維物件的各種屬性。
2D 物件的操作
如果我們將多個形狀新增到一個組中,則第一個形狀會被第二個形狀覆蓋,如下所示。

除了轉換(旋轉、縮放、平移等)和轉換(動畫)之外,您還可以對二維物件執行三種操作,即 - 聯合、減法 和 交集。
| 序號 | 操作和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
聯合操作
此操作將兩個或多個形狀作為輸入,並返回它們佔據的區域。 |
| 2 |
交集操作
此操作將兩個或多個形狀作為輸入,並返回它們之間的交集區域。 |
| 3 |
減法操作
此操作將兩個或多個形狀作為輸入。然後,它返回第一個形狀的區域,不包括被第二個形狀覆蓋的區域。 |
JavaFX - 文字
就像各種形狀一樣,您也可以在 JavaFX 中建立文字節點。文字節點由名為 Text 的類表示,該類屬於 javafx.scene.text 包。
此類包含在 JavaFX 中建立文字並修改其外觀的多個屬性。此類還繼承屬於 javafx.scene.shape 包的 Shape 類。
因此,除了文字的字型、對齊方式、行間距、文字等屬性之外,它還繼承了基本形狀節點屬性,如 strokeFill、stroke、strokeWidth、strokeType 等。
建立文字節點
由於 javafx.scene.text 包中的 Text 類表示 JavaFX 中的文字節點,因此您可以透過例項化此類來建立文字,如下所示:
Text text = new Text();
Text 類包含一個名為 text 的字串型別屬性,該屬性表示要建立的文字。
例項化 Text 類後,您需要使用 setText() 方法為此屬性設定值,如下所示。
String text = "Hello how are you" Text.setText(text);
您還可以透過為 x 和 y 屬性指定值(使用它們各自的 setter 方法,即 setX() 和 setY())來設定文字的位置(原點),如下面的程式碼塊所示:
text.setX(50); text.setY(50);
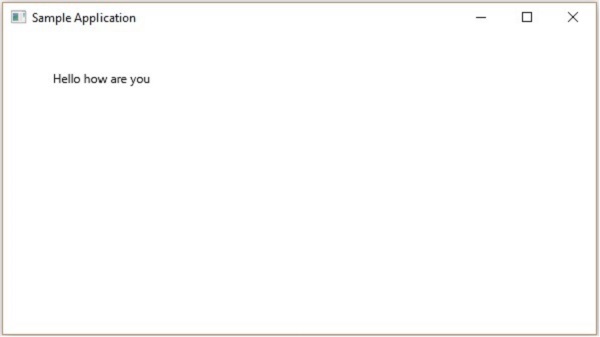
示例
以下程式是一個演示如何在 JavaFX 中建立文字節點的示例。將此程式碼儲存在名為 TextExample.java 的檔案中。
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.scene.text.Text;
public class TextExample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
//Creating a Text object
Text text = new Text();
//Setting the text to be added.
text.setText("Hello how are you");
//setting the position of the text
text.setX(50);
text.setY(50);
//Creating a Group object
Group root = new Group(text);
//Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 300);
//Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("Sample Application");
//Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的 java 檔案。
javac TextExample.java java TextExample
執行後,上述程式生成一個 JavaFX 視窗,顯示指定的文字,如下所示:
文字的位置和字型
預設情況下,由 text 類建立的文字的字型為…,大小為…,顏色為黑色。
您可以使用 setFont() 方法更改文字的字型大小和顏色。此方法接受 Font 類的物件。
名為 Font 的類屬於 javafx.scene.text 包,用於定義文字的字型。此類包含一個名為 font() 的靜態方法。
此方法接受四個引數:
family - 它是字串型別,表示我們要應用於文字的字型的族。
weight − 此屬性表示字型的粗細。它接受9個值,分別是 − FontWeight.BLACK, FontWeight.BOLD, FontWeight.EXTRA_BOLD, FontWeight.EXTRA_LIGHT, LIGHT, MEDIUM, NORMAL, SEMI_BOLD, THIN。
posture − 此屬性表示字型的姿態(常規或斜體)。它接受兩個值 FontPosture.REGULAR 和 FontPosture.ITALIC。
size − 此屬性為double型別,表示字型的尺寸。
您可以使用以下方法設定文字的字型 −
text.setFont(Font.font("verdana", FontWeight.BOLD, FontPosture.REGULAR, 20));
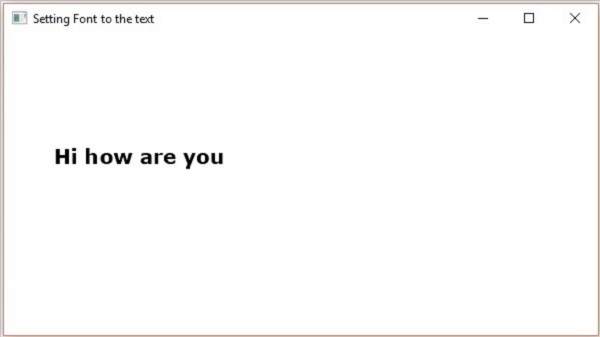
示例
以下程式是一個示例,演示如何在JavaFX中設定文字節點的字型。在這裡,我們將字型設定為Verdana,粗細設定為粗體,姿態設定為常規,尺寸設定為20。
將此程式碼儲存到名為TextFontExample.java的檔案中。
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.scene.text.Font;
import javafx.scene.text.FontPosture;
import javafx.scene.text.FontWeight;
import javafx.scene.text.Text;
public class TextFontExample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
//Creating a Text object
Text text = new Text();
//Setting font to the text
text.setFont(Font.font("verdana", FontWeight.BOLD, FontPosture.REGULAR, 20));
//setting the position of the text
text.setX(50);
text.setY(130);
//Setting the text to be added.
text.setText("Hi how are you");
//Creating a Group object
Group root = new Group(text);
//Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 300);
//Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("Setting Font to the text");
//Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的 java 檔案。
javac TextFontExample.java java TextFontExample
執行上述程式後,會生成一個JavaFX視窗,顯示帶有指定字型的文字,如下所示 −
描邊和顏色
Text類也繼承了包中的Shape類。因此,您可以使用javafx.scene.shape,透過它也可以為文字節點設定描邊和顏色。
您可以使用shape(繼承)類的setFill()方法設定文字的顏色,如下所示 −
text.setFill(Color.BEIGE);
類似地,您可以使用setStroke()方法設定文字的描邊顏色。而描邊的寬度可以使用setStrokeWidth()方法設定,如下所示 −
//Setting the color
text.setFill(Color.BROWN);
//Setting the Stroke
text.setStrokeWidth(2);
//Setting the stroke color
text.setStroke(Color.BLUE);
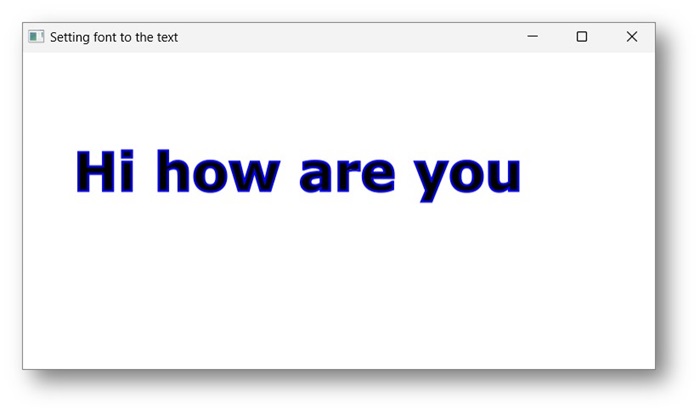
示例
以下程式是一個示例,演示如何設定文字節點的顏色、strokeWidth和strokeColor。在此程式碼中,我們將描邊顏色設定為藍色,文字顏色設定為棕色,描邊寬度設定為2。
將此程式碼儲存到名為StrokeExample.java的檔案中。
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.scene.text.Font;
import javafx.scene.text.FontPosture;
import javafx.scene.text.FontWeight;
import javafx.scene.text.Text;
public class StrokeExample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
//Creating a Text object
Text text = new Text();
//Setting font to the text
text.setFont(Font.font("verdana", FontWeight.BOLD, FontPosture.REGULAR, 50));
//setting the position of the text
text.setX(50);
text.setY(130);
//Setting the color
text.setFill(Color.BROWN);
//Setting the Stroke
text.setStrokeWidth(2);
// Setting the stroke color
text.setStroke(Color.BLUE);
//Setting the text to be added.
text.setText("Hi how are you");
//Creating a Group object
Group root = new Group(text);
//Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 300);
//Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("Setting font to the text");
//Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的 java 檔案。
javac StrokeExample.java java StrokeExample
執行上述程式後,會生成一個JavaFX視窗,顯示帶有指定描邊和顏色屬性的文字,如下所示 −
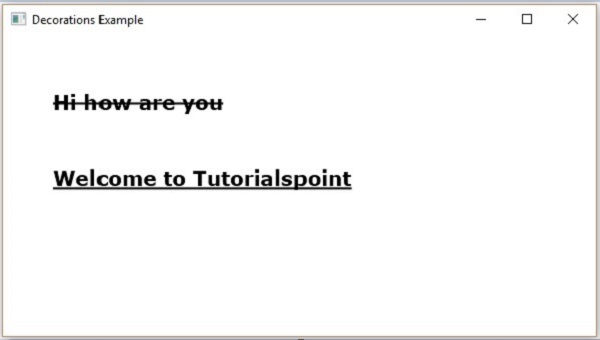
對文字應用裝飾
您還可以應用裝飾,例如刪除線;在這種情況下,文字中會穿過一條線。您可以使用Text類的相關方法為文字新增下劃線。
您可以使用setStrikethrough()方法刪除文字。它接受一個布林值,將值true傳遞給此方法以刪除文字,如下面的程式碼框所示 −
//Striking through the text text1.setStrikethrough(true);
同樣,您可以透過將值true傳遞給setUnderLine()方法來為文字新增下劃線,如下所示 −
//underlining the text text2.setUnderline(true);
示例
以下程式是一個示例,演示如何對文字應用裝飾,例如下劃線或刪除線。將此程式碼儲存到名為DecorationsExample.java的檔案中。
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.scene.text.Font;
import javafx.scene.text.FontPosture;
import javafx.scene.text.FontWeight;
import javafx.scene.text.Text;
public class DecorationsExample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
//Creating a Text_Example object
Text text1 = new Text("Hi how are you");
//Setting font to the text
text1.setFont(Font.font("verdana", FontWeight.BOLD, FontPosture.REGULAR, 20));
//setting the position of the text
text1.setX(50);
text1.setY(75);
//Striking through the text
text1.setStrikethrough(true);
//Creating a Text_Example object
Text text2 = new Text("Welcome to Tutorialspoint");
//Setting font to the text
text2.setFont(Font.font("verdana", FontWeight.BOLD, FontPosture.REGULAR, 20));
//setting the position of the text
text2.setX(50);
text2.setY(150);
//underlining the text
text2.setUnderline(true);
//Creating a Group object
Group root = new Group(text1, text2);
//Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 300);
//Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("Decorations Example");
//Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的Java檔案。
javac DecorationsExample.java java DecorationsExample
執行上述程式後,會生成一個JavaFX視窗,如下所示 −
JavaFX - 效果
效果是任何增強圖形外觀的動作。在JavaFX中,效果是應用於節點以視覺上增強其外觀的演算法。Node類的effect屬性用於指定效果。
在JavaFX中,您可以為節點設定各種效果,例如bloom、blur和glow。這些效果中的每一個都由一個類表示,並且所有這些類都位於名為javafx.scene.effect的包中。
將效果應用於節點
您可以使用setEffect()方法將效果應用於節點。對於此方法,您需要傳遞效果的物件。
要將效果應用於節點,您需要 −
建立節點。
例項化需要應用的效果的相應類。
設定效果的屬性。
使用setEffect()方法將效果應用於節點。
建立節點
首先,透過例項化其各自的類在JavaFX應用程式中建立節點。
例如,如果您想在應用程式中將輝光效果應用於影像。首先,您需要透過例項化Image類來建立影像節點,並設定其檢視,如下所示。
//Creating an image
Image image = new Image("https://tutorialspoint.tw/green/images/logo.png");
//Setting the image view
ImageView imageView = new ImageView(image);
//Setting the position of the image
imageView.setX(100);
imageView.setY(70);
//setting the fit height and width of the image view
imageView.setFitHeight(200);
imageView.setFitWidth(400);
//Setting the preserve ratio of the image view
imageView.setPreserveRatio(true);
例項化相應類
例項化表示需要應用於已建立節點的效果的類。
例如 − 要應用輝光效果,您需要例項化Glow類,如下面的程式碼框所示 −
Glow glow = new Glow();
設定效果的屬性
例項化類後,您需要使用其setter方法設定效果的屬性。
例如 − 要繪製一個三維框,您需要傳遞其寬度、高度和深度。您可以使用其各自的setter方法指定這些值,如下所示 −
//setting the level property glow.setLevel(0.9);
將效果新增到節點
最後,您可以使用setEffect()方法將所需效果應用於節點。例如:要將輝光效果設定為影像節點,您需要將Glow類的物件傳遞給此方法,如下所示 −
imageView.setEffect(glow);
JavaFX效果 − 下表列出了JavaFX提供的各種效果(類)。這些類存在於名為javafx.scene.effect的包中。
| 序號 | 形狀和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 顏色調整
您可以透過將顏色調整效果應用於影像來調整影像的顏色。這包括調整每個畫素的色調、飽和度、亮度和對比度 名為ColorAdjust的類位於javafx.scene.effect包中,表示顏色調整效果。 |
| 2 | 顏色輸入
顏色輸入效果產生的輸出與繪製一個矩形並用顏色填充它相同。與其他效果不同,如果此效果應用於任何節點,它只會顯示一個矩形框(而不是節點)。此效果主要用作其他效果的輸入。 名為ColorInput的類位於javafx.scene.effect包中,表示顏色輸入效果。 |
| 3 | 影像輸入
JavaFX中的影像輸入效果只是將影像嵌入到JavaFX螢幕中。 就像顏色輸入效果(它用於將指定的彩色矩形區域作為輸入傳遞給其他效果一樣),影像輸入效果用於將指定的影像作為輸入傳遞給另一個效果。 名為ImageInput的類位於javafx.scene.effect包中,表示影像輸入效果。 |
| 4 | 混合
通常,混合表示兩種或多種不同事物或物質的混合。如果我們應用此混合效果,它將獲取兩個不同輸入在相同位置的畫素,並根據混合模式生成組合輸出。 名為Blend的類位於javafx.scene.effect包中,表示混合效果。 |
| 5 | 綻放
應用綻放效果時,節點某些部分的畫素會發光。 名為Bloom的類位於javafx.scene.effect包中,表示綻放效果。 |
| 6 | 輝光
就像綻放一樣,輝光效果使給定的輸入影像發光,此效果使輸入的亮畫素更亮。 名為Glow的類位於javafx.scene.effect包中,表示輝光效果。 |
| 7 | 方框模糊
將此模糊效果應用於節點時,會使其變得不清楚。方框模糊是JavaFX提供的模糊效果的一種。在此效果中,當我們將模糊應用於節點時,會使用一個簡單的方框濾鏡。 名為BoxBlur的類位於javafx.scene.effect包中,表示方框模糊效果。 |
| 8 | 高斯模糊
就像方框模糊一樣,高斯模糊是用於模糊JavaFX中節點的效果。高斯模糊效果的唯一區別在於,使用高斯卷積核來產生模糊效果。 名為GaussianBlur的類位於javafx.scene.effect包中,表示高斯模糊效果。 |
| 9 | 運動模糊
就像高斯效果一樣,運動模糊是用於模糊JavaFX中節點的效果。它也使用高斯卷積核來產生模糊效果,但區別在於在此效果中,高斯卷積核與指定的角度一起使用。 名為MotionBlur的類位於javafx.scene.effect包中,表示運動模糊效果。 |
| 10 | 反射
將反射效果應用於JavaFX中的節點時,會在節點底部新增其反射。 名為Reflection的類位於javafx.scene.effect包中,表示反射效果。 |
| 11 |
棕褐色
將棕褐色效果應用於JavaFX中的節點(通常是影像)時,會將其調成紅棕色。 名為SepiaTone的類位於javafx.scene.effect包中,表示棕褐色效果。 |
| 12 | 陰影
此效果會建立指定節點的副本,並具有模糊的邊緣。 名為Shadow的類位於javafx.scene.effect包中,表示棕褐色效果。 |
| 13 | 投影
將此效果應用於節點時,將在指定節點後面建立陰影。 名為DropShadow的類位於javafx.scene.effect包中,表示投影效果。 |
| 14 | 內陰影
將此效果應用於節點時,將在節點邊緣內部建立陰影。 名為InnerShadow的類位於javafx.scene.effect包中,表示內陰影效果。 |
| 15 | 照明
照明效果用於模擬光源發出的光。有不同型別的光源,即點光源、平行光源和聚光燈。 名為Lighting的類位於javafx.scene.effect包中,表示照明效果。 |
| 16 | Light.Distant
將此效果應用於節點時,會模擬其上的光,就像它是由遠處的光源產生的。 平行光源 − 一個距離節點很遠的源。在這裡,光從源向一個方向衰減。 名為Light.Distant的類位於javafx.scene.effect包中,表示平行光源。 |
| 17 | Light.Spot
將此效果應用於節點時,會模擬其上的光,就像它是由聚光燈產生的。 聚光燈源 - 此光源的光線向所有方向衰減。光線的強度取決於物體與光源的距離。 名為Light.Spot的類,位於javafx.scene.effect包中,表示遠光源。 |
| 18 | Point.Spot
將此效果應用於節點時,會在其上模擬光線,就好像它是由點光源產生的。 點光源 - 此光源的光線從一個點向所有方向衰減。光線的強度取決於物體與光源的距離。 名為Point.Spot的類,位於javafx.scene.effect包中,表示點光源。 |
JavaFX - 變換
變換是指透過應用規則將某些圖形更改為其他內容。我們可以有各種型別的變換,例如平移、縮放、旋轉、錯切等。
使用 JavaFX,您可以對節點應用變換,例如旋轉、縮放和平移。所有這些變換都由不同的類表示,這些類屬於javafx.scene.transform包。
| 序號 | 變換與描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 旋轉
在旋轉中,我們將物體圍繞其原點以特定角度θ (theta)旋轉。 |
| 2 | 縮放
要更改物件的大小,可以使用縮放變換。 |
| 3 | 平移
將物件移動到螢幕上的不同位置。 |
| 4 | 錯切
使物體形狀傾斜的變換稱為錯切變換。 |
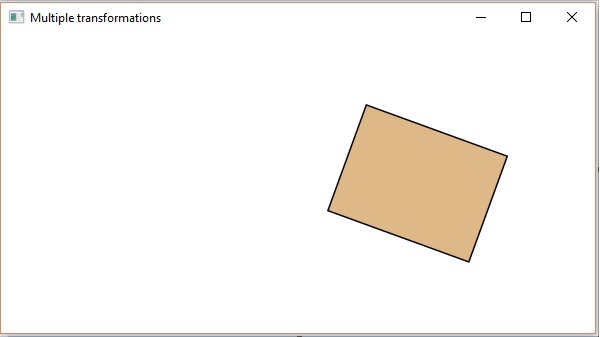
多個變換
您還可以對 JavaFX 中的節點應用多個變換。以下程式是一個示例,它同時對矩形執行旋轉、縮放和平移變換。
將此程式碼儲存在名為以下的檔案中:
MultipleTransformationsExample.java.
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.shape.Rectangle;
import javafx.scene.transform.Rotate;
import javafx.scene.transform.Scale;
import javafx.scene.transform.Translate;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class MultipleTransformationsExample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
//Drawing a Rectangle
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(50, 50, 100, 75);
//Setting the color of the rectangle
rectangle.setFill(Color.BURLYWOOD);
//Setting the stroke color of the rectangle
rectangle.setStroke(Color.BLACK);
//creating the rotation transformation
Rotate rotate = new Rotate();
//Setting the angle for the rotation
rotate.setAngle(20);
//Setting pivot points for the rotation
rotate.setPivotX(150);
rotate.setPivotY(225);
//Creating the scale transformation
Scale scale = new Scale();
//Setting the dimensions for the transformation
scale.setX(1.5);
scale.setY(1.5);
//Setting the pivot point for the transformation
scale.setPivotX(300);
scale.setPivotY(135);
//Creating the translation transformation
Translate translate = new Translate();
//Setting the X,Y,Z coordinates to apply the translation
translate.setX(250);
translate.setY(0);
translate.setZ(0);
//Adding all the transformations to the rectangle
rectangle.getTransforms().addAll(rotate, scale, translate);
//Creating a Group object
Group root = new Group(rectangle);
//Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 300);
//Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("Multiple transformations");
//Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的 java 檔案。
javac MultipleTransformationsExample.java java MultipleTransformationsExample
執行後,上述程式將生成一個 JavaFX 視窗,如下所示。
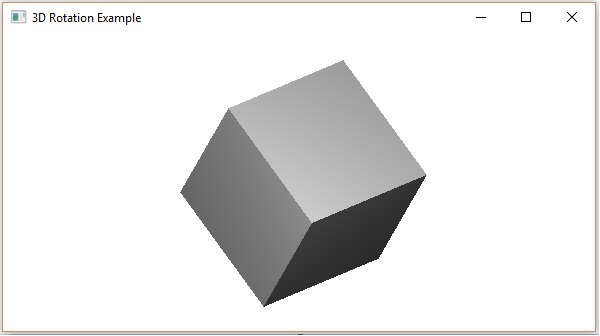
3D 物件的變換
您還可以對 3D 物件應用變換。以下是一個示例,它旋轉和平移一個三維框。
將此程式碼儲存在名為RotationExample3D.java的檔案中。
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.shape.Box;
import javafx.scene.transform.Rotate;
import javafx.scene.transform.Translate;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class RotationExample3D extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
//Drawing a Box
Box box = new Box();
//Setting the properties of the Box
box.setWidth(150.0);
box.setHeight(150.0);
box.setDepth(150.0);
//Creating the translation transformation
Translate translate = new Translate();
translate.setX(400);
translate.setY(150);
translate.setZ(25);
Rotate rxBox = new Rotate(0, 0, 0, 0, Rotate.X_AXIS);
Rotate ryBox = new Rotate(0, 0, 0, 0, Rotate.Y_AXIS);
Rotate rzBox = new Rotate(0, 0, 0, 0, Rotate.Z_AXIS);
rxBox.setAngle(30);
ryBox.setAngle(50);
rzBox.setAngle(30);
box.getTransforms().addAll(translate,rxBox, ryBox, rzBox);
//Creating a Group object
Group root = new Group(box);
//Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 300);
//Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("Drawing a cylinder");
//Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的 java 檔案。
javac RotationExample3D.java java RotationExample3D
執行後,上述程式將生成一個 JavaFX 視窗,如下所示。
JavaFX - 動畫
通常,動畫化一個物件意味著透過快速顯示來建立其運動的錯覺。在 JavaFX 中,可以透過隨時間推移更改節點的屬性來對其進行動畫處理。JavaFX 提供了一個名為javafx.animation的包。此包包含用於為節點建立動畫的類。Animation 是所有這些類的基類。
使用 JavaFX,您可以應用動畫(過渡),例如淡入淡出過渡、填充過渡、旋轉過渡、縮放過渡、描邊過渡、平移過渡、路徑過渡、順序過渡、暫停過渡、並行過渡等。
所有這些過渡都由javafx.animation包中的各個類表示。
要將特定動畫應用於節點,您必須按照以下步驟操作:
使用相應的類建立所需的節點。
例項化要應用的相應過渡(動畫)類
設定過渡的屬性,以及
最後使用Animation類的play()方法播放過渡。
在本章中,我們將討論基本過渡(旋轉、縮放、平移)的示例。
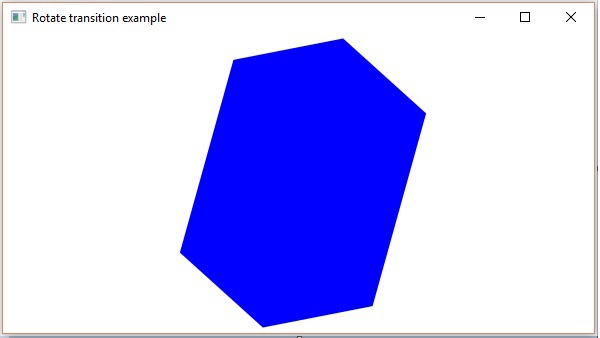
旋轉過渡
以下程式演示了 JavaFX 中的旋轉過渡。將此程式碼儲存在名為RotateTransitionExample.java的檔案中。
import javafx.animation.RotateTransition;
import javafx.application.Application;
import static javafx.application.Application.launch;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.shape.Polygon;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.util.Duration;
public class RotateTransitionExample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
//Creating a hexagon
Polygon hexagon = new Polygon();
//Adding coordinates to the hexagon
hexagon.getPoints().addAll(new Double[]{
200.0, 50.0,
400.0, 50.0,
450.0, 150.0,
400.0, 250.0,
200.0, 250.0,
150.0, 150.0,
});
//Setting the fill color for the hexagon
hexagon.setFill(Color.BLUE);
//Creating a rotate transition
RotateTransition rotateTransition = new RotateTransition();
//Setting the duration for the transition
rotateTransition.setDuration(Duration.millis(1000));
//Setting the node for the transition
rotateTransition.setNode(hexagon);
//Setting the angle of the rotation
rotateTransition.setByAngle(360);
//Setting the cycle count for the transition
rotateTransition.setCycleCount(50);
//Setting auto reverse value to false
rotateTransition.setAutoReverse(false);
//Playing the animation
rotateTransition.play();
//Creating a Group object
Group root = new Group(hexagon);
//Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 300);
//Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("Rotate transition example ");
//Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的 java 檔案。
javac RotateTransitionExample.java java RotateTransitionExample
執行後,上述程式將生成一個 JavaFX 視窗,如下所示。
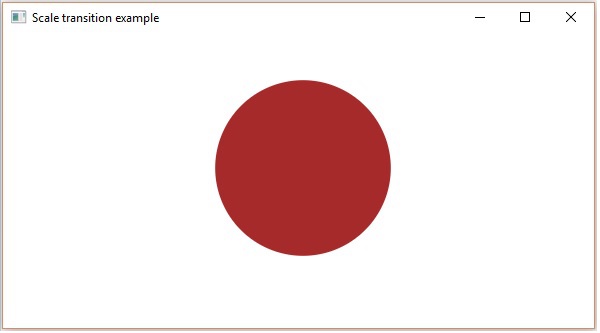
縮放過渡
以下程式演示了 JavaFX 中的縮放過渡。將此程式碼儲存在名為ScaleTransitionExample.java的檔案中。
import javafx.animation.ScaleTransition;
import javafx.application.Application;
import static javafx.application.Application.launch;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.shape.Circle;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.util.Duration;
public class ScaleTransitionExample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
//Drawing a Circle
Circle circle = new Circle();
//Setting the position of the circle
circle.setCenterX(300.0f);
circle.setCenterY(135.0f);
//Setting the radius of the circle
circle.setRadius(50.0f);
//Setting the color of the circle
circle.setFill(Color.BROWN);
//Setting the stroke width of the circle
circle.setStrokeWidth(20);
//Creating scale Transition
ScaleTransition scaleTransition = new ScaleTransition();
//Setting the duration for the transition
scaleTransition.setDuration(Duration.millis(1000));
//Setting the node for the transition
scaleTransition.setNode(circle);
//Setting the dimensions for scaling
scaleTransition.setByY(1.5);
scaleTransition.setByX(1.5);
//Setting the cycle count for the translation
scaleTransition.setCycleCount(50);
//Setting auto reverse value to true
scaleTransition.setAutoReverse(false);
//Playing the animation
scaleTransition.play();
//Creating a Group object
Group root = new Group(circle);
//Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 300);
//Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("Scale transition example");
//Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的 java 檔案。
javac ScaleTransitionExample.java java ScaleTransitionExample
執行後,上述程式將生成一個 JavaFX 視窗,如下所示。
平移過渡
以下程式演示了 JavaFX 中的平移過渡。將此程式碼儲存在名為TranslateTransitionExample.java的檔案中。
import javafx.animation.TranslateTransition;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.shape.Circle;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.util.Duration;
public class TranslateTransitionExample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
//Drawing a Circle
Circle circle = new Circle();
//Setting the position of the circle
circle.setCenterX(150.0f);
circle.setCenterY(135.0f);
//Setting the radius of the circle
circle.setRadius(100.0f);
//Setting the color of the circle
circle.setFill(Color.BROWN);
//Setting the stroke width of the circle
circle.setStrokeWidth(20);
//Creating Translate Transition
TranslateTransition translateTransition = new TranslateTransition();
//Setting the duration of the transition
translateTransition.setDuration(Duration.millis(1000));
//Setting the node for the transition
translateTransition.setNode(circle);
//Setting the value of the transition along the x axis.
translateTransition.setByX(300);
//Setting the cycle count for the transition
translateTransition.setCycleCount(50);
//Setting auto reverse value to false
translateTransition.setAutoReverse(false);
//Playing the animation
translateTransition.play();
//Creating a Group object
Group root = new Group(circle);
//Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 300);
//Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("Translate transition example");
//Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的 java 檔案。
javac TranslateTransitionExample.java java TranslateTransitionExample
執行後,上述程式將生成一個 JavaFX 視窗,如下所示。

除此之外,JavaFX 還提供類來對節點應用更多過渡。以下是 JavaFX 支援的其他型別的過渡。
影響節點屬性的過渡 淡入淡出、填充、描邊
涉及多個基本過渡的過渡 順序、並行、暫停
沿著指定路徑平移物件的過渡 路徑過渡
JavaFX - 顏色
要將顏色應用於應用程式,JavaFX 在javafx.scene.paint包中提供了各種類。此包包含一個名為 Paint 的抽象類,它是所有用於應用顏色的類的基類。
使用這些類,您可以以下列模式應用顏色:
均勻 - 在此模式下,顏色在整個節點中均勻應用。
影像圖案 - 這允許您使用影像圖案填充節點的區域。
漸變 - 在此模式下,應用於節點的顏色從一個點到另一個點變化。它有兩種漸變,即線性漸變和徑向漸變。
所有可以應用顏色的節點類,例如Shape、Text(包括 Scene),都有名為setFill()和setStroke()的方法。這些將分別幫助設定節點及其描邊的顏色值。
這些方法接受 Paint 型別的物件。因此,要建立這些型別的影像中的任何一個,您需要例項化這些類並將物件作為引數傳遞給這些方法。
將顏色應用於節點
要將均勻顏色圖案設定為節點,您需要將 Color 類的物件傳遞給setFill()、setStroke()方法,如下所示:
//Setting color to the text Color color = new Color.BEIGE text.setFill(color); //Setting color to the stroke Color color = new Color.DARKSLATEBLUE circle.setStroke(color);
在上面的程式碼塊中,我們使用 Color 類的靜態變數來建立顏色物件。
同樣,您還可以使用 RGB 值或 HSB 顏色標準或顏色的 Web 雜湊程式碼,如下所示:
//creating color object by passing RGB values
Color c = Color.rgb(0,0,255);
//creating color object by passing HSB values
Color c = Color.hsb(270,1.0,1.0);
//creating color object by passing the hash code for web
Color c = Color.web("0x0000FF",1.0);
示例
以下是一個示例,演示如何在 JavaFX 中將顏色應用於節點。在這裡,我們建立了一個圓形和文字節點,併為其應用顏色。
將此程式碼儲存在名為ColorExample.java的檔案中。
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.scene.shape.Circle;
import javafx.scene.text.Font;
import javafx.scene.text.Text;
public class ColorExample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
//Drawing a Circle
Circle circle = new Circle();
//Setting the properties of the circle
circle.setCenterX(300.0f);
circle.setCenterY(180.0f);
circle.setRadius(90.0f);
//Setting color to the circle
circle.setFill(Color.DARKRED);
//Setting the stroke width
circle.setStrokeWidth(3);
//Setting color to the stroke
circle.setStroke(Color.DARKSLATEBLUE);
//Drawing a text
Text text = new Text("This is a colored circle");
//Setting the font of the text
text.setFont(Font.font("Edwardian Script ITC", 50));
//Setting the position of the text
text.setX(155);
text.setY(50);
//Setting color to the text
text.setFill(Color.BEIGE);
text.setStrokeWidth(2);
text.setStroke(Color.DARKSLATEBLUE);
//Creating a Group object
Group root = new Group(circle, text);
//Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 300);
//Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("Color Example");
//Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的 java 檔案。
Javac ColorExample.java java ColorExample
執行後,上述程式生成一個 JavaFX 視窗,如下所示:

將影像圖案應用於節點
要將影像圖案應用於節點,請例項化ImagePattern類並將它的物件傳遞給setFill()、setStroke()方法。
此類的建構函式接受六個引數,即:
Image - 要使用其建立圖案的影像物件。
x 和 y - 表示錨矩形原點 (x, y) 座標的雙精度變數。
height 和 width - 表示用於建立圖案的影像的高度和寬度的雙精度變數。
isProportional - 這是一個布林變數;將此屬性設定為 true 時,起始和結束位置將設定為成比例的。
ImagePattern radialGradient = new ImagePattern(dots, 20, 20, 40, 40, false);
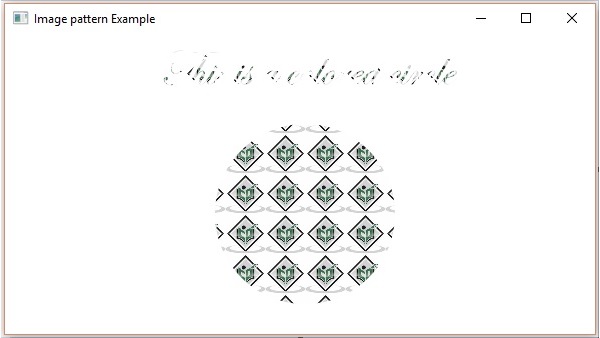
示例
以下是一個示例,演示如何在 JavaFX 中將影像圖案應用於節點。在這裡,我們建立了一個圓形和一個文字節點,併為其應用了影像圖案。
將此程式碼儲存在名為ImagePatternExample.java的檔案中。
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.image.Image;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.paint.ImagePattern;
import javafx.scene.paint.Stop;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.scene.shape.Circle;
import javafx.scene.text.Font;
import javafx.scene.text.Text;
public class ImagePatternExample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
//Drawing a Circle
Circle circle = new Circle();
//Setting the properties of the circle
circle.setCenterX(300.0f);
circle.setCenterY(180.0f);
circle.setRadius(90.0f);
//Drawing a text
Text text = new Text("This is a colored circle");
//Setting the font of the text
text.setFont(Font.font("Edwardian Script ITC", 50));
//Setting the position of the text
text.setX(155);
text.setY(50);
//Setting the image pattern
String link = "https://encrypted-tbn1.gstatic.com"
+ "/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcRQub4GvEezKMsiIf67U"
+ "rOxSzQuQ9zl5ysnjRn87VOC8tAdgmAJjcwZ2qM";
Image image = new Image(link);
ImagePattern radialGradient = new ImagePattern(image, 20, 20, 40, 40, false);
//Setting the linear gradient to the circle and text
circle.setFill(radialGradient);
text.setFill(radialGradient);
//Creating a Group object
Group root = new Group(circle, text);
//Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 300);
//Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("Image pattern Example");
//Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的 java 檔案。
Javac ImagePatternExample.java java ImagePatternExample
執行後,上述程式生成一個 JavaFX 視窗,如下所示:
應用線性漸變圖案
要將線性漸變圖案應用於節點,請例項化LinearGradient類並將它的物件傳遞給setFill()、setStroke()方法。
此類的建構函式接受五個引數,即:
startX、startY - 這些雙精度屬性表示漸變起點的 x 和 y 座標。
endX、endY - 這些雙精度屬性表示漸變終點的 x 和 y 座標。
cycleMethod - 此引數定義如何填充漸變邊界之外的區域(由起點和終點定義)。
proportional - 這是一個布林變數;將此屬性設定為true時,起始和結束位置將設定為成比例的。
Stops - 此引數定義沿漸變線的顏色停止點。
//Setting the linear gradient
Stop[] stops = new Stop[] {
new Stop(0, Color.DARKSLATEBLUE),
new Stop(1, Color.DARKRED)
};
LinearGradient linearGradient =
new LinearGradient(0, 0, 1, 0, true, CycleMethod.NO_CYCLE, stops);
示例
以下是一個示例,演示如何在 JavaFX 中將漸變圖案應用於節點。在這裡,我們建立了一個圓形和一個文字節點,併為其應用了線性漸變圖案。
將此程式碼儲存在名為LinearGradientExample.java的檔案中。
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.paint.CycleMethod;
import javafx.scene.paint.LinearGradient;
import javafx.scene.paint.Stop;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.scene.shape.Circle;
import javafx.scene.text.Font;
import javafx.scene.text.Text;
public class LinearGradientExample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
//Drawing a Circle
Circle circle = new Circle();
//Setting the properties of the circle
circle.setCenterX(300.0f);
circle.setCenterY(180.0f);
circle.setRadius(90.0f);
//Drawing a text
Text text = new Text("This is a colored circle");
//Setting the font of the text
text.setFont(Font.font("Edwardian Script ITC", 55));
//Setting the position of the text
text.setX(140);
text.setY(50);
//Setting the linear gradient
Stop[] stops = new Stop[] {
new Stop(0, Color.DARKSLATEBLUE),
new Stop(1, Color.DARKRED)
};
LinearGradient linearGradient =
new LinearGradient(0, 0, 1, 0, true, CycleMethod.NO_CYCLE, stops);
//Setting the linear gradient to the circle and text
circle.setFill(linearGradient);
text.setFill(linearGradient);
//Creating a Group object
Group root = new Group(circle, text);
//Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 300);
//Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("Linear Gradient Example");
//Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的 java 檔案。
Javac LinearGradientExample.java java LinearGradientExample
執行後,上述程式生成一個 JavaFX 視窗,如下所示:

應用徑向漸變圖案
要將徑向漸變圖案應用於節點,請例項化GradientPattern類並將它的物件傳遞給setFill()、setStroke()方法。
此類的建構函式接受一些引數,其中一些是:
startX、startY - 這些雙精度屬性表示漸變起點的 x 和 y 座標。
endX、endY - 這些雙精度屬性表示漸變終點的 x 和 y 座標。
cycleMethod - 此引數定義如何填充由起點和終點定義的顏色漸變邊界之外的區域。
proportional - 這是一個布林變數;將此屬性設定為true時,起始和結束位置將設定為成比例的。
Stops - 此引數定義沿漸變線的顏色停止點。
//Setting the radial gradient
Stop[] stops = new Stop[] {
new Stop(0.0, Color.WHITE),
new Stop(0.3, Color.RED),
new Stop(1.0, Color.DARKRED)
};
RadialGradient radialGradient =
new RadialGradient(0, 0, 300, 178, 60, false, CycleMethod.NO_CYCLE, stops);
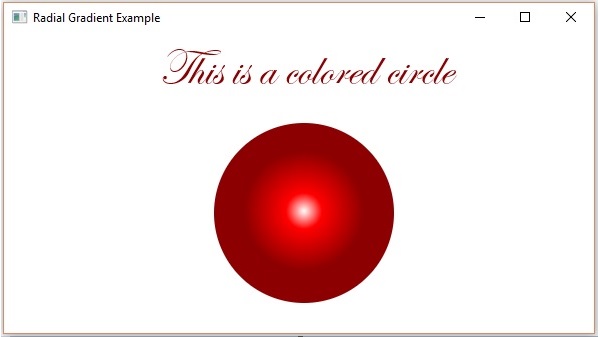
示例
以下是一個示例,演示如何在 JavaFX 中將徑向漸變圖案應用於節點。在這裡,我們建立了一個圓形和一個文字節點,併為其應用了漸變圖案。
將此程式碼儲存在名為RadialGradientExample.java的檔案中。
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.paint.CycleMethod;
import javafx.scene.paint.RadialGradient;
import javafx.scene.paint.Stop;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.scene.shape.Circle;
import javafx.scene.text.Font;
import javafx.scene.text.Text;
public class RadialGradientExample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
//Drawing a Circle
Circle circle = new Circle();
//Setting the properties of the circle
circle.setCenterX(300.0f);
circle.setCenterY(180.0f);
circle.setRadius(90.0f);
//Drawing a text
Text text = new Text("This is a colored circle");
//Setting the font of the text
text.setFont(Font.font("Edwardian Script ITC", 50));
//Setting the position of the text
text.setX(155);
text.setY(50);
//Setting the radial gradient
Stop[] stops = new Stop[] {
new Stop(0.0, Color.WHITE),
new Stop(0.3, Color.RED),
new Stop(1.0, Color.DARKRED)
};
RadialGradient radialGradient =
new RadialGradient(0, 0, 300, 178, 60, false, CycleMethod.NO_CYCLE, stops);
//Setting the radial gradient to the circle and text
circle.setFill(radialGradient);
text.setFill(radialGradient);
//Creating a Group object
Group root = new Group(circle, text);
//Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 300);
//Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("Radial Gradient Example");
//Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的 java 檔案。
Javac RadialGradientExample.java java RadialGradientExample
執行後,上述程式生成一個 JavaFX 視窗,如下所示:
JavaFX - 影像
您可以使用 JavaFX 在javafx.scene.image包中提供的類載入和修改影像。JavaFX 支援Bmp、Gif、Jpeg、Png等影像格式。
本章將教您如何在 JavaFX 中載入影像,如何在多個檢視中投影影像以及如何更改影像的畫素。
載入影像
您可以透過例項化javafx.scene.image包中的名為Image的類來載入 JavaFX 中的影像。
對於類的建構函式,您必須傳遞以下內容之一:
要載入的影像的InputStream物件,或者
包含影像 URL 的字串變數。
//Passing FileInputStream object as a parameter
FileInputStream inputstream = new FileInputStream("C:\\images\\image.jpg");
Image image = new Image(inputstream);
//Loading image from URL
//Image image = new Image(new FileInputStream("url for the image));
載入影像後,您可以透過例項化ImageView類並將影像傳遞給它的建構函式來設定影像的檢視,如下所示:
ImageView imageView = new ImageView(image);
示例
以下是一個示例,演示如何在 JavaFX 中載入影像並設定檢視。
將此程式碼儲存在名為ImageExample.java的檔案中。
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.image.Image;
import javafx.scene.image.ImageView;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class ImageExample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) throws FileNotFoundException {
//Creating an image
Image image = new Image(new FileInputStream("path of the image"));
//Setting the image view
ImageView imageView = new ImageView(image);
//Setting the position of the image
imageView.setX(50);
imageView.setY(25);
//setting the fit height and width of the image view
imageView.setFitHeight(455);
imageView.setFitWidth(500);
//Setting the preserve ratio of the image view
imageView.setPreserveRatio(true);
//Creating a Group object
Group root = new Group(imageView);
//Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 500);
//Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("Loading an image");
//Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的 java 檔案。
Javac ImageExample.java java ImageExample
執行後,上述程式生成一個 JavaFX 視窗,如下所示:

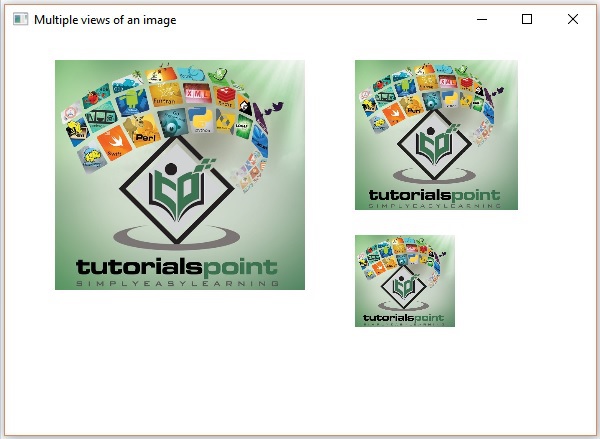
影像的多個檢視
您還可以在同一場景中為影像設定多個檢視。以下程式是一個示例,演示如何在 JavaFX 中的場景中為影像設定各種檢視。
將此程式碼儲存在名為MultipleViews.java的檔案中。
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.image.Image;
import javafx.scene.image.ImageView;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class MultipleViews extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) throws FileNotFoundException {
//Creating an image
Image image = new Image(new FileInputStream("file path"));
//Setting the image view 1
ImageView imageView1 = new ImageView(image);
//Setting the position of the image
imageView1.setX(50);
imageView1.setY(25);
//setting the fit height and width of the image view
imageView1.setFitHeight(300);
imageView1.setFitWidth(250);
//Setting the preserve ratio of the image view
imageView1.setPreserveRatio(true);
//Setting the image view 2
ImageView imageView2 = new ImageView(image);
//Setting the position of the image
imageView2.setX(350);
imageView2.setY(25);
//setting the fit height and width of the image view
imageView2.setFitHeight(150);
imageView2.setFitWidth(250);
//Setting the preserve ratio of the image view
imageView2.setPreserveRatio(true);
//Setting the image view 3
ImageView imageView3 = new ImageView(image);
//Setting the position of the image
imageView3.setX(350);
imageView3.setY(200);
//setting the fit height and width of the image view
imageView3.setFitHeight(100);
imageView3.setFitWidth(100);
//Setting the preserve ratio of the image view
imageView3.setPreserveRatio(true);
//Creating a Group object
Group root = new Group(imageView1, imageView2, imageView3);
//Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 400);
//Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("Multiple views of an image");
//Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的 java 檔案。
Javac MultipleViews.java java MultipleViews
執行後,上述程式生成一個 JavaFX 視窗,如下所示:
寫入畫素
JavaFX 提供名為 **PixelReader** 和 **PixelWriter** 的類來讀取和寫入影像的畫素。**WritableImage** 類用於建立可寫入的影像。
下面是一個演示如何讀取和寫入影像畫素的示例。在這裡,我們讀取影像的顏色值並使其變暗。
將此程式碼儲存在名為 **WritingPixelsExample.java** 的檔案中。
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.image.Image;
import javafx.scene.image.ImageView;
import javafx.scene.image.PixelReader;
import javafx.scene.image.PixelWriter;
import javafx.scene.image.WritableImage;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class WritingPixelsExample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) throws FileNotFoundException {
//Creating an image
Image image = new Image(new FileInputStream("C:\\images\\logo.jpg"));
int width = (int)image.getWidth();
int height = (int)image.getHeight();
//Creating a writable image
WritableImage wImage = new WritableImage(width, height);
//Reading color from the loaded image
PixelReader pixelReader = image.getPixelReader();
//getting the pixel writer
PixelWriter writer = wImage.getPixelWriter();
//Reading the color of the image
for(int y = 0; y < height; y++) {
for(int x = 0; x < width; x++) {
//Retrieving the color of the pixel of the loaded image
Color color = pixelReader.getColor(x, y);
//Setting the color to the writable image
writer.setColor(x, y, color.darker());
}
}
//Setting the view for the writable image
ImageView imageView = new ImageView(wImage);
//Creating a Group object
Group root = new Group(imageView);
//Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 500);
//Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("Writing pixels ");
//Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的 java 檔案。
Javac WritingPixelsExample.java java WritingPixelsExample
執行後,上述程式生成一個 JavaFX 視窗,如下所示:
JavaFX - 3D 形狀
在前面的章節中,我們已經瞭解瞭如何在 XY 平面上繪製 2D 形狀。除了這些 2D 形狀之外,我們還可以使用 JavaFX 繪製其他一些 3D 形狀。
3D 形狀
通常,3D 形狀是在 XYZ 平面上繪製的幾何圖形。這些包括 **圓柱體、球體** 和 **長方體**。
上述每個 3D 形狀都由一個類表示,所有這些類都屬於 **javafx.scene.shape** 包。名為 **Shape3D** 的類是 JavaFX 中所有三維形狀的基類。
建立 3D 形狀
要建立三維形狀,您需要 -
例項化所需 3D 形狀的相應類。
設定 3D 形狀的屬性。
將 3D 形狀物件新增到組中。
例項化相應類
要建立三維形狀,首先需要例項化其相應的類。例如,如果您想建立一個 3D 長方體,則需要例項化名為 Box 的類,如下所示 -
Box box = new Box();
設定形狀的屬性
例項化類後,需要使用 setter 方法設定形狀的屬性。
例如,要繪製一個 3D 長方體,您需要傳遞其寬度、高度、深度。您可以使用其各自的 setter 方法指定這些值,如下所示 -
//Setting the properties of the Box box.setWidth(200.0); box.setHeight(400.0); box.setDepth(200.0);
將形狀物件新增到組
最後,您需要將形狀的物件作為建構函式的引數傳遞給組,如下所示。
//Creating a Group object Group root = new Group(box);
下表提供了 JavaFX 提供的各種 3D 形狀的列表。
| 序號 | 形狀和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
長方體
長方體是一個三維形狀,具有 **長度**(深度)、**寬度** 和 **高度**。 在 JavaFX 中,三維長方體由名為 **Box** 的類表示。此類屬於 **javafx.scene.shape** 包。 透過例項化此類,您可以在 JavaFX 中建立一個長方體節點。 此類具有 3 個雙精度資料型別屬性,即 -
|
| 2 | 圓柱體
圓柱體是一個封閉的立體圖形,有兩個平行的(大多是圓形的)底面,由一個曲面連線。 它由兩個引數描述,即其圓形底面的 **半徑** 和圓柱體的 **高度**。 在 JavaFX 中,圓柱體由名為 **Cylinder** 的類表示。此類屬於 **javafx.scene.shape** 包。 透過例項化此類,您可以在 JavaFX 中建立一個圓柱體節點。此類具有 2 個雙精度資料型別屬性,即 -
|
| 3 | 球體
球體定義為在 3D 空間中與給定點距離 r 相同的所有點的集合。此距離 r 是球體的半徑,給定點是球體的中心。 在 JavaFX 中,球體由名為 **Sphere** 的類表示。此類屬於 **javafx.scene.shape** 包。 透過例項化此類,您可以在 JavaFX 中建立一個球體節點。 此類具有名為 **radius** 的雙精度資料型別屬性。它表示球體的半徑。 |
3D 物件的屬性
對於所有三維物件,您可以設定各種屬性,例如剔除面、繪製模式、材質。
下一節討論 3D 物件的屬性。
剔除面
通常,剔除是指刪除形狀方向不正確的部分(在檢視區域中不可見的部分)。
Cull Face 屬性的型別為 **CullFace**,它表示 3D 形狀的剔除面。您可以使用如下所示的 **setCullFace()** 方法設定形狀的剔除面 -
box.setCullFace(CullFace.NONE);
形狀的筆畫型別可以是 -
**None** - 不執行剔除 (CullFace.NONE)。
**Front** - 所有正面多邊形都被剔除。(CullFace.FRONT)。
**Back** - 所有背面多邊形都被剔除。(StrokeType.BACK)。
預設情況下,三維形狀的剔除面為背面。
示例
以下程式是一個示例,演示了球體的各種剔除面。將此程式碼儲存在名為 **SphereCullFace.java** 的檔案中。
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.shape.CullFace;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.scene.shape.Sphere;
public class SphereCullFace extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
//Drawing Sphere1
Sphere sphere1 = new Sphere();
//Setting the radius of the Sphere
sphere1.setRadius(50.0);
//Setting the position of the sphere
sphere1.setTranslateX(100);
sphere1.setTranslateY(150);
//setting the cull face of the sphere to front
sphere1.setCullFace(CullFace.FRONT);
//Drawing Sphere2
Sphere sphere2 = new Sphere();
//Setting the radius of the Sphere
sphere2.setRadius(50.0);
//Setting the position of the sphere
sphere2.setTranslateX(300);
sphere2.setTranslateY(150);
//Setting the cull face of the sphere to back
sphere2.setCullFace(CullFace.BACK);
//Drawing Sphere3
Sphere sphere3 = new Sphere();
//Setting the radius of the Sphere
sphere3.setRadius(50.0);
//Setting the position of the sphere
sphere3.setTranslateX(500);
sphere3.setTranslateY(150);
//Setting the cull face of the sphere to none
sphere2.setCullFace(CullFace.NONE);
//Creating a Group object
Group root = new Group(sphere1, sphere2, sphere3);
//Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 300);
//Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("Drawing a Sphere");
//Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的Java檔案。
javac SphereCullFace.java java SphereCullFace
執行後,上述程式會生成一個 JavaFX 視窗,顯示三個分別具有剔除面值 **FRONT、BACK** 和 **NONE** 的球體,如下所示 -

繪製模式
它是型別為 **DrawMode** 的屬性,它表示用於繪製當前 3D 形狀的繪製模式。您可以使用如下所示的 setDrawMode() 方法選擇繪製模式來繪製 3D 形狀 -
box.setDrawMode(DrawMode.FILL);
在 JavaFX 中,您可以選擇兩種繪製模式來繪製 3D 形狀,它們是 -
**Fill** - 此模式繪製並填充 2D 形狀 (DrawMode.FILL)。
**Line** - 此模式使用線條繪製 3D 形狀 (DrawMode.LINE)。
預設情況下,三維形狀的繪製模式為填充。
示例
以下程式是一個示例,演示了 3D 長方體的各種繪製模式。將此程式碼儲存在名為 **BoxDrawMode.java** 的檔案中。
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.PerspectiveCamera;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.shape.Box;
import javafx.scene.shape.DrawMode;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class BoxDrawMode extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
//Drawing a Box
Box box1 = new Box();
//Setting the properties of the Box
box1.setWidth(100.0);
box1.setHeight(100.0);
box1.setDepth(100.0);
//Setting the position of the box
box1.setTranslateX(200);
box1.setTranslateY(150);
box1.setTranslateZ(0);
//Setting the drawing mode of the box
box1.setDrawMode(DrawMode.LINE);
//Drawing a Box
Box box2 = new Box();
//Setting the properties of the Box
box2.setWidth(100.0);
box2.setHeight(100.0);
box2.setDepth(100.0);
//Setting the position of the box
box2.setTranslateX(450); //450
box2.setTranslateY(150);//150
box2.setTranslateZ(300);
//Setting the drawing mode of the box
box2.setDrawMode(DrawMode.FILL);
//Creating a Group object
Group root = new Group(box1, box2);
//Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 300);
//Setting camera
PerspectiveCamera camera = new PerspectiveCamera(false);
camera.setTranslateX(0);
camera.setTranslateY(0);
camera.setTranslateZ(0);
scene.setCamera(camera);
//Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("Drawing a Box");
//Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的 java 檔案。
javac BoxDrawMode.java java BoxDrawMode
執行後,上述程式會生成一個 JavaFX 視窗,顯示兩個分別具有繪製模式值 LINE 和 FILL 的長方體,如下所示 -

材質
Cull Face 屬性的型別為 **Material**,它用於選擇 3D 形狀材質的表面。您可以使用如下所示的 **setCullFace()** 方法設定 3D 形狀的材質 -
cylinder.setMaterial(material);
如上所述,對於此方法,您需要傳遞型別為 Material 的物件。**javafx.scene.paint** 包的 **PhongMaterial** 類是此類的子類,並提供 7 個表示 Phong 著色材質的屬性。您可以使用這些屬性的 setter 方法將所有這些型別的材質應用於 3D 形狀的表面。
以下是 JavaFX 中可用的材質型別 -
**bumpMap** - 它表示儲存為 RGB 影像的法線貼圖。
**diffuseMap** - 它表示漫反射貼圖。
**selfIlluminationMap** - 它表示此 PhongMaterial 的自發光貼圖。
**specularMap** - 它表示此 PhongMaterial 的鏡面反射貼圖。
**diffuseColor** - 它表示此 PhongMaterial 的漫反射顏色。
**specularColor** - 它表示此 PhongMaterial 的鏡面反射顏色。
**specularPower** - 它表示此 PhongMaterial 的鏡面反射強度。
預設情況下,三維形狀的材質是具有淺灰色漫反射顏色的 PhongMaterial。
示例
以下是一個示例,在圓柱體上顯示各種材質。將此程式碼儲存在名為 **CylinderMaterials.java** 的檔案中。
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.PerspectiveCamera;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.image.Image;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.paint.PhongMaterial;
import javafx.scene.shape.Cylinder;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class CylinderMaterials extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
//Drawing Cylinder1
Cylinder cylinder1 = new Cylinder();
//Setting the properties of the Cylinder
cylinder1.setHeight(130.0f);
cylinder1.setRadius(30.0f);
//Setting the position of the Cylinder
cylinder1.setTranslateX(100);
cylinder1.setTranslateY(75);
//Preparing the phong material of type bump map
PhongMaterial material1 = new PhongMaterial();
material1.setBumpMap(new Image
("https://tutorialspoint.tw/images/tplogo.gif"));
//Setting the bump map material to Cylinder1
cylinder1.setMaterial(material1);
//Drawing Cylinder2
Cylinder cylinder2 = new Cylinder();
//Setting the properties of the Cylinder
cylinder2.setHeight(130.0f);
cylinder2.setRadius(30.0f);
//Setting the position of the Cylinder
cylinder2.setTranslateX(200);
cylinder2.setTranslateY(75);
//Preparing the phong material of type diffuse map
PhongMaterial material2 = new PhongMaterial();
material2.setDiffuseMap(new Image
("https://tutorialspoint.tw/images/tp-logo.gif"));
//Setting the diffuse map material to Cylinder2
cylinder2.setMaterial(material2);
//Drawing Cylinder3
Cylinder cylinder3 = new Cylinder();
//Setting the properties of the Cylinder
cylinder3.setHeight(130.0f);
cylinder3.setRadius(30.0f);
//Setting the position of the Cylinder
cylinder3.setTranslateX(300);
cylinder3.setTranslateY(75);
//Preparing the phong material of type Self Illumination Map
PhongMaterial material3 = new PhongMaterial();
material3.setSelfIlluminationMap(new Image
("https://tutorialspoint.tw/images/tp-logo.gif"));
//Setting the Self Illumination Map material to Cylinder3
cylinder3.setMaterial(material3);
//Drawing Cylinder4
Cylinder cylinder4 = new Cylinder();
//Setting the properties of the Cylinder
cylinder4.setHeight(130.0f);
cylinder4.setRadius(30.0f);
//Setting the position of the Cylinder
cylinder4.setTranslateX(400);
cylinder4.setTranslateY(75);
//Preparing the phong material of type Specular Map
PhongMaterial material4 = new PhongMaterial();
material4.setSpecularMap(new Image
("https://tutorialspoint.tw/images/tp-logo.gif"));
//Setting the Specular Map material to Cylinder4
cylinder4.setMaterial(material4);
//Drawing Cylinder5
Cylinder cylinder5 = new Cylinder();
//Setting the properties of the Cylinder
cylinder5.setHeight(130.0f);
cylinder5.setRadius(30.0f);
//Setting the position of the Cylinder
cylinder5.setTranslateX(100);
cylinder5.setTranslateY(300);
//Preparing the phong material of type diffuse color
PhongMaterial material5 = new PhongMaterial();
material5.setDiffuseColor(Color.BLANCHEDALMOND);
//Setting the diffuse color material to Cylinder5
cylinder5.setMaterial(material5);
//Drawing Cylinder6
Cylinder cylinder6 = new Cylinder();
//Setting the properties of the Cylinder
cylinder6.setHeight(130.0f);
cylinder6.setRadius(30.0f);
//Setting the position of the Cylinder
cylinder6.setTranslateX(200);
cylinder6.setTranslateY(300);
//Preparing the phong material of type specular color
PhongMaterial material6 = new PhongMaterial();
//setting the specular color map to the material
material6.setSpecularColor(Color.BLANCHEDALMOND);
//Setting the specular color material to Cylinder6
cylinder6.setMaterial(material6);
//Drawing Cylinder7
Cylinder cylinder7 = new Cylinder();
//Setting the properties of the Cylinder
cylinder7.setHeight(130.0f);
cylinder7.setRadius(30.0f);
//Setting the position of the Cylinder
cylinder7.setTranslateX(300);
cylinder7.setTranslateY(300);
//Preparing the phong material of type Specular Power
PhongMaterial material7 = new PhongMaterial();
material7.setSpecularPower(0.1);
//Setting the Specular Power material to the Cylinder
cylinder7.setMaterial(material7);
//Creating a Group object
Group root = new Group(cylinder1 ,cylinder2, cylinder3,
cylinder4, cylinder5, cylinder6, cylinder7);
//Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 400);
//Setting camera
PerspectiveCamera camera = new PerspectiveCamera(false);
camera.setTranslateX(0);
camera.setTranslateY(0);
camera.setTranslateZ(-10);
scene.setCamera(camera);
//Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("Drawing a cylinder");
//Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的 java 檔案。
Javac CylinderMaterials.java java CylinderMaterials
執行後,上述程式會生成一個 JavaFX 視窗,顯示 7 個分別具有材質、凹凸貼圖、漫反射貼圖、自發光貼圖、鏡面反射貼圖、漫反射顏色、鏡面反射顏色、(BLANCHEDALMOND)鏡面反射強度的圓柱體,如下面的螢幕截圖所示 -

JavaFX - 事件處理
在 JavaFX 中,我們可以開發 GUI 應用程式、Web 應用程式和圖形應用程式。在這些應用程式中,每當使用者與應用程式(節點)互動時,就會發生一個事件。
例如,單擊按鈕、移動滑鼠、透過鍵盤輸入字元、從列表中選擇專案、滾動頁面等活動會導致事件發生。
事件型別
事件可以大致分為以下兩類 -
**前臺事件** - 這些事件需要使用者的直接互動。它們是作為使用者與圖形使用者介面中的圖形元件互動的結果而生成的。例如,單擊按鈕、移動滑鼠、透過鍵盤輸入字元、從列表中選擇專案、滾動頁面等。
**後臺事件** - 這些不需要終端使用者互動的事件稱為後臺事件。作業系統中斷、硬體或軟體故障、計時器到期、操作完成是後臺事件的示例。
JavaFX 中的事件
JavaFX 提供了對處理各種事件的支援。名為 **Event** 的類(位於 **javafx.event** 包中)是事件的基類。
其任何子類的例項都是一個事件。JavaFX 提供了各種各樣的事件。其中一些列在下面。
**滑鼠事件** - 這是在單擊滑鼠時發生的輸入事件。它由名為 **MouseEvent** 的類表示。它包括滑鼠單擊、滑鼠按下、滑鼠釋放、滑鼠移動、滑鼠進入目標、滑鼠退出目標等操作。
**鍵盤事件** - 這是指示節點上發生的擊鍵的輸入事件。它由名為 **KeyEvent** 的類表示。此事件包括按鍵按下、按鍵釋放和按鍵輸入等操作。
**拖動事件** - 這是在拖動滑鼠時發生的輸入事件。它由名為 **DragEvent** 的類表示。它包括拖動進入、拖動放下、拖動進入目標、拖動退出目標、拖動經過等操作。
**視窗事件** - 這是與視窗顯示/隱藏操作相關的事件。它由名為 **WindowEvent** 的類表示。它包括視窗隱藏、視窗顯示、視窗隱藏、視窗顯示等操作。
事件處理
事件處理是控制事件並確定如果發生事件應該發生什麼的機制。此機制具有稱為事件處理程式的程式碼,該程式碼在事件發生時執行。
JavaFX 提供處理程式和過濾器來處理事件。在 JavaFX 中,每個事件都有 -
**目標** - 事件發生的節點。目標可以是視窗、場景和節點。
**源** - 生成事件的源將是事件的源。在上述場景中,滑鼠是事件的源。
**型別** - 發生的事件型別;如果是滑鼠事件 - 滑鼠按下、滑鼠釋放是事件型別。
假設我們有一個應用程式,其中包含一個圓形以及停止和播放按鈕,這些按鈕使用組物件插入,如下所示 -

如果您單擊播放按鈕,則源將是滑鼠,目標節點將是播放按鈕,並且生成的事件型別是滑鼠單擊。
JavaFX 中事件處理的階段
每當生成事件時,JavaFX 都會經歷以下階段。
路由構建
每當生成一個事件時,事件的預設/初始路由由事件分發鏈的構建決定。它是從舞臺到源節點的路徑。
以下是當我們在上述場景中點選播放按鈕時,生成的事件的事件分發鏈。
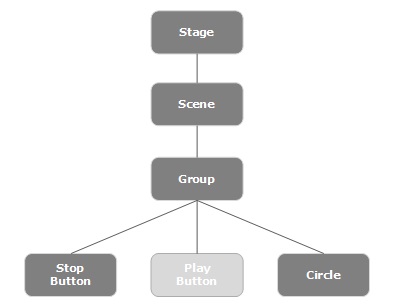
事件捕獲階段
在構建事件分發鏈之後,應用程式的根節點分發事件。此事件傳播到分發鏈中的所有節點(從上到下)。如果這些節點中的任何一個為生成的事件註冊了過濾器,則將執行該過濾器。如果分發鏈中的任何節點都沒有為生成的事件註冊過濾器,則將其傳遞給目標節點,最後目標節點處理該事件。
事件冒泡階段
在事件冒泡階段,事件從目標節點傳播到舞臺節點(從下到上)。如果事件分發鏈中的任何節點為生成的事件註冊了處理程式,則將執行該處理程式。如果這些節點都沒有處理程式來處理該事件,則該事件到達根節點,最後處理過程完成。
事件處理程式和過濾器
事件過濾器和處理程式包含用於處理事件的應用程式邏輯。一個節點可以註冊多個處理程式/過濾器。在父子節點的情況下,您可以為父節點提供一個公共過濾器/處理程式,該過濾器/處理程式將作為所有子節點的預設值處理。
如上所述,在事件處理過程中,過濾器被執行,而在事件冒泡階段,處理程式被執行。所有處理程式和過濾器都實現了包javafx.event的介面EventHandler。
新增和移除事件過濾器
要向節點新增事件過濾器,您需要使用Node類的addEventFilter()方法註冊此過濾器。
//Creating the mouse event handler
EventHandler<MouseEvent> eventHandler = new EventHandler<MouseEvent>() {
@Override
public void handle(MouseEvent e) {
System.out.println("Hello World");
circle.setFill(Color.DARKSLATEBLUE);
}
};
//Adding event Filter
Circle.addEventFilter(MouseEvent.MOUSE_CLICKED, eventHandler);
同樣,您可以使用removeEventFilter()方法移除過濾器,如下所示:
circle.removeEventFilter(MouseEvent.MOUSE_CLICKED, eventHandler);
事件處理示例
以下是一個演示 JavaFX 中使用事件過濾器的事件處理的示例。將此程式碼儲存在名為EventFiltersExample.java的檔案中。
import javafx.application.Application;
import static javafx.application.Application.launch;
import javafx.event.EventHandler;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.input.MouseEvent;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.shape.Circle;
import javafx.scene.text.Font;
import javafx.scene.text.FontWeight;
import javafx.scene.text.Text;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class EventFiltersExample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
//Drawing a Circle
Circle circle = new Circle();
//Setting the position of the circle
circle.setCenterX(300.0f);
circle.setCenterY(135.0f);
//Setting the radius of the circle
circle.setRadius(25.0f);
//Setting the color of the circle
circle.setFill(Color.BROWN);
//Setting the stroke width of the circle
circle.setStrokeWidth(20);
//Setting the text
Text text = new Text("Click on the circle to change its color");
//Setting the font of the text
text.setFont(Font.font(null, FontWeight.BOLD, 15));
//Setting the color of the text
text.setFill(Color.CRIMSON);
//setting the position of the text
text.setX(150);
text.setY(50);
//Creating the mouse event handler
EventHandler<MouseEvent> eventHandler = new EventHandler<MouseEvent>() {
@Override
public void handle(MouseEvent e) {
System.out.println("Hello World");
circle.setFill(Color.DARKSLATEBLUE);
}
};
//Registering the event filter
circle.addEventFilter(MouseEvent.MOUSE_CLICKED, eventHandler);
//Creating a Group object
Group root = new Group(circle, text);
//Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 300);
//Setting the fill color to the scene
scene.setFill(Color.LAVENDER);
//Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("Event Filters Example");
//Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的 java 檔案。
javac EventFiltersExample.java java EventFiltersExample
執行後,上述程式將生成一個 JavaFX 視窗,如下所示。

新增和移除事件處理程式
要向節點新增事件處理程式,您需要使用Node類的addEventHandler()方法註冊此處理程式,如下所示。
//Creating the mouse event handler
EventHandler<javafx.scene.input.MouseEvent> eventHandler =
new EventHandler<javafx.scene.input.MouseEvent>() {
@Override
public void handle(javafx.scene.input.MouseEvent e) {
System.out.println("Hello World");
circle.setFill(Color.DARKSLATEBLUE);
}
};
//Adding the event handler
circle.addEventHandler(javafx.scene.input.MouseEvent.MOUSE_CLICKED, eventHandler);
同樣,您可以使用removeEventHandler()方法移除事件處理程式,如下所示:
circle.removeEventHandler(MouseEvent.MOUSE_CLICKED, eventHandler);
示例
以下程式是一個演示 JavaFX 中使用事件處理程式的事件處理的示例。
將此程式碼儲存在名為EventHandlersExample.java的檔案中。
import javafx.animation.RotateTransition;
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.event.EventHandler;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.PerspectiveCamera;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.TextField;
import javafx.scene.input.KeyEvent;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.paint.PhongMaterial;
import javafx.scene.shape.Box;
import javafx.scene.text.Font;
import javafx.scene.text.FontWeight;
import javafx.scene.text.Text;
import javafx.scene.transform.Rotate;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.util.Duration;
public class EventHandlersExample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
//Drawing a Box
Box box = new Box();
//Setting the properties of the Box
box.setWidth(150.0);
box.setHeight(150.0);
box.setDepth(100.0);
//Setting the position of the box
box.setTranslateX(350);
box.setTranslateY(150);
box.setTranslateZ(50);
//Setting the text
Text text = new Text("Type any letter to rotate the box,
and click on the box to stop the rotation");
//Setting the font of the text
text.setFont(Font.font(null, FontWeight.BOLD, 15));
//Setting the color of the text
text.setFill(Color.CRIMSON);
//setting the position of the text
text.setX(20);
text.setY(50);
//Setting the material of the box
PhongMaterial material = new PhongMaterial();
material.setDiffuseColor(Color.DARKSLATEBLUE);
//Setting the diffuse color material to box
box.setMaterial(material);
//Setting the rotation animation to the box
RotateTransition rotateTransition = new RotateTransition();
//Setting the duration for the transition
rotateTransition.setDuration(Duration.millis(1000));
//Setting the node for the transition
rotateTransition.setNode(box);
//Setting the axis of the rotation
rotateTransition.setAxis(Rotate.Y_AXIS);
//Setting the angle of the rotation
rotateTransition.setByAngle(360);
//Setting the cycle count for the transition
rotateTransition.setCycleCount(50);
//Setting auto reverse value to false
rotateTransition.setAutoReverse(false);
//Creating a text filed
TextField textField = new TextField();
//Setting the position of the text field
textField.setLayoutX(50);
textField.setLayoutY(100);
//Handling the key typed event
EventHandler<KeyEvent> eventHandlerTextField = new EventHandler<KeyEvent>() {
@Override
public void handle(KeyEvent event) {
//Playing the animation
rotateTransition.play();
}
};
//Adding an event handler to the text feld
textField.addEventHandler(KeyEvent.KEY_TYPED, eventHandlerTextField);
//Handling the mouse clicked event(on box)
EventHandler<javafx.scene.input.MouseEvent> eventHandlerBox =
new EventHandler<javafx.scene.input.MouseEvent>() {
@Override
public void handle(javafx.scene.input.MouseEvent e) {
rotateTransition.stop();
}
};
//Adding the event handler to the box
box.addEventHandler(javafx.scene.input.MouseEvent.MOUSE_CLICKED, eventHandlerBox);
//Creating a Group object
Group root = new Group(box, textField, text);
//Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 300);
//Setting camera
PerspectiveCamera camera = new PerspectiveCamera(false);
camera.setTranslateX(0);
camera.setTranslateY(0);
camera.setTranslateZ(0);
scene.setCamera(camera);
//Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("Event Handlers Example");
//Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的 java 檔案。
javac EventHandlersExample.java java EventHandlersExample
執行上述程式後,將生成一個 JavaFX 視窗,顯示一個文字欄位和一個 3D 盒,如下所示:

在這裡,如果您在文字欄位中鍵入一個字母,則 3D 盒將開始沿 x 軸旋轉。如果您再次點選該盒子,旋轉將停止。
使用便捷方法進行事件處理
JavaFX 中的一些類定義了事件處理程式屬性。透過使用其各自的 setter 方法將值設定為這些屬性,您可以註冊到事件處理程式。這些方法被稱為便捷方法。
大多數這些方法存在於 Node、Scene、Window 等類中,並且它們對所有子類可用。
例如,要向按鈕新增滑鼠事件監聽器,您可以使用便捷方法setOnMouseClicked(),如下所示。
playButton.setOnMouseClicked((new EventHandler<MouseEvent>() {
public void handle(MouseEvent event) {
System.out.println("Hello World");
pathTransition.play();
}
}));
示例
以下程式是一個演示 JavaFX 中使用便捷方法的事件處理的示例。
將此程式碼儲存在名為ConvinienceMethodsExample.java的檔案中。
import javafx.animation.PathTransition;
import javafx.application.Application;
import static javafx.application.Application.launch;
import javafx.event.EventHandler;
import javafx.scene.Group;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.input.MouseEvent;
import javafx.scene.paint.Color;
import javafx.scene.shape.Circle;
import javafx.scene.shape.LineTo;
import javafx.scene.shape.MoveTo;
import javafx.scene.shape.Path;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
import javafx.util.Duration;
public class ConvinienceMethodsExample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
//Drawing a Circle
Circle circle = new Circle();
//Setting the position of the circle
circle.setCenterX(300.0f);
circle.setCenterY(135.0f);
//Setting the radius of the circle
circle.setRadius(25.0f);
//Setting the color of the circle
circle.setFill(Color.BROWN);
//Setting the stroke width of the circle
circle.setStrokeWidth(20);
//Creating a Path
Path path = new Path();
//Moving to the staring point
MoveTo moveTo = new MoveTo(208, 71);
//Creating 1st line
LineTo line1 = new LineTo(421, 161);
//Creating 2nd line
LineTo line2 = new LineTo(226,232);
//Creating 3rd line
LineTo line3 = new LineTo(332,52);
//Creating 4th line
LineTo line4 = new LineTo(369, 250);
//Creating 5th line
LineTo line5 = new LineTo(208, 71);
//Adding all the elements to the path
path.getElements().add(moveTo);
path.getElements().addAll(line1, line2, line3, line4, line5);
//Creating the path transition
PathTransition pathTransition = new PathTransition();
//Setting the duration of the transition
pathTransition.setDuration(Duration.millis(1000));
//Setting the node for the transition
pathTransition.setNode(circle);
//Setting the path for the transition
pathTransition.setPath(path);
//Setting the orientation of the path
pathTransition.setOrientation(
PathTransition.OrientationType.ORTHOGONAL_TO_TAN GENT);
//Setting the cycle count for the transition
pathTransition.setCycleCount(50);
//Setting auto reverse value to true
pathTransition.setAutoReverse(false);
//Creating play button
Button playButton = new Button("Play");
playButton.setLayoutX(300);
playButton.setLayoutY(250);
circle.setOnMouseClicked (new EventHandler<javafx.scene.input.MouseEvent>() {
@Override
public void handle(javafx.scene.input.MouseEvent e) {
System.out.println("Hello World");
circle.setFill(Color.DARKSLATEBLUE);
}
});
playButton.setOnMouseClicked((new EventHandler<MouseEvent>() {
public void handle(MouseEvent event) {
System.out.println("Hello World");
pathTransition.play();
}
}));
//Creating stop button
Button stopButton = new Button("stop");
stopButton.setLayoutX(250);
stopButton.setLayoutY(250);
stopButton.setOnMouseClicked((new EventHandler<MouseEvent>() {
public void handle(MouseEvent event) {
System.out.println("Hello World");
pathTransition.stop();
}
}));
//Creating a Group object
Group root = new Group(circle, playButton, stopButton);
//Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(root, 600, 300);
scene.setFill(Color.LAVENDER);
//Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("Convenience Methods Example");
//Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的 java 檔案。
javac ConvinienceMethodsExample.java java ConvinienceMethodsExample
執行上述程式後,將生成一個 JavaFX 視窗,如下所示。在這裡,點選播放按鈕開始動畫,點選停止按鈕停止動畫。
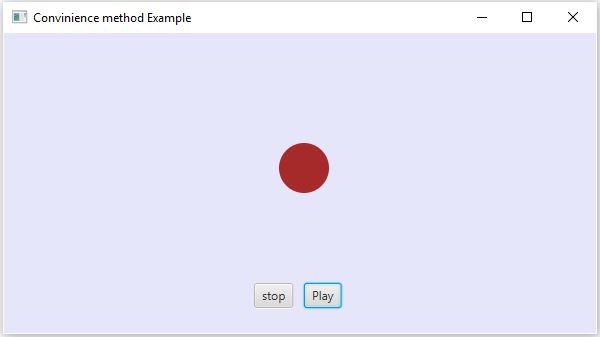
JavaFX - UI 控制元件
每個使用者介面都考慮以下三個主要方面:
UI 元素 - 這些是使用者最終看到並與其互動的核心視覺元素。JavaFX 提供了大量廣泛使用和常見的元素,從基本到複雜,我們將在本教程中介紹這些元素。
佈局 - 它們定義了 UI 元素如何在螢幕上組織,併為 GUI(圖形使用者介面)提供最終的外觀和感覺。這部分將在佈局章節中介紹。
行為 - 這些是使用者與 UI 元素互動時發生的事件。這部分將在事件處理章節中介紹。
JavaFX 在包javafx.scene.control中提供了多個類。為了建立各種 GUI 元件(控制元件),JavaFX 支援多種控制元件,例如日期選擇器、按鈕文字欄位等。
每個控制元件都由一個類表示;您可以透過例項化其相應的類來建立一個控制元件。
以下是使用 JavaFX 設計 GUI 時常用的控制元件列表。
| 序號 | 控制元件 & 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 標籤 Label 物件是放置文字的元件。 |
| 2 | 按鈕 此類建立一個帶標籤的按鈕。 |
| 3 | 顏色選擇器 ColorPicker 提供了一個控制元件面板,用於允許使用者操作和選擇顏色。 |
| 4 | 複選框 CheckBox 是一種圖形元件,可以處於開啟(true)或關閉(false)狀態。 |
| 5 | 單選按鈕 RadioButton 類是一種圖形元件,在一個組中可以處於開啟(true)或關閉(false)狀態。 |
| 6 | 列表檢視 ListView 元件向用戶呈現一個可滾動的文字項列表。 |
| 7 | 文字欄位 TextField 物件是一個文字元件,允許編輯單行文字。 |
| 8 | 密碼欄位 PasswordField 物件是一個專門用於密碼輸入的文字元件。 |
| 9 | 捲軸 Scrollbar 控制元件表示一個捲軸元件,以便使用者能夠從一系列值中進行選擇。 |
| 10 | 檔案選擇器 FileChooser 控制元件表示一個對話方塊視窗,使用者可以在其中選擇檔案。 |
| 11 | 進度條 隨著任務的完成,進度條顯示任務的完成百分比。 |
| 12 | 滑塊 Slider 允許使用者透過在有界區間內滑動旋鈕以圖形方式選擇值。 |
示例
以下程式是一個示例,它在 JavaFX 中顯示一個登入頁面。在這裡,我們使用標籤、文字欄位、密碼欄位和按鈕控制元件。
將此程式碼儲存在名為LoginPage.java的檔案中。
import javafx.application.Application;
import static javafx.application.Application.launch;
import javafx.geometry.Insets;
import javafx.geometry.Pos;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.control.PasswordField;
import javafx.scene.layout.GridPane;
import javafx.scene.text.Text;
import javafx.scene.control.TextField;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class LoginPage extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
//creating label email
Text text1 = new Text("Email");
//creating label password
Text text2 = new Text("Password");
//Creating Text Filed for email
TextField textField1 = new TextField();
//Creating Text Filed for password
PasswordField textField2 = new PasswordField();
//Creating Buttons
Button button1 = new Button("Submit");
Button button2 = new Button("Clear");
//Creating a Grid Pane
GridPane gridPane = new GridPane();
//Setting size for the pane
gridPane.setMinSize(400, 200);
//Setting the padding
gridPane.setPadding(new Insets(10, 10, 10, 10));
//Setting the vertical and horizontal gaps between the columns
gridPane.setVgap(5);
gridPane.setHgap(5);
//Setting the Grid alignment
gridPane.setAlignment(Pos.CENTER);
//Arranging all the nodes in the grid
gridPane.add(text1, 0, 0);
gridPane.add(textField1, 1, 0);
gridPane.add(text2, 0, 1);
gridPane.add(textField2, 1, 1);
gridPane.add(button1, 0, 2);
gridPane.add(button2, 1, 2);
//Styling nodes
button1.setStyle("-fx-background-color: darkslateblue; -fx-text-fill: white;");
button2.setStyle("-fx-background-color: darkslateblue; -fx-text-fill: white;");
text1.setStyle("-fx-font: normal bold 20px 'serif' ");
text2.setStyle("-fx-font: normal bold 20px 'serif' ");
gridPane.setStyle("-fx-background-color: BEIGE;");
//Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(gridPane);
//Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("CSS Example");
//Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的 java 檔案。
javac LoginPage.java java LoginPage
執行後,上述程式將生成一個 JavaFX 視窗,如下所示。
以下程式是一個登錄檔單的示例,它演示了 JavaFX 中的控制元件,例如日期選擇器、單選按鈕、切換按鈕、複選框、列表檢視、選擇列表等。
將此程式碼儲存在名為Registration.java的檔案中。
import javafx.application.Application;
import javafx.collections.FXCollections;
import javafx.collections.ObservableList;
import javafx.geometry.Insets;
import javafx.geometry.Pos;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.control.CheckBox;
import javafx.scene.control.ChoiceBox;
import javafx.scene.control.DatePicker;
import javafx.scene.control.ListView;
import javafx.scene.control.RadioButton;
import javafx.scene.layout.GridPane;
import javafx.scene.text.Text;
import javafx.scene.control.TextField;
import javafx.scene.control.ToggleGroup;
import javafx.scene.control.ToggleButton;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class Registration extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
//Label for name
Text nameLabel = new Text("Name");
//Text field for name
TextField nameText = new TextField();
//Label for date of birth
Text dobLabel = new Text("Date of birth");
//date picker to choose date
DatePicker datePicker = new DatePicker();
//Label for gender
Text genderLabel = new Text("gender");
//Toggle group of radio buttons
ToggleGroup groupGender = new ToggleGroup();
RadioButton maleRadio = new RadioButton("male");
maleRadio.setToggleGroup(groupGender);
RadioButton femaleRadio = new RadioButton("female");
femaleRadio.setToggleGroup(groupGender);
//Label for reservation
Text reservationLabel = new Text("Reservation");
//Toggle button for reservation
ToggleButton Reservation = new ToggleButton();
ToggleButton yes = new ToggleButton("Yes");
ToggleButton no = new ToggleButton("No");
ToggleGroup groupReservation = new ToggleGroup();
yes.setToggleGroup(groupReservation);
no.setToggleGroup(groupReservation);
//Label for technologies known
Text technologiesLabel = new Text("Technologies Known");
//check box for education
CheckBox javaCheckBox = new CheckBox("Java");
javaCheckBox.setIndeterminate(false);
//check box for education
CheckBox dotnetCheckBox = new CheckBox("DotNet");
javaCheckBox.setIndeterminate(false);
//Label for education
Text educationLabel = new Text("Educational qualification");
//list View for educational qualification
ObservableList<String> names = FXCollections.observableArrayList(
"Engineering", "MCA", "MBA", "Graduation", "MTECH", "Mphil", "Phd");
ListView<String> educationListView = new ListView<String>(names);
//Label for location
Text locationLabel = new Text("location");
//Choice box for location
ChoiceBox locationchoiceBox = new ChoiceBox();
locationchoiceBox.getItems().addAll
("Hyderabad", "Chennai", "Delhi", "Mumbai", "Vishakhapatnam");
//Label for register
Button buttonRegister = new Button("Register");
//Creating a Grid Pane
GridPane gridPane = new GridPane();
//Setting size for the pane
gridPane.setMinSize(500, 500);
//Setting the padding
gridPane.setPadding(new Insets(10, 10, 10, 10));
//Setting the vertical and horizontal gaps between the columns
gridPane.setVgap(5);
gridPane.setHgap(5);
//Setting the Grid alignment
gridPane.setAlignment(Pos.CENTER);
//Arranging all the nodes in the grid
gridPane.add(nameLabel, 0, 0);
gridPane.add(nameText, 1, 0);
gridPane.add(dobLabel, 0, 1);
gridPane.add(datePicker, 1, 1);
gridPane.add(genderLabel, 0, 2);
gridPane.add(maleRadio, 1, 2);
gridPane.add(femaleRadio, 2, 2);
gridPane.add(reservationLabel, 0, 3);
gridPane.add(yes, 1, 3);
gridPane.add(no, 2, 3);
gridPane.add(technologiesLabel, 0, 4);
gridPane.add(javaCheckBox, 1, 4);
gridPane.add(dotnetCheckBox, 2, 4);
gridPane.add(educationLabel, 0, 5);
gridPane.add(educationListView, 1, 5);
gridPane.add(locationLabel, 0, 6);
gridPane.add(locationchoiceBox, 1, 6);
gridPane.add(buttonRegister, 2, 8);
//Styling nodes
buttonRegister.setStyle(
"-fx-background-color: darkslateblue; -fx-textfill: white;");
nameLabel.setStyle("-fx-font: normal bold 15px 'serif' ");
dobLabel.setStyle("-fx-font: normal bold 15px 'serif' ");
genderLabel.setStyle("-fx-font: normal bold 15px 'serif' ");
reservationLabel.setStyle("-fx-font: normal bold 15px 'serif' ");
technologiesLabel.setStyle("-fx-font: normal bold 15px 'serif' ");
educationLabel.setStyle("-fx-font: normal bold 15px 'serif' ");
locationLabel.setStyle("-fx-font: normal bold 15px 'serif' ");
//Setting the back ground color
gridPane.setStyle("-fx-background-color: BEIGE;");
//Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(gridPane);
//Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("Registration Form");
//Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的 java 檔案。
javac Registration.java java Registration
執行後,上述程式將生成一個 JavaFX 視窗,如下所示。
JavaFX - 圖表
通常,圖表是資料的圖形表示。有各種型別的圖表來表示資料,例如條形圖、餅圖、折線圖、散點圖等。
JavaFX 支援各種餅圖和XY 圖表。在 XY 平面上表示的圖表包括面積圖、條形圖、氣泡圖、折線圖、散點圖、堆積面積圖、堆積條形圖等。
每個圖表都由一個類表示,所有這些圖表都屬於包javafx.scene.chart。名為Chart的類是 JavaFX 中所有圖表的基類,XYChart是所有在 XY 平面上繪製的圖表的基類。
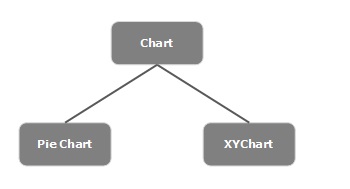
建立圖表
要建立圖表,您需要:−
- 定義圖表的軸
- 例項化相應的類
- 準備資料並將其傳遞給圖表
例項化相應類
要建立圖表,請例項化其相應的類。例如,如果您想建立一個折線圖,則需要例項化名為Line的類,如下所示:
LineChart linechart = new LineChart(xAxis, yAxis);
如上述程式碼所示,在例項化時,您需要傳遞兩個分別表示圖表 X 軸和 Y 軸的物件。
定義軸
通常,圖表的軸可以表示為:
- 數字,例如人口、年齡等
- 類別,例如一週中的幾天、國家/地區。
在 JavaFX 中,軸是一個抽象類,表示 X 軸或 Y 軸。它有兩個子類來定義每種型別的軸,即CategoryAxis和NumberAxis,如下所示:

Category Axis(類別軸) - 透過例項化此類,您可以定義(建立)一個 X 軸或 Y 軸,其中每個值表示一個類別。您可以透過例項化此類來定義類別軸,如下所示:
CategoryAxis xAxis = new CategoryAxis();
在此軸上,您需要設定類別的列表並將標籤設定為軸,如下所示:
//setting the list of categories.
xAxis.setCategories(FXCollections.<String>observableArrayList
(Arrays.asList("n ame1", "name2"….)));
//Setting label to the axis
xAxis.setLabel("name of the axis ");
NumberAxis(數值軸) - 透過例項化此類,您可以定義(建立)一個 X 軸或 Y 軸,其中每個值表示一個數值。您可以使用任何 Number 型別與此Axis一起使用,例如 Long、Double、BigDecimal 等。您可以透過例項化此類來定義數值軸,如下所示:
//Defining the axis
NumberAxis yAxis = new NumberAxis();
//Setting labelto the axis
yAxis.setLabel("name of the axis");
將資料傳遞給 XY 圖表
所有 XY 圖表都沿 XY 平面表示。要在圖表中繪製一組點,我們需要指定一系列 XY 座標。
包javafx.scene.chart的<X,Y>類是一個類,您可以使用它將資料傳送到圖表。此類儲存一個命名系列的可觀察列表。您可以使用XYChart.Series類的getData()方法獲取此列表,如下所示:
ObservableList list = series.getData();
其中,series是XYChart.Series類的物件。您可以使用add()方法將資料新增到此列表中,如下所示:
list.add(new XYChart.Data(x-axis data, y-axis data));
這兩行可以一起編寫,如下所示:
series.getData().add(new XYChart.Data(x-axis data, y-axis data));
下表描述了 JavaFX 提供的各種圖表(類):
| 序號 | 圖表 & 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 餅圖
餅圖是將值表示為圓的不同顏色切片。這些切片被標記,並且對應於每個切片的值在圖表中表示。 在 JavaFX 中,餅圖由名為PieChart的類表示。此類屬於包javafx.scene.chart。 |
| 2 | 折線圖
折線圖或線形圖以一系列資料點(標記)連線直線段的形式顯示資訊。折線圖顯示資料如何在相等的時間頻率下變化。 在 JavaFX 中,折線圖由名為LineChart的類表示。此類屬於包javafx.scene.chart。透過例項化此類,您可以在 JavaFX 中建立一個 LineChart 節點。 |
| 3 | 面積圖
面積圖用於繪製基於區域的圖表。它繪製給定點序列和軸之間的區域。通常,此圖表用於比較兩個量。 在 JavaFX 中,面積圖由名為AreaChart的類表示。此類屬於包javafx.scene.chart。透過例項化此類,您可以在 JavaFX 中建立一個 AreaChart 節點。 |
| 4 | 條形圖
條形圖用於使用矩形條表示分組資料。這些條的長度描繪了值。條形圖中的條可以垂直或水平繪製。 在 JavaFX 中,條形圖由名為BarChart的類表示。此類屬於包javafx.scene.chart。透過例項化此類,您可以在 JavaFX 中建立一個 BarChart 節點。 |
| 5 |
氣泡圖
氣泡圖用於繪製三維資料。第三維將由氣泡的大小(半徑)表示。 在 JavaFX 中,氣泡圖由名為BubbleChart的類表示。此類屬於javafx.scene.chart包。透過例項化此類,您可以在 JavaFX 中建立 BubbleChart 節點。 |
| 6 | 散點圖
散點圖是一種圖表型別,它使用笛卡爾平面中繪製的兩個變數的值。它通常用於找出兩個變數之間的關係。 在 JavaFX 中,散點圖由名為ScatterChart的類表示。此類屬於javafx.scene.chart包。透過例項化此類,您可以在 JavaFX 中建立 ScatterChart 節點。 |
| 7 | 堆積面積圖
在 JavaFX 中,堆積面積圖由名為StackedAreaChart的類表示。 此類屬於javafx.scene.chart包。透過例項化此類,您可以在 JavaFX 中建立 StackedAreaChart 節點。 |
| 8 | 堆積條形圖
在 JavaFX 中,堆積條形圖由名為StackedBarChart的類表示。 此類屬於javafx.scene.chart包。透過例項化此類,您可以在 JavaFX 中建立 StackedBarChart 節點。 |
JavaFX - 佈局窗格(容器)
在場景中構建所有所需的節點後,我們通常會按順序排列它們。
容器內元件的這種排列稱為容器的佈局。我們也可以說我們遵循了一種佈局,因為它包括將所有元件放置在容器內的特定位置。
JavaFX 提供了幾種預定義的佈局,例如HBox、VBox、Border Pane、Stack Pane、Text Flow、Anchor Pane、Title Pane、Grid Pane、Flow Panel等。
上面提到的每個佈局都由一個類表示,所有這些類都屬於javafx.layout包。名為Pane的類是 JavaFX 中所有佈局的基類。
建立佈局
要建立佈局,您需要 -
- 建立節點。
- 例項化所需佈局的相應類。
- 設定佈局的屬性。
- 將所有建立的節點新增到佈局中。
建立節點
首先,透過例項化其各自的類來建立 JavaFX 應用程式所需的節點。
例如,如果您希望在 HBox 佈局中有一個文字欄位和兩個按鈕(分別為播放和停止),則必須首先建立這些節點,如下面的程式碼塊所示 -
//Creating a text field
TextField textField = new TextField();
//Creating the play button
Button playButton = new Button("Play");
//Creating the stop button
Button stopButton = new Button("stop");
例項化相應類
建立節點(並在其上完成所有操作)後,例項化所需佈局的類。
例如,如果您想建立一個 Hbox 佈局,則需要按如下方式例項化此類。
HBox hbox = new HBox();
設定佈局的屬性
例項化類後,您需要使用其各自的 setter 方法設定佈局的屬性。
例如 - 如果您想在 HBox 佈局中建立的節點之間設定間距,則需要為名為 spacing 的屬性設定值。這可以透過使用 setter 方法setSpacing()來完成,如下所示 -
hbox.setSpacing(10);
將形狀物件新增到組
最後,您需要將形狀的物件作為建構函式的引數傳遞給組,如下所示。
//Creating a Group object Group root = new Group(line);
佈局窗格
以下是 JavaFX 提供的各種佈局窗格(類)。這些類存在於javafx.scene.layout包中。
| 序號 | 形狀和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | HBox
HBox 佈局將應用程式中的所有節點排列在同一水平行中。 javafx.scene.layout包中的HBox類表示水平盒佈局。 |
| 2 | VBox
VBox 佈局將應用程式中的所有節點排列在同一垂直列中。 javafx.scene.layout包中的VBox類表示垂直盒佈局。 |
| 3 | BorderPane
Border Pane 佈局將應用程式中的節點排列在頂部、左側、右側、底部和中心位置。 javafx.scene.layout包中的BorderPane類表示邊框窗格佈局。 |
| 4 | StackPane
Stack Pane 佈局將應用程式中的節點一個疊放在另一個上面,就像堆疊一樣。首先新增的節點放置在堆疊的底部,下一個節點放置在其頂部。 javafx.scene.layout包中的StackPane類表示堆疊窗格佈局。 |
| 5 | TextFlow
Text Flow 佈局將多個文字節點排列在一個流中。 javafx.scene.layout包中的TextFlow類表示文字流佈局。 |
| 6 | AnchorPane
Anchor Pane 佈局將應用程式中的節點錨定在距窗格特定距離的位置。 javafx.scene.layout包中的AnchorPane類表示錨點窗格佈局。 |
| 7 | TilePane
Tile Pane 佈局以統一大小的平鋪形式新增應用程式中的所有節點。 javafx.scene.layout包中的TilePane類表示 TilePane 佈局。 |
| 8 | GridPane
Grid Pane 佈局將應用程式中的節點排列成一個行和列的網格。在使用 JavaFX 建立表單時,此佈局非常方便。 javafx.scene.layout包中的GridPane類表示 GridPane 佈局。 |
| 9 | FlowPane
Flow Pane 佈局將所有節點包裝在一個流中。水平 Flow Pane 在其高度處包裝窗格的元素,而垂直 Flow Pane 在其寬度處包裝元素。 javafx.scene.layout包中的FlowPane類表示 Flow Pane 佈局。 |
JavaFX - CSS
層疊樣式表,也稱為 CSS,是一種簡單的設計語言,旨在簡化使網頁美觀的流程。
CSS 處理網頁的視覺效果部分。使用 CSS,您可以控制文字的顏色、字型的樣式、段落之間的間距、列的大小和佈局。除此之外,您還可以控制使用的背景影像或顏色、佈局設計、不同裝置和螢幕尺寸的顯示變化以及各種其他效果。
JavaFX 中的 CSS
JavaFX 為您提供了使用 CSS 來增強應用程式外觀的功能。javafx.css包包含用於為 JavaFX 應用程式應用 CSS 的類。
CSS 包含由瀏覽器解釋然後應用於文件中相應元素的樣式規則。
樣式規則由三個部分組成,它們是 -
選擇器 - 選擇器是將應用樣式的 HTML 標籤。這可以是任何標籤,例如<h1>或<table>等。
屬性 - 屬性是 HTML 標籤的屬性型別。簡單來說,所有 HTML 屬性都轉換為 CSS 屬性。它們可以是顏色、邊框等。
值 - 值分配給屬性。例如,顏色屬性可以具有值紅色或#F1F1F1等。
您可以按如下方式放置 CSS 樣式規則語法 -
selector { property: value }
JavaFX 使用的預設樣式表是modena.css。它位於 JavaFX 執行時 jar 中。
新增您自己的樣式表
您可以按如下方式將您自己的樣式表新增到 JavaFX 中的場景中 -
Scene scene = new Scene(new Group(), 500, 400);
scene.getStylesheets().add("path/stylesheet.css");
新增內聯樣式表
您還可以使用setStyle()方法新增內聯樣式。這些樣式僅包含鍵值對,並且適用於設定它們的節點。以下是將內聯樣式表設定為按鈕的示例程式碼。
.button {
-fx-background-color: red;
-fx-text-fill: white;
}
示例
假設我們已經開發了一個 JavaFX 應用程式,該應用程式顯示一個包含文字欄位、密碼欄位和兩個按鈕的表單。預設情況下,此表單的外觀如下面的螢幕截圖所示 -
以下程式是一個示例,演示如何在 JavaFX 中向上述應用程式新增樣式。
將此程式碼儲存在名為CssExample.java的檔案中
import javafx.application.Application;
import static javafx.application.Application.launch;
import javafx.geometry.Insets;
import javafx.geometry.Pos;
import javafx.scene.Scene;
import javafx.scene.control.Button;
import javafx.scene.control.PasswordField;
import javafx.scene.layout.GridPane;
import javafx.scene.text.Text;
import javafx.scene.control.TextField;
import javafx.stage.Stage;
public class CssExample extends Application {
@Override
public void start(Stage stage) {
//creating label email
Text text1 = new Text("Email");
//creating label password
Text text2 = new Text("Password");
//Creating Text Filed for email
TextField textField1 = new TextField();
//Creating Text Filed for password
PasswordField textField2 = new PasswordField();
//Creating Buttons
Button button1 = new Button("Submit");
Button button2 = new Button("Clear");
//Creating a Grid Pane
GridPane gridPane = new GridPane();
//Setting size for the pane
gridPane.setMinSize(400, 200);
//Setting the padding
gridPane.setPadding(new Insets(10, 10, 10, 10));
//Setting the vertical and horizontal gaps between the columns
gridPane.setVgap(5);
gridPane.setHgap(5);
//Setting the Grid alignment
gridPane.setAlignment(Pos.CENTER);
//Arranging all the nodes in the grid
gridPane.add(text1, 0, 0);
gridPane.add(textField1, 1, 0);
gridPane.add(text2, 0, 1);
gridPane.add(textField2, 1, 1);
gridPane.add(button1, 0, 2);
gridPane.add(button2, 1, 2);
//Styling nodes
button1.setStyle("-fx-background-color: darkslateblue; -fx-text-fill: white;");
button2.setStyle("-fx-background-color: darkslateblue; -fx-text-fill: white;");
text1.setStyle("-fx-font: normal bold 20px 'serif' ");
text2.setStyle("-fx-font: normal bold 20px 'serif' ");
gridPane.setStyle("-fx-background-color: BEIGE;");
// Creating a scene object
Scene scene = new Scene(gridPane);
// Setting title to the Stage
stage.setTitle("CSS Example");
// Adding scene to the stage
stage.setScene(scene);
//Displaying the contents of the stage
stage.show();
}
public static void main(String args[]){
launch(args);
}
}
使用以下命令從命令提示符編譯並執行儲存的 java 檔案。
javac CssExample.java java CssExample
執行後,上述程式將生成一個 JavaFX 視窗,如下所示。
