
- 資料結構與演算法
- DSA - 首頁
- DSA - 概述
- DSA - 環境搭建
- DSA - 演算法基礎
- DSA - 漸近分析
- 資料結構
- DSA - 資料結構基礎
- DSA - 資料結構和型別
- DSA - 陣列資料結構
- 連結串列
- DSA - 連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 雙向連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 迴圈連結串列資料結構
- 棧與佇列
- DSA - 棧資料結構
- DSA - 表示式解析
- DSA - 佇列資料結構
- 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 線性搜尋演算法
- DSA - 二分搜尋演算法
- DSA - 插值搜尋
- DSA - 跳躍搜尋演算法
- DSA - 指數搜尋
- DSA - 斐波那契搜尋
- DSA - 子列表搜尋
- DSA - 雜湊表
- 排序演算法
- DSA - 排序演算法
- DSA - 氣泡排序演算法
- DSA - 插入排序演算法
- DSA - 選擇排序演算法
- DSA - 歸併排序演算法
- DSA - 希爾排序演算法
- DSA - 堆排序
- DSA - 桶排序演算法
- DSA - 計數排序演算法
- DSA - 基數排序演算法
- DSA - 快速排序演算法
- 圖資料結構
- DSA - 圖資料結構
- DSA - 深度優先遍歷
- DSA - 廣度優先遍歷
- DSA - 生成樹
- 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹的遍歷
- DSA - 二叉搜尋樹
- DSA - AVL樹
- DSA - 紅黑樹
- DSA - B樹
- DSA - B+樹
- DSA - 伸展樹
- DSA - 字典樹
- DSA - 堆資料結構
- 遞迴
- DSA - 遞迴演算法
- DSA - 使用遞迴實現漢諾塔
- DSA - 使用遞迴實現斐波那契數列
- 分治法
- DSA - 分治法
- DSA - 最大最小問題
- DSA - Strassen矩陣乘法
- DSA - Karatsuba演算法
- 貪心演算法
- DSA - 貪心演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(貪心法)
- DSA - Prim最小生成樹
- DSA - Kruskal最小生成樹
- DSA - Dijkstra最短路徑演算法
- DSA - 地圖著色演算法
- DSA - 分數揹包問題
- DSA - 帶截止時間的作業排序
- DSA - 最優合併模式演算法
- 動態規劃
- DSA - 動態規劃
- DSA - 矩陣鏈乘法
- DSA - Floyd-Warshall演算法
- DSA - 0-1揹包問題
- DSA - 最長公共子序列演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(動態規劃法)
- 近似演算法
- DSA - 近似演算法
- DSA - 頂點覆蓋演算法
- DSA - 集合覆蓋問題
- DSA - 旅行商問題(近似演算法)
- 隨機化演算法
- DSA - 隨機化演算法
- DSA - 隨機化快速排序演算法
- DSA - Karger最小割演算法
- DSA - Fisher-Yates洗牌演算法
- DSA有用資源
- DSA - 問答
- DSA - 快速指南
- DSA -有用資源
- DSA - 討論
資料結構中的字串
什麼是字串?
字串是一種用於儲存字元序列的原始資料結構型別。它通常用於儲存、操作和處理文字,例如使用者輸入、訊息、標籤等。每種程式語言都有自己獨特的字串表示規則。例如,在Java中,字串被視為物件,而在C中,它表示為char資料型別的陣列。在下圖中,我們可以看到一個字串:
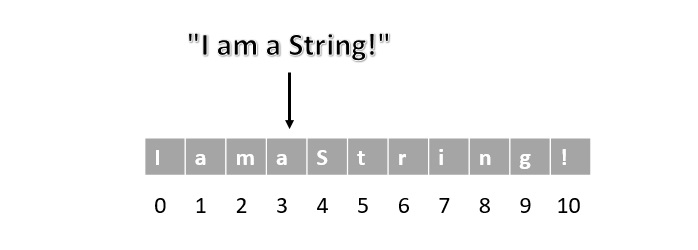
在本教程中,我們將探討字串的一些屬性和操作,以及它們如何在不同的程式語言中實現。
語法
在C程式語言中建立字串的語法:
char string_name[string_size] = {chars within single quotes and separated by commas};
or,
char string_name[string_size] = "string in double quotes";
除了上述語法外,C++還提供了一種建立字串的替代方法:
string string_name = "string in double quotes";
在Java程式語言中建立字串:
String string_name = "string in double quotes";
or,
String string_name = new String("values");
在Python程式語言中建立字串:
string_name = "string in double quotes"
字串的必要性
字串是應用程式與使用者互動最簡單且最常用的方式。它們易於理解和使用,因為它們基於人類可讀的字元。此外,它們還用於儲存各種資料,例如文字、數字、符號、二進位制、十六進位制等。
字串表示
與陣列類似,字串也表示為儲存桶的集合,每個儲存桶儲存一個字元。這些儲存桶的索引從“0”到“n-1”,其中n是該特定字串的長度。例如,大小為10的字串將具有從0到9的索引儲存桶。下圖說明了字串是如何表示的:
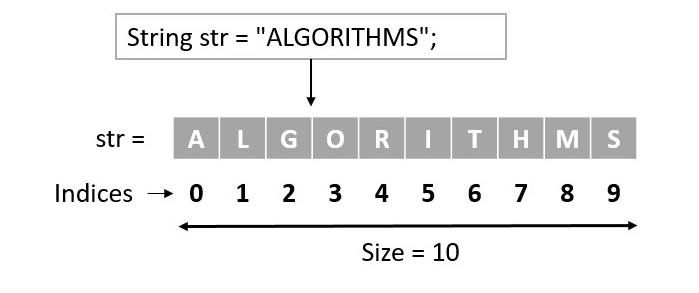
以下是上述表示的一些要點。
索引總是從0開始。
如果索引從0到9,則表示字串有10個元素。
可以透過其索引訪問每個字元。
字串的基本操作
可以對字串執行許多操作,例如搜尋、分割、修剪、索引等等。每種程式語言都有自己的一套內建函式或方法,可以輕鬆地執行這些操作。
以下是可對給定字串執行的基本操作:
- 連線 - 將兩個或多個字串連線在一起。
- 長度 - 列印字串中的字元數。
- 子字串 - 查詢更大字串的一部分。
- 反轉 - 反向列印字串字元。
- 索引 - 使用其索引訪問特定字元。
連線操作
連線操作是將兩個或多個字串連線在一起以形成新字串的過程。例如,將兩個字串“Tutorials”和“Point”連線在一起將得到“TutorialsPoint”。這可以使用不同的運算子或方法來完成,具體取決於程式語言。
演算法
以下是連線兩個字串的演算法。
1. Start 2. Declare and Initialize two strings. 3. Perform concatenation. 4. Print the result. 5. Stop
示例
在這裡,我們看到連線操作的實際實現,我們使用兩個不同的字串來形成一個新的字串:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(){
// defining two strings
char sOne[15] = "Tutorials";
char sTwo[15] = "Point";
// concatenating the strings
strcat(sOne, sTwo);
// printing the result
printf("New String: %s\n", sOne);
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// defining two strings
string sOne = "Tutorials";
string sTwo = "Point";
// concatenating the strings
string newStr = sOne + sTwo;
// printing the result
cout <<"New String: " << newStr << endl;
}
public class ConctStr {
public static void main(String []args){
// defining two strings
String sOne = "Tutorials";
String sTwo = "Point";
// concatenating the strings
String newStr = sOne + sTwo;
// printing the result
System.out.println("New String: " + newStr);
}
}
# defining two strings
sOne = "Tutorials"
sTwo = "Point"
# concatenating the strings
newStr = sOne + sTwo
# printing the result
print("New String: " + newStr)
輸出
New String: TutorialsPoint
查詢字串的長度
查詢字串的長度意味著列印該字串中的字元數。例如,字串“Tutorix”的長度為7。字串的長度可用於迭代其字元、訪問給定索引處的特定字元或從原始字串中切片子字串。
演算法
查詢字串長度的演算法如下:
1. Start 2. Declare and Initialize a string. 3. Find the number of characters. 4. Print the result. 5. Stop
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
// the string given as
char name[] = "tutorialspoint";
// loop to find the length of given string
int strLength = 0;
while (name[strLength] != '\0') {
strLength++;
}
// to print the result
printf("The length of given string is: %d\n", strLength);
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// the string given as
string name = "tutorialspoint";
// to ind the length of given string
int strLength = name.length();
// to print the result
cout << "The length of given string is: " << strLength << endl;
return 0;
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// the string given as
String name = "tutorialspoint";
// to ind the length of given string
int strLength = name.length();
// to print the result
System.out.println("The length of given string is: " + strLength);
}
}
# the string given as
name = "tutorialspoint"
# to find the length of given string
length = len(name)
# Print the result
print("The length of given string is:", length)
輸出
The length of given string is: 14
在字串中查詢子字串
子字串指的是字串的一部分或子集。在此操作中,我們需要找到給定子字串的索引。
演算法
假設我們有一個名為newSubStr的子字串,我們需要找到它的索引號。以下是查詢子字串的演算法。
1. Start 2. Declare and Initialize a string. 3. Define a sub-string. 4. Check index of sub-string. 5. If found, print index of first character of sub-string otherwise print "-1". 6. Stop
示例
在下面的示例中,我們演示了此操作在各種程式語言中的實現:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
// Original string
char orgnlStr[] = "tutorialspoint";
// Substring to find
char newSubStr[] = "point";
// to find the pointer to the substring
char *indX = strstr(orgnlStr, newSubStr);
// to check if the substring is present
if (indX == NULL) {
printf("-1\n");
} else {
printf("Substring found at index: %ld\n", indX - orgnlStr);
}
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// Original string
string orgnlStr = "tutorialspoint";
// Substring to find
string newSubStr = "point";
// to find index of the substring
int indX = orgnlStr.find(newSubStr);
// Check if the substring is present
if (indX == -1) {
cout << "-1" << endl;
} else {
cout << "Substring found at index: " << indX << endl;
}
return 0;
}
public class Substr {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Original string
String orgnlStr = "tutorialspoint";
// Substring to find
String newSubStr = "point";
// to find index of the substring
int indX = orgnlStr.indexOf(newSubStr);
// to check if the substring is found
if (indX == -1) {
System.out.println("-1");
} else {
System.out.println("Substring found at index: " + indX);
}
}
}
# Original string
orgnlStr = "tutorialspoint"
# Substring to find
newSubStr = "point"
# to find index of the substring
indX = orgnlStr.find(newSubStr)
# to check if the substring is found
if indX == -1:
print("-1")
else:
print("Substring found at index:", indX)
輸出
Substring found at index: 9
反轉字串的內容
在反轉操作中,我們反轉字串中字元的順序。這將產生一個新字串,其中包含與原始字串相同的字元,但順序相反。
演算法
假設我們有一個字串,我們需要反轉它。以下是反轉字串的演算法。
1. Start 2. Declare an empty string. 3. Define a for loop to iterate over the characters of original string. 4. Append each character to the reversed string. 5. Print the result. 6. Stop
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// function to reverse the string
char* rev_str(char* orgnlStr) {
int len = strlen(orgnlStr);
// to store the reversed string
char* revStr = (char*)malloc(len + 1);
// loop to reverse the string
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
revStr[i] = orgnlStr[len - i - 1];
}
// Return the reversed string
revStr[len] = '\0';
return revStr;
}
int main() {
printf("Printing the string in reverse order: \n");
// calling the function to print the result
printf("%s\n", rev_str("tutorials"));
printf("%s\n", rev_str("point"));
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
// function to reverse the string
string rev_str(string orgnlStr) {
// Initializing an empty string
string revStr = "";
// loop to reverse the string
for (int i = orgnlStr.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
// Append each character to the reversed string
revStr += orgnlStr[i];
}
// Return the reversed string
return revStr;
}
int main() {
cout << "Printing the string in reverse order: " << endl;
// calling the function to print the result
cout << rev_str("tutorials") << endl;
cout << rev_str("point") << endl;
return 0;
}
public class Main {
// method to reverse the string
public static String rev_str(String orgnlStr) {
// Initializing an empty string
String revStr = "";
// loop to reverse the string
for (int i = orgnlStr.length() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
// Append each character to the reversed string
revStr += orgnlStr.charAt(i);
}
// Return the reversed string
return revStr;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Printing the string in reverse order:");
// calling the method to print the result
System.out.println(rev_str("tutorials"));
System.out.println(rev_str("point"));
}
}
# function to reverse the string
def rev_str(orgnlStr):
# Initializing an empty string
revStr = ""
# loop to reverse the string
for i in range(len(orgnlStr) - 1, -1, -1):
# Append each character to the reversed string
revStr += orgnlStr[i]
# Return the reversed string
return revStr
# calling the function to print the result
print("Printing the string in reverse order:")
print(rev_str("tutorials"))
print(rev_str("point"))
輸出
Printing the string in reverse order: slairotut tniop
字串中的索引
在此操作中,我們嘗試在索引的幫助下訪問或定位特定字元。
演算法
從給定字串中訪問指定字元的演算法如下:
1. Start 2. Declare and Initialize a string. 3. Find the index number of specified character. 4. Print the result. 5. Stop
示例
在這裡,我們看到了索引操作的實際實現:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(){
char str[] = "Tutorials Point";
char *ptr = strchr(str, 'o');
int indX = ptr - str;
// print the result
printf("The index of given character is: %d\n", indX);
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main() {
string str = "Tutorials Point";
int indX = str.find('o');
// print the result
cout << "The index of given character is: " << indX << endl;
return 0;
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "Tutorials Point";
int indX = str.indexOf('o');
System.out.println("The index of given character is: " + indX);
}
}
# defining a string
str = "Tutorials Point"
indX = str.find('o')
# print the result
print("The index of given character is:", indX)
輸出
The index of given character is: 3