
- 資料結構與演算法
- DSA - 首頁
- DSA - 概覽
- DSA - 環境設定
- DSA - 演算法基礎
- DSA - 漸進分析
- 資料結構
- DSA - 資料結構基礎
- DSA - 資料結構和型別
- DSA - 陣列資料結構
- 連結串列
- DSA - 連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 雙向連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 迴圈連結串列資料結構
- 棧與佇列
- DSA - 棧資料結構
- DSA - 表示式解析
- DSA - 佇列資料結構
- 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 線性搜尋演算法
- DSA - 二分搜尋演算法
- DSA - 插值搜尋
- DSA - 跳躍搜尋演算法
- DSA - 指數搜尋
- DSA - 斐波那契搜尋
- DSA - 子列表搜尋
- DSA - 雜湊表
- 排序演算法
- DSA - 排序演算法
- DSA - 氣泡排序演算法
- DSA - 插入排序演算法
- DSA - 選擇排序演算法
- DSA - 歸併排序演算法
- DSA - 希爾排序演算法
- DSA - 堆排序
- DSA - 桶排序演算法
- DSA - 計數排序演算法
- DSA - 基數排序演算法
- DSA - 快速排序演算法
- 圖資料結構
- DSA - 圖資料結構
- DSA - 深度優先遍歷
- DSA - 廣度優先遍歷
- DSA - 生成樹
- 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹遍歷
- DSA - 二叉搜尋樹
- DSA - AVL 樹
- DSA - 紅黑樹
- DSA - B 樹
- DSA - B+ 樹
- DSA - 伸展樹
- DSA - 字典樹
- DSA - 堆資料結構
- 遞迴
- DSA - 遞迴演算法
- DSA - 使用遞迴實現漢諾塔
- DSA - 使用遞迴實現斐波那契數列
- 分治法
- DSA - 分治法
- DSA - 最大最小問題
- DSA - Strassen 矩陣乘法
- DSA - Karatsuba 演算法
- 貪心演算法
- DSA - 貪心演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(貪心演算法)
- DSA - Prim 最小生成樹
- DSA - Kruskal 最小生成樹
- DSA - Dijkstra 最短路徑演算法
- DSA - 地圖著色演算法
- DSA - 分數揹包問題
- DSA - 帶截止日期的作業排序
- DSA - 最優合併模式演算法
- 動態規劃
- DSA - 動態規劃
- DSA - 矩陣鏈乘法
- DSA - Floyd-Warshall 演算法
- DSA - 0-1 揹包問題
- DSA - 最長公共子序列演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(動態規劃方法)
- 近似演算法
- DSA - 近似演算法
- DSA - 頂點覆蓋演算法
- DSA - 集合覆蓋問題
- DSA - 旅行商問題(近似演算法)
- 隨機化演算法
- DSA - 隨機化演算法
- DSA - 隨機化快速排序演算法
- DSA - Karger 最小割演算法
- DSA - Fisher-Yates 洗牌演算法
- DSA 有用資源
- DSA - 問答
- DSA - 快速指南
- DSA - 有用資源
- DSA - 討論
樹遍歷
遍歷是訪問樹中所有節點的過程,也可能列印它們的的值。因為所有節點都透過邊(連結)連線,我們總是從根(頭部)節點開始。也就是說,我們無法隨機訪問樹中的節點。有三種方法用於遍歷樹:
中序遍歷
先序遍歷
後序遍歷
通常,我們遍歷樹是為了搜尋或定位樹中給定的項或鍵,或者列印它包含的所有值。
中序遍歷
在這種遍歷方法中,先訪問左子樹,然後訪問根節點,最後訪問右子樹。我們應該始終記住,每個節點本身都可以表示一個子樹。
如果二叉樹以**中序**方式遍歷,則輸出將以升序產生排序的鍵值。
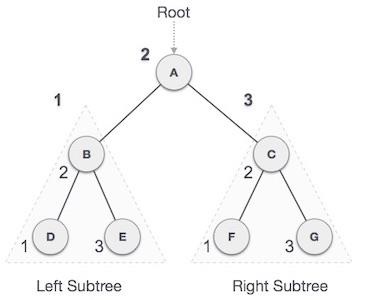
我們從**A**開始,按照中序遍歷,移動到它的左子樹**B**。**B**也以中序方式遍歷。這個過程一直持續到所有節點都被訪問。此樹的中序遍歷輸出將為:
D → B → E → A → F → C → G
演算法
直到所有節點都被遍歷:
Step 1 − Recursively traverse left subtree. Step 2 − Visit root node. Step 3 − Recursively traverse right subtree.
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild;
struct node *rightChild;
};
struct node *root = NULL;
void insert(int data){
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//if tree is empty
if(root == NULL) {
root = tempNode;
} else {
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1) {
parent = current;
//go to left of the tree
if(data < parent->data) {
current = current->leftChild;
//insert to the left
if(current == NULL) {
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}//go to right of the tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
//insert to the right
if(current == NULL) {
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
void inorder_traversal(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL) {
inorder_traversal(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ",root->data);
inorder_traversal(root->rightChild);
}
}
int main(){
int i;
int array[7] = { 27, 14, 35, 10, 19, 31, 42 };
for(i = 0; i < 7; i++)
insert(array[i]);
printf("Inorder traversal: ");
inorder_traversal(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
Inorder traversal: 10 14 19 27 31 35 42
#include <iostream>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild;
struct node *rightChild;
};
struct node *root = NULL;
void insert(int data){
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//if tree is empty
if(root == NULL) {
root = tempNode;
} else {
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1) {
parent = current;
//go to left of the tree
if(data < parent->data) {
current = current->leftChild;
//insert to the left
if(current == NULL) {
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}//go to right of the tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
//insert to the right
if(current == NULL) {
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
void inorder_traversal(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL) {
inorder_traversal(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ",root->data);
inorder_traversal(root->rightChild);
}
}
int main(){
int i;
int array[7] = { 27, 14, 35, 10, 19, 31, 42 };
for(i = 0; i < 7; i++)
insert(array[i]);
printf("Inorder traversal: ");
inorder_traversal(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
Inorder traversal: 10 14 19 27 31 35 42
class Node {
int data;
Node leftChild;
Node rightChild;
public Node(int key) {
data = key;
leftChild = rightChild = null;
}
}
public class TreeDataStructure {
Node root = null;
void inorder_traversal(Node node) {
if(node != null) {
inorder_traversal(node.leftChild);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
inorder_traversal(node.rightChild);
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
TreeDataStructure tree = new TreeDataStructure();
tree.root = new Node(27);
tree.root.leftChild = new Node(12);
tree.root.rightChild = new Node(3);
tree.root.leftChild.leftChild = new Node(44);
tree.root.leftChild.rightChild = new Node(17);
tree.root.rightChild.leftChild = new Node(56);
System.out.println("Inorder traversal: ");
tree.inorder_traversal(tree.root);
}
}
輸出
Inorder traversal: 44 12 17 27 56 3
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.leftChild = None
self.rightChild = None
self.data = key
# Create a function to perform inorder tree traversal
def InorderTraversal(root):
if root:
InorderTraversal(root.leftChild)
print(root.data)
InorderTraversal(root.rightChild)
# Main class
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = Node(3)
root.leftChild = Node(26)
root.rightChild = Node(42)
root.leftChild.leftChild = Node(54)
root.leftChild.rightChild = Node(65)
root.rightChild.leftChild = Node(12)
# Function call
print("Inorder traversal of binary tree is")
InorderTraversal(root)
輸出
Inorder traversal of binary tree is 54 26 65 3 12 42
先序遍歷
在這種遍歷方法中,先訪問根節點,然後訪問左子樹,最後訪問右子樹。
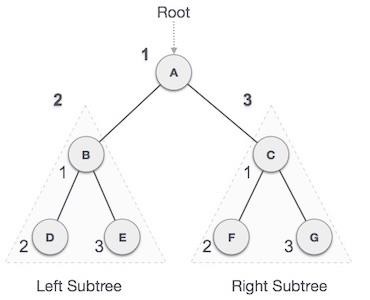
我們從**A**開始,按照先序遍歷,首先訪問**A**本身,然後移動到它的左子樹**B**。**B**也以先序方式遍歷。這個過程一直持續到所有節點都被訪問。此樹的先序遍歷輸出將為:
A → B → D → E → C → F → G
演算法
直到所有節點都被遍歷:
Step 1 − Visit root node. Step 2 − Recursively traverse left subtree. Step 3 − Recursively traverse right subtree.
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild;
struct node *rightChild;
};
struct node *root = NULL;
void insert(int data){
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//if tree is empty
if(root == NULL) {
root = tempNode;
} else {
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1) {
parent = current;
//go to left of the tree
if(data < parent->data) {
current = current->leftChild;
//insert to the left
if(current == NULL) {
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}//go to right of the tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
//insert to the right
if(current == NULL) {
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
void pre_order_traversal(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL) {
printf("%d ",root->data);
pre_order_traversal(root->leftChild);
pre_order_traversal(root->rightChild);
}
}
int main(){
int i;
int array[7] = { 27, 14, 35, 10, 19, 31, 42 };
for(i = 0; i < 7; i++)
insert(array[i]);
printf("Preorder traversal: ");
pre_order_traversal(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
Preorder traversal: 27 14 10 19 35 31 42
#include <iostream>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild;
struct node *rightChild;
};
struct node *root = NULL;
void insert(int data){
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//if tree is empty
if(root == NULL) {
root = tempNode;
} else {
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1) {
parent = current;
//go to left of the tree
if(data < parent->data) {
current = current->leftChild;
//insert to the left
if(current == NULL) {
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}//go to right of the tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
//insert to the right
if(current == NULL) {
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
void pre_order_traversal(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL) {
printf("%d ",root->data);
pre_order_traversal(root->leftChild);
pre_order_traversal(root->rightChild);
}
}
int main(){
int i;
int array[7] = { 27, 14, 35, 10, 19, 31, 42 };
for(i = 0; i < 7; i++)
insert(array[i]);
printf("Preorder traversal: ");
pre_order_traversal(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
Preorder traversal: 27 14 10 19 35 31 42
class Node {
int data;
Node leftChild;
Node rightChild;
public Node(int key) {
data = key;
leftChild = rightChild = null;
}
}
public class TreeDataStructure {
Node root = null;
void pre_order_traversal(Node node) {
if(node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
pre_order_traversal(node.leftChild);
pre_order_traversal(node.rightChild);
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
TreeDataStructure tree = new TreeDataStructure();
tree.root = new Node(27);
tree.root.leftChild = new Node(12);
tree.root.rightChild = new Node(3);
tree.root.leftChild.leftChild = new Node(44);
tree.root.leftChild.rightChild = new Node(17);
tree.root.rightChild.leftChild = new Node(56);
System.out.println("Preorder traversal: ");
tree.pre_order_traversal(tree.root);
}
}
輸出
Preorder traversal: 27 12 44 17 3 56
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.leftChild = None
self.rightChild = None
self.data = key
# Create a function to perform postorder tree traversal
def PreorderTraversal(root):
if root:
print(root.data)
PreorderTraversal(root.leftChild)
PreorderTraversal(root.rightChild)
# Main class
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = Node(3)
root.leftChild = Node(26)
root.rightChild = Node(42)
root.leftChild.leftChild = Node(54)
root.leftChild.rightChild = Node(65)
root.rightChild.leftChild = Node(12)
print("Preorder traversal of binary tree is")
PreorderTraversal(root)
輸出
Preorder traversal of binary tree is 3 26 54 65 42 12
後序遍歷
在這種遍歷方法中,根節點最後被訪問,因此得名。首先遍歷左子樹,然後遍歷右子樹,最後遍歷根節點。
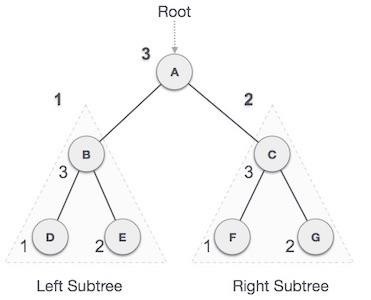
我們從**A**開始,按照先序遍歷,首先訪問左子樹**B**。**B**也以後序方式遍歷。這個過程一直持續到所有節點都被訪問。此樹的後序遍歷輸出將為:
D → E → B → F → G → C → A
演算法
直到所有節點都被遍歷:
Step 1 − Recursively traverse left subtree. Step 2 − Recursively traverse right subtree. Step 3 − Visit root node.
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild;
struct node *rightChild;
};
struct node *root = NULL;
void insert(int data){
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//if tree is empty
if(root == NULL) {
root = tempNode;
} else {
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1) {
parent = current;
//go to left of the tree
if(data < parent->data) {
current = current->leftChild;
//insert to the left
if(current == NULL) {
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}//go to right of the tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
//insert to the right
if(current == NULL) {
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
void post_order_traversal(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL) {
post_order_traversal(root->leftChild);
post_order_traversal(root->rightChild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
}
}
int main(){
int i;
int array[7] = { 27, 14, 35, 10, 19, 31, 42 };
for(i = 0; i < 7; i++)
insert(array[i]);
printf("Post order traversal: ");
post_order_traversal(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
Post order traversal: 10 19 14 31 42 35 27
#include <iostream>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild;
struct node *rightChild;
};
struct node *root = NULL;
void insert(int data){
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//if tree is empty
if(root == NULL) {
root = tempNode;
} else {
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1) {
parent = current;
//go to left of the tree
if(data < parent->data) {
current = current->leftChild;
//insert to the left
if(current == NULL) {
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}//go to right of the tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
//insert to the right
if(current == NULL) {
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
void post_order_traversal(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL) {
post_order_traversal(root->leftChild);
post_order_traversal(root->rightChild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
}
}
int main(){
int i;
int array[7] = { 27, 14, 35, 10, 19, 31, 42 };
for(i = 0; i < 7; i++)
insert(array[i]);
printf("Post order traversal: ");
post_order_traversal(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
Post order traversal: 10 19 14 31 42 35 27
class Node {
int data;
Node leftChild;
Node rightChild;
public Node(int key) {
data = key;
leftChild = rightChild = null;
}
}
public class TreeDataStructure {
Node root = null;
void post_order_traversal(Node node) {
if(node != null) {
post_order_traversal(node.leftChild);
post_order_traversal(node.rightChild);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
TreeDataStructure tree = new TreeDataStructure();
tree.root = new Node(27);
tree.root.leftChild = new Node(12);
tree.root.rightChild = new Node(3);
tree.root.leftChild.leftChild = new Node(44);
tree.root.leftChild.rightChild = new Node(17);
tree.root.rightChild.leftChild = new Node(56);
System.out.println("Post order traversal: ");
tree.post_order_traversal(tree.root);
}
}
輸出
Post order traversal: 44 17 12 56 3 27
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.leftChild = None
self.rightChild = None
self.data = key
# Create a function to perform preorder tree traversal
def PostorderTraversal(root):
if root:
PostorderTraversal(root.leftChild)
PostorderTraversal(root.rightChild)
print(root.data)
# Main class
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = Node(3)
root.leftChild = Node(26)
root.rightChild = Node(42)
root.leftChild.leftChild = Node(54)
root.leftChild.rightChild = Node(65)
root.rightChild.leftChild = Node(12)
print("Postorder traversal of binary tree is")
PostorderTraversal(root)
輸出
Postorder traversal of binary tree is 54 65 26 12 42 3
完整實現
現在讓我們看看樹遍歷在各種程式語言中的完整實現:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild;
struct node *rightChild;
};
struct node *root = NULL;
void insert(int data){
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//if tree is empty
if(root == NULL) {
root = tempNode;
} else {
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1) {
parent = current;
//go to left of the tree
if(data < parent->data) {
current = current->leftChild;
//insert to the left
if(current == NULL) {
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}//go to right of the tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
//insert to the right
if(current == NULL) {
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
void pre_order_traversal(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL) {
printf("%d ",root->data);
pre_order_traversal(root->leftChild);
pre_order_traversal(root->rightChild);
}
}
void inorder_traversal(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL) {
inorder_traversal(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ",root->data);
inorder_traversal(root->rightChild);
}
}
void post_order_traversal(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL) {
post_order_traversal(root->leftChild);
post_order_traversal(root->rightChild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
}
}
int main(){
int i;
int array[7] = { 27, 14, 35, 10, 19, 31, 42 };
for(i = 0; i < 7; i++)
insert(array[i]);
printf("Preorder traversal: ");
pre_order_traversal(root);
printf("\nInorder traversal: ");
inorder_traversal(root);
printf("\nPost order traversal: ");
post_order_traversal(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
Preorder traversal: 27 14 10 19 35 31 42 Inorder traversal: 10 14 19 27 31 35 42 Post order traversal: 10 19 14 31 42 35 27
#include <iostream>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild;
struct node *rightChild;
};
struct node *root = NULL;
void insert(int data){
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//if tree is empty
if(root == NULL) {
root = tempNode;
} else {
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1) {
parent = current;
//go to left of the tree
if(data < parent->data) {
current = current->leftChild;
//insert to the left
if(current == NULL) {
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}//go to right of the tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
//insert to the right
if(current == NULL) {
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
void pre_order_traversal(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL) {
printf("%d ",root->data);
pre_order_traversal(root->leftChild);
pre_order_traversal(root->rightChild);
}
}
void inorder_traversal(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL) {
inorder_traversal(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ",root->data);
inorder_traversal(root->rightChild);
}
}
void post_order_traversal(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL) {
post_order_traversal(root->leftChild);
post_order_traversal(root->rightChild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
}
}
int main(){
int i;
int array[7] = { 27, 14, 35, 10, 19, 31, 42 };
for(i = 0; i < 7; i++)
insert(array[i]);
printf("Preorder traversal: ");
pre_order_traversal(root);
printf("\nInorder traversal: ");
inorder_traversal(root);
printf("\nPost order traversal: ");
post_order_traversal(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
Preorder traversal: 27 14 10 19 35 31 42 Inorder traversal: 10 14 19 27 31 35 42 Post order traversal: 10 19 14 31 42 35 27
class Node {
int data;
Node leftChild;
Node rightChild;
public Node(int key) {
data = key;
leftChild = rightChild = null;
}
}
public class TreeDataStructure {
Node root = null;
void inorder_traversal(Node node) {
if(node != null) {
inorder_traversal(node.leftChild);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
inorder_traversal(node.rightChild);
}
}
void pre_order_traversal(Node node) {
if(node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
pre_order_traversal(node.leftChild);
pre_order_traversal(node.rightChild);
}
}
void post_order_traversal(Node node) {
if(node != null) {
post_order_traversal(node.leftChild);
post_order_traversal(node.rightChild);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
TreeDataStructure tree = new TreeDataStructure();
tree.root = new Node(27);
tree.root.leftChild = new Node(12);
tree.root.rightChild = new Node(3);
tree.root.leftChild.leftChild = new Node(44);
tree.root.leftChild.rightChild = new Node(17);
tree.root.rightChild.leftChild = new Node(56);
System.out.println("Inorder traversal: ");
tree.inorder_traversal(tree.root);
System.out.println("\nPreorder traversal: ");
tree.pre_order_traversal(tree.root);
System.out.println("\nPost order traversal: ");
tree.post_order_traversal(tree.root);
}
}
輸出
Inorder traversal: 44 12 17 27 56 3 Preorder traversal: 27 12 44 17 3 56 Post order traversal: 44 17 12 56 3 27
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.leftChild = None
self.rightChild = None
self.data = key
# Create a function to perform inorder tree traversal
def InorderTraversal(root):
if root:
InorderTraversal(root.leftChild)
print(root.data)
InorderTraversal(root.rightChild)
# Create a function to perform preorder tree traversal
def PostorderTraversal(root):
if root:
PostorderTraversal(root.leftChild)
PostorderTraversal(root.rightChild)
print(root.data)
# Create a function to perform postorder tree traversal
def PreorderTraversal(root):
if root:
print(root.data)
PreorderTraversal(root.leftChild)
PreorderTraversal(root.rightChild)
# Main class
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = Node(3)
root.leftChild = Node(26)
root.rightChild = Node(42)
root.leftChild.leftChild = Node(54)
root.leftChild.rightChild = Node(65)
root.rightChild.leftChild = Node(12)
# Function call
print("Inorder traversal of binary tree is")
InorderTraversal(root)
print("\nPreorder traversal of binary tree is")
PreorderTraversal(root)
print("\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is")
PostorderTraversal(root)
輸出
Inorder traversal of binary tree is 54 26 65 3 12 42 Preorder traversal of binary tree is 3 26 54 65 42 12 Postorder traversal of binary tree is 54 65 26 12 42 3
廣告
