
- 資料結構與演算法
- DSA - 首頁
- DSA - 概述
- DSA - 環境設定
- DSA - 演算法基礎
- DSA - 漸近分析
- 資料結構
- DSA - 資料結構基礎
- DSA - 資料結構和型別
- DSA - 陣列資料結構
- 連結串列
- DSA - 連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 雙向連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 迴圈連結串列資料結構
- 棧與佇列
- DSA - 棧資料結構
- DSA - 表示式解析
- DSA - 佇列資料結構
- 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 線性搜尋演算法
- DSA - 二分搜尋演算法
- DSA - 插值搜尋
- DSA - 跳躍搜尋演算法
- DSA - 指數搜尋
- DSA - 斐波那契搜尋
- DSA - 子列表搜尋
- DSA - 散列表
- 排序演算法
- DSA - 排序演算法
- DSA - 氣泡排序演算法
- DSA - 插入排序演算法
- DSA - 選擇排序演算法
- DSA - 歸併排序演算法
- DSA - 希爾排序演算法
- DSA - 堆排序
- DSA - 桶排序演算法
- DSA - 計數排序演算法
- DSA - 基數排序演算法
- DSA - 快速排序演算法
- 圖資料結構
- DSA - 圖資料結構
- DSA - 深度優先遍歷
- DSA - 廣度優先遍歷
- DSA - 生成樹
- 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹的遍歷
- DSA - 二叉搜尋樹
- DSA - AVL樹
- DSA - 紅黑樹
- DSA - B樹
- DSA - B+樹
- DSA - 伸展樹
- DSA - 字典樹 (Trie)
- DSA - 堆資料結構
- 遞迴
- DSA - 遞迴演算法
- DSA - 使用遞迴的漢諾塔
- DSA - 使用遞迴的斐波那契數列
- 分治法
- DSA - 分治法
- DSA - 最大最小問題
- DSA - Strassen矩陣乘法
- DSA - Karatsuba演算法
- 貪心演算法
- DSA - 貪心演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(貪心法)
- DSA - Prim最小生成樹
- DSA - Kruskal最小生成樹
- DSA - Dijkstra最短路徑演算法
- DSA - 地圖著色演算法
- DSA - 分數揹包問題
- DSA - 帶截止期限的作業排序
- DSA - 最優合併模式演算法
- 動態規劃
- DSA - 動態規劃
- DSA - 矩陣鏈乘法
- DSA - Floyd-Warshall演算法
- DSA - 0-1揹包問題
- DSA - 最長公共子序列演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(動態規劃法)
- 近似演算法
- DSA - 近似演算法
- DSA - 頂點覆蓋演算法
- DSA - 集合覆蓋問題
- DSA - 旅行商問題(近似演算法)
- 隨機化演算法
- DSA - 隨機化演算法
- DSA - 隨機化快速排序演算法
- DSA - Karger最小割演算法
- DSA - Fisher-Yates洗牌演算法
- DSA有用資源
- DSA - 問答
- DSA - 快速指南
- DSA - 有用資源
- DSA - 討論
廣度優先搜尋 (BFS) 演算法
廣度優先搜尋 (BFS) 演算法
廣度優先搜尋 (BFS) 演算法以廣度優先的方式遍歷圖資料結構,以搜尋滿足一組條件的節點。它使用佇列來記住下次搜尋的起始頂點,當任何迭代中出現死鎖時。
廣度優先搜尋 (BFS) 演算法從樹根開始,在移動到下一深度級別的節點之前,探索當前深度級別上的所有節點。
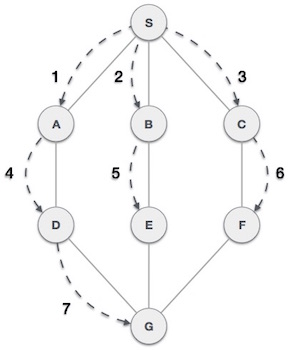
如上例所示,BFS演算法首先從A到B到E到F遍歷,然後到C和G,最後到D。它採用以下規則。
規則1 - 訪問相鄰的未訪問頂點。將其標記為已訪問。顯示它。將其插入佇列。
規則2 - 如果找不到相鄰頂點,則從佇列中移除第一個頂點。
規則3 - 重複規則1和規則2,直到佇列為空。
| 步驟 | 遍歷 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 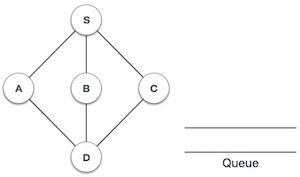 |
初始化佇列。 |
| 2 | 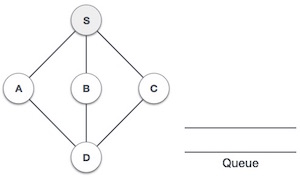 |
我們從訪問S(起始節點)開始,並將其標記為已訪問。 |
| 3 | 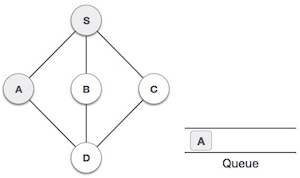 |
然後我們看到S的未訪問相鄰節點。在這個例子中,我們有三個節點,但按字母順序我們選擇A,將其標記為已訪問並將其入隊。 |
| 4 | 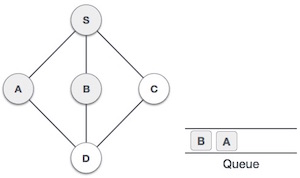 |
接下來,S的未訪問相鄰節點是B。我們將其標記為已訪問並將其入隊。 |
| 5 | 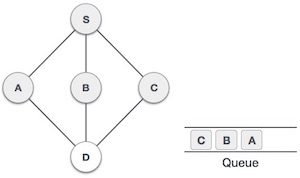 |
接下來,S的未訪問相鄰節點是C。我們將其標記為已訪問並將其入隊。 |
| 6 | 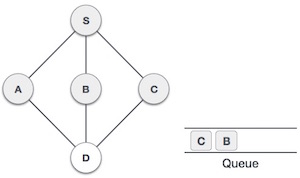 |
現在,S沒有未訪問的相鄰節點了。因此,我們出隊並找到A。 |
| 7 | 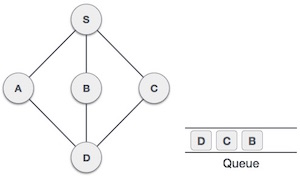 |
從A我們有D作為未訪問的相鄰節點。我們將其標記為已訪問並將其入隊。 |
在這個階段,我們沒有未標記(未訪問)的節點了。但是根據演算法,我們繼續出隊以獲得所有未訪問的節點。當佇列為空時,程式結束。
示例
以下是各種程式語言中廣度優先搜尋 (BFS) 演算法的實現:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAX 5
struct Vertex {
char label;
bool visited;
};
//queue variables
int queue[MAX];
int rear = -1;
int front = 0;
int queueItemCount = 0;
//graph variables
//array of vertices
struct Vertex* lstVertices[MAX];
//adjacency matrix
int adjMatrix[MAX][MAX];
//vertex count
int vertexCount = 0;
//queue functions
void insert(int data) {
queue[++rear] = data;
queueItemCount++;
}
int removeData() {
queueItemCount--;
return queue[front++];
}
bool isQueueEmpty() {
return queueItemCount == 0;
}
//graph functions
//add vertex to the vertex list
void addVertex(char label) {
struct Vertex* vertex = (struct Vertex*) malloc(sizeof(struct Vertex));
vertex->label = label;
vertex->visited = false;
lstVertices[vertexCount++] = vertex;
}
//add edge to edge array
void addEdge(int start,int end) {
adjMatrix[start][end] = 1;
adjMatrix[end][start] = 1;
}
//display the vertex
void displayVertex(int vertexIndex) {
printf("%c ",lstVertices[vertexIndex]->label);
}
//get the adjacent unvisited vertex
int getAdjUnvisitedVertex(int vertexIndex) {
int i;
for(i = 0; i<vertexCount; i++) {
if(adjMatrix[vertexIndex][i] == 1 && lstVertices[i]->visited == false)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
void breadthFirstSearch() {
int i;
//mark first node as visited
lstVertices[0]->visited = true;
//display the vertex
displayVertex(0);
//insert vertex index in queue
insert(0);
int unvisitedVertex;
while(!isQueueEmpty()) {
//get the unvisited vertex of vertex which is at front of the queue
int tempVertex = removeData();
//no adjacent vertex found
while((unvisitedVertex = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(tempVertex)) != -1) {
lstVertices[unvisitedVertex]->visited = true;
displayVertex(unvisitedVertex);
insert(unvisitedVertex);
}
}
//queue is empty, search is complete, reset the visited flag
for(i = 0;i<vertexCount;i++) {
lstVertices[i]->visited = false;
}
}
int main() {
int i, j;
for(i = 0; i<MAX; i++) { // set adjacency
for(j = 0; j<MAX; j++) // matrix to 0
adjMatrix[i][j] = 0;
}
addVertex('S'); // 0
addVertex('A'); // 1
addVertex('B'); // 2
addVertex('C'); // 3
addVertex('D'); // 4
addEdge(0, 1); // S - A
addEdge(0, 2); // S - B
addEdge(0, 3); // S - C
addEdge(1, 4); // A - D
addEdge(2, 4); // B - D
addEdge(3, 4); // C - D
printf("\nBreadth First Search: ");
breadthFirstSearch();
return 0;
}
輸出
Breadth First Search: S A B C D
//C++ code for Breadth First Traversal
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAX 5
struct Vertex {
char label;
bool visited;
};
//queue variables
int queue[MAX];
int rear = -1;
int front = 0;
int queueItemCount = 0;
//graph variables
//array of vertices
struct Vertex* lstVertices[MAX];
//adjacency matrix
int adjMatrix[MAX][MAX];
//vertex count
int vertexCount = 0;
//queue functions
void insert(int data) {
queue[++rear] = data;
queueItemCount++;
}
int removeData() {
queueItemCount--;
return queue[front++];
}
bool isQueueEmpty() {
return queueItemCount == 0;
}
//graph functions
//add vertex to the vertex list
void addVertex(char label) {
struct Vertex* vertex = (struct Vertex*) malloc(sizeof(struct Vertex));
vertex->label = label;
vertex->visited = false;
lstVertices[vertexCount++] = vertex;
}
//add edge to edge array
void addEdge(int start,int end) {
adjMatrix[start][end] = 1;
adjMatrix[end][start] = 1;
}
//display the vertex
void displayVertex(int vertexIndex) {
std::cout << lstVertices[vertexIndex]->label << " ";
}
//get the adjacent unvisited vertex
int getAdjUnvisitedVertex(int vertexIndex) {
int i;
for(i = 0; i<vertexCount; i++) {
if(adjMatrix[vertexIndex][i] == 1 && lstVertices[i]->visited == false)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
void breadthFirstSearch() {
int i;
//mark first node as visited
lstVertices[0]->visited = true;
//display the vertex
displayVertex(0);
//insert vertex index in queue
insert(0);
int unvisitedVertex;
while(!isQueueEmpty()) {
//get the unvisited vertex of vertex which is at front of the queue
int tempVertex = removeData();
//no adjacent vertex found
while((unvisitedVertex = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(tempVertex)) != -1) {
lstVertices[unvisitedVertex]->visited = true;
displayVertex(unvisitedVertex);
insert(unvisitedVertex);
}
}
//queue is empty, search is complete, reset the visited flag
for(i = 0;i<vertexCount;i++) {
lstVertices[i]->visited = false;
}
}
int main() {
int i, j;
for(i = 0; i<MAX; i++) { // set adjacency
for(j = 0; j<MAX; j++) // matrix to 0
adjMatrix[i][j] = 0;
}
addVertex('S'); // 0
addVertex('A'); // 1
addVertex('B'); // 2
addVertex('C'); // 3
addVertex('D'); // 4
addEdge(0, 1); // S - A
addEdge(0, 2); // S - B
addEdge(0, 3); // S - C
addEdge(1, 4); // A - D
addEdge(2, 4); // B - D
addEdge(3, 4); // C - D
std::cout << "Breadth First Search: ";
breadthFirstSearch();
return 0;
}
輸出
Breadth First Search: S A B C D
//Java code for Breadth First Traversal
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class Vertex {
char label;
boolean visited;
public Vertex(char label) {
this.label = label;
visited = false;
}
}
public class Graph {
private static final int MAX = 5;
private Vertex[] lstVertices;
private int[][] adjMatrix;
private int vertexCount;
public Graph() {
lstVertices = new Vertex[MAX];
adjMatrix = new int[MAX][MAX];
vertexCount = 0;
}
private void addVertex(char label) {
Vertex vertex = new Vertex(label);
lstVertices[vertexCount++] = vertex;
}
private void addEdge(int start, int end) {
adjMatrix[start][end] = 1;
adjMatrix[end][start] = 1;
}
private void displayVertex(int vertexIndex) {
System.out.print(lstVertices[vertexIndex].label + " ");
}
private int getAdjUnvisitedVertex(int vertexIndex) {
for (int i = 0; i < vertexCount; i++) {
if (adjMatrix[vertexIndex][i] == 1 && !lstVertices[i].visited)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
private void breadthFirstSearch() {
lstVertices[0].visited = true;
displayVertex(0);
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(0);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int tempVertex = queue.poll();
int unvisitedVertex;
while ((unvisitedVertex = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(tempVertex)) != -1) {
lstVertices[unvisitedVertex].visited = true;
displayVertex(unvisitedVertex);
queue.add(unvisitedVertex);
}
}
// Reset the visited flag
for (int i = 0; i < vertexCount; i++) {
lstVertices[i].visited = false;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Graph graph = new Graph();
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < MAX; j++)
graph.adjMatrix[i][j] = 0;
}
graph.addVertex('S'); // 0
graph.addVertex('A'); // 1
graph.addVertex('B'); // 2
graph.addVertex('C'); // 3
graph.addVertex('D'); // 4
graph.addEdge(0, 1); // S - A
graph.addEdge(0, 2); // S - B
graph.addEdge(0, 3); // S - C
graph.addEdge(1, 4); // A - D
graph.addEdge(2, 4); // B - D
graph.addEdge(3, 4); // C - D
System.out.print("Breadth First Search: ");
graph.breadthFirstSearch();
}
}
輸出
Breadth First Search: S A B C D
#Python program for Breadth First Search
# defining MAX 5
MAX = 5
class Vertex:
def __init__(self, label):
self.label = label
self.visited = False
# queue variables
queue = [0] * MAX
rear = -1
front = 0
queueItemCount = 0
# graph variables
#array of vertices
lstVertices = [None] * MAX
#adjacency matrix
adjMatrix = [[0] * MAX for _ in range(MAX)]
#vertex count
vertexCount = 0
# queue functions
def insert(data):
global rear, queueItemCount
rear += 1
queue[rear] = data
queueItemCount += 1
def removeData():
global front, queueItemCount
queueItemCount -= 1
data = queue[front]
front += 1
return data
def isQueueEmpty():
return queueItemCount == 0
# graph functions
#add vertex to the vertex list
def addVertex(label):
global vertexCount
vertex = Vertex(label)
lstVertices[vertexCount] = vertex
vertexCount += 1
#add edge to edge array
def addEdge(start, end):
adjMatrix[start][end] = 1
adjMatrix[end][start] = 1
#Display the vertex
def displayVertex(vertexIndex):
print(lstVertices[vertexIndex].label, end=" ")
#Get the adjacent unvisited vertex
def getAdjUnvisitedVertex(vertexIndex):
for i in range(vertexCount):
if adjMatrix[vertexIndex][i] == 1 and not lstVertices[i].visited:
return i
return -1
def breadthFirstSearch():
#mark first node as visited
lstVertices[0].visited = True
#Display the vertex
displayVertex(0)
#insert vertex index in queue
insert(0)
while not isQueueEmpty():
#get the unvisited vertex of vertex which is at front of the queue
tempVertex = removeData()
#no adjacent vertex found
unvisitedVertex = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(tempVertex)
while unvisitedVertex != -1:
lstVertices[unvisitedVertex].visited = True
displayVertex(unvisitedVertex)
insert(unvisitedVertex)
unvisitedVertex = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(tempVertex)
#queue is empty, search is complete, reset the visited flag
for i in range(vertexCount):
lstVertices[i].visited = False
# main function
if __name__ == "__main__":
#set adjacency
for i in range(MAX):
#matrix to 0
for j in range(MAX):
adjMatrix[i][j] = 0
addVertex('S')
addVertex('A')
addVertex('B')
addVertex('C')
addVertex('D')
addEdge(0, 1)
addEdge(0, 2)
addEdge(0, 3)
addEdge(1, 4)
addEdge(2, 4)
addEdge(3, 4)
print("Breadth First Search: ", end="")
breadthFirstSearch()
輸出
Breadth First Search: S A B C D
BFS演算法的複雜度
時間複雜度
BFS演算法的時間複雜度表示為O(V + E),其中V是節點數,E是邊數。
空間複雜度
BFS演算法的空間複雜度為O(V)。
廣告