
- 資料結構與演算法
- DSA - 首頁
- DSA - 概述
- DSA - 環境搭建
- DSA - 演算法基礎
- DSA - 漸進分析
- 資料結構
- DSA - 資料結構基礎
- DSA - 資料結構和型別
- DSA - 陣列資料結構
- 連結串列
- DSA - 連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 雙向連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 迴圈連結串列資料結構
- 棧與佇列
- DSA - 棧資料結構
- DSA - 表示式解析
- DSA - 佇列資料結構
- 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 線性搜尋演算法
- DSA - 二分搜尋演算法
- DSA - 插值搜尋
- DSA - 跳躍搜尋演算法
- DSA - 指數搜尋
- DSA - 斐波那契搜尋
- DSA - 子列表搜尋
- DSA - 雜湊表
- 排序演算法
- DSA - 排序演算法
- DSA - 氣泡排序演算法
- DSA - 插入排序演算法
- DSA - 選擇排序演算法
- DSA - 歸併排序演算法
- DSA - 希爾排序演算法
- DSA - 堆排序
- DSA - 桶排序演算法
- DSA - 計數排序演算法
- DSA - 基數排序演算法
- DSA - 快速排序演算法
- 圖資料結構
- DSA - 圖資料結構
- DSA - 深度優先遍歷
- DSA - 廣度優先遍歷
- DSA - 生成樹
- 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹的遍歷
- DSA - 二叉搜尋樹
- DSA - AVL樹
- DSA - 紅黑樹
- DSA - B樹
- DSA - B+樹
- DSA - 伸展樹
- DSA - 字典樹
- DSA - 堆資料結構
- 遞迴
- DSA - 遞迴演算法
- DSA - 使用遞迴實現漢諾塔
- DSA - 使用遞迴實現斐波那契數列
- 分治法
- DSA - 分治法
- DSA - 最大最小問題
- DSA - Strassen矩陣乘法
- DSA - Karatsuba演算法
- 貪心演算法
- DSA - 貪心演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(貪心演算法)
- DSA - Prim最小生成樹
- DSA - Kruskal最小生成樹
- DSA - Dijkstra最短路徑演算法
- DSA - 地圖著色演算法
- DSA - 分數揹包問題
- DSA - 帶截止日期的作業排序
- DSA - 最佳合併模式演算法
- 動態規劃
- DSA - 動態規劃
- DSA - 矩陣鏈乘法
- DSA - Floyd-Warshall演算法
- DSA - 0-1揹包問題
- DSA - 最長公共子序列演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(動態規劃)
- 近似演算法
- DSA - 近似演算法
- DSA - 頂點覆蓋演算法
- DSA - 集合覆蓋問題
- DSA - 旅行商問題(近似演算法)
- 隨機演算法
- DSA - 隨機演算法
- DSA - 隨機快速排序演算法
- DSA - Karger最小割演算法
- DSA - Fisher-Yates洗牌演算法
- DSA有用資源
- DSA - 問答
- DSA - 快速指南
- DSA - 有用資源
- DSA - 討論
線性搜尋演算法
線性搜尋是一種順序搜尋演算法。在這種方法中,遍歷輸入陣列中的每個元素並將其與要查詢的關鍵元素進行比較。如果在陣列中找到匹配項,則搜尋被認為是成功的;如果沒有找到匹配項,則搜尋被認為是不成功的,並給出最壞情況下的時間複雜度。
例如,在給定的動畫圖中,我們正在搜尋元素 33。因此,線性搜尋方法從第一個元素開始順序搜尋,直到找到匹配項。這返回一個成功的搜尋。

在同一張圖中,如果我們必須搜尋元素 46,則它會返回一個不成功的搜尋,因為 46 不存在於輸入中。
線性搜尋演算法
線性搜尋的演算法相對簡單。該過程從要搜尋的輸入陣列的第一個索引開始。
步驟 1 - 從輸入陣列的第 0 個索引開始,將關鍵值與第 0 個索引中存在的值進行比較。
步驟 2 - 如果值與鍵匹配,則返回找到該值的位置。
步驟 3 - 如果值與鍵不匹配,則比較陣列中的下一個元素。
步驟 4 - 重複步驟 3,直到找到匹配項。返回找到匹配項的位置。
步驟 5 - 如果搜尋不成功,則列印該元素不存在於陣列中並退出程式。
虛擬碼
procedure linear_search (list, value)
for each item in the list
if match item == value
return the item's location
end if
end for
end procedure
分析
線性搜尋依次遍歷每個元素,因此,最佳情況是在第一次迭代中找到元素。最佳情況下的時間複雜度為O(1)。
但是,線性搜尋方法的最壞情況將是不成功的搜尋,它在陣列中找不到關鍵值,它執行 n 次迭代。因此,線性搜尋演算法的最壞情況下的時間複雜度為O(n)。
示例
讓我們看看使用線性搜尋方法在陣列中逐步搜尋關鍵元素(例如 47)的過程。
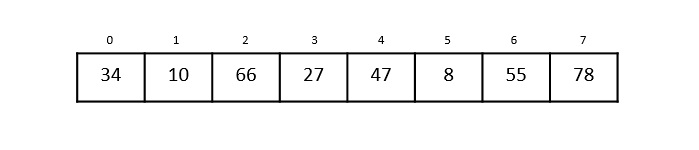
步驟 1
線性搜尋從第 0 個索引開始。將關鍵元素與第 0 個索引中的值 34 進行比較。
但是,47 ≠ 34。所以它移動到下一個元素。
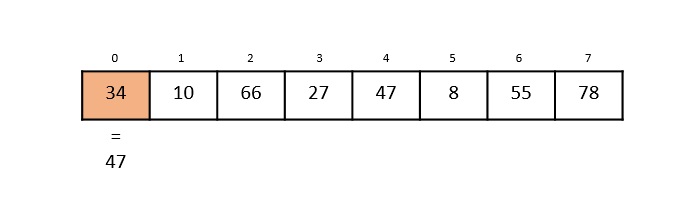
步驟 2
現在,關鍵元素與陣列中第 1 個索引的值進行比較。

仍然,47 ≠ 10,使演算法繼續進行另一次迭代。
步驟 3
將下一個元素 66 與 47 進行比較。它們都不匹配,因此演算法繼續比較後續元素。
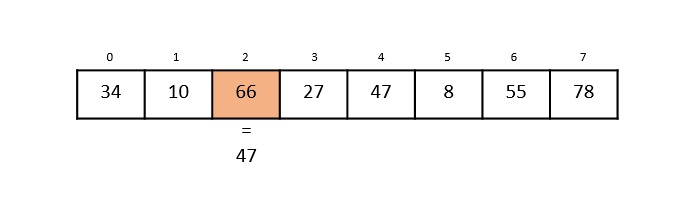
步驟 4
現在,將第 3 個索引中的元素 27 與關鍵值 47 進行比較。它們不相等,因此演算法被推送到檢查下一個元素。
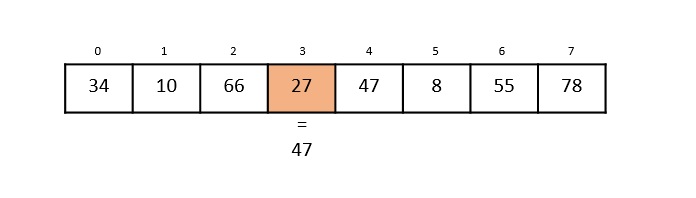
步驟 5
將陣列中第 4 個索引中的元素 47 與關鍵值 47 進行比較。發現這兩個元素匹配。現在,返回 47 所在的位置,即 4。
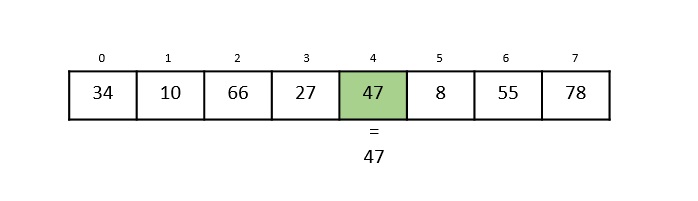
獲得的輸出為“在第 4 個索引處找到元素”。
實現
在本教程中,可以看出線性搜尋程式在四種程式語言中實現。該函式將輸入的元素與關鍵值進行比較,並返回鍵在陣列中的位置,或者如果鍵不存在於陣列中,則返回不成功的搜尋提示。
#include <stdio.h>
void linear_search(int a[], int n, int key){
int i, count = 0;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(a[i] == key) { // compares each element of the array
printf("The element is found at %d position\n", i+1);
count = count + 1;
}
}
if(count == 0) // for unsuccessful search
printf("The element is not present in the array\n");
}
int main(){
int i, n, key;
n = 6;
int a[10] = {12, 44, 32, 18, 4, 10};
key = 18;
linear_search(a, n, key);
key = 23;
linear_search(a, n, key);
return 0;
}
輸出
The element is found at 4 position The element is not present in the array
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void linear_search(int a[], int n, int key){
int i, count = 0;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(a[i] == key) { // compares each element of the array
cout << "The element is found at position " << i+1 <<endl;
count = count + 1;
}
}
if(count == 0) // for unsuccessful search
cout << "The element is not present in the array" <<endl;
}
int main(){
int i, n, key;
n = 6;
int a[10] = {12, 44, 32, 18, 4, 10};
key = 18;
linear_search(a, n, key);
key = 23;
linear_search(a, n, key);
return 0;
}
輸出
The element is found at position 4 The element is not present in the array
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class LinearSearch {
static void linear_search(int a[], int n, int key) {
int i, count = 0;
for(i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(a[i] == key) { // compares each element of the array
System.out.println("The element is found at position " + (i+1));
count = count + 1;
}
}
if(count == 0) // for unsuccessful search
System.out.println("The element is not present in the array");
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int i, n, key;
n = 6;
int a[] = {12, 44, 32, 18, 4, 10, 66};
key = 10;
linear_search(a, n, key);
key = 54;
linear_search(a, n, key);
}
}
輸出
The element is found at position 6 The element is not present in the array
def linear_search(a, n, key):
count = 0
for i in range(n):
if(a[i] == key):
print("The element is found at position", (i+1))
count = count + 1
if(count == 0):
print("The element is not present in the array")
a = [14, 56, 77, 32, 84, 9, 10]
n = len(a)
key = 32
linear_search(a, n, key)
key = 3
linear_search(a, n, key)
輸出
The element is found at position 4 The element is not present in the array
