
- 資料結構與演算法
- DSA - 首頁
- DSA - 概述
- DSA - 環境設定
- DSA - 演算法基礎
- DSA - 漸進分析
- 資料結構
- DSA - 資料結構基礎
- DSA - 資料結構和型別
- DSA - 陣列資料結構
- 連結串列
- DSA - 連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 雙向連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 迴圈連結串列資料結構
- 棧與佇列
- DSA - 棧資料結構
- DSA - 表示式解析
- DSA - 佇列資料結構
- 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 線性搜尋演算法
- DSA - 二分搜尋演算法
- DSA - 插值搜尋
- DSA - 跳躍搜尋演算法
- DSA - 指數搜尋
- DSA - 斐波那契搜尋
- DSA - 子列表搜尋
- DSA - 雜湊表
- 排序演算法
- DSA - 排序演算法
- DSA - 氣泡排序演算法
- DSA - 插入排序演算法
- DSA - 選擇排序演算法
- DSA - 歸併排序演算法
- DSA - 希爾排序演算法
- DSA - 堆排序
- DSA - 桶排序演算法
- DSA - 計數排序演算法
- DSA - 基數排序演算法
- DSA - 快速排序演算法
- 圖資料結構
- DSA - 圖資料結構
- DSA - 深度優先遍歷
- DSA - 廣度優先遍歷
- DSA - 生成樹
- 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹的遍歷
- DSA - 二叉搜尋樹
- DSA - AVL樹
- DSA - 紅黑樹
- DSA - B樹
- DSA - B+樹
- DSA - 伸展樹
- DSA - 字典樹
- DSA - 堆資料結構
- 遞迴
- DSA - 遞迴演算法
- DSA - 使用遞迴實現漢諾塔問題
- DSA - 使用遞迴實現斐波那契數列
- 分治法
- DSA - 分治法
- DSA - 最大最小問題
- DSA - Strassen矩陣乘法
- DSA - Karatsuba演算法
- 貪心演算法
- DSA - 貪心演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(貪心演算法)
- DSA - Prim最小生成樹
- DSA - Kruskal最小生成樹
- DSA - Dijkstra最短路徑演算法
- DSA - 地圖著色演算法
- DSA - 分數揹包問題
- DSA - 帶截止日期的作業排序
- DSA - 最佳合併模式演算法
- 動態規劃
- DSA - 動態規劃
- DSA - 矩陣鏈乘法
- DSA - Floyd-Warshall演算法
- DSA - 0-1揹包問題
- DSA - 最長公共子序列演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(動態規劃方法)
- 近似演算法
- DSA - 近似演算法
- DSA - 頂點覆蓋演算法
- DSA - 集合覆蓋問題
- DSA - 旅行商問題(近似方法)
- 隨機化演算法
- DSA - 隨機化演算法
- DSA - 隨機化快速排序演算法
- DSA - Karger最小割演算法
- DSA - Fisher-Yates洗牌演算法
- DSA 有用資源
- DSA - 常見問題解答
- DSA - 快速指南
- DSA - 有用資源
- DSA - 討論
資料結構與演算法 - 快速指南
概述
資料結構是以一種系統化的方式組織資料,以便高效地使用它。以下術語是資料結構的基礎術語。
介面 - 每個資料結構都有一個介面。介面表示資料結構支援的操作集合。介面僅提供支援的操作列表、它們可以接受的引數型別以及這些操作的返回型別。
實現 - 實現提供了資料結構的內部表示。實現還提供了資料結構操作中使用的演算法的定義。
資料結構的特徵
正確性 - 資料結構的實現應正確實現其介面。
時間複雜度 - 資料結構操作的執行時間或執行時間必須儘可能短。
空間複雜度 - 資料結構操作的記憶體使用量應儘可能少。
資料結構的必要性
隨著應用程式變得越來越複雜和資料豐富,如今應用程式面臨著三個常見問題。
資料搜尋 - 考慮一個商店擁有 100 萬 (106) 件商品的庫存。如果應用程式要搜尋一件商品,它每次都必須在 100 萬 (106) 件商品中搜索,從而降低搜尋速度。隨著資料量的增長,搜尋將變得更慢。
處理器速度 - 儘管處理器速度非常高,但如果資料增長到數十億條記錄,它也會受到限制。
多個請求 - 由於數千名使用者可以在 Web 伺服器上同時搜尋資料,即使是速度最快的伺服器在搜尋資料時也會失效。
為了解決上述問題,資料結構可以提供幫助。資料可以以這樣一種方式組織在資料結構中,即可能不需要搜尋所有專案,並且可以幾乎立即搜尋所需的資料。
執行時間案例
通常使用三種情況以相對的方式比較各種資料結構的執行時間。
最壞情況 - 這是資料結構操作可能花費的最長時間的情況。如果操作的最壞情況時間為 ƒ(n),則此操作不會花費超過 ƒ(n) 時間,其中 ƒ(n) 表示 n 的函式。
平均情況 - 這種情況描述了資料結構操作的平均執行時間。如果一個操作需要 ƒ(n) 時間執行,則 m 個操作將需要 mƒ(n) 時間。
最佳情況 - 這種情況描述了資料結構操作的最小可能執行時間。如果操作需要 ƒ(n) 時間執行,則實際操作可能花費的時間與隨機數相同,該隨機數最大為 ƒ(n)。
基本術語
資料 - 資料是值或一組值。
資料項 - 資料項指的是單個值的單元。
分組項 - 被劃分為子項的資料項稱為分組項。
基本項 - 無法再細分的資料項稱為基本項。
屬性和實體 - 實體是包含某些屬性或特性的東西,這些屬性或特性可以被賦予值。
實體集 - 具有相似屬性的實體構成一個實體集。
欄位 - 欄位是表示實體屬性的單個基本資訊單元。
記錄 - 記錄是給定實體的欄位值的集合。
檔案 - 檔案是給定實體集中實體的記錄的集合。
環境設定
本地環境設定
如果您仍然希望為 C 程式語言設定您的環境,則需要在您的計算機上提供以下兩個工具:(a) 文字編輯器和 (b) C 編譯器。
文字編輯器
這將用於鍵入您的程式。一些編輯器的示例包括 Windows 記事本、OS Edit 命令、Brief、Epsilon、EMACS 以及 vim 或 vi。
文字編輯器的名稱和版本在不同的作業系統上可能有所不同。例如,Notepad 將用於 Windows,而 vim 或 vi 既可以用於 Windows,也可以用於 Linux 或 UNIX。
您使用編輯器建立的檔案稱為原始檔,其中包含程式原始碼。C 程式的原始檔通常以副檔名“.c”命名。
在開始程式設計之前,請確保您已準備好一個文字編輯器,並且您擁有足夠的經驗來編寫計算機程式,將其儲存在檔案中,編譯它,最後執行它。
C 編譯器
原始檔中編寫的原始碼是程式的人類可讀原始碼。它需要“編譯”才能轉換為機器語言,以便您的 CPU 能夠根據給定的指令實際執行程式。
此 C 程式語言編譯器將用於將您的原始碼編譯成最終的可執行程式。我們假設您具備關於程式語言編譯器的基本知識。
最常使用且免費提供的編譯器是 GNU C/C++ 編譯器。或者,如果您有相應的作業系統 (OS),則可以使用 HP 或 Solaris 的編譯器。
以下部分指導您如何在各種作業系統上安裝 GNU C/C++ 編譯器。我們一起提到 C/C++,因為 GNU GCC 編譯器適用於 C 和 C++ 程式語言。
在 UNIX/Linux 上安裝
如果您使用的是Linux 或 UNIX,請透過從命令列輸入以下命令來檢查您的系統上是否安裝了 GCC:
$ gcc -v
如果您的機器上安裝了 GNU 編譯器,則它應該列印類似於以下內容的訊息:
Using built-in specs. Target: i386-redhat-linux Configured with: ../configure --prefix = /usr ....... Thread model: posix gcc version 4.1.2 20080704 (Red Hat 4.1.2-46)
如果未安裝 GCC,則您需要使用 https://gcc.gnu.org/install/ 中提供的詳細說明自行安裝。
本教程是基於 Linux 編寫的,所有給出的示例都已在 Cent OS 版本的 Linux 系統上編譯。
在 Mac OS 上安裝
如果您使用 Mac OS X,獲取 GCC 的最簡單方法是從 Apple 的網站下載 Xcode 開發環境,並按照簡單的安裝說明進行操作。設定好 Xcode 後,您就可以使用 GNU 編譯器來編譯 C/C++ 了。
Xcode 目前可在 developer.apple.com/technologies/tools/ 獲取。
在 Windows 上安裝
要在 Windows 上安裝 GCC,您需要安裝 MinGW。要安裝 MinGW,請訪問 MinGW 主頁 www.mingw.org,並按照連結到 MinGW 下載頁面的連結進行操作。下載最新版本的 MinGW 安裝程式,其名稱應為 MinGW-<version>.exe。
在安裝 MinWG 時,至少必須安裝 gcc-core、gcc-g++、binutils 和 MinGW 執行時,但您可能希望安裝更多內容。
將 MinGW 安裝的 bin 子目錄新增到您的PATH環境變數中,以便您可以在命令列中透過其簡單的名稱指定這些工具。
安裝完成後,您將能夠從 Windows 命令列執行 gcc、g++、ar、ranlib、dlltool 和其他幾個 GNU 工具。
資料結構基礎
本章解釋了與資料結構相關的基本術語。
資料定義
資料定義使用以下特徵定義特定資料。
原子性 - 定義應定義單個概念。
可追溯的 - 定義應該能夠對映到某些資料元素。
準確的 - 定義應該明確無誤。
清晰簡潔 - 定義應該易於理解。
資料物件
資料物件表示具有資料的一個物件。
資料型別
資料型別是將各種型別的資料(例如整數、字串等)進行分類的一種方式,它決定了可以與相應型別的資料一起使用的值,以及可以對相應型別的資料執行的操作型別。有兩種資料型別 -
- 內建資料型別
- 派生資料型別
內建資料型別
語言內建支援的那些資料型別稱為內建資料型別。例如,大多數語言提供以下內建資料型別。
- 整數
- 布林值(真,假)
- 浮點數(十進位制數)
- 字元和字串
派生資料型別
那些與實現無關的資料型別,因為它們可以以一種或另一種方式實現,被稱為派生資料型別。這些資料型別通常由基本或內建資料型別及其相關操作組合而成。例如 -
- 列表
- 陣列
- 棧
- 佇列
基本操作
資料結構中的資料透過某些操作進行處理。選擇特定的資料結構很大程度上取決於需要對資料結構執行的操作的頻率。
- 遍歷
- 搜尋
- 插入
- 刪除
- 排序
- 合併
資料結構和型別
資料結構是為了在程式語言中儲存、組織和操作資料而引入的。它們的設計方式使資料訪問和處理更加容易和簡單。這些資料結構不限於一種特定的程式語言;它們只是在記憶體中組織資料的程式碼片段。
資料型別經常被誤認為是一種資料結構,但即使它們被稱為抽象資料型別,這也不完全正確。資料型別表示資料的性質,而資料結構只是一組相似或不同的資料型別的集合。

通常只有兩種型別的資料結構 -
線性
非線性
線性資料結構
資料線上性資料結構中按順序儲存。這些是基本的結構,因為元素一個接一個地儲存,無需應用任何數學運算。
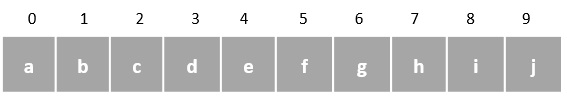
線性資料結構通常易於實現,但由於記憶體分配可能會變得複雜,因此時間和空間複雜度會增加。線性資料結構的一些示例包括 -
陣列
連結串列
棧
佇列
根據資料儲存方法,這些線性資料結構分為兩種子型別。它們是 - 靜態和動態資料結構。
靜態線性資料結構
在靜態線性資料結構中,記憶體分配不可擴充套件。一旦使用完所有記憶體,就無法檢索更多空間來儲存更多資料。因此,需要根據程式的大小預留記憶體。這也會成為一個缺點,因為預留比所需更多的記憶體會導致記憶體塊的浪費。
靜態線性資料結構的最佳示例是陣列。
動態線性資料結構
在動態線性資料結構中,可以在需要時動態地進行記憶體分配。考慮到程式的空間複雜度,這些資料結構是有效的。
動態線性資料結構的一些示例包括:連結串列、棧和佇列。
非線性資料結構
非線性資料結構以層次結構的形式儲存資料。因此,與線性資料結構相反,資料可以在多個級別中找到,並且難以遍歷。
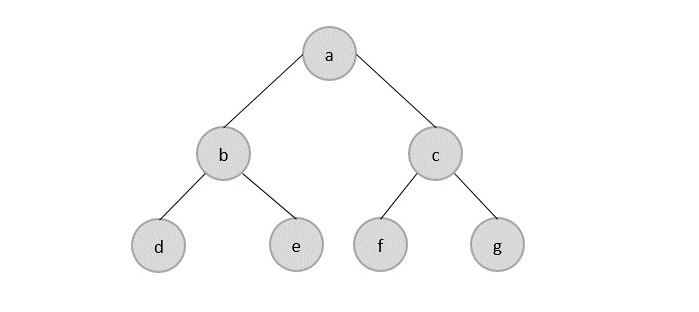
但是,它們旨在克服線性資料結構的問題和侷限性。例如,線性資料結構的主要缺點是記憶體分配。由於資料線上性資料結構中按順序分配,因此這些資料結構中的每個元素都使用一個完整的記憶體塊。但是,如果資料使用的記憶體少於分配的塊可以容納的記憶體,則塊中的額外記憶體空間就會浪費。因此,引入了非線性資料結構。它們降低了空間複雜度並優化了記憶體使用。
非線性資料結構的一些型別是 -
圖
樹
字典樹
對映
陣列資料結構
陣列是一種線性資料結構型別,定義為具有相同或不同資料型別的元素的集合。它們存在於單維和多維中。當需要將多個類似性質的元素儲存在一個地方時,這些資料結構就會出現。
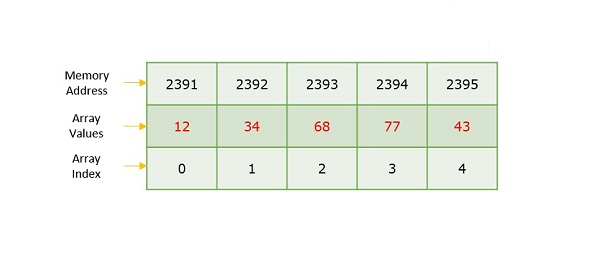
陣列索引和記憶體地址之間的區別在於,陣列索引充當標記陣列中元素的鍵值。但是,記憶體地址是可用空閒記憶體的起始地址。
以下是理解陣列概念的重要術語。
元素 - 儲存在陣列中的每個專案稱為元素。
索引 - 陣列中每個元素的位置都有一個數字索引,用於識別該元素。
語法
在C和C++程式語言中建立陣列 -
data_type array_name[array_size] = {elements separated using commas}
or,
data_type array_name[array_size];
在Java程式語言中建立陣列 -
data_type[] array_name = {elements separated by commas}
or,
data_type array_name = new data_type[array_size];
陣列的必要性
陣列被用作從小型排序問題到更復雜問題(如旅行商問題)的許多問題的解決方案。除了陣列之外,還有許多其他資料結構為這些問題提供了有效的時間和空間複雜度,那麼是什麼使使用陣列更好呢?答案在於隨機訪問查詢時間。
陣列提供O(1)隨機訪問查詢時間。這意味著訪問陣列的第一個索引和陣列的第 1000 個索引將花費相同的時間。這是因為陣列帶有一個指標和一個偏移值。指標指向記憶體的正確位置,偏移值顯示在所述記憶體中查詢多遠。
array_name[index]
| |
Pointer Offset
因此,在一個包含 6 個元素的陣列中,要訪問第一個元素,陣列指向第 0 個索引。類似地,要訪問第 6 個元素,陣列指向第 5 個索引。
陣列表示
陣列表示為儲存桶的集合,每個儲存桶儲存一個元素。這些儲存桶從“0”到“n-1”索引,其中 n 是該特定陣列的大小。例如,大小為 10 的陣列將具有從 0 到 9 索引的儲存桶。
此索引對於多維陣列也類似。如果它是二維陣列,則每個儲存桶中將有子儲存桶。然後它將被索引為 array_name[m][n],其中 m 和 n 是陣列中每個級別的尺寸。
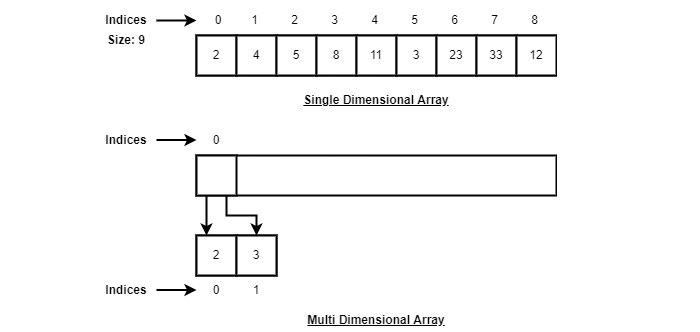
根據以上說明,以下是要考慮的重要事項。
索引從 0 開始。
陣列長度為 9,這意味著它可以儲存 9 個元素。
可以透過其索引訪問每個元素。例如,我們可以獲取索引為 6 的元素作為 23。
陣列中的基本操作
陣列中的基本操作是插入、刪除、搜尋、顯示、遍歷和更新。這些操作通常用於修改陣列中的資料或報告陣列的狀態。
以下是陣列支援的基本操作。
遍歷 - 一個接一個地列印所有陣列元素。
插入 - 在給定索引處新增元素。
刪除 - 刪除給定索引處的元素。
搜尋 - 使用給定索引或值搜尋元素。
更新 - 更新給定索引處的元素。
顯示 - 顯示陣列的內容。
在 C 中,當陣列初始化為指定大小時,它會按照以下順序為其元素分配預設值。
| 資料型別 | 預設值 |
|---|---|
| bool | false |
| char | 0 |
| int | 0 |
| float | 0.0 |
| double | 0.0f |
| void | |
| wchar_t | 0 |
插入操作
在插入操作中,我們向陣列中新增一個或多個元素。根據需要,可以在陣列的開頭、結尾或任何給定索引處新增新元素。這是使用程式語言的輸入語句完成的。
演算法
以下是將元素插入線性陣列直到到達陣列末尾的演算法 -
1. Start 2. Create an Array of a desired datatype and size. 3. Initialize a variable ‘i’ as 0. 4. Enter the element at ith index of the array. 5. Increment i by 1. 6. Repeat Steps 4 & 5 until the end of the array. 7. Stop
在這裡,我們看到了插入操作的實際實現,我們將在陣列末尾新增資料 -
示例
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int LA[3] = {}, i;
printf("Array Before Insertion:\n");
for(i = 0; i < 3; i++)
printf("LA[%d] = %d \n", i, LA[i]);
printf("Inserting Elements.. \n");
printf("The array elements after insertion :\n"); // prints array values
for(i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
LA[i] = i + 2;
printf("LA[%d] = %d \n", i, LA[i]);
}
return 0;
}
輸出
Array Before Insertion: LA[0] = 0 LA[1] = 0 LA[2] = 0 Inserting Elements.. The array elements after insertion : LA[0] = 2 LA[1] = 3 LA[2] = 4
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int LA[3] = {}, i;
cout << "Array Before Insertion:" << endl;
for(i = 0; i < 3; i++)
cout << "LA[" << i <<"] = " << LA[i] << endl;
//prints garbage values
cout << "Inserting elements.." <<endl;
cout << "Array After Insertion:" << endl; // prints array values
for(i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
LA[i] = i + 2;
cout << "LA[" << i <<"] = " << LA[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
輸出
Array Before Insertion: LA[0] = 0 LA[1] = 0 LA[2] = 0 Inserting elements.. Array After Insertion: LA[0] = 2 LA[1] = 3 LA[2] = 4 LA[3] = 5 LA[4] = 6
public class ArrayDemo {
public static void main(String []args) {
int LA[] = new int[3];
System.out.println("Array Before Insertion:");
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
System.out.println("LA[" + i + "] = " + LA[i]); //prints empty array
System.out.println("Inserting Elements..");
// Printing Array after Insertion
System.out.println("Array After Insertion:");
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
LA[i] = i+3;
System.out.println("LA[" + i + "] = " + LA[i]);
}
}
}
輸出
Array Before Insertion: LA[0] = 0 LA[1] = 0 LA[2] = 0 Inserting Elements.. Array After Insertion: LA[0] = 3 LA[1] = 4 LA[2] = 5
# python program to insert element using insert operation
def insert(arr, element):
arr.append(element)
# Driver's code
if __name__ == '__main__':
# declaring array and value to insert
LA = [0, 0, 0]
x = 0
# array before inserting an element
print("Array Before Insertion: ")
for x in range(len(LA)):
print("LA", [x], " = " , LA[x])
print("Inserting elements....")
# array after Inserting element
for x in range(len(LA)):
LA.append(x);
LA[x] = x+1;
print("Array After Insertion: ")
for x in range(len(LA)):
print("LA", [x], " = " , LA[x])
輸出
Array Before Insertion: LA [0] = 0 LA [1] = 0 LA [2] = 0 Inserting elements.... Array After Insertion: LA [0] = 1 LA [1] = 2 LA [2] = 3 LA [3] = 0 LA [4] = 1 LA [5] = 2
有關陣列插入操作的其他變體,點選此處。
刪除操作
在此陣列操作中,我們從陣列的特定索引中刪除一個元素。此刪除操作發生在我們為後續索引中的值分配給當前索引時。
演算法
假設 LA 是一個包含 N 個元素的線性陣列,K 是一個正整數,使得 K<=N。以下是刪除 LA 第 K 個位置上的元素的演算法。
1. Start 2. Set J = K 3. Repeat steps 4 and 5 while J < N 4. Set LA[J] = LA[J + 1] 5. Set J = J+1 6. Set N = N-1 7. Stop
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
void main(){
int LA[] = {1,3,5};
int n = 3;
int i;
printf("The original array elements are :\n");
for(i = 0; i<n; i++)
printf("LA[%d] = %d \n", i, LA[i]);
for(i = 1; i<n; i++) {
LA[i] = LA[i+1];
n = n - 1;
}
printf("The array elements after deletion :\n");
for(i = 0; i<n; i++)
printf("LA[%d] = %d \n", i, LA[i]);
}
輸出
The original array elements are : LA[0] = 1 LA[1] = 3 LA[2] = 5 The array elements after deletion : LA[0] = 1 LA[1] = 5
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int LA[] = {1,3,5};
int i, n = 3;
cout << "The original array elements are :"<<endl;
for(i = 0; i<n; i++) {
cout << "LA[" << i << "] = " << LA[i] << endl;
}
for(i = 1; i<n; i++) {
LA[i] = LA[i+1];
n = n - 1;
}
cout << "The array elements after deletion :"<<endl;
for(i = 0; i<n; i++) {
cout << "LA[" << i << "] = " << LA[i] <<endl;
}
}
輸出
The original array elements are : LA[0] = 1 LA[1] = 3 LA[2] = 5 The array elements after deletion : LA[0] = 1 LA[1] = 5
public class ArrayDemo {
public static void main(String []args) {
int LA[] = new int[3];
int n = LA.length;
System.out.println("Array Before Deletion:");
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
LA[i] = i + 3;
System.out.println("LA[" + i + "] = " + LA[i]);
}
for(int i = 1; i<n-1; i++) {
LA[i] = LA[i+1];
n = n - 1;
}
System.out.println("Array After Deletion:");
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.println("LA[" + i + "] = " + LA[i]);
}
}
}
輸出
Array Before Deletion: LA[0] = 3 LA[1] = 4 LA[2] = 5 Array After Deletion: LA[0] = 3 LA[1] = 5
#python program to delete the value using delete operation
if __name__ == '__main__':
# Declaring array and deleting value
LA = [0,0,0]
n = len(LA)
print("Array Before Deletion: ")
for x in range(len(LA)):
LA.append(x)
LA[x] = x + 3
print("LA", [x], " = " , LA[x])
# delete the value if exists
# or show error it does not exist in the list
for x in range(1, n-1):
LA[x] = LA[x+1]
n = n-1
print("Array After Deletion: ")
for x in range(n):
print("LA", [x], " = " , LA[x])
輸出
Array Before Deletion: LA [0] = 3 LA [1] = 4 LA [2] = 5 Array After Deletion: LA [0] = 3 LA [1] = 5
搜尋操作
使用鍵在陣列中搜索元素;鍵元素依次比較陣列中的每個值,以檢查鍵是否存在於陣列中。
演算法
假設 LA 是一個包含 N 個元素的線性陣列,K 是一個正整數,使得 K<=N。以下是使用順序搜尋查詢值為 ITEM 的元素的演算法。
1. Start 2. Set J = 0 3. Repeat steps 4 and 5 while J < N 4. IF LA[J] is equal ITEM THEN GOTO STEP 6 5. Set J = J +1 6. PRINT J, ITEM 7. Stop
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
void main(){
int LA[] = {1,3,5,7,8};
int item = 5, n = 5;
int i = 0, j = 0;
printf("The original array elements are :\n");
for(i = 0; i<n; i++) {
printf("LA[%d] = %d \n", i, LA[i]);
}
for(i = 0; i<n; i++) {
if( LA[i] == item ) {
printf("Found element %d at position %d\n", item, i+1);
}
}
}
輸出
The original array elements are : LA[0] = 1 LA[1] = 3 LA[2] = 5 LA[3] = 7 LA[4] = 8 Found element 5 at position 3
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int LA[] = {1,3,5,7,8};
int item = 5, n = 5;
int i = 0;
cout << "The original array elements are : " <<endl;
for(i = 0; i<n; i++) {
cout << "LA[" << i << "] = " << LA[i] << endl;
}
for(i = 0; i<n; i++) {
if( LA[i] == item ) {
cout << "Found element " << item << " at position " << i+1 <<endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
輸出
The original array elements are : LA[0] = 1 LA[1] = 3 LA[2] = 5 LA[3] = 7 LA[4] = 8 Found element 5 at position 3
public class ArrayDemo{
public static void main(String []args){
int LA[] = new int[5];
System.out.println("Array:");
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
LA[i] = i + 3;
System.out.println("LA[" + i + "] = " + LA[i]);
}
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
if(LA[i] == 6)
System.out.println("Element " + 6 + " is found at index " + i);
}
}
}
輸出
Array: LA[0] = 3 LA[1] = 4 LA[2] = 5 LA[3] = 6 LA[4] = 7 Element 6 is found at index 3
#search operation using python
def findElement(arr, n, value):
for i in range(n):
if (arr[i] == value):
return i
# If the key is not found
return -1
# Driver's code
if __name__ == '__main__':
LA = [1,3,5,7,8]
print("Array element are: ")
for x in range(len(LA)):
print("LA", [x], " = ", LA[x])
value = 5
n = len(LA)
# element found using search operation
index = findElement(LA, n, value)
if index != -1:
print("Element", value, "Found at position = " + str(index + 1))
else:
print("Element not found")
輸出
Array element are: LA [0] = 1 LA [1] = 3 LA [2] = 5 LA [3] = 7 LA [4] = 8 Element 5 Found at position = 3
遍歷操作
此操作遍歷陣列的所有元素。我們使用迴圈語句來執行此操作。
演算法
以下是遍歷線性陣列中所有元素的演算法 -
1 Start 2. Initialize an Array of certain size and datatype. 3. Initialize another variable ‘i’ with 0. 4. Print the ith value in the array and increment i. 5. Repeat Step 4 until the end of the array is reached. 6. End
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int LA[] = {1,3,5,7,8};
int item = 10, k = 3, n = 5;
int i = 0, j = n;
printf("The original array elements are :\n");
for(i = 0; i<n; i++) {
printf("LA[%d] = %d \n", i, LA[i]);
}
}
輸出
The original array elements are : LA[0] = 1 LA[1] = 3 LA[2] = 5 LA[3] = 7 LA[4] = 8
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int LA[] = {1,3,5,7,8};
int item = 10, k = 3, n = 5;
int i = 0, j = n;
cout << "The original array elements are:\n";
for(i = 0; i<n; i++)
cout << "LA[" << i << "] = " << LA[i] << endl;
return 0;
}
輸出
The original array elements are: LA[0] = 1 LA[1] = 3 LA[2] = 5 LA[3] = 7 LA[4] = 8
public class ArrayDemo {
public static void main(String []args) {
int LA[] = new int[5];
System.out.println("The array elements are: ");
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
LA[i] = i + 2;
System.out.println("LA[" + i + "] = " + LA[i]);
}
}
}
輸出
The array elements are: LA[0] = 2 LA[1] = 3 LA[2] = 4 LA[3] = 5 LA[4] = 6
# Python code to iterate over a array using python
LA = [1, 3, 5, 7, 8]
# length of the elements
length = len(LA)
# Traversing the elements using For loop and range
# same as 'for x in range(len(array))'
print("Array elements are: ")
for x in range(length):
print("LA", [x], " = ", LA[x])
輸出
Array elements are: LA [0] = 1 LA [1] = 3 LA [2] = 5 LA [3] = 7 LA [4] = 8
更新操作
更新操作是指更新陣列中給定索引處的現有元素。
演算法
假設 LA 是一個包含 N 個元素的線性陣列,K 是一個正整數,使得 K<=N。以下是更新 LA 第 K 個位置上的元素的演算法。
1. Start 2. Set LA[K-1] = ITEM 3. Stop
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
void main(){
int LA[] = {1,3,5,7,8};
int k = 3, n = 5, item = 10;
int i, j;
printf("The original array elements are :\n");
for(i = 0; i<n; i++) {
printf("LA[%d] = %d \n", i, LA[i]);
}
LA[k-1] = item;
printf("The array elements after updation :\n");
for(i = 0; i<n; i++) {
printf("LA[%d] = %d \n", i, LA[i]);
}
}
輸出
The original array elements are : LA[0] = 1 LA[1] = 3 LA[2] = 5 LA[3] = 7 LA[4] = 8 The array elements after updation : LA[0] = 1 LA[1] = 3 LA[2] = 10 LA[3] = 7 LA[4] = 8
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int LA[] = {1,3,5,7,8};
int item = 10, k = 3, n = 5;
int i = 0, j = n;
cout << "The original array elements are :\n";
for(i = 0; i<n; i++)
cout << "LA[" << i << "] = " << LA[i] << endl;
LA[2] = item;
cout << "The array elements after updation are :\n";
for(i = 0; i<n; i++)
cout << "LA[" << i << "] = " << LA[i] << endl;
return 0;
}
輸出
The original array elements are : LA[0] = 1 LA[1] = 3 LA[2] = 5 LA[3] = 7 LA[4] = 8 The array elements after updation are : LA[0] = 1 LA[1] = 3 LA[2] = 10 LA[3] = 7 LA[4] = 8
public class ArrayDemo {
public static void main(String []args) {
int LA[] = new int[5];
int item = 15;
System.out.println("The array elements are: ");
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
LA[i] = i + 2;
System.out.println("LA[" + i + "] = " + LA[i]);
}
LA[3] = item;
System.out.println("The array elements after updation are: ");
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
System.out.println("LA[" + i + "] = " + LA[i]);
}
}
輸出
The array elements are: LA[0] = 2 LA[1] = 3 LA[2] = 4 LA[3] = 5 LA[4] = 6 The array elements after updation are: LA[0] = 2 LA[1] = 3 LA[2] = 4 LA[3] = 15 LA[4] = 6
#update operation using python
#Declaring array elements
LA = [1,3,5,7,8]
#before updation
print("The original array elements are :");
for x in range(len(LA)):
print("LA", [x], " = ", LA[x])
#after updation
LA[2] = 10
print("The array elements after updation are: ")
for x in range(len(LA)):
print("LA", [x], " = ", LA[x])
輸出
The original array elements are : LA [0] = 1 LA [1] = 3 LA [2] = 5 LA [3] = 7 LA [4] = 8 The array elements after updation are: LA [0] = 1 LA [1] = 3 LA [2] = 10 LA [3] = 7 LA [4] = 8
顯示操作
此操作使用列印語句顯示整個陣列中的所有元素。
演算法
1. Start 2. Print all the elements in the Array 3. Stop
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
int LA[] = {1,3,5,7,8};
int n = 5;
int i;
printf("The original array elements are :\n");
for(i = 0; i<n; i++) {
printf("LA[%d] = %d \n", i, LA[i]);
}
}
輸出
The original array elements are : LA[0] = 1 LA[1] = 3 LA[2] = 5 LA[3] = 7 LA[4] = 8
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(){
int LA[] = {1,3,5,7,8};
int n = 5;
int i;
cout << "The original array elements are :\n";
for(i = 0; i<n; i++)
cout << "LA[" << i << "] = " << LA[i] << endl;
return 0;
}
輸出
The original array elements are : LA[0] = 1 LA[1] = 3 LA[2] = 5 LA[3] = 7 LA[4] = 8
public class ArrayDemo {
public static void main(String []args) {
int LA[] = new int[5];
System.out.println("The array elements are: ");
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
LA[i] = i + 2;
System.out.println("LA[" + i + "] = " + LA[i]);
}
}
}
輸出
The array elements are: LA[0] = 2 LA[1] = 3 LA[2] = 4 LA[3] = 5 LA[4] = 6
#Display operation using python
#Display operation using python
#Declaring array elements
LA = [2,3,4,5,6]
#Displaying the array
print("The array elements are: ")
for x in range(len(LA)):
print("LA", [x], " = " , LA[x])
輸出
The array elements are: LA [0] = 2 LA [1] = 3 LA [2] = 4 LA [3] = 5 LA [4] = 6
連結串列資料結構
如果陣列容納類似型別的資料型別,則連結串列由具有不同資料型別的元素組成,這些元素也按順序排列。
但是這些連結串列是如何建立的呢?
連結串列是由一系列稱為“節點”的元素透過連結連線而成的資料結構。每個節點包含要儲存的資料以及指向連結串列中下一個節點地址的指標。陣列的大小受定義限制,但連結串列沒有固定的大小。可以在其中儲存任意數量的資料,也可以從中刪除資料。
連結串列主要分為三種類型:
單向連結串列 - 節點只指向列表中下一個節點的地址。
雙向連結串列 - 節點同時指向其前一個節點和後一個節點的地址。
迴圈連結串列 - 連結串列中的最後一個節點指向連結串列中的第一個節點。迴圈連結串列可以是單向的,也可以是雙向的。
連結串列表示
連結串列可以被形象地理解為節點組成的鏈條,每個節點都指向下一個節點。
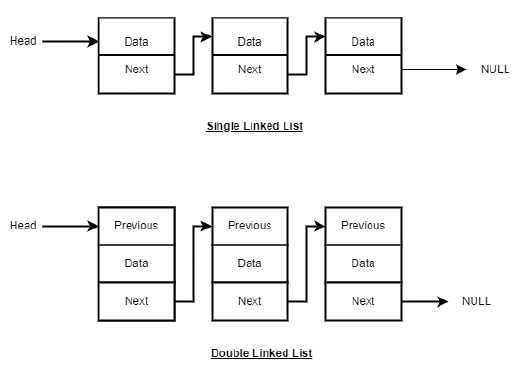
根據以上說明,以下是要考慮的重要事項。
連結串列包含一個稱為 first(頭節點)的連結元素。
每個連結都包含一個或多個數據域和一個稱為 next 的連結域。
每個連結都使用其 next 連結與其下一個連結連線。
最後一個連結的 next 連結為 null,用於標記連結串列的結尾。
連結串列的型別
以下是各種型別的連結串列。
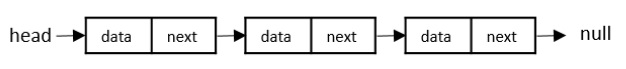
單向連結串列
單向連結串列的每個節點包含兩個“儲存單元”:一個儲存資料,另一個儲存列表中下一個節點的地址。由於節點之間只有一個連結,因此只能單向遍歷連結串列。
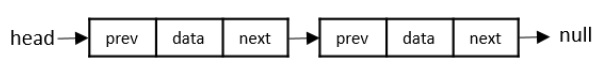
雙向連結串列
雙向連結串列的每個節點包含三個“儲存單元”:一個儲存資料,另外兩個分別儲存列表中前一個節點和後一個節點的地址。由於列表中的節點從兩側相互連線,因此可以雙向遍歷連結串列。
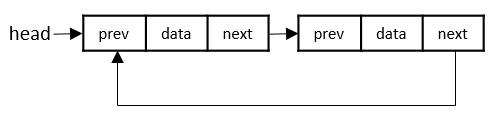
迴圈連結串列
迴圈連結串列可以是單向連結串列,也可以是雙向連結串列。
由於迴圈連結串列的最後一個節點和第一個節點是連線的,因此遍歷此連結串列將無限迴圈,直到鏈條被斷開。
連結串列的基本操作
連結串列的基本操作包括插入、刪除、搜尋、顯示以及刪除指定鍵值元素。以下是在單向連結串列上執行這些操作的方法:
插入 - 在列表開頭新增一個元素。
刪除 - 刪除列表開頭的一個元素。
顯示 - 顯示整個列表。
搜尋 - 使用給定的鍵值搜尋元素。
刪除 - 使用給定的鍵值刪除元素。
插入操作
在連結串列中新增新節點是一個多步驟的操作。我們將在這裡用圖表學習它。首先,使用相同的結構建立一個節點,並找到要插入節點的位置。
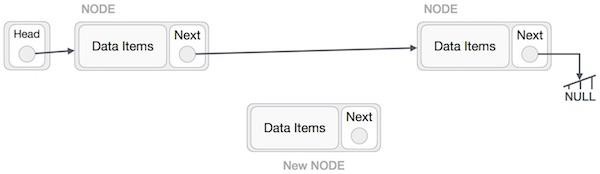
假設我們要在節點 A(LeftNode)和節點 C(RightNode)之間插入節點 B(NewNode)。然後將 B.next 指向 C -
NewNode.next −> RightNode;
它應該看起來像這樣 -
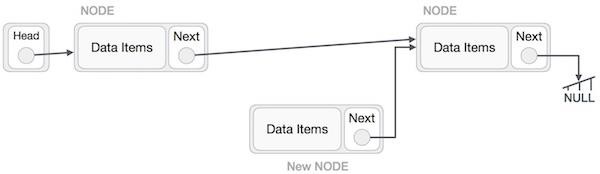
現在,左側的下一個節點應該指向新節點。
LeftNode.next −> NewNode;
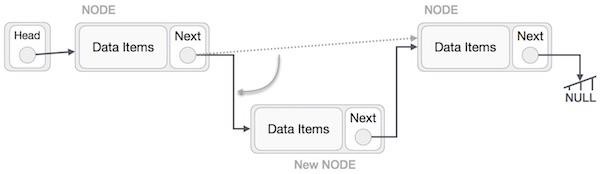
這將把新節點放在這兩個節點的中間。新的列表應該看起來像這樣 -
連結串列的插入操作可以分為三種不同的方式。解釋如下:
頭部插入
在此操作中,我們在列表的開頭新增一個元素。
演算法
1. START 2. Create a node to store the data 3. Check if the list is empty 4. If the list is empty, add the data to the node and assign the head pointer to it. 5 If the list is not empty, add the data to a node and link to the current head. Assign the head to the newly added node. 6. END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
printf("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
printf(" %d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void main(){
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertatbegin(50);
printf("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 50 44 30 22 12 ]
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
cout << "\n[";
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
cout << " " << p->data << " ";
p = p->next;
}
cout << "]";
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
int main(){
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertatbegin(50);
cout << "Linked List: ";
// print list
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 50 44 30 22 12 ]
public class Linked_List {
static class node {
int data;
node next;
node (int value) {
data = value;
next = null;
}
}
static node head;
// display the list
static void printList() {
node p = head;
System.out.print("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != null) {
System.out.print(" " + p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
}
System.out.print("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
static void insertatbegin(int data) {
//create a link
node lk = new node(data);;
// point it to old first node
lk.next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertatbegin(50);
insertatbegin(33);
System.out.println("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
}
}
輸出
Linked List: [33 50 44 30 22 12 ]
class Node:
def __init__(self, data=None):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class SLL:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Print the linked list
def listprint(self):
printval = self.head
print("Linked List: ")
while printval is not None:
print (printval.data)
printval = printval.next
def AddAtBeginning(self,newdata):
NewNode = Node(newdata)
# Update the new nodes next val to existing node
NewNode.next = self.head
self.head = NewNode
l1 = SLL()
l1.head = Node("731")
e2 = Node("672")
e3 = Node("63")
l1.head.next = e2
e2.next = e3
l1.AddAtBeginning("122")
l1.listprint()
輸出
Linked List: 122 731 672 63
尾部插入
在此操作中,我們在列表的末尾新增一個元素。
演算法
1. START 2. Create a new node and assign the data 3. Find the last node 4. Point the last node to new node 5. END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
printf("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
printf(" %d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void insertatend(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
struct node *linkedlist = head;
// point it to old first node
while(linkedlist->next != NULL)
linkedlist = linkedlist->next;
//point first to new first node
linkedlist->next = lk;
}
void main(){
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatend(22);
insertatend(30);
insertatend(44);
insertatend(50);
printf("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 12 22 30 44 50 ]
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
cout << "\n[";
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
cout << " " << p->data << " ";
p = p->next;
}
cout << "]";
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void insertatend(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
struct node *linkedlist = head;
// point it to old first node
while(linkedlist->next != NULL)
linkedlist = linkedlist->next;
//point first to new first node
linkedlist->next = lk;
}
int main(){
insertatbegin(12);
insertatend(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatend(44);
insertatbegin(50);
cout << "Linked List: ";
// print list
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 50 30 12 22 44 ]
public class Linked_List {
static class node {
int data;
node next;
node (int value) {
data = value;
next = null;
}
}
static node head;
// display the list
static void printList() {
node p = head;
System.out.print("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != null) {
System.out.print(" " + p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
}
System.out.print("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
static void insertatbegin(int data) {
//create a link
node lk = new node(data);;
// point it to old first node
lk.next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
static void insertatend(int data) {
//create a link
node lk = new node(data);
node linkedlist = head;
// point it to old first node
while(linkedlist.next != null)
linkedlist = linkedlist.next;
//point first to new first node
linkedlist.next = lk;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatend(44);
insertatend(50);
insertatend(33);
System.out.println("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
}
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 30 22 12 44 50 33 ]
class Node:
def __init__(self, data=None):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LL:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def listprint(self):
val = self.head
print("Linked List:")
while val is not None:
print(val.data)
val = val.next
l1 = LL()
l1.head = Node("23")
l2 = Node("12")
l3 = Node("7")
l4 = Node("14")
l5 = Node("61")
# Linking the first Node to second node
l1.head.next = l2
# Linking the second Node to third node
l2.next = l3
l3.next = l4
l4.next = l5
l1.listprint()
輸出
Linked List: 23 12 7 14 61
指定位置插入
在此操作中,我們在列表中的任何位置新增一個元素。
演算法
1. START 2. Create a new node and assign data to it 3. Iterate until the node at position is found 4. Point first to new first node 5. END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
printf("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
printf(" %d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void insertafternode(struct node *list, int data){
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
lk->next = list->next;
list->next = lk;
}
void main(){
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertafternode(head->next, 30);
printf("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 22 12 30 ]
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
cout << "\n[";
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
cout << " " << p->data << " ";
p = p->next;
}
cout << "]";
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void insertafternode(struct node *list, int data){
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
lk->next = list->next;
list->next = lk;
}
int main(){
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertafternode(head->next,44);
insertafternode(head->next->next, 50);
cout << "Linked List: ";
// print list
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 30 22 44 50 12 ]
public class Linked_List {
static class node {
int data;
node next;
node (int value) {
data = value;
next = null;
}
}
static node head;
// display the list
static void printList() {
node p = head;
System.out.print("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != null) {
System.out.print(" " + p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
}
System.out.print("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
static void insertatbegin(int data) {
//create a link
node lk = new node(data);;
// point it to old first node
lk.next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
static void insertafternode(node list, int data) {
node lk = new node(data);
lk.next = list.next;
list.next = lk;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertafternode(head.next, 50);
insertafternode(head.next.next, 33);
System.out.println("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
}
}
輸出
Linked List: [44 30 50 33 22 12 ]
class Node:
def __init__(self, data=None):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class SLL:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Print the linked list
def listprint(self):
printval = self.head
print("Linked List: ")
while printval is not None:
print (printval.data)
printval = printval.next
# Function to add node
def InsertAtPos(self,nodeatpos,newdata):
if nodeatpos is None:
print("The mentioned node is absent")
return
NewNode = Node(newdata)
NewNode.next = nodeatpos.next
nodeatpos.next = NewNode
l1 = SLL()
l1.head = Node("731")
e2 = Node("672")
e3 = Node("63")
l1.head.next = e2
e2.next = e3
l1.InsertAtPos(l1.head.next, "122")
l1.listprint()
輸出
Linked List: 731 672 122 63
刪除操作
刪除也是一個多步驟的過程。我們將用圖形表示來學習。首先,使用搜索演算法找到要刪除的目標節點。

目標節點左側(前一個)節點現在應該指向目標節點的下一個節點 -
LeftNode.next −> TargetNode.next;

這將刪除指向目標節點的連結。現在,使用以下程式碼,我們將刪除目標節點指向的內容。
TargetNode.next −> NULL;

我們需要使用已刪除的節點。我們可以將其保留在記憶體中,或者可以簡單地釋放記憶體並完全清除目標節點。


如果節點要插入到列表的開頭,則應採取類似的步驟。在末尾插入時,列表的倒數第二個節點應指向新節點,而新節點將指向 NULL。
連結串列的刪除操作也可以分為三種不同的方式。它們如下:
頭部刪除
在此連結串列的刪除操作中,我們從列表的開頭刪除一個元素。為此,我們將 head 指向第二個節點。
演算法
1. START 2. Assign the head pointer to the next node in the list 3. END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
printf("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
printf(" %d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void deleteatbegin(){
head = head->next;
}
int main(){
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(40);
insertatbegin(55);
printf("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
deleteatbegin();
printf("\nLinked List after deletion: ");
// print list
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 55 40 30 22 12 ] Linked List after deletion: [ 40 30 22 12 ]
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
cout << "\n[";
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
cout << " " << p->data << " ";
p = p->next;
}
cout << "]";
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void deleteatbegin(){
head = head->next;
}
int main(){
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertatbegin(50);
cout << "Linked List: ";
// print list
printList();
deleteatbegin();
cout << "Linked List after deletion: ";
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 50 44 30 22 12 ] Linked List after deletion: [ 44 30 22 12 ]
public class Linked_List {
static class node {
int data;
node next;
node (int value) {
data = value;
next = null;
}
}
static node head;
// display the list
static void printList() {
node p = head;
System.out.print("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != null) {
System.out.print(" " + p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
}
System.out.print("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
static void insertatbegin(int data) {
//create a link
node lk = new node(data);;
// point it to old first node
lk.next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
static void deleteatbegin() {
head = head.next;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertatbegin(50);
insertatbegin(33);
System.out.println("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
deleteatbegin();
System.out.println("\nLinked List after deletion: ");
// print list
printList();
}
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 33 50 44 30 22 12 ] Linked List after deletion: [50 44 30 22 12 ]
#python code for deletion at beginning using linked list.
from typing import Optional
class Node:
def __init__(self, data: int, next: Optional['Node'] = None):
self.data = data
self.next = next
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
#display the list
def print_list(self):
p = self.head
print("\n[", end="")
while p:
print(f" {p.data} ", end="")
p = p.next
print("]")
#Insertion at the beginning
def insert_at_begin(self, data: int):
lk = Node(data)
#point it to old first node
lk.next = self.head
#point firt to new first node
self.head = lk
def delete_at_begin(self):
self.head = self.head.next
if __name__ == "__main__":
linked_list = LinkedList()
linked_list.insert_at_begin(12)
linked_list.insert_at_begin(22)
linked_list.insert_at_begin(30)
linked_list.insert_at_begin(44)
linked_list.insert_at_begin(50)
#print list
print("Linked List: ", end="")
linked_list.print_list()
linked_list.delete_at_begin()
print("Linked List after deletion: ", end="")
linked_list.print_list()
輸出
Linked List: [ 50 44 30 22 12 ] Linked List after deletion: [ 44 30 22 12 ]
尾部刪除
在此連結串列的刪除操作中,我們從列表的末尾刪除一個元素。
演算法
1. START 2. Iterate until you find the second last element in the list. 3. Assign NULL to the second last element in the list. 4. END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
printf("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
printf(" %d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void deleteatend(){
struct node *linkedlist = head;
while (linkedlist->next->next != NULL)
linkedlist = linkedlist->next;
linkedlist->next = NULL;
}
void main(){
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(40);
insertatbegin(55);
printf("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
deleteatend();
printf("\nLinked List after deletion: ");
// print list
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 55 40 30 22 12 ] Linked List after deletion: [ 55 40 30 22 ]
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// Displaying the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
while(p != NULL) {
cout << " " << p->data << " ";
p = p->next;
}
}
// Insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void deleteatend(){
struct node *linkedlist = head;
while (linkedlist->next->next != NULL)
linkedlist = linkedlist->next;
linkedlist->next = NULL;
}
int main(){
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertatbegin(50);
cout << "Linked List: ";
// print list
printList();
deleteatend();
cout << "\nLinked List after deletion: ";
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: 50 44 30 22 12 Linked List after deletion: 50 44 30 22
public class Linked_List {
static class node {
int data;
node next;
node (int value) {
data = value;
next = null;
}
}
static node head;
// display the list
static void printList() {
node p = head;
System.out.print("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != null) {
System.out.print(" " + p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
}
System.out.print("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
static void insertatbegin(int data) {
//create a link
node lk = new node(data);;
// point it to old first node
lk.next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
static void deleteatend() {
node linkedlist = head;
while (linkedlist.next.next != null)
linkedlist = linkedlist.next;
linkedlist.next = null;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertatbegin(50);
insertatbegin(33);
System.out.println("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
//deleteatbegin();
deleteatend();
System.out.println("\nLinked List after deletion: ");
// print list
printList();
}
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 33 50 44 30 22 12 ] Linked List after deletion: [ 33 50 44 30 22 ]
#python code for deletion at beginning using linked list.
class Node:
def __init__(self, data=None):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
#Displaying the list
def printList(self):
p = self.head
print("\n[", end="")
while p != None:
print(" " + str(p.data) + " ", end="")
p = p.next
print("]")
#Insertion at the beginning
def insertatbegin(self, data):
#create a link
lk = Node(data)
#point it to old first node
lk.next = self.head
#point first to new first node
self.head = lk
def deleteatend(self):
linkedlist = self.head
while linkedlist.next.next != None:
linkedlist = linkedlist.next
linkedlist.next = None
if __name__ == "__main__":
linked_list = LinkedList()
linked_list.insertatbegin(12)
linked_list.insertatbegin(22)
linked_list.insertatbegin(30)
linked_list.insertatbegin(40)
linked_list.insertatbegin(55)
#print list
print("Linked List: ", end="")
linked_list.printList()
linked_list.deleteatend()
print("Linked List after deletion: ", end="")
linked_list.printList()
輸出
Linked List: [ 55 40 30 22 12 ] Linked List after deletion: [ 55 40 30 22 ]
指定位置刪除
在此連結串列的刪除操作中,我們從列表的任何位置刪除一個元素。
演算法
1. START 2. Iterate until find the current node at position in the list 3. Assign the adjacent node of current node in the list to its previous node. 4. END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
printf("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
printf(" %d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void deletenode(int key){
struct node *temp = head, *prev;
if (temp != NULL && temp->data == key) {
head = temp->next;
return;
}
// Find the key to be deleted
while (temp != NULL && temp->data != key) {
prev = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
// If the key is not present
if (temp == NULL) return;
// Remove the node
prev->next = temp->next;
}
void main(){
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(40);
insertatbegin(55);
printf("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
deletenode(30);
printf("\nLinked List after deletion: ");
// print list
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 55 40 30 22 12 ] Linked List after deletion: [ 55 40 22 12 ]
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
cout << "\n[";
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
cout << " " << p->data << " ";
p = p->next;
}
cout << "]";
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void deletenode(int key){
struct node *temp = head, *prev;
if (temp != NULL && temp->data == key) {
head = temp->next;
return;
}
// Find the key to be deleted
while (temp != NULL && temp->data != key) {
prev = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
// If the key is not present
if (temp == NULL) return;
// Remove the node
prev->next = temp->next;
}
int main(){
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertatbegin(50);
cout << "Linked List: ";
// print list
printList();
deletenode(30);
cout << "Linked List after deletion: ";
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 50 44 30 22 12 ]Linked List after deletion: [ 50 44 22 12 ]
public class Linked_List {
static class node {
int data;
node next;
node (int value) {
data = value;
next = null;
}
}
static node head;
// display the list
static void printList() {
node p = head;
System.out.print("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != null) {
System.out.print(" " + p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
}
System.out.print("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
static void insertatbegin(int data) {
//create a link
node lk = new node(data);;
// point it to old first node
lk.next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
static void deletenode(int key) {
node temp = head;
node prev = null;
if (temp != null && temp.data == key) {
head = temp.next;
return;
}
// Find the key to be deleted
while (temp != null && temp.data != key) {
prev = temp;
temp = temp.next;
}
// If the key is not present
if (temp == null) return;
// Remove the node
prev.next = temp.next;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertatbegin(50);
insertatbegin(33);
System.out.println("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
//deleteatbegin();
//deleteatend();
deletenode(12);
System.out.println("\nLinked List after deletion: ");
// print list
printList();
}
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 33 50 44 30 22 12 ] Linked List after deletion: [ 33 50 44 30 22 ]
#python code for deletion at given position using linked list.
class Node:
def __init__(self, data=None):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# display the list
def printList(self):
p = self.head
print("\n[", end="")
#start from the beginning
while(p != None):
print(" ", p.data, " ", end="")
p = p.next
print("]")
#insertion at the beginning
def insertatbegin(self, data):
#create a link
lk = Node(data)
# point it to old first node
lk.next = self.head
#point first to new first node
self.head = lk
def deletenode(self, key):
temp = self.head
if (temp != None and temp.data == key):
self.head = temp.next
return
# Find the key to be deleted
while (temp != None and temp.data != key):
prev = temp
temp = temp.next
# If the key is not present
if (temp == None):
return
# Remove the node
prev.next = temp.next
llist = LinkedList()
llist.insertatbegin(12)
llist.insertatbegin(22)
llist.insertatbegin(30)
llist.insertatbegin(40)
llist.insertatbegin(55)
print("Original Linked List: ", end="")
# print list
llist.printList()
llist.deletenode(30)
print("\nLinked List after deletion: ", end="")
# print list
llist.printList()
輸出
Linked List: [ 55 40 30 22 12 ] Linked List after deletion: [ 55 40 22 12 ]
反轉操作
此操作比較複雜。我們需要使最後一個節點由頭節點指向,並反轉整個連結串列。

首先,我們遍歷到列表的末尾。它應該指向 NULL。現在,我們將使其指向其前一個節點 -

我們必須確保最後一個節點不是最後一個節點。所以我們將有一些 temp 節點,它看起來像 head 節點指向最後一個節點。現在,我們將一個接一個地使所有左側節點指向其前一個節點。

除了 head 節點指向的節點(第一個節點)之外,所有節點都應該指向其前驅節點,使其成為其新的後繼節點。第一個節點將指向 NULL。
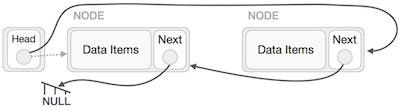
我們將使用 temp 節點使 head 節點指向新的第一個節點。

演算法
反轉連結串列的分步過程如下:
1 START 2. We use three pointers to perform the reversing: prev, next, head. 3. Point the current node to head and assign its next value to the prev node. 4. Iteratively repeat the step 3 for all the nodes in the list. 5. Assign head to the prev node.
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
printf("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
printf(" %d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void reverseList(struct node** head){
struct node *prev = NULL, *cur=*head, *tmp;
while(cur!= NULL) {
tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
*head = prev;
}
void main(){
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(40);
insertatbegin(55);
printf("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
reverseList(&head);
printf("\nReversed Linked List: ");
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 55 40 30 22 12 ] Reversed Linked List: [ 12 22 30 40 55 ]
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
printf("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
printf(" %d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void reverseList(struct node** head){
struct node *prev = NULL, *cur=*head, *tmp;
while(cur!= NULL) {
tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
*head = prev;
}
int main(){
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(40);
insertatbegin(55);
printf("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
reverseList(&head);
printf("\nReversed Linked List: ");
printList();
return 0;
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 55 40 30 22 12 ] Reversed Linked List: [ 12 22 30 40 55 ]
public class Linked_List {
static Node head;
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node (int value) {
data = value;
next = null;
}
}
// display the list
static void printList(Node node) {
System.out.print("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(node != null) {
System.out.print(" " + node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
System.out.print("]");
}
static Node reverseList(Node head) {
Node prev = null;
Node cur = head;
Node temp = null;
while (cur != null) {
temp = cur.next;
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = temp;
}
head = prev;
return head;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Linked_List list = new Linked_List();
list.head = new Node(33);
list.head.next = new Node(50);
list.head.next.next = new Node(44);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(22);
list.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(12);
System.out.println("Linked List: ");
// print list
list.printList(head);
head = list.reverseList(head);
System.out.println("\nReversed linked list ");
list.printList(head);
}
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 33 50 44 22 12 ] Reversed linked list [ 12 22 44 50 33 ]
class Node:
def __init__(self, data=None):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class SLL:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Print the linked list
def listprint(self):
printval = self.head
print("Linked List: ")
while printval is not None:
print (printval.data)
printval = printval.next
def reverse(self):
prev = None
curr = self.head
while(curr is not None):
next = curr.next
curr.next = prev
prev = curr
curr = next
self.head = prev
l1 = SLL()
l1.head = Node("731")
e2 = Node("672")
e3 = Node("63")
l1.head.next = e2
e2.next = e3
l1.listprint()
l1.reverse()
print("After reversing: ")
l1.listprint()
輸出
Linked List: 731 672 63 After reversing: Linked List: 63 672 731
搜尋操作
使用鍵值元素搜尋列表中的元素。此操作與陣列搜尋的方式相同;將列表中的每個元素與給定的鍵值元素進行比較。
演算法
1 START 2 If the list is not empty, iteratively check if the list contains the key 3 If the key element is not present in the list, unsuccessful search 4 END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
printf("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
printf(" %d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
int searchlist(int key){
struct node *temp = head;
while(temp != NULL) {
if (temp->data == key) {
return 1;
}
temp=temp->next;
}
return 0;
}
void main(){
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(40);
insertatbegin(55);
printf("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
k = searchlist(30);
if (k == 1)
printf("\nElement is found");
else
printf("\nElement is not present in the list");
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 55 40 30 22 12 ] Element is found
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
cout << "\n[";
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
cout << " " << p->data << " ";
p = p->next;
}
cout << "]";
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
int searchlist(int key){
struct node *temp = head;
while(temp != NULL) {
if (temp->data == key) {
return 1;
}
temp=temp->next;
}
return 0;
}
int main(){
int k = 0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertatbegin(50);
cout << "Linked List: ";
// print list
printList();
k = searchlist(16);
if (k == 1)
cout << "\nElement is found";
else
cout << "\nElement is not present in the list";
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 50 44 30 22 12 ] Element is not present in the list
public class Linked_List {
static class node {
int data;
node next;
node (int value) {
data = value;
next = null;
}
}
static node head;
// display the list
static void printList() {
node p = head;
System.out.print("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != null) {
System.out.print(" " + p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
}
System.out.print("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
static void insertatbegin(int data) {
//create a link
node lk = new node(data);;
// point it to old first node
lk.next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
static int searchlist(int key) {
node temp = head;
while(temp != null) {
if (temp.data == key) {
return 1;
}
temp=temp.next;
}
return 0;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertatbegin(50);
insertatbegin(33);
System.out.println("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
k = searchlist(44);
if (k == 1)
System.out.println("\nElement is found");
else
System.out.println("\nElement is not present in the list");
}
}
輸出
Linked List: [33 50 44 30 22 12 ] Element is found
class Node:
def __init__(self, data=None):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class SLL:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def search(self, x):
count = 0
# Initialize current to head
current = self.head
# loop till current not equal to None
while current != None:
if current.data == x:
print("data found")
count = count + 1
current = current.next
if count == 0:
print("Data Not found")
l1 = SLL()
l1.head = Node("731")
e2 = Node("672")
e3 = Node("63")
l1.head.next = e2
e2.next = e3
l1.search("63")
輸出
data found
遍歷操作
遍歷操作按順序遍歷列表的所有元素,並按該順序顯示元素。
演算法
1. START 2. While the list is not empty and did not reach the end of the list, print the data in each node 3. END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
printf("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
printf(" %d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void main(){
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
printf("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 30 22 12 ]
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// Displaying the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
while(p != NULL) {
cout << " " << p->data << " ";
p = p->next;
}
}
// Insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
int main(){
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertatbegin(50);
cout << "Linked List: ";
// print list
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: 50 44 30 22 12
public class Linked_List {
static class node {
int data;
node next;
node (int value) {
data = value;
next = null;
}
}
static node head;
// display the list
static void printList() {
node p = head;
System.out.print("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != null) {
System.out.print(" " + p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
}
System.out.print("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
static void insertatbegin(int data) {
//create a link
node lk = new node(data);;
// point it to old first node
lk.next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertatbegin(50);
insertatbegin(33);
System.out.println("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
}
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 33 50 44 30 22 12 ]
class Node:
def __init__(self, data=None):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class SLL:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Print the linked list
def listprint(self):
printval = self.head
print("Linked List: ")
while printval is not None:
print (printval.data)
printval = printval.next
l1 = SLL()
l1.head = Node("731")
e2 = Node("672")
e3 = Node("63")
l1.head.next = e2
e2.next = e3
l1.listprint()
輸出
Linked List: 731 672 63
完整實現
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
printf("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
printf(" %d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void insertatend(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
struct node *linkedlist = head;
// point it to old first node
while(linkedlist->next != NULL)
linkedlist = linkedlist->next;
//point first to new first node
linkedlist->next = lk;
}
void insertafternode(struct node *list, int data){
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
lk->next = list->next;
list->next = lk;
}
void deleteatbegin(){
head = head->next;
}
void deleteatend(){
struct node *linkedlist = head;
while (linkedlist->next->next != NULL)
linkedlist = linkedlist->next;
linkedlist->next = NULL;
}
void deletenode(int key){
struct node *temp = head, *prev;
if (temp != NULL && temp->data == key) {
head = temp->next;
return;
}
// Find the key to be deleted
while (temp != NULL && temp->data != key) {
prev = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
// If the key is not present
if (temp == NULL) return;
// Remove the node
prev->next = temp->next;
}
int searchlist(int key){
struct node *temp = head;
while(temp != NULL) {
if (temp->data == key) {
return 1;
}
temp=temp->next;
}
return 0;
}
void main(){
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatend(30);
insertatend(44);
insertatbegin(50);
insertafternode(head->next->next, 33);
printf("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
deleteatbegin();
deleteatend();
deletenode(12);
printf("\nLinked List after deletion: ");
// print list
printList();
insertatbegin(4);
insertatbegin(16);
printf("\nUpdated Linked List: ");
printList();
k = searchlist(16);
if (k == 1)
printf("\nElement is found");
else
printf("\nElement is not present in the list");
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 50 22 12 33 30 44 ] Linked List after deletion: [ 22 33 30 ] Updated Linked List: [ 16 4 22 33 30 ] Element is found
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
cout << "\n[";
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
cout << " " << p->data << " ";
p = p->next;
}
cout << "]";
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void insertatend(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
struct node *linkedlist = head;
// point it to old first node
while(linkedlist->next != NULL)
linkedlist = linkedlist->next;
//point first to new first node
linkedlist->next = lk;
}
void insertafternode(struct node *list, int data){
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
lk->next = list->next;
list->next = lk;
}
void deleteatbegin(){
head = head->next;
}
void deleteatend(){
struct node *linkedlist = head;
while (linkedlist->next->next != NULL)
linkedlist = linkedlist->next;
linkedlist->next = NULL;
}
void deletenode(int key){
struct node *temp = head, *prev;
if (temp != NULL && temp->data == key) {
head = temp->next;
return;
}
// Find the key to be deleted
while (temp != NULL && temp->data != key) {
prev = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
// If the key is not present
if (temp == NULL) return;
// Remove the node
prev->next = temp->next;
}
int searchlist(int key){
struct node *temp = head;
while(temp != NULL) {
if (temp->data == key) {
temp=temp->next;
return 1;
} else
return 0;
}
}
int main(){
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatend(30);
insertatend(44);
insertatbegin(50);
insertafternode(head->next->next, 33);
cout << "Linked List: ";
// print list
printList();
deleteatbegin();
deleteatend();
deletenode(12);
cout << "\nLinked List after deletion: ";
// print list
printList();
insertatbegin(4);
insertatbegin(16);
cout << "\nUpdated Linked List: ";
printList();
k = searchlist(16);
if (k == 1)
cout << "\nElement is found";
else
cout << "\nElement is not present in the list";
return 0;
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 50 22 12 33 30 44 ] Linked List after deletion: [ 22 33 30 ] Updated Linked List: [ 16 4 22 33 30 ] Element is found
public class Linked_List {
static class node {
int data;
node next;
node (int value) {
data = value;
next = null;
}
}
static node head;
// display the list
static void printList() {
node p = head;
System.out.print("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != null) {
System.out.print(" " + p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
}
System.out.print("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
static void insertatbegin(int data) {
//create a link
node lk = new node(data);;
// point it to old first node
lk.next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
static void insertatend(int data) {
//create a link
node lk = new node(data);
node linkedlist = head;
// point it to old first node
while(linkedlist.next != null)
linkedlist = linkedlist.next;
//point first to new first node
linkedlist.next = lk;
}
static void insertafternode(node list, int data) {
node lk = new node(data);
lk.next = list.next;
list.next = lk;
}
static void deleteatbegin() {
head = head.next;
}
static void deleteatend() {
node linkedlist = head;
while (linkedlist.next.next != null)
linkedlist = linkedlist.next;
linkedlist.next = null;
}
static void deletenode(int key) {
node temp = head;
node prev = null;
if (temp != null && temp.data == key) {
head = temp.next;
return;
}
// Find the key to be deleted
while (temp != null && temp.data != key) {
prev = temp;
temp = temp.next;
}
// If the key is not present
if (temp == null) return;
// Remove the node
prev.next = temp.next;
}
static int searchlist(int key) {
node temp = head;
while(temp != null) {
if (temp.data == key) {
temp=temp.next;
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatend(30);
insertatend(44);
insertatbegin(50);
insertafternode(head.next.next, 33);
System.out.println("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
deleteatbegin();
deleteatend();
deletenode(12);
System.out.println("\nLinked List after deletion: ");
// print list
printList();
insertatbegin(4);
insertatbegin(16);
System.out.println("\nUpdated Linked List: ");
printList();
k = searchlist(16);
if (k == 1)
System.out.println("\nElement is found");
else
System.out.println("\nElement is not present in the list");
}
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 50 22 12 33 30 44 ] Linked List after deletion: [ 22 33 30 ] Updated Linked List: [ 16 4 22 33 30 ] Element is found
class LLNode:
def __init__(self, data=None):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LL:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def listprint(self):
printval = self.head
while printval is not None:
print(printval.data)
printval = printval.next
def AddAtBeginning(self,newdata):
NewNode = LLNode(newdata)
# Update the new nodes next val to existing node
NewNode.next = self.head
self.head = NewNode
# Function to add node at a position
def InsertAtPos(self,nodeatpos,newdata):
if nodeatpos is None:
print("The mentioned node is absent")
return
NewNode = LLNode(newdata)
NewNode.next = nodeatpos.next
nodeatpos.next = NewNode
def reverse(self):
prev = None
curr = self.head
while(curr is not None):
next = curr.next
curr.next = prev
prev = curr
curr = next
self.head = prev
def search(self, x):
count = 0
# Initialize current to head
current = self.head
# loop till current not equal to None
while current != None:
if current.data == x:
print("data found")
count = count + 1
current = current.next
if count == 0:
print("Data Not found")
l1 = LL()
l1.head = LLNode("23")
l2 = LLNode("12")
l3 = LLNode("7")
l4 = LLNode("14")
l5 = LLNode("61")
# Linking the first Node to second node
l1.head.next = l2
# Linking the second Node to third node
l2.next = l3
l3.next = l4
l4.next = l5
print("Original Linked List: ")
l1.listprint()
l1.AddAtBeginning("45")
l1.InsertAtPos(l1.head.next.next, "4")
print("Updated Linked List:")
l1.listprint()
l1.reverse()
print("Reversed Linked List:")
l1.listprint()
l1.search("7")
輸出
Original Linked List: 23 12 7 14 61 Updated Linked List: 45 23 12 4 7 14 61 Reversed Linked List: 61 14 7 4 12 23 45 data found
雙向連結串列資料結構
雙向連結串列是連結串列的一種變體,與單向連結串列相比,它可以更容易地向前和向後導航。以下是一些理解雙向連結串列概念的重要術語。
連結 - 連結串列的每個連結都可以儲存稱為元素的資料。
Next - 連結串列的每個連結都包含一個指向下一個連結的連結,稱為 Next。
Prev - 連結串列的每個連結都包含一個指向前一個連結的連結,稱為 Prev。
連結串列 - 連結串列包含一個指向第一個連結(稱為 First)和最後一個連結(稱為 Last)的連線連結。
雙向連結串列表示

根據以上說明,以下是要考慮的重要事項。
雙向連結串列包含一個稱為 first 和 last 的連結元素。
每個連結都包含一個或多個數據域和一個稱為 next 的連結域。
每個連結都使用其 next 連結與其下一個連結連線。
每個連結都使用其前一個連結與其前一個連結連線。
最後一個連結的連結為 null,用於標記列表的結尾。
基本操作
以下是列表支援的基本操作。
插入 - 在列表開頭新增一個元素。
刪除 - 刪除列表開頭的一個元素。
尾部插入 - 在列表末尾新增一個元素。
尾部刪除 - 從列表末尾刪除一個元素。
指定元素後插入 - 在列表的某個元素之後新增一個元素。
刪除 - 使用鍵值從列表中刪除一個元素。
正向顯示 - 以正向方式顯示整個列表。
反向顯示 - 以反向方式顯示整個列表。
頭部插入
在此操作中,我們建立一個包含三個儲存單元的新節點,一個儲存資料,另外兩個分別儲存列表中其前一個節點和後一個節點的地址。此新節點插入到列表的開頭。
演算法
1. START 2. Create a new node with three variables: prev, data, next. 3. Store the new data in the data variable 4. If the list is empty, make the new node as head. 5. Otherwise, link the address of the existing first node to the next variable of the new node, and assign null to the prev variable. 6. Point the head to the new node. 7. END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node *next;
struct node *prev;
};
//this link always point to first Link
struct node *head = NULL;
//this link always point to last Link
struct node *last = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
//is list empty
bool isEmpty(){
return head == NULL;
}
//display the doubly linked list
void printList(){
struct node *ptr = head;
while(ptr != NULL) {
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if(isEmpty()) {
//make it the last link
last = link;
} else {
//update first prev link
head->prev = link;
}
//point it to old first link
link->next = head;
//point first to new first link
head = link;
}
void main(){
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertFirst(5,40);
insertFirst(6,56);
printf("\nDoubly Linked List: ");
printList();
}
輸出
Doubly Linked List: (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) (1,10)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdbool>
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node *next;
struct node *prev;
};
//this link always point to first Link
struct node *head = NULL;
//this link always point to last Link
struct node *last = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
//is list empty
bool isEmpty(){
return head == NULL;
}
//display the doubly linked list
void printList(){
struct node *ptr = head;
while(ptr != NULL) {
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if(isEmpty()) {
//make it the last link
last = link;
} else {
//update first prev link
head->prev = link;
}
//point it to old first link
link->next = head;
//point first to new first link
head = link;
}
int main(){
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertFirst(5,40);
insertFirst(6,56);
printf("\nDoubly Linked List: ");
printList();
return 0;
}
輸出
Doubly Linked List: (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) (1,10)
//Java code for doubly linked list
import java.util.*;
class Node {
public int data;
public int key;
public Node next;
public Node prev;
public Node(int data, int key) {
this.data = data;
this.key = key;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
public class Main {
//this link always point to first Link
static Node head = null;
//this link always point to last Link
static Node last = null;
static Node current = null;
// is list empty
public static boolean is_empty() {
return head == null;
}
//display the doubly linked list
public static void print_list() {
Node ptr = head;
while (ptr != null) {
System.out.println("(" + ptr.key + "," + ptr.data + ")");
ptr = ptr.next;
}
}
//insert link at the first location
public static void insert_first(int key, int data) {
//create a link
Node link = new Node(data, key);
if (is_empty()) {
//make it the last link
last = link;
} else {
//update first prev link
head.prev = link;
}
//point it to old first link
link.next = head;
//point first to new first link
head = link;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
insert_first(1, 10);
insert_first(2, 20);
insert_first(3, 30);
insert_first(4, 1);
insert_first(5, 40);
insert_first(6, 56);
System.out.println("\nDoubly Linked List: ");
print_list();
}
}
輸出
Doubly Linked List: (6,56)(5,40)(4,1)(3,30)(2,20)(1,10)
#Python code for doubly linked list
class Node:
def __init__(self, data=None, key=None):
self.data = data
self.key = key
self.next = None
self.prev = None
#this link always point to first Link
head = None
#this link always point to last Link
last = None
current = None
#is list empty
def is_empty():
return head == None
#display the doubly linked list
def print_list():
ptr = head
while ptr != None:
print(f"({ptr.key},{ptr.data})")
ptr = ptr.next
#insert link at the first location
def insert_first(key, data):
global head, last
#create a link
link = Node(data, key)
if is_empty():
#make it the last link
last = link
else:
#update first prev link
head.prev = link
#point it to old first link
link.next = head
#point first to new first link
head = link
insert_first(1,10)
insert_first(2,20)
insert_first(3,30)
insert_first(4,1)
insert_first(5,40)
insert_first(6,56)
print("\nDoubly Linked List: ")
print_list()
輸出
Doubly Linked List: (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) (1,10)
頭部刪除
此刪除操作刪除雙向連結串列中現有的第一個節點。head 指標移到下一個節點,並刪除連結。
演算法
1. START 2. Check the status of the doubly linked list 3. If the list is empty, deletion is not possible 4. If the list is not empty, the head pointer is shifted to the next node. 5. END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node *next;
struct node *prev;
};
//this link always point to first Link
struct node *head = NULL;
//this link always point to last Link
struct node *last = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
//is list empty
bool isEmpty(){
return head == NULL;
}
//display the doubly linked list
void printList(){
struct node *ptr = head;
while(ptr != NULL) {
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if(isEmpty()) {
//make it the last link
last = link;
} else {
//update first prev link
head->prev = link;
}
//point it to old first link
link->next = head;
//point first to new first link
head = link;
}
//delete first item
struct node* deleteFirst(){
//save reference to first link
struct node *tempLink = head;
//if only one link
if(head->next == NULL) {
last = NULL;
} else {
head->next->prev = NULL;
}
head = head->next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
void main(){
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertFirst(5,40);
insertFirst(6,56);
printf("\nDoubly Linked List: ");
printList();
printf("\nList after deleting first record: ");
deleteFirst();
printList();
}
輸出
Doubly Linked List: (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) (1,10) List after deleting first record: (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) (1,10)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdbool>
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node *next;
struct node *prev;
};
//this link always point to first Link
struct node *head = NULL;
//this link always point to last Link
struct node *last = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
//is list empty
bool isEmpty(){
return head == NULL;
}
//display the doubly linked list
void printList(){
struct node *ptr = head;
while(ptr != NULL) {
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if(isEmpty()) {
//make it the last link
last = link;
} else {
//update first prev link
head->prev = link;
}
//point it to old first link
link->next = head;
//point first to new first link
head = link;
}
//delete first item
struct node* deleteFirst(){
//save reference to first link
struct node *tempLink = head;
//if only one link
if(head->next == NULL) {
last = NULL;
} else {
head->next->prev = NULL;
}
head = head->next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
int main(){
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertFirst(5,40);
insertFirst(6,56);
printf("\nDoubly Linked List: ");
printList();
printf("\nList after deleting first record: ");
deleteFirst();
printList();
return 0;
}
輸出
Doubly Linked List: (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) (1,10) List after deleting first record: (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) (1,10)
//Java code for doubly linked list
import java.util.*;
class Node {
public int data;
public int key;
public Node next;
public Node prev;
public Node(int data, int key) {
this.data = data;
this.key = key;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
public class Main {
//this link always point to first Link
public static Node head = null;
//this link always point to last Link
public static Node last = null;
//this link always point to current Link
public static Node current = null;
//is list empty
public static boolean isEmpty() {
return head == null;
}
//display the doubly linked list
public static void printList() {
Node ptr = head;
while (ptr != null) {
System.out.print("(" + ptr.key + "," + ptr.data + ") ");
ptr = ptr.next;
}
}
//insert link at the first location
public static void insertFirst(int key, int data) {
//create a link
Node link = new Node(data, key);
if (isEmpty()) {
//make it the last link
last = link;
} else {
//update first prev link
head.prev = link;
}
//point it to old first link
link.next = head;
head = link;
}
//delete the first item
public static Node deleteFirst() {
//save reference to first link
Node tempLink = head;
//if only one link
if (head.next == null) {
last = null;
} else {
head.next.prev = null;
}
head = head.next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
insertFirst(1, 10);
insertFirst(2, 20);
insertFirst(3, 30);
insertFirst(4, 1);
insertFirst(5, 40);
insertFirst(6, 56);
System.out.print("\nDoubly Linked List: ");
printList();
System.out.print("\nList after deleting first record: ");
deleteFirst();
printList();
}
}
輸出
Doubly Linked List: (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) (1,10) List after deleting first record: (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) (1,10)
#Python code for doubly linked list
class Node:
def __init__(self, data=None, key=None):
self.data = data
self.key = key
self.next = None
self.prev = None
#this link always point to first Link
head = None
#this link always point to last Link
last = None
current = None
#is list empty
def isEmpty():
return head == None
#display the doubly linked list
def printList():
ptr = head
while ptr != None:
print(f"({ptr.key},{ptr.data}) ", end="")
ptr = ptr.next
#insert link at the first location
def insertFirst(key, data):
#create a link
global head, last
link = Node(data, key)
if isEmpty():
#make it the last link
last = link
else:
#update first prev link
head.prev = link
#point it to old first link
link.next = head
head = link
#delete first item
def deleteFirst():
#save reference to first link
global head, last
tempLink = head
#if only one link
if head.next == None:
last = None
else:
head.next.prev = None
head = head.next
#return the deleted link
return tempLink
insertFirst(1,10)
insertFirst(2,20)
insertFirst(3,30)
insertFirst(4,1)
insertFirst(5,40)
insertFirst(6,56)
print("\nDoubly Linked List: ", end="")
printList()
print("\nList after deleting first record: ")
deleteFirst()
printList()
輸出
Doubly Linked List: (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) (1,10) List after deleting first record: (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) (1,10)
尾部插入
在此插入操作中,新的輸入節點新增到雙向連結串列的末尾;如果列表不為空。如果列表為空,則 head 將指向新節點。
演算法
1. START 2. If the list is empty, add the node to the list and point the head to it. 3. If the list is not empty, find the last node of the list. 4. Create a link between the last node in the list and the new node. 5. The new node will point to NULL as it is the new last node. 6. END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node *next;
struct node *prev;
};
//this link always point to first Link
struct node *head = NULL;
//this link always point to last Link
struct node *last = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
//is list empty
bool isEmpty(){
return head == NULL;
}
//display the doubly linked list
void printList(){
struct node *ptr = head;
while(ptr != NULL) {
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if(isEmpty()) {
//make it the last link
last = link;
} else {
//update first prev link
head->prev = link;
}
//point it to old first link
link->next = head;
//point first to new first link
head = link;
}
//insert link at the last location
void insertLast(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if(isEmpty()) {
//make it the last link
last = link;
} else {
//make link a new last link
last->next = link;
//mark old last node as prev of new link
link->prev = last;
}
//point last to new last node
last = link;
}
void main(){
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertLast(5,40);
insertLast(6,56);
printf("\nDoubly Linked List: ");
printList();
}
輸出
Doubly Linked List: (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) (1,10) (5,40) (6,56)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdbool>
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node *next;
struct node *prev;
};
//this link always point to first Link
struct node *head = NULL;
//this link always point to last Link
struct node *last = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
//is list empty
bool isEmpty(){
return head == NULL;
}
//display the doubly linked list
void printList(){
struct node *ptr = head;
while(ptr != NULL) {
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if(isEmpty()) {
//make it the last link
last = link;
} else {
//update first prev link
head->prev = link;
}
//point it to old first link
link->next = head;
//point first to new first link
head = link;
}
//insert link at the last location
void insertLast(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if(isEmpty()) {
//make it the last link
last = link;
} else {
//make link a new last link
last->next = link;
//mark old last node as prev of new link
link->prev = last;
}
//point last to new last node
last = link;
}
int main(){
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertLast(5,40);
insertLast(6,56);
printf("\nDoubly Linked List: ");
printList();
return 0;
}
輸出
Doubly Linked List: (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) (1,10) (5,40) (6,56)
import java.util.*;
class Node {
public int data;
public int key;
public Node next;
public Node prev;
public Node(int data, int key) {
this.data = data;
this.key = key;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
public class Main {
static Node head = null;
static Node last = null;
static Node current = null;
public static boolean isEmpty() {
return head == null;
}
public static void printList() {
Node ptr = head;
while (ptr != null) {
System.out.print("(" + ptr.key + "," + ptr.data + ") ");
ptr = ptr.next;
}
}
public static void insertFirst(int key, int data) {
Node link = new Node(data, key);
if (isEmpty()) {
last = link;
} else {
head.prev = link;
}
link.next = head;
head = link;
}
public static void insertLast(int key, int data) {
Node link = new Node(data, key);
if (isEmpty()) {
last = link;
} else {
last.next = link;
link.prev = last;
}
last = link;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertLast(5,40);
insertLast(6,56);
System.out.print("\nDoubly Linked List: ");
printList();
}
}
輸出
Doubly Linked List: (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) (1,10) (5,40) (6,56)
class Node:
def __init__(self, data=None, key=None):
self.data = data
self.key = key
self.next = None
self.prev = None
head = None
last = None
current = None
def isEmpty():
return head == None
def printList():
ptr = head
while ptr != None:
print(f"({ptr.key},{ptr.data})", end=" ")
ptr = ptr.next
def insertFirst(key, data):
global head, last
link = Node(data, key)
if isEmpty():
last = link
else:
head.prev = link
link.next = head
head = link
def insertLast(key, data):
global head, last
link = Node(data, key)
if isEmpty():
last = link
else:
last.next = link
link.prev = last
last = link
insertFirst(1,10)
insertFirst(2,20)
insertFirst(3,30)
insertFirst(4,1)
insertLast(5,40)
insertLast(6,56)
print("\nDoubly Linked List: ", end="")
printList()
輸出
Doubly Linked List: (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) (1,10) (5,40) (6,56)
完整實現
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node *next;
struct node *prev;
};
//this link always point to first Link
struct node *head = NULL;
//this link always point to last Link
struct node *last = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
//is list empty
bool isEmpty(){
return head == NULL;
}
//display the list in from first to last
void displayForward(){
//start from the beginning
struct node *ptr = head;
//navigate till the end of the list
printf("\n[ ");
while(ptr != NULL) {
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
printf(" ]");
}
//display the list from last to first
void displayBackward(){
//start from the last
struct node *ptr = last;
//navigate till the start of the list
printf("\n[ ");
while(ptr != NULL) {
//print data
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
//move to next item
ptr = ptr ->prev;
printf(" ");
}
printf(" ]");
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if(isEmpty()) {
//make it the last link
last = link;
} else {
//update first prev link
head->prev = link;
}
//point it to old first link
link->next = head;
//point first to new first link
head = link;
}
//insert link at the last location
void insertLast(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if(isEmpty()) {
//make it the last link
last = link;
} else {
//make link a new last link
last->next = link;
//mark old last node as prev of new link
link->prev = last;
}
//point last to new last node
last = link;
}
//delete first item
struct node* deleteFirst(){
//save reference to first link
struct node *tempLink = head;
//if only one link
if(head->next == NULL) {
last = NULL;
} else {
head->next->prev = NULL;
}
head = head->next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
//delete link at the last location
struct node* deleteLast(){
//save reference to last link
struct node *tempLink = last;
//if only one link
if(head->next == NULL) {
head = NULL;
} else {
last->prev->next = NULL;
}
last = last->prev;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
//delete a link with given key
struct node* delete(int key){
//start from the first link
struct node* current = head;
struct node* previous = NULL;
//if list is empty
if(head == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
//navigate through list
while(current->key != key) {
//if it is last node
if(current->next == NULL) {
return NULL;
} else {
//store reference to current link
previous = current;
//move to next link
current = current->next;
}
}
//found a match, update the link
if(current == head) {
//change first to point to next link
head = head->next;
} else {
//bypass the current link
current->prev->next = current->next;
}
if(current == last) {
//change last to point to prev link
last = current->prev;
} else {
current->next->prev = current->prev;
}
return current;
}
bool insertAfter(int key, int newKey, int data){
//start from the first link
struct node *current = head;
//if list is empty
if(head == NULL) {
return false;
}
//navigate through list
while(current->key != key) {
//if it is last node
if(current->next == NULL) {
return false;
} else {
//move to next link
current = current->next;
}
}
//create a link
struct node *newLink = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newLink->key = key;
newLink->data = data;
if(current == last) {
newLink->next = NULL;
last = newLink;
} else {
newLink->next = current->next;
current->next->prev = newLink;
}
newLink->prev = current;
current->next = newLink;
return true;
}
int main(){
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertFirst(5,40);
insertFirst(6,56);
printf("\nList (First to Last): ");
displayForward();
printf("\n");
printf("\nList (Last to first): ");
displayBackward();
printf("\nList , after deleting first record: ");
deleteFirst();
displayForward();
printf("\nList , after deleting last record: ");
deleteLast();
displayForward();
printf("\nList , insert after key(4) : ");
insertAfter(4,7, 13);
displayForward();
printf("\nList , after delete key(4) : ");
delete(4);
displayForward();
}
輸出
List (First to Last): [ (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) (1,10) ] List (Last to first): [ (1,10) (2,20) (3,30) (4,1) (5,40) (6,56) ] List , after deleting first record: [ (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) (1,10) ] List , after deleting last record: [ (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) ] List , insert after key(4) : [ (5,40) (4,1) (4,13) (3,30) (2,20) ] List , after delete key(4) : [ (5,40) (4,13) (3,30) (2,20) ]
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdbool>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node *next;
struct node *prev;
};
//this link always point to first Link
struct node *head = NULL;
//this link always point to last Link
struct node *last = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
//is list empty
bool isEmpty(){
return head == NULL;
}
//display the list in from first to last
void displayForward(){
//start from the beginning
struct node *ptr = head;
//navigate till the end of the list
cout << "\n[ ";
while(ptr != NULL) {
cout << "(" << ptr->key << "," << ptr->data << ")";
ptr = ptr->next;
}
cout << " ]" << endl;
}
//display the list from last to first
void displayBackward(){
//start from the last
struct node *ptr = last;
//navigate till the start of the list
cout << "\n[ ";
while(ptr != NULL) {
//print data
cout << "(" << ptr->key << "," << ptr->data << ")";
//move to next item
ptr = ptr ->prev;
cout << " ";
}
cout << " ]" << endl;
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if(isEmpty()) {
//make it the last link
last = link;
} else {
//update first prev link
head->prev = link;
}
//point it to old first link
link->next = head;
//point first to new first link
head = link;
}
//insert link at the last location
void insertLast(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if(isEmpty()) {
//make it the last link
last = link;
} else {
//make link a new last link
last->next = link;
//mark old last node as prev of new link
link->prev = last;
}
//point last to new last node
last = link;
}
//delete first item
struct node* deleteFirst(){
//save reference to first link
struct node *tempLink = head;
//if only one link
if(head->next == NULL) {
last = NULL;
} else {
head->next->prev = NULL;
}
head = head->next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
//delete link at the last location
struct node* deleteLast(){
//save reference to last link
struct node *tempLink = last;
//if only one link
if(head->next == NULL) {
head = NULL;
} else {
last->prev->next = NULL;
}
last = last->prev;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
//delete a link with given key
struct node* deletenode(int key){
//start from the first link
struct node* current = head;
struct node* previous = NULL;
//if list is empty
if(head == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
//navigate through list
while(current->key != key) {
//if it is last node
if(current->next == NULL) {
return NULL;
} else {
//store reference to current link
previous = current;
//move to next link
current = current->next;
}
}
//found a match, update the link
if(current == head) {
//change first to point to next link
head = head->next;
} else {
//bypass the current link
current->prev->next = current->next;
}
if(current == last) {
//change last to point to prev link
last = current->prev;
} else {
current->next->prev = current->prev;
}
return current;
}
bool insertAfter(int key, int newKey, int data){
//start from the first link
struct node *current = head;
//if list is empty
if(head == NULL) {
return false;
}
//navigate through list
while(current->key != key) {
//if it is last node
if(current->next == NULL) {
return false;
} else {
//move to next link
current = current->next;
}
}
//create a link
struct node *newLink = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
newLink->key = key;
newLink->data = data;
if(current == last) {
newLink->next = NULL;
last = newLink;
} else {
newLink->next = current->next;
current->next->prev = newLink;
}
newLink->prev = current;
current->next = newLink;
return true;
}
int main(){
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertFirst(5,40);
insertFirst(6,56);
printf("\nList (First to Last): ");
displayForward();
printf("\n");
printf("\nList (Last to first): ");
displayBackward();
printf("\nList , after deleting first record: ");
deleteFirst();
displayForward();
printf("\nList , after deleting last record: ");
deleteLast();
displayForward();
printf("\nList , insert after key(4) : ");
insertAfter(4, 7, 13);
displayForward();
printf("\nList , after delete key(4) : ");
deletenode(4);
displayForward();
return 0;
}
輸出
List (First to Last): [ (6, 56) (5, 40) (4, 1) (3, 30) (2, 20) (1, 10) ] List (Last to First): [ (1, 10) (2, 20) (3, 30) (4, 1) (5, 40) (6, 56) ] List, after deleting first record: [ (5, 40) (4, 1) (3, 30) (2, 20) (1, 10) ] List, after deleting last record: [ (5, 40) (4, 1) (3, 30) (2, 20) ] List, insert after key(4): [ (5, 40) (4, 1) (7, 13) (3, 30) (2, 20) ] List, after delete key(4): [ (5, 40) (7, 13) (3, 30) (2, 20) ]
class Node {
int data;
int key;
Node next;
Node prev;
public Node(int key, int data) {
this.key = key;
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
class DoublyLinkedList {
Node head;
Node last;
boolean isEmpty() {
return head == null;
}
void displayForward() {
Node ptr = head;
System.out.print("[ ");
while (ptr != null) {
System.out.print("(" + ptr.key + "," + ptr.data + ") ");
ptr = ptr.next;
}
System.out.println("]");
}
void displayBackward() {
Node ptr = last;
System.out.print("[ ");
while (ptr != null) {
System.out.print("(" + ptr.key + "," + ptr.data + ") ");
ptr = ptr.prev;
}
System.out.println("]");
}
void insertFirst(int key, int data) {
Node link = new Node(key, data);
if (isEmpty()) {
last = link;
} else {
head.prev = link;
}
link.next = head;
head = link;
}
void insertLast(int key, int data) {
Node link = new Node(key, data);
if (isEmpty()) {
last = link;
} else {
last.next = link;
link.prev = last;
}
last = link;
}
Node deleteFirst() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
Node tempLink = head;
if (head.next == null) {
last = null;
} else {
head.next.prev = null;
}
head = head.next;
return tempLink;
}
Node deleteLast() {
if (isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
Node tempLink = last;
if (head.next == null) {
head = null;
} else {
last.prev.next = null;
}
last = last.prev;
return tempLink;
}
Node delete(int key) {
Node current = head;
Node previous = null;
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
while (current.key != key) {
if (current.next == null) {
return null;
} else {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
}
if (current == head) {
head = head.next;
} else {
current.prev.next = current.next;
}
if (current == last) {
last = current.prev;
} else {
current.next.prev = current.prev;
}
return current;
}
boolean insertAfter(int key, int newKey, int data) {
Node current = head;
if (head == null) {
return false;
}
while (current.key != key) {
if (current.next == null) {
return false;
} else {
current = current.next;
}
}
Node newLink = new Node(newKey, data);
if (current == last) {
newLink.next = null;
last = newLink;
} else {
newLink.next = current.next;
current.next.prev = newLink;
}
newLink.prev = current;
current.next = newLink;
return true;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DoublyLinkedList dll = new DoublyLinkedList();
dll.insertFirst(1, 10);
dll.insertFirst(2, 20);
dll.insertFirst(3, 30);
dll.insertFirst(4, 1);
dll.insertFirst(5, 40);
dll.insertFirst(6, 56);
System.out.println("List (First to Last):");
dll.displayForward();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("List (Last to First):");
dll.displayBackward();
System.out.println("List, after deleting first record:");
dll.deleteFirst();
dll.displayForward();
System.out.println("List, after deleting last record:");
dll.deleteLast();
dll.displayForward();
System.out.println("List, insert after key(4):");
dll.insertAfter(4, 7, 13);
dll.displayForward();
System.out.println("List, after delete key(4):");
dll.delete(4);
dll.displayForward();
}
}
輸出
List (First to Last): [ (6, 56) (5, 40) (4, 1) (3, 30) (2, 20) (1, 10) ] List (Last to First): [ (1, 10) (2, 20) (3, 30) (4, 1) (5, 40) (6, 56) ] List, after deleting first record: [ (5, 40) (4, 1) (3, 30) (2, 20) (1, 10) ] List, after deleting last record: [ (5, 40) (4, 1) (3, 30) (2, 20) ] List, insert after key(4): [ (5, 40) (4, 1) (7, 13) (3, 30) (2, 20) ] List, after delete key(4): [ (5, 40) (7, 13) (3, 30) (2, 20) ]
class Node:
def __init__(self, key, data):
self.key = key
self.data = data
self.next = None
self.prev = None
class DoublyLinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.last = None
def is_empty(self):
return self.head is None
def display_forward(self):
ptr = self.head
print("[", end=" ")
while ptr:
print("({}, {})".format(ptr.key, ptr.data), end=" ")
ptr = ptr.next
print("]")
def display_backward(self):
ptr = self.last
print("[", end=" ")
while ptr:
print("({}, {})".format(ptr.key, ptr.data), end=" ")
ptr = ptr.prev
print("]")
def insert_first(self, key, data):
link = Node(key, data)
if self.is_empty():
self.last = link
else:
self.head.prev = link
link.next = self.head
self.head = link
def insert_last(self, key, data):
link = Node(key, data)
if self.is_empty():
self.last = link
else:
self.last.next = link
link.prev = self.last
self.last = link
def delete_first(self):
if self.is_empty():
return None
temp_link = self.head
if self.head.next is None:
self.last = None
else:
self.head.next.prev = None
self.head = self.head.next
return temp_link
def delete_last(self):
if self.is_empty():
return None
temp_link = self.last
if self.head.next is None:
self.head = None
else:
self.last.prev.next = None
self.last = self.last.prev
return temp_link
def delete(self, key):
current = self.head
while current and current.key != key:
current = current.next
if current is None:
return None
if current == self.head:
self.head = self.head.next
else:
current.prev.next = current.next
if current == self.last:
self.last = current.prev
else:
current.next.prev = current.prev
return current
def insert_after(self, key, new_key, data):
current = self.head
while current and current.key != key:
current = current.next
if current is None:
return False
new_link = Node(new_key, data)
if current == self.last:
new_link.next = None
self.last = new_link
else:
new_link.next = current.next
current.next.prev = new_link
new_link.prev = current
current.next = new_link
return True
# Example usage
dll = DoublyLinkedList()
dll.insert_first(1, 10)
dll.insert_first(2, 20)
dll.insert_first(3, 30)
dll.insert_first(4, 1)
dll.insert_first(5, 40)
dll.insert_first(6, 56)
print("List (First to Last):")
dll.display_forward()
print()
print("List (Last to First):")
dll.display_backward()
print("List, after deleting first record:")
dll.delete_first()
dll.display_forward()
print("List, after deleting last record:")
dll.delete_last()
dll.display_forward()
print("List, insert after key(4):")
dll.insert_after(4, 7, 13)
dll.display_forward()
print("List, after delete key(4):")
dll.delete(4)
dll.display_forward()
輸出
List (First to Last): [ (6, 56) (5, 40) (4, 1) (3, 30) (2, 20) (1, 10) ] List (Last to First): [ (1, 10) (2, 20) (3, 30) (4, 1) (5, 40) (6, 56) ] List, after deleting first record: [ (5, 40) (4, 1) (3, 30) (2, 20) (1, 10) ] List, after deleting last record: [ (5, 40) (4, 1) (3, 30) (2, 20) ] List, insert after key(4): [ (5, 40) (4, 1) (7, 13) (3, 30) (2, 20) ] List, after delete key(4): [ (5, 40) (7, 13) (3, 30) (2, 20) ]
迴圈連結串列資料結構
迴圈連結串列是連結串列的一種變體,其中第一個元素指向最後一個元素,最後一個元素指向第一個元素。單向連結串列和雙向連結串列都可以轉換為迴圈連結串列。
單向迴圈連結串列
在單向連結串列中,最後一個節點的 next 指標指向第一個節點。

雙向迴圈連結串列
在雙向連結串列中,最後一個節點的 next 指標指向第一個節點,第一個節點的 prev 指標指向最後一個節點,從而形成雙向迴圈。
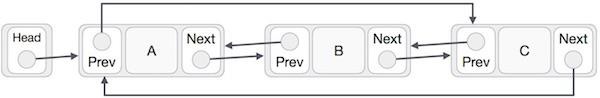
根據以上說明,以下是要考慮的重要事項。
在單向和雙向連結串列的兩種情況下,最後一個連結的 next 都指向列表的第一個連結。
在雙向連結串列的情況下,第一個連結的 prev 指向列表的最後一個連結。
基本操作
以下是迴圈列表支援的重要操作。
插入 (insert) − 在列表開頭插入一個元素。
刪除 (delete) − 從列表開頭刪除一個元素。
顯示 (display) − 顯示列表。
插入操作
迴圈連結串列的插入操作只在列表開頭插入元素。這與通常的單向和雙向連結串列不同,因為此列表沒有特定的起點和終點。插入操作可以在開頭進行,或者在列表中的特定節點(或給定位置)之後進行。
演算法
1. START 2. Check if the list is empty 3. If the list is empty, add the node and point the head to this node 4. If the list is not empty, link the existing head as the next node to the new node. 5. Make the new node as the new head. 6. END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
bool isEmpty(){
return head == NULL;
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if (isEmpty()) {
head = link;
head->next = head;
} else {
//point it to old first node
link->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
}
//display the list
void printList(){
struct node *ptr = head;
printf("\n[ ");
//start from the beginning
if(head != NULL) {
while(ptr->next != ptr) {
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
printf(" ]");
}
void main(){
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertFirst(5,40);
insertFirst(6,56);
printf("Circular Linked List: ");
//print list
printList();
}
輸出
Circular Linked List: [ (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) ]
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdbool>
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
bool isEmpty(){
return head == NULL;
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if (isEmpty()) {
head = link;
head->next = head;
} else {
//point it to old first node
link->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
}
//display the list
void printList(){
struct node *ptr = head;
printf("\n[ ");
//start from the beginning
if(head != NULL) {
while(ptr->next != ptr) {
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
printf(" ]");
}
int main(){
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertFirst(5,40);
insertFirst(6,56);
printf("Circular Linked List: ");
//print list
printList();
return 0;
}
輸出
Circular Linked List: [ (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) ]
//Java program for circular link list
import java.util.*;
class Node {
int data;
int key;
Node next;
}
public class Main {
static Node head = null;
static Node current = null;
static boolean isEmpty() {
return head == null;
}
//insert link at the first location
static void insertFirst(int key, int data) {
//create a link
Node link = new Node();
link.key = key;
link.data = data;
if (isEmpty()) {
head = link;
head.next = head;
} else {
//point it to old first node
link.next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
}
//display the list
static void printList() {
Node ptr = head;
System.out.print("\n[ ");
//start from the beginning
if (head != null) {
while (ptr.next != ptr) {
System.out.print("(" + ptr.key + "," + ptr.data + ") ");
ptr = ptr.next;
}
}
System.out.print(" ]");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
insertFirst(1, 10);
insertFirst(2, 20);
insertFirst(3, 30);
insertFirst(4, 1);
insertFirst(5, 40);
insertFirst(6, 56);
System.out.print("Circular Linked List: ");
//print list
printList();
}
}
輸出
Circular Linked List: [ (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) ]
#python program for circular linked list
class Node:
def __init__(self, key, data):
self.key = key
self.data = data
self.next = None
head = None
current = None
def is_empty():
return head is None
#insert link at the first location
def insert_first(key, data):
#create a link
global head
new_node = Node(key, data)
if is_empty():
head = new_node
head.next = head
else:
#point it to old first node
new_node.next = head
#point first to the new first node
head = new_node
#display the list
def print_list():
global head
ptr = head
print("[", end=" ")
#start from the beginning
if head is not None:
while ptr.next != ptr:
print("({}, {})".format(ptr.key, ptr.data), end=" ")
ptr = ptr.next
print("]")
insert_first(1, 10)
insert_first(2, 20)
insert_first(3, 30)
insert_first(4, 1)
insert_first(5, 40)
insert_first(6, 56)
#printlist
print("Circular Linked List: ")
print_list()
輸出
Circular Linked List: [ (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) ]
刪除操作
迴圈連結串列中的刪除操作會從列表中刪除某個節點。這種型別的列表中的刪除操作可以在開頭、給定位置或結尾進行。
演算法
1. START 2. If the list is empty, then the program is returned. 3. If the list is not empty, we traverse the list using a current pointer that is set to the head pointer and create another pointer previous that points to the last node. 4. Suppose the list has only one node, the node is deleted by setting the head pointer to NULL. 5. If the list has more than one node and the first node is to be deleted, the head is set to the next node and the previous is linked to the new head. 6. If the node to be deleted is the last node, link the preceding node of the last node to head node. 7. If the node is neither first nor last, remove the node by linking its preceding node to its succeeding node. 8. END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
bool isEmpty(){
return head == NULL;
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if (isEmpty()) {
head = link;
head->next = head;
} else {
//point it to old first node
link->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
}
//delete first item
struct node * deleteFirst(){
//save reference to first link
struct node *tempLink = head;
if(head->next == head) {
head = NULL;
return tempLink;
}
//mark next to first link as first
head = head->next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
//display the list
void printList(){
struct node *ptr = head;
//start from the beginning
if(head != NULL) {
while(ptr->next != ptr) {
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
}
void main(){
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertFirst(5,40);
insertFirst(6,56);
printf("Circular Linked List: ");
//print list
printList();
deleteFirst();
printf("\nList after deleting the first item: ");
printList();
}
輸出
Circular Linked List: (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) List after deleting the first item: (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdbool>
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
bool isEmpty(){
return head == NULL;
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if (isEmpty()) {
head = link;
head->next = head;
} else {
//point it to old first node
link->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
}
//delete first item
struct node * deleteFirst(){
//save reference to first link
struct node *tempLink = head;
if(head->next == head) {
head = NULL;
return tempLink;
}
//mark next to first link as first
head = head->next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
//display the list
void printList(){
struct node *ptr = head;
//start from the beginning
if(head != NULL) {
while(ptr->next != ptr) {
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
}
int main(){
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertFirst(5,40);
insertFirst(6,56);
printf("Circular Linked List: ");
//print list
printList();
deleteFirst();
printf("\nList after deleting the first item: ");
printList();
return 0;
}
輸出
Circular Linked List: (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) List after deleting the first item: (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20)
//Java program for circular linked list
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static class Node {
int data;
int key;
Node next;
}
static Node head = null;
static Node current = null;
static boolean isEmpty() {
return head == null;
}
//insert link at the first location
static void insertFirst(int key, int data) {
//create a link
Node link = new Node();
link.key = key;
link.data = data;
if (isEmpty()) {
head = link;
head.next = head;
} else {
//point it to old first node
link.next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
}
//delete first item
static Node deleteFirst() {
//save reference to first link
Node tempLink = head;
if (head.next == head) {
head = null;
return tempLink;
}
//mark next to first link as first
head = head.next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
//display the list
static void printList() {
Node ptr = head;
//start from the beginning
if (head != null) {
while (ptr.next != ptr) {
System.out.printf("(%d,%d) ", ptr.key, ptr.data);
ptr = ptr.next;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
insertFirst(1, 10);
insertFirst(2, 20);
insertFirst(3, 30);
insertFirst(4, 1);
insertFirst(5, 40);
insertFirst(6, 56);
System.out.print("Circular Linked List: ");
//print list
printList();
deleteFirst();
}
}
輸出
Circular Linked List: (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) List after deleting the first item: (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20)
#python program for circular linked list
class Node:
def __init__(self, key, data):
self.key = key
self.data = data
self.next = None
head = None
current = None
def is_empty():
return head is None
#insert link at the first location
def insert_first(key, data):
#create a link
global head
new_node = Node(key, data)
if is_empty():
head = new_node
head.next = head
else:
#point it to old first node
new_node.next = head
#point first to the new first node
head = new_node
def print_list():
global head
ptr = head
print("[", end=" ")
#start from the beginning
if head is not None:
while ptr.next != ptr:
print("({}, {})".format(ptr.key, ptr.data), end=" ")
ptr = ptr.next
print("]")
def delete_first():
global head
temp_link = head
if head.next == head:
head = None
return temp_link
head = head.next
return temp_link
insert_first(1, 10)
insert_first(2, 20)
insert_first(3, 30)
insert_first(4, 1)
insert_first(5, 40)
insert_first(6, 56)
#printlist
print("Circular Linked List: ")
print_list()
delete_first()
print("\nList after deleting the first item: ")
print_list();
輸出
Circular Linked List: (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) List after deleting the first item: (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20)
顯示列表操作
顯示列表操作訪問列表中的每個節點,並將它們全部列印到輸出中。
演算法
1. START 2. Walk through all the nodes of the list and print them 3. END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
bool isEmpty(){
return head == NULL;
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if (isEmpty()) {
head = link;
head->next = head;
} else {
//point it to old first node
link->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
}
//display the list
void printList(){
struct node *ptr = head;
printf("\n[ ");
//start from the beginning
if(head != NULL) {
while(ptr->next != ptr) {
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
printf(" ]");
}
void main(){
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertFirst(5,40);
insertFirst(6,56);
printf("Circular Linked List: ");
//print list
printList();
}
輸出
Circular Linked List: [ (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) ]
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdbool>
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
bool isEmpty(){
return head == NULL;
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if (isEmpty()) {
head = link;
head->next = head;
} else {
//point it to old first node
link->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
}
//display the list
void printList(){
struct node *ptr = head;
printf("\n[ ");
//start from the beginning
if(head != NULL) {
while(ptr->next != ptr) {
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
printf(" ]");
}
int main(){
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertFirst(5,40);
insertFirst(6,56);
printf("Circular Linked List: ");
//print list
printList();
return 0;
}
輸出
Circular Linked List: [ (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) ]
//Java program for circular link list
import java.util.*;
class Node {
int data;
int key;
Node next;
}
public class Main {
static Node head = null;
static Node current = null;
static boolean isEmpty() {
return head == null;
}
//insert link at the first location
static void insertFirst(int key, int data) {
//create a link
Node link = new Node();
link.key = key;
link.data = data;
if (isEmpty()) {
head = link;
head.next = head;
} else {
//point it to old first node
link.next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
}
//display the list
static void printList() {
Node ptr = head;
System.out.print("\n[ ");
//start from the beginning
if (head != null) {
while (ptr.next != ptr) {
System.out.print("(" + ptr.key + "," + ptr.data + ") ");
ptr = ptr.next;
}
}
System.out.print(" ]");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
insertFirst(1, 10);
insertFirst(2, 20);
insertFirst(3, 30);
insertFirst(4, 1);
insertFirst(5, 40);
insertFirst(6, 56);
System.out.print("Circular Linked List: ");
//print list
printList();
}
}
輸出
Circular Linked List: [ (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) ]
#python program for circular linked list
class Node:
def __init__(self, key, data):
self.key = key
self.data = data
self.next = None
head = None
current = None
def is_empty():
return head is None
#insert link at the first location
def insert_first(key, data):
#create a link
global head
new_node = Node(key, data)
if is_empty():
head = new_node
head.next = head
else:
#point it to old first node
new_node.next = head
#point first to the new first node
head = new_node
#display the list
def print_list():
global head
ptr = head
print("[", end=" ")
#start from the beginning
if head is not None:
while ptr.next != ptr:
print("({}, {})".format(ptr.key, ptr.data), end=" ")
ptr = ptr.next
print("]")
insert_first(1, 10)
insert_first(2, 20)
insert_first(3, 30)
insert_first(4, 1)
insert_first(5, 40)
insert_first(6, 56)
#printlist
print("Circular Linked List: ")
print_list()
輸出
Circular Linked List: [ (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) ]
完整實現
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
bool isEmpty(){
return head == NULL;
}
int length(){
int length = 0;
//if list is empty
if(head == NULL) {
return 0;
}
current = head->next;
while(current != head) {
length++;
current = current->next;
}
return length;
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if (isEmpty()) {
head = link;
head->next = head;
} else {
//point it to old first node
link->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
}
//delete first item
struct node * deleteFirst(){
//save reference to first link
struct node *tempLink = head;
if(head->next == head) {
head = NULL;
return tempLink;
}
//mark next to first link as first
head = head->next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
//display the list
void printList(){
struct node *ptr = head;
printf("\n[ ");
//start from the beginning
if(head != NULL) {
while(ptr->next != ptr) {
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
printf(" ]");
}
int main(){
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertFirst(5,40);
insertFirst(6,56);
printf("Original List: ");
//print list
printList();
while(!isEmpty()) {
struct node *temp = deleteFirst();
printf("\nDeleted value:");
printf("(%d,%d) ",temp->key,temp->data);
}
printf("\nList after deleting all items: ");
printList();
}
輸出
Original List: [ (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) ] Deleted value:(6,56) Deleted value:(5,40) Deleted value:(4,1) Deleted value:(3,30) Deleted value:(2,20) Deleted value:(1,10) List after deleting all items: [ ]
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdbool>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
bool isEmpty(){
return head == NULL;
}
int length(){
int length = 0;
//if list is empty
if(head == NULL) {
return 0;
}
current = head->next;
while(current != head) {
length++;
current = current->next;
}
return length;
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if (isEmpty()) {
head = link;
head->next = head;
} else {
//point it to old first node
link->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
}
//delete first item
struct node * deleteFirst(){
//save reference to first link
struct node *tempLink = head;
if(head->next == head) {
head = NULL;
return tempLink;
}
//mark next to first link as first
head = head->next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
//display the list
void printList(){
struct node *ptr = head;
cout << "\n[ ";
//start from the beginning
if(head != NULL) {
while(ptr->next != ptr) {
cout << "(" << ptr->key << "," << ptr->data << ") ";
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
cout << " ]";
}
int main(){
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertFirst(5,40);
insertFirst(6,56);
cout << "Original List: ";
//print list
printList();
while(!isEmpty()) {
struct node *temp = deleteFirst();
cout << "\n Deleted value:";
cout << "(" << temp->key << "," << temp->data << ") ";
}
cout << "\n List after deleting all items: ";
printList();
return 0;
}
輸出
Original List: [ (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) ] Deleted value:(6,56) Deleted value:(5,40) Deleted value:(4,1) Deleted value:(3,30) Deleted value:(2,20) Deleted value:(1,10) List after deleting all items: [ ]
class Node {
int data;
int key;
Node next;
Node(int key, int data) {
this.key = key;
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
public class LinkedList {
private Node head;
private Node current;
boolean isEmpty() {
return head == null;
}
int length() {
int length = 0;
//if list is empty
if (head == null) {
return 0;
}
current = head.next;
while (current != head) {
length++;
current = current.next;
}
return length;
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data) {
//create a link
Node link = new Node(key, data);
if (isEmpty()) {
head = link;
head.next = head;
} else {
//point it to old first node
link.next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
}
//delete first item
Node deleteFirst() {
if (head.next == head) {
//save reference to first link
Node tempLink = head;
head = null;
return tempLink;
}
Node tempLink = head;
//mark next to first link as first
head = head.next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
//display the list
void printList() {
Node ptr = head;
System.out.print("\n[ ");
//start from the beginning
if (head != null) {
while (ptr.next != ptr) {
System.out.print("(" + ptr.key + "," + ptr.data + ") ");
ptr = ptr.next;
}
}
System.out.print(" ]");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
linkedList.insertFirst(1, 10);
linkedList.insertFirst(2, 20);
linkedList.insertFirst(3, 30);
linkedList.insertFirst(4, 1);
linkedList.insertFirst(5, 40);
linkedList.insertFirst(6, 56);
System.out.print("Original List: ");
linkedList.printList();
//print list
while (!linkedList.isEmpty()) {
Node temp = linkedList.deleteFirst();
System.out.println("\nDeleted value: (" + temp.key + "," + temp.data + ")");
}
System.out.print("\nList after deleting all items: ");
linkedList.printList();
}
}
輸出
Original List: [ (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) ] Deleted value: (6,56) Deleted value: (5,40) Deleted value: (4,1) Deleted value: (3,30) Deleted value: (2,20) Deleted value: (1,10) List after deleting all items: [ ]
class Node:
def __init__(self, key, data):
self.key = key
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.current = None
def is_empty(self):
return self.head is None
def length(self):
length = 0
# If list is empty
if self.head is None:
return 0
self.current = self.head.next
while self.current != self.head:
length += 1
self.current = self.current.next
return length
# insert link at the first location
def insert_first(self, key, data):
# create a link
new_node = Node(key, data)
if self.is_empty():
self.head = new_node
self.head.next = self.head
else:
# point it to old first node
new_node.next = self.head
# point first to new first node
self.head = new_node
# delete first item
def delete_first(self):
# save reference to first link
if self.head.next == self.head:
temp_link = self.head
self.head = None
return temp_link
# mark next to first link as first
temp_link = self.head
self.head = self.head.next
# return the deleted link
return temp_link
# Diplay the list
def print_list(self):
ptr = self.head
print("[", end=" ")
# start from the beginning
if self.head is not None:
while ptr.next != ptr:
print("({}, {})".format(ptr.key, ptr.data), end=" ")
ptr = ptr.next
print("]")
# Main function
if __name__ == '__main__':
linked_list = LinkedList()
linked_list.insert_first(1, 10)
linked_list.insert_first(2, 20)
linked_list.insert_first(3, 30)
linked_list.insert_first(4, 1)
linked_list.insert_first(5, 40)
linked_list.insert_first(6, 56)
print("Original List: ", end="")
linked_list.print_list()
while not linked_list.is_empty():
temp = linked_list.delete_first()
print("\nDeleted value: ({}, {})".format(temp.key, temp.data))
# print list
print("List after deleting all items: ", end="")
linked_list.print_list()
輸出
Original List: [ (6, 56) (5, 40) (4, 1) (3, 30) (2, 20) ] Deleted value: (6, 56) Deleted value: (5, 40) Deleted value: (4, 1) Deleted value: (3, 30) Deleted value: (2, 20)Deleted value: (1, 10) List after deleting all items: [ ]
棧資料結構
棧是一種抽象資料型別 (ADT),在大多數程式語言中被廣泛使用。它之所以被稱為棧,是因為它具有與現實世界中的棧類似的操作,例如 – 一疊卡片或一堆盤子等。

棧遵循 LIFO(後進先出)結構,其中最後插入的元素將是第一個被刪除的元素。
棧的表示
棧 ADT 僅允許在一端進行所有資料操作。在任何給定時間,我們只能訪問棧的頂部元素。
下圖描述了一個棧及其操作:

棧可以透過陣列、結構體、指標和連結串列來實現。棧可以是固定大小的,也可以具有動態調整大小的功能。在這裡,我們將使用陣列來實現棧,這使得它成為一個固定大小的棧實現。
棧的基本操作
棧操作通常用於棧 ADT 的初始化、使用和反初始化。
棧 ADT 中最基本的操作包括:push()、pop()、peek()、isFull()、isEmpty()。這些都是內建操作,用於執行資料操作並檢查棧的狀態。
棧使用指標始終指向棧中最頂部的元素,因此稱為頂部 (top) 指標。
插入:push()
push() 是一種將元素插入棧的操作。以下是更簡單地描述 push() 操作的演算法。
演算法
1 − Checks if the stack is full. 2 − If the stack is full, produces an error and exit. 3 − If the stack is not full, increments top to point next empty space. 4 − Adds data element to the stack location, where top is pointing. 5 − Returns success.
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
int MAXSIZE = 8;
int stack[8];
int top = -1;
/* Check if the stack is full*/
int isfull(){
if(top == MAXSIZE)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
/* Function to insert into the stack */
int push(int data){
if(!isfull()) {
top = top + 1;
stack[top] = data;
} else {
printf("Could not insert data, Stack is full.\n");
}
}
/* Main function */
int main(){
int i;
push(44);
push(10);
push(62);
push(123);
push(15);
printf("Stack Elements: \n");
// print stack data
for(i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
printf("%d ", stack[i]);
}
return 0;
}
輸出
Stack Elements: 44 10 62 123 15 0 0 0
#include <iostream>
int MAXSIZE = 8;
int stack[8];
int top = -1;
/* Check if the stack is full*/
int isfull(){
if(top == MAXSIZE)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
/* Function to insert into the stack */
int push(int data){
if(!isfull()) {
top = top + 1;
stack[top] = data;
} else {
printf("Could not insert data, Stack is full.\n");
}
}
/* Main function */
int main(){
int i;
push(44);
push(10);
push(62);
push(123);
push(15);
printf("Stack Elements: \n");
// print stack data
for(i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
printf("%d ", stack[i]);
}
return 0;
}
輸出
Stack Elements: 44 10 62 123 15 0 0 0
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*; // util imports the stack class
public class StackExample {
public static void main (String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> stk = new Stack<Integer>();
// inserting elements into the stack
stk.push(52);
stk.push(19);
stk.push(33);
stk.push(14);
stk.push(6);
System.out.print("The stack is: " + stk);
}
}
輸出
The stack is: [52, 19, 33, 14, 6]
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.stack = []
def __str__(self):
return str(self.stack)
def push(self, data):
if data not in self.stack:
self.stack.append(data)
return True
else:
return False
stk = Stack()
stk.push(1)
stk.push(2)
stk.push(3)
stk.push(4)
stk.push(5)
print("Stack Elements:")
print(stk)
輸出
Stack Elements: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
注意 - 在 Java 中,我們使用內建方法push()來執行此操作。
刪除:pop()
pop() 是一種資料操作,用於從棧中刪除元素。以下虛擬碼更簡單地描述了 pop() 操作。
演算法
1 − Checks if the stack is empty. 2 − If the stack is empty, produces an error and exit. 3 − If the stack is not empty, accesses the data element at which top is pointing. 4 − Decreases the value of top by 1. 5 − Returns success.
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
int MAXSIZE = 8;
int stack[8];
int top = -1;
/* Check if the stack is empty */
int isempty(){
if(top == -1)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
/* Check if the stack is full*/
int isfull(){
if(top == MAXSIZE)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
/* Function to delete from the stack */
int pop(){
int data;
if(!isempty()) {
data = stack[top];
top = top - 1;
return data;
} else {
printf("Could not retrieve data, Stack is empty.\n");
}
}
/* Function to insert into the stack */
int push(int data){
if(!isfull()) {
top = top + 1;
stack[top] = data;
} else {
printf("Could not insert data, Stack is full.\n");
}
}
/* Main function */
int main(){
int i;
push(44);
push(10);
push(62);
push(123);
push(15);
printf("Stack Elements: \n");
// print stack data
for(i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
printf("%d ", stack[i]);
}
/*printf("Element at top of the stack: %d\n" ,peek());*/
printf("\nElements popped: \n");
// print stack data
while(!isempty()) {
int data = pop();
printf("%d ",data);
}
return 0;
}
輸出
Stack Elements: 44 10 62 123 15 0 0 0 Elements popped: 15 123 62 10 44
#include <iostream>
int MAXSIZE = 8;
int stack[8];
int top = -1;
/* Check if the stack is empty */
int isempty(){
if(top == -1)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
/* Check if the stack is full*/
int isfull(){
if(top == MAXSIZE)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
/* Function to delete from the stack */
int pop(){
int data;
if(!isempty()) {
data = stack[top];
top = top - 1;
return data;
} else {
printf("Could not retrieve data, Stack is empty.\n");
}
}
/* Function to insert into the stack */
int push(int data){
if(!isfull()) {
top = top + 1;
stack[top] = data;
} else {
printf("Could not insert data, Stack is full.\n");
}
}
/* Main function */
int main(){
int i;
push(44);
push(10);
push(62);
push(123);
push(15);
printf("Stack Elements: \n");
// print stack data
for(i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
printf("%d ", stack[i]);
}
/*printf("Element at top of the stack: %d\n" ,peek());*/
printf("\nElements popped: \n");
// print stack data
while(!isempty()) {
int data = pop();
printf("%d ",data);
}
return 0;
}
輸出
Stack Elements: 44 10 62 123 15 0 0 0 Elements popped: 15 123 62 10 44
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// util imports the stack class
public class StackExample {
public static void main (String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> stk = new Stack<Integer>();
// Inserting elements into the stack
stk.push(52);
stk.push(19);
stk.push(33);
stk.push(14);
stk.push(6);
System.out.print("The stack is: " + stk);
// Deletion from the stack
System.out.print("\nThe popped element is: ");
Integer n = (Integer) stk.pop();
System.out.print(n);
}
}
輸出
The stack is: [52, 19, 33, 14, 6] The popped element is: 6
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.stack = []
def __str__(self):
return str(self.stack)
def push(self, data):
if data not in self.stack:
self.stack.append(data)
return True
else:
return False
def remove(self):
if len(self.stack) <= 0:
return ("No element in the Stack")
else:
return self.stack.pop()
stk = Stack()
stk.push(1)
stk.push(2)
stk.push(3)
stk.push(4)
stk.push(5)
print("Stack Elements:")
print(stk)
print("----Deletion operation in stack----")
p = stk.remove()
print("The popped element is: " + str(p))
print("Updated Stack:")
print(stk)
輸出
Stack Elements: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] ----Deletion operation in stack---- The popped element is: 5 Updated Stack: [1, 2, 3, 4]
注意 - 在 Java 中,我們使用內建方法 pop()。
peek()
peek() 是一種操作,用於檢索棧中最頂部的元素,而不會刪除它。此操作用於藉助頂部指標檢查棧的狀態。
演算法
1. START 2. return the element at the top of the stack 3. END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
int MAXSIZE = 8;
int stack[8];
int top = -1;
/* Check if the stack is full */
int isfull(){
if(top == MAXSIZE)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
/* Function to return the topmost element in the stack */
int peek(){
return stack[top];
}
/* Function to insert into the stack */
int push(int data){
if(!isfull()) {
top = top + 1;
stack[top] = data;
} else {
printf("Could not insert data, Stack is full.\n");
}
}
/* Main function */
int main(){
int i;
push(44);
push(10);
push(62);
push(123);
push(15);
printf("Stack Elements: \n");
// print stack data
for(i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
printf("%d ", stack[i]);
}
printf("\nElement at top of the stack: %d\n" ,peek());
return 0;
}
輸出
Stack Elements: 44 10 62 123 15 0 0 0 Element at top of the stack: 15
#include <iostream>
int MAXSIZE = 8;
int stack[8];
int top = -1;
/* Check if the stack is full */
int isfull(){
if(top == MAXSIZE)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
/* Function to return the topmost element in the stack */
int peek(){
return stack[top];
}
/* Function to insert into the stack */
int push(int data){
if(!isfull()) {
top = top + 1;
stack[top] = data;
} else {
printf("Could not insert data, Stack is full.\n");
}
}
/* Main function */
int main(){
int i;
push(44);
push(10);
push(62);
push(123);
push(15);
printf("Stack Elements: \n");
// print stack data
for(i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
printf("%d ", stack[i]);
}
printf("\nElement at top of the stack: %d\n" ,peek());
return 0;
}
輸出
Stack Elements: 44 10 62 123 15 0 0 0 Element at top of the stack: 15
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
// util imports the stack class
public class StackExample {
public static void main (String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> stk = new Stack<Integer>();
// inserting elements into the stack
stk.push(52);
stk.push(19);
stk.push(33);
stk.push(14);
stk.push(6);
System.out.print("The stack is: " + stk);
Integer pos = (Integer) stk.peek();
System.out.print("\nThe element found is " + pos);
}
}
輸出
The stack is: [52, 19, 33, 14, 6] The element found is 6
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.stack = []
def __str__(self):
return str(self.stack)
def push(self, data):
if data not in self.stack:
self.stack.append(data)
return True
else:
return False
# Use peek to look at the top of the stack
def peek(self):
return self.stack[-1]
stk = Stack()
stk.push(1)
stk.push(2)
stk.push(3)
stk.push(4)
stk.push(5)
print("Stack Elements:")
print(stk)
print("topmost element: ",stk.peek())
輸出
Stack Elements: [1, 2, 3, 4, 5] topmost element: 5
isFull()
isFull() 操作檢查棧是否已滿。此操作用於藉助頂部指標檢查棧的狀態。
演算法
1. START 2. If the size of the stack is equal to the top position of the stack, the stack is full. Return 1. 3. Otherwise, return 0. 4. END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
int MAXSIZE = 8;
int stack[8];
int top = -1;
/* Check if the stack is full */
int isfull(){
if(top == MAXSIZE)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
/* Main function */
int main(){
printf("Stack full: %s\n" , isfull()?"true":"false");
return 0;
}
輸出
Stack full: false
#include <iostream>
int MAXSIZE = 8;
int stack[8];
int top = -1;
/* Check if the stack is full */
int isfull(){
if(top == MAXSIZE)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
/* Main function */
int main(){
printf("Stack full: %s\n" , isfull()?"true":"false");
return 0;
}
輸出
Stack full: false
import java.io.*;
public class StackExample {
private int arr[];
private int top;
private int capacity;
StackExample(int size) {
arr = new int[size];
capacity = size;
top = -1;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return top == capacity - 1;
}
public void push(int key) {
if (isFull()) {
System.out.println("Stack is Full\n");
return;
}
arr[++top] = key;
}
public static void main (String[] args) {
StackExample stk = new StackExample(5);
stk.push(1); // inserting 1 in the stack
stk.push(2);
stk.push(3);
stk.push(4);
stk.push(5);
System.out.println("Stack Full? " + stk.isFull());
}
}
輸出
Stack Full? true
#python code for stack(IsFull)
MAXSIZE = 8
stack = [None] * MAXSIZE
top = -1
#Check if the stack is empty
def isfull():
if top == MAXSIZE - 1:
return True
else:
return False
#main function
print("Stack full:", isfull())
輸出
Stack full: False
isEmpty()
isEmpty() 操作驗證棧是否為空。此操作用於藉助頂部指標檢查棧的狀態。
演算法
1. START 2. If the top value is -1, the stack is empty. Return 1. 3. Otherwise, return 0. 4. END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
int MAXSIZE = 8;
int stack[8];
int top = -1;
/* Check if the stack is empty */
int isempty() {
if(top == -1)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
/* Main function */
int main() {
printf("Stack empty: %s\n" , isempty()?"true":"false");
return 0;
}
輸出
Stack empty: true
#include <iostream>
int MAXSIZE = 8;
int stack[8];
int top = -1;
/* Check if the stack is empty */
int isempty(){
if(top == -1)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
/* Main function */
int main(){
printf("Stack empty: %s\n" , isempty()?"true":"false");
return 0;
}
輸出
Stack empty: true
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*; // util imports the stack class
public class StackExample {
public static void main (String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> stk = new Stack<Integer>();
// Inserting elements into the stack
stk.push(52);
stk.push(19);
stk.push(33);
stk.push(14);
stk.push(6);
System.out.println("Stack empty? "+ stk.isEmpty());
}
}
輸出
Stack empty? false
#python code for stack(IsFull)
MAXSIZE = 8
stack = [None] * MAXSIZE
top = -1
#Check if the stack is empty
def isempty():
if top == -1:
return True
else:
return False
#main function
print("Stack empty:", isempty())
輸出
Stack empty: True
完整實現
#include <stdio.h>
int MAXSIZE = 8;
int stack[8];
int top = -1;
/* Check if the stack is empty */
int isempty(){
if(top == -1)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
/* Check if the stack is full */
int isfull(){
if(top == MAXSIZE)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
/* Function to return the topmost element in the stack */
int peek(){
return stack[top];
}
/* Function to delete from the stack */
int pop(){
int data;
if(!isempty()) {
data = stack[top];
top = top - 1;
return data;
} else {
printf("Could not retrieve data, Stack is empty.\n");
}
}
/* Function to insert into the stack */
int push(int data){
if(!isfull()) {
top = top + 1;
stack[top] = data;
} else {
printf("Could not insert data, Stack is full.\n");
}
}
/* Main function */
int main(){
push(44);
push(10);
push(62);
push(123);
push(15);
printf("Element at top of the stack: %d\n" ,peek());
printf("Elements: \n");
// print stack data
while(!isempty()) {
int data = pop();
printf("%d\n",data);
}
printf("Stack full: %s\n" , isfull()?"true":"false");
printf("Stack empty: %s\n" , isempty()?"true":"false");
return 0;
}
輸出
Element at top of the stack: 15 Elements: 15123 62 10 44 Stack full: false Stack empty: true
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int MAXSIZE = 8;
int stack[8];
int top = -1;
/* Check if the stack is empty */
int isempty(){
if(top == -1)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
/* Check if the stack is full */
int isfull(){
if(top == MAXSIZE)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
/* Function to return the topmost element in the stack */
int peek(){
return stack[top];
}
/* Function to delete from the stack */
int pop(){
int data;
if(!isempty()) {
data = stack[top];
top = top - 1;
return data;
} else
cout << "Could not retrieve data, Stack is empty." << endl;
}
/* Function to insert into the stack */
int push(int data){
if(!isfull()) {
top = top + 1;
stack[top] = data;
} else
cout << "Could not insert data, Stack is full." << endl;
}
/* Main function */
int main(){
push(44);
push(10);
push(62);
push(123);
push(15);
cout << "Element at top of the stack: " << peek() << endl;
printf("Elements: \n");
// print stack data
while(!isempty()) {
int data = pop();
cout << data <<endl;
}
printf("Stack full: %s\n" , isfull()?"true":"false");
printf("Stack empty: %s\n" , isempty()?"true":"false");
return 0;
}
輸出
Element at top of the stack: 15 Elements: 15 123 62 10 44 Stack full: false Stack empty: true
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*; // util imports the stack class
public class StackExample {
public static void main (String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> stk = new Stack<Integer>();
// inserting elements into the stack
stk.push(52);
stk.push(19);
stk.push(33);
stk.push(14);
stk.push(6);
System.out.print("The stack is: " + stk);
// deletion from the stack
System.out.print("\nThe popped element is: ");
Integer n = (Integer) stk.pop();
System.out.print(n);
// searching for an element in the stack
Integer pos = (Integer) stk.search(19);
if(pos == -1)
System.out.print("\nThe element 19 not found in stack");
else
System.out.print("\nThe element 19 is found at " + pos);
}
}
輸出
The stack is: [52, 19, 33, 14, 6] The popped element is: 6 The element 19 is found at 3
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.stack = []
def add(self, data):
if data not in self.stack:
self.stack.append(data)
return True
else:
return False
# Use peek to look at the top of the stack
def peek(self):
return self.stack[-1]
# Use list pop method to remove element
def remove(self):
if len(self.stack) <= 0:
return ("No element in the Stack")
else:
return self.stack.pop()
stk = Stack()
stk.add(1)
stk.add(2)
stk.add(3)
stk.add(4)
stk.add(5)
print("topmost element: ",stk.peek())
print("----Deletion operation in stack----")
stk.remove()
stk.peek()
print("topmost element after deletion: ",stk.peek())
輸出
topmost element: 5 ----Deletion operation in stack---- topmost element after deletion: 4
表示式解析
編寫算術表示式的 方式稱為表示法。算術表示式可以用三種不同但等價的表示法來編寫,即不改變表示式的本質或輸出。這些表示法是:
- 中綴表示法
- 字首(波蘭)表示法
- 字尾(逆波蘭)表示法
這些表示法以它們在表示式中使用運算子的方式命名。我們將在本章中學習這些內容。
中綴表示法
我們用中綴表示法編寫表示式,例如 a - b + c,其中運算子位於運算元之間。對於我們人類來說,用中綴表示法閱讀、編寫和說話很容易,但對於計算裝置來說卻並非如此。處理中綴表示法的演算法在時間和空間消耗方面可能很複雜且成本很高。
字首表示法
在這種表示法中,運算子位於運算元之前,即運算子寫在運算元前面。例如,+ab。這等價於其中綴表示法a + b。字首表示法也稱為波蘭表示法。
字尾表示法
這種表示法風格稱為逆波蘭表示法。在這種表示法風格中,運算子位於運算元之後,即運算子寫在運算元後面。例如,ab+。這等價於其中綴表示法a + b。
下表簡要地試圖顯示三種表示法的區別:
| 序號 | 中綴表示法 | 字首表示法 | 字尾表示法 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | a + b | + a b | a b + |
| 2 | (a + b) ∗ c | ∗ + a b c | a b + c ∗ |
| 3 | a ∗ (b + c) | ∗ a + b c | a b c + ∗ |
| 4 | a / b + c / d | + / a b / c d | a b / c d / + |
| 5 | (a + b) ∗ (c + d) | ∗ + a b + c d | a b + c d + ∗ |
| 6 | ((a + b) ∗ c) - d | - ∗ + a b c d | a b + c ∗ d - |
解析表示式
正如我們所討論的,設計算法或程式來解析中綴表示法並不是一種非常有效的方法。相反,這些中綴表示法首先被轉換為字尾或字首表示法,然後進行計算。
要解析任何算術表示式,我們還需要考慮運算子的優先順序和結合性。
優先順序
當一個運算元位於兩個不同的運算子之間時,哪個運算子將首先獲取該運算元,這由一個運算子相對於其他運算子的優先順序決定。例如:

由於乘法運算優先於加法運算,因此 b * c 將首先被計算。稍後將提供運算子優先順序表。
結合性
結合性描述了在表示式中出現優先順序相同的運算子時的規則。例如,在表示式 a + b - c 中,+ 和 - 具有相同的優先順序,那麼表示式的哪一部分將首先被計算,這由這些運算子的結合性決定。這裡,+ 和 - 都是左結合的,因此表示式將被計算為(a + b) - c。
優先順序和結合性決定了表示式的計算順序。以下是運算子優先順序和結合性表(從高到低):
| 序號 | 運算子 | 優先順序 | 結合性 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 指數 ^ | 最高 | 右結合 |
| 2 | 乘法 ( ∗ ) & 除法 ( / ) | 第二高 | 左結合 |
| 3 | 加法 ( + ) & 減法 ( − ) | 最低 | 左結合 |
上表顯示了運算子的預設行為。在表示式計算的任何時間點,都可以使用括號更改順序。例如:
在a + b*c中,表示式部分b*c將首先被計算,因為乘法的優先順序高於加法。在這裡,我們使用括號使a + b首先被計算,例如(a + b)*c。
字尾表示式計算演算法
我們現在來看一下如何計算字尾表示法的演算法:
Step 1 − scan the expression from left to right Step 2 − if it is an operand push it to stack Step 3 − if it is an operator pull operand from stack and perform operation Step 4 − store the output of step 3, back to stack Step 5 − scan the expression until all operands are consumed Step 6 − pop the stack and perform operation
完整實現
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<ctype.h>
//char stack
char stack[25];
int top = -1;
void push(char item) {
stack[++top] = item;
}
char pop() {
return stack[top--];
}
//returns precedence of operators
int precedence(char symbol) {
switch(symbol) {
case '+':
case '-':
return 2;
break;
case '*':
case '/':
return 3;
break;
case '^':
return 4;
break;
case '(':
case ')':
case '#':
return 1;
break;
}
}
//check whether the symbol is operator?
int isOperator(char symbol) {
switch(symbol) {
case '+':
case '-':
case '*':
case '/':
case '^':
case '(':
case ')':
return 1;
break;
default:
return 0;
}
}
//converts infix expression to postfix
void convert(char infix[],char postfix[]) {
int i,symbol,j = 0;
stack[++top] = '#';
for(i = 0;i<strlen(infix);i++) {
symbol = infix[i];
if(isOperator(symbol) == 0) {
postfix[j] = symbol;
j++;
} else {
if(symbol == '(') {
push(symbol);
} else {
if(symbol == ')') {
while(stack[top] != '(') {
postfix[j] = pop();
j++;
}
pop(); //pop out (.
} else {
if(precedence(symbol)>precedence(stack[top])) {
push(symbol);
} else {
while(precedence(symbol)<=precedence(stack[top])) {
postfix[j] = pop();
j++;
}
push(symbol);
}
}
}
}
}
while(stack[top] != '#') {
postfix[j] = pop();
j++;
}
postfix[j]='\0'; //null terminate string.
}
//int stack
int stack_int[25];
int top_int = -1;
void push_int(int item) {
stack_int[++top_int] = item;
}
char pop_int() {
return stack_int[top_int--];
}
//evaluates postfix expression
int evaluate(char *postfix){
char ch;
int i = 0,operand1,operand2;
while( (ch = postfix[i++]) != '\0') {
if(isdigit(ch)) {
push_int(ch-'0'); // Push the operand
} else {
//Operator,pop two operands
operand2 = pop_int();
operand1 = pop_int();
switch(ch) {
case '+':
push_int(operand1+operand2);
break;
case '-':
push_int(operand1-operand2);
break;
case '*':
push_int(operand1*operand2);
break;
case '/':
push_int(operand1/operand2);
break;
}
}
}
return stack_int[top_int];
}
void main() {
char infix[25] = "1*(2+3)",postfix[25];
convert(infix,postfix);
printf("Infix expression is: %s\n" , infix);
printf("Postfix expression is: %s\n" , postfix);
printf("Evaluated expression is: %d\n" , evaluate(postfix));
}
輸出
Infix expression is: 1*(2+3) Postfix expression is: 123+* Evaluated expression is: 5
// C++ Code for Expression Parsing Using Stack
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <cctype>
#include <stack>
// char stack
std::stack<char> stack;
void push(char item) {
stack.push(item);
}
char pop() {
char top = stack.top();
stack.pop();
return top;
}
// returns precedence of operators
int precedence(char symbol) {
switch(symbol) {
case '+':
case '-':
return 2;
case '*':
case '/':
return 3;
case '^':
return 4;
case '(':
case ')':
case '#':
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// check whether the symbol is an operator
int isOperator(char symbol) {
switch(symbol) {
case '+':
case '-':
case '*':
case '/':
case '^':
case '(':
case ')':
return 1;
default:
return 0;
}
}
// converts infix expression to postfix
void convert(const std::string& infix, std::string& postfix) {
int j = 0;
stack.push('#');
for (char symbol : infix) {
if (isOperator(symbol) == 0) {
postfix += symbol;
j++;
} else {
if (symbol == '(') {
push(symbol);
} else {
if (symbol == ')') {
while (stack.top() != '(') {
postfix += pop();
j++;
}
stack.pop(); // pop out '('
} else {
if (precedence(symbol) > precedence(stack.top())) {
push(symbol);
} else {
while (precedence(symbol) <= precedence(stack.top())) {
postfix += pop();
j++;
}
push(symbol);
}
}
}
}
}
while (stack.top() != '#') {
postfix += pop();
j++;
}
postfix[j] = '\0'; // null terminate string
}
// evaluates postfix expression
int evaluate(const std::string& postfix) {
std::stack<int> stack_int;
int operand1, operand2;
for (char ch : postfix) {
if (std::isdigit(ch)) {
stack_int.push(ch - '0'); // Push the operand
} else {
// Operator, pop two operands
operand2 = stack_int.top();
stack_int.pop();
operand1 = stack_int.top();
stack_int.pop();
switch (ch) {
case '+':
stack_int.push(operand1 + operand2);
break;
case '-':
stack_int.push(operand1 - operand2);
break;
case '*':
stack_int.push(operand1 * operand2);
break;
case '/':
stack_int.push(operand1 / operand2);
break;
}
}
}
return stack_int.top();
}
int main() {
std::string infix = "1*(2+3)", postfix;
convert(infix, postfix);
std::cout << "Infix expression is: " << infix << std::endl;
std::cout << "Postfix expression is: " << postfix << std::endl;
std::cout << "Evaluated expression is: " << evaluate(postfix) << std::endl;
return 0;
}
輸出
Infix expression is: 1*(2+3) Postfix expression is: 123+* Evaluated expression is: 5
// Java Code for Expression Parsing Using Stack
import java.util.Stack;
public class Main {
// char stack
static Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
static void push(char item) {
stack.push(item);
}
static char pop() {
return stack.pop();
}
// returns precedence of operators
static int precedence(char symbol) {
switch (symbol) {
case '+':
case '-':
return 2;
case '*':
case '/':
return 3;
case '^':
return 4;
case '(':
case ')':
case '#':
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
// check whether the symbol is an operator
static int isOperator(char symbol) {
switch (symbol) {
case '+':
case '-':
case '*':
case '/':
case '^':
case '(':
case ')':
return 1;
default:
return 0;
}
}
// converts infix expression to postfix
static void convert(String infix, StringBuilder postfix) {
int j = 0;
stack.push('#');
for (char symbol : infix.toCharArray()) {
if (isOperator(symbol) == 0) {
postfix.append(symbol);
j++;
} else {
if (symbol == '(') {
push(symbol);
} else {
if (symbol == ')') {
while (stack.peek() != '(') {
postfix.append(pop());
j++;
}
stack.pop(); // pop out '('
} else {
if (precedence(symbol) > precedence(stack.peek())) {
push(symbol);
} else {
while (precedence(symbol) <= precedence(stack.peek())) {
postfix.append(pop());
j++;
}
push(symbol);
}
}
}
}
}
while (stack.peek() != '#') {
postfix.append(pop());
j++;
}
}
// evaluates postfix expression
static int evaluate(String postfix) {
Stack<Integer> stackInt = new Stack<>();
int operand1, operand2;
for (char ch : postfix.toCharArray()) {
if (Character.isDigit(ch)) {
stackInt.push(ch - '0'); // Push the operand
} else {
// Operator, pop two operands
operand2 = stackInt.pop();
operand1 = stackInt.pop();
switch (ch) {
case '+':
stackInt.push(operand1 + operand2);
break;
case '-':
stackInt.push(operand1 - operand2);
break;
case '*':
stackInt.push(operand1 * operand2);
break;
case '/':
stackInt.push(operand1 / operand2);
break;
}
}
}
return stackInt.peek();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String infix = "1*(2+3)";
StringBuilder postfix = new StringBuilder();
convert(infix, postfix);
System.out.println("Infix expression is: " + infix);
System.out.println("Postfix expression is: " + postfix);
System.out.println("Evaluated expression is: " + evaluate(postfix.toString()));
}
}
< h3>輸出Infix expression is: 1*(2+3) Postfix expression is: 123+* Evaluated expression is: 5
class Main:
stack = []
@staticmethod
def push(item):
Main.stack.append(item)
@staticmethod
def pop():
return Main.stack.pop()
#returns precedence of operators
@staticmethod
def precedence(symbol):
if symbol in ['+', '-']:
return 2
elif symbol in ['*', '/']:
return 3
elif symbol == '^':
return 4
elif symbol in ['(', ')', '#']:
return 1
return 0
#check whether the symbol is an operator
@staticmethod
def is_operator(symbol):
return symbol in ['+', '-', '*', '/', '^', '(', ')']
@staticmethod
def convert(infix):
postfix = ""
j = 0
Main.push('#')
for symbol in infix:
if not Main.is_operator(symbol):
postfix += symbol
j += 1
else:
if symbol == '(':
Main.push(symbol)
else:
if symbol == ')':
while Main.stack[-1] != '(':
postfix += Main.pop()
j += 1
Main.pop() # pop out '('
else:
if Main.precedence(symbol) > Main.precedence(Main.stack[-1]):
Main.push(symbol)
else:
while Main.precedence(symbol) <= Main.precedence(Main.stack[-1]):
postfix += Main.pop()
j += 1
Main.push(symbol)
while Main.stack[-1] != '#':
postfix += Main.pop()
j += 1
return postfix
@staticmethod
def evaluate(postfix):
stack_int = []
for ch in postfix:
if ch.isdigit():
stack_int.append(int(ch))
else:
operand2 = stack_int.pop()
operand1 = stack_int.pop()
if ch == '+':
stack_int.append(operand1 + operand2)
elif ch == '-':
stack_int.append(operand1 - operand2)
elif ch == '*':
stack_int.append(operand1 * operand2)
elif ch == '/':
stack_int.append(operand1 / operand2)
return stack_int[0]
@staticmethod
def main():
infix = "1*(2+3)"
postfix = Main.convert(infix)
print("Infix expression is:", infix)
print("Postfix expression is:", postfix)
print("Evaluated expression is:", Main.evaluate(postfix))
Main.main()
輸出
Infix expression is: 1*(2+3) Postfix expression is: 123+* Evaluated expression is: 5
佇列資料結構
佇列與棧類似,也是一種抽象資料結構。使佇列與棧不同的特點是佇列的兩端都是開放的。因此,它遵循 FIFO(先進先出)結構,即第一個插入的資料項也將被第一個訪問。資料透過一端插入佇列,並透過另一端刪除。
佇列的一個現實世界例子可以是一條單車道單行道,其中先進入的車輛先退出。更多現實世界的例子可以看作是售票視窗和公交車站的隊伍。
佇列的表示
與棧 ADT 類似,佇列 ADT 也可以使用陣列、連結串列或指標來實現。在本教程中的一個小例子中,我們使用一維陣列來實現佇列。
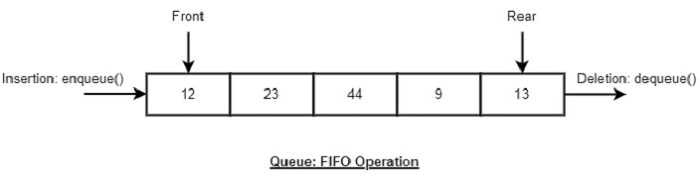
基本操作
佇列操作還包括佇列的初始化、使用以及永久地從記憶體中刪除資料。
佇列 ADT 中最基本的操作包括:enqueue()、dequeue()、peek()、isFull()、isEmpty()。這些都是內建操作,用於執行資料操作並檢查佇列的狀態。
佇列使用兩個指標:front 和 rear。front 指標從前端訪問資料(幫助入隊),而 rear 指標從後端訪問資料(幫助出隊)。
插入操作:enqueue()
enqueue() 是一種資料操作,用於將元素插入棧。以下演算法更簡單地描述了 enqueue() 操作。
演算法
1 − START 2 – Check if the queue is full. 3 − If the queue is full, produce overflow error and exit. 4 − If the queue is not full, increment rear pointer to point the next empty space. 5 − Add data element to the queue location, where the rear is pointing. 6 − return success. 7 – END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAX 6
int intArray[MAX];
int front = 0;
int rear = -1;
int itemCount = 0;
bool isFull(){
return itemCount == MAX;
}
bool isEmpty(){
return itemCount == 0;
}
int removeData(){
int data = intArray[front++];
if(front == MAX) {
front = 0;
}
itemCount--;
return data;
}
void insert(int data){
if(!isFull()) {
if(rear == MAX-1) {
rear = -1;
}
intArray[++rear] = data;
itemCount++;
}
}
int main(){
insert(3);
insert(5);
insert(9);
insert(1);
insert(12);
insert(15);
printf("Queue: ");
while(!isEmpty()) {
int n = removeData();
printf("%d ",n);
}
}
輸出
Queue: 3 5 9 1 12 15
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#define MAX 6
int intArray[MAX];
int front = 0;
int rear = -1;
int itemCount = 0;
bool isFull(){
return itemCount == MAX;
}
bool isEmpty(){
return itemCount == 0;
}
int removeData(){
int data = intArray[front++];
if(front == MAX) {
front = 0;
}
itemCount--;
return data;
}
void insert(int data){
if(!isFull()) {
if(rear == MAX-1) {
rear = -1;
}
intArray[++rear] = data;
itemCount++;
}
}
int main(){
insert(3);
insert(5);
insert(9);
insert(1);
insert(12);
insert(15);
printf("Queue: ");
while(!isEmpty()) {
int n = removeData();
printf("%d ",n);
}
}
輸出
Queue: 3 5 9 1 12 15
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class QueueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(6);
q.add(1);
q.add(8);
q.add(4);
q.add(7);
System.out.println("The queue is: " + q);
}
}
輸出
The queue is: [6, 1, 8, 4, 7]
class Queue:
def __init__(self):
self.queue = list()
def __str__(self):
return str(self.queue)
def addtoqueue(self,data):
# Insert method to add element
if data not in self.queue:
self.queue.insert(0,data)
return True
return False
q = Queue()
q.addtoqueue("36")
q.addtoqueue("24")
q.addtoqueue("48")
q.addtoqueue("12")
q.addtoqueue("66")
print("Queue:")
print(q)
輸出
Queue: ['66', '12', '48', '24', '36']
刪除操作:dequeue()
dequeue() 是一種資料操作,用於從棧中刪除元素。以下演算法更簡單地描述了 dequeue() 操作。
演算法
1 – START 2 − Check if the queue is empty. 3 − If the queue is empty, produce underflow error and exit. 4 − If the queue is not empty, access the data where front is pointing. 5 − Increment front pointer to point to the next available data element. 6 − Return success. 7 – END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAX 6
int intArray[MAX];
int front = 0;
int rear = -1;
int itemCount = 0;
bool isFull(){
return itemCount == MAX;
}
bool isEmpty(){
return itemCount == 0;
}
void insert(int data){
if(!isFull()) {
if(rear == MAX-1) {
rear = -1;
}
intArray[++rear] = data;
itemCount++;
}
}
int removeData(){
int data = intArray[front++];
if(front == MAX) {
front = 0;
}
itemCount--;
return data;
}
int main(){
int i;
/* insert 5 items */
insert(3);
insert(5);
insert(9);
insert(1);
insert(12);
insert(15);
printf("Queue: ");
for(i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
printf("%d ", intArray[i]);
// remove one item
int num = removeData();
printf("\nElement removed: %d\n",num);
printf("Updated Queue: ");
while(!isEmpty()) {
int n = removeData();
printf("%d ",n);
}
}
輸出
Queue: 3 5 9 1 12 15 Element removed: 3 Updated Queue: 5 9 1 12 15
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#define MAX 6
int intArray[MAX];
int front = 0;
int rear = -1;
int itemCount = 0;
bool isFull(){
return itemCount == MAX;
}
bool isEmpty(){
return itemCount == 0;
}
void insert(int data){
if(!isFull()) {
if(rear == MAX-1) {
rear = -1;
}
intArray[++rear] = data;
itemCount++;
}
}
int removeData(){
int data = intArray[front++];
if(front == MAX) {
front = 0;
}
itemCount--;
return data;
}
int main(){
int i;
/* insert 5 items */
insert(3);
insert(5);
insert(9);
insert(1);
insert(12);
insert(15);
printf("Queue: ");
for(i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
printf("%d ", intArray[i]);
// remove one item
int num = removeData();
printf("\nElement removed: %d\n",num);
printf("Updated Queue: ");
while(!isEmpty()) {
int n = removeData();
printf("%d ",n);
}
}
輸出
Queue: 3 5 9 1 12 15 Element removed: 3 Updated Queue: 5 9 1 12 15
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class QueueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(6);
q.add(1);
q.add(8);
q.add(4);
q.add(7);
System.out.println("The queue is: " + q);
int n = q.remove();
System.out.println("The element deleted is: " + n);
System.out.println("Queue after deletion: " + q);
}
}
輸出
The queue is: [6, 1, 8, 4, 7] The element deleted is: 6 Queue after deletion: [1, 8, 4, 7]
class Queue:
def __init__(self):
self.queue = list()
def __str__(self):
return str(self.queue)
def addtoqueue(self,data):
# Insert method to add element
if data not in self.queue:
self.queue.insert(0,data)
return True
return False
def removefromqueue(self):
if len(self.queue)>0:
return self.queue.pop()
return ("Queue is empty")
q = Queue()
q.addtoqueue("36")
q.addtoqueue("24")
q.addtoqueue("48")
q.addtoqueue("12")
q.addtoqueue("66")
print("Queue:")
print(q)
print("Element deleted from queue: ",q.removefromqueue())
輸出
Queue: ['66', '12', '48', '24', '36'] Element deleted from queue: 36
peek() 操作
peek() 是一種操作,用於檢索佇列中最前面的元素,而不會刪除它。此操作用於藉助指標檢查佇列的狀態。
演算法
1 – START 2 – Return the element at the front of the queue 3 – END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAX 6
int intArray[MAX];
int front = 0;
int rear = -1;
int itemCount = 0;
int peek(){
return intArray[front];
}
bool isFull(){
return itemCount == MAX;
}
void insert(int data){
if(!isFull()) {
if(rear == MAX-1) {
rear = -1;
}
intArray[++rear] = data;
itemCount++;
}
}
int main(){
int i;
/* insert 5 items */
insert(3);
insert(5);
insert(9);
insert(1);
insert(12);
insert(15);
printf("Queue: ");
for(i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
printf("%d ", intArray[i]);
printf("\nElement at front: %d\n",peek());
}
輸出
Queue: 3 5 9 1 12 15 Element at front: 3
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#define MAX 6
int intArray[MAX];
int front = 0;
int rear = -1;
int itemCount = 0;
int peek(){
return intArray[front];
}
bool isFull(){
return itemCount == MAX;
}
void insert(int data){
if(!isFull()) {
if(rear == MAX-1) {
rear = -1;
}
intArray[++rear] = data;
itemCount++;
}
}
int main(){
int i;
/* insert 5 items */
insert(3);
insert(5);
insert(9);
insert(1);
insert(12);
insert(15);
printf("Queue: ");
for(i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
printf("%d ", intArray[i]);
printf("\nElement at front: %d\n",peek());
}
輸出
Queue: 3 5 9 1 12 15 Element at front: 3
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class QueueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(6);
q.add(1);
q.add(8);
q.add(4);
q.add(7);
System.out.println("The queue is: " + q);
}
}
輸出
The queue is: [6, 1, 8, 4, 7]
class Queue:
def __init__(self):
self.queue = list()
def __str__(self):
return str(self.queue)
def addtoqueue(self,data):
# Insert method to add element
if data not in self.queue:
self.queue.insert(0,data)
return True
return False
def peek(self):
return self.queue[-1]
q = Queue()
q.addtoqueue("36")
q.addtoqueue("24")
q.addtoqueue("48")
q.addtoqueue("12")
q.addtoqueue("66")
print("Queue:")
print(q)
print("The frontmost element of the queue: ",q.peek())
輸出
Queue: ['66', '12', '48', '24', '36'] The frontmost element of the queue: 36
isFull() 操作
isFull() 操作驗證棧是否已滿。
演算法
1 – START 2 – If the count of queue elements equals the queue size, return true 3 – Otherwise, return false 4 – END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAX 6
int intArray[MAX];
int front = 0;
int rear = -1;
int itemCount = 0;
bool isFull(){
return itemCount == MAX;
}
void insert(int data){
if(!isFull()) {
if(rear == MAX-1) {
rear = -1;
}
intArray[++rear] = data;
itemCount++;
}
}
int main(){
int i;
/* insert 5 items */
insert(3);
insert(5);
insert(9);
insert(1);
insert(12);
insert(15);
printf("Queue: ");
for(i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
printf("%d ", intArray[i]);
printf("\n");
if(isFull()) {
printf("Queue is full!\n");
}
}
輸出
Queue: 3 5 9 1 12 15 Queue is full!
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#define MAX 6
int intArray[MAX];
int front = 0;
int rear = -1;
int itemCount = 0;
bool isFull(){
return itemCount == MAX;
}
void insert(int data){
if(!isFull()) {
if(rear == MAX-1) {
rear = -1;
}
intArray[++rear] = data;
itemCount++;
}
}
int main(){
int i;
/* insert 5 items */
insert(3);
insert(5);
insert(9);
insert(1);
insert(12);
insert(15);
printf("Queue: ");
for(i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
printf("%d ", intArray[i]);
printf("\n");
if(isFull()) {
printf("Queue is full!\n");
}
}
輸出
Queue: 3 5 9 1 12 15 Queue is full!
import java.io.*;
public class QueueExample {
private int intArray[];
private int front;
private int rear;
private int itemCount;
private int MAX;
QueueExample(int size) {
intArray = new int[size];
front = 0;
rear = -1;
MAX = size;
itemCount = 0;
}
public boolean isFull() {
return itemCount == MAX;
}
public void insert(int key) {
if(!isFull()) {
if(rear == MAX-1) {
rear = -1;
}
intArray[++rear] = key;
itemCount++;
}
}
public static void main (String[] args) {
QueueExample q = new QueueExample(5);
q.insert(1); // inserting 1 in the stack
q.insert(2);
q.insert(3);
q.insert(4);
q.insert(5);
System.out.println("Stack Full? " + q.isFull());
}
}
輸出
Stack Full? true
#python code for isFull in Queue
MAX = 6
intArray = [None] * MAX
front = 0
rear = -1
itemCount = 0
def isFull():
return itemCount == MAX
def insert(data):
global rear, itemCount
if not isFull():
if rear == MAX-1:
rear = -1
rear += 1
intArray[rear] = data
itemCount += 1
#inserting 5 items into the Queue
insert(3)
insert(5)
insert(9)
insert(1)
insert(12)
insert(15)
print("Queue: ", end="")
for i in range(MAX):
print(intArray[i], end=" ")
print()
if isFull():
print("Queue is full!")
輸出
Queue: 3 5 9 1 12 15 Queue is full!
isEmpty() 操作
isEmpty() 操作驗證棧是否為空。此操作用於藉助頂部指標檢查棧的狀態。
演算法
1 – START 2 – If the count of queue elements equals zero, return true 3 – Otherwise, return false 4 – END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAX 6
int intArray[MAX];
int front = 0;
int rear = -1;
int itemCount = 0;
bool isEmpty(){
return itemCount == 0;
}
int main(){
int i;
printf("Queue: ");
for(i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
printf("%d ", intArray[i]);
printf("\n");
if(isEmpty()) {
printf("Queue is Empty!\n");
}
}
輸出
Queue: 0 0 0 0 0 0 Queue is Empty!
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#define MAX 6
int intArray[MAX];
int front = 0;
int rear = -1;
int itemCount = 0;
bool isEmpty(){
return itemCount == 0;
}
int main(){
int i;
printf("Queue: ");
for(i = 0; i < MAX; i++)
printf("%d ", intArray[i]);
printf("\n");
if(isEmpty()) {
printf("Queue is Empty!\n");
}
}
輸出
Queue: 0 0 0 0 0 0 Queue is Empty!
import java.io.*;
public class QueueExample {
private int intArray[];
private int front;
private int rear;
private int itemCount;
private int MAX;
QueueExample(int size) {
intArray = new int[size];
front = 0;
rear = -1;
MAX = size;
itemCount = 0;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return itemCount == 0;
}
public static void main (String[] args) {
QueueExample q = new QueueExample(5);
System.out.println("Stack Empty? " + q.isEmpty());
}
}
輸出
Stack Empty? true
#python code for isFull in Queue
MAX = 6
intArray = [None] * MAX
front = 0
rear = -1
itemCount = 0
def isEmpty():
return itemCount == 0
print("Queue: ", end="")
for i in range(MAX):
print(intArray[i], end=" ")
print()
if isEmpty():
print("Queue is empty!")
輸出
Queue: None None None None None None Queue is empty!
佇列的實現
在本章中,佇列資料結構的演算法實現是在四種程式語言中進行的。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAX 6
int intArray[MAX];
int front = 0;
int rear = -1;
int itemCount = 0;
int peek(){
return intArray[front];
}
bool isEmpty(){
return itemCount == 0;
}
bool isFull(){
return itemCount == MAX;
}
int size(){
return itemCount;
}
void insert(int data){
if(!isFull()) {
if(rear == MAX-1) {
rear = -1;
}
intArray[++rear] = data;
itemCount++;
}
}
int removeData(){
int data = intArray[front++];
if(front == MAX) {
front = 0;
}
itemCount--;
return data;
}
int main(){
/* insert 5 items */
insert(3);
insert(5);
insert(9);
insert(1);
insert(12);
// front : 0
// rear : 4
// ------------------
// index : 0 1 2 3 4
// ------------------
// queue : 3 5 9 1 12
insert(15);
// front : 0
// rear : 5
// ---------------------
// index : 0 1 2 3 4 5
// ---------------------
// queue : 3 5 9 1 12 15
if(isFull()) {
printf("Queue is full!\n");
}
// remove one item
int num = removeData();
printf("Element removed: %d\n",num);
// front : 1
// rear : 5
// -------------------
// index : 1 2 3 4 5
// -------------------
// queue : 5 9 1 12 15
// insert more items
insert(16);
// front : 1
// rear : -1
// ----------------------
// index : 0 1 2 3 4 5
// ----------------------
// queue : 16 5 9 1 12 15
// As queue is full, elements will not be inserted.
insert(17);
insert(18);
// ----------------------
// index : 0 1 2 3 4 5
// ----------------------
// queue : 16 5 9 1 12 15
printf("Element at front: %d\n",peek());
printf("----------------------\n");
printf("index : 5 4 3 2 1 0\n");
printf("----------------------\n");
printf("Queue: ");
while(!isEmpty()) {
int n = removeData();
printf("%d ",n);
}
}
輸出
Queue is full! Element removed: 3 Element at front: 5 ---------------------- index : 5 4 3 2 1 0 ---------------------- Queue: 5 9 1 12 15 16
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#define MAX 6
int intArray[MAX];
int front = 0;
int rear = -1;
int itemCount = 0;
int peek(){
return intArray[front];
}
bool isEmpty(){
return itemCount == 0;
}
bool isFull(){
return itemCount == MAX;
}
int size(){
return itemCount;
}
void insert(int data){
if(!isFull()) {
if(rear == MAX-1) {
rear = -1;
}
intArray[++rear] = data;
itemCount++;
}
}
int removeData(){
int data = intArray[front++];
if(front == MAX) {
front = 0;
}
itemCount--;
return data;
}
int main(){
/* insert 5 items */
insert(3);
insert(5);
insert(9);
insert(1);
insert(12);
// front : 0
// rear : 4
// ------------------
// index : 0 1 2 3 4
// ------------------
// queue : 3 5 9 1 12
insert(15);
// front : 0
// rear : 5
// ---------------------
// index : 0 1 2 3 4 5
// ---------------------
// queue : 3 5 9 1 12 15
if(isFull()) {
printf("Queue is full!\n");
}
// remove one item
int num = removeData();
printf("Element removed: %d\n",num);
// front : 1
// rear : 5
// -------------------
// index : 1 2 3 4 5
// -------------------
// queue : 5 9 1 12 15
// insert more items
insert(16);
// front : 1
// rear : -1
// ----------------------
// index : 0 1 2 3 4 5
// ----------------------
// queue : 16 5 9 1 12 15
// As queue is full, elements will not be inserted.
insert(17);
insert(18);
// ----------------------
// index : 0 1 2 3 4 5
// ----------------------
// queue : 16 5 9 1 12 15
printf("Element at front: %d\n",peek());
printf("----------------------\n");
printf("index : 5 4 3 2 1 0\n");
printf("----------------------\n");
printf("Queue: ");
while(!isEmpty()) {
int n = removeData();
printf("%d ",n);
}
}
輸出
Queue is full! Element removed: 3 Element at front: 5 ---------------------- index : 5 4 3 2 1 0 ---------------------- Queue: 5 9 1 12 15 16
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
public class QueueExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<>();
q.add(6);
q.add(1);
q.add(8);
q.add(4);
q.add(7);
System.out.println("The queue is: " + q);
int n = q.remove();
System.out.println("The element deleted is: " + n);
System.out.println("Queue after deletion: " + q);
int size = q.size();
System.out.println("Size of the queue is: " + size);
}
}
輸出
The queue is: [6, 1, 8, 4, 7]The element deleted is: 6 Queue after deletion: [1, 8, 4, 7] Size of the queue is: 4
class Queue:
def __init__(self):
self.queue = list()
def addtoqueue(self,data):
# Insert method to add element
if data not in self.queue:
self.queue.insert(0,data)
return True
return False
def size(self):
return len(self.queue)
def removefromqueue(self):
if len(self.queue)>0:
return self.queue.pop()
return ("Queue is empty")
q = Queue()
q.addtoqueue("36")
q.addtoqueue("24")
q.addtoqueue("48")
q.addtoqueue("12")
q.addtoqueue("66")
print("size of the queue: ",q.size())
print("Element deleted from queue: ",q.removefromqueue())
print("size of the queue after deletion: ",q.size())
輸出
size of the queue: 5 Element deleted from queue: 36 size of the queue after deletion: 4
圖資料結構
圖是一種抽象資料型別 (ADT),它由一組透過連結相互連線的物件組成。這些物件稱為頂點,連結稱為邊。
通常,圖表示為 G = {V, E},其中 G 是圖空間,V 是頂點集,E 是邊集。如果 E 為空,則該圖稱為森林。
在我們繼續之前,讓我們先熟悉一些重要的術語:
頂點 - 圖的每個節點都表示為一個頂點。在下面的示例中,帶標籤的圓圈表示頂點。因此,A 到 G 是頂點。我們可以使用陣列來表示它們,如下面的影像所示。這裡 A 可以用索引 0 來識別。B 可以用索引 1 來識別,依此類推。
邊 - 邊表示兩個頂點之間的路徑或兩個頂點之間的線。在下面的示例中,從 A 到 B、B 到 C 等的線表示邊。我們可以使用二維陣列來表示陣列,如下面的影像所示。這裡 AB 可以用第 0 行第 1 列的 1 來表示,BC 可以用第 1 行第 2 列的 1 來表示,依此類推,保持其他組合為 0。
鄰接 - 如果兩個節點或頂點透過邊連線,則它們是鄰接的。在下面的示例中,B 與 A 鄰接,C 與 B 鄰接,依此類推。
路徑 - 路徑表示兩個頂點之間的一系列邊。在下面的示例中,ABCD 表示從 A 到 D 的路徑。
圖的操作
圖的主要操作包括建立具有頂點和邊的圖,以及顯示所述圖。但是,使用圖執行的最常見和最流行的操作之一是遍歷,即以特定順序訪問圖的每個頂點。
圖中有兩種遍歷方式:
深度優先搜尋遍歷
廣度優先搜尋遍歷
深度優先搜尋遍歷
深度優先搜尋是一種遍歷演算法,它按照節點深度的遞減順序訪問圖中的所有節點。在這個演算法中,選擇一個任意節點作為起始點,並透過標記未訪問的相鄰節點來回遍歷圖,直到所有節點都被標記。
DFS 遍歷使用棧資料結構來跟蹤未訪問的節點。
廣度優先搜尋遍歷
廣度優先搜尋是一種遍歷演算法,它在訪問圖中下一層節點之前,會訪問同一深度層的所有節點。在這個演算法中,選擇一個任意節點作為起始點,並透過訪問同一深度層上的相鄰節點並標記它們來遍歷圖,直到沒有剩餘的節點。
BFS 遍歷使用佇列資料結構來跟蹤未訪問的節點。
圖的表示
在表示圖時,我們必須仔細描繪圖中存在的元素(頂點和邊)以及它們之間的關係。從圖示上看,圖由一組有限的節點和它們之間的連線線表示。但是,我們也可以使用其他最常用的方法來表示圖,例如:
鄰接矩陣
鄰接表
鄰接矩陣
鄰接矩陣是一個 V×V 的矩陣,其值填充為 0 或 1。如果 Vi 和 Vj 之間存在連線,則記錄為 1;否則為 0。
對於下面給定的圖,讓我們構建一個鄰接矩陣:
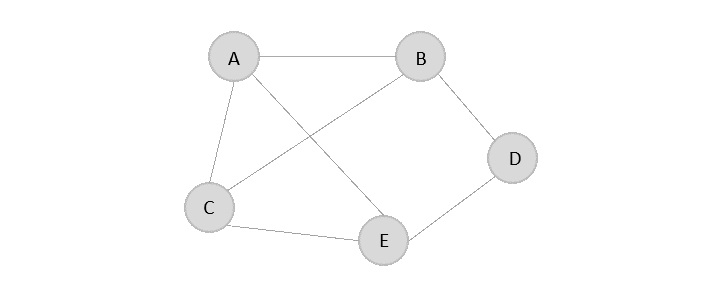
鄰接矩陣為:
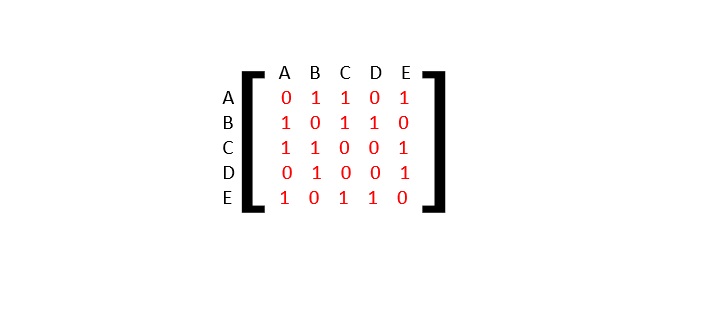
鄰接表
鄰接表是圖中直接連線到其他頂點的頂點的列表。

鄰接表為:
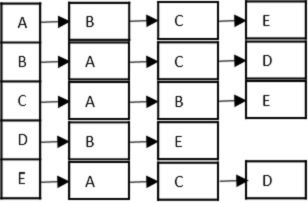
圖的型別
圖主要有兩種型別:
有向圖
無向圖
顧名思義,有向圖包含具有方向的邊,這些方向要麼遠離頂點,要麼指向頂點。無向圖的邊沒有任何方向。
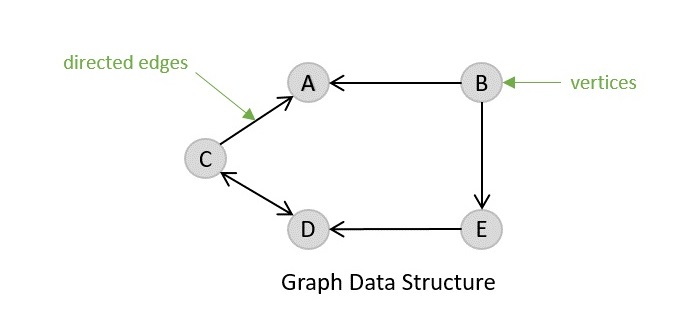
有向圖
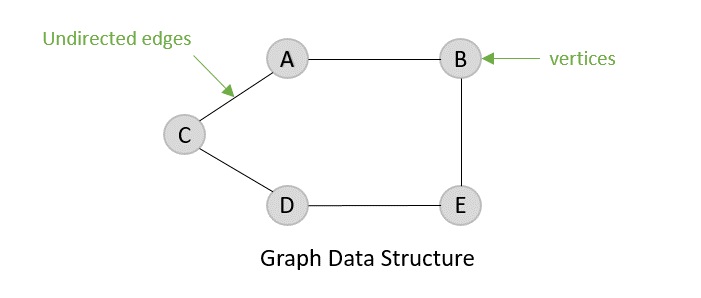
無向圖
生成樹
生成樹是無向圖的一個子集,它包含圖的所有頂點,並使用圖中最小數量的邊連線起來。準確地說,生成樹的邊是原始圖中邊的子集。
如果圖中的所有頂點都連線在一起,則至少存在一棵生成樹。在一個圖中,可能存在多棵生成樹。
特性
生成樹不包含任何環。
任何頂點都可以從任何其他頂點到達。
示例
在下圖中,突出顯示的邊構成一棵生成樹。
最小生成樹
最小生成樹 (MST) 是連通加權無向圖的邊的子集,它以最小的總邊權重將所有頂點連線在一起。要匯出 MST,可以使用 Prim 演算法或 Kruskal 演算法。因此,我們將在本章中討論 Prim 演算法。
正如我們所討論的,一個圖可能有多棵生成樹。如果存在 n 個頂點,則生成樹應具有 𝒏−𝟏 條邊。在這種情況下,如果圖的每條邊都與權重相關聯,並且存在多棵生成樹,我們需要找到圖的最小生成樹。
此外,如果存在任何重複的加權邊,則圖可能有多個最小生成樹。
在上圖中,我們展示了一棵生成樹,儘管它不是最小生成樹。這棵生成樹的成本為(5+7+3+3+5+8+3+4)=38。
最短路徑
圖中最短路徑定義為從一個頂點到另一個頂點的最小成本路徑。這在加權有向圖中最常見,但也適用於無向圖。
在圖中查詢最短路徑的一個流行的現實世界應用是地圖。使用各種最短路徑演算法可以使導航變得更容易和更簡單,其中目的地被視為圖的頂點,路線被視為邊。兩種常見的最短路徑演算法是:
迪傑斯特拉最短路徑演算法
貝爾曼-福特最短路徑演算法
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define V 5
// Maximum number of vertices in the graph
struct graph {
// declaring graph data structure
struct vertex *point[V];
};
struct vertex {
// declaring vertices
int end;
struct vertex *next;
};
struct Edge {
// declaring edges
int end, start;
};
struct graph *create_graph (struct Edge edges[], int x){
int i;
struct graph *graph = (struct graph *) malloc (sizeof (struct graph));
for (i = 0; i < V; i++) {
graph->point[i] = NULL;
}
for (i = 0; i < x; i++) {
int start = edges[i].start;
int end = edges[i].end;
struct vertex *v = (struct vertex *) malloc (sizeof (struct vertex));
v->end = end;
v->next = graph->point[start];
graph->point[start] = v;
}
return graph;
}
int main (){
struct Edge edges[] = { {0, 1}, {0, 2}, {0, 3}, {1, 2}, {1, 4}, {2, 4}, {2, 3}, {3, 1} };
int n = sizeof (edges) / sizeof (edges[0]);
struct graph *graph = create_graph (edges, n);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < V; i++) {
struct vertex *ptr = graph->point[i];
while (ptr != NULL) {
printf ("(%d -> %d)\t", i, ptr->end);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
printf ("\n");
}
return 0;
}
輸出
(1 -> 3) (1 -> 0) (2 -> 1) (2 -> 0) (3 -> 2) (3 -> 0) (4 -> 2) (4 -> 1)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define V 5
// Maximum number of vertices in the graph
struct graph {
// declaring graph data structure
struct vertex *point[V];
};
struct vertex {
// declaring vertices
int end;
struct vertex *next;
};
struct Edge {
// declaring edges
int end, start;
};
struct graph *create_graph (struct Edge edges[], int x){
int i;
struct graph *graph = (struct graph *) malloc (sizeof (struct graph));
for (i = 0; i < V; i++) {
graph->point[i] = NULL;
}
for (i = 0; i < x; i++) {
int start = edges[i].start;
int end = edges[i].end;
struct vertex *v = (struct vertex *) malloc (sizeof (struct vertex));
v->end = end;
v->next = graph->point[start];
graph->point[start] = v;
}
return graph;
}
int main (){
struct Edge edges[] = { {0, 1}, {0, 2}, {0, 3}, {1, 2}, {1, 4}, {2, 4}, {2, 3}, {3, 1} };
int n = sizeof (edges) / sizeof (edges[0]);
struct graph *graph = create_graph (edges, n);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < V; i++) {
struct vertex *ptr = graph->point[i];
while (ptr != NULL) {
cout << "(" << i << " -> " << ptr->end << ")\t";
ptr = ptr->next;
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
輸出
(1 -> 3) (1 -> 0) (2 -> 1) (2 -> 0) (3 -> 2) (3 -> 0) (4 -> 2) (4 -> 1)
import java.util.*;
//class to store edges of the graph
class Edge {
int src, dest;
Edge(int src, int dest) {
this.src = src;
this.dest = dest;
}
}
// Graph class
public class Graph {
// node of adjacency list
static class vertex {
int v;
vertex(int v) {
this.v = v;
}
};
// define adjacency list to represent the graph
List<List<vertex>> adj_list = new ArrayList<>();
//Graph Constructor
public Graph(List<Edge> edges){
// adjacency list memory allocation
for (int i = 0; i < edges.size(); i++)
adj_list.add(i, new ArrayList<>());
// add edges to the graph
for (Edge e : edges){
// allocate new node in adjacency List from src to dest
adj_list.get(e.src).add(new vertex(e.dest));
}
}
public static void main (String[] args) {
// define edges of the graph
List<Edge> edges = Arrays.asList(new Edge(0, 1),new Edge(0, 2),
new Edge(0, 3),new Edge(1, 2), new Edge(1, 4),
new Edge(2, 4), new Edge(2, 3),new Edge(3, 1));
// call graph class Constructor to construct a graph
Graph graph = new Graph(edges);
// print the graph as an adjacency list
int src = 0;
int lsize = graph.adj_list.size();
System.out.println("The graph created is:");
while (src < lsize) {
//traverse through the adjacency list and print the edges
for (vertex edge : graph.adj_list.get(src)) {
System.out.print(src + " -> " + edge.v + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
src++;
}
}
}
輸出
The graph created is: 0 -> 1 0 -> 2 0 -> 3 1 -> 2 1 -> 4 2 -> 4 2 -> 3 3 -> 1
#Python code for Graph Data Struture
V = 5
#Maximum number of vertices in th graph
#Declaring vertices
class Vertex:
def __init__(self, end):
self.end = end
self.next = None
#Declaring Edges
class Edge:
def __init__(self, start, end):
self.start = start
self.end = end
#Declaring graph data structure
class Graph:
def __init__(self):
self.point = [None] * V
def create_graph(edges, x):
graph = Graph()
for i in range(V):
graph.point[i] = None
for i in range(x):
start = edges[i].start
end = edges[i].end
v = Vertex(end)
v.next = graph.point[start]
graph.point[start] = v
return graph
edges = [Edge(0, 1), Edge(0, 2), Edge(0, 3), Edge(1, 2), Edge(1, 4), Edge(2, 4), Edge(2, 3), Edge(3, 1)]
n = len(edges)
graph = create_graph(edges, n)
#Range
for i in range(V):
ptr = graph.point[i]
while ptr is not None:
print("({} -> {})".format(i, ptr.end), end="\t")
ptr = ptr.next
print()
輸出
(0 -> 3) (0 -> 2) (0 -> 1) (1 -> 4) (1 -> 2) (2 -> 3) (2 -> 4) (3 -> 1)
深度優先遍歷
深度優先搜尋 (DFS) 演算法以深度優先的方式遍歷圖,並使用棧來記住在任何迭代中遇到死衚衕時要開始搜尋的下一個頂點。

如上例所示,DFS 演算法首先從 S 遍歷到 A、D、G、E、B,然後到 F,最後到 C。它採用以下規則。
規則 1 - 訪問相鄰的未訪問頂點。將其標記為已訪問。顯示它。將其壓入棧中。
規則 2 - 如果未找到相鄰頂點,則從棧中彈出頂點。(它將彈出棧中所有沒有相鄰頂點的頂點。)
規則 3 - 重複規則 1 和規則 2,直到棧為空。
| 步驟 | 遍歷 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 |  |
初始化棧。 |
| 2 | 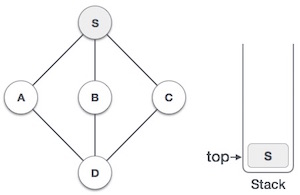 |
將S標記為已訪問並將其壓入棧中。探索S的任何未訪問的相鄰節點。我們有三個節點,我們可以選擇其中的任何一個。在本例中,我們將按照字母順序選擇節點。 |
| 3 | 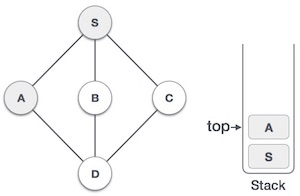 |
將A標記為已訪問並將其壓入棧中。探索A的任何未訪問的相鄰節點。S和D都與A相鄰,但我們只關心未訪問的節點。 |
| 4 | 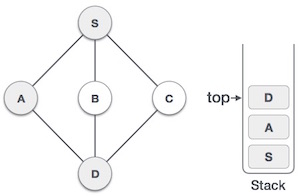 |
訪問D,將其標記為已訪問並壓入棧中。這裡,我們有B和C節點,它們與D相鄰,並且都未被訪問。但是,我們將再次按照字母順序選擇。 |
| 5 | 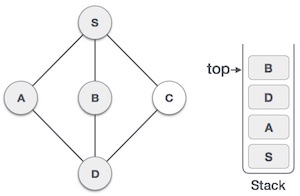 |
我們選擇B,將其標記為已訪問並壓入棧中。這裡B沒有任何未訪問的相鄰節點。因此,我們從棧中彈出B。 |
| 6 | 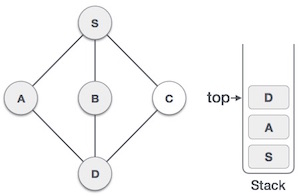 |
我們檢查棧頂以返回到前一個節點,並檢查它是否具有任何未訪問的節點。在這裡,我們發現D位於棧頂。 |
| 7 | 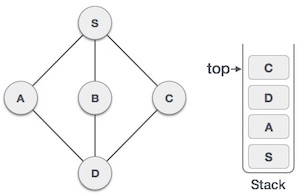 |
現在,D唯一的未訪問的相鄰節點是C。因此,我們訪問C,將其標記為已訪問並壓入棧中。 |
由於C沒有任何未訪問的相鄰節點,因此我們不斷彈出棧,直到找到一個具有未訪問的相鄰節點的節點。在本例中,沒有這樣的節點,我們一直彈出直到棧為空。
示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAX 5
struct Vertex {
char label;
bool visited;
};
//stack variables
int stack[MAX];
int top = -1;
//graph variables
//array of vertices
struct Vertex* lstVertices[MAX];
//adjacency matrix
int adjMatrix[MAX][MAX];
//vertex count
int vertexCount = 0;
//stack functions
void push(int item) {
stack[++top] = item;
}
int pop() {
return stack[top--];
}
int peek() {
return stack[top];
}
bool isStackEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
//graph functions
//add vertex to the vertex list
void addVertex(char label) {
struct Vertex* vertex = (struct Vertex*) malloc(sizeof(struct Vertex));
vertex->label = label;
vertex->visited = false;
lstVertices[vertexCount++] = vertex;
}
//add edge to edge array
void addEdge(int start,int end) {
adjMatrix[start][end] = 1;
adjMatrix[end][start] = 1;
}
//display the vertex
void displayVertex(int vertexIndex) {
printf("%c ",lstVertices[vertexIndex]->label);
}
//get the adjacent unvisited vertex
int getAdjUnvisitedVertex(int vertexIndex) {
int i;
for(i = 0; i < vertexCount; i++) {
if(adjMatrix[vertexIndex][i] == 1 && lstVertices[i]->visited == false) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
void depthFirstSearch() {
int i;
//mark first node as visited
lstVertices[0]->visited = true;
//display the vertex
displayVertex(0);
//push vertex index in stack
push(0);
while(!isStackEmpty()) {
//get the unvisited vertex of vertex which is at top of the stack
int unvisitedVertex = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(peek());
//no adjacent vertex found
if(unvisitedVertex == -1) {
pop();
} else {
lstVertices[unvisitedVertex]->visited = true;
displayVertex(unvisitedVertex);
push(unvisitedVertex);
}
}
//stack is empty, search is complete, reset the visited flag
for(i = 0;i < vertexCount;i++) {
lstVertices[i]->visited = false;
}
}
int main() {
int i, j;
for(i = 0; i < MAX; i++) { // set adjacency
for(j = 0; j < MAX; j++) // matrix to 0
adjMatrix[i][j] = 0;
}
addVertex('S'); // 0
addVertex('A'); // 1
addVertex('B'); // 2
addVertex('C'); // 3
addVertex('D'); // 4
addEdge(0, 1); // S - A
addEdge(0, 2); // S - B
addEdge(0, 3); // S - C
addEdge(1, 4); // A - D
addEdge(2, 4); // B - D
addEdge(3, 4); // C - D
printf("Depth First Search: ");
depthFirstSearch();
return 0;
}
輸出
Depth First Search: S A D B C
//C++ code for Depth First Traversal
#include <iostream>
#include <array>
#include <vector>
constexpr int MAX = 5;
struct Vertex {
char label;
bool visited;
};
//stack variables
std::array<int, MAX> stack;
int top = -1;
//graph variables
//array of vertices
std::array<Vertex*, MAX> lstVertices;
//adjacency matrix
std::array<std::array<int, MAX>, MAX> adjMatrix;
//vertex count
int vertexCount = 0;
//stack functions
void push(int item) {
stack[++top] = item;
}
int pop() {
return stack[top--];
}
int peek() {
return stack[top];
}
bool isStackEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
//graph functions
//add vertex to the vertex list
void addVertex(char label) {
Vertex* vertex = new Vertex;
vertex->label = label;
vertex->visited = false;
lstVertices[vertexCount++] = vertex;
}
//add edge to edge array
void addEdge(int start, int end) {
adjMatrix[start][end] = 1;
adjMatrix[end][start] = 1;
}
//display the vertex
void displayVertex(int vertexIndex) {
std::cout << lstVertices[vertexIndex]->label << " ";
}
//get the adjacent unvisited vertex
int getAdjUnvisitedVertex(int vertexIndex) {
for (int i = 0; i < vertexCount; i++) {
if (adjMatrix[vertexIndex][i] == 1 && !lstVertices[i]->visited) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//mark first node as visited
void depthFirstSearch() {
lstVertices[0]->visited = true;
//display the vertex
displayVertex(0);
//push vertex index in stack
push(0);
while (!isStackEmpty()) {
//get the unvisited vertex of vertex which is at top of the stack
int unvisitedVertex = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(peek());
//no adjacent vertex found
if (unvisitedVertex == -1) {
pop();
} else {
lstVertices[unvisitedVertex]->visited = true;
displayVertex(unvisitedVertex);
push(unvisitedVertex);
}
}
//stack is empty, search is complete, reset the visited flag
for (int i = 0; i < vertexCount; i++) {
lstVertices[i]->visited = false;
}
}
int main() {
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++) { //set adjacency
for (int j = 0; j < MAX; j++) { // matrix to 0
adjMatrix[i][j] = 0;
}
}
addVertex('S');
addVertex('A');
addVertex('B');
addVertex('C');
addVertex('D');
addEdge(0, 1);
addEdge(0, 2);
addEdge(0, 3);
addEdge(1, 4);
addEdge(2, 4);
addEdge(3, 4);
std::cout << "Depth First Search: ";
depthFirstSearch();
return 0;
}
輸出
Depth First Search: S A D B C
//Java program for Depth First Traversal
public class DepthFirstSearch {
private static final int MAX = 5;
private static class Vertex {
char label;
boolean visited;
}
private static int[] stack = new int[MAX];
private static int top = -1;
private static Vertex[] lstVertices = new Vertex[MAX];
private static int[][] adjMatrix = new int[MAX][MAX];
private static int vertexCount = 0;
private static void push(int item) {
stack[++top] = item;
}
private static int pop() {
return stack[top--];
}
private static int peek() {
return stack[top];
}
private static boolean isStackEmpty() {
return top == -1;
}
private static void addVertex(char label) {
Vertex vertex = new Vertex();
vertex.label = label;
vertex.visited = false;
lstVertices[vertexCount++] = vertex;
}
private static void addEdge(int start, int end) {
adjMatrix[start][end] = 1;
adjMatrix[end][start] = 1;
}
private static void displayVertex(int vertexIndex) {
System.out.print(lstVertices[vertexIndex].label + " ");
}
private static int getAdjUnvisitedVertex(int vertexIndex) {
for (int i = 0; i < vertexCount; i++) {
if (adjMatrix[vertexIndex][i] == 1 && !lstVertices[i].visited) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
private static void depthFirstSearch() {
lstVertices[0].visited = true;
displayVertex(0);
push(0);
while (!isStackEmpty()) {
int unvisitedVertex = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(peek());
if (unvisitedVertex == -1) {
pop();
} else {
lstVertices[unvisitedVertex].visited = true;
displayVertex(unvisitedVertex);
push(unvisitedVertex);
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < vertexCount; i++) {
lstVertices[i].visited = false;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < MAX; j++) {
adjMatrix[i][j] = 0;
}
}
addVertex('S'); // 0
addVertex('A'); // 1
addVertex('B'); // 2
addVertex('C'); // 3
addVertex('D'); // 4
addEdge(0, 1); // S - A
addEdge(0, 2); // S - B
addEdge(0, 3); // S - C
addEdge(1, 4); // A - D
addEdge(2, 4); // B - D
addEdge(3, 4); // C - D
System.out.print("Depth First Search: ");
depthFirstSearch();
}
}
輸出
Depth First Search: S A D B C
#Python program for Depth First Traversal
MAX = 5
class Vertex:
def __init__(self, label):
self.label = label
self.visited = False
#stack variables
stack = []
top = -1
#graph variables
#array of vertices
lstVertices = [None] * MAX
#adjacency matrix
adjMatrix = [[0] * MAX for _ in range(MAX)]
#vertex count
vertexCount = 0
#stack functions
def push(item):
global top
top += 1
stack.append(item)
def pop():
global top
item = stack[top]
del stack[top]
top -= 1
return item
def peek():
return stack[top]
def isStackEmpty():
return top == -1
#graph functions
#add vertex to the vertex list
def addVertex(label):
global vertexCount
vertex = Vertex(label)
lstVertices[vertexCount] = vertex
vertexCount += 1
#add edge to edge array
def addEdge(start, end):
adjMatrix[start][end] = 1
adjMatrix[end][start] = 1
#Display the Vertex
def displayVertex(vertexIndex):
print(lstVertices[vertexIndex].label, end=' ')
def getAdjUnvisitedVertex(vertexIndex):
for i in range(vertexCount):
if adjMatrix[vertexIndex][i] == 1 and not lstVertices[i].visited:
return i
return -1
def depthFirstSearch():
lstVertices[0].visited = True
displayVertex(0)
push(0)
while not isStackEmpty():
unvisitedVertex = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(peek())
if unvisitedVertex == -1:
pop()
else:
lstVertices[unvisitedVertex].visited = True
displayVertex(unvisitedVertex)
push(unvisitedVertex)
for i in range(vertexCount):
lstVertices[i].visited = False
for i in range(MAX):
for j in range(MAX):
adjMatrix[i][j] = 0
addVertex('S') # 0
addVertex('A') # 1
addVertex('B') # 2
addVertex('C') # 3
addVertex('D') # 4
addEdge(0, 1) # S - A
addEdge(0, 2) # S - B
addEdge(0, 3) # S - C
addEdge(1, 4) # A - D
addEdge(2, 4) # B - D
addEdge(3, 4) # C - D
print("Depth First Search:", end=' ')
depthFirstSearch()
輸出
Depth First Search: S A D B C
廣度優先遍歷
廣度優先搜尋 (BFS) 演算法以廣度優先的方式遍歷圖,並使用佇列來記住在任何迭代中遇到死衚衕時要開始搜尋的下一個頂點。
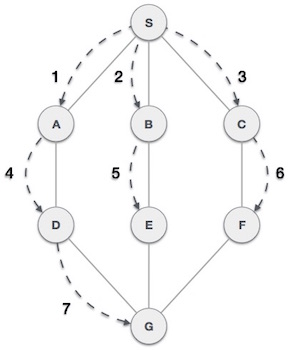
如上例所示,BFS 演算法首先從 A 遍歷到 B、E、F,然後到 C 和 G,最後到 D。它採用以下規則。
規則 1 - 訪問相鄰的未訪問頂點。將其標記為已訪問。顯示它。將其插入佇列中。
規則 2 - 如果未找到相鄰頂點,則從佇列中刪除第一個頂點。
規則 3 - 重複規則 1 和規則 2,直到佇列為空。
| 步驟 | 遍歷 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 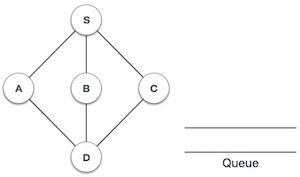 |
初始化佇列。 |
| 2 | 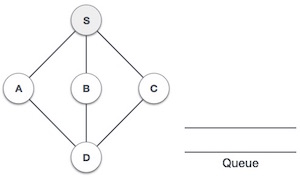 |
我們從訪問S(起始節點)開始,並將其標記為已訪問。 |
| 3 | 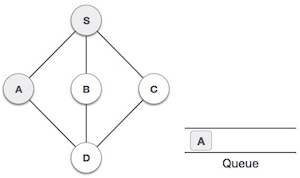 |
然後我們看到S的一個未訪問的相鄰節點。在本例中,我們有三個節點,但按照字母順序我們選擇A,將其標記為已訪問並將其入隊。 |
| 4 | 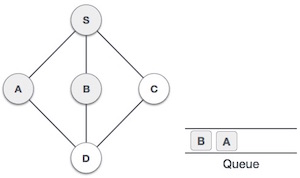 |
接下來,S的未訪問的相鄰節點是B。我們將其標記為已訪問並將其入隊。 |
| 5 | 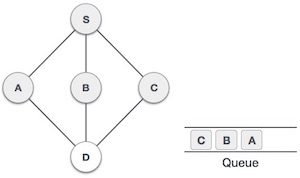 |
接下來,S的未訪問的相鄰節點是C。我們將其標記為已訪問並將其入隊。 |
| 6 | 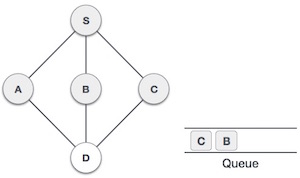 |
現在,S沒有未訪問的相鄰節點了。因此,我們出隊並找到A。 |
| 7 | 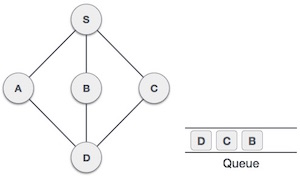 |
從A我們有D作為未訪問的相鄰節點。我們將其標記為已訪問並將其入隊。 |
在這個階段,我們沒有未標記(未訪問)的節點了。但根據演算法,我們繼續出隊以獲取所有未訪問的節點。當佇列清空時,程式結束。
示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAX 5
struct Vertex {
char label;
bool visited;
};
//queue variables
int queue[MAX];
int rear = -1;
int front = 0;
int queueItemCount = 0;
//graph variables
//array of vertices
struct Vertex* lstVertices[MAX];
//adjacency matrix
int adjMatrix[MAX][MAX];
//vertex count
int vertexCount = 0;
//queue functions
void insert(int data) {
queue[++rear] = data;
queueItemCount++;
}
int removeData() {
queueItemCount--;
return queue[front++];
}
bool isQueueEmpty() {
return queueItemCount == 0;
}
//graph functions
//add vertex to the vertex list
void addVertex(char label) {
struct Vertex* vertex = (struct Vertex*) malloc(sizeof(struct Vertex));
vertex->label = label;
vertex->visited = false;
lstVertices[vertexCount++] = vertex;
}
//add edge to edge array
void addEdge(int start,int end) {
adjMatrix[start][end] = 1;
adjMatrix[end][start] = 1;
}
//display the vertex
void displayVertex(int vertexIndex) {
printf("%c ",lstVertices[vertexIndex]->label);
}
//get the adjacent unvisited vertex
int getAdjUnvisitedVertex(int vertexIndex) {
int i;
for(i = 0; i<vertexCount; i++) {
if(adjMatrix[vertexIndex][i] == 1 && lstVertices[i]->visited == false)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
void breadthFirstSearch() {
int i;
//mark first node as visited
lstVertices[0]->visited = true;
//display the vertex
displayVertex(0);
//insert vertex index in queue
insert(0);
int unvisitedVertex;
while(!isQueueEmpty()) {
//get the unvisited vertex of vertex which is at front of the queue
int tempVertex = removeData();
//no adjacent vertex found
while((unvisitedVertex = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(tempVertex)) != -1) {
lstVertices[unvisitedVertex]->visited = true;
displayVertex(unvisitedVertex);
insert(unvisitedVertex);
}
}
//queue is empty, search is complete, reset the visited flag
for(i = 0;i<vertexCount;i++) {
lstVertices[i]->visited = false;
}
}
int main() {
int i, j;
for(i = 0; i<MAX; i++) { // set adjacency
for(j = 0; j<MAX; j++) // matrix to 0
adjMatrix[i][j] = 0;
}
addVertex('S'); // 0
addVertex('A'); // 1
addVertex('B'); // 2
addVertex('C'); // 3
addVertex('D'); // 4
addEdge(0, 1); // S - A
addEdge(0, 2); // S - B
addEdge(0, 3); // S - C
addEdge(1, 4); // A - D
addEdge(2, 4); // B - D
addEdge(3, 4); // C - D
printf("\nBreadth First Search: ");
breadthFirstSearch();
return 0;
}
輸出
Breadth First Search: S A B C D
//C++ code for Breadth First Traversal
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAX 5
struct Vertex {
char label;
bool visited;
};
//queue variables
int queue[MAX];
int rear = -1;
int front = 0;
int queueItemCount = 0;
//graph variables
//array of vertices
struct Vertex* lstVertices[MAX];
//adjacency matrix
int adjMatrix[MAX][MAX];
//vertex count
int vertexCount = 0;
//queue functions
void insert(int data) {
queue[++rear] = data;
queueItemCount++;
}
int removeData() {
queueItemCount--;
return queue[front++];
}
bool isQueueEmpty() {
return queueItemCount == 0;
}
//graph functions
//add vertex to the vertex list
void addVertex(char label) {
struct Vertex* vertex = (struct Vertex*) malloc(sizeof(struct Vertex));
vertex->label = label;
vertex->visited = false;
lstVertices[vertexCount++] = vertex;
}
//add edge to edge array
void addEdge(int start,int end) {
adjMatrix[start][end] = 1;
adjMatrix[end][start] = 1;
}
//display the vertex
void displayVertex(int vertexIndex) {
std::cout << lstVertices[vertexIndex]->label << " ";
}
//get the adjacent unvisited vertex
int getAdjUnvisitedVertex(int vertexIndex) {
int i;
for(i = 0; i<vertexCount; i++) {
if(adjMatrix[vertexIndex][i] == 1 && lstVertices[i]->visited == false)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
void breadthFirstSearch() {
int i;
//mark first node as visited
lstVertices[0]->visited = true;
//display the vertex
displayVertex(0);
//insert vertex index in queue
insert(0);
int unvisitedVertex;
while(!isQueueEmpty()) {
//get the unvisited vertex of vertex which is at front of the queue
int tempVertex = removeData();
//no adjacent vertex found
while((unvisitedVertex = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(tempVertex)) != -1) {
lstVertices[unvisitedVertex]->visited = true;
displayVertex(unvisitedVertex);
insert(unvisitedVertex);
}
}
//queue is empty, search is complete, reset the visited flag
for(i = 0;i<vertexCount;i++) {
lstVertices[i]->visited = false;
}
}
int main() {
int i, j;
for(i = 0; i<MAX; i++) { // set adjacency
for(j = 0; j<MAX; j++) // matrix to 0
adjMatrix[i][j] = 0;
}
addVertex('S'); // 0
addVertex('A'); // 1
addVertex('B'); // 2
addVertex('C'); // 3
addVertex('D'); // 4
addEdge(0, 1); // S - A
addEdge(0, 2); // S - B
addEdge(0, 3); // S - C
addEdge(1, 4); // A - D
addEdge(2, 4); // B - D
addEdge(3, 4); // C - D
std::cout << "Breadth First Search: ";
breadthFirstSearch();
return 0;
}
輸出
Breadth First Search: S A B C D
//Java code for Breadth First Traversal
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.Queue;
class Vertex {
char label;
boolean visited;
public Vertex(char label) {
this.label = label;
visited = false;
}
}
public class Graph {
private static final int MAX = 5;
private Vertex[] lstVertices;
private int[][] adjMatrix;
private int vertexCount;
public Graph() {
lstVertices = new Vertex[MAX];
adjMatrix = new int[MAX][MAX];
vertexCount = 0;
}
private void addVertex(char label) {
Vertex vertex = new Vertex(label);
lstVertices[vertexCount++] = vertex;
}
private void addEdge(int start, int end) {
adjMatrix[start][end] = 1;
adjMatrix[end][start] = 1;
}
private void displayVertex(int vertexIndex) {
System.out.print(lstVertices[vertexIndex].label + " ");
}
private int getAdjUnvisitedVertex(int vertexIndex) {
for (int i = 0; i < vertexCount; i++) {
if (adjMatrix[vertexIndex][i] == 1 && !lstVertices[i].visited)
return i;
}
return -1;
}
private void breadthFirstSearch() {
lstVertices[0].visited = true;
displayVertex(0);
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(0);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int tempVertex = queue.poll();
int unvisitedVertex;
while ((unvisitedVertex = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(tempVertex)) != -1) {
lstVertices[unvisitedVertex].visited = true;
displayVertex(unvisitedVertex);
queue.add(unvisitedVertex);
}
}
// Reset the visited flag
for (int i = 0; i < vertexCount; i++) {
lstVertices[i].visited = false;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Graph graph = new Graph();
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < MAX; j++)
graph.adjMatrix[i][j] = 0;
}
graph.addVertex('S'); // 0
graph.addVertex('A'); // 1
graph.addVertex('B'); // 2
graph.addVertex('C'); // 3
graph.addVertex('D'); // 4
graph.addEdge(0, 1); // S - A
graph.addEdge(0, 2); // S - B
graph.addEdge(0, 3); // S - C
graph.addEdge(1, 4); // A - D
graph.addEdge(2, 4); // B - D
graph.addEdge(3, 4); // C - D
System.out.print("Breadth First Search: ");
graph.breadthFirstSearch();
}
}
輸出
Breadth First Search: S A B C D
#Python program for Breadth First Search
# defining MAX 5
MAX = 5
class Vertex:
def __init__(self, label):
self.label = label
self.visited = False
# queue variables
queue = [0] * MAX
rear = -1
front = 0
queueItemCount = 0
# graph variables
#array of vertices
lstVertices = [None] * MAX
#adjacency matrix
adjMatrix = [[0] * MAX for _ in range(MAX)]
#vertex count
vertexCount = 0
# queue functions
def insert(data):
global rear, queueItemCount
rear += 1
queue[rear] = data
queueItemCount += 1
def removeData():
global front, queueItemCount
queueItemCount -= 1
data = queue[front]
front += 1
return data
def isQueueEmpty():
return queueItemCount == 0
# graph functions
#add vertex to the vertex list
def addVertex(label):
global vertexCount
vertex = Vertex(label)
lstVertices[vertexCount] = vertex
vertexCount += 1
#add edge to edge array
def addEdge(start, end):
adjMatrix[start][end] = 1
adjMatrix[end][start] = 1
#Display the vertex
def displayVertex(vertexIndex):
print(lstVertices[vertexIndex].label, end=" ")
#Get the adjacent unvisited vertex
def getAdjUnvisitedVertex(vertexIndex):
for i in range(vertexCount):
if adjMatrix[vertexIndex][i] == 1 and not lstVertices[i].visited:
return i
return -1
def breadthFirstSearch():
#mark first node as visited
lstVertices[0].visited = True
#Display the vertex
displayVertex(0)
#insert vertex index in queue
insert(0)
while not isQueueEmpty():
#get the unvisited vertex of vertex which is at front of the queue
tempVertex = removeData()
#no adjacent vertex found
unvisitedVertex = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(tempVertex)
while unvisitedVertex != -1:
lstVertices[unvisitedVertex].visited = True
displayVertex(unvisitedVertex)
insert(unvisitedVertex)
unvisitedVertex = getAdjUnvisitedVertex(tempVertex)
#queue is empty, search is complete, reset the visited flag
for i in range(vertexCount):
lstVertices[i].visited = False
# main function
if __name__ == "__main__":
#set adjacency
for i in range(MAX):
#matrix to 0
for j in range(MAX):
adjMatrix[i][j] = 0
addVertex('S')
addVertex('A')
addVertex('B')
addVertex('C')
addVertex('D')
addEdge(0, 1)
addEdge(0, 2)
addEdge(0, 3)
addEdge(1, 4)
addEdge(2, 4)
addEdge(3, 4)
print("Breadth First Search: ", end="")
breadthFirstSearch()
輸出
Breadth First Search: S A B C D
生成樹
生成樹是圖 G 的一個子集,它覆蓋了所有頂點,並且邊數最少。因此,生成樹不包含環,並且不能斷開連線。
根據此定義,我們可以得出結論,每個連通的無向圖 G 至少有一棵生成樹。斷開的圖沒有任何生成樹,因為它無法擴充套件到其所有頂點。

我們發現了一個完整圖的三棵生成樹。一個完整的無向圖最多可以有nn-2棵生成樹,其中n是節點數。在上述示例中,n 為 3,因此33−2 = 3棵生成樹是可能的。
生成樹的一般性質
現在我們理解了一個圖可以有多棵生成樹。以下是與圖 G 相連的生成樹的一些屬性:
一個連通圖 G 可以有多棵生成樹。
圖 G 的所有可能的生成樹都具有相同數量的邊和頂點。
生成樹不包含任何環(迴路)。
從生成樹中移除一條邊將使圖斷開連線,即生成樹是最小連通的。
向生成樹中新增一條邊將建立一個迴路或環,即生成樹是最大無環的。
生成樹的數學性質
生成樹有n-1條邊,其中n是節點(頂點)的數量。
從一個完整圖中,透過移除最多e - n + 1條邊,我們可以構建一棵生成樹。
一個完整圖最多可以有nn-2棵生成樹。
因此,我們可以得出結論,生成樹是連通圖 G 的子集,而斷開的圖沒有生成樹。
生成樹的應用
生成樹基本上用於查詢連線圖中所有節點的最小路徑。生成樹的常見應用包括:
民用網路規劃
計算機網路路由協議
聚類分析
讓我們透過一個小例子來理解這一點。假設,城市網路是一個巨大的圖,現在計劃以最少的線路部署電話線,以便連線到所有城市節點。這就是生成樹發揮作用的地方。
最小生成樹 (MST)
在加權圖中,最小生成樹是指權重小於同一圖所有其他生成樹的生成樹。在現實世界中,該權重可以衡量為距離、擁塞、交通負荷或分配給邊的任何任意值。
最小生成樹演算法
我們將在這裡學習兩種最重要的生成樹演算法:
兩者都是貪心演算法。
樹資料結構
樹是一種非線性抽象資料型別,具有基於層次結構的結構。它由節點(資料儲存的地方)組成,這些節點透過連結連線。樹資料結構源於一個稱為根節點的單個節點,並且具有連線到根的子樹。
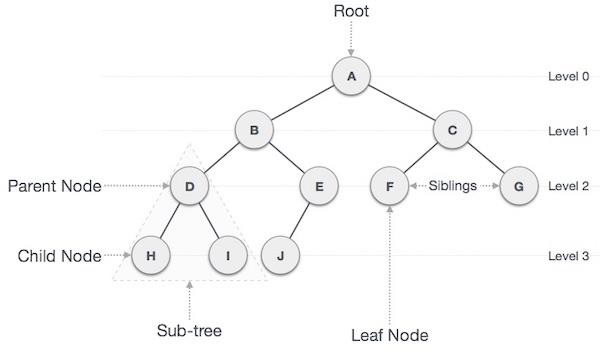
重要術語
以下是關於樹的一些重要術語。
路徑 - 路徑指的是沿著樹的邊上的節點序列。
根 - 樹頂部的節點稱為根。每棵樹只有一個根,並且從根節點到任何節點只有一條路徑。
父節點 - 除根節點之外的任何節點都有一條向上連線到稱為父節點的節點的邊。
子節點 - 下方透過其向下邊連線的給定節點稱為其子節點。
葉子節點 - 沒有子節點的節點稱為葉子節點。
子樹 - 子樹表示節點的後代。
訪問 - 訪問是指當控制權在節點上時檢查節點的值。
遍歷 - 遍歷意味著按特定順序穿過節點。
層級 - 節點的層級表示節點的代數。如果根節點在第 0 層,則其下一個子節點在第 1 層,其孫子節點在第 2 層,依此類推。
鍵 - 鍵表示節點的值,基於該值將對節點執行搜尋操作。
樹的型別
樹有三種類型:
一般樹
二叉樹
二叉搜尋樹
一般樹
一般樹是無序的樹形資料結構,其中根節點至少有 0 個或最多有 'n' 個子樹。
一般樹對它們的層次結構沒有約束。因此,根節點充當所有其他子樹的超集。
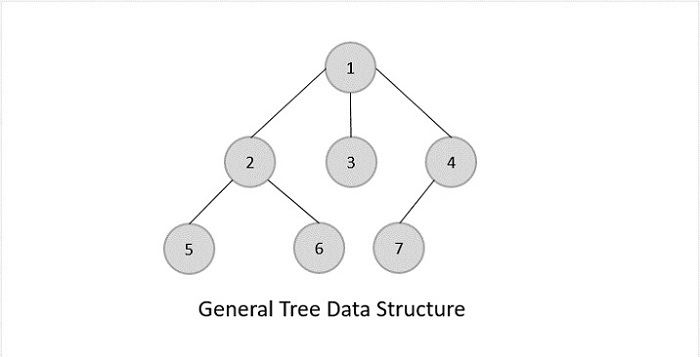
二叉樹
二叉樹是一般樹,其中根節點最多隻能包含 2 個子樹:左子樹和右子樹。根據子節點的數量,二叉樹分為三種類型。
滿二叉樹
滿二叉樹是一種二叉樹型別,其中每個節點要麼有 0 個,要麼有 2 個子節點。
完全二叉樹
完全二叉樹是一種二叉樹型別,其中所有葉子節點都必須在同一層級。但是,完全二叉樹中的根節點和內部節點可以有 0、1 或 2 個子節點。
完美二叉樹
完美二叉樹是一種二叉樹型別,其中所有葉子節點都在同一層級,並且除葉子節點之外的每個節點都有 2 個子節點。
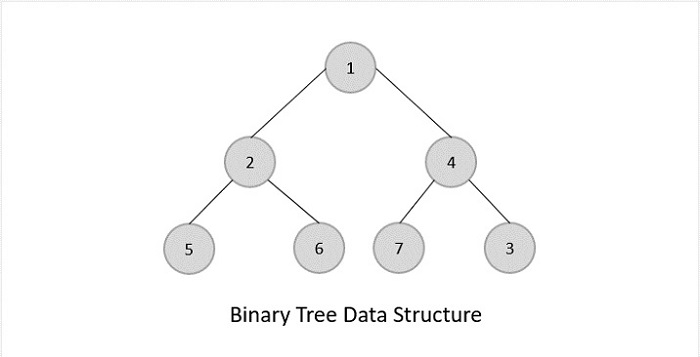
二叉搜尋樹
二叉搜尋樹擁有二叉樹的所有屬性,包括一些基於某些約束的自身額外屬性,使其比二叉樹更有效率。
二叉搜尋樹 (BST) 中的資料始終以這樣的方式儲存:左子樹中的值始終小於根節點中的值,而右子樹中的值始終大於根節點中的值,即左子樹 < 根節點 ≤ 右子樹。
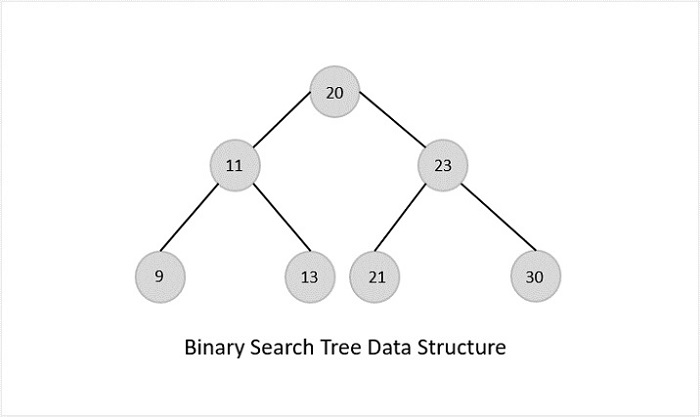
BST 的優點
二叉搜尋樹比二叉樹更有效率,因為執行各種操作的時間複雜度降低了。
由於鍵的順序僅基於父節點,因此搜尋操作變得更簡單。
BST 的對齊方式也有利於範圍查詢,範圍查詢用於查詢兩個鍵之間存在的值。這有助於資料庫管理系統。
BST 的缺點
二叉搜尋樹的主要缺點是,如果節點中的所有元素都大於或小於根節點,樹將變得傾斜。簡單來說,樹完全向一邊傾斜。
這種傾斜將使樹成為一個連結串列而不是 BST,因為搜尋操作的最壞情況時間複雜度變為 O(n)。
為了克服二叉搜尋樹中傾斜的問題,引入了平衡二叉搜尋樹的概念。
平衡二叉搜尋樹
考慮一個二叉搜尋樹,其中左子樹的高度為 'm',右子樹的高度為 'n'。如果 (m-n) 的值等於 0、1 或 -1,則該樹被稱為平衡二叉搜尋樹。
樹的設計方式是,一旦高度差超過 1,它們就會自動平衡。二叉搜尋樹使用旋轉作為自動平衡演算法。旋轉有四種不同的型別:左左、右右、左右、右左。
有各種型別的自平衡二叉搜尋樹:
AVL 樹
紅黑樹
B 樹
B+ 樹
伸展樹
優先搜尋樹
樹的遍歷
遍歷是一個訪問樹的所有節點並可能列印其值的流程。因為所有節點都透過邊(連結)連線,所以我們始終從根(頭部)節點開始。也就是說,我們不能隨機訪問樹中的節點。我們使用三種方法來遍歷樹:
中序遍歷
前序遍歷
後序遍歷
通常,我們遍歷樹是為了搜尋或定位樹中給定的專案或鍵,或者列印它包含的所有值。
中序遍歷
在這種遍歷方法中,首先訪問左子樹,然後訪問根,最後訪問右子樹。我們應該始終記住,每個節點本身可能表示一個子樹。
如果二叉樹中序遍歷,輸出將產生按升序排序的鍵值。
我們從A開始,按照中序遍歷,我們移動到它的左子樹B。B也進行中序遍歷。此過程一直持續到訪問所有節點。這棵樹的中序遍歷輸出將是:
D → B → E → A → F → C → G
演算法
直到所有節點都被遍歷:
步驟 1 - 遞迴遍歷左子樹。
步驟 2 - 訪問根節點。
步驟 3 - 遞迴遍歷右子樹。
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild;
struct node *rightChild;
};
struct node *root = NULL;
void insert(int data){
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//if tree is empty
if(root == NULL) {
root = tempNode;
} else {
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1) {
parent = current;
//go to left of the tree
if(data < parent->data) {
current = current->leftChild;
//insert to the left
if(current == NULL) {
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}//go to right of the tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
//insert to the right
if(current == NULL) {
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
void inorder_traversal(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL) {
inorder_traversal(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ",root->data);
inorder_traversal(root->rightChild);
}
}
int main(){
int i;
int array[7] = { 27, 14, 35, 10, 19, 31, 42 };
for(i = 0; i < 7; i++)
insert(array[i]);
printf("\nInorder traversal: ");
inorder_traversal(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
Inorder traversal: 10 14 19 27 31 35 42
#include <iostream>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild;
struct node *rightChild;
};
struct node *root = NULL;
void insert(int data){
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//if tree is empty
if(root == NULL) {
root = tempNode;
} else {
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1) {
parent = current;
//go to left of the tree
if(data < parent->data) {
current = current->leftChild;
//insert to the left
if(current == NULL) {
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}//go to right of the tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
//insert to the right
if(current == NULL) {
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
void inorder_traversal(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL) {
inorder_traversal(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ",root->data);
inorder_traversal(root->rightChild);
}
}
int main(){
int i;
int array[7] = { 27, 14, 35, 10, 19, 31, 42 };
for(i = 0; i < 7; i++)
insert(array[i]);
printf("\nInorder traversal: ");
inorder_traversal(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
Inorder traversal: 10 14 19 27 31 35 42
class Node {
int data;
Node leftChild;
Node rightChild;
public Node(int key) {
data = key;
leftChild = rightChild = null;
}
}
public class TreeDataStructure {
Node root = null;
void inorder_traversal(Node node) {
if(node != null) {
inorder_traversal(node.leftChild);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
inorder_traversal(node.rightChild);
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
TreeDataStructure tree = new TreeDataStructure();
tree.root = new Node(27);
tree.root.leftChild = new Node(12);
tree.root.rightChild = new Node(3);
tree.root.leftChild.leftChild = new Node(44);
tree.root.leftChild.rightChild = new Node(17);
tree.root.rightChild.leftChild = new Node(56);
System.out.println("\nInorder traversal: ");
tree.inorder_traversal(tree.root);
}
}
輸出
Inorder traversal: 44 12 17 27 56 3
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.leftChild = None
self.rightChild = None
self.data = key
# Create a function to perform inorder tree traversal
def InorderTraversal(root):
if root:
InorderTraversal(root.leftChild)
print(root.data)
InorderTraversal(root.rightChild)
# Main class
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = Node(3)
root.leftChild = Node(26)
root.rightChild = Node(42)
root.leftChild.leftChild = Node(54)
root.leftChild.rightChild = Node(65)
root.rightChild.leftChild = Node(12)
# Function call
print("\nInorder traversal of binary tree is")
InorderTraversal(root)
輸出
Inorder traversal of binary tree is 54 26 65 3 12 42
前序遍歷
在這種遍歷方法中,首先訪問根節點,然後訪問左子樹,最後訪問右子樹。
我們從A開始,按照前序遍歷,我們首先訪問A本身,然後移動到它的左子樹B。B也進行前序遍歷。此過程一直持續到訪問所有節點。這棵樹的前序遍歷輸出將是:
A → B → D → E → C → F → G
演算法
直到所有節點都被遍歷:
步驟 1 - 訪問根節點。
步驟 2 - 遞迴遍歷左子樹。
步驟 3 - 遞迴遍歷右子樹。
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild;
struct node *rightChild;
};
struct node *root = NULL;
void insert(int data){
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//if tree is empty
if(root == NULL) {
root = tempNode;
} else {
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1) {
parent = current;
//go to left of the tree
if(data < parent->data) {
current = current->leftChild;
//insert to the left
if(current == NULL) {
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}//go to right of the tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
//insert to the right
if(current == NULL) {
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
void pre_order_traversal(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL) {
printf("%d ",root->data);
pre_order_traversal(root->leftChild);
pre_order_traversal(root->rightChild);
}
}
int main(){
int i;
int array[7] = { 27, 14, 35, 10, 19, 31, 42 };
for(i = 0; i < 7; i++)
insert(array[i]);
printf("\nPreorder traversal: ");
pre_order_traversal(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
Preorder traversal: 27 14 10 19 35 31 42
#include <iostream>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild;
struct node *rightChild;
};
struct node *root = NULL;
void insert(int data){
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//if tree is empty
if(root == NULL) {
root = tempNode;
} else {
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1) {
parent = current;
//go to left of the tree
if(data < parent->data) {
current = current->leftChild;
//insert to the left
if(current == NULL) {
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}//go to right of the tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
//insert to the right
if(current == NULL) {
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
void pre_order_traversal(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL) {
printf("%d ",root->data);
pre_order_traversal(root->leftChild);
pre_order_traversal(root->rightChild);
}
}
int main(){
int i;
int array[7] = { 27, 14, 35, 10, 19, 31, 42 };
for(i = 0; i < 7; i++)
insert(array[i]);
printf("\nPreorder traversal: ");
pre_order_traversal(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
Preorder traversal: 27 14 10 19 35 31 42
class Node {
int data;
Node leftChild;
Node rightChild;
public Node(int key) {
data = key;
leftChild = rightChild = null;
}
}
public class TreeDataStructure {
Node root = null;
void pre_order_traversal(Node node) {
if(node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
pre_order_traversal(node.leftChild);
pre_order_traversal(node.rightChild);
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
TreeDataStructure tree = new TreeDataStructure();
tree.root = new Node(27);
tree.root.leftChild = new Node(12);
tree.root.rightChild = new Node(3);
tree.root.leftChild.leftChild = new Node(44);
tree.root.leftChild.rightChild = new Node(17);
tree.root.rightChild.leftChild = new Node(56);
System.out.println("\nPreorder traversal: ");
tree.pre_order_traversal(tree.root);
}
}
輸出
Preorder traversal: 27 12 44 17 3 56
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.leftChild = None
self.rightChild = None
self.data = key
# Create a function to perform postorder tree traversal
def PreorderTraversal(root):
if root:
print(root.data)
PreorderTraversal(root.leftChild)
PreorderTraversal(root.rightChild)
# Main class
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = Node(3)
root.leftChild = Node(26)
root.rightChild = Node(42)
root.leftChild.leftChild = Node(54)
root.leftChild.rightChild = Node(65)
root.rightChild.leftChild = Node(12)
print("\nPreorder traversal of binary tree is")
PreorderTraversal(root)
輸出
Preorder traversal of binary tree is 3 26 54 65 42 12
後序遍歷
在這種遍歷方法中,最後訪問根節點,因此得名。我們首先遍歷左子樹,然後遍歷右子樹,最後遍歷根節點。
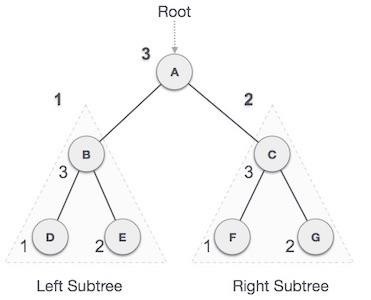
我們從A開始,按照前序遍歷,我們首先訪問左子樹B。B也進行後序遍歷。此過程一直持續到訪問所有節點。這棵樹的後序遍歷輸出將是:
D → E → B → F → G → C → A
演算法
直到所有節點都被遍歷:
步驟 1 - 遞迴遍歷左子樹。
步驟 2 - 遞迴遍歷右子樹。
步驟 3 - 訪問根節點。
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild;
struct node *rightChild;
};
struct node *root = NULL;
void insert(int data){
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//if tree is empty
if(root == NULL) {
root = tempNode;
} else {
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1) {
parent = current;
//go to left of the tree
if(data < parent->data) {
current = current->leftChild;
//insert to the left
if(current == NULL) {
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}//go to right of the tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
//insert to the right
if(current == NULL) {
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
void post_order_traversal(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL) {
post_order_traversal(root->leftChild);
post_order_traversal(root->rightChild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
}
}
int main(){
int i;
int array[7] = { 27, 14, 35, 10, 19, 31, 42 };
for(i = 0; i < 7; i++)
insert(array[i]);
printf("\nPost order traversal: ");
post_order_traversal(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
Post order traversal: 10 19 14 31 42 35 27
#include <iostream>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild;
struct node *rightChild;
};
struct node *root = NULL;
void insert(int data){
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//if tree is empty
if(root == NULL) {
root = tempNode;
} else {
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1) {
parent = current;
//go to left of the tree
if(data < parent->data) {
current = current->leftChild;
//insert to the left
if(current == NULL) {
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}//go to right of the tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
//insert to the right
if(current == NULL) {
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
void post_order_traversal(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL) {
post_order_traversal(root->leftChild);
post_order_traversal(root->rightChild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
}
}
int main(){
int i;
int array[7] = { 27, 14, 35, 10, 19, 31, 42 };
for(i = 0; i < 7; i++)
insert(array[i]);
printf("\nPost order traversal: ");
post_order_traversal(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
Post order traversal: 10 19 14 31 42 35 27
class Node {
int data;
Node leftChild;
Node rightChild;
public Node(int key) {
data = key;
leftChild = rightChild = null;
}
}
public class TreeDataStructure {
Node root = null;
void post_order_traversal(Node node) {
if(node != null) {
post_order_traversal(node.leftChild);
post_order_traversal(node.rightChild);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
TreeDataStructure tree = new TreeDataStructure();
tree.root = new Node(27);
tree.root.leftChild = new Node(12);
tree.root.rightChild = new Node(3);
tree.root.leftChild.leftChild = new Node(44);
tree.root.leftChild.rightChild = new Node(17);
tree.root.rightChild.leftChild = new Node(56);
System.out.println("\nPost order traversal: ");
tree.post_order_traversal(tree.root);
}
}
輸出
Post order traversal: 44 17 12 56 3 27
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.leftChild = None
self.rightChild = None
self.data = key
# Create a function to perform preorder tree traversal
def PostorderTraversal(root):
if root:
PostorderTraversal(root.leftChild)
PostorderTraversal(root.rightChild)
print(root.data)
# Main class
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = Node(3)
root.leftChild = Node(26)
root.rightChild = Node(42)
root.leftChild.leftChild = Node(54)
root.leftChild.rightChild = Node(65)
root.rightChild.leftChild = Node(12)
print("\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is")
PostorderTraversal(root)
輸出
Postorder traversal of binary tree is 54 65 26 12 42 3
要檢查樹遍歷的 C 語言實現,請點選此處
實現
遍歷是一個訪問樹的所有節點並可能列印其值的流程。因為所有節點都透過邊(連結)連線,所以我們始終從根(頭部)節點開始。也就是說,我們不能隨機訪問樹中的節點。我們使用三種方法來遍歷樹:
中序遍歷
前序遍歷
後序遍歷
我們現在將在這裡看到使用以下二叉樹在 C 程式語言中實現樹遍歷:

示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild;
struct node *rightChild;
};
struct node *root = NULL;
void insert(int data){
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//if tree is empty
if(root == NULL) {
root = tempNode;
} else {
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1) {
parent = current;
//go to left of the tree
if(data < parent->data) {
current = current->leftChild;
//insert to the left
if(current == NULL) {
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}//go to right of the tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
//insert to the right
if(current == NULL) {
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
void pre_order_traversal(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL) {
printf("%d ",root->data);
pre_order_traversal(root->leftChild);
pre_order_traversal(root->rightChild);
}
}
void inorder_traversal(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL) {
inorder_traversal(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ",root->data);
inorder_traversal(root->rightChild);
}
}
void post_order_traversal(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL) {
post_order_traversal(root->leftChild);
post_order_traversal(root->rightChild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
}
}
int main(){
int i;
int array[7] = { 27, 14, 35, 10, 19, 31, 42 };
for(i = 0; i < 7; i++)
insert(array[i]);
printf("\nPreorder traversal: ");
pre_order_traversal(root);
printf("\nInorder traversal: ");
inorder_traversal(root);
printf("\nPost order traversal: ");
post_order_traversal(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
Preorder traversal: 27 14 10 19 35 31 42 Inorder traversal: 10 14 19 27 31 35 42 Post order traversal: 10 19 14 31 42 35 27
#include <iostream>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild;
struct node *rightChild;
};
struct node *root = NULL;
void insert(int data){
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//if tree is empty
if(root == NULL) {
root = tempNode;
} else {
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1) {
parent = current;
//go to left of the tree
if(data < parent->data) {
current = current->leftChild;
//insert to the left
if(current == NULL) {
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}//go to right of the tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
//insert to the right
if(current == NULL) {
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
void pre_order_traversal(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL) {
printf("%d ",root->data);
pre_order_traversal(root->leftChild);
pre_order_traversal(root->rightChild);
}
}
void inorder_traversal(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL) {
inorder_traversal(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ",root->data);
inorder_traversal(root->rightChild);
}
}
void post_order_traversal(struct node* root){
if(root != NULL) {
post_order_traversal(root->leftChild);
post_order_traversal(root->rightChild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
}
}
int main(){
int i;
int array[7] = { 27, 14, 35, 10, 19, 31, 42 };
for(i = 0; i < 7; i++)
insert(array[i]);
printf("\nPreorder traversal: ");
pre_order_traversal(root);
printf("\nInorder traversal: ");
inorder_traversal(root);
printf("\nPost order traversal: ");
post_order_traversal(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
Preorder traversal: 27 14 10 19 35 31 42 Inorder traversal: 10 14 19 27 31 35 42 Post order traversal: 10 19 14 31 42 35 27
class Node {
int data;
Node leftChild;
Node rightChild;
public Node(int key) {
data = key;
leftChild = rightChild = null;
}
}
public class TreeDataStructure {
Node root = null;
void inorder_traversal(Node node) {
if(node != null) {
inorder_traversal(node.leftChild);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
inorder_traversal(node.rightChild);
}
}
void pre_order_traversal(Node node) {
if(node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
pre_order_traversal(node.leftChild);
pre_order_traversal(node.rightChild);
}
}
void post_order_traversal(Node node) {
if(node != null) {
post_order_traversal(node.leftChild);
post_order_traversal(node.rightChild);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
TreeDataStructure tree = new TreeDataStructure();
tree.root = new Node(27);
tree.root.leftChild = new Node(12);
tree.root.rightChild = new Node(3);
tree.root.leftChild.leftChild = new Node(44);
tree.root.leftChild.rightChild = new Node(17);
tree.root.rightChild.leftChild = new Node(56);
System.out.println("\nInorder traversal: ");
tree.inorder_traversal(tree.root);
System.out.println("\nPreorder traversal: ");
tree.pre_order_traversal(tree.root);
System.out.println("\nPost order traversal: ");
tree.post_order_traversal(tree.root);
}
}
輸出
Inorder traversal: 44 12 17 27 56 3 Preorder traversal: 27 12 44 17 3 56 Post order traversal: 44 17 12 56 3 27
class Node:
def __init__(self, key):
self.leftChild = None
self.rightChild = None
self.data = key
# Create a function to perform inorder tree traversal
def InorderTraversal(root):
if root:
InorderTraversal(root.leftChild)
print(root.data)
InorderTraversal(root.rightChild)
# Create a function to perform preorder tree traversal
def PostorderTraversal(root):
if root:
PostorderTraversal(root.leftChild)
PostorderTraversal(root.rightChild)
print(root.data)
# Create a function to perform postorder tree traversal
def PreorderTraversal(root):
if root:
print(root.data)
PreorderTraversal(root.leftChild)
PreorderTraversal(root.rightChild)
# Main class
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = Node(3)
root.leftChild = Node(26)
root.rightChild = Node(42)
root.leftChild.leftChild = Node(54)
root.leftChild.rightChild = Node(65)
root.rightChild.leftChild = Node(12)
# Function call
print("\nInorder traversal of binary tree is")
InorderTraversal(root)
print("\nPreorder traversal of binary tree is")
PreorderTraversal(root)
print("\nPostorder traversal of binary tree is")
PostorderTraversal(root)
輸出
Inorder traversal of binary tree is 54 26 65 3 12 42 Preorder traversal of binary tree is 3 26 54 65 42 12 Postorder traversal of binary tree is 54 65 26 12 42 3
二叉搜尋樹
二叉搜尋樹 (BST) 是一棵樹,其中所有節點都遵循以下屬性:
節點的左子樹的鍵小於或等於其父節點的鍵。
節點的右子樹的鍵大於或等於其父節點的鍵。
因此,BST 將所有子樹劃分為兩個部分:左子樹和右子樹,並且可以定義為:
left_subtree (keys) ≤ node (key) ≤ right_subtree (keys)
表示
BST 是一組以某種方式排列的節點,它們保持 BST 屬性。每個節點都有一個鍵和一個關聯的值。在搜尋時,將所需的鍵與 BST 中的鍵進行比較,如果找到,則檢索關聯的值。
以下是 BST 的圖形表示:

我們觀察到根節點鍵 (27) 在左子樹上具有所有較小值的鍵,在右子樹上具有較高值的鍵。
基本操作
以下是樹的基本操作:
搜尋 - 在樹中搜索元素。
插入 - 在樹中插入元素。
前序遍歷 - 以前序方式遍歷樹。
中序遍歷 - 以中序方式遍歷樹。
後序遍歷 - 以後序方式遍歷樹。
定義節點
定義一個節點,它儲存一些資料,以及對其左右子節點的引用。
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild;
struct node *rightChild;
};
搜尋操作
每當要搜尋元素時,都從根節點開始搜尋。然後,如果資料小於鍵值,則在左子樹中搜索元素。否則,在右子樹中搜索元素。對每個節點遵循相同的演算法。
演算法
1. START 2. Check whether the tree is empty or not 3. If the tree is empty, search is not possible 4. Otherwise, first search the root of the tree. 5. If the key does not match with the value in the root, search its subtrees. 6. If the value of the key is less than the root value, search the left subtree 7. If the value of the key is greater than the root value, search the right subtree. 8. If the key is not found in the tree, return unsuccessful search. 9. END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild, *rightChild;
};
struct node *root = NULL;
struct node *newNode(int item){
struct node *temp = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
temp->data = item;
temp->leftChild = temp->rightChild = NULL;
return temp;
}
void insert(int data){
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//if tree is empty
if(root == NULL) {
root = tempNode;
} else {
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1) {
parent = current;
//go to left of the tree
if(data < parent->data) {
current = current->leftChild;
//insert to the left
if(current == NULL) {
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}//go to right of the tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
//insert to the right
if(current == NULL) {
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
struct node* search(int data){
struct node *current = root;
printf("\nVisiting elements: ");
while(current->data != data) {
if(current != NULL) {
printf("%d ",current->data);
//go to left tree
if(current->data > data) {
current = current->leftChild;
}//else go to right tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
}
//not found
if(current == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
}
}
return current;
}
void printTree(struct node* Node){
if(Node == NULL)
return;
printTree(Node->leftChild);
printf(" --%d", Node->data);
printTree(Node->rightChild);
}
int main(){
insert(55);
insert(20);
insert(90);
insert(50);
insert(35);
insert(15);
insert(65);
printf("Insertion done\n");
printTree(root);
struct node* k;
k = search(35);
if(k != NULL)
printf("\nElement %d found", k->data);
else
printf("\nElement not found");
return 0;
}
輸出
Insertion done --15 --20 --35 --50 --55 --65 --90 Visiting elements: 55 20 50 Element 35 found
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild, *rightChild;
};
struct node *root = NULL;
struct node *newNode(int item){
struct node *temp = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
temp->data = item;
temp->leftChild = temp->rightChild = NULL;
return temp;
}
void insert(int data){
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//if tree is empty
if(root == NULL) {
root = tempNode;
} else {
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1) {
parent = current;
//go to left of the tree
if(data < parent->data) {
current = current->leftChild;
//insert to the left
if(current == NULL) {
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}//go to right of the tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
//insert to the right
if(current == NULL) {
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
struct node* search(int data){
struct node *current = root;
printf("\nVisiting elements: ");
while(current->data != data) {
if(current != NULL) {
printf("%d ",current->data);
//go to left tree
if(current->data > data) {
current = current->leftChild;
}//else go to right tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
}
//not found
if(current == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
}
}
return current;
}
void printTree(struct node* Node){
if(Node == NULL)
return;
printTree(Node->leftChild);
printf(" --%d", Node->data);
printTree(Node->rightChild);
}
int main(){
insert(55);
insert(20);
insert(90);
insert(50);
insert(35);
insert(15);
insert(65);
printf("Insertion done\n");
printTree(root);
struct node* k;
k = search(35);
if(k != NULL)
printf("\nElement %d found", k->data);
else
printf("\nElement not found");
return 0;
}
輸出
Insertion done --15 --20 --35 --50 --55 --65 --90 Visiting elements: 55 20 50 Element 35 found
import java.util.Scanner;
class BSTNode {
BSTNode left, right;
int data;
public BSTNode(int n) {
left = null;
right = null;
data = n;
}
}
public class BST {
static BSTNode root;
public BST() {
root = null;
}
private BSTNode insert(BSTNode node, int data) {
if(node == null)
node = new BSTNode(data);
else {
if(data <= node.data)
node.left = insert(node.left, data);
else
node.right = insert(node.right, data);
}
return node;
}
private boolean search(BSTNode r, int val) {
boolean found = false;
while ((r != null) && !found) {
int rval = r.data;
if(val < rval)
r = r.left;
else if (val > rval)
r = r.right;
else {
found = true;
break;
}
found = search(r, val);
}
return found;
}
void printTree(BSTNode node, String prefix) {
if(node == null)
return;
printTree(node.left , " " + prefix);
System.out.println(prefix + "--" + node.data);
printTree(node.right , prefix + " ");
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
BST bst = new BST();
root = bst.insert(root, 55);
root = bst.insert(root, 20);
root = bst.insert(root, 90);
root = bst.insert(root, 80);
root = bst.insert(root, 50);
root = bst.insert(root, 35);
root = bst.insert(root, 15);
root = bst.insert(root, 65);
bst.printTree(root, " ");
System.out.println("Element found = " + bst.search(root, 80));
}
}
輸出
--15
--20--35
--50
--55
--65
--80
--90
Element found = true
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.data = data
# Insert method to create nodes
def insert(self, data):
if self.data:
if data < self.data:
if self.left is None:
self.left = Node(data)
else:
self.left.insert(data)
elif data > self.data:
if self.right is None:
self.right = Node(data)
else:
self.right.insert(data)
else:
self.data = data
# search method to compare the value with nodes
def search(self, key):
if key < self.data:
if self.left is None:
return str(key)+" Not Found"
return self.left.search(key)
elif key > self.data:
if self.right is None:
return str(key)+" Not Found"
return self.right.search(key)
else:
print(str(self.data) + ' is found')
root = Node(54)
root.insert(34)
root.insert(46)
root.insert(12)
root.insert(23)
root.insert(5)
print(root.search(17))
print(root.search(12))
輸出
17 Not Found 12 is found None
插入操作
每當要插入元素時,首先找到其正確的位置。從根節點開始搜尋,然後,如果資料小於鍵值,則在左子樹中搜索空位置並插入資料。否則,在右子樹中搜索空位置並插入資料。
演算法
1 – START 2 – If the tree is empty, insert the first element as the root node of the tree. The following elements are added as the leaf nodes. 3 – If an element is less than the root value, it is added into the left subtree as a leaf node. 4 – If an element is greater than the root value, it is added into the right subtree as a leaf node. 5 – The final leaf nodes of the tree point to NULL values as their child nodes. 6 – END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild, *rightChild;
};
struct node *root = NULL;
struct node *newNode(int item){
struct node *temp = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
temp->data = item;
temp->leftChild = temp->rightChild = NULL;
return temp;
}
void insert(int data){
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//if tree is empty
if(root == NULL) {
root = tempNode;
} else {
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1) {
parent = current;
//go to left of the tree
if(data < parent->data) {
current = current->leftChild;
//insert to the left
if(current == NULL) {
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}//go to right of the tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
//insert to the right
if(current == NULL) {
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
void printTree(struct node* Node){
if(Node == NULL)
return;
printTree(Node->leftChild);
printf(" --%d", Node->data);
printTree(Node->rightChild);
}
int main(){
insert(55);
insert(20);
insert(90);
insert(50);
insert(35);
insert(15);
insert(65);
printf("Insertion done\n");
printTree(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
Insertion done --15 --20 --35 --50 --55 --65 --90
#include <iostream>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild, *rightChild;
};
struct node *root = NULL;
struct node *newNode(int item){
struct node *temp = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
temp->data = item;
temp->leftChild = temp->rightChild = NULL;
return temp;
}
void insert(int data){
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//if tree is empty
if(root == NULL) {
root = tempNode;
} else {
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1) {
parent = current;
//go to left of the tree
if(data < parent->data) {
current = current->leftChild;
//insert to the left
if(current == NULL) {
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}//go to right of the tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
//insert to the right
if(current == NULL) {
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
void printTree(struct node* Node){
if(Node == NULL)
return;
printTree(Node->leftChild);
printf(" --%d", Node->data);
printTree(Node->rightChild);
}
int main(){
insert(55);
insert(20);
insert(90);
insert(50);
insert(35);
insert(15);
insert(65);
printf("Insertion done\n");
printTree(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
Insertion done --15 --20 --35 --50 --55 --65 --90
import java.util.Scanner;
class BSTNode {
BSTNode left, right;
int data;
public BSTNode(int n) {
left = null;
right = null;
data = n;
}
}
public class BST {
static BSTNode root;
public BST() {
root = null;
}
private BSTNode insert(BSTNode node, int data) {
if(node == null)
node = new BSTNode(data);
else {
if(data <= node.data)
node.left = insert(node.left, data);
else
node.right = insert(node.right, data);
}
return node;
}
void printTree(BSTNode node, String prefix) {
if(node == null)
return;
printTree(node.left , " " + prefix);
System.out.println(prefix + "--" + node.data);
printTree(node.right , prefix + " ");
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
BST bst = new BST();
root = bst.insert(root, 55);
root = bst.insert(root, 20);
root = bst.insert(root, 90);
root = bst.insert(root, 80);
root = bst.insert(root, 50);
root = bst.insert(root, 35);
root = bst.insert(root, 15);
root = bst.insert(root, 65);
bst.printTree(root, " ");
}
}
輸出
--15
--20
--35
--50
--55
--65
--80
--90
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.data = data
# Insert method to create nodes
def insert(self, data):
if self.data:
if data < self.data:
if self.left is None:
self.left = Node(data)
else:
self.left.insert(data)
elif data > self.data:
if self.right is None:
self.right = Node(data)
else:
self.right.insert(data)
else:
self.data = data
root = Node(54)
root.insert(34)
root.insert(46)
root.insert(12)
root.insert(23)
root.insert(5)
print("Insertion Done")
輸出
Insertion Done
中序遍歷
二叉搜尋樹中的中序遍歷操作按以下順序訪問其所有節點:
首先,我們遍歷根節點/當前節點的左子節點(如果有)。
接下來,遍歷當前節點。
最後,遍歷當前節點的右子節點(如果有)。
演算法
1. START 2. Traverse the left subtree, recursively 3. Then, traverse the root node 4. Traverse the right subtree, recursively. 5. END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int key;
struct node *left, *right;
};
struct node *newNode(int item){
struct node *temp = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
temp->key = item;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Inorder Traversal
void inorder(struct node *root){
if (root != NULL) {
inorder(root->left);
printf("%d -> ", root->key);
inorder(root->right);
}
}
// Insertion operation
struct node *insert(struct node *node, int key){
if (node == NULL) return newNode(key);
if (key < node->key)
node->left = insert(node->left, key);
else
node->right = insert(node->right, key);
return node;
}
int main(){
struct node *root = NULL;
root = insert(root, 55);
root = insert(root, 20);
root = insert(root, 90);
root = insert(root, 50);
root = insert(root, 35);
root = insert(root, 15);
root = insert(root, 65);
printf("Inorder traversal: ");
inorder(root);
}
輸出
Inorder traversal: 15 -> 20 -> 35 -> 50 -> 55 -> 65 -> 90 ->
#include <iostream>
struct node {
int key;
struct node *left, *right;
};
struct node *newNode(int item){
struct node *temp = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
temp->key = item;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Inorder Traversal
void inorder(struct node *root){
if (root != NULL) {
inorder(root->left);
printf("%d -> ", root->key);
inorder(root->right);
}
}
// Insertion operation
struct node *insert(struct node *node, int key){
if (node == NULL) return newNode(key);
if (key < node->key)
node->left = insert(node->left, key);
else
node->right = insert(node->right, key);
return node;
}
int main(){
struct node *root = NULL;
root = insert(root, 55);
root = insert(root, 20);
root = insert(root, 90);
root = insert(root, 50);
root = insert(root, 35);
root = insert(root, 15);
root = insert(root, 65);
printf("Inorder traversal: ");
inorder(root);
}
輸出
Inorder traversal: 15 -> 20 -> 35 -> 50 -> 55 -> 65 -> 90 ->
class Node {
int data;
Node leftChild;
Node rightChild;
public Node(int key) {
data = key;
leftChild = rightChild = null;
}
}
public class TreeDataStructure {
Node root = null;
void inorder_traversal(Node node) {
if(node != null) {
inorder_traversal(node.leftChild);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
inorder_traversal(node.rightChild);
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
TreeDataStructure tree = new TreeDataStructure();
tree.root = new Node(27);
tree.root.leftChild = new Node(12);
tree.root.rightChild = new Node(30);
tree.root.leftChild.leftChild = new Node(4);
tree.root.leftChild.rightChild = new Node(17);
tree.root.rightChild.leftChild = new Node(56);
System.out.println("\nInorder traversal: ");
tree.inorder_traversal(tree.root);
}
}
輸出
Inorder traversal: 4 12 17 27 56 30
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.data = data
# Insert method to create nodes
def insert(self, data):
if self.data:
if data < self.data:
if self.left is None:
self.left = Node(data)
else:
self.left.insert(data)
elif data > self.data:
if self.right is None:
self.right = Node(data)
else:
self.right.insert(data)
else:
self.data = data
# Print the tree
def Inorder(self):
if self.left:
self.left.Inorder()
print(self.data)
if self.right:
self.right.Inorder()
root = Node(54)
root.insert(34)
root.insert(46)
root.insert(12)
root.insert(23)
root.insert(5)
print("Inorder Traversal of Binary Search Tree: ")
root.Inorder()
輸出
Inorder Traversal of Binary Search Tree: 12 34 54
前序遍歷
二叉搜尋樹中的先序遍歷操作會訪問其所有節點。但是,它首先列印根節點,然後列印其左子樹,最後列印其右子樹。
演算法
1. START 2. Traverse the root node first. 3. Then traverse the left subtree, recursively 4. Later, traverse the right subtree, recursively. 5. END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int key;
struct node *left, *right;
};
struct node *newNode(int item){
struct node *temp = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
temp->key = item;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Preorder Traversal
void preorder(struct node *root){
if (root != NULL) {
printf("%d -> ", root->key);
preorder(root->left);
preorder(root->right);
}
}
// Insertion operation
struct node *insert(struct node *node, int key){
if (node == NULL) return newNode(key);
if (key < node->key)
node->left = insert(node->left, key);
else
node->right = insert(node->right, key);
return node;
}
int main(){
struct node *root = NULL;
root = insert(root, 55);
root = insert(root, 20);
root = insert(root, 90);
root = insert(root, 50);
root = insert(root, 35);
root = insert(root, 15);
root = insert(root, 65);
printf("Preorder traversal: ");
preorder(root);
}
輸出
Preorder traversal: 55 -> 20 -> 15 -> 50 -> 35 -> 90 -> 65 ->
#include <iostream>
struct node {
int key;
struct node *left, *right;
};
struct node *newNode(int item){
struct node *temp = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
temp->key = item;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Preorder Traversal
void preorder(struct node *root){
if (root != NULL) {
printf("%d -> ", root->key);
preorder(root->left);
preorder(root->right);
}
}
// Insertion operation
struct node *insert(struct node *node, int key){
if (node == NULL) return newNode(key);
if (key < node->key)
node->left = insert(node->left, key);
else
node->right = insert(node->right, key);
return node;
}
int main(){
struct node *root = NULL;
root = insert(root, 55);
root = insert(root, 20);
root = insert(root, 90);
root = insert(root, 50);
root = insert(root, 35);
root = insert(root, 15);
root = insert(root, 65);
printf("Preorder traversal: ");
preorder(root);
}
輸出
Preorder traversal: 55 -> 20 -> 15 -> 50 -> 35 -> 90 -> 65 ->
class Node {
int data;
Node leftChild;
Node rightChild;
public Node(int key) {
data = key;
leftChild = rightChild = null;
}
}
public class TreeDataStructure {
Node root = null;
void preorder_traversal(Node node) {
if(node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
preorder_traversal(node.leftChild);
preorder_traversal(node.rightChild);
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
TreeDataStructure tree = new TreeDataStructure();
tree.root = new Node(27);
tree.root.leftChild = new Node(12);
tree.root.rightChild = new Node(30);
tree.root.leftChild.leftChild = new Node(4);
tree.root.leftChild.rightChild = new Node(17);
tree.root.rightChild.leftChild = new Node(56);
System.out.println("\nPreorder traversal: ");
tree.preorder_traversal(tree.root);
}
}
輸出
Preorder traversal: 27 12 4 17 30 56
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.data = data
# Insert method to create nodes
def insert(self, data):
if self.data:
if data < self.data:
if self.left is None:
self.left = Node(data)
else:
self.left.insert(data)
elif data > self.data:
if self.right is None:
self.right = Node(data)
else:
self.right.insert(data)
else:
self.data = data
# Print the tree
def Preorder(self):
print(self.data)
if self.left:
self.left.Preorder()
if self.right:
self.right.Preorder()
root = Node(54)
root.insert(34)
root.insert(46)
root.insert(12)
root.insert(23)
root.insert(5)
print("Preorder Traversal of Binary Search Tree: ")
root.Preorder()
輸出
Preorder Traversal of Binary Search Tree: 54 34 12 5 23 46
後序遍歷
與其他遍歷一樣,後序遍歷也會訪問二叉搜尋樹中的所有節點並顯示它們。但是,它首先列印左子樹,然後列印右子樹,最後列印根節點。
演算法
1. START 2. Traverse the left subtree, recursively 3. Traverse the right subtree, recursively. 4. Then, traverse the root node 5. END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int key;
struct node *left, *right;
};
struct node *newNode(int item){
struct node *temp = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
temp->key = item;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Postorder Traversal
void postorder(struct node *root){
if (root != NULL) {
printf("%d -> ", root->key);
postorder(root->left);
postorder(root->right);
}
}
// Insertion operation
struct node *insert(struct node *node, int key){
if (node == NULL) return newNode(key);
if (key < node->key)
node->left = insert(node->left, key);
else
node->right = insert(node->right, key);
return node;
}
int main(){
struct node *root = NULL;
root = insert(root, 55);
root = insert(root, 20);
root = insert(root, 90);
root = insert(root, 50);
root = insert(root, 35);
root = insert(root, 15);
root = insert(root, 65);
printf("Postorder traversal: ");
postorder(root);
}
輸出
Postorder traversal: 55 -> 20 -> 15 -> 50 -> 35 -> 90 > 65 ->
#include <iostream>
struct node {
int key;
struct node *left, *right;
};
struct node *newNode(int item){
struct node *temp = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
temp->key = item;
temp->left = temp->right = NULL;
return temp;
}
// Postorder Traversal
void postorder(struct node *root){
if (root != NULL) {
printf("%d -> ", root->key);
postorder(root->left);
postorder(root->right);
}
}
// Insertion operation
struct node *insert(struct node *node, int key){
if (node == NULL) return newNode(key);
if (key < node->key)
node->left = insert(node->left, key);
else
node->right = insert(node->right, key);
return node;
}
int main(){
struct node *root = NULL;
root = insert(root, 55);
root = insert(root, 20);
root = insert(root, 90);
root = insert(root, 50);
root = insert(root, 35);
root = insert(root, 15);
root = insert(root, 65);
printf("Postorder traversal: ");
postorder(root);
}
輸出
Postorder traversal: 55 -> 20 -> 15 -> 50 -> 35 -> 90 -> 65 ->
class Node {
int data;
Node leftChild;
Node rightChild;
public Node(int key) {
data = key;
leftChild = rightChild = null;
}
}
public class TreeDataStructure {
Node root = null;
void postorder_traversal(Node node) {
if(node != null) {
postorder_traversal(node.leftChild);
postorder_traversal(node.rightChild);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
TreeDataStructure tree = new TreeDataStructure();
tree.root = new Node(27);
tree.root.leftChild = new Node(12);
tree.root.rightChild = new Node(30);
tree.root.leftChild.leftChild = new Node(4);
tree.root.leftChild.rightChild = new Node(17);
tree.root.rightChild.leftChild = new Node(56);
System.out.println("\nPostorder traversal: ");
tree.postorder_traversal(tree.root);
}
}
輸出
Postorder traversal: 4 17 12 56 30 27
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.data = data
# Insert method to create nodes
def insert(self, data):
if self.data:
if data < self.data:
if self.left is None:
self.left = Node(data)
else:
self.left.insert(data)
elif data > self.data:
if self.right is None:
self.right = Node(data)
else:
self.right.insert(data)
else:
self.data = data
# Print the tree
def Postorder(self):
if self.left:
self.left.Postorder()
if self.right:
self.right.Postorder()
print(self.data)
root = Node(54)
root.insert(34)
root.insert(46)
root.insert(12)
root.insert(23)
root.insert(5)
print("Postorder Traversal of Binary Search Tree: ")
root.Postorder()
輸出
Postorder Traversal of Binary Search Tree: 5 23 12 46 34 54
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild, *rightChild;
};
struct node *root = NULL;
struct node *newNode(int item){
struct node *temp = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
temp->data = item;
temp->leftChild = temp->rightChild = NULL;
return temp;
}
void insert(int data){
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//if tree is empty
if(root == NULL) {
root = tempNode;
} else {
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1) {
parent = current;
//go to left of the tree
if(data < parent->data) {
current = current->leftChild;
//insert to the left
if(current == NULL) {
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}//go to right of the tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
//insert to the right
if(current == NULL) {
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
struct node* search(int data){
struct node *current = root;
printf("\n\nVisiting elements: ");
while(current->data != data) {
if(current != NULL) {
printf("%d ",current->data);
//go to left tree
if(current->data > data) {
current = current->leftChild;
}//else go to right tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
}
//not found
if(current == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
}
}
return current;
}
// Inorder Traversal
void inorder(struct node *root){
if (root != NULL) {
inorder(root->leftChild);
printf("%d -> ", root->data);
inorder(root->rightChild);
}
}
// Preorder Traversal
void preorder(struct node *root){
if (root != NULL) {
printf("%d -> ", root->data);
preorder(root->leftChild);
preorder(root->rightChild);
}
}
// Postorder Traversal
void postorder(struct node *root){
if (root != NULL) {
printf("%d -> ", root->data);
postorder(root->leftChild);
postorder(root->rightChild);
}
}
int main(){
insert(55);
insert(20);
insert(90);
insert(50);
insert(35);
insert(15);
insert(65);
printf("Insertion done\n");
printf("\nPreorder Traversal: ");
preorder(root);
printf("\nInorder Traversal: ");
inorder(root);
printf("\nPostorder Traversal: ");
postorder(root);
struct node* k;
k = search(35);
if(k != NULL)
printf("\nElement %d found", k->data);
else
printf("\nElement not found");
return 0;
}
輸出
Insertion done Preorder Traversal: 55 -> 20 -> 15 -> 50 -> 35 -> 90 -> 65 -> Inorder Traversal: 15 -> 20 -> 35 -> 50 -> 55 -> 65 -> 90 -> Postorder Traversal: 55 -> 20 -> 15 -> 50 -> 35 -> 90 -> 65 -> Visiting elements: 55 20 50 Element 35 found
#include <iostream>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild, *rightChild;
};
struct node *root = NULL;
struct node *newNode(int item){
struct node *temp = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
temp->data = item;
temp->leftChild = temp->rightChild = NULL;
return temp;
}
void insert(int data){
struct node *tempNode = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
struct node *current;
struct node *parent;
tempNode->data = data;
tempNode->leftChild = NULL;
tempNode->rightChild = NULL;
//if tree is empty
if(root == NULL) {
root = tempNode;
} else {
current = root;
parent = NULL;
while(1) {
parent = current;
//go to left of the tree
if(data < parent->data) {
current = current->leftChild;
//insert to the left
if(current == NULL) {
parent->leftChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}//go to right of the tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
//insert to the right
if(current == NULL) {
parent->rightChild = tempNode;
return;
}
}
}
}
}
struct node* search(int data){
struct node *current = root;
printf("\n\nVisiting elements: ");
while(current->data != data) {
if(current != NULL) {
printf("%d ",current->data);
//go to left tree
if(current->data > data) {
current = current->leftChild;
}//else go to right tree
else {
current = current->rightChild;
}
//not found
if(current == NULL) {
return NULL;
}
}
}
return current;
}
// Inorder Traversal
void inorder(struct node *root){
if (root != NULL) {
inorder(root->leftChild);
printf("%d -> ", root->data);
inorder(root->rightChild);
}
}
// Preorder Traversal
void preorder(struct node *root){
if (root != NULL) {
printf("%d -> ", root->data);
preorder(root->leftChild);
preorder(root->rightChild);
}
}
// Postorder Traversal
void postorder(struct node *root){
if (root != NULL) {
printf("%d -> ", root->data);
postorder(root->leftChild);
postorder(root->rightChild);
}
}
int main(){
insert(55);
insert(20);
insert(90);
insert(50);
insert(35);
insert(15);
insert(65);
printf("Insertion done\n");
printf("\nPreorder Traversal: ");
preorder(root);
printf("\nInorder Traversal: ");
inorder(root);
printf("\nPostorder Traversal: ");
postorder(root);
struct node* k;
k = search(35);
if(k != NULL)
printf("\nElement %d found", k->data);
else
printf("\nElement not found");
return 0;
}
輸出
Insertion done Preorder Traversal: 55 -> 20 -> 15 -> 50 -> 35 -> 90 -> 65 -> Inorder Traversal: 15 -> 20 -> 35 -> 50 -> 55 -> 65 -> 90 -> Postorder Traversal: 55 -> 20 -> 15 -> 50 -> 35 -> 90 -> 65 -> Visiting elements: 55 20 50 Element 35 found
import java.util.Scanner;
class BSTNode {
BSTNode left, right;
int data;
public BSTNode(int n) {
left = null;
right = null;
data = n;
}
}
public class BST {
static BSTNode root;
public BST() {
root = null;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return root == null;
}
private BSTNode insert(BSTNode node, int data) {
if(node == null)
node = new BSTNode(data);
else {
if(data <= node.data)
node.left = insert(node.left, data);
else
node.right = insert(node.right, data);
}
return node;
}
public void delete(int k) {
if(isEmpty ())
System.out.println("TREE EMPTY");
else if(search (k) == false)
System.out.println("SORRY " + k + " IS NOT PRESENT");
else {
root=delete(root,k);
System.out.println(k + " DELETED FROM THE TREE");
}
}
public BSTNode delete(BSTNode root, int k) {
BSTNode p, p2, n;
if(root.data == k) {
BSTNode lt, rt;
lt = root.left;
rt = root.right;
if(lt == null && rt == null) {
return null;
} else if(lt == null) {
p = rt;
return p;
} else if(rt == null) {
p = lt;
return p;
} else {
p2 = rt;
p = rt;
while(p.left != null)
p = p.left;
p.left = lt;
return p2;
}
}
if (k < root.data) {
n = delete(root.left, k);
root.left = n;
} else {
n = delete(root.right, k);
root.right = n;
}
return root;
}
public boolean search(int val) {
return search(root, val);
}
private boolean search(BSTNode r, int val) {
boolean found = false;
while ((r != null) && !found) {
int rval = r.data;
if(val < rval)
r = r.left;
else if (val > rval)
r = r.right;
else {
found = true;
break;
}
found = search(r, val);
}
return found;
}
void printTree(BSTNode node, String prefix) {
if(node == null)
return;
printTree(node.left , " " + prefix);
System.out.println(prefix + "--" + node.data);
printTree(node.right , prefix + " ");
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
BST bst = new BST();
root = bst.insert(root, 55);
root = bst.insert(root, 20);
root = bst.insert(root, 90);
root = bst.insert(root, 80);
root = bst.insert(root, 50);
root = bst.insert(root, 35);
root = bst.insert(root, 15);
root = bst.insert(root, 65);
bst.printTree(root, " ");
bst.delete(55);
System.out.println("Element found = " + bst.search(80));
System.out.println("Is Tree Empty? " + bst.isEmpty());
}
}
輸出
--15
--20--35
--50
--55
--65
--80
--90
55 DELETED FROM THE TREE
Element found = true
Is Tree Empty? false
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.data = data
# Insert method to create nodes
def insert(self, data):
if self.data:
if data < self.data:
if self.left is None:
self.left = Node(data)
else:
self.left.insert(data)
elif data > self.data:
if self.right is None:
self.right = Node(data)
else:
self.right.insert(data)
else:
self.data = data
# search method to compare the value with nodes
def search(self, key):
if key < self.data:
if self.left is None:
return str(key)+" Not Found"
return self.left.search(key)
elif key > self.data:
if self.right is None:
return str(key)+" Not Found"
return self.right.search(key)
else:
print(str(self.data) + ' is found')
# Print the tree
def Inorder(self):
if self.left:
self.left.Inorder()
print(self.data)
if self.right:
self.right.Inorder()
# Print the tree
def Preorder(self):
print(self.data)
if self.left:
self.left.Preorder()
if self.right:
self.right.Preorder()
# Print the tree
def Postorder(self):
if self.left:
self.left.Postorder()
if self.right:
self.right.Postorder()
print(self.data)
root = Node(54)
root.insert(34)
root.insert(46)
root.insert(12)
root.insert(23)
root.insert(5)
print("Preorder Traversal of Binary Search Tree: ")
root.Preorder()
print("Inorder Traversal of Binary Search Tree: ")
root.Inorder()
print("Postorder Traversal of Binary Search Tree: ")
root.Postorder()
print(root.search(17))
print(root.search(12))
輸出
Preorder Traversal of Binary Search Tree: 54 34 12 5 23 46 Inorder Traversal of Binary Search Tree: 5 12 23 34 46 54 Postorder Traversal of Binary Search Tree: 5 23 12 46 34 54 17 Not Found 12 is found None
AVL 樹
第一個被髮明的自平衡二叉搜尋樹是 AVL 樹。AVL 樹的名字來源於其發明者的名字——Adelson-Velsky 和 Landis。
在 AVL 樹中,左子樹和右子樹的高度差(稱為**平衡因子**)必須最多為 1。一旦差異超過 1,樹就會自動執行平衡演算法,直到差異再次變為 1。
BALANCE FACTOR = HEIGHT(LEFT SUBTREE) – HEIGHT(RIGHT SUBTREE)
AVL 樹的平衡演算法中通常有四種旋轉情況:LL、RR、LR、RL。
LL 旋轉
當節點插入到右子樹導致樹不平衡時,執行 LL 旋轉。這是一種單一的左旋轉,用於使樹再次平衡:
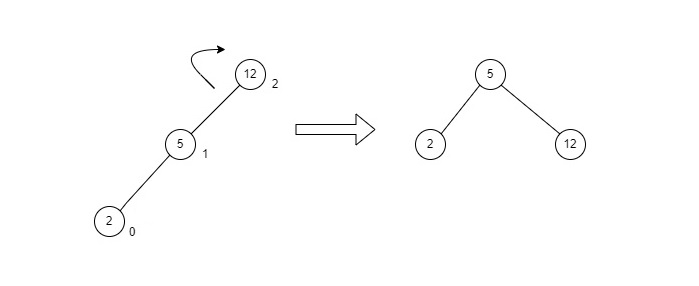
圖:LL 旋轉
發生不平衡的節點成為左子節點,新新增的節點成為右子節點,中間節點作為父節點。
RR 旋轉
當節點插入到左子樹導致樹不平衡時,執行 RR 旋轉。這是一種單一的右旋轉,用於使樹再次平衡:

圖:RR 旋轉
發生不平衡的節點成為右子節點,新新增的節點成為左子節點,中間節點作為父節點。
LR 旋轉
LR 旋轉是前面單旋轉的擴充套件版本,也稱為雙旋轉。當節點插入到左子樹的右子樹時執行。LR 旋轉是左旋轉後跟右旋轉的組合。執行此操作需要遵循多個步驟。
考慮一個示例,其中“A”作為根節點,“B”作為“A”的左子節點,“C”作為“B”的右子節點。
由於不平衡發生在 A 處,因此對 A 的子節點(即 B 和 C)應用左旋轉。
旋轉後,C 節點成為 A 的左子節點,B 成為 C 的左子節點。
不平衡仍然存在,因此在根節點 A 和左子節點 C 處應用右旋轉。
最終右旋轉後,C 成為根節點,A 成為右子節點,B 成為左子節點。
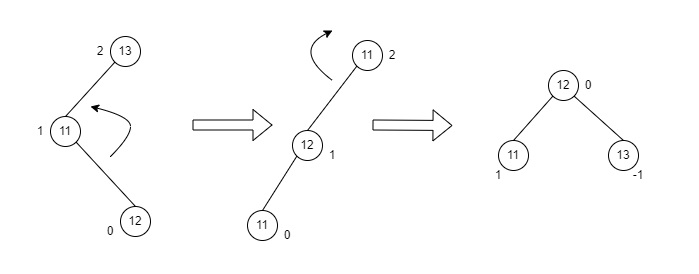
圖:LR 旋轉
RL 旋轉
RL 旋轉也是前面單旋轉的擴充套件版本,因此稱為雙旋轉,如果節點插入到右子樹的左子樹中,則執行。RL 旋轉是右旋轉後跟左旋轉的組合。執行此操作需要遵循多個步驟。
考慮一個示例,其中“A”作為根節點,“B”作為“A”的右子節點,“C”作為“B”的左子節點。
由於不平衡發生在 A 處,因此對 A 的子節點(即 B 和 C)應用右旋轉。
旋轉後,C 節點成為 A 的右子節點,B 成為 C 的右子節點。
不平衡仍然存在,因此在根節點 A 和右子節點 C 處應用左旋轉。
最終左旋轉後,C 成為根節點,A 成為左子節點,B 成為右子節點。

圖:RL 旋轉
AVL 樹的基本操作
在 AVL 樹結構上執行的基本操作包括在二叉搜尋樹上執行的所有操作,因為 AVL 樹在其核心實際上只是一個保持其所有屬性的二叉搜尋樹。因此,在 AVL 樹上執行的基本操作是——**插入**和**刪除**。
插入
透過遵循二叉搜尋樹的插入屬性將資料插入 AVL 樹,即左子樹必須包含小於根值的元素,右子樹必須包含所有大於的元素。但是,在 AVL 樹中,在插入每個元素後,會檢查樹的平衡因子;如果它不超過 1,則樹保持不變。但如果平衡因子超過 1,則會應用平衡演算法重新調整樹,使平衡因子再次小於或等於 1。
演算法
執行 AVL 樹的插入操作涉及以下步驟:
**步驟 1**——建立節點
**步驟 2**——檢查樹是否為空
**步驟 3**——如果樹為空,則建立的新節點將成為 AVL 樹的根節點。
**步驟 4**——如果樹不為空,我們執行二叉搜尋樹插入操作並檢查樹中節點的平衡因子。
**步驟 5**——假設平衡因子超過 ±1,我們對該節點應用合適的旋轉並從步驟 4 恢復插入。
START
if node == null then:
return new node
if key < node.key then:
node.left = insert (node.left, key)
else if (key > node.key) then:
node.right = insert (node.right, key)
else
return node
node.height = 1 + max (height (node.left), height (node.right))
balance = getBalance (node)
if balance > 1 and key < node.left.key then:
rightRotate
if balance < -1 and key > node.right.key then:
leftRotate
if balance > 1 and key > node.left.key then:
node.left = leftRotate (node.left)
rightRotate
if balance < -1 and key < node.right.key then:
node.right = rightRotate (node.right)
leftRotate (node)
return node
END
插入示例
讓我們透過構建一個包含 1 到 7 個整數的 AVL 樹示例來了解插入操作。
從第一個元素 1 開始,我們建立一個節點並測量平衡,即 0。

由於二叉搜尋屬性和平衡因子都滿足,因此我們將另一個元素插入到樹中。
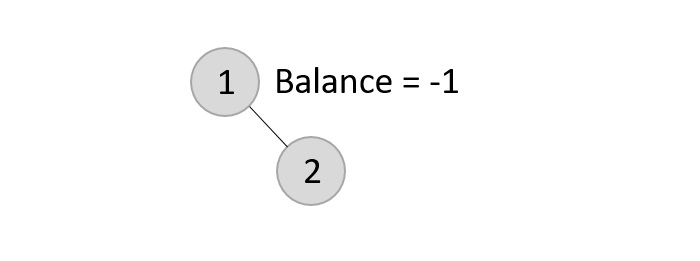
計算兩個節點的平衡因子,發現為 -1(左子樹的高度為 0,右子樹的高度為 1)。由於它不超過 1,因此我們將另一個元素新增到樹中。
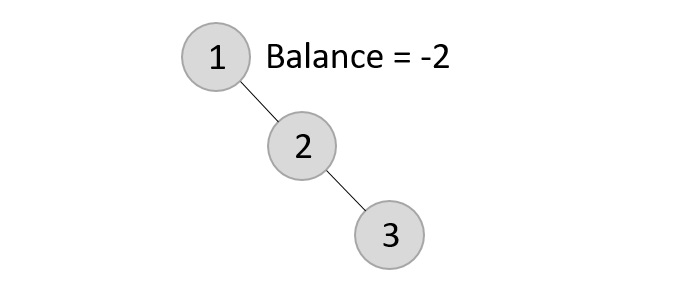
現在,新增第三個元素後,平衡因子超過 1 並變為 2。因此,應用旋轉。在這種情況下,應用 RR 旋轉,因為不平衡發生在兩個右節點上。
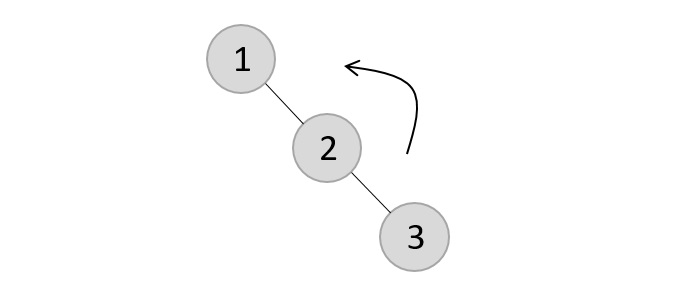
樹重新排列為:
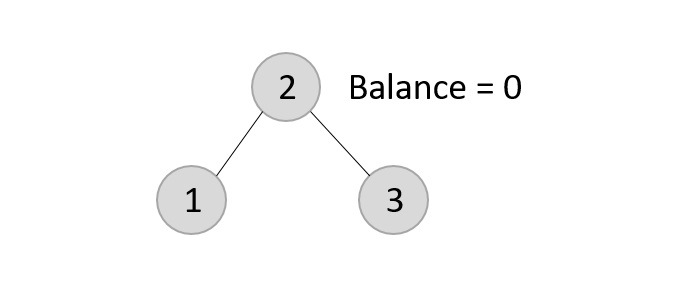
類似地,使用這些旋轉插入和重新排列後續元素。重新排列後,我們得到如下樹:
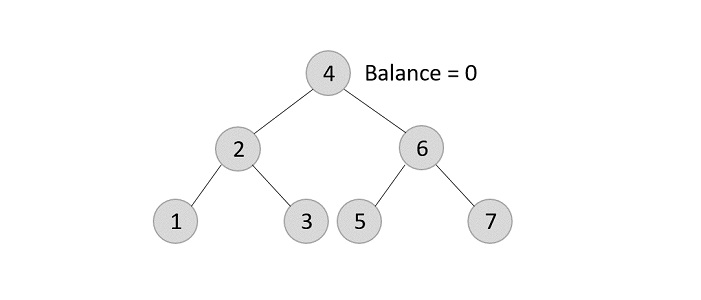
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *leftChild;
struct Node *rightChild;
int height;
};
int max(int a, int b);
int height(struct Node *N){
if (N == NULL)
return 0;
return N->height;
}
int max(int a, int b){
return (a > b) ? a : b;
}
struct Node *newNode(int data){
struct Node *node = (struct Node *) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
node->data = data;
node->leftChild = NULL;
node->rightChild = NULL;
node->height = 1;
return (node);
}
struct Node *rightRotate(struct Node *y){
struct Node *x = y->leftChild;
struct Node *T2 = x->rightChild;
x->rightChild = y;
y->leftChild = T2;
y->height = max(height(y->leftChild), height(y->rightChild)) + 1;
x->height = max(height(x->leftChild), height(x->rightChild)) + 1;
return x;
}
struct Node *leftRotate(struct Node *x){
struct Node *y = x->rightChild;
struct Node *T2 = y->leftChild;
y->leftChild = x;
x->rightChild = T2;
x->height = max(height(x->leftChild), height(x->rightChild)) + 1;
y->height = max(height(y->leftChild), height(y->rightChild)) + 1;
return y;
}
int getBalance(struct Node *N){
if (N == NULL)
return 0;
return height(N->leftChild) - height(N->rightChild);
}
struct Node *insertNode(struct Node *node, int data){
if (node == NULL)
return (newNode(data));
if (data < node->data)
node->leftChild = insertNode(node->leftChild, data);
else if (data > node->data)
node->rightChild = insertNode(node->rightChild, data);
else
return node;
node->height = 1 + max(height(node->leftChild),
height(node->rightChild));
int balance = getBalance(node);
if (balance > 1 && data < node->leftChild->data)
return rightRotate(node);
if (balance < -1 && data > node->rightChild->data)
return leftRotate(node);
if (balance > 1 && data > node->leftChild->data) {
node->leftChild = leftRotate(node->leftChild);
return rightRotate(node);
}
if (balance < -1 && data < node->rightChild->data) {
node->rightChild = rightRotate(node->rightChild);
return leftRotate(node);
}
return node;
}
struct Node *minValueNode(struct Node *node){
struct Node *current = node;
while (current->leftChild != NULL)
current = current->leftChild;
return current;
}
void printTree(struct Node *root){
if (root == NULL)
return;
if (root != NULL) {
printTree(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
printTree(root->rightChild);
}
}
int main(){
struct Node *root = NULL;
root = insertNode(root, 22);
root = insertNode(root, 14);
root = insertNode(root, 72);
root = insertNode(root, 44);
root = insertNode(root, 25);
root = insertNode(root, 63);
root = insertNode(root, 98);
printf("AVL Tree: ");
printTree(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
AVL Tree: 14 22 25 44 63 72 98
#include <iostream>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *leftChild;
struct Node *rightChild;
int height;
};
int max(int a, int b);
int height(struct Node *N){
if (N == NULL)
return 0;
return N->height;
}
int max(int a, int b){
return (a > b) ? a : b;
}
struct Node *newNode(int data){
struct Node *node = (struct Node *) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
node->data = data;
node->leftChild = NULL;
node->rightChild = NULL;
node->height = 1;
return (node);
}
struct Node *rightRotate(struct Node *y){
struct Node *x = y->leftChild;
struct Node *T2 = x->rightChild;
x->rightChild = y;
y->leftChild = T2;
y->height = max(height(y->leftChild), height(y->rightChild)) + 1;
x->height = max(height(x->leftChild), height(x->rightChild)) + 1;
return x;
}
struct Node *leftRotate(struct Node *x){
struct Node *y = x->rightChild;
struct Node *T2 = y->leftChild;
y->leftChild = x;
x->rightChild = T2;
x->height = max(height(x->leftChild), height(x->rightChild)) + 1;
y->height = max(height(y->leftChild), height(y->rightChild)) + 1;
return y;
}
int getBalance(struct Node *N){
if (N == NULL)
return 0;
return height(N->leftChild) - height(N->rightChild);
}
struct Node *insertNode(struct Node *node, int data){
if (node == NULL)
return (newNode(data));
if (data < node->data)
node->leftChild = insertNode(node->leftChild, data);
else if (data > node->data)
node->rightChild = insertNode(node->rightChild, data);
else
return node;
node->height = 1 + max(height(node->leftChild),
height(node->rightChild));
int balance = getBalance(node);
if (balance > 1 && data < node->leftChild->data)
return rightRotate(node);
if (balance < -1 && data > node->rightChild->data)
return leftRotate(node);
if (balance > 1 && data > node->leftChild->data) {
node->leftChild = leftRotate(node->leftChild);
return rightRotate(node);
}
if (balance < -1 && data < node->rightChild->data) {
node->rightChild = rightRotate(node->rightChild);
return leftRotate(node);
}
return node;
}
struct Node *minValueNode(struct Node *node){
struct Node *current = node;
while (current->leftChild != NULL)
current = current->leftChild;
return current;
}
void printTree(struct Node *root){
if (root == NULL)
return;
if (root != NULL) {
printTree(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
printTree(root->leftChild);
}
}
int main(){
struct Node *root = NULL;
root = insertNode(root, 22);
root = insertNode(root, 14);
root = insertNode(root, 72);
root = insertNode(root, 44);
root = insertNode(root, 25);
root = insertNode(root, 63);
root = insertNode(root, 98);
printf("AVL Tree: ");
printTree(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
AVL Tree: 14 22 14 44 14 22 14
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Node {
int key, height;
Node left, right;
Node (int d) {
key = d;
height = 1;
}
}
public class AVLTree {
Node root;
int height (Node N) {
if (N == null)
return 0;
return N.height;
}
int max (int a, int b) {
return (a > b) ? a : b;
}
Node rightRotate (Node y) {
Node x = y.left;
Node T2 = x.right;
x.right = y;
y.left = T2;
y.height = max (height (y.left), height (y.right)) + 1;
x.height = max (height (x.left), height (x.right)) + 1;
return x;
}
Node leftRotate (Node x) {
Node y = x.right;
Node T2 = y.left;
y.left = x;
x.right = T2;
x.height = max (height (x.left), height (x.right)) + 1;
y.height = max (height (y.left), height (y.right)) + 1;
return y;
}
int getBalance (Node N) {
if (N == null)
return 0;
return height (N.left) - height (N.right);
}
Node insert (Node node, int key) {
if (node == null)
return (new Node (key));
if (key < node.key)
node.left = insert (node.left, key);
else if (key > node.key)
node.right = insert (node.right, key);
else
return node;
node.height = 1 + max (height (node.left), height (node.right));
int balance = getBalance (node);
if (balance > 1 && key < node.left.key)
return rightRotate (node);
if (balance < -1 && key > node.right.key)
return leftRotate (node);
if (balance > 1 && key > node.left.key) {
node.left = leftRotate (node.left);
return rightRotate (node);
}
if (balance < -1 && key < node.right.key) {
node.right = rightRotate (node.right);
return leftRotate (node);
}
return node;
}
void printTree(Node root){
if (root == null)
return;
if (root != null) {
printTree(root.left);
System.out.print(root.key + " ");
printTree(root.left);
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
AVLTree tree = new AVLTree();
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 10);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 11);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 12);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 13);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 14);
tree.root = tree.insert(tree.root, 15);
System.out.println("AVL Tree: ");
tree.printTree(tree.root);
}
}
輸出
AVL Tree: 10 11 10 13 10 11 10
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.height = 1
class AVLTree(object):
def insert(self, root, key):
if not root:
return Node(key)
elif key < root.data:
root.left = self.insert(root.left, key)
else:
root.right = self.insert(root.right, key)
root.h = 1 + max(self.getHeight(root.left),
self.getHeight(root.right))
b = self.getBalance(root)
if b > 1 and key < root.left.data:
return self.rightRotate(root)
if b < -1 and key > root.right.data:
return self.leftRotate(root)
if b > 1 and key > root.left.data:
root.left = self.lefttRotate(root.left)
return self.rightRotate(root)
if b < -1 and key < root.right.data:
root.right = self.rightRotate(root.right)
return self.leftRotate(root)
return root
def leftRotate(self, z):
y = z.right
T2 = y.left
y.left = z
z.right = T2
z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left),
self.getHeight(z.right))
y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left),
self.getHeight(y.right))
return y
def rightRotate(self, z):
y = z.left
T3 = y.right
y.right = z
z.left = T3
z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left),
self.getHeight(z.right))
y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left),
self.getHeight(y.right))
return y
def getHeight(self, root):
if not root:
return 0
return root.height
def getBalance(self, root):
if not root:
return 0
return self.getHeight(root.left) - self.getHeight(root.right)
def Inorder(self, root):
if root.left:
self.Inorder(root.left)
print(root.data)
if root.right:
self.Inorder(root.right)
Tree = AVLTree()
root = None
root = Tree.insert(root, 10)
root = Tree.insert(root, 13)
root = Tree.insert(root, 11)
root = Tree.insert(root, 14)
root = Tree.insert(root, 12)
root = Tree.insert(root, 15)
# Inorder Traversal
print("Inorder traversal of the AVL tree is")
Tree.Inorder(root)
輸出
Inorder traversal of the AVL tree is 10 11 12 13 14 15
刪除
AVL 樹中的刪除發生在三種不同的場景中:
**場景 1(刪除葉子節點)**——如果要刪除的節點是葉子節點,則無需替換即可刪除它,因為它不會干擾二叉搜尋樹屬性。但是,平衡因子可能會受到干擾,因此會應用旋轉以恢復它。
**場景 2(刪除只有一個子節點的節點)**——如果要刪除的節點只有一個子節點,則用其子節點中的值替換該節點中的值。然後刪除子節點。如果平衡因子受到干擾,則應用旋轉。
**場景 3(刪除有兩個子節點的節點)**——如果要刪除的節點有兩個子節點,則找到該節點的中序後繼並將其值替換為中序後繼值。然後嘗試刪除中序後繼節點。如果刪除後平衡因子超過 1,則應用平衡演算法。
START
if root == null: return root
if key < root.key:
root.left = delete Node
else if key > root.key:
root.right = delete Node
else:
if root.left == null or root.right == null then:
Node temp = null
if (temp == root.left)
temp = root.right
else
temp = root.left
if temp == null then:
temp = root
root = null
else
root = temp
else:
temp = minimum valued node
root.key = temp.key
root.right = delete Node
if (root == null) then:
return root
root.height = max (height (root.left), height (root.right)) + 1
balance = getBalance
if balance > 1 and getBalance (root.left) >= 0:
rightRotate
if balance > 1 and getBalance (root.left) < 0:
root.left = leftRotate (root.left);
rightRotate
if balance < -1 and getBalance (root.right) <= 0:
leftRotate
if balance < -1 and getBalance (root.right) > 0:
root.right = rightRotate (root.right);
leftRotate
return root
END
刪除示例
使用上面給出的相同樹,讓我們在三種場景中執行刪除:
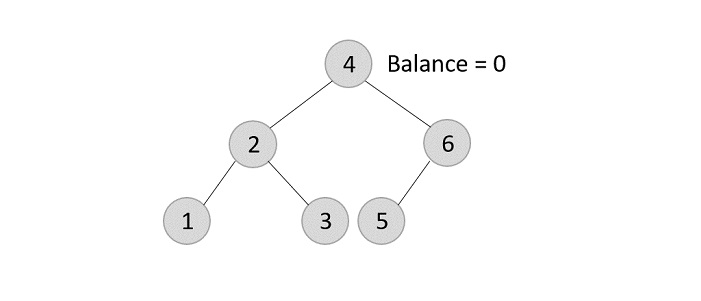
從上面的樹中刪除元素 7:
由於元素 7 是葉子節點,因此我們通常刪除該元素而不會干擾樹中的任何其他節點
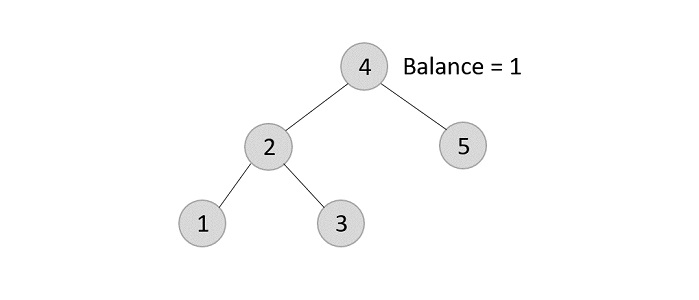
從獲得的輸出樹中刪除元素 6:
但是,元素 6 不是葉子節點,並且有一個子節點附加到它。在這種情況下,我們將節點 6 替換為其子節點:節點 5。
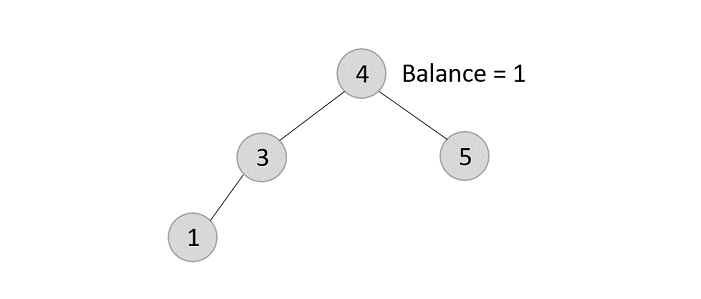
樹的平衡變為 1,並且由於它不超過 1,因此樹保持不變。如果我們進一步刪除元素 5,則需要應用左旋轉;要麼 LL 要麼 LR,因為不平衡發生在 1-2-4 和 3-2-4 處。
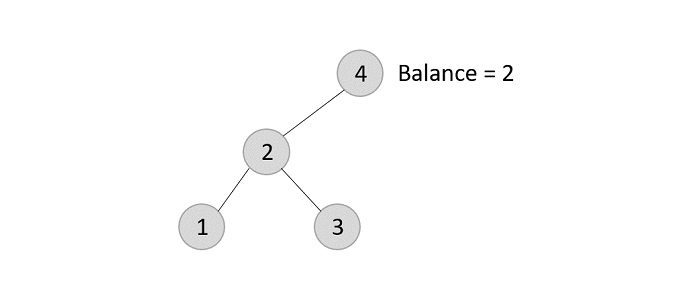
刪除元素 5 後,平衡因子受到干擾,因此我們應用 LL 旋轉(我們也可以在此處應用 LR 旋轉)。
在 1-2-4 路徑上應用 LL 旋轉後,節點 3 保持原樣,因為它應該成為節點 2 的右子節點(現在由節點 4 佔據)。因此,將節點新增到節點 2 的右子樹中,並作為節點 4 的左子節點。
從剩餘的樹中刪除元素 2:
如場景 3 中所述,此節點有兩個子節點。因此,我們找到它的中序後繼(例如,3)並將其值替換為中序後繼。
樹的平衡仍然保持 1,因此我們保持樹不變,不執行任何旋轉。
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *leftChild;
struct Node *rightChild;
int height;
};
int max(int a, int b);
int height(struct Node *N){
if (N == NULL)
return 0;
return N->height;
}
int max(int a, int b){
return (a > b) ? a : b;
}
struct Node *newNode(int data){
struct Node *node = (struct Node *) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
node->data = data;
node->leftChild = NULL;
node->rightChild = NULL;
node->height = 1;
return (node);
}
struct Node *rightRotate(struct Node *y){
struct Node *x = y->leftChild;
struct Node *T2 = x->rightChild;
x->rightChild = y;
y->leftChild = T2;
y->height = max(height(y->leftChild), height(y->rightChild)) + 1;
x->height = max(height(x->leftChild), height(x->rightChild)) + 1;
return x;
}
struct Node *leftRotate(struct Node *x){
struct Node *y = x->rightChild;
struct Node *T2 = y->leftChild;
y->leftChild = x;
x->rightChild = T2;
x->height = max(height(x->leftChild), height(x->rightChild)) + 1;
y->height = max(height(y->leftChild), height(y->rightChild)) + 1;
return y;
}
int getBalance(struct Node *N){
if (N == NULL)
return 0;
return height(N->leftChild) - height(N->rightChild);
}
struct Node *insertNode(struct Node *node, int data){
if (node == NULL)
return (newNode(data));
if (data < node->data)
node->leftChild = insertNode(node->leftChild, data);
else if (data > node->data)
node->rightChild = insertNode(node->rightChild, data);
else
return node;
node->height = 1 + max(height(node->leftChild),
height(node->rightChild));
int balance = getBalance(node);
if (balance > 1 && data < node->leftChild->data)
return rightRotate(node);
if (balance < -1 && data > node->rightChild->data)
return leftRotate(node);
if (balance > 1 && data > node->leftChild->data) {
node->leftChild = leftRotate(node->leftChild);
return rightRotate(node);
}
if (balance < -1 && data < node->rightChild->data) {
node->rightChild = rightRotate(node->rightChild);
return leftRotate(node);
}
return node;
}
struct Node *minValueNode(struct Node *node){
struct Node *current = node;
while (current->leftChild != NULL)
current = current->leftChild;
return current;
}
struct Node *deleteNode(struct Node *root, int data){
if (root == NULL)
return root;
if (data < root->data)
root->leftChild = deleteNode(root->leftChild, data);
else if (data > root->data)
root->rightChild = deleteNode(root->rightChild, data);
else {
if ((root->leftChild == NULL) || (root->rightChild == NULL)) {
struct Node *temp = root->leftChild ? root->leftChild : root->rightChild;
if (temp == NULL) {
temp = root;
root = NULL;
} else
*root = *temp;
free(temp);
} else {
struct Node *temp = minValueNode(root->rightChild);
root->data = temp->data;
root->rightChild = deleteNode(root->rightChild, temp->data);
}
}
if (root == NULL)
return root;
root->height = 1 + max(height(root->leftChild),
height(root->rightChild));
int balance = getBalance(root);
if (balance > 1 && getBalance(root->leftChild) >= 0)
return rightRotate(root);
if (balance > 1 && getBalance(root->leftChild) < 0) {
root->leftChild = leftRotate(root->leftChild);
return rightRotate(root);
}
if (balance < -1 && getBalance(root->rightChild) <= 0)
return leftRotate(root);
if (balance < -1 && getBalance(root->rightChild) > 0) {
root->rightChild = rightRotate(root->rightChild);
return leftRotate(root);
}
return root;
}
// Print the tree
void printTree(struct Node *root){
if (root != NULL) {
printTree(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
printTree(root->rightChild);
}
}
int main(){
struct Node *root = NULL;
root = insertNode(root, 22);
root = insertNode(root, 14);
root = insertNode(root, 72);
root = insertNode(root, 44);
root = insertNode(root, 25);
root = insertNode(root, 63);
root = insertNode(root, 98);
printf("AVL Tree: ");
printTree(root);
root = deleteNode(root, 25);
printf("\nAfter deletion: ");
printTree(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
AVL Tree: 14 22 25 44 63 72 98 After deletion: 14 22 44 63 72 98
#include <iostream>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *leftChild;
struct Node *rightChild;
int height;
};
int max(int a, int b);
int height(struct Node *N){
if (N == NULL)
return 0;
return N->height;
}
int max(int a, int b){
return (a > b) ? a : b;
}
struct Node *newNode(int data){
struct Node *node = (struct Node *) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
node->data = data;
node->leftChild = NULL;
node->rightChild = NULL;
node->height = 1;
return (node);
}
struct Node *rightRotate(struct Node *y){
struct Node *x = y->leftChild;
struct Node *T2 = x->rightChild;
x->rightChild = y;
y->leftChild = T2;
y->height = max(height(y->leftChild), height(y->rightChild)) + 1;
x->height = max(height(x->leftChild), height(x->rightChild)) + 1;
return x;
}
struct Node *leftRotate(struct Node *x){
struct Node *y = x->rightChild;
struct Node *T2 = y->leftChild;
y->leftChild = x;
x->rightChild = T2;
x->height = max(height(x->leftChild), height(x->rightChild)) + 1;
y->height = max(height(y->leftChild), height(y->rightChild)) + 1;
return y;
}
int getBalance(struct Node *N){
if (N == NULL)
return 0;
return height(N->leftChild) - height(N->rightChild);
}
struct Node *insertNode(struct Node *node, int data){
if (node == NULL)
return (newNode(data));
if (data < node->data)
node->leftChild = insertNode(node->leftChild, data);
else if (data > node->data)
node->rightChild = insertNode(node->rightChild, data);
else
return node;
node->height = 1 + max(height(node->leftChild),
height(node->rightChild));
int balance = getBalance(node);
if (balance > 1 && data < node->leftChild->data)
return rightRotate(node);
if (balance < -1 && data > node->rightChild->data)
return leftRotate(node);
if (balance > 1 && data > node->leftChild->data) {
node->leftChild = leftRotate(node->leftChild);
return rightRotate(node);
}
if (balance < -1 && data < node->rightChild->data) {
node->rightChild = rightRotate(node->rightChild);
return leftRotate(node);
}
return node;
}
struct Node *minValueNode(struct Node *node){
struct Node *current = node;
while (current->leftChild != NULL)
current = current->leftChild;
return current;
}
struct Node *deleteNode(struct Node *root, int data){
if (root == NULL)
return root;
if (data < root->data)
root->leftChild = deleteNode(root->leftChild, data);
else if (data > root->data)
root->rightChild = deleteNode(root->rightChild, data);
else {
if ((root->leftChild == NULL) || (root->rightChild == NULL)) {
struct Node *temp = root->leftChild ? root->leftChild : root->rightChild;
if (temp == NULL) {
temp = root;
root = NULL;
} else
*root = *temp;
free(temp);
} else {
struct Node *temp = minValueNode(root->rightChild);
root->data = temp->data;
root->rightChild = deleteNode(root->rightChild, temp->data);
}
}
if (root == NULL)
return root;
root->height = 1 + max(height(root->leftChild),
height(root->rightChild));
int balance = getBalance(root);
if (balance > 1 && getBalance(root->leftChild) >= 0)
return rightRotate(root);
if (balance > 1 && getBalance(root->leftChild) < 0) {
root->leftChild = leftRotate(root->leftChild);
return rightRotate(root);
}
if (balance < -1 && getBalance(root->rightChild) <= 0)
return leftRotate(root);
if (balance < -1 && getBalance(root->rightChild) > 0) {
root->rightChild = rightRotate(root->rightChild);
return leftRotate(root);
}
return root;
}
// Print the tree
void printTree(struct Node *root){
if (root != NULL) {
printTree(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
printTree(root->rightChild);
}
}
int main(){
struct Node *root = NULL;
root = insertNode(root, 22);
root = insertNode(root, 14);
root = insertNode(root, 72);
root = insertNode(root, 44);
root = insertNode(root, 25);
root = insertNode(root, 63);
root = insertNode(root, 98);
printf("AVL Tree: ");
printTree(root);
root = deleteNode(root, 25);
printf("\nAfter deletion: ");
printTree(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
AVL Tree: 14 22 25 44 63 72 98 After deletion: 14 22 44 63 72 98
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Node {
int key, height;
Node left, right;
Node (int d) {
key = d;
height = 1;
}
}
public class AVLTree {
Node root;
int height (Node N) {
if (N == null)
return 0;
return N.height;
}
int max (int a, int b) {
return (a > b) ? a : b;
}
Node rightRotate (Node y) {
Node x = y.left;
Node T2 = x.right;
x.right = y;
y.left = T2;
y.height = max (height (y.left), height (y.right)) + 1;
x.height = max (height (x.left), height (x.right)) + 1;
return x;
}
Node leftRotate (Node x) {
Node y = x.right;
Node T2 = y.left;
y.left = x;
x.right = T2;
x.height = max (height (x.left), height (x.right)) + 1;
y.height = max (height (y.left), height (y.right)) + 1;
return y;
}
int getBalance (Node N) {
if (N == null)
return 0;
return height (N.left) - height (N.right);
}
Node minValueNode (Node node) {
Node current = node;
while (current.left != null)
current = current.left;
return current;
}
Node deleteNode (Node root, int key) {
if (root == null)
return root;
if (key < root.key)
root.left = deleteNode (root.left, key);
else if (key > root.key)
root.right = deleteNode (root.right, key);
else {
if ((root.left == null) || (root.right == null)) {
Node temp = null;
if (temp == root.left)
temp = root.right;
else
temp = root.left;
if (temp == null) {
temp = root;
root = null;
} else
root = temp;
} else {
Node temp = minValueNode (root.right);
root.key = temp.key;
root.right = deleteNode (root.right, temp.key);
}
}
if (root == null)
return root;
root.height = max (height (root.left), height (root.right)) + 1;
int balance = getBalance (root);
if (balance > 1 && getBalance (root.left) >= 0)
return rightRotate (root);
if (balance > 1 && getBalance (root.left) < 0) {
root.left = leftRotate (root.left);
return rightRotate (root);
}
if (balance < -1 && getBalance (root.right) <= 0)
return leftRotate (root);
if (balance < -1 && getBalance (root.right) > 0) {
root.right = rightRotate (root.right);
return leftRotate (root);
}
return root;
}
public void printTree(Node root) {
if (root == null) return;
printTree(root.left);
System.out.print(root.key + " ");
printTree(root.right);
}
public static void main (String[]args) {
AVLTree tree = new AVLTree();
tree.root = new Node(13);
tree.root.left = new Node(12);
tree.root.left.left = new Node(11);
tree.root.left.left.left = new Node(10);
tree.root.right = new Node(14);
tree.root.right.right = new Node(15);
System.out.println("The AVL Tree is: ");
tree.printTree(tree.root);
tree.root = tree.deleteNode (tree.root, 10);
System.out.println("\n----------------------------------------------\n");
System.out.println("The AVL Tree after deleting 10 is: ");
tree.printTree(tree.root);
System.out.println ("");
}
}
輸出
The AVL Tree is: 10 11 12 13 14 15 ---------------------------------------------- The AVL Tree after deleting 10 is: 11 12 13 14 15
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.height = 1
class AVLTree(object):
def insert(self, root, key):
if not root:
return Node(key)
elif key < root.data:
root.left = self.insert(root.left, key)
else:
root.right = self.insert(root.right, key)
root.h = 1 + max(self.getHeight(root.left),
self.getHeight(root.right))
b = self.getBalance(root)
if b > 1 and key < root.left.data:
return self.rightRotate(root)
if b < -1 and key > root.right.data:
return self.leftRotate(root)
if b > 1 and key > root.left.data:
root.left = self.lefttRotate(root.left)
return self.rightRotate(root)
if b < -1 and key < root.right.data:
root.right = self.rightRotate(root.right)
return self.leftRotate(root)
return root
def delete(self, root, key):
if not root:
return root
elif key < root.data:
root.left = self.delete(root.left, key)
elif key > root.data:
root.right = self.delete(root.right, key)
else:
if root.left is None:
temp = root.right
root = None
return temp
elif root.right is None:
temp = root.left
root = None
return temp
temp = self.getMindataueNode(root.right)
root.data = temp.data
root.right = self.delete(root.right, temp.data)
if root is None:
return root
root.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(root.left), self.getHeight(root.right))
balance = self.getBalance(root)
if balance > 1 and self.getBalance(root.left) >= 0:
return self.rightRotate(root)
if balance < -1 and self.getBalance(root.right) <= 0:
return self.leftRotate(root)
if balance > 1 and self.getBalance(root.left) < 0:
root.left = self.leftRotate(root.left)
return self.rightRotate(root)
if balance < -1 and self.getBalance(root.right) > 0:
root.right = self.rightRotate(root.right)
return self.leftRotate(root)
return root
def leftRotate(self, z):
y = z.right
T2 = y.left
y.left = z
z.right = T2
z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left),
self.getHeight(z.right))
y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left),
self.getHeight(y.right))
return y
def rightRotate(self, z):
y = z.left
T3 = y.right
y.right = z
z.left = T3
z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left),
self.getHeight(z.right))
y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left),
self.getHeight(y.right))
return y
def getHeight(self, root):
if not root:
return 0
return root.height
def getBalance(self, root):
if not root:
return 0
return self.getHeight(root.left) - self.getHeight(root.right)
def Inorder(self, root):
if root.left:
self.Inorder(root.left)
print(root.data)
if root.right:
self.Inorder(root.right)
Tree = AVLTree()
root = None
root = Tree.insert(root, 10)
root = Tree.insert(root, 13)
root = Tree.insert(root, 11)
root = Tree.insert(root, 14)
root = Tree.insert(root, 12)
root = Tree.insert(root, 15)
# Inorder Traversal
print("Inorder traversal of the AVL tree is")
Tree.Inorder(root)
root = Tree.delete(root, 14)
print("Inorder traversal of the modified AVL tree is")
Tree.Inorder(root)
輸出
Inorder traversal of the AVL tree is 10 11 12 13 14 15 Inorder traversal of the modified AVL tree is 10 11 12 13 15
AVL 樹的實現
在以下實現中,我們考慮按升序排列的輸入,並透過計算平衡因子和應用旋轉將其儲存在 AVL 樹中。
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *leftChild;
struct Node *rightChild;
int height;
};
int max(int a, int b);
int height(struct Node *N){
if (N == NULL)
return 0;
return N->height;
}
int max(int a, int b){
return (a > b) ? a : b;
}
struct Node *newNode(int data){
struct Node *node = (struct Node *) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
node->data = data;
node->leftChild = NULL;
node->rightChild = NULL;
node->height = 1;
return (node);
}
struct Node *rightRotate(struct Node *y){
struct Node *x = y->leftChild;
struct Node *T2 = x->rightChild;
x->rightChild = y;
y->leftChild = T2;
y->height = max(height(y->leftChild), height(y->rightChild)) + 1;
x->height = max(height(x->leftChild), height(x->rightChild)) + 1;
return x;
}
struct Node *leftRotate(struct Node *x){
struct Node *y = x->rightChild;
struct Node *T2 = y->leftChild;
y->leftChild = x;
x->rightChild = T2;
x->height = max(height(x->leftChild), height(x->rightChild)) + 1;
y->height = max(height(y->leftChild), height(y->rightChild)) + 1;
return y;
}
int getBalance(struct Node *N){
if (N == NULL)
return 0;
return height(N->leftChild) - height(N->rightChild);
}
struct Node *insertNode(struct Node *node, int data){
if (node == NULL)
return (newNode(data));
if (data < node->data)
node->leftChild = insertNode(node->leftChild, data);
else if (data > node->data)
node->rightChild = insertNode(node->rightChild, data);
else
return node;
node->height = 1 + max(height(node->leftChild),
height(node->rightChild));
int balance = getBalance(node);
if (balance > 1 && data < node->leftChild->data)
return rightRotate(node);
if (balance < -1 && data > node->rightChild->data)
return leftRotate(node);
if (balance > 1 && data > node->leftChild->data) {
node->leftChild = leftRotate(node->leftChild);
return rightRotate(node);
}
if (balance < -1 && data < node->rightChild->data) {
node->rightChild = rightRotate(node->rightChild);
return leftRotate(node);
}
return node;
}
struct Node *minValueNode(struct Node *node){
struct Node *current = node;
while (current->leftChild != NULL)
current = current->leftChild;
return current;
}
struct Node *deleteNode(struct Node *root, int data){
if (root == NULL)
return root;
if (data < root->data)
root->leftChild = deleteNode(root->leftChild, data);
else if (data > root->data)
root->rightChild = deleteNode(root->rightChild, data);
else {
if ((root->leftChild == NULL) || (root->rightChild == NULL)) {
struct Node *temp = root->leftChild ? root->leftChild : root->rightChild;
if (temp == NULL) {
temp = root;
root = NULL;
} else
*root = *temp;
free(temp);
} else {
struct Node *temp = minValueNode(root->rightChild);
root->data = temp->data;
root->rightChild = deleteNode(root->rightChild, temp->data);
}
}
if (root == NULL)
return root;
root->height = 1 + max(height(root->leftChild),
height(root->rightChild));
int balance = getBalance(root);
if (balance > 1 && getBalance(root->leftChild) >= 0)
return rightRotate(root);
if (balance > 1 && getBalance(root->leftChild) < 0) {
root->leftChild = leftRotate(root->leftChild);
return rightRotate(root);
}
if (balance < -1 && getBalance(root->rightChild) <= 0)
return leftRotate(root);
if (balance < -1 && getBalance(root->rightChild) > 0) {
root->rightChild = rightRotate(root->rightChild);
return leftRotate(root);
}
return root;
}
// Print the tree
void printTree(struct Node *root){
if (root != NULL) {
printTree(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
printTree(root->rightChild);
}
}
int main(){
struct Node *root = NULL;
root = insertNode(root, 22);
root = insertNode(root, 14);
root = insertNode(root, 72);
root = insertNode(root, 44);
root = insertNode(root, 25);
root = insertNode(root, 63);
root = insertNode(root, 98);
printf("AVL Tree: ");
printTree(root);
root = deleteNode(root, 25);
printf("\nAfter deletion: ");
printTree(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
AVL Tree: 14 22 25 44 63 72 98 After deletion: 14 22 44 63 72 98
#include <iostream>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node *leftChild;
struct Node *rightChild;
int height;
};
int max(int a, int b);
int height(struct Node *N){
if (N == NULL)
return 0;
return N->height;
}
int max(int a, int b){
return (a > b) ? a : b;
}
struct Node *newNode(int data){
struct Node *node = (struct Node *) malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
node->data = data;
node->leftChild = NULL;
node->rightChild = NULL;
node->height = 1;
return (node);
}
struct Node *rightRotate(struct Node *y){
struct Node *x = y->leftChild;
struct Node *T2 = x->rightChild;
x->rightChild = y;
y->leftChild = T2;
y->height = max(height(y->leftChild), height(y->rightChild)) + 1;
x->height = max(height(x->leftChild), height(x->rightChild)) + 1;
return x;
}
struct Node *leftRotate(struct Node *x){
struct Node *y = x->rightChild;
struct Node *T2 = y->leftChild;
y->leftChild = x;
x->rightChild = T2;
x->height = max(height(x->leftChild), height(x->rightChild)) + 1;
y->height = max(height(y->leftChild), height(y->rightChild)) + 1;
return y;
}
int getBalance(struct Node *N){
if (N == NULL)
return 0;
return height(N->leftChild) - height(N->rightChild);
}
struct Node *insertNode(struct Node *node, int data){
if (node == NULL)
return (newNode(data));
if (data < node->data)
node->leftChild = insertNode(node->leftChild, data);
else if (data > node->data)
node->rightChild = insertNode(node->rightChild, data);
else
return node;
node->height = 1 + max(height(node->leftChild),
height(node->rightChild));
int balance = getBalance(node);
if (balance > 1 && data < node->leftChild->data)
return rightRotate(node);
if (balance < -1 && data > node->rightChild->data)
return leftRotate(node);
if (balance > 1 && data > node->leftChild->data) {
node->leftChild = leftRotate(node->leftChild);
return rightRotate(node);
}
if (balance < -1 && data < node->rightChild->data) {
node->rightChild = rightRotate(node->rightChild);
return leftRotate(node);
}
return node;
}
struct Node *minValueNode(struct Node *node){
struct Node *current = node;
while (current->leftChild != NULL)
current = current->leftChild;
return current;
}
struct Node *deleteNode(struct Node *root, int data){
if (root == NULL)
return root;
if (data < root->data)
root->leftChild = deleteNode(root->leftChild, data);
else if (data > root->data)
root->rightChild = deleteNode(root->rightChild, data);
else {
if ((root->leftChild == NULL) || (root->rightChild == NULL)) {
struct Node *temp = root->leftChild ? root->leftChild : root->rightChild;
if (temp == NULL) {
temp = root;
root = NULL;
} else
*root = *temp;
free(temp);
} else {
struct Node *temp = minValueNode(root->rightChild);
root->data = temp->data;
root->rightChild = deleteNode(root->rightChild, temp->data);
}
}
if (root == NULL)
return root;
root->height = 1 + max(height(root->leftChild),
height(root->rightChild));
int balance = getBalance(root);
if (balance > 1 && getBalance(root->leftChild) >= 0)
return rightRotate(root);
if (balance > 1 && getBalance(root->leftChild) < 0) {
root->leftChild = leftRotate(root->leftChild);
return rightRotate(root);
}
if (balance < -1 && getBalance(root->rightChild) <= 0)
return leftRotate(root);
if (balance < -1 && getBalance(root->rightChild) > 0) {
root->rightChild = rightRotate(root->rightChild);
return leftRotate(root);
}
return root;
}
// Print the tree
void printTree(struct Node *root){
if (root != NULL) {
printTree(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
printTree(root->rightChild);
}
}
int main(){
struct Node *root = NULL;
root = insertNode(root, 22);
root = insertNode(root, 14);
root = insertNode(root, 72);
root = insertNode(root, 44);
root = insertNode(root, 25);
root = insertNode(root, 63);
root = insertNode(root, 98);
printf("AVL Tree: ");
printTree(root);
root = deleteNode(root, 25);
printf("\nAfter deletion: ");
printTree(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
AVL Tree: 14 22 25 44 63 72 98 After deletion: 14 22 44 63 72 98
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
class Node {
int key, height;
Node left, right;
Node (int d) {
key = d;
height = 1;
}
}
public class AVLTree {
Node root;
int height (Node N) {
if (N == null)
return 0;
return N.height;
}
int max (int a, int b) {
return (a > b) ? a : b;
}
Node rightRotate (Node y) {
Node x = y.left;
Node T2 = x.right;
x.right = y;
y.left = T2;
y.height = max (height (y.left), height (y.right)) + 1;
x.height = max (height (x.left), height (x.right)) + 1;
return x;
}
Node leftRotate (Node x) {
Node y = x.right;
Node T2 = y.left;
y.left = x;
x.right = T2;
x.height = max (height (x.left), height (x.right)) + 1;
y.height = max (height (y.left), height (y.right)) + 1;
return y;
}
int getBalance (Node N) {
if (N == null)
return 0;
return height (N.left) - height (N.right);
}
Node insert (Node node, int key) {
if (node == null)
return (new Node (key));
if (key < node.key)
node.left = insert (node.left, key);
else if (key > node.key)
node.right = insert (node.right, key);
else
return node;
node.height = 1 + max (height (node.left), height (node.right));
int balance = getBalance (node);
if (balance > 1 && key < node.left.key)
return rightRotate (node);
if (balance < -1 && key > node.right.key)
return leftRotate (node);
if (balance > 1 && key > node.left.key) {
node.left = leftRotate (node.left);
return rightRotate (node);
}
if (balance < -1 && key < node.right.key) {
node.right = rightRotate (node.right);
return leftRotate (node);
}
return node;
}
Node minValueNode (Node node) {
Node current = node;
while (current.left != null)
current = current.left;
return current;
}
Node deleteNode (Node root, int key) {
if (root == null)
return root;
if (key < root.key)
root.left = deleteNode (root.left, key);
else if (key > root.key)
root.right = deleteNode (root.right, key);
else {
if ((root.left == null) || (root.right == null)) {
Node temp = null;
if (temp == root.left)
temp = root.right;
else
temp = root.left;
if (temp == null) {
temp = root;
root = null;
} else
root = temp;
} else {
Node temp = minValueNode (root.right);
root.key = temp.key;
root.right = deleteNode (root.right, temp.key);
}
}
if (root == null)
return root;
root.height = max (height (root.left), height (root.right)) + 1;
int balance = getBalance (root);
if (balance > 1 && getBalance (root.left) >= 0)
return rightRotate (root);
if (balance > 1 && getBalance (root.left) < 0) {
root.left = leftRotate (root.left);
return rightRotate (root);
}
if (balance < -1 && getBalance (root.right) <= 0)
return leftRotate (root);
if (balance < -1 && getBalance (root.right) > 0) {
root.right = rightRotate (root.right);
return leftRotate (root);
}
return root;
}
public void printTree(Node root) {
if (root == null) return;
printTree(root.left);
System.out.println(root.key);
printTree(root.right);
}
public static void main (String[]args) {
AVLTree tree = new AVLTree();
tree.root = tree.insert (tree.root, 10);
tree.root = tree.insert (tree.root, 11);
tree.root = tree.insert (tree.root, 12);
tree.root = tree.insert (tree.root, 13);
tree.root = tree.insert (tree.root, 14);
tree.root = tree.insert (tree.root, 15);
System.out.println("The AVL Tree is: ");
tree.printTree(tree.root);
tree.root = tree.deleteNode (tree.root, 10);
System.out.println("\n----------------------------------------------\n");
System.out.println("The AVL Tree after deleting 10 is: ");
tree.printTree(tree.root);
System.out.println ("");
}
}
輸出
The AVL Tree is: 10 11 12 13 14 15 ---------------------------------------------- The AVL Tree after deleting 10 is: 11 12 13 14 15
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.height = 1
class AVLTree(object):
def insert(self, root, key):
if not root:
return Node(key)
elif key < root.data:
root.left = self.insert(root.left, key)
else:
root.right = self.insert(root.right, key)
root.h = 1 + max(self.getHeight(root.left),
self.getHeight(root.right))
b = self.getBalance(root)
if b > 1 and key < root.left.data:
return self.rightRotate(root)
if b < -1 and key > root.right.data:
return self.leftRotate(root)
if b > 1 and key > root.left.data:
root.left = self.lefttRotate(root.left)
return self.rightRotate(root)
if b < -1 and key < root.right.data:
root.right = self.rightRotate(root.right)
return self.leftRotate(root)
return root
def delete(self, root, key):
if not root:
return root
elif key < root.data:
root.left = self.delete(root.left, key)
elif key > root.data:
root.right = self.delete(root.right, key)
else:
if root.left is None:
temp = root.right
root = None
return temp
elif root.right is None:
temp = root.left
root = None
return temp
temp = self.getMindataueNode(root.right)
root.data = temp.data
root.right = self.delete(root.right, temp.data)
if root is None:
return root
root.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(root.left), self.getHeight(root.right))
balance = self.getBalance(root)
if balance > 1 and self.getBalance(root.left) >= 0:
return self.rightRotate(root)
if balance < -1 and self.getBalance(root.right) <= 0:
return self.leftRotate(root)
if balance > 1 and self.getBalance(root.left) < 0:
root.left = self.leftRotate(root.left)
return self.rightRotate(root)
if balance < -1 and self.getBalance(root.right) > 0:
root.right = self.rightRotate(root.right)
return self.leftRotate(root)
return root
def leftRotate(self, z):
y = z.right
T2 = y.left
y.left = z
z.right = T2
z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left),
self.getHeight(z.right))
y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left),
self.getHeight(y.right))
return y
def rightRotate(self, z):
y = z.left
T3 = y.right
y.right = z
z.left = T3
z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left),
self.getHeight(z.right))
y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left),
self.getHeight(y.right))
return y
def getHeight(self, root):
if not root:
return 0
return root.height
def getBalance(self, root):
if not root:
return 0
return self.getHeight(root.left) - self.getHeight(root.right)
def Inorder(self, root):
if root.left:
self.Inorder(root.left)
print(root.data)
if root.right:
self.Inorder(root.right)
Tree = AVLTree()
root = None
root = Tree.insert(root, 10)
root = Tree.insert(root, 13)
root = Tree.insert(root, 11)
root = Tree.insert(root, 14)
root = Tree.insert(root, 12)
root = Tree.insert(root, 15)
# Inorder Traversal
print("Inorder traversal of the AVL tree is")
Tree.Inorder(root)
root = Tree.delete(root, 14)
print("Inorder traversal of the modified AVL tree is")
Tree.Inorder(root)
輸出
Inorder traversal of the AVL tree is 10 11 12 13 14 15 Inorder traversal of the modified AVL tree is 10 11 12 13 15
紅黑樹
紅黑樹是另一種型別的平衡二叉搜尋樹,它有兩個顏色的節點:紅色和黑色。它是一種自平衡二叉搜尋樹,利用這些顏色在插入和刪除操作期間保持平衡因子。因此,在紅黑樹操作期間,記憶體使用 1 位儲存來容納每個節點的顏色資訊
在紅黑樹(也稱為 RB 樹)中,在為節點分配顏色時需要遵循不同的條件。
根節點始終為黑色。
不允許兩個相鄰節點都是紅色。
樹中的每條路徑(從根節點到葉子節點)必須具有相同數量的黑色節點。
儘管 AVL 樹比 RB 樹更平衡,並且 AVL 樹中的平衡演算法比 RB 樹更嚴格,但透過 RB 樹可以使多次和更快的插入和刪除操作效率更高。
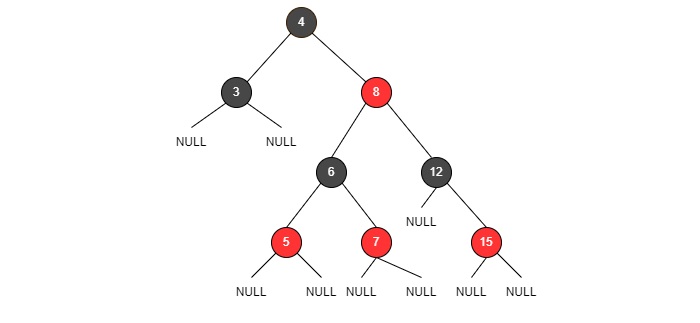
圖:RB 樹
紅黑樹的基本操作
紅黑樹上的操作包括通常在二叉搜尋樹上執行的所有基本操作。RB 樹的一些基本操作包括:
插入
刪除
搜尋
紅黑樹的插入操作遵循與二叉搜尋樹相同的插入演算法。元素按照二叉搜尋屬性插入,並且作為補充,節點被顏色編碼為紅色和黑色,以根據紅黑樹屬性平衡樹。
按照以下步驟,透過維護二叉搜尋樹和紅黑樹屬性,將元素插入紅黑樹。
**情況 1**——檢查樹是否為空;如果為空,則將當前節點設為根節點並將其顏色設定為黑色。
**情況 2**——但如果樹不為空,我們建立一個新節點並將其顏色設定為紅色。這裡我們面臨兩種不同的情況:
如果新節點的父節點是黑色節點,則退出操作,樹保持不變。
如果新節點的父節點是紅色,並且父節點的兄弟節點的顏色為黑色或不存在,則應用合適的旋轉並相應地重新著色。
如果新節點的父節點是紅色,並且父節點的兄弟節點的顏色是紅色,則將父節點、兄弟節點和祖父母節點重新著色為黑色。僅當祖父母節點**不是**根節點時才重新著色;如果是根節點,則僅重新著色父節點和兄弟節點。
插入示例
讓我們為前 7 個整數構建一個 RB 樹,以便詳細瞭解插入操作:
檢查樹是否為空,因此新增的第一個節點是根節點,顏色為黑色。

現在,樹不為空,因此我們建立一個新節點並新增下一個整數,顏色為紅色,

節點不違反二叉搜尋樹和 RB 樹屬性,因此我們繼續新增另一個節點。
樹不為空;我們建立一個新的紅色節點,並將其與下一個整數連線。但是,新節點的父節點不是黑色節點,
當前這棵樹違反了二叉搜尋樹和紅黑樹的性質;由於父節點的兄弟節點為NULL,我們應用合適的旋轉並重新著色節點。

現在紅黑樹的性質已經恢復,我們向樹中新增另一個節點 -

這棵樹再次違反了紅黑樹的平衡性質,所以我們檢查父節點的兄弟節點顏色,在本例中為紅色,所以我們只需重新著色父節點和兄弟節點。
接下來我們插入元素5,這使得樹再次違反了紅黑樹的平衡性質。
並且由於兄弟節點為NULL,我們應用合適的旋轉和重新著色。
現在,我們插入元素6,但紅黑樹的性質被違反,需要應用插入情況之一 -

父節點的兄弟節點為紅色,所以我們重新著色父節點、父節點的兄弟節點和祖父母節點,因為祖父母節點不是根節點。

現在,我們新增最後一個元素7,但這個新節點的父節點為紅色。

由於父節點的兄弟節點為NULL,我們應用合適的旋轉(RR旋轉)

最終得到了紅黑樹。
刪除
紅黑樹上的刪除操作必須以這樣一種方式執行,即它必須恢復二叉搜尋樹和紅黑樹的所有性質。按照以下步驟在紅黑樹上執行刪除操作 -
首先,我們根據二叉搜尋樹的性質執行刪除操作。
情況1 - 如果要刪除的節點或節點的父節點為紅色,則直接刪除它。
情況2 - 如果節點為雙黑節點,則只需移除雙黑節點(當要刪除的節點是黑色葉子節點時,會發生雙黑節點,因為它累加了被認為是黑色節點的NULL節點)
情況3 - 如果雙黑節點的兄弟節點也是黑色節點,並且它的子節點也是黑色,則按照以下步驟 -
移除雙黑節點
將其父節點重新著色為黑色(如果父節點是紅色節點,則變為黑色;如果父節點已經是黑色節點,則變為雙黑節點)
將父節點的兄弟節點重新著色為紅色
如果雙黑節點仍然存在,則應用其他情況。
情況4 - 如果雙黑節點的兄弟節點為紅色,則執行以下步驟 -
交換父節點和父節點的兄弟節點的顏色。
朝雙黑節點的方向旋轉父節點
重新應用其他合適的情況。
情況5 - 如果雙黑節點的兄弟節點是黑色節點,但兄弟節點中距離雙黑節點最近的子節點是紅色,則按照以下步驟 -
交換雙黑節點的兄弟節點和該兄弟節點的子節點的顏色
朝與雙黑節點相反的方向旋轉兄弟節點(即如果雙黑節點是右孩子,則應用左旋轉,反之亦然)
應用情況6。
情況6 - 如果雙黑節點的兄弟節點是黑色節點,但兄弟節點中距離雙黑節點較遠的子節點是紅色,則按照以下步驟 -
交換雙黑節點的父節點和兄弟節點的顏色
朝雙黑節點的方向旋轉父節點(即如果雙黑節點是右孩子,則應用右旋轉,反之亦然)
移除雙黑節點
將紅色子節點的顏色改為黑色。
刪除示例
考慮上面構建的相同的紅黑樹,讓我們從樹中刪除一些元素。

從樹中刪除元素4、5、3。
要刪除元素4,讓我們首先執行二叉搜尋刪除。
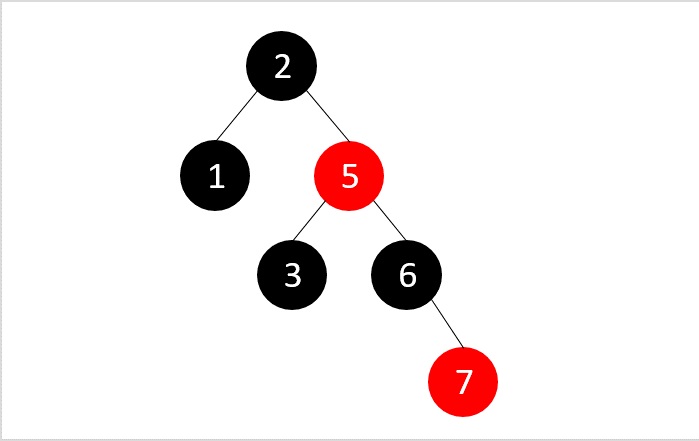
執行二叉搜尋刪除後,紅黑樹的性質沒有受到干擾,因此樹保持不變。
然後,我們使用二叉搜尋刪除來刪除元素5
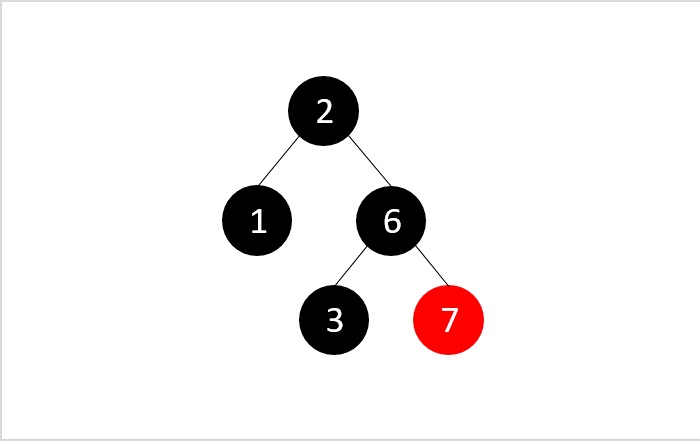
但是執行二叉搜尋刪除後,紅黑樹的性質被破壞了,即樹中所有路徑不包含相同數量的黑色節點;所以我們交換顏色來平衡樹。
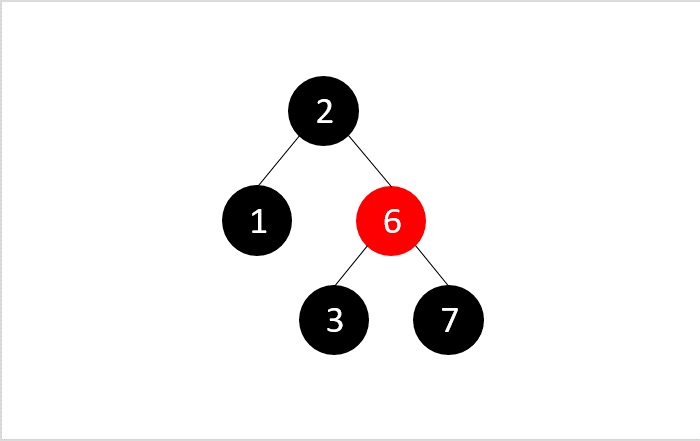
然後,我們從得到的樹中刪除節點3 -
應用二叉搜尋刪除,我們正常刪除節點3,因為它是一個葉子節點。並且我們得到一個雙節點,因為3是一個黑色節點。
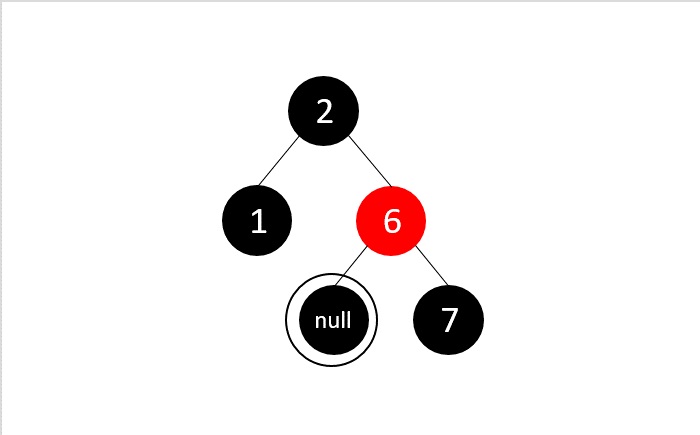
我們應用情況3刪除,因為雙黑節點的兄弟節點是黑色,並且它的子節點也是黑色。在這裡,我們移除雙黑節點,重新著色雙黑節點的父節點和兄弟節點。
所有需要的節點都被刪除,並且紅黑樹的性質得以維護。
搜尋
紅黑樹中的搜尋操作遵循與二叉搜尋樹相同的演算法。遍歷樹,並將每個節點與要搜尋的關鍵元素進行比較;如果找到,則返回成功搜尋。否則,返回不成功搜尋。
完整實現
輸出
// C++ program for Red black trees algorithmn
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node *parent;
Node *left;
Node *right;
int color;
};
typedef Node *NodePtr;
class RedBlackTree {
private:
NodePtr root;
NodePtr TNULL;
void initializeNULLNode(NodePtr node, NodePtr parent) {
node->data = 0;
node->parent = parent;
node->left = nullptr;
node->right = nullptr;
node->color = 0;
}
// Preorder
void preOrderHelper(NodePtr node) {
if (node != TNULL) {
cout << node->data << " ";
preOrderHelper(node->left);
preOrderHelper(node->right);
}
}
// Inorder
void inOrderHelper(NodePtr node) {
if (node != TNULL) {
inOrderHelper(node->left);
cout << node->data << " ";
inOrderHelper(node->right);
}
}
// Post order
void postOrderHelper(NodePtr node) {
if (node != TNULL) {
postOrderHelper(node->left);
postOrderHelper(node->right);
cout << node->data << " ";
}
}
NodePtr searchTreeHelper(NodePtr node, int key) {
if (node == TNULL || key == node->data) {
return node;
}
if (key < node->data) {
return searchTreeHelper(node->left, key);
}
return searchTreeHelper(node->right, key);
}
// For balancing the tree after deletion
void deleteFix(NodePtr x) {
NodePtr s;
while (x != root && x->color == 0) {
if (x == x->parent->left) {
s = x->parent->right;
if (s->color == 1) {
s->color = 0;
x->parent->color = 1;
leftRotate(x->parent);
s = x->parent->right;
}
if (s->left->color == 0 && s->right->color == 0) {
s->color = 1;
x = x->parent;
} else {
if (s->right->color == 0) {
s->left->color = 0;
s->color = 1;
rightRotate(s);
s = x->parent->right;
}
s->color = x->parent->color;
x->parent->color = 0;
s->right->color = 0;
leftRotate(x->parent);
x = root;
}
} else {
s = x->parent->left;
if (s->color == 1) {
s->color = 0;
x->parent->color = 1;
rightRotate(x->parent);
s = x->parent->left;
}
if (s->right->color == 0 && s->right->color == 0) {
s->color = 1;
x = x->parent;
} else {
if (s->left->color == 0) {
s->right->color = 0;
s->color = 1;
leftRotate(s);
s = x->parent->left;
}
s->color = x->parent->color;
x->parent->color = 0;
s->left->color = 0;
rightRotate(x->parent);
x = root;
}
}
}
x->color = 0;
}
void rbTransplant(NodePtr u, NodePtr v) {
if (u->parent == nullptr) {
root = v;
} else if (u == u->parent->left) {
u->parent->left = v;
} else {
u->parent->right = v;
}
v->parent = u->parent;
}
void deleteNodeHelper(NodePtr node, int key) {
NodePtr z = TNULL;
NodePtr x, y;
while (node != TNULL) {
if (node->data == key) {
z = node;
}
if (node->data <= key) {
node = node->right;
} else {
node = node->left;
}
}
if (z == TNULL) {
cout << "Key not found in the tree" << endl;
return;
}
y = z;
int y_original_color = y->color;
if (z->left == TNULL) {
x = z->right;
rbTransplant(z, z->right);
} else if (z->right == TNULL) {
x = z->left;
rbTransplant(z, z->left);
} else {
y = minimum(z->right);
y_original_color = y->color;
x = y->right;
if (y->parent == z) {
x->parent = y;
} else {
rbTransplant(y, y->right);
y->right = z->right;
y->right->parent = y;
}
rbTransplant(z, y);
y->left = z->left;
y->left->parent = y;
y->color = z->color;
}
delete z;
if (y_original_color == 0) {
deleteFix(x);
}
}
// For balancing the tree after insertion
void insertFix(NodePtr k) {
NodePtr u;
while (k->parent->color == 1) {
if (k->parent == k->parent->parent->right) {
u = k->parent->parent->left;
if (u->color == 1) {
u->color = 0;
k->parent->color = 0;
k->parent->parent->color = 1;
k = k->parent->parent;
} else {
if (k == k->parent->left) {
k = k->parent;
rightRotate(k);
}
k->parent->color = 0;
k->parent->parent->color = 1;
leftRotate(k->parent->parent);
}
} else {
u = k->parent->parent->right;
if (u->color == 1) {
u->color = 0;
k->parent->color = 0;
k->parent->parent->color = 1;
k = k->parent->parent;
} else {
if (k == k->parent->right) {
k = k->parent;
leftRotate(k);
}
k->parent->color = 0;
k->parent->parent->color = 1;
rightRotate(k->parent->parent);
}
}
if (k == root) {
break;
}
}
root->color = 0;
}
void printHelper(NodePtr root, string indent, bool last) {
if (root != TNULL) {
cout << indent;
if (last) {
cout << "R----";
indent += " ";
} else {
cout << "L----";
indent += "| ";
}
string sColor = root->color ? "RED" : "BLACK";
cout << root->data << "(" << sColor << ")" << endl;
printHelper(root->left, indent, false);
printHelper(root->right, indent, true);
}
}
public:
RedBlackTree() {
TNULL = new Node;
TNULL->color = 0;
TNULL->left = nullptr;
TNULL->right = nullptr;
root = TNULL;
}
void preorder() {
preOrderHelper(this->root);
}
void inorder() {
inOrderHelper(this->root);
}
void postorder() {
postOrderHelper(this->root);
}
NodePtr searchTree(int k) {
return searchTreeHelper(this->root, k);
}
NodePtr minimum(NodePtr node) {
while (node->left != TNULL) {
node = node->left;
}
return node;
}
NodePtr maximum(NodePtr node) {
while (node->right != TNULL) {
node = node->right;
}
return node;
}
NodePtr successor(NodePtr x) {
if (x->right != TNULL) {
return minimum(x->right);
}
NodePtr y = x->parent;
while (y != TNULL && x == y->right) {
x = y;
y = y->parent;
}
return y;
}
NodePtr predecessor(NodePtr x) {
if (x->left != TNULL) {
return maximum(x->left);
}
NodePtr y = x->parent;
while (y != TNULL && x == y->left) {
x = y;
y = y->parent;
}
return y;
}
void leftRotate(NodePtr x) {
NodePtr y = x->right;
x->right = y->left;
if (y->left != TNULL) {
y->left->parent = x;
}
y->parent = x->parent;
if (x->parent == nullptr) {
this->root = y;
} else if (x == x->parent->left) {
x->parent->left = y;
} else {
x->parent->right = y;
}
y->left = x;
x->parent = y;
}
void rightRotate(NodePtr x) {
NodePtr y = x->left;
x->left = y->right;
if (y->right != TNULL) {
y->right->parent = x;
}
y->parent = x->parent;
if (x->parent == nullptr) {
this->root = y;
} else if (x == x->parent->right) {
x->parent->right = y;
} else {
x->parent->left = y;
}
y->right = x;
x->parent = y;
}
// Inserting a node
void insert(int key) {
NodePtr node = new Node;
node->parent = nullptr;
node->data = key;
node->left = TNULL;
node->right = TNULL;
node->color = 1;
NodePtr y = nullptr;
NodePtr x = this->root;
while (x != TNULL) {
y = x;
if (node->data < x->data) {
x = x->left;
} else {
x = x->right;
}
}
node->parent = y;
if (y == nullptr) {
root = node;
} else if (node->data < y->data) {
y->left = node;
} else {
y->right = node;
}
if (node->parent == nullptr) {
node->color = 0;
return;
}
if (node->parent->parent == nullptr) {
return;
}
insertFix(node);
}
NodePtr getRoot() {
return this->root;
}
void deleteNode(int data) {
deleteNodeHelper(this->root, data);
}
void printTree() {
if (root) {
printHelper(this->root, "", true);
}
}
};
int main() {
RedBlackTree V;
V.insert(24);
V.insert(33);
V.insert(42);
V.insert(51);
V.insert(60);
V.insert(40);
V.insert(22);
V.printTree();
cout << endl
<< "After deleting an element" << endl;
V.deleteNode(40);
V.printTree();
}
輸出
R----33(BLACK)
L----24(BLACK)
| L----22(RED)
R----51(RED)
L----42(BLACK)
| L----40(RED)
R----60(BLACK)
After deleting an element
R----33(BLACK)
L----24(BLACK)
| L----22(RED)
R----51(RED)
L----42(BLACK)
R----60(BLACK)
// Implementing Red-Black Tree in Java
class Node {
int data;
Node parent;
Node left;
Node right;
int color;
}
public class RedBlackTree {
private Node root;
private Node TNULL;
// Preorder
private void preOrderHelper(Node node) {
if (node != TNULL) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
preOrderHelper(node.left);
preOrderHelper(node.right);
}
}
// Inorder
private void inOrderHelper(Node node) {
if (node != TNULL) {
inOrderHelper(node.left);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
inOrderHelper(node.right);
}
}
// Post order
private void postOrderHelper(Node node) {
if (node != TNULL) {
postOrderHelper(node.left);
postOrderHelper(node.right);
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
}
}
// Search the tree
private Node searchTreeHelper(Node node, int key) {
if (node == TNULL || key == node.data) {
return node;
}
if (key < node.data) {
return searchTreeHelper(node.left, key);
}
return searchTreeHelper(node.right, key);
}
// Balance the tree after deletion of a node
private void fixDelete(Node x) {
Node s;
while (x != root && x.color == 0) {
if (x == x.parent.left) {
s = x.parent.right;
if (s.color == 1) {
s.color = 0;
x.parent.color = 1;
leftRotate(x.parent);
s = x.parent.right;
}
if (s.left.color == 0 && s.right.color == 0) {
s.color = 1;
x = x.parent;
} else {
if (s.right.color == 0) {
s.left.color = 0;
s.color = 1;
rightRotate(s);
s = x.parent.right;
}
s.color = x.parent.color;
x.parent.color = 0;
s.right.color = 0;
leftRotate(x.parent);
x = root;
}
} else {
s = x.parent.left;
if (s.color == 1) {
s.color = 0;
x.parent.color = 1;
rightRotate(x.parent);
s = x.parent.left;
}
if (s.right.color == 0 && s.right.color == 0) {
s.color = 1;
x = x.parent;
} else {
if (s.left.color == 0) {
s.right.color = 0;
s.color = 1;
leftRotate(s);
s = x.parent.left;
}
s.color = x.parent.color;
x.parent.color = 0;
s.left.color = 0;
rightRotate(x.parent);
x = root;
}
}
}
x.color = 0;
}
private void rbTransplant(Node u, Node v) {
if (u.parent == null) {
root = v;
} else if (u == u.parent.left) {
u.parent.left = v;
} else {
u.parent.right = v;
}
v.parent = u.parent;
}
private void deleteNodeHelper(Node node, int key) {
Node z = TNULL;
Node x, y;
while (node != TNULL) {
if (node.data == key) {
z = node;
}
if (node.data <= key) {
node = node.right;
} else {
node = node.left;
}
}
if (z == TNULL) {
System.out.println("Couldn't find key in the tree");
return;
}
y = z;
int yOriginalColor = y.color;
if (z.left == TNULL) {
x = z.right;
rbTransplant(z, z.right);
} else if (z.right == TNULL) {
x = z.left;
rbTransplant(z, z.left);
} else {
y = minimum(z.right);
yOriginalColor = y.color;
x = y.right;
if (y.parent == z) {
x.parent = y;
} else {
rbTransplant(y, y.right);
y.right = z.right;
y.right.parent = y;
}
rbTransplant(z, y);
y.left = z.left;
y.left.parent = y;
y.color = z.color;
}
if (yOriginalColor == 0) {
fixDelete(x);
}
}
// Balance the node after insertion
private void fixInsert(Node k) {
Node u;
while (k.parent.color == 1) {
if (k.parent == k.parent.parent.right) {
u = k.parent.parent.left;
if (u.color == 1) {
u.color = 0;
k.parent.color = 0;
k.parent.parent.color = 1;
k = k.parent.parent;
} else {
if (k == k.parent.left) {
k = k.parent;
rightRotate(k);
}
k.parent.color = 0;
k.parent.parent.color = 1;
leftRotate(k.parent.parent);
}
} else {
u = k.parent.parent.right;
if (u.color == 1) {
u.color = 0;
k.parent.color = 0;
k.parent.parent.color = 1;
k = k.parent.parent;
} else {
if (k == k.parent.right) {
k = k.parent;
leftRotate(k);
}
k.parent.color = 0;
k.parent.parent.color = 1;
rightRotate(k.parent.parent);
}
}
if (k == root) {
break;
}
}
root.color = 0;
}
private void printHelper(Node root, String indent, boolean last) {
if (root != TNULL) {
System.out.print(indent);
if (last) {
System.out.print("R----");
indent += " ";
} else {
System.out.print("L----");
indent += "| ";
}
String sColor = root.color == 1 ? "RED" : "BLACK";
System.out.println(root.data + "(" + sColor + ")");
printHelper(root.left, indent, false);
printHelper(root.right, indent, true);
}
}
public RedBlackTree() {
TNULL = new Node();
TNULL.color = 0;
TNULL.left = null;
TNULL.right = null;
root = TNULL;
}
public void preorder() {
preOrderHelper(this.root);
}
public void inorder() {
inOrderHelper(this.root);
}
public void postorder() {
postOrderHelper(this.root);
}
public Node searchTree(int k) {
return searchTreeHelper(this.root, k);
}
public Node minimum(Node node) {
while (node.left != TNULL) {
node = node.left;
}
return node;
}
public Node maximum(Node node) {
while (node.right != TNULL) {
node = node.right;
}
return node;
}
public Node successor(Node x) {
if (x.right != TNULL) {
return minimum(x.right);
}
Node y = x.parent;
while (y != TNULL && x == y.right) {
x = y;
y = y.parent;
}
return y;
}
public Node predecessor(Node x) {
if (x.left != TNULL) {
return maximum(x.left);
}
Node y = x.parent;
while (y != TNULL && x == y.left) {
x = y;
y = y.parent;
}
return y;
}
public void leftRotate(Node x) {
Node y = x.right;
x.right = y.left;
if (y.left != TNULL) {
y.left.parent = x;
}
y.parent = x.parent;
if (x.parent == null) {
this.root = y;
} else if (x == x.parent.left) {
x.parent.left = y;
} else {
x.parent.right = y;
}
y.left = x;
x.parent = y;
}
public void rightRotate(Node x) {
Node y = x.left;
x.left = y.right;
if (y.right != TNULL) {
y.right.parent = x;
}
y.parent = x.parent;
if (x.parent == null) {
this.root = y;
} else if (x == x.parent.right) {
x.parent.right = y;
} else {
x.parent.left = y;
}
y.right = x;
x.parent = y;
}
public void insert(int key) {
Node node = new Node();
node.parent = null;
node.data = key;
node.left = TNULL;
node.right = TNULL;
node.color = 1;
Node y = null;
Node x = this.root;
while (x != TNULL) {
y = x;
if (node.data < x.data) {
x = x.left;
} else {
x = x.right;
}
}
node.parent = y;
if (y == null) {
root = node;
} else if (node.data < y.data) {
y.left = node;
} else {
y.right = node;
}
if (node.parent == null) {
node.color = 0;
return;
}
if (node.parent.parent == null) {
return;
}
fixInsert(node);
}
public Node getRoot() {
return this.root;
}
public void deleteNode(int data) {
deleteNodeHelper(this.root, data);
}
public void printTree() {
printHelper(this.root, "", true);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
RedBlackTree V = new RedBlackTree();
V.insert(24);
V.insert(33);
V.insert(42);
V.insert(51);
V.insert(60);
V.insert(40);
V.insert(22);
V.printTree();
System.out.println("\nAfter deleting an element:");
V.deleteNode(40);
V.printTree();
}
}
輸出
R----33(BLACK)
L----24(BLACK)
| L----22(RED)
R----51(RED)
L----42(BLACK)
| L----40(RED)
R----60(BLACK)
After deleting an element:
R----33(BLACK)
L----24(BLACK)
| L----22(RED)
R----51(RED)
L----42(BLACK)
R----60(BLACK)
#python program for Red black trees
import sys
# Node creation
class Node():
def __init__(self, item):
self.item = item
self.parent = None
self.left = None
self.right = None
self.color = 1
class RedBlackTree():
def __init__(self):
self.TNULL = Node(0)
self.TNULL.color = 0
self.TNULL.left = None
self.TNULL.right = None
self.root = self.TNULL
# Preorder
def pre_order_helper(self, node):
if node != TNULL:
sys.stdout.write(node.item + " ")
self.pre_order_helper(node.left)
self.pre_order_helper(node.right)
# Inorder
def in_order_helper(self, node):
if node != TNULL:
self.in_order_helper(node.left)
sys.stdout.write(node.item + " ")
self.in_order_helper(node.right)
# Postorder
def post_order_helper(self, node):
if node != TNULL:
self.post_order_helper(node.left)
self.post_order_helper(node.right)
sys.stdout.write(node.item + " ")
# Search the tree
def search_tree_helper(self, node, key):
if node == TNULL or key == node.item:
return node
if key < node.item:
return self.search_tree_helper(node.left, key)
return self.search_tree_helper(node.right, key)
# Balancing the tree after deletion
def delete_fix(self, x):
while x != self.root and x.color == 0:
if x == x.parent.left:
s = x.parent.right
if s.color == 1:
s.color = 0
x.parent.color = 1
self.left_rotate(x.parent)
s = x.parent.right
if s.left.color == 0 and s.right.color == 0:
s.color = 1
x = x.parent
else:
if s.right.color == 0:
s.left.color = 0
s.color = 1
self.right_rotate(s)
s = x.parent.right
s.color = x.parent.color
x.parent.color = 0
s.right.color = 0
self.left_rotate(x.parent)
x = self.root
else:
s = x.parent.left
if s.color == 1:
s.color = 0
x.parent.color = 1
self.right_rotate(x.parent)
s = x.parent.left
if s.right.color == 0 and s.right.color == 0:
s.color = 1
x = x.parent
else:
if s.left.color == 0:
s.right.color = 0
s.color = 1
self.left_rotate(s)
s = x.parent.left
s.color = x.parent.color
x.parent.color = 0
s.left.color = 0
self.right_rotate(x.parent)
x = self.root
x.color = 0
def __rb_transplant(self, u, v):
if u.parent == None:
self.root = v
elif u == u.parent.left:
u.parent.left = v
else:
u.parent.right = v
v.parent = u.parent
# Node deletion
def delete_node_helper(self, node, key):
z = self.TNULL
while node != self.TNULL:
if node.item == key:
z = node
if node.item <= key:
node = node.right
else:
node = node.left
if z == self.TNULL:
print("Cannot find key in the tree")
return
y = z
y_original_color = y.color
if z.left == self.TNULL:
x = z.right
self.__rb_transplant(z, z.right)
elif (z.right == self.TNULL):
x = z.left
self.__rb_transplant(z, z.left)
else:
y = self.minimum(z.right)
y_original_color = y.color
x = y.right
if y.parent == z:
x.parent = y
else:
self.__rb_transplant(y, y.right)
y.right = z.right
y.right.parent = y
self.__rb_transplant(z, y)
y.left = z.left
y.left.parent = y
y.color = z.color
if y_original_color == 0:
self.delete_fix(x)
# Balance the tree after insertion
def fix_insert(self, k):
while k.parent.color == 1:
if k.parent == k.parent.parent.right:
u = k.parent.parent.left
if u.color == 1:
u.color = 0
k.parent.color = 0
k.parent.parent.color = 1
k = k.parent.parent
else:
if k == k.parent.left:
k = k.parent
self.right_rotate(k)
k.parent.color = 0
k.parent.parent.color = 1
self.left_rotate(k.parent.parent)
else:
u = k.parent.parent.right
if u.color == 1:
u.color = 0
k.parent.color = 0
k.parent.parent.color = 1
k = k.parent.parent
else:
if k == k.parent.right:
k = k.parent
self.left_rotate(k)
k.parent.color = 0
k.parent.parent.color = 1
self.right_rotate(k.parent.parent)
if k == self.root:
break
self.root.color = 0
# Printing the tree
def __print_helper(self, node, indent, last):
if node != self.TNULL:
sys.stdout.write(indent)
if last:
sys.stdout.write("R----")
indent += " "
else:
sys.stdout.write("L----")
indent += "| "
s_color = "RED" if node.color == 1 else "BLACK"
print(str(node.item) + "(" + s_color + ")")
self.__print_helper(node.left, indent, False)
self.__print_helper(node.right, indent, True)
def preorder(self):
self.pre_order_helper(self.root)
def inorder(self):
self.in_order_helper(self.root)
def postorder(self):
self.post_order_helper(self.root)
def searchTree(self, k):
return self.search_tree_helper(self.root, k)
def minimum(self, node):
while node.left != self.TNULL:
node = node.left
return node
def maximum(self, node):
while node.right != self.TNULL:
node = node.right
return node
def successor(self, x):
if x.right != self.TNULL:
return self.minimum(x.right)
y = x.parent
while y != self.TNULL and x == y.right:
x = y
y = y.parent
return y
def predecessor(self, x):
if (x.left != self.TNULL):
return self.maximum(x.left)
y = x.parent
while y != self.TNULL and x == y.left:
x = y
y = y.parent
return y
def left_rotate(self, x):
y = x.right
x.right = y.left
if y.left != self.TNULL:
y.left.parent = x
y.parent = x.parent
if x.parent == None:
self.root = y
elif x == x.parent.left:
x.parent.left = y
else:
x.parent.right = y
y.left = x
x.parent = y
def right_rotate(self, x):
y = x.left
x.left = y.right
if y.right != self.TNULL:
y.right.parent = x
y.parent = x.parent
if x.parent == None:
self.root = y
elif x == x.parent.right:
x.parent.right = y
else:
x.parent.left = y
y.right = x
x.parent = y
def insert(self, key):
node = Node(key)
node.parent = None
node.item = key
node.left = self.TNULL
node.right = self.TNULL
node.color = 1
y = None
x = self.root
while x != self.TNULL:
y = x
if node.item < x.item:
x = x.left
else:
x = x.right
node.parent = y
if y == None:
self.root = node
elif node.item < y.item:
y.left = node
else:
y.right = node
if node.parent == None:
node.color = 0
return
if node.parent.parent == None:
return
self.fix_insert(node)
def get_root(self):
return self.root
def delete_node(self, item):
self.delete_node_helper(self.root, item)
def print_tree(self):
self.__print_helper(self.root, "", True)
if __name__ == "__main__":
V = RedBlackTree()
V.insert(24)
V.insert(33)
V.insert(42)
V.insert(51)
V.insert(60)
V.insert(40)
V.insert(22)
V.print_tree()
print("\nAfter deleting an element")
V.delete_node(40)
V.print_tree()
輸出
R----33(BLACK)
L----24(BLACK)
| L----22(RED)
R----51(RED)
L----42(BLACK)
| L----40(RED)
R----60(BLACK)
After deleting an element
R----33(BLACK)
L----24(BLACK)
| L----22(RED)
R----51(RED)
L----42(BLACK)
R----60(BLACK)
B 樹
B樹是擴充套件的二叉搜尋樹,專門用於m路搜尋,因為B樹的階數為'm'。樹的階數定義為一個節點可以容納的最大子節點數。因此,B樹的高度相對小於AVL樹和紅黑樹的高度。
它們是二叉搜尋樹的一般形式,因為它可以儲存多個鍵和兩個子節點。
B樹的各種性質包括 -
B樹中的每個節點最多包含m個子節點和(m-1)個鍵,因為樹的階數為m。
B樹中除根節點和葉子節點外的每個節點至少包含m/2個子節點
根節點必須至少有兩個子節點。
B樹中的所有路徑必須在同一級別結束,即葉子節點必須在同一級別。
B樹始終保持資料排序。

B樹也廣泛用於磁碟訪問,最大限度地減少磁碟訪問時間,因為B樹的高度較低。
注意 - 磁碟訪問是訪問儲存資訊的計算機磁碟的記憶體訪問,磁碟訪問時間是系統訪問磁碟記憶體所需的時間。
B樹的基本操作
B樹支援的操作包括插入、刪除和搜尋,每個操作的時間複雜度為O(log n)。
插入
B樹的插入操作類似於二叉搜尋樹,但元素被插入到同一個節點,直到達到最大鍵數。插入使用以下過程完成 -
步驟1 - 計算節點可以容納的最大$\mathrm{\left ( m-1 \right )}$和最小$\mathrm{\left ( \left \lceil \frac{m}{2}\right \rceil-1 \right )}$鍵數,其中m表示B樹的階數。

步驟2 - 使用二叉搜尋插入將資料插入到樹中,一旦鍵達到最大數量,節點就被分成兩半,中間鍵成為內部節點,而左右鍵成為其子節點。

步驟3 - 所有葉子節點必須在同一級別。
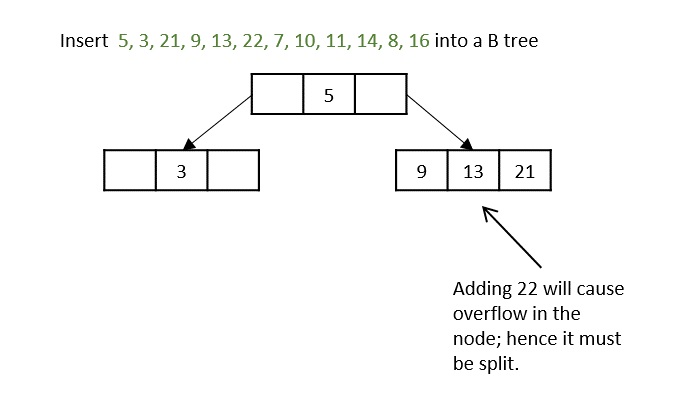
鍵5、3、21、9、13都根據二叉搜尋屬性新增到節點中,但如果我們新增鍵22,它將違反最大鍵屬性。因此,節點被分成兩半,中間鍵被移到父節點,然後繼續插入。
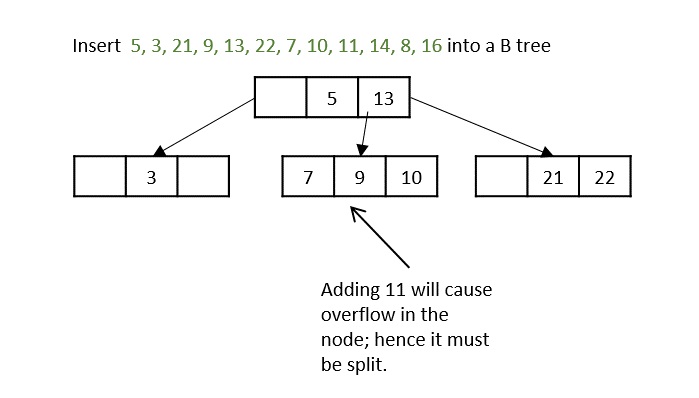
在插入11時發生另一個問題,因此節點被分割,中間鍵被移到父節點。
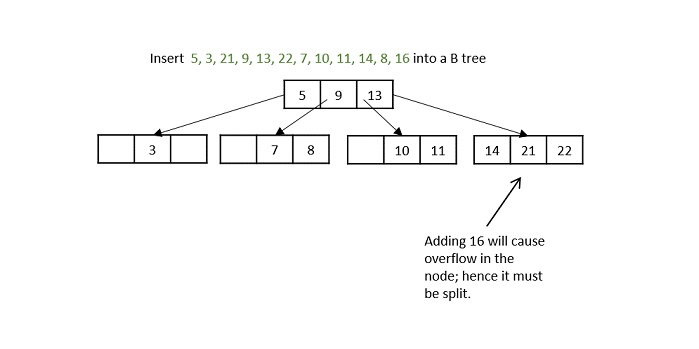
在插入16時,即使節點被分成兩部分,父節點也會溢位,因為它達到了最大鍵數。因此,父節點首先被分割,中間鍵成為根節點。然後,葉子節點被分成兩半,葉子節點的中值被移到其父節點。

插入所有元素後的最終B樹。
示例
// Insert the value
void insertion(int item) {
int flag, i;
struct btreeNode *child;
flag = setNodeValue(item, &i, root, &child);
if (flag)
root = createNode(i, child);
}
刪除
B樹中的刪除操作與二叉搜尋樹的刪除操作略有不同。從B樹中刪除節點的過程如下 -
情況1 - 如果要刪除的鍵位於葉子節點中,並且刪除不會違反最小鍵屬性,則只需刪除該節點。
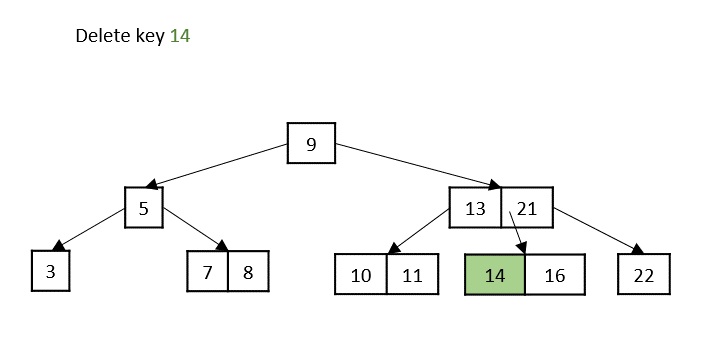
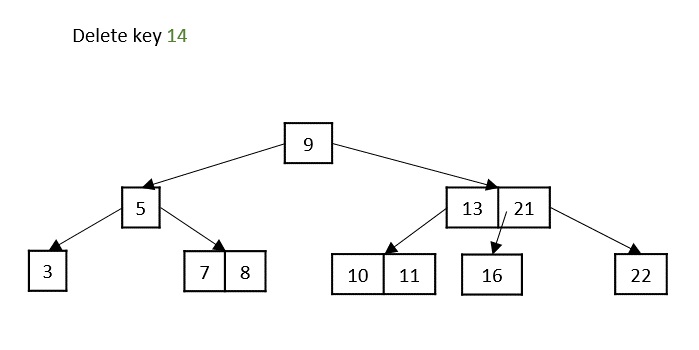
情況2 - 如果要刪除的鍵位於葉子節點中,但刪除違反了最小鍵屬性,則從其左兄弟節點或右兄弟節點借用一個鍵。如果兩個兄弟節點都恰好具有最少的鍵數,則將該節點合併到其中一箇中。
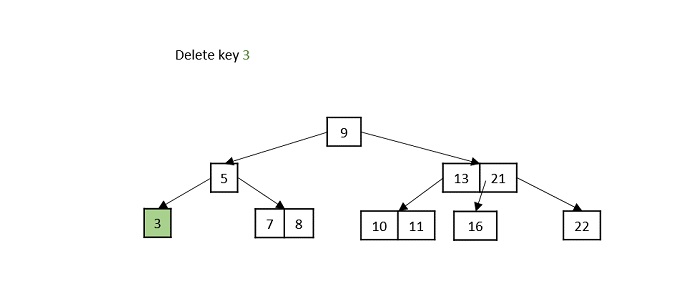
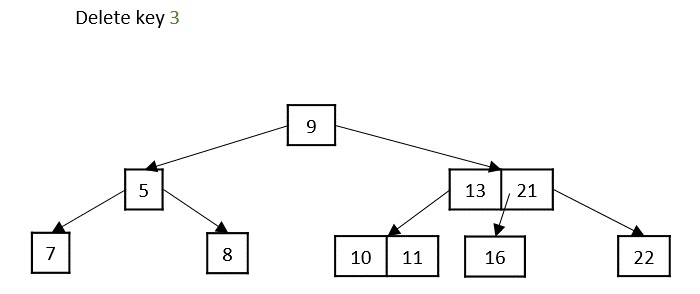
情況3 - 如果要刪除的鍵位於內部節點中,則將其替換為左子節點或右子節點中的一個鍵,具體取決於哪個子節點具有更多鍵。但如果兩個子節點都具有最少的鍵數,則將它們合併在一起。
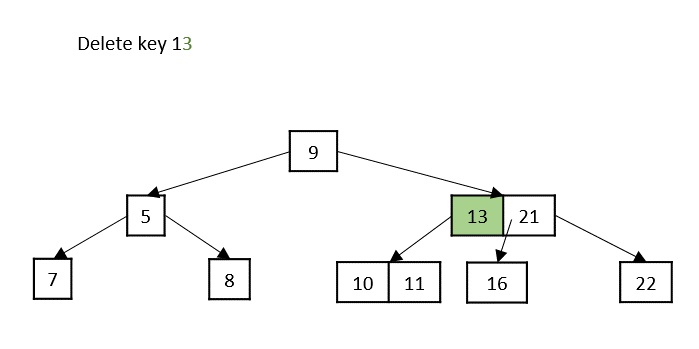
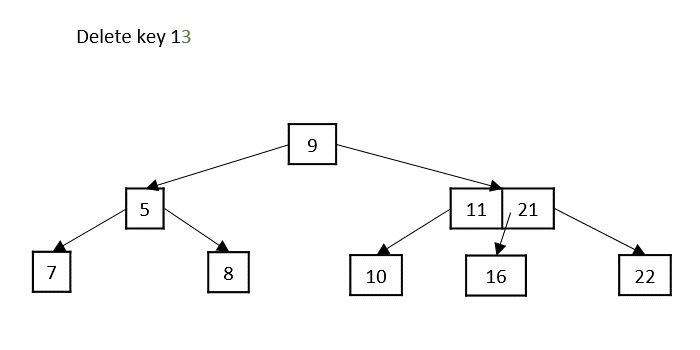
情況4 - 如果要刪除的鍵位於內部節點中,違反了最小鍵屬性,並且其兩個子節點和兄弟節點都具有最少的鍵數,則合併子節點。然後將其兄弟節點與其父節點合併。
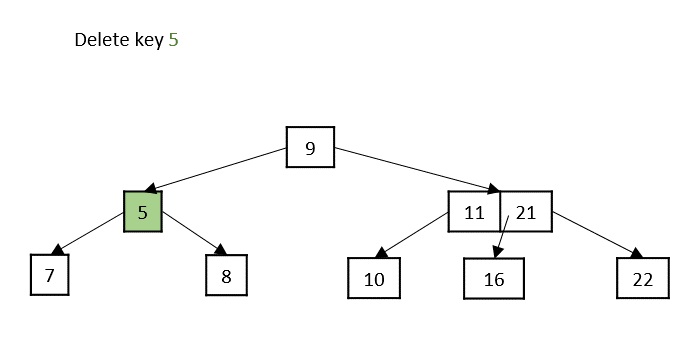
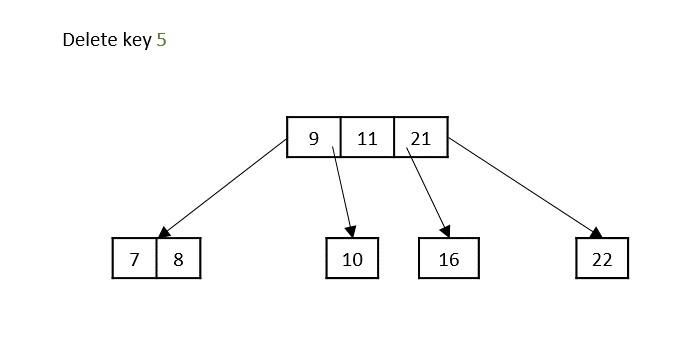
以下是B樹中刪除操作的功能性C++程式碼片段 -
// Deletion operation
void deletion(int key){
int index = searchkey(key);
if (index < n && keys[index] == key) {
if (leaf)
deletion_at_leaf(index);
else
deletion_at_nonleaf(index);
} else {
if (leaf) {
cout << "key " << key << " does not exist in the tree\n";
return;
}
bool flag = ((index == n) ? true : false);
if (C[index]->n < t)
fill(index);
if (flag && index > n)
C[index - 1]->deletion(key);
else
C[index]->deletion(key);
}
return;
}
// Deletion at the leaf nodes
void deletion_at_leaf(int index){
for (int i = index + 1; i < n; ++i)
keys[i - 1] = keys[i];
n--;
return;
}
// Deletion at the non leaf node
void deletion_at_nonleaf(int index){
int key = keys[index];
if (C[index]->n >= t) {
int pred = get_Predecessor(index);
keys[index] = pred;
C[index]->deletion(pred);
} else if (C[index + 1]->n >= t) {
int successor = copysuccessoressor(index);
keys[index] = successor;
C[index + 1]->deletion(successor);
} else {
merge(index);
C[index]->deletion(key);
}
return;
}
示例
// C Program for B trees
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct BTree {
//node declaration
int *d;
struct BTree **child_ptr;
int l;
int n;
};
struct BTree *r = NULL;
struct BTree *np = NULL;
struct BTree *x = NULL;
//creation of node
struct BTree* init() {
int i;
np = (struct BTree*)malloc(sizeof(struct BTree));
//order 6
np->d = (int*)malloc(6 * sizeof(int));
np->child_ptr = (struct BTree**)malloc(7 * sizeof(struct BTree*));
np->l = 1;
np->n = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
np->child_ptr[i] = NULL;
}
return np;
}
//traverse the tree
void traverse(struct BTree *p) {
printf("\n");
int i;
for (i = 0; i < p->n; i++) {
if (p->l == 0) {
traverse(p->child_ptr[i]);
}
printf(" %d", p->d[i]);
}
if (p->l == 0) {
traverse(p->child_ptr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
//sort the tree
void sort(int *p, int n) {
int i, j, t;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (j = i; j <= n; j++) {
if (p[i] > p[j]) {
t = p[i];
p[i] = p[j];
p[j] = t;
}
}
}
}
int split_child(struct BTree *x, int i) {
int j, mid;
struct BTree *np1, *np3, *y;
np3 = init();
//create new node
np3->l = 1;
if (i == -1) {
mid = x->d[2];
//find mid
x->d[2] = 0;
x->n--;
np1 = init();
np1->l = 0;
x->l = 1;
for (j = 3; j < 6; j++) {
np3->d[j - 3] = x->d[j];
np3->child_ptr[j - 3] = x->child_ptr[j];
np3->n++;
x->d[j] = 0;
x->n--;
}
for (j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
x->child_ptr[j] = NULL;
}
np1->d[0] = mid;
np1->child_ptr[np1->n] = x;
np1->child_ptr[np1->n + 1] = np3;
np1->n++;
r = np1;
} else {
y = x->child_ptr[i];
mid = y->d[2];
y->d[2] = 0;
y->n--;
for (j = 3; j < 6; j++) {
np3->d[j - 3] = y->d[j];
np3->n++;
y->d[j] = 0;
y->n--;
}
x->child_ptr[i + 1] = y;
x->child_ptr[i + 1] = np3;
}
return mid;
}
void insert(int a) {
int i, t;
x = r;
if (x == NULL) {
r = init();
x = r;
} else {
if (x->l == 1 && x->n == 6) {
t = split_child(x, -1);
x = r;
for (i = 0; i < x->n; i++) {
if (a > x->d[i] && a < x->d[i + 1]) {
i++;
break;
} else if (a < x->d[0]) {
break;
} else {
continue;
}
}
x = x->child_ptr[i];
} else {
while (x->l == 0) {
for (i = 0; i < x->n; i++) {
if (a > x->d[i] && a < x->d[i + 1]) {
i++;
break;
} else if (a < x->d[0]) {
break;
} else {
continue;
}
}
if (x->child_ptr[i]->n == 6) {
t = split_child(x, i);
x->d[x->n] = t;
x->n++;
continue;
} else {
x = x->child_ptr[i];
}
}
}
}
x->d[x->n] = a;
sort(x->d, x->n);
x->n++;
}
int main() {
int i, n, t;
insert(10);
insert(20);
insert(30);
insert(40);
insert(50);
printf("B tree:\n");
traverse(r);
return 0;
}
輸出
B tree: 10 20 30 40 50
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct BTree {//node declaration
int *d;
BTree **child_ptr;
bool l;
int n;
}*r = NULL, *np = NULL, *x = NULL;
BTree* init() {//creation of node
int i;
np = new BTree;
np->d = new int[6];//order 6
np->child_ptr = new BTree *[7];
np->l = true;
np->n = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
np->child_ptr[i] = NULL;
}
return np;
}
void traverse(BTree *p) { //traverse the tree
cout<<endl;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < p->n; i++) {
if (p->l == false) {
traverse(p->child_ptr[i]);
}
cout << " " << p->d[i];
}
if (p->l == false) {
traverse(p->child_ptr[i]);
}
cout<<endl;
}
void sort(int *p, int n){ //sort the tree
int i, j, t;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (j = i; j <= n; j++) {
if (p[i] >p[j]) {
t = p[i];
p[i] = p[j];
p[j] = t;
}
}
}
}
int split_child(BTree *x, int i) {
int j, mid;
BTree *np1, *np3, *y;
np3 = init();//create new node
np3->l = true;
if (i == -1) {
mid = x->d[2];//find mid
x->d[2] = 0;
x->n--;
np1 = init();
np1->l= false;
x->l= true;
for (j = 3; j < 6; j++) {
np3->d[j - 3] = x->d[j];
np3->child_ptr[j - 3] = x->child_ptr[j];
np3->n++;
x->d[j] = 0;
x->n--;
}
for (j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
x->child_ptr[j] = NULL;
}
np1->d[0] = mid;
np1->child_ptr[np1->n] = x;
np1->child_ptr[np1->n + 1] = np3;
np1->n++;
r = np1;
} else {
y = x->child_ptr[i];
mid = y->d[2];
y->d[2] = 0;
y->n--;
for (j = 3; j <6 ; j++) {
np3->d[j - 3] = y->d[j];
np3->n++;
y->d[j] = 0;
y->n--;
}
x->child_ptr[i + 1] = y;
x->child_ptr[i + 1] = np3;
}
return mid;
}
void insert(int a) {
int i, t;
x = r;
if (x == NULL) {
r = init();
x = r;
} else {
if (x->l== true && x->n == 6) {
t = split_child(x, -1);
x = r;
for (i = 0; i < (x->n); i++) {
if ((a >x->d[i]) && (a < x->d[i + 1])) {
i++;
break;
} else if (a < x->d[0]) {
break;
} else {
continue;
}
}
x = x->child_ptr[i];
} else {
while (x->l == false) {
for (i = 0; i < (x->n); i++) {
if ((a >x->d[i]) && (a < x->d[i + 1])) {
i++;
break;
} else if (a < x->d[0]) {
break;
} else {
continue;
}
}
if ((x->child_ptr[i])->n == 6) {
t = split_child(x, i);
x->d[x->n] = t;
x->n++;
continue;
} else {
x = x->child_ptr[i];
}
}
}
}
x->d[x->n] = a;
sort(x->d, x->n);
x->n++;
}
int main() {
int i, n, t;
insert(10);
insert(20);
insert(30);
insert(40);
insert(50);
cout<<"B tree:\n";
traverse(r);
}
輸出
B tree: 10 20 30 40 50
//Java code for B trees
import java.util.Arrays;
class BTree {
private int[] d;
private BTree[] child_ptr;
private boolean l;
private int n;
public BTree() {
d = new int[6]; // order 6
child_ptr = new BTree[7];
l = true;
n = 0;
Arrays.fill(child_ptr, null);
}
public void traverse() {
System.out.println("B tree: ");
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!l) {
child_ptr[i].traverse();
}
System.out.print(d[i] + " ");
}
if (!l) {
child_ptr[n].traverse();
}
System.out.println();
}
public void sort() {
Arrays.sort(d, 0, n);
}
public int splitChild(int i) {
int j, mid;
BTree np1, np3, y;
np3 = new BTree();
np3.l = true;
if (i == -1) {
mid = d[2];
d[2] = 0;
n--;
np1 = new BTree();
np1.l = false;
l = true;
for (j = 3; j < 6; j++) {
np3.d[j - 3] = d[j];
np3.n++;
d[j] = 0;
n--;
}
for (j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
np3.child_ptr[j] = child_ptr[j + 3];
child_ptr[j + 3] = null;
}
np1.d[0] = mid;
np1.child_ptr[0] = this;
np1.child_ptr[1] = np3;
np1.n++;
return mid;
} else {
y = child_ptr[i];
mid = y.d[2];
y.d[2] = 0;
y.n--;
for (j = 3; j < 6; j++) {
np3.d[j - 3] = y.d[j];
np3.n++;
y.d[j] = 0;
y.n--;
}
child_ptr[i + 1] = y;
child_ptr[i + 2] = np3;
return mid;
}
}
public void insert(int a) {
int i, t;
BTree x = this;
if (x.l && x.n == 6) {
t = x.splitChild(-1);
x = this;
for (i = 0; i > x.n; i++) {
if (a > x.d[i] && a < x.d[i + 1]) {
i++;
break;
} else if (a < x.d[0]) {
break;
}
}
x = x.child_ptr[i];
} else {
while (!x.l) {
for (i = 0; i < x.n; i++) {
if (a > x.d[i] && a < x.d[i + 1]) {
i++;
break;
} else if (a < x.d[0]) {
break;
}
}
if (x.child_ptr[i].n == 6) {
t = x.splitChild(i);
x.d[x.n] = t;
x.n++;
continue;
}
x = x.child_ptr[i];
}
}
x.d[x.n] = a;
x.sort();
x.n++;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BTree bTree = new BTree();
bTree.insert(20);
bTree.insert(10);
bTree.insert(40);
bTree.insert(30);
bTree.insert(50); // Duplicate value, ignored
//call the traverse method
bTree.traverse();
}
}
輸出
B tree: 10 20 30 40 50
#python program for B treesa
class BTree:
def __init__(self):
#node declartion
self.d = [0] * 6
self.child_ptr = [None] * 7
self.l = True
self.n = 0
#creation of node
def init():
np = BTree()
np.l = True
np.n = 0
return np
#traverse the tree
def traverse(p):
if p is not None:
for i in range(p.n):
if not p.l:
traverse(p.child_ptr[i])
print(p.d[i], end=" ")
if not p.l:
traverse(p.child_ptr[p.n])
#sort the tree
def sort(p, n):
for i in range(n):
for j in range(i, n+1):
if p[i] > p[j]:
p[i], p[j] = p[j], p[i]
def split_child(x, i):
np3 = init()
#create new node
np3.l = True
if i == -1:
mid = x.d[2]
#find mid
x.d[2] = 0
x.n -= 1
np1 = init()
np1.l = False
x.l = True
for j in range(3, 6):
np3.d[j-3] = x.d[j]
np3.child_ptr[j-3] = x.child_ptr[j]
np3.n += 1
x.d[j] = 0
x.n -= 1
for j in range(6):
x.child_ptr[j] = None
np1.d[0] = mid
np1.child_ptr[np1.n] = x
np1.child_ptr[np1.n + 1] = np3
np1.n += 1
return np1
else:
y = x.child_ptr[i]
mid = y.d[2]
y.d[2] = 0
y.n -= 1
for j in range(3, 6):
np3.d[j-3] = y.d[j]
np3.n += 1
y.d[j] = 0
y.n -= 1
x.child_ptr[i + 1] = y
x.child_ptr[i + 1] = np3
return mid
def insert(a):
global r, x
if r is None:
r = init()
x = r
else:
if x.l and x.n == 6:
t = split_child(x, -1)
x = r
for i in range(x.n):
if a > x.d[i] and a < x.d[i + 1]:
i += 1
break
elif a < x.d[0]:
break
else:
continue
x = x.child_ptr[i]
else:
while not x.l:
for i in range(x.n):
if a > x.d[i] and a < x.d[i + 1]:
i += 1
break
elif a < x.d[0]:
break
else:
continue
if x.child_ptr[i].n == 6:
t = split_child(x, i)
x.d[x.n] = t
x.n += 1
continue
else:
x = x.child_ptr[i]
x.d[x.n] = a
sort(x.d, x.n)
x.n += 1
if __name__ == '__main__':
r = None
x = None
insert(10)
insert(20)
insert(30)
insert(40)
insert(50)
print("B tree:")
traverse(r)
輸出
B tree: 10 20 30 40 50
B+ 樹
B+樹是B樹的擴充套件,旨在使插入、刪除和搜尋操作更有效率。
B+樹的性質與B樹的性質相似,不同之處在於B樹可以在所有內部節點和葉子節點中儲存鍵和記錄,而B+樹在葉子節點中儲存記錄,在內部節點中儲存鍵。B+樹的一個顯著性質是所有葉子節點都以單個連結列表格式相互連線,並且有一個數據指標可用於指向磁碟檔案中存在的資料。這有助於以相同數量的磁碟訪問次數獲取記錄。
由於主儲存器的容量有限,B+樹充當無法儲存在主儲存器中的記錄的資料儲存。為此,內部節點儲存在主儲存器中,葉子節點儲存在輔助儲存器中。
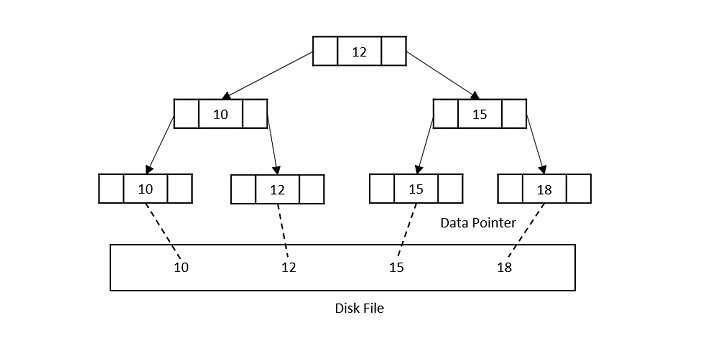
B+樹的性質
B+樹中除根節點外的每個節點最多包含m個子節點和(m-1)個鍵,最少包含$\mathrm{\left \lceil \frac{m}{2}\right \rceil}$個子節點和$\mathrm{\left \lceil \frac{m-1}{2}\right \rceil}$個鍵,因為樹的階數為m。
根節點必須至少有兩個子節點和至少一個搜尋鍵。
B樹中的所有路徑必須在同一級別結束,即葉子節點必須在同一級別。
B+樹始終保持資料排序。
B+樹的基本操作
B+樹支援的操作包括插入、刪除和查詢,每種操作的時間複雜度均為O(log n)。
它們與B樹的操作非常相似,因為這兩種資料結構儲存資料的基本思想相同。但是,不同之處在於,B+樹的資料僅儲存在葉子節點中,而B樹則不是。
插入
向B+樹插入資料從葉子節點開始。
步驟1 - 計算要新增到B+樹節點中的鍵的最大值和最小值。

步驟2 - 將元素逐個插入到葉子節點中,直到超過最大鍵數。

步驟3 - 將節點分成兩半,左子節點包含最小數量的鍵,其餘鍵儲存在右子節點中。
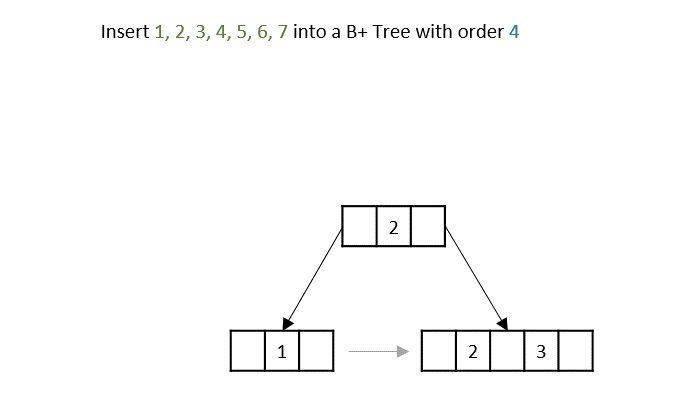
步驟4 - 但是,如果內部節點也超過了最大鍵數,則將節點分成兩半,左子節點包含最小數量的鍵,其餘鍵儲存在右子節點中。但是,右子節點中最小的數字將成為父節點。

步驟5 - 如果葉子節點和內部節點都具有最大數量的鍵,則兩者都以類似的方式進行分割,並將右子節點中最小的鍵新增到父節點中。

刪除
在B+樹中進行刪除操作時,我們需要考慮資料結構中的冗餘性。
情況1 - 如果鍵存在於葉子節點中,並且該節點的鍵數超過最小數量,並且其副本不存在於內部節點中,則直接將其刪除。


情況2 - 如果鍵存在於葉子節點中,並且該節點的鍵數正好為最小數量,並且其副本不存在於內部節點中,則從其兄弟節點借用一個鍵,然後刪除所需的鍵。
情況3 - 如果葉子節點中的鍵在內部節點中存在副本,則可能有多種情況 -
葉子節點和內部節點中都存在超過最小數量的鍵:只需刪除鍵並將中序後繼新增到內部節點中即可。
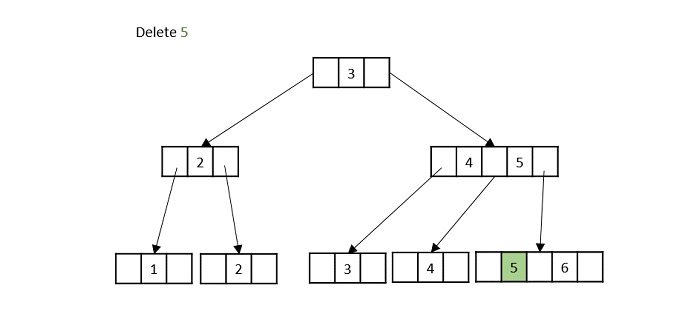

葉子節點中存在正好為最小數量的鍵:刪除節點並從其直接兄弟節點借用一個節點,並將其值替換為內部節點的值。

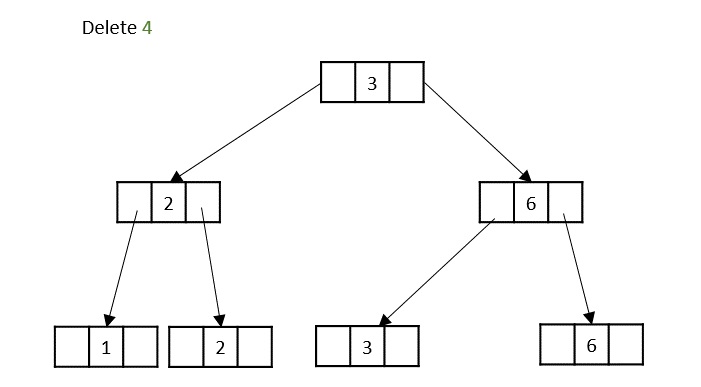
如果要刪除的葉子節點的副本在其祖父母節點中,則刪除該節點並移除空位。祖父母節點將填充已刪除節點的中序後繼。
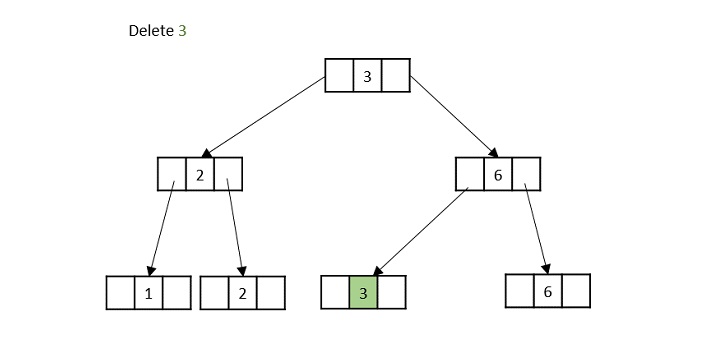
情況4 - 如果要刪除的鍵所在的節點違反了最小鍵數屬性,並且其父節點和兄弟節點的鍵數都為最小數量,則刪除該鍵並將其兄弟節點與其父節點合併。
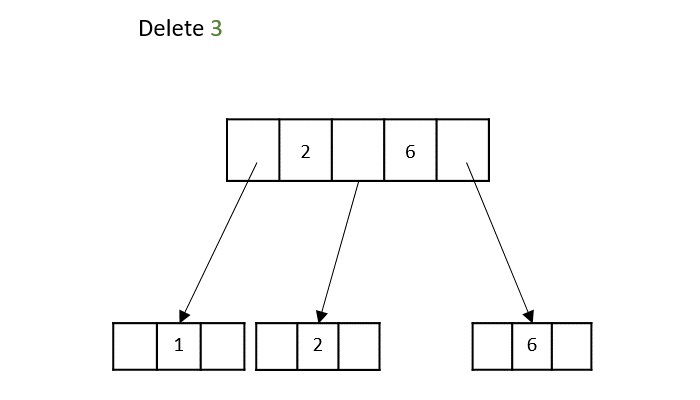
示例
// C program for Bplus tree
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct BplusTree {
int *d;
struct BplusTree **child_ptr;
int l;
int n;
};
struct BplusTree *r = NULL, *np = NULL, *x = NULL;
struct BplusTree* init() {
//to create nodes
int i;
np = (struct BplusTree*)malloc(sizeof(struct BplusTree));
np->d = (int*)malloc(6 * sizeof(int)); // order 6
np->child_ptr = (struct BplusTree**)malloc(7 * sizeof(struct BplusTree*));
np->l = 1;
np->n = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
np->child_ptr[i] = NULL;
}
return np;
}
void traverse(struct BplusTree *p) {
//traverse tree
printf("\n");
int i;
for (i = 0; i < p->n; i++) {
if (p->l == 0) {
traverse(p->child_ptr[i]);
}
printf(" %d", p->d[i]);
}
if (p->l == 0) {
traverse(p->child_ptr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void sort(int *p, int n) {
int i, j, t;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (j = i; j <= n; j++) {
if (p[i] > p[j]) {
t = p[i];
p[i] = p[j];
p[j] = t;
}
}
}
}
int split_child(struct BplusTree *x, int i) {
int j, mid;
struct BplusTree *np1, *np3, *y;
np3 = init();
np3->l = 1;
if (i == -1) {
mid = x->d[2];
x->d[2] = 0;
x->n--;
np1 = init();
np1->l = 0;
x->l = 1;
for (j = 3; j < 6; j++) {
np3->d[j - 3] = x->d[j];
np3->child_ptr[j - 3] = x->child_ptr[j];
np3->n++;
x->d[j] = 0;
x->n--;
}
for (j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
x->child_ptr[j] = NULL;
}
np1->d[0] = mid;
np1->child_ptr[np1->n] = x;
np1->child_ptr[np1->n + 1] = np3;
np1->n++;
r = np1;
} else {
y = x->child_ptr[i];
mid = y->d[2];
y->d[2] = 0;
y->n--;
for (j = 3; j < 6; j++) {
np3->d[j - 3] = y->d[j];
np3->n++;
y->d[j] = 0;
y->n--;
}
x->child_ptr[i + 1] = y;
x->child_ptr[i + 1] = np3;
}
return mid;
}
void insert(int a) {
int i, t;
x = r;
if (x == NULL) {
r = init();
x = r;
} else {
if (x->l == 1 && x->n == 6) {
t = split_child(x, -1);
x = r;
for (i = 0; i < x->n; i++) {
if (a > x->d[i] && a < x->d[i + 1]) {
i++;
break;
} else if (a < x->d[0]) {
break;
} else {
continue;
}
}
x = x->child_ptr[i];
} else {
while (x->l == 0) {
for (i = 0; i < x->n; i++) {
if (a > x->d[i] && a < x->d[i + 1]) {
i++;
break;
} else if (a < x->d[0]) {
break;
} else {
continue;
}
}
if (x->child_ptr[i]->n == 6) {
t = split_child(x, i);
x->d[x->n] = t;
x->n++;
continue;
} else {
x = x->child_ptr[i];
}
}
}
}
x->d[x->n] = a;
sort(x->d, x->n);
x->n++;
}
int main() {
int i, n, t;
insert(10);
insert(20);
insert(30);
insert(40);
insert(50);
printf("B+ tree:\n");
traverse(r);
return 0;
}
輸出
B+ tree: 10 20 30 40 50
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct BplusTree {
int *d;
BplusTree **child_ptr;
bool l;
int n;
}
*r = NULL, *np = NULL, *x = NULL;
BplusTree* init() { //to create nodes
int i;
np = new BplusTree;
np->d = new int[6];//order 6
np->child_ptr = new BplusTree *[7];
np->l = true;
np->n = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
np->child_ptr[i] = NULL;
}
return np;
}
void traverse(BplusTree *p) { //traverse tree
cout<<endl;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < p->n; i++) {
if (p->l == false) {
traverse(p->child_ptr[i]);
}
cout << " " << p->d[i];
}
if (p->l == false) {
traverse(p->child_ptr[i]);
}
cout<<endl;
}
void sort(int *p, int n) { //sort the tree
int i, j, t;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (j = i; j <= n; j++) {
if (p[i] >p[j]) {
t = p[i];
p[i] = p[j];
p[j] = t;
}
}
}
}
int split_child(BplusTree *x, int i) {
int j, mid;
BplusTree *np1, *np3, *y;
np3 = init();
np3->l = true;
if (i == -1) {
mid = x->d[2];
x->d[2] = 0;
x->n--;
np1 = init();
np1->l = false;
x->l = true;
for (j = 3; j < 6; j++) {
np3->d[j - 3] = x->d[j];
np3->child_ptr[j - 3] = x->child_ptr[j];
np3->n++;
x->d[j] = 0;
x->n--;
}
for (j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
x->child_ptr[j] = NULL;
}
np1->d[0] = mid;
np1->child_ptr[np1->n] = x;
np1->child_ptr[np1->n + 1] = np3;
np1->n++;
r = np1;
} else {
y = x->child_ptr[i];
mid = y->d[2];
y->d[2] = 0;
y->n--;
for (j = 3; j <6 ; j++) {
np3->d[j - 3] = y->d[j];
np3->n++;
y->d[j] = 0;
y->n--;
}
x->child_ptr[i + 1] = y;
x->child_ptr[i + 1] = np3;
}
return mid;
}
void insert(int a) {
int i, t;
x = r;
if (x == NULL) {
r = init();
x = r;
} else {
if (x->l== true && x->n == 6) {
t = split_child(x, -1);
x = r;
for (i = 0; i < (x->n); i++) {
if ((a >x->d[i]) && (a < x->d[i + 1])) {
i++;
break;
} else if (a < x->d[0]) {
break;
} else {
continue;
}
}
x = x->child_ptr[i];
} else {
while (x->l == false) {
for (i = 0; i < (x->n); i++) {
if ((a >x->d[i]) && (a < x->d[i + 1])) {
i++;
break;
} else if (a < x->d[0]) {
break;
} else {
continue;
}
}
if ((x->child_ptr[i])->n == 6) {
t = split_child(x, i);
x->d[x->n] = t;
x->n++;
continue;
} else {
x = x->child_ptr[i];
}
}
}
}
x->d[x->n] = a;
sort(x->d, x->n);
x->n++;
}
int main() {
int i, n, t;
insert(10);
insert(20);
insert(30);
insert(40);
insert(50);
cout<<"B+ tree:\n";
traverse(r);
}
輸出
B+ tree: 10 20 30 40 50
//Java program for Bplus code
import java.util.*;
class BplusTree {
int[] d;
BplusTree[] child_ptr;
boolean l;
int n;
}
public class Main {
static BplusTree r = null, np = null, x = null;
static BplusTree init() { // to create nodes
int i;
np = new BplusTree();
np.d = new int[6]; // order 6
np.child_ptr = new BplusTree[7];
np.l = true;
np.n = 0;
for (i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
np.child_ptr[i] = null;
}
return np;
}
static void traverse(BplusTree p) { // traverse tree
System.out.println();
int i;
for (i = 0; i < p.n; i++) {
if (p.l == false) {
traverse(p.child_ptr[i]);
}
System.out.print(" " + p.d[i]);
}
if (p.l == false) {
traverse(p.child_ptr[i]);
}
System.out.println();
}
static void sort(int[] p, int n) { // sort the tree
int i, j, t;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (j = i; j <= n; j++) {
if (p[i] > p[j]) {
t = p[i];
p[i] = p[j];
p[j] = t;
}
}
}
}
static int split_child(BplusTree x, int i) {
int j, mid;
BplusTree np1, np3, y;
np3 = init();
np3.l = true;
if (i == -1) {
mid = x.d[2];
x.d[2] = 0;
x.n--;
np1 = init();
np1.l = false;
x.l = true;
for (j = 3; j < 6; j++) {
np3.d[j - 3] = x.d[j];
np3.child_ptr[j - 3] = x.child_ptr[j];
np3.n++;
x.d[j] = 0;
x.n--;
}
for (j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
x.child_ptr[j] = null;
}
np1.d[0] = mid;
np1.child_ptr[np1.n] = x;
np1.child_ptr[np1.n + 1] = np3;
np1.n++;
r = np1;
} else {
y = x.child_ptr[i];
mid = y.d[2];
y.d[2] = 0;
y.n--;
for (j = 3; j < 6; j++) {
np3.d[j - 3] = y.d[j];
np3.n++;
y.d[j] = 0;
y.n--;
}
x.child_ptr[i + 1] = y;
x.child_ptr[i + 1] = np3;
}
return mid;
}
static void insert(int a) {
int i, t;
x = r;
if (x == null) {
r = init();
x = r;
} else {
if (x.l == true && x.n == 6) {
t = split_child(x, -1);
x = r;
for (i = 0; i < x.n; i++) {
if (a > x.d[i] && a < x.d[i + 1]) {
i++;
break;
} else if (a < x.d[0]) {
break;
} else {
continue;
}
}
x = x.child_ptr[i];
} else {
while (x.l == false) {
for (i = 0; i < x.n; i++) {
if (a > x.d[i] && a < x.d[i + 1]) {
i++;
break;
} else if (a < x.d[0]) {
break;
} else {
continue;
}
}
if (x.child_ptr[i].n == 6) {
t = split_child(x, i);
x.d[x.n] = t;
x.n++;
continue;
} else {
x = x.child_ptr[i];
}
}
}
}
x.d[x.n] = a;
sort(x.d, x.n);
x.n++;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i, n, t;
insert(10);
insert(20);
insert(30);
insert(40);
insert(50);
System.out.println("B+ tree:");
traverse(r);
}
}
輸出
B+ tree: 10 20 30 40 50
#Python Program for Bplus tree
#to create nodes
class BplusTree:
def __init__(self):
self.d = [0] * 6 # order 6
self.child_ptr = [None] * 7
self.l = True
self.n = 0
def init():
np = BplusTree()
np.l = True
np.n = 0
return np
#traverse tree
def traverse(p):
print()
for i in range(p.n):
if not p.l:
traverse(p.child_ptr[i])
print(" ", p.d[i], end="")
if not p.l:
traverse(p.child_ptr[p.n])
print()
#sort the tree
def sort(p, n):
for i in range(n):
for j in range(i, n + 1):
if p[i] > p[j]:
p[i], p[j] = p[j], p[i]
def split_child(x, i):
np3 = init()
np3.l = True
if i == -1:
mid = x.d[2]
x.d[2] = 0
x.n -= 1
np1 = init()
np1.l = False
x.l = True
for j in range(3, 6):
np3.d[j - 3] = x.d[j]
np3.child_ptr[j - 3] = x.child_ptr[j]
np3.n += 1
x.d[j] = 0
x.n -= 1
for j in range(6):
x.child_ptr[j] = None
np1.d[0] = mid
np1.child_ptr[np1.n] = x
np1.child_ptr[np1.n + 1] = np3
np1.n += 1
r = np1
else:
y = x.child_ptr[i]
mid = y.d[2]
y.d[2] = 0
y.n -= 1
for j in range(3, 6):
np3.d[j - 3] = y.d[j]
np3.n += 1
y.d[j] = 0
y.n -= 1
x.child_ptr[i + 1] = y
x.child_ptr[i + 1] = np3
return mid
def insert(a):
global r, x
x = r
if x is None:
r = init()
x = r
else:
if x.l and x.n == 6:
t = split_child(x, -1)
x = r
for i in range(x.n):
if a > x.d[i] and a < x.d[i + 1]:
i += 1
break
elif a < x.d[0]:
break
else:
continue
x = x.child_ptr[i]
else:
while not x.l:
for i in range(x.n):
if a > x.d[i] and a < x.d[i + 1]:
i += 1
break
elif a < x.d[0]:
break
else:
continue
if x.child_ptr[i].n == 6:
t = split_child(x, i)
x.d[x.n] = t
x.n += 1
continue
else:
x = x.child_ptr[i]
x.d[x.n] = a
sort(x.d, x.n)
x.n += 1
r = None
x = None
insert(10)
insert(20)
insert(30)
insert(40)
insert(50)
print("B+ tree:")
traverse(r)
輸出
B+ tree: 10 20 30 40 50
伸展樹
伸展樹是二叉搜尋樹的修改版本,因為它包含BST的所有操作,如插入、刪除和查詢,以及另一個擴充套件操作,稱為伸展。
例如,假設要將值“A”插入到樹中。如果樹為空,則將“A”新增到樹的根節點並退出;但如果樹不為空,則使用二叉搜尋插入操作插入元素,然後對新節點執行伸展操作。
類似地,在伸展樹中搜索元素後,包含該元素的節點也必須進行伸展。
但是我們如何執行伸展操作呢?簡單來說,伸展操作就是將一個操作節點移到根節點的過程。它有六種型別的旋轉。
Zig旋轉
Zag旋轉
Zig-Zig旋轉
Zag-Zag旋轉
Zig-Zag旋轉
Zag-Zig旋轉
Zig旋轉
當操作節點是根節點或根節點的左子節點時,執行Zig旋轉。節點向右旋轉。

旋轉後,樹將如下所示 -
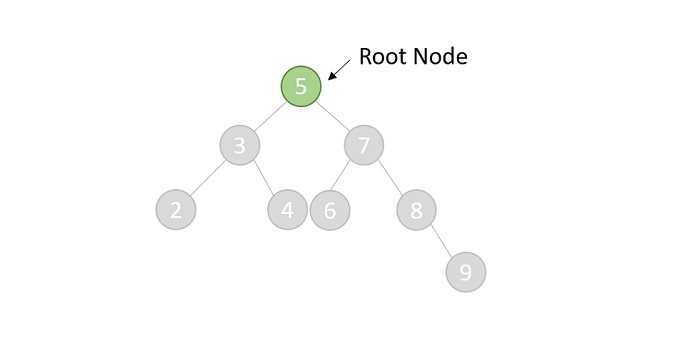
Zag旋轉
當操作節點是根節點或根節點的右子節點時,也執行Zag旋轉。節點向左旋轉。
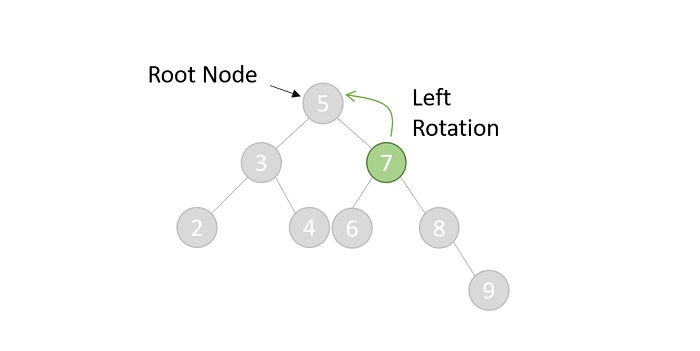
旋轉後,操作節點將成為根節點 -
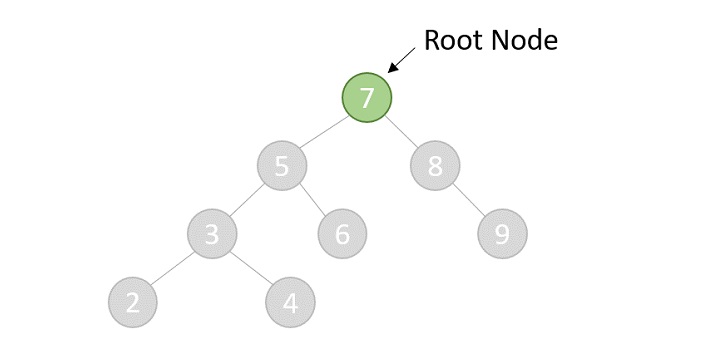
Zig-Zig旋轉
當操作節點同時具有父節點和祖父母節點時,執行Zig-Zig旋轉。節點向右旋轉兩次。

第一次旋轉將使樹向右移動一個位置 -
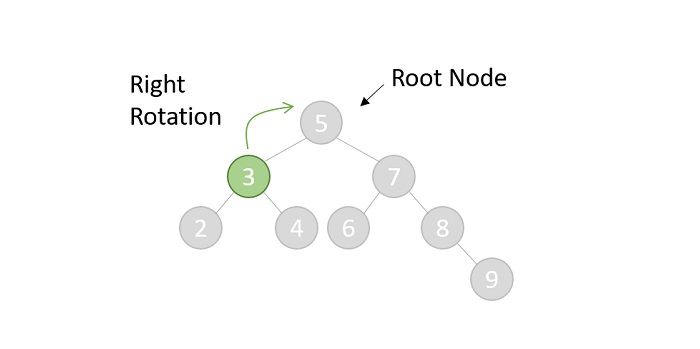
第二次右旋轉將再次使節點移動一個位置。旋轉後的最終樹將如下所示 -

Zag-Zag旋轉
當操作節點同時具有父節點和祖父母節點時,也執行Zag-Zag旋轉。節點向左旋轉兩次。

第一次旋轉後,樹將如下所示 -
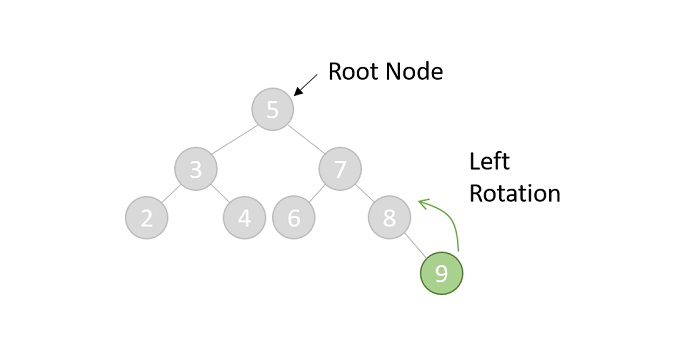
然後是第二次旋轉後的最終樹。但是,操作節點仍然不是根節點,因此伸展操作被認為是不完整的。因此,在這種情況下,將再次應用其他合適的旋轉,直到節點成為根節點。
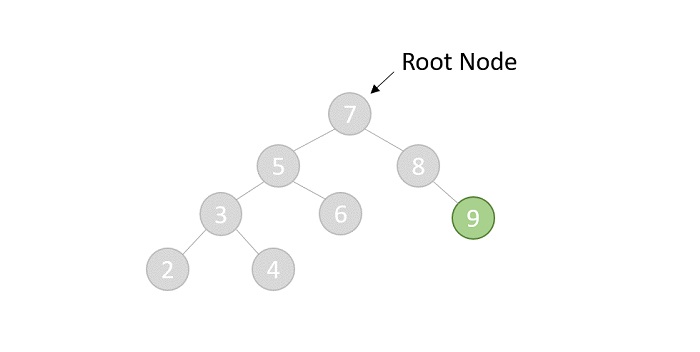
Zig-Zag旋轉
當操作節點同時具有父節點和祖父母節點時,執行Zig-Zag旋轉。但不同之處在於祖父母節點、父節點和子節點的格式為LRL。節點先向右旋轉,然後向左旋轉。
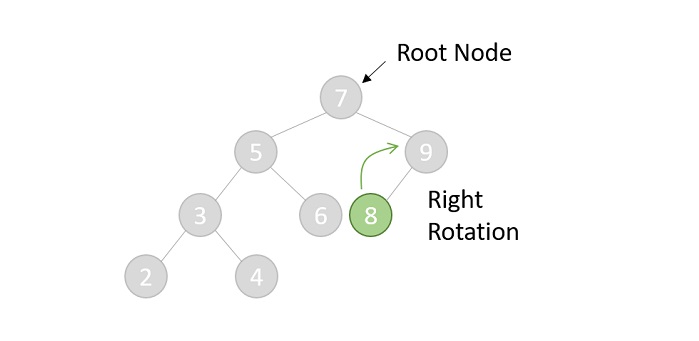
第一次旋轉後,樹為 -

第二次旋轉後的最終樹 -

Zag-Zig旋轉
當操作節點同時具有父節點和祖父母節點時,也執行Zag-Zig旋轉。但不同之處在於祖父母節點、父節點和子節點的格式為RLR。節點先向左旋轉,然後向右旋轉。
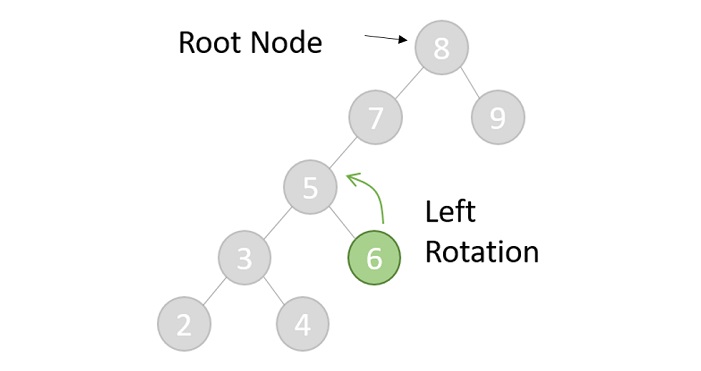
執行第一次旋轉,得到如下樹 -
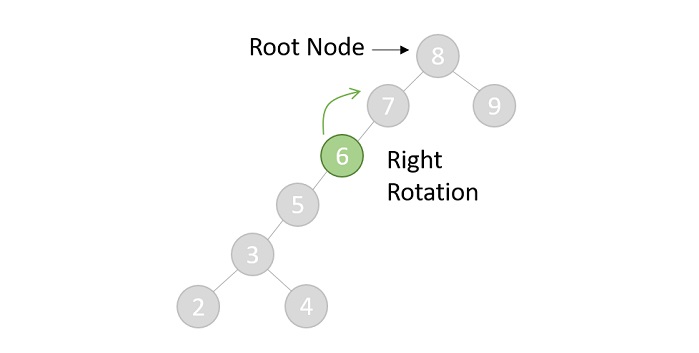
第二次旋轉後,最終樹如下所示。但是,操作節點尚未成為根節點,因此需要執行一次以上的旋轉才能使該節點成為根節點。

伸展樹的基本操作
伸展樹包含與二叉搜尋樹提供的相同的基本操作:插入、刪除和查詢。但是,在每次操作之後,還有一個額外的操作使它們與二叉搜尋樹操作有所不同:伸展。我們已經瞭解了伸展操作,所以讓我們瞭解其他操作的過程。
插入
伸展樹中的插入操作與二叉搜尋樹中的插入操作完全相同。在伸展樹中執行插入操作的過程如下 -
檢查樹是否為空;如果是,則新增新節點並退出

如果樹不為空,則使用二叉搜尋插入將新節點新增到現有樹中。

然後,選擇合適的伸展操作並將其應用於新新增的節點。

對新節點應用Zag(左)旋轉
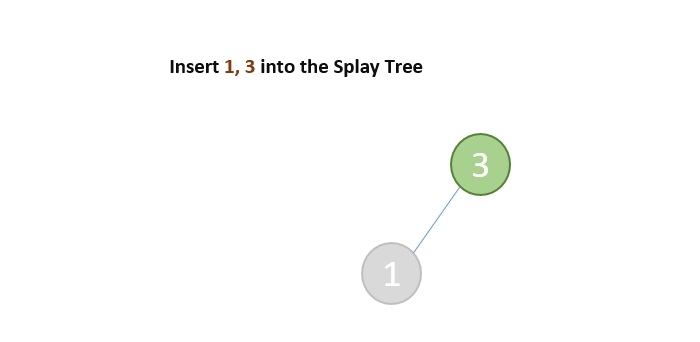
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild, *rightChild;
};
struct node* newNode(int data){
struct node* Node = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
Node->data = data;
Node->leftChild = Node->rightChild = NULL;
return (Node);
}
struct node* rightRotate(struct node *x){
struct node *y = x->leftChild;
x->leftChild = y->rightChild;
y->rightChild = x;
return y;
}
struct node* leftRotate(struct node *x){
struct node *y = x->rightChild;
x->rightChild = y->leftChild;
y->leftChild = x;
return y;
}
struct node* splay(struct node *root, int data){
if (root == NULL || root->data == data)
return root;
if (root->data > data) {
if (root->leftChild == NULL) return root;
if (root->leftChild->data > data) {
root->leftChild->leftChild = splay(root->leftChild->leftChild, data);
root = rightRotate(root);
} else if (root->leftChild->data < data) {
root->leftChild->rightChild = splay(root->leftChild->rightChild, data);
if (root->leftChild->rightChild != NULL)
root->leftChild = leftRotate(root->leftChild);
}
return (root->leftChild == NULL)? root: rightRotate(root);
} else {
if (root->rightChild == NULL) return root;
if (root->rightChild->data > data) {
root->rightChild->leftChild = splay(root->rightChild->leftChild, data);
if (root->rightChild->leftChild != NULL)
root->rightChild = rightRotate(root->rightChild);
} else if (root->rightChild->data < data) {
root->rightChild->rightChild = splay(root->rightChild->rightChild, data);
root = leftRotate(root);
}
return (root->rightChild == NULL)? root: leftRotate(root);
}
}
struct node* insert(struct node *root, int k){
if (root == NULL) return newNode(k);
root = splay(root, k);
if (root->data == k) return root;
struct node *newnode = newNode(k);
if (root->data > k) {
newnode->rightChild = root;
newnode->leftChild = root->leftChild;
root->leftChild = NULL;
} else {
newnode->leftChild = root;
newnode->rightChild = root->rightChild;
root->rightChild = NULL;
}
return newnode;
}
void printTree(struct node *root){
if (root == NULL)
return;
if (root != NULL) {
printTree(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
printTree(root->rightChild);
}
}
int main(){
struct node* root = newNode(34);
root->leftChild = newNode(15);
root->rightChild = newNode(40);
root->leftChild->leftChild = newNode(12);
root->leftChild->leftChild->rightChild = newNode(14);
root->rightChild->rightChild = newNode(59);
printf("The Splay tree is: \n");
printTree(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
The Splay tree is: 12 14 15 34 40 59
#include <iostream>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild, *rightChild;
};
struct node* newNode(int data){
struct node* Node = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
Node->data = data;
Node->leftChild = Node->rightChild = NULL;
return (Node);
}
struct node* rightRotate(struct node *x){
struct node *y = x->leftChild;
x->leftChild = y->rightChild;
y->rightChild = x;
return y;
}
struct node* leftRotate(struct node *x){
struct node *y = x->rightChild;
x->rightChild = y->leftChild;
y->leftChild = x;
return y;
}
struct node* splay(struct node *root, int data){
if (root == NULL || root->data == data)
return root;
if (root->data > data) {
if (root->leftChild == NULL) return root;
if (root->leftChild->data > data) {
root->leftChild->leftChild = splay(root->leftChild->leftChild, data);
root = rightRotate(root);
} else if (root->leftChild->data < data) {
root->leftChild->rightChild = splay(root->leftChild->rightChild, data);
if (root->leftChild->rightChild != NULL)
root->leftChild = leftRotate(root->leftChild);
}
return (root->leftChild == NULL)? root: rightRotate(root);
} else {
if (root->rightChild == NULL) return root;
if (root->rightChild->data > data) {
root->rightChild->leftChild = splay(root->rightChild->leftChild, data);
if (root->rightChild->leftChild != NULL)
root->rightChild = rightRotate(root->rightChild);
} else if (root->rightChild->data < data) {
root->rightChild->rightChild = splay(root->rightChild->rightChild, data);
root = leftRotate(root);
}
return (root->rightChild == NULL)? root: leftRotate(root);
}
}
struct node* insert(struct node *root, int k){
if (root == NULL) return newNode(k);
root = splay(root, k);
if (root->data == k) return root;
struct node *newnode = newNode(k);
if (root->data > k) {
newnode->rightChild = root;
newnode->leftChild = root->leftChild;
root->leftChild = NULL;
} else {
newnode->leftChild = root;
newnode->rightChild = root->rightChild;
root->rightChild = NULL;
}
return newnode;
}
void printTree(struct node *root){
if (root == NULL)
return;
if (root != NULL) {
printTree(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
printTree(root->rightChild);
}
}
int main(){
struct node* root = newNode(34);
root->leftChild = newNode(15);
root->rightChild = newNode(40);
root->leftChild->leftChild = newNode(12);
root->leftChild->leftChild->rightChild = newNode(14);
root->rightChild->rightChild = newNode(59);
printf("The Splay tree is: \n");
printTree(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
The Splay tree is: 12 14 15 34 40 59
import java.io.*;
public class SplayTree {
static class node {
int data;
node leftChild, rightChild;
};
static node newNode(int data) {
node Node = new node();
Node.data = data;
Node.leftChild = Node.rightChild = null;
return (Node);
}
static node rightRotate(node x) {
node y = x.leftChild;
x.leftChild = y.rightChild;
y.rightChild = x;
return y;
}
static node leftRotate(node x) {
node y = x.rightChild;
x.rightChild = y.leftChild;
y.leftChild = x;
return y;
}
static node splay(node root, int data) {
if (root == null || root.data == data)
return root;
if (root.data > data) {
if (root.leftChild == null) return root;
if (root.leftChild.data > data) {
root.leftChild.leftChild = splay(root.leftChild.leftChild, data);
root = rightRotate(root);
} else if (root.leftChild.data < data) {
root.leftChild.rightChild = splay(root.leftChild.rightChild, data);
if (root.leftChild.rightChild != null)
root.leftChild = leftRotate(root.leftChild);
}
return (root.leftChild == null)? root: rightRotate(root);
} else {
if (root.rightChild == null) return root;
if (root.rightChild.data > data) {
root.rightChild.leftChild = splay(root.rightChild.leftChild, data);
if (root.rightChild.leftChild != null)
root.rightChild = rightRotate(root.rightChild);
} else if (root.rightChild.data < data) {
root.rightChild.rightChild = splay(root.rightChild.rightChild, data);
root = leftRotate(root);
}
return (root.rightChild == null)? root: leftRotate(root);
}
}
static node insert(node root, int k) {
if (root == null) return newNode(k);
root = splay(root, k);
if (root.data == k) return root;
node newnode = newNode(k);
if (root.data > k) {
newnode.rightChild = root;
newnode.leftChild = root.leftChild;
root.leftChild = null;
} else {
newnode.leftChild = root;
newnode.rightChild = root.rightChild;
root.rightChild = null;
}
return newnode;
}
static void printTree(node root) {
if (root == null)
return;
if (root != null) {
printTree(root.leftChild);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
printTree(root.rightChild);
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
node root = newNode(34);
root.leftChild = newNode(15);
root.rightChild = newNode(40);
root.leftChild.leftChild = newNode(12);
root.leftChild.leftChild.rightChild = newNode(14);
root.rightChild.rightChild = newNode(59);
System.out.println("The Splay tree is: ");
printTree(root);
}
}
輸出
The Splay tree is: 12 14 15 34 40 59
#Python Code for Insertion Operation of Splay Trees
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.leftChild = None
self.rightChild = None
def newNode(data):
return Node(data)
def rightRotate(x):
y = x.leftChild
x.leftChild = y.rightChild
y.rightChild = x
return y
def leftRotate(x):
y = x.rightChild
x.rightChild = y.leftChild
y.leftChild = x
return y
def splay(root, data):
if root is None or root.data == data:
return root
if root.data > data:
if root.leftChild is None:
return root
if root.leftChild.data > data:
root.leftChild.leftChild = splay(root.leftChild.leftChild, data)
root = rightRotate(root)
elif root.leftChild.data < data:
root.leftChild.rightChild = splay(root.leftChild.rightChild, data)
if root.leftChild.rightChild is not None:
root.leftChild = leftRotate(root.leftChild)
return root if root.leftChild is None else rightRotate(root)
else:
if root.rightChild is None:
return root
if root.rightChild.data > data:
root.rightChild.leftChild = splay(root.rightChild.leftChild, data)
if root.rightChild.leftChild is not None:
root.rightChild = rightRotate(root.rightChild)
elif root.rightChild.data < data:
root.rightChild.rightChild = splay(root.rightChild.rightChild, data)
root = leftRotate(root)
return root if root.rightChild is None else leftRotate(root)
def insert(root, k):
if root is None:
return newNode(k)
root = splay(root, k)
if root.data == k:
return root
newnode = newNode(k)
if root.data > k:
newnode.rightChild = root
newnode.leftChild = root.leftChild
root.leftChild = None
else:
newnode.leftChild = root
newnode.rightChild = root.rightChild
root.rightChild = None
return newnode
def printTree(root):
if root is None:
return
if root is not None:
printTree(root.leftChild)
print(root.data, end=" ")
printTree(root.rightChild)
if __name__ == "__main__":
root = newNode(34)
root.leftChild = newNode(15)
root.rightChild = newNode(40)
root.leftChild.leftChild = newNode(12)
root.leftChild.leftChild.rightChild = newNode(14)
root.rightChild.rightChild = newNode(59)
print("The Splay tree is: ")
printTree(root)
輸出
The Splay tree is: 12 14 15 34 40 59
刪除
伸展樹中的刪除操作執行如下 -
對要刪除的節點應用伸展操作。
一旦節點成為根節點,就刪除該節點。
現在,樹被分成兩棵樹,左子樹和右子樹;它們各自的第一個節點作為根節點:例如root_left和root_right。
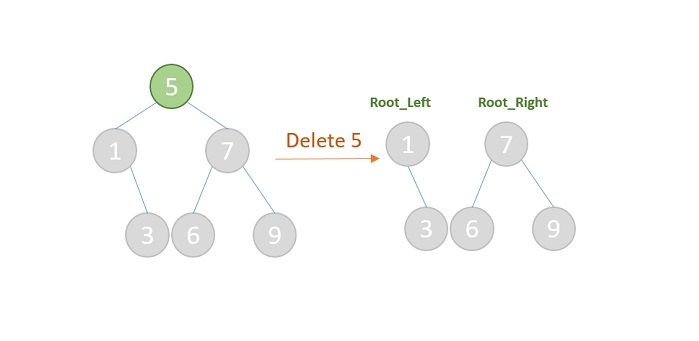
如果root_left為NULL值,則root_right將成為樹的根節點。反之亦然。
但是,如果root_left和root_right都不為NULL值,則選擇左子樹中的最大值並將其設為新的根節點,並將子樹連線起來。
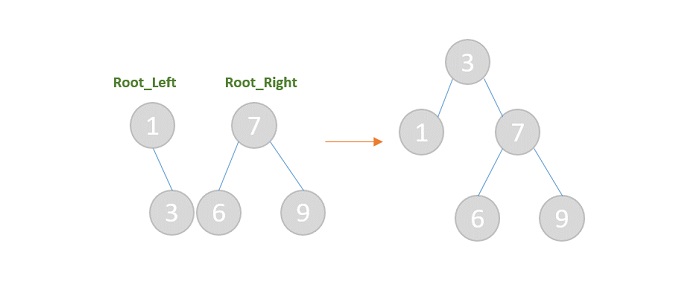
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild, *rightChild;
};
struct node* newNode(int data){
struct node* Node = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
Node->data = data;
Node->leftChild = Node->rightChild = NULL;
return (Node);
}
struct node* rightRotate(struct node *x){
struct node *y = x->leftChild;
x->leftChild = y->rightChild;
y->rightChild = x;
return y;
}
struct node* leftRotate(struct node *x){
struct node *y = x->rightChild;
x->rightChild = y->leftChild;
y->leftChild = x;
return y;
}
struct node* splay(struct node *root, int data){
if (root == NULL || root->data == data)
return root;
if (root->data > data) {
if (root->leftChild == NULL) return root;
if (root->leftChild->data > data) {
root->leftChild->leftChild = splay(root->leftChild->leftChild, data);
root = rightRotate(root);
} else if (root->leftChild->data < data) {
root->leftChild->rightChild = splay(root->leftChild->rightChild, data);
if (root->leftChild->rightChild != NULL)
root->leftChild = leftRotate(root->leftChild);
}
return (root->leftChild == NULL)? root: rightRotate(root);
} else {
if (root->rightChild == NULL) return root;
if (root->rightChild->data > data) {
root->rightChild->leftChild = splay(root->rightChild->leftChild, data);
if (root->rightChild->leftChild != NULL)
root->rightChild = rightRotate(root->rightChild);
} else if (root->rightChild->data < data) {
root->rightChild->rightChild = splay(root->rightChild->rightChild, data);
root = leftRotate(root);
}
return (root->rightChild == NULL)? root: leftRotate(root);
}
}
struct node* insert(struct node *root, int k){
if (root == NULL) return newNode(k);
root = splay(root, k);
if (root->data == k) return root;
struct node *newnode = newNode(k);
if (root->data > k) {
newnode->rightChild = root;
newnode->leftChild = root->leftChild;
root->leftChild = NULL;
} else {
newnode->leftChild = root;
newnode->rightChild = root->rightChild;
root->rightChild = NULL;
}
return newnode;
}
struct node* deletenode(struct node* root, int data){
struct node* temp;
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
root = splay(root, data);
if (data != root->data)
return root;
if (!root->leftChild) {
temp = root;
root = root->rightChild;
} else {
temp = root;
root = splay(root->leftChild, data);
root->rightChild = temp->rightChild;
}
free(temp);
return root;
}
void printTree(struct node *root){
if (root == NULL)
return;
if (root != NULL) {
printTree(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
printTree(root->rightChild);
}
}
int main(){
struct node* root = newNode(34);
root->leftChild = newNode(15);
root->rightChild = newNode(40);
printf("The Splay tree is \n");
printTree(root);
root = deletenode(root, 40);
printf("\nThe Splay tree after deletion is \n");
printTree(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
The Splay tree is 15 34 40 The Splay tree after deletion is 15 34
#include <iostream>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild, *rightChild;
};
struct node* newNode(int data){
struct node* Node = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
Node->data = data;
Node->leftChild = Node->rightChild = NULL;
return (Node);
}
struct node* rightRotate(struct node *x){
struct node *y = x->leftChild;
x->leftChild = y->rightChild;
y->rightChild = x;
return y;
}
struct node* leftRotate(struct node *x){
struct node *y = x->rightChild;
x->rightChild = y->leftChild;
y->leftChild = x;
return y;
}
struct node* splay(struct node *root, int data){
if (root == NULL || root->data == data)
return root;
if (root->data > data) {
if (root->leftChild == NULL) return root;
if (root->leftChild->data > data) {
root->leftChild->leftChild = splay(root->leftChild->leftChild, data);
root = rightRotate(root);
} else if (root->leftChild->data < data) {
root->leftChild->rightChild = splay(root->leftChild->rightChild, data);
if (root->leftChild->rightChild != NULL)
root->leftChild = leftRotate(root->leftChild);
}
return (root->leftChild == NULL)? root: rightRotate(root);
} else {
if (root->rightChild == NULL) return root;
if (root->rightChild->data > data) {
root->rightChild->leftChild = splay(root->rightChild->leftChild, data);
if (root->rightChild->leftChild != NULL)
root->rightChild = rightRotate(root->rightChild);
} else if (root->rightChild->data < data) {
root->rightChild->rightChild = splay(root->rightChild->rightChild, data);
root = leftRotate(root);
}
return (root->rightChild == NULL)? root: leftRotate(root);
}
}
struct node* insert(struct node *root, int k){
if (root == NULL) return newNode(k);
root = splay(root, k);
if (root->data == k) return root;
struct node *newnode = newNode(k);
if (root->data > k) {
newnode->rightChild = root;
newnode->leftChild = root->leftChild;
root->leftChild = NULL;
} else {
newnode->leftChild = root;
newnode->rightChild = root->rightChild;
root->rightChild = NULL;
}
return newnode;
}
struct node* deletenode(struct node* root, int data){
struct node* temp;
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
root = splay(root, data);
if (data != root->data)
return root;
if (!root->leftChild) {
temp = root;
root = root->rightChild;
} else {
temp = root;
root = splay(root->leftChild, data);
root->rightChild = temp->rightChild;
}
free(temp);
return root;
}
void printTree(struct node *root){
if (root == NULL)
return;
if (root != NULL) {
printTree(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
printTree(root->rightChild);
}
}
int main(){
struct node* root = newNode(34);
root->leftChild = newNode(15);
root->rightChild = newNode(40);
printf("The Splay tree is \n");
printTree(root);
root = deletenode(root, 40);
printf("\nThe Splay tree after deletion is \n");
printTree(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
The Splay tree is 15 34 40 The Splay tree after deletion is 15 34
import java.io.*;
public class SplayTree {
static class node {
int data;
node leftChild, rightChild;
};
static node newNode(int data) {
node Node = new node();
Node.data = data;
Node.leftChild = Node.rightChild = null;
return (Node);
}
static node rightRotate(node x) {
node y = x.leftChild;
x.leftChild = y.rightChild;
y.rightChild = x;
return y;
}
static node leftRotate(node x) {
node y = x.rightChild;
x.rightChild = y.leftChild;
y.leftChild = x;
return y;
}
static node splay(node root, int data) {
if (root == null || root.data == data)
return root;
if (root.data > data) {
if (root.leftChild == null) return root;
if (root.leftChild.data > data) {
root.leftChild.leftChild = splay(root.leftChild.leftChild, data);
root = rightRotate(root);
} else if (root.leftChild.data < data) {
root.leftChild.rightChild = splay(root.leftChild.rightChild, data);
if (root.leftChild.rightChild != null)
root.leftChild = leftRotate(root.leftChild);
}
return (root.leftChild == null)? root: rightRotate(root);
} else {
if (root.rightChild == null) return root;
if (root.rightChild.data > data) {
root.rightChild.leftChild = splay(root.rightChild.leftChild, data);
if (root.rightChild.leftChild != null)
root.rightChild = rightRotate(root.rightChild);
} else if (root.rightChild.data < data) {
root.rightChild.rightChild = splay(root.rightChild.rightChild, data);
root = leftRotate(root);
}
return (root.rightChild == null)? root: leftRotate(root);
}
}
static node insert(node root, int k) {
if (root == null) return newNode(k);
root = splay(root, k);
if (root.data == k) return root;
node newnode = newNode(k);
if (root.data > k) {
newnode.rightChild = root;
newnode.leftChild = root.leftChild;
root.leftChild = null;
} else {
newnode.leftChild = root;
newnode.rightChild = root.rightChild;
root.rightChild = null;
}
return newnode;
}
static node deletenode(node root, int data) {
node temp;
if (root == null)
return null;
root = splay(root, data);
if (data != root.data)
return root;
if (root.leftChild == null) {
temp = root;
root = root.rightChild;
} else {
temp = root;
root = splay(root.leftChild, data);
root.rightChild = temp.rightChild;
}
return root;
}
static void printTree(node root) {
if (root == null)
return;
if (root != null) {
printTree(root.leftChild);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
printTree(root.rightChild);
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
node root = newNode(34);
root.leftChild = newNode(15);
root.rightChild = newNode(40);
System.out.println("The Splay tree is: ");
printTree(root);
root = deletenode(root, 40);
System.out.println("\nThe Splay tree after deletion is: ");
printTree(root);
}
}
輸出
The Splay tree is: 15 34 40 The Splay tree after deletion is: 15 34
#Python Code for Deletion operation of Splay Trees
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.leftChild = None
self.rightChild = None
def newNode(data):
node = Node(data)
return node
def rightRotate(x):
y = x.leftChild
x.leftChild = y.rightChild
y.rightChild = x
return y
def leftRotate(x):
y = x.rightChild
x.rightChild = y.leftChild
y.leftChild = x
return y
def splay(root, data):
if root is None or root.data == data:
return root
if root.data > data:
if root.leftChild is None:
return root
if root.leftChild.data > data:
root.leftChild.leftChild = splay(root.leftChild.leftChild, data)
root = rightRotate(root)
elif root.leftChild.data < data:
root.leftChild.rightChild = splay(root.leftChild.rightChild, data)
if root.leftChild.rightChild is not None:
root.leftChild = leftRotate(root.leftChild)
return root if root.leftChild is None else rightRotate(root)
else:
if root.rightChild is None:
return root
if root.rightChild.data > data:
root.rightChild.leftChild = splay(root.rightChild.leftChild, data)
if root.rightChild.leftChild is not None:
root.rightChild = rightRotate(root.rightChild)
elif root.rightChild.data < data:
root.rightChild.rightChild = splay(root.rightChild.rightChild, data)
root = leftRotate(root)
return root if root.rightChild is None else leftRotate(root)
def insert(root, k):
if root is None:
return newNode(k)
root = splay(root, k)
if root.data == k:
return root
newnode = newNode(k)
if root.data > k:
newnode.rightChild = root
newnode.leftChild = root.leftChild
root.leftChild = None
else:
newnode.leftChild = root
newnode.rightChild = root.rightChild
root.rightChild = None
return newnode
def deletenode(root, data):
temp = None
if root is None:
return None
root = splay(root, data)
if data != root.data:
return root
if root.leftChild is None:
temp = root
root = root.rightChild
else:
temp = root
root = splay(root.leftChild, data)
root.rightChild = temp.rightChild
del temp
return root
def printTree(root):
if root is None:
return
if root is not None:
printTree(root.leftChild)
print(root.data, end=" ")
printTree(root.rightChild)
root = newNode(34)
root.leftChild = newNode(15)
root.rightChild = newNode(40)
print("The Splay tree is:")
printTree(root)
root = deletenode(root, 40)
print("\nThe Splay tree after deletion is:")
printTree(root)
輸出
The Splay tree is: 15 34 40 The Splay tree after deletion is: 15 34
搜尋
伸展樹中的查詢操作遵循二叉搜尋樹操作的相同過程。但是,在完成查詢並找到元素後,將在搜尋到的節點上應用伸展操作。如果未找到元素,則會提示查詢失敗。
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現 -
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *leftChild, *rightChild;
};
struct node* newNode(int data){
struct node* Node = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
Node->data = data;
Node->leftChild = Node->rightChild = NULL;
return (Node);
}
struct node* rightRotate(struct node *x){
struct node *y = x->leftChild;
x->leftChild = y->rightChild;
y->rightChild = x;
return y;
}
struct node* leftRotate(struct node *x){
struct node *y = x->rightChild;
x->rightChild = y->leftChild;
y->leftChild = x;
return y;
}
struct node* splay(struct node *root, int data){
if (root == NULL || root->data == data)
return root;
if (root->data > data) {
if (root->leftChild == NULL) return root;
if (root->leftChild->data > data) {
root->leftChild->leftChild = splay(root->leftChild->leftChild, data);
root = rightRotate(root);
} else if (root->leftChild->data < data) {
root->leftChild->rightChild = splay(root->leftChild->rightChild, data);
if (root->leftChild->rightChild != NULL)
root->leftChild = leftRotate(root->leftChild);
}
return (root->leftChild == NULL)? root: rightRotate(root);
} else {
if (root->rightChild == NULL) return root;
if (root->rightChild->data > data) {
root->rightChild->leftChild = splay(root->rightChild->leftChild, data);
if (root->rightChild->leftChild != NULL)
root->rightChild = rightRotate(root->rightChild);
} else if (root->rightChild->data < data) {
root->rightChild->rightChild = splay(root->rightChild->rightChild, data);
root = leftRotate(root);
}
return (root->rightChild == NULL)? root: leftRotate(root);
}
}
struct node* insert(struct node *root, int k){
if (root == NULL) return newNode(k);
root = splay(root, k);
if (root->data == k) return root;
struct node *newnode = newNode(k);
if (root->data > k) {
newnode->rightChild = root;
newnode->leftChild = root->leftChild;
root->leftChild = NULL;
} else {
newnode->leftChild = root;
newnode->rightChild = root->rightChild;
root->rightChild = NULL;
}
return newnode;
}
struct node* deletenode(struct node* root, int data){
struct node* temp;
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
root = splay(root, data);
if (data != root->data)
return root;
if (!root->leftChild) {
temp = root;
root = root->rightChild;
} else {
temp = root;
root = splay(root->leftChild, data);
root->rightChild = temp->rightChild;
}
free(temp);
return root;
}
void printTree(struct node *root){
if (root == NULL)
return;
if (root != NULL) {
printTree(root->leftChild);
printf("%d ", root->data);
printTree(root->rightChild);
}
}
int main(){
struct node* root = newNode(34);
root->leftChild = newNode(15);
root->rightChild = newNode(40);
root->leftChild->leftChild = newNode(12);
root->leftChild->leftChild->rightChild = newNode(14);
root->rightChild->rightChild = newNode(59);
printf("The Splay tree is \n");
printTree(root);
root = deletenode(root, 40);
printf("\nThe Splay tree after deletion is \n");
printTree(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
The Splay tree is 12 14 15 34 40 59 The Splay tree after deletion is 12 14 15 34 59
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
class node{
public:
int data;
node *leftChild, *rightChild;
};
node* newNode(int data){
node* Node = new node();
Node->data = data;
Node->leftChild = Node->rightChild = NULL;
return (Node);
}
node *rightRotate(node *x){
node *y = x->leftChild;
x->leftChild = y->rightChild;
y->rightChild = x;
return y;
}
node *leftRotate(node *x){
node *y = x->rightChild;
x->rightChild = y->leftChild;
y->leftChild = x;
return y;
}
node *splay(node *root, int data){
if (root == NULL || root->data == data)
return root;
if (root->data > data) {
if (root->leftChild == NULL) return root;
if (root->leftChild->data > data) {
root->leftChild->leftChild = splay(root->leftChild->leftChild, data);
root = rightRotate(root);
} else if (root->leftChild->data < data) {
root->leftChild->rightChild = splay(root->leftChild->rightChild, data);
if (root->leftChild->rightChild != NULL)
root->leftChild = leftRotate(root->leftChild);
}
return (root->leftChild == NULL)? root: rightRotate(root);
} else {
if (root->rightChild == NULL) return root;
if (root->rightChild->data > data) {
root->rightChild->leftChild = splay(root->rightChild->leftChild, data);
if (root->rightChild->leftChild != NULL)
root->rightChild = rightRotate(root->rightChild);
} else if (root->rightChild->data < data) {
root->rightChild->rightChild = splay(root->rightChild->rightChild, data);
root = leftRotate(root);
}
return (root->rightChild == NULL)? root: leftRotate(root);
}
}
node* insert(node *root, int k)
{
if (root == NULL) return newNode(k);
root = splay(root, k);
if (root->data == k) return root;
node *newnode = newNode(k);
if (root->data > k) {
newnode->rightChild = root;
newnode->leftChild = root->leftChild;
root->leftChild = NULL;
} else {
newnode->leftChild = root;
newnode->rightChild = root->rightChild;
root->rightChild = NULL;
}
return newnode;
}
node* deletenode(struct node* root, int data){
struct node* temp;
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
root = splay(root, data);
if (data != root->data)
return root;
if (!root->leftChild) {
temp = root;
root = root->rightChild;
} else {
temp = root;
root = splay(root->leftChild, data);
root->rightChild = temp->rightChild;
}
free(temp);
return root;
}
void printTree(node *root){
if (root == NULL)
return;
if (root != NULL) {
printTree(root->leftChild);
cout<<root->data<<" ";
printTree(root->rightChild);
}
}
int main(){
node* root = newNode(34);
root->leftChild = newNode(15);
root->rightChild = newNode(40);
root->leftChild->leftChild = newNode(12);
root->leftChild->leftChild->rightChild = newNode(14);
root->rightChild->rightChild = newNode(59);
cout<<"The Splay tree is \n";
printTree(root);
root = deletenode(root, 40);
cout<<"\nThe Splay tree after deletion is \n";
printTree(root);
return 0;
}
輸出
The Splay tree is 12 14 15 34 40 59 The Splay tree after deletion is 12 14 15 34 59
import java.io.*;
public class SplayTree {
static class node {
int data;
node leftChild, rightChild;
};
static node newNode(int data) {
node Node = new node();
Node.data = data;
Node.leftChild = Node.rightChild = null;
return (Node);
}
static node rightRotate(node x) {
node y = x.leftChild;
x.leftChild = y.rightChild;
y.rightChild = x;
return y;
}
static node leftRotate(node x) {
node y = x.rightChild;
x.rightChild = y.leftChild;
y.leftChild = x;
return y;
}
static node splay(node root, int data) {
if (root == null || root.data == data)
return root;
if (root.data > data) {
if (root.leftChild == null) return root;
if (root.leftChild.data > data) {
root.leftChild.leftChild = splay(root.leftChild.leftChild, data);
root = rightRotate(root);
} else if (root.leftChild.data < data) {
root.leftChild.rightChild = splay(root.leftChild.rightChild, data);
if (root.leftChild.rightChild != null)
root.leftChild = leftRotate(root.leftChild);
}
return (root.leftChild == null)? root: rightRotate(root);
} else {
if (root.rightChild == null) return root;
if (root.rightChild.data > data) {
root.rightChild.leftChild = splay(root.rightChild.leftChild, data);
if (root.rightChild.leftChild != null)
root.rightChild = rightRotate(root.rightChild);
} else if (root.rightChild.data < data) {
root.rightChild.rightChild = splay(root.rightChild.rightChild, data);
root = leftRotate(root);
}
return (root.rightChild == null)? root: leftRotate(root);
}
}
static node insert(node root, int k) {
if (root == null) return newNode(k);
root = splay(root, k);
if (root.data == k) return root;
node newnode = newNode(k);
if (root.data > k) {
newnode.rightChild = root;
newnode.leftChild = root.leftChild;
root.leftChild = null;
} else {
newnode.leftChild = root;
newnode.rightChild = root.rightChild;
root.rightChild = null;
}
return newnode;
}
static node deletenode(node root, int data) {
node temp;
if (root == null)
return null;
root = splay(root, data);
if (data != root.data)
return root;
if (root.leftChild == null) {
temp = root;
root = root.rightChild;
} else {
temp = root;
root = splay(root.leftChild, data);
root.rightChild = temp.rightChild;
}
return root;
}
static void printTree(node root) {
if (root == null)
return;
if (root != null) {
printTree(root.leftChild);
System.out.print(root.data + " ");
printTree(root.rightChild);
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
node root = newNode(34);
root.leftChild = newNode(15);
root.rightChild = newNode(40);
root.leftChild.leftChild = newNode(12);
root.leftChild.leftChild.rightChild = newNode(14);
root.rightChild.rightChild = newNode(59);
System.out.println("The Splay tree is: ");
printTree(root);
root = deletenode(root, 40);
System.out.println("\nThe Splay tree after deletion is: ");
printTree(root);
}
}
輸出
The Splay tree is: 12 14 15 34 40 59 The Splay tree after deletion is: 12 14 15 34 59
#Python Code for Search Operation of splay Trees
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.leftChild = None
self.rightChild = None
def newNode(data):
newNode = Node(data)
newNode.leftChild = newNode.rightChild = None
return newNode
def rightRotate(x):
y = x.leftChild
x.leftChild = y.rightChild
y.rightChild = x
return y
def leftRotate(x):
y = x.rightChild
x.rightChild = y.leftChild
y.leftChild = x
return y
def splay(root, data):
if root is None or root.data == data:
return root
if root.data > data:
if root.leftChild is None:
return root
if root.leftChild.data > data:
root.leftChild.leftChild = splay(root.leftChild.leftChild, data)
root = rightRotate(root)
elif root.leftChild.data < data:
root.leftChild.rightChild = splay(root.leftChild.rightChild, data)
if root.leftChild.rightChild is not None:
root.leftChild = leftRotate(root.leftChild)
return root if root.leftChild is None else rightRotate(root)
else:
if root.rightChild is None:
return root
if root.rightChild.data > data:
root.rightChild.leftChild = splay(root.rightChild.leftChild, data)
if root.rightChild.leftChild is not None:
root.rightChild = rightRotate(root.rightChild)
elif root.rightChild.data < data:
root.rightChild.rightChild = splay(root.rightChild.rightChild, data)
root = leftRotate(root)
return root if root.rightChild is None else leftRotate(root)
def insert(root, k):
if root is None:
return newNode(k)
root = splay(root, k)
if root.data == k:
return root
newnode = newNode(k)
if root.data > k:
newnode.rightChild = root
newnode.leftChild = root.leftChild
root.leftChild = None
else:
newnode.leftChild = root
newnode.rightChild = root.rightChild
root.rightChild = None
return newnode
def deletenode(root, data):
temp = None
if root is None:
return None
root = splay(root, data)
if data != root.data:
return root
if root.leftChild is None:
temp = root
root = root.rightChild
else:
temp = root
root = splay(root.leftChild, data)
root.rightChild = temp.rightChild
del temp
return root
def printTree(root):
if root is None:
return
if root is not None:
printTree(root.leftChild)
print(root.data, end=" ")
printTree(root.rightChild)
root = newNode(34)
root.leftChild = newNode(15)
root.rightChild = newNode(40)
root.leftChild.leftChild = newNode(12)
root.leftChild.leftChild.rightChild = newNode(14)
root.rightChild.rightChild = newNode(59)
print("The Splay tree is")
printTree(root)
root = deletenode(root, 40)
print("\nThe Splay tree after deletion is")
printTree(root)
輸出
The Splay tree is 12 14 15 34 40 59 The Splay tree after deletion is 12 14 15 34 59
Trie資料結構
Trie是一種多路搜尋樹,主要用於從字串或一組字串中檢索特定的鍵。它以一種有序且高效的方式儲存資料,因為它使用指標指向字母表中的每個字母。
Trie資料結構基於字串的公共字首。根節點可以具有任意數量的節點,具體取決於集合中存在的字串數量。Trie的根節點不包含任何值,只包含指向其子節點的指標。
Trie資料結構有三種類型 -
標準Trie
壓縮Trie
字尾Trie
Trie的實際應用包括 - 自動更正、文字預測、情感分析和資料科學。

Trie的基本操作
Trie資料結構也執行樹資料結構執行的相同操作。它們是 -
插入
刪除
搜尋
插入
Trie中的插入操作很簡單。Trie中的根節點不儲存任何值,插入操作從根節點的直接子節點開始,這些子節點充當其子節點的鍵。但是,我們觀察到Trie中的每個節點都表示輸入字串中的單個字元。因此,字元一個接一個地新增到Trie中,而Trie中的連結充當指向下一級節點的指標。
示例
//C code for insertion operation of tries algorithm
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define ALPHABET_SIZE 26
struct TrieNode {
struct TrieNode* children[ALPHABET_SIZE];
bool isEndOfWord;
};
struct TrieNode* createNode() {
struct TrieNode* node = (struct TrieNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct TrieNode));
node->isEndOfWord = false;
for (int i = 0; i < ALPHABET_SIZE; i++) {
node->children[i] = NULL;
}
return node;
}
void insert(struct TrieNode* root, char* word) {
struct TrieNode* curr = root;
for (int i = 0; word[i] != '\0'; i++) {
int index = word[i] - 'a';
if (curr->children[index] == NULL) {
curr->children[index] = createNode();
}
curr = curr->children[index];
}
curr->isEndOfWord = true;
}
bool search(struct TrieNode* root, char* word) {
struct TrieNode* curr = root;
for (int i = 0; word[i] != '\0'; i++) {
int index = word[i] - 'a';
if (curr->children[index] == NULL) {
return false;
}
curr = curr->children[index];
}
return (curr != NULL && curr->isEndOfWord);
}
bool startsWith(struct TrieNode* root, char* prefix) {
struct TrieNode* curr = root;
for (int i = 0; prefix[i] != '\0'; i++) {
int index = prefix[i] - 'a';
if (curr->children[index] == NULL) {
return false;
}
curr = curr->children[index];
}
return true;
}
int main() {
struct TrieNode* root = createNode();
//inserting the elements
insert(root, "Lamborghini");
insert(root, "Mercedes-Benz");
insert(root, "Land Rover");
insert(root, "Maruti Suzuki");
//printing the elements
printf("Inserted values are: \n");
printf("Lamborghini\n");
printf( "Mercedes-Benz\n");
printf( "Land Rover\n");
printf( "Maruti Suzuki");
return 0;
}
輸出
Inserted values are: Lamborghini Mercedes-Benz Land Rover Maruti Suzuki
// C++ code for Insertion operation of tries algorithm
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
class TrieNode
{
public:
unordered_map<char, TrieNode*> children;
bool isEndOfWord;
TrieNode()
{
isEndOfWord = false;
}
};
class Trie
{
private:
TrieNode* root;
public:
Trie()
{
root = new TrieNode();
}
void insert(string word)
{
TrieNode* curr = root;
for (char ch : word) {
if (curr->children.find(ch) == curr->children.end()) {
curr->children[ch] = new TrieNode();
}
curr = curr->children[ch];
}
curr->isEndOfWord = true;
}
bool search(string word)
{
TrieNode* curr = root;
for (char ch : word) {
if (curr->children.find(ch) == curr->children.end()) {
return false;
}
curr = curr->children[ch];
}
return curr->isEndOfWord;
}
bool startsWith(string prefix)
{
TrieNode* curr = root;
for (char ch : prefix) {
if (curr->children.find(ch) == curr->children.end()) {
return false;
}
curr = curr->children[ch];
}
return true;
}
};
int main()
{
Trie car;
//inserting the elements
car.insert("Lamborghini");
car.insert("Mercedes-Benz");
car.insert("Land Rover");
car.insert("Maruti Suzuki");
//printing the elmenents
printf("Inserted values are: \n");
cout << "Lamborghini" << endl;
cout <<"Mercedes-Benz"<< endl;
cout <<"Land Rover" << endl;
cout << "Maruti Suzuki" << endl;
return 0;
}
輸出
Inserted values are: Lamborghini Mercedes-Benz Land Rover Maruti Suzuki
//Java Code for insertion operation of tries Algorithm
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
class TrieNode {
Map<Character, TrieNode> children;
boolean isEndOfWord;
TrieNode() {
children = new HashMap<>();
isEndOfWord = false;
}
}
class Trie {
private TrieNode root;
Trie() {
root = new TrieNode();
}
void insert(String word) {
TrieNode curr = root;
for (char ch : word.toCharArray()) {
curr.children.putIfAbsent(ch, new TrieNode());
curr = curr.children.get(ch);
}
curr.isEndOfWord = true;
}
boolean search(String word) {
TrieNode curr = root;
for (char ch : word.toCharArray()) {
if (!curr.children.containsKey(ch)) {
return false;
}
curr = curr.children.get(ch);
}
return curr.isEndOfWord;
}
boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
TrieNode curr = root;
for (char ch : prefix.toCharArray()) {
if (!curr.children.containsKey(ch)) {
return false;
}
curr = curr.children.get(ch);
}
return true;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Trie car = new Trie();
//Inserting the elements
car.insert("Lamborghini");
car.insert("Mercedes-Benz");
car.insert("Land Rover");
car.insert("Maruti Suzuki");
//Printing the elements
System.out.println("Inserted values are: ");
System.out.println("Lamborghini");
System.out.println("Mercedes-Benz");
System.out.println("Land Rover");
System.out.println("Maruti Suzuki");
}
}
輸出
Inserted values are: Lamborghini Mercedes-Benz Land Rover Maruti Suzuki
#Python Code for insertion operation of tries Algorithm
class TrieNode:
def __init__(self):
self.children = {}
self.isEndOfWord = False
class Trie:
def __init__(self):
self.root = TrieNode()
def insert(self, word):
curr = self.root
for ch in word:
if ch not in curr.children:
curr.children[ch] = TrieNode()
curr = curr.children[ch]
curr.isEndOfWord = True
def search(self, word):
curr = self.root
for ch in word:
if ch not in curr.children:
return False
curr = curr.children[ch]
return curr.isEndOfWord
def startsWith(self, prefix):
curr = self.root
for ch in prefix:
if ch not in curr.children:
return False
curr = curr.children[ch]
return True
if __name__ == '__main__':
car = Trie()
#inserting the elements
car.insert("Lamborghini")
car.insert("Mercedes-Benz")
car.insert("Land Rover")
car.insert("Maruti Suzuki")
#printing the elements
print("Inserted values are: ")
print("Lamborghini")
print("Mercedes-Benz")
print("Land Rover")
print("Maruti Suzuki")
輸出
Inserted values are: Lamborghini Mercedes-Benz Land Rover Maruti Suzuki
刪除
Trie中的刪除操作使用自下而上的方法執行。在Trie中搜索要刪除的元素,如果找到則刪除。但是,在執行刪除操作時,需要牢記一些特殊情況。
情況1 - 鍵是唯一的 - 在這種情況下,從節點中刪除整個鍵路徑。(唯一的鍵表示沒有其他路徑從一條路徑分支出來)。
情況2 - 鍵不是唯一的 - 更新葉子節點。例如,如果要刪除的鍵為see,但它是另一個鍵seethe的字首;我們刪除see並將t、h和e的布林值更改為false。
情況3 - 要刪除的鍵已經有一個字首 - 刪除到字首為止的值,並將字首保留在樹中。例如,如果要刪除的鍵為heart,但存在另一個鍵he;因此我們刪除a、r和t,直到只剩下he。
示例
//C code for Deletion Operation of tries Algorithm
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
//Define size 26
#define ALPHABET_SIZE 26
struct TrieNode {
struct TrieNode* children[ALPHABET_SIZE];
bool isEndOfWord;
};
struct TrieNode* createNode() {
struct TrieNode* node = (struct TrieNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct TrieNode));
node->isEndOfWord = false;
for (int i = 0; i < ALPHABET_SIZE; i++) {
node->children[i] = NULL;
}
return node;
}
void insert(struct TrieNode* root, char* word) {
struct TrieNode* curr = root;
for (int i = 0; word[i] != '\0'; i++) {
int index = word[i] - 'a';
if (curr->children[index] == NULL) {
curr->children[index] = createNode();
}
curr = curr->children[index];
}
curr->isEndOfWord = true;
}
bool search(struct TrieNode* root, char* word) {
struct TrieNode* curr = root;
for (int i = 0; word[i] != '\0'; i++) {
int index = word[i] - 'a';
if (curr->children[index] == NULL) {
return false;
}
curr = curr->children[index];
}
return (curr != NULL && curr->isEndOfWord);
}
bool startsWith(struct TrieNode* root, char* prefix) {
struct TrieNode* curr = root;
for (int i = 0; prefix[i] != '\0'; i++) {
int index = prefix[i] - 'a';
if (curr->children[index] == NULL) {
return false;
}
curr = curr->children[index];
}
return true;
}
bool deleteWord(struct TrieNode* root, char* word) {
struct TrieNode* curr = root;
struct TrieNode* parent = NULL;
int index;
for (int i = 0; word[i] != '\0'; i++) {
index = word[i] - 'a';
if (curr->children[index] == NULL) {
return false; // Word does not exist in the Trie
}
parent = curr;
curr = curr->children[index];
}
if (!curr->isEndOfWord) {
return false; // Word does not exist in the Trie
}
curr->isEndOfWord = false; // Mark as deleted
if (parent != NULL) {
parent->children[index] = NULL; // Remove the child node
}
return true;
}
int main() {
struct TrieNode* root = createNode();
//Inserting the elements
insert(root, "lamborghini");
insert(root, "mercedes-benz");
insert(root, "land rover");
insert(root, "maruti suzuki");
//Before Deletion
printf("Before Deletion\n");
printf("%d\n", search(root, "lamborghini")); // Output: 1 (true)
printf("%d\n", search(root, "mercedes-benz")); // Output: 1 (true)
printf("%d\n", search(root, "land rover")); // Output: 1 (true)
printf("%d\n", search(root, "maruti suzuki")); // Output: 1 (true)
//Deleting the elements
deleteWord(root, "lamborghini");
deleteWord(root, "land rover");
//After Deletion
printf("After Deletion\n");
printf("%d\n", search(root, "lamborghini")); // Output: 0 (false)
printf("%d\n", search(root, "mercedes-benz")); // Output: 1 (true)
printf("%d\n", search(root, "land rover")); // Output: 0 (false)
printf("%d\n", search(root, "maruti suzuki")); // Output: 1 (true)
return 0;
}
輸出
Before Deletion 1 1 1 1 After Deletion 0 1 0 1
//C++ code for Deletion operation of tries algorithm
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
class TrieNode {
public:
unordered_map<char, TrieNode*> children;
bool isEndOfWord;
TrieNode() {
isEndOfWord = false;
}
};
class Trie {
private:
TrieNode* root;
public:
Trie() {
root = new TrieNode();
}
void insert(string word) {
TrieNode* curr = root;
for (char ch : word) {
if (curr->children.find(ch) == curr->children.end()) {
curr->children[ch] = new TrieNode();
}
curr = curr->children[ch];
}
curr->isEndOfWord = true;
}
bool search(string word) {
TrieNode* curr = root;
for (char ch : word) {
if (curr->children.find(ch) == curr->children.end()) {
return false;
}
curr = curr->children[ch];
}
return curr->isEndOfWord;
}
bool startsWith(string prefix) {
TrieNode* curr = root;
for (char ch : prefix) {
if (curr->children.find(ch) == curr->children.end()) {
return false;
}
curr = curr->children[ch];
}
return true;
}
bool deleteWord(string word) {
return deleteHelper(root, word, 0);
}
private:
bool deleteHelper(TrieNode* curr, string word, int index) {
if (index == word.length()) {
if (!curr->isEndOfWord) {
return false; // Word does not exist in the Trie
}
curr->isEndOfWord = false; // Mark as deleted
return curr->children.empty(); // Return true if no more children
}
char ch = word[index];
if (curr->children.find(ch) == curr->children.end()) {
return false; // Word does not exist in the Trie
}
TrieNode* child = curr->children[ch];
bool shouldDeleteChild = deleteHelper(child, word, index + 1);
if (shouldDeleteChild) {
curr->children.erase(ch); // Remove the child node if necessary
return curr->children.empty(); // Return true if no more children
}
return false;
}
};
int main() {
Trie car;
//inserting the elemnets
car.insert("Lamborghini");
car.insert("Mercedes-Benz");
car.insert("Land Rover");
car.insert("Maruti Suzuki");
//Before Deletion
cout << "Before Deletion" << endl;
cout << car.search("Lamborghini") << endl; // Output: 1 (true)
cout << car.search("Mercedes-Benz") << endl; // Output: 1 (true)
cout << car.search("Land Rover") << endl; // Output: 1 (true)
cout << car.search("Maruti Suzuki") << endl; // Output: 1 (true)
//Deleting elements using deletion operation
car.deleteWord("Lamborghini");
car.deleteWord("Land Rover");
//After Deletion
cout << "After Deletion" << endl;
cout << car.search("Lamborghini") << endl; // Output: 0 (false)
cout << car.search("Mercedes-Benz") << endl; // Output: 1 (true)
cout << car.search("Land Rover") << endl; // Output: 0 (false)
cout << car.search("Maruti Suzuki") << endl; // Output: 1 (true)
return 0;
}
輸出
Before Deletion 1 1 1 1 After Deletion 0 1 0 1
//Java code for Deletion operator of tries algotrithm
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
class TrieNode {
Map<Character, TrieNode> children;
boolean isEndOfWord;
TrieNode() {
children = new HashMap<>();
isEndOfWord = false;
}
}
class Trie {
private TrieNode root;
Trie() {
root = new TrieNode();
}
void insert(String word) {
TrieNode curr = root;
for (char ch : word.toCharArray()) {
curr.children.putIfAbsent(ch, new TrieNode());
curr = curr.children.get(ch);
}
curr.isEndOfWord = true;
}
boolean search(String word) {
TrieNode curr = root;
for (char ch : word.toCharArray()) {
if (!curr.children.containsKey(ch)) {
return false;
}
curr = curr.children.get(ch);
}
return curr.isEndOfWord;
}
boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
TrieNode curr = root;
for (char ch : prefix.toCharArray()) {
if (!curr.children.containsKey(ch)) {
return false;
}
curr = curr.children.get(ch);
}
return true;
}
boolean delete(String word) {
return deleteHelper(root, word, 0);
}
private boolean deleteHelper(TrieNode curr, String word, int index) {
if (index == word.length()) {
if (!curr.isEndOfWord) {
return false; // Word does not exist in the Trie
}
curr.isEndOfWord = false; // Mark as deleted
return curr.children.isEmpty(); // Return true if no more children
}
char ch = word.charAt(index);
if (!curr.children.containsKey(ch)) {
return false; // Word does not exist in the Trie
}
TrieNode child = curr.children.get(ch);
boolean shouldDeleteChild = deleteHelper(child, word, index + 1);
if (shouldDeleteChild) {
curr.children.remove(ch); // Remove the child node if necessary
return curr.children.isEmpty(); // Return true if no more children
}
return false;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Trie car = new Trie();
//Inserting the elements
car.insert("Lamborghini");
car.insert("Mercedes-Benz");
car.insert("Land Rover");
car.insert("Maruti Suzuki");
//Before Deletion
System.out.println("Before Deletion");
//Printing the elements
System.out.println(car.search("Lamborghini")); // Output: true
System.out.println(car.search("Mercedes-Benz")); // Output: true
System.out.println(car.search("Land Rover")); // Output: true
System.out.println(car.search("Maruti Suzuki")); // Output: true
//Deleting the elements using deletion operation
car.delete("Lamborghini");
car.delete("Land Rover");
// After Deletion
System.out.println("After Deletion");
// Prints the elements in the Boolean expression
System.out.println(car.search("Lamborghini")); // Output: false
System.out.println(car.search("Mercedes-Benz")); // Output: true
System.out.println(car.search("Land Rover")); // Output: false
System.out.println(car.search("Maruti Suzuki")); // Output: true
}
}
輸出
Before Deletion true true true true After Deletion false true false true
#python Code for Deletion operation of tries algorithm
class TrieNode:
def __init__(self):
self.children = {}
self.isEndOfWord = False
class Trie:
def __init__(self):
self.root = TrieNode()
def insert(self, word):
curr = self.root
for ch in word:
if ch not in curr.children:
curr.children[ch] = TrieNode()
curr = curr.children[ch]
curr.isEndOfWord = True
def search(self, word):
curr = self.root
for ch in word:
if ch not in curr.children:
return False
curr = curr.children[ch]
return curr.isEndOfWord
def startsWith(self, prefix):
curr = self.root
for ch in prefix:
if ch not in curr.children:
return False
curr = curr.children[ch]
return True
def delete(self, word):
return self.deleteHelper(self.root, word, 0)
def deleteHelper(self, curr, word, index):
if index == len(word):
if not curr.isEndOfWord:
return False # Word does not exist in the Trie
curr.isEndOfWord = False # Mark as deleted
return len(curr.children) == 0 # Return True if no more children
ch = word[index]
if ch not in curr.children:
return False # Word does not exist in the Trie
child = curr.children[ch]
shouldDeleteChild = self.deleteHelper(child, word, index + 1)
if shouldDeleteChild:
del curr.children[ch] # Remove the child node if necessary
return len(curr.children) == 0 # Return True if no more children
return False
trie = Trie()
#inserting the elements
trie.insert("Lamborghini")
trie.insert("Mercedes-Benz")
trie.insert("Land Rover")
trie.insert("Maruti Suzuki")
#Before Deletion
print("Before Deletion:")
print(trie.search("Lamborghini")) # Output: True
print(trie.search("Mercedes-Benz")) # Output: True
print(trie.search("Land Rover")) # Output: True
print(trie.search("Maruti Suzuki")) # Output: True
#deleting the elements using Deletion operation
trie.delete("Lamborghini")
trie.delete("Land Rover")
#After Deletion
print("After Deletion:")
#print elements
print(trie.search("Lamborghini")) # Output: False
print(trie.search("Mercedes-Benz")) # Output: True
print(trie.search("Land Rover")) # Output: False
print(trie.search("Maruti Suzuki")) # Output: True
輸出
Before Deletion: True True True True After Deletion: False True False True
搜尋
在Trie中搜索是一種相當直接的方法。我們只能根據鍵節點(插入操作開始的節點)向下移動Trie的級別。搜尋直到到達路徑的末尾。如果找到元素,則搜尋成功;否則,搜尋失敗。
示例
//C program for search operation of tries algorithm
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define ALPHABET_SIZE 26
struct TrieNode {
struct TrieNode* children[ALPHABET_SIZE];
bool isEndOfWord;
};
struct TrieNode* createNode() {
struct TrieNode* node = (struct TrieNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct TrieNode));
node->isEndOfWord = false;
for (int i = 0; i < ALPHABET_SIZE; i++) {
node->children[i] = NULL;
}
return node;
}
void insert(struct TrieNode* root, char* word) {
struct TrieNode* curr = root;
for (int i = 0; word[i] != '\0'; i++) {
int index = word[i] - 'a';
if (curr->children[index] == NULL) {
curr->children[index] = createNode();
}
curr = curr->children[index];
}
curr->isEndOfWord = true;
}
bool search(struct TrieNode* root, char* word) {
struct TrieNode* curr = root;
for (int i = 0; word[i] != '\0'; i++) {
int index = word[i] - 'a';
if (curr->children[index] == NULL) {
return false;
}
curr = curr->children[index];
}
return (curr != NULL && curr->isEndOfWord);
}
bool startsWith(struct TrieNode* root, char* prefix) {
struct TrieNode* curr = root;
for (int i = 0; prefix[i] != '\0'; i++) {
int index = prefix[i] - 'a';
if (curr->children[index] == NULL) {
return false;
}
curr = curr->children[index];
}
return true;
}
int main() {
struct TrieNode* root = createNode();
//inserting the elements
insert(root, "Lamborghini");
insert(root, "Mercedes-Benz");
insert(root, "Land Rover");
insert(root, "Maruti Suzuki");
//Searching elements
printf("Searching Cars\n");
//Printing searched elements
printf("%d\n", search(root, "Lamborghini")); // Output: 1 (true)
printf("%d\n", search(root, "Mercedes-Benz")); // Output: 1 (true)
printf("%d\n", search(root, "Honda")); // Output: 0 (false)
printf("%d\n", search(root, "Land Rover")); // Output: 1 (true)
printf("%d\n", search(root, "BMW")); // Output: 0 (false)
//Searching the elements the name starts with?
printf("Cars name starts with\n");
//Printing the elements
printf("%d\n", startsWith(root, "Lambo")); // Output: 1 (true)
printf("%d\n", startsWith(root, "Hon")); // Output: 0 (false)
printf("%d\n", startsWith(root, "Hy")); // Output: 0 (false)
printf("%d\n", startsWith(root, "Mar")); // Output: 1 (true)
printf("%d\n", startsWith(root, "Land")); // Output: 1 (true)
return 0;
}
輸出
Searching Cars 1 1 0 1 0 Cars name starts with 1 0 0 1 1
//C++ code for Search operation of tries algorithm
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
class TrieNode {
public:
unordered_map<char, TrieNode*> children;
bool isEndOfWord;
TrieNode() {
isEndOfWord = false;
}
};
class Trie {
private:
TrieNode* root;
public:
Trie() {
root = new TrieNode();
}
void insert(string word) {
TrieNode* curr = root;
for (char ch : word) {
if (curr->children.find(ch) == curr->children.end()) {
curr->children[ch] = new TrieNode();
}
curr = curr->children[ch];
}
curr->isEndOfWord = true;
}
bool search(string word) {
TrieNode* curr = root;
for (char ch : word) {
if (curr->children.find(ch) == curr->children.end()) {
return false;
}
curr = curr->children[ch];
}
return curr->isEndOfWord;
}
bool startsWith(string prefix) {
TrieNode* curr = root;
for (char ch : prefix) {
if (curr->children.find(ch) == curr->children.end()) {
return false;
}
curr = curr->children[ch];
}
return true;
}
};
int main() {
Trie car;
//inserting the elements
car.insert("Lamborghini");
car.insert("Mercedes-Benz");
car.insert("Land Rover");
car.insert("Maruti Suzuki");
//searching elements
cout<< "Searching Cars"<< endl;
// Printing searched elements in Boolean expression
cout << car.search("Lamborghini") << endl; // Output: 1 (true)
cout << car.search("Mercedes-Benz") << endl; // Output: 1 (true)
cout << car.search("Honda") << endl; // Output: 0 (false)
cout << car.search("Land Rover") << endl; // Output: 1 (true)
cout << car.search("BMW") << endl; // Output: 0 (false)
//searching names starts with?
cout<<"cars name starts with" << endl;
//Printing the elements
cout << car.startsWith("Lambo") << endl; // Output: 1 (true)
cout << car.startsWith("Hon") << endl; // Output: 0 (false)
cout << car.startsWith("Hy") << endl; // Output: 0 (false)
cout << car.startsWith("Mar") << endl; // Output: 1 (true)
cout << car.startsWith("Land") << endl; // Output: 1 (true)
return 0;
}
輸出
Searching Cars 1 1 0 1 0 cars name starts with 1 0 0 1 1
//Java program for tries Algorithm
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
class TrieNode {
Map<Character, TrieNode> children;
boolean isEndOfWord;
TrieNode() {
children = new HashMap<>();
isEndOfWord = false;
}
}
class Trie {
private TrieNode root;
Trie() {
root = new TrieNode();
}
void insert(String word) {
TrieNode curr = root;
for (char ch : word.toCharArray()) {
curr.children.putIfAbsent(ch, new TrieNode());
curr = curr.children.get(ch);
}
curr.isEndOfWord = true;
}
boolean search(String word) {
TrieNode curr = root;
for (char ch : word.toCharArray()) {
if (!curr.children.containsKey(ch)) {
return false;
}
curr = curr.children.get(ch);
}
return curr.isEndOfWord;
}
boolean startsWith(String prefix) {
TrieNode curr = root;
for (char ch : prefix.toCharArray()) {
if (!curr.children.containsKey(ch)) {
return false;
}
curr = curr.children.get(ch);
}
return true;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Trie car = new Trie();
//Inserting the elements
car.insert("Lamborghini");
car.insert("Mercedes-Benz");
car.insert("Land Rover");
car.insert("Maruti Suzuki");
//searching the elements
System.out.println("Searching Cars");
//Printing the searched elements
System.out.println(car.search("Lamborghini")); // Output: true
System.out.println(car.search("Mercedes-Benz")); // Output: true
System.out.println(car.search("Honda")); // Output: false
System.out.println(car.search("Land Rover")); // Output: true
System.out.println(car.search("BMW")); // Output: false
//searching the elements name start with?
System.out.println("Cars name starts with");
//Printing the elements
System.out.println(car.startsWith("Lambo")); // Output: true
System.out.println(car.startsWith("Hon")); // Output: false
System.out.println(car.startsWith("Hy")); // Output: false
System.out.println(car.startsWith("Mar")); // Output: true
System.out.println(car.startsWith("Land")); // Output: true
}
}
輸出
Searching Cars true true false true false Cars name starts with true false false true true
#Python code for Search operation of tries algorithm
class TrieNode:
def __init__(self):
self.children = {}
self.isEndOfWord = False
class Trie:
def __init__(self):
self.root = TrieNode()
def insert(self, word):
curr = self.root
for ch in word:
if ch not in curr.children:
curr.children[ch] = TrieNode()
curr = curr.children[ch]
curr.isEndOfWord = True
def search(self, word):
curr = self.root
for ch in word:
if ch not in curr.children:
return False
curr = curr.children[ch]
return curr.isEndOfWord
def startsWith(self, prefix):
curr = self.root
for ch in prefix:
if ch not in curr.children:
return False
curr = curr.children[ch]
return True
if __name__ == '__main__':
car = Trie()
#Inserting the elements
car.insert("Lamborghini")
car.insert("Mercedes-Benz")
car.insert("Land Rover")
car.insert("Maruti Suzuki")
#Searching elements
print("Searching Cars")
#Printing the searched elements
print(car.search("Lamborghini")) # Output: True
print(car.search("Mercedes-Benz")) # Output: True
print(car.search("Honda")) # Output: False
print(car.search("Land Rover")) # Output: True
print(car.search("BMW")) # Output: False
#printing elements name starts with?
print("Cars name starts with")
print(car.startsWith("Lambo")) # Output: True
print(car.startsWith("Hon")) # Output: False
print(car.startsWith("Hy")) # Output: False
print(car.startsWith("Mar")) # Output: True
print(car.startsWith("Land")) # Output: True
輸出
Before Deletion: True True True True After Deletion: False True False True
堆資料結構
堆是平衡二叉樹資料結構的一種特殊情況,其中根節點鍵與其子節點進行比較並相應地排列。如果α具有子節點β,則 -
key(α) ≥ key(β)
由於父節點的值大於子節點的值,因此此屬性生成最大堆。根據此標準,堆可以分為兩種型別 -
For Input → 35 33 42 10 14 19 27 44 26 31
最小堆 (Min-Heap) − 根節點的值小於或等於其任何一個子節點的值。
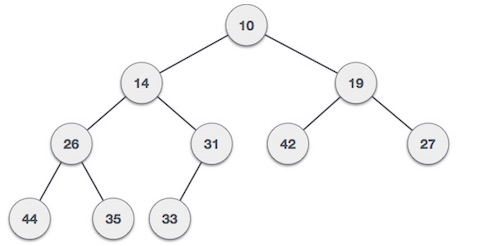
最大堆 (Max-Heap) − 根節點的值大於或等於其任何一個子節點的值。
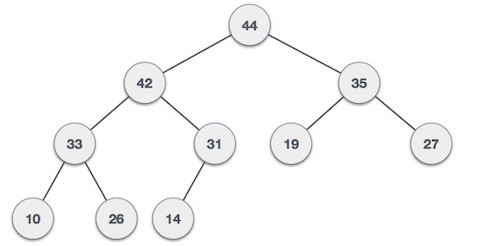
這兩棵樹都是使用相同的輸入和到達順序構建的。
最大堆構建演算法
我們將使用相同的示例來演示如何建立一個最大堆。建立最小堆的過程類似,但我們選擇最小值而不是最大值。
我們將推匯出一個最大堆的演算法,該演算法一次插入一個元素。在任何時候,堆都必須保持其屬性。在插入過程中,我們還假設我們將節點插入到一個已經堆化的樹中。
Step 1 − Create a new node at the end of heap. Step 2 − Assign new value to the node. Step 3 − Compare the value of this child node with its parent. Step 4 − If value of parent is less than child, then swap them. Step 5 − Repeat step 3 & 4 until Heap property holds.
注意 − 在最小堆構建演算法中,我們期望父節點的值小於子節點的值。
讓我們透過動畫來說明來理解最大堆的構建。我們考慮之前使用的相同輸入樣本。

示例
//C code for Max Heap construction Algorithm
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Structure to represent a heap
typedef struct {
int* array; // Array to store heap elements
int capacity; // Maximum capacity of the heap
int size; // Current size of the heap
} Heap;
// Function to create a new heap
Heap* createHeap(int capacity)
{
Heap* heap = (Heap*)malloc(sizeof(Heap));
heap->array = (int*)malloc(capacity * sizeof(int));
heap->capacity = capacity;
heap->size = 0;
return heap;
}
// Function to swap two elements in the heap
void swap(int* a, int* b)
{
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
// Function to heapify a subtree rooted at index i
void heapify(Heap* heap, int i)
{
int largest = i;
int left = 2 * i + 1;
int right = 2 * i + 2;
// Check if the left child is larger than the root
if (left < heap->size && heap->array[left] > heap->array[largest])
largest = left;
// Check if the right child is larger than the largest so far
if (right < heap->size && heap->array[right] > heap->array[largest])
largest = right;
// If the largest is not the root, swap the root with the largest
if (largest != i) {
swap(&heap->array[i], &heap->array[largest]);
heapify(heap, largest);
}
}
// Function to insert a new element into the heap
void insert(Heap* heap, int value)
{
if (heap->size == heap->capacity) {
printf("Heap is full. Cannot insert more elements.\n");
return;
}
// Insert the new element at the end
int i = heap->size++;
heap->array[i] = value;
// Fix the heap property if it is violated
while (i != 0 && heap->array[(i - 1) / 2] < heap->array[i]) {
swap(&heap->array[i], &heap->array[(i - 1) / 2]);
i = (i - 1) / 2;
}
}
// Function to extract the maximum element from the heap
int extractMax(Heap* heap)
{
if (heap->size == 0) {
printf("Heap is empty. Cannot extract maximum element.\n");
return -1;
}
// Store the root element
int max = heap->array[0];
// Replace the root with the last element
heap->array[0] = heap->array[heap->size - 1];
heap->size--;
// Heapify the root
heapify(heap, 0);
return max;
}
// Function to print the elements of the heap
void printHeap(Heap* heap)
{
printf("Heap elements: ");
for (int i = 0; i < heap->size; i++) {
printf("%d ", heap-<array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// Example usage of the heap
int main()
{
Heap* heap = createHeap(10);
insert(heap, 35);
insert(heap, 33);
insert(heap, 42);
insert(heap, 10);
insert(heap, 14);
insert(heap, 19);
insert(heap, 27);
insert(heap, 44);
insert(heap, 26);
insert(heap, 31);
printHeap(heap);
int max = extractMax(heap);
printf("Maximum element: %d\n", max);
return 0;
}
輸出
Heap elements: 44 42 35 33 31 19 27 10 26 14 Maximum element: 44
//C++ code for Max Heap construction Algorithm
#include <iostream>
// Structure to represent a heap
struct Heap {
int* array; // Array to store heap elements
int capacity; // Maximum capacity of the heap
int size; // Current size of the heap
};
// Function to create a new heap
Heap* createHeap(int capacity)
{
Heap* heap = new Heap;
heap->array = new int[capacity];
heap->capacity = capacity;
heap->size = 0;
return heap;
}
// Function to swap two elements in the heap
void swap(int& a, int& b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
// Function to heapify a subtree rooted at index i
void heapify(Heap* heap, int i)
{
int largest = i;
int left = 2 * i + 1;
int right = 2 * i + 2;
// Check if the left child is larger than the root
if (left <heap->size && heap->array[left] > heap->array[largest])
largest = left;
// Check if the right child is larger than the largest so far
if (right <heap->size && heap->array[right] > heap->array[largest])
largest = right;
// If the largest is not the root, swap the root with the largest
if (largest != i) {
swap(heap->array[i], heap->array[largest]);
heapify(heap, largest);
}
}
// Function to insert a new element into the heap
void insert(Heap* heap, int value)
{
if (heap->size == heap->capacity) {
std::cout << "Heap is full. Cannot insert more elements." << std::endl;
return;
}
// Insert the new element at the end
int i = heap->size++;
heap->array[i] = value;
// Fix the heap property if it is violated
while (i != 0 && heap->array[(i - 1) / 2] < heap->array[i]) {
swap(heap->array[i], heap->array[(i - 1) / 2]);
i = (i - 1) / 2;
}
}
// Function to extract the maximum element from the heap
int extractMax(Heap* heap)
{
if (heap->size == 0) {
std::cout << "Heap is empty. Cannot extract maximum element." << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// Store the root element
int max = heap->array[0];
// Replace the root with the last element
heap->array[0] = heap->array[heap->size - 1];
heap->size--;
// Heapify the root
heapify(heap, 0);
return max;
}
// Function to print the elements of the heap
void printHeap(Heap* heap)
{
std::cout << "Heap elements: ";
for (int i = 0; i < heap->size; i++) {
std::cout << heap->array[i] << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
// Example usage of the heap
int main()
{
Heap* heap = createHeap(10);
insert(heap, 35);
insert(heap, 33);
insert(heap, 42);
insert(heap, 10);
insert(heap, 14);
insert(heap, 19);
insert(heap, 27);
insert(heap, 44);
insert(heap, 26);
insert(heap, 31);
printHeap(heap);
int max = extractMax(heap);
std::cout << "Maximum element: " << max << std::endl;
return 0;
}
輸出
Heap elements: 44 42 35 33 31 19 27 10 26 14 Maximum element: 44
// Java code for for Max Heap construction Algorithm
//Structure to represent a heap
public class MaxHeap {
private int[] heap; // To store heap elements
private int capacity; // Maximum capacity of the heap
private int size; // Current size of the heap
// To create a new heap
public MaxHeap(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
this.size = 0;
this.heap = new int[capacity];
}
private int parent(int i) {
return (i - 1) / 2;
}
private int leftChild(int i) {
return 2 * i + 1;
}
private int rightChild(int i) {
return 2 * i + 2;
}
private void swap(int i, int j) {
int temp = heap[i];
heap[i] = heap[j];
heap[j] = temp;
}
// Heapify a subtree rooted at index i
private void heapifyDown(int i) {
int largest = i;
int left = leftChild(i);
int right = rightChild(i);
// Check if the left child is larger than the root
if (left < size && heap[left] > heap[largest])
largest = left;
// Check if the right child is larger than the largest so far
if (right < size && heap[right] > heap[largest])
largest = right;
// If the largest is not the root, swap the root with the largest
if (largest != i) {
swap(i, largest);
heapifyDown(largest);
}
}
private void heapifyUp(int i) {
while (i > 0 && heap[i] > heap[parent(i)]) {
int parent = parent(i);
swap(i, parent);
i = parent;
}
}
// Insert the new element at the end
public void insert(int value) {
if (size == capacity) {
System.out.println("Heap is full. Cannot insert more elements.");
return;
}
heap[size] = value;
size++;
heapifyUp(size - 1);
}
// Function to extract the maximum element from the heap
public int extractMax() {
if (size == 0) {
System.out.println("Heap is empty. Cannot extract maximum element.");
return -1;
}
// store th root element
int max = heap[0];
//Replace the root with the last elements
heap[0] = heap[size - 1];
size--;
heapifyDown(0);
return max;
}
//print the elements of the heap
public void printHeap() {
System.out.print("Heap elements: ");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
System.out.print(heap[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MaxHeap heap = new MaxHeap(10);
heap.insert(35);
heap.insert(33);
heap.insert(42);
heap.insert(10);
heap.insert(14);
heap.insert(19);
heap.insert(27);
heap.insert(44);
heap.insert(26);
heap.insert(31);
heap.printHeap();
int max = heap.extractMax();
System.out.println("Maximum element: " + max);
}
}
輸出
Heap elements: 44 42 35 33 31 19 27 10 26 14 Maximum element: 44
# Python code for for Max Heap construction Algorithm
class MaxHeap:
def __init__(self):
self.heap = []
def parent(self, i):
return (i - 1) // 2
def left_child(self, i):
return 2 * i + 1
def right_child(self, i):
return 2 * i + 2
#Function to swap two elements in the heap
def swap(self, i, j):
self.heap[i], self.heap[j] = self.heap[j], self.heap[i]
# Function to heapify a subtree rooted at index i
def heapify_down(self, i):
left = self.left_child(i)
right = self.right_child(i)
largest = i
#Check if the left child is larger than the root
if left < len(self.heap) and self.heap[left] >self.heap[largest]:
largest = left
# Check if the right child is larger than the largest so far
if right < len(self.heap) and self.heap[right] > self.heap[largest]:
largest = right
# If the largest is not the root, swap the root with the largest
if largest != i:
self.swap(i, largest)
self.heapify_down(largest)
def heapify_up(self, i):
while i > 0 and self.heap[i] > self.heap[self.parent(i)]:
parent = self.parent(i)
self.swap(i, parent)
i = parent
# Insert the new element at the end
def insert(self, value):
self.heap.append(value)
# Fix the heap property if it is violated
self.heapify_up(len(self.heap) - 1)
# Function to extract the maximum element from the heap
def extract_max(self):
if len(self.heap) == 0:
print("Heap is empty. Cannot extract maximum element.")
return None
max_value = self.heap[0]
self.heap[0] = self.heap[-1]
self.heap.pop()
self.heapify_down(0)
return max_value
# Function to print the elements of the heap
def print_heap(self):
print("Heap elements:", end=" ")
for value in self.heap:
print(value, end=" ")
print()
# Example usage of the heap
heap = MaxHeap()
heap.insert(35)
heap.insert(33)
heap.insert(42)
heap.insert(10)
heap.insert(14)
heap.insert(19)
heap.insert(27)
heap.insert(44)
heap.insert(26)
heap.insert(31)
heap.print_heap()
max_value = heap.extract_max()
print("Maximum element:", max_value)
輸出
Heap elements: 44 42 35 33 31 19 27 10 26 14 Maximum element: 44s
最大堆刪除演算法
讓我們推匯出一個從最大堆中刪除的演算法。最大(或最小)堆中的刪除總是發生在根節點,以移除最大(或最小)值。
Step 1 − Remove root node. Step 2 − Move the last element of last level to root. Step 3 − Compare the value of this child node with its parent. Step 4 − If value of parent is less than child, then swap them. Step 5 − Repeat step 3 & 4 until Heap property holds.
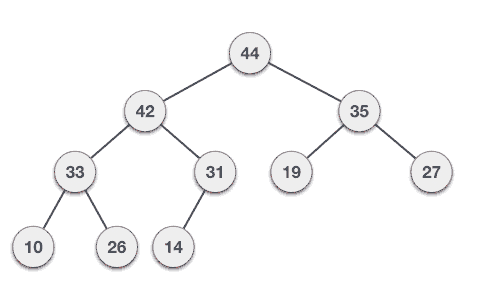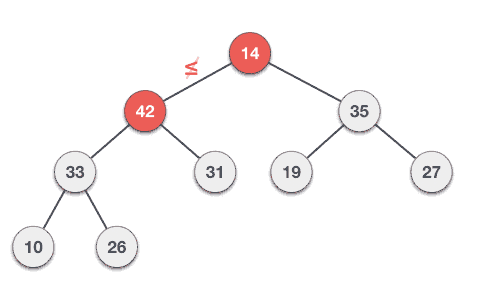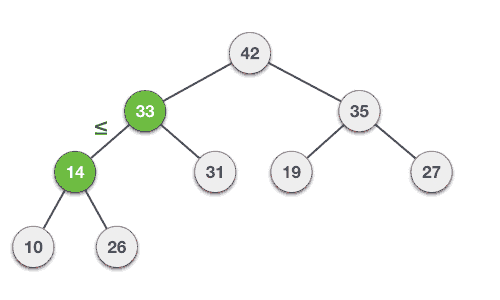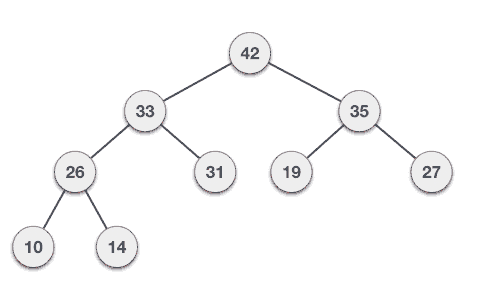
示例
//C code for Max Heap Deletion Algorithm
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Structure to represent a heap
typedef struct {
int* array; // Array to store heap elements
int capacity; // Maximum capacity of the heap
int size; // Current size of the heap
} Heap;
// create a new heap
Heap* createHeap(int capacity)
{
Heap* heap = (Heap*)malloc(sizeof(Heap));
heap->array = (int*)malloc(capacity * sizeof(int));
heap->capacity = capacity;
heap->size = 0;
return heap;
}
// swap two elements in the heap
void swap(int* a, int* b)
{
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
// Heapify a subtree rooted at index i
void heapify(Heap* heap, int i)
{
int largest = i;
int left = 2 * i + 1;
int right = 2 * i + 2;
// Check if the left child is larger than the root
if (left < heap->size && heap->array[left] > heap->array[largest])
largest = left;
// Check if the right child is larger than the largest so far
if (right < heap->size && heap->array[right] > heap->array[largest])
largest = right;
// If the largest is not the root, swap the root with the largest
if (largest != i) {
swap(&heap->array[i], &heap->array[largest]);
heapify(heap, largest);
}
}
// Function to insert a new element into the heap
void insert(Heap* heap, int value)
{
if (heap->size == heap->capacity) {
printf("Heap is full. Cannot insert more elements.\n");
return;
}
// Insert the new element at the end
int i = heap->size++;
heap->array[i] = value;
// Fix the heap property if it is violated
while (i != 0 && heap->array[(i - 1) / 2] < heap->array[i]) {
swap(&heap->array[i], &heap->array[(i - 1) / 2]);
i = (i - 1) / 2;
}
}
// delete the maximum element from the heap
int deleteMax(Heap* heap)
{
if (heap->size == 0) {
printf("Heap is empty. Cannot extract maximum element.\n");
return -1;
}
// Store the root element
int max = heap->array[0];
// Replace the root with the last element
heap->array[0] = heap->array[heap->size - 1];
heap->size--;
// Heapify the root
heapify(heap, 0);
return max;
}
// print the elements of the heap
void printHeap(Heap* heap)
{
printf("Heap elements: ");
for (int i = 0; i < heap->size; i++) {
printf("%d ", heap->array[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
// Deallocate memory occupied by the heap
void destroyHeap(Heap* heap)
{
free(heap->array);
free(heap);
}
// Example usage of the heap
int main()
{
Heap* heap = createHeap(10);
insert(heap, 35);
insert(heap, 33);
insert(heap, 42);
insert(heap, 10);
insert(heap, 14);
insert(heap, 19);
insert(heap, 27);
insert(heap, 44);
insert(heap, 26);
insert(heap, 31);
printHeap(heap);
// Deleting the maximum element in the heap
int max = deleteMax(heap);
printf("Maximum element: %d\n", max);
printHeap(heap);
destroyHeap(heap);
return 0;
}
輸出
Heap elements: 44 42 35 33 31 19 27 10 26 14 Maximum element: 44 Heap elements: 42 33 35 26 31 19 27 10 14
//C++ code for Max Heap Deletion Algorithm
#include <iostream>
// Structure to represent a heap
struct Heap {
int* array; // Array to store heap elements
int capacity; // Maximum capacity of the heap
int size; // Current size of the heap
};
// Create a new heap
Heap* createHeap(int capacity)
{
Heap* heap = new Heap;
heap->array = new int[capacity];
heap->capacity = capacity;
heap->size = 0;
return heap;
}
// Swap two elements in the heap
void swap(int& a, int& b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
// Heapify a subtree rooted at index i
void heapify(Heap* heap, int i)
{
int largest = i;
int left = 2 * i + 1;
int right = 2 * i + 2;
// Check if the left child is larger than the root
if (left < heap->size && heap->array[left] > heap->array[largest])
largest = left;
// Check if the right child is larger than the largest so far
if (right < heap->size && heap->array[right] > heap->array[largest])
largest = right;
// If the largest is not the root, swap the root with the largest
if (largest != i) {
swap(heap->array[i], heap->array[largest]);
heapify(heap, largest);
}
}
// Function to insert a new element into the heap
void insert(Heap* heap, int value)
{
if (heap->size == heap->capacity) {
std::cout << "Heap is full. Cannot insert more elements." << std::endl;
return;
}
// Insert the new element at the end
int i = heap->size++;
heap->array[i] = value;
// Fix the heap property if it is violated
while (i != 0 && heap->array[(i - 1) / 2] < heap->array[i]) {
swap(heap->array[i], heap->array[(i - 1) / 2]);
i = (i - 1) / 2;
}
}
// Function to delete the maximum element from the heap
int deleteMax(Heap* heap)
{
if (heap->size == 0) {
std::cout << "Heap is empty. Cannot extract maximum element." << std::endl;
return -1;
}
// Store the root element
int max = heap->array[0];
// Replace the root with the last element
heap->array[0] = heap->array[heap->size - 1];
heap->size--;
// Heapify the root
heapify(heap, 0);
return max;
}
// Function to print the elements of the heap
void printHeap(Heap* heap)
{
std::cout << "Heap elements: ";
for (int i = 0; i < heap->size; i++) {
std::cout << heap->array[i] << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
// Function to deallocate memory occupied by the heap
void destroyHeap(Heap* heap)
{
delete[] heap->array;
delete heap;
}
// Example usage of the heap
int main()
{
Heap* heap = createHeap(10);
insert(heap, 35);
insert(heap, 33);
insert(heap, 42);
insert(heap, 10);
insert(heap, 14);
insert(heap, 19);
insert(heap, 27);
insert(heap, 44);
insert(heap, 26);
insert(heap, 31);
printHeap(heap);
int max = deleteMax(heap);
std::cout << "Maximum element: " << max << std::endl;
printHeap(heap);
destroyHeap(heap);
return 0;
}
輸出
Heap elements: 44 42 35 33 31 19 27 10 26 14 Maximum element: 44 Heap elements: 42 33 35 26 31 19 27 10 14
// Java code for for Max Heap Deletion Algorithm
// Structure to represent a heap
class Heap {
private int[] array; // Array to store heap elements
private int capacity; // Maximum capacity of the heap
private int size; // Current size of the heap
// To create a new heap
public Heap(int capacity) {
this.array = new int[capacity];
this.capacity = capacity;
this.size = 0;
}
// Swap two elements in the heap
private void swap(int a, int b) {
int temp = array[a];
array[a] = array[b];
array[b] = temp;
}
// Heapify a subtree rooted at index i
private void heapify(int i) {
int largest = i;
int left = 2 * i + 1;
int right = 2 * i + 2;
// Check if the left child is larger than the root
if (left < size && array[left] > array[largest])
largest = left;
// Check if the right child is larger than the largest so far
if (right < size && array[right] > array[largest])
largest = right;
// If the largest is not the root, swap the root with the largest
if (largest != i) {
swap(i, largest);
heapify(largest);
}
}
// Insert a new element into the heap
public void insert(int value) {
if (size == capacity) {
System.out.println("Heap is full. Cannot insert more elements.");
return;
}
// Insert the new element at the end
int i = size++;
array[i] = value;
// Fix the heap property if it is violated
while (i != 0 && array[(i - 1) / 2] < array[i]) {
swap(i, (i - 1) / 2);
i = (i - 1) / 2;
}
}
// Delete the maximum element from the heap
public int deleteMax() {
if (size == 0) {
System.out.println("Heap is empty. Cannot extract maximum element.");
return -1;
}
// Store the root element
int max = array[0];
// Replace the root with the last element
array[0] = array[size - 1];
size--;
// Heapify the root
heapify(0);
return max;
}
// Print the elements of the heap
public void printHeap() {
System.out.print("Heap elements: ");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
System.out.print(array[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
// Deallocate memory occupied by the heap
public void destroyHeap() {
array = null;
size = 0;
}
}
//Inserting the elements
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Heap heap = new Heap(10);
heap.insert(35);
heap.insert(33);
heap.insert(42);
heap.insert(10);
heap.insert(14);
heap.insert(19);
heap.insert(27);
heap.insert(44);
heap.insert(26);
heap.insert(31);
heap.printHeap();
int max = heap.deleteMax();
System.out.println("Maximum element: " + max);
//Printing the heap elements after deletion of max element
heap.printHeap();
heap.destroyHeap();
}
}
輸出
Heap elements: 44 42 35 33 31 19 27 10 26 14 Maximum element: 44 Heap elements: 42 33 35 26 31 19 27 10 14
#Python code for Max Heap Deletion Algorithm
class Heap:
def __init__(self, capacity):
self.array = [0] * capacity #array to store heap elements
self.capacity = capacity #maximum capacity of the heap
self.size = 0 #Current size of the heap
# swap two elements in the heap
def swap(self, a, b):
self.array[a], self.array[b] = self.array[b], self.array[a]
# Heapify a subtree rooted at index i
def heapify(self, i):
largest = i
left = 2 * i + 1
right = 2 * i + 2
# Check if the left child is larger than the root
if left < self.size and self.array[left] > self.array[largest]:
largest = left
# Check if the right child is larger than the largest so far
if right < self.size and self.array[right] > self.array[largest]:
largest = right
# If the largest is not the root, swap the root with the largest
if largest != i:
self.swap(i, largest)
self.heapify(largest)
# insert a new element into the heap
def insert(self, value):
if self.size == self.capacity:
print("Heap is full. Cannot insert more elements.")
return
# Insert the new element at the end
i = self.size
self.size += 1
self.array[i] = value
# Fix the heap property if it is violated
while i != 0 and self.array[(i - 1) // 2] < self.array[i]:
self.swap(i, (i - 1) // 2)
i = (i - 1) // 2
# delete the maximum element from the heap
def deleteMax(self):
if self.size == 0:
print("Heap is empty. Cannot extract maximum element.")
return -1
# store the root element
max_value = self.array[0]
# Replace the root with the last element
self.array[0] = self.array[self.size - 1]
self.size -= 1
# Heapify the root
self.heapify(0)
return max_value
# print the elements of the heap
def printHeap(self):
print("Heap elements:", end=" ")
for i in range(self.size):
print(self.array[i], end=" ")
print()
# deallocate memory occupied by the heap
def destroyHeap(self):
self.array = []
self.size = 0
# Example usage of the heap
heap = Heap(10)
heap.insert(35)
heap.insert(33)
heap.insert(42)
heap.insert(10)
heap.insert(14)
heap.insert(19)
heap.insert(27)
heap.insert(44)
heap.insert(26)
heap.insert(31)
heap.printHeap()
max_value = heap.deleteMax()
print("Maximum element:", max_value)
heap.printHeap()
heap.destroyHeap()
輸出
Heap elements: 44 42 35 33 31 19 27 10 26 14 Maximum element: 44 Heap elements: 42 33 35 26 31 19 27 10 14
遞迴演算法
一些計算機程式語言允許模組或函式呼叫自身。這種技術稱為遞迴。在遞迴中,函式α要麼直接呼叫自身,要麼呼叫一個函式β,而β又反過來呼叫原始函式α。函式α稱為遞迴函式。
示例 − 函式呼叫自身。
int function(int value) {
if(value < 1)
return;
function(value - 1);
printf("%d ",value);
}
示例 − 一個函式呼叫另一個函式,而另一個函式又反過來再次呼叫它。
int function1(int value1) {
if(value1 < 1)
return;
function2(value1 - 1);
printf("%d ",value1);
}
int function2(int value2) {
function1(value2);
}
特性
遞迴函式可能會像迴圈一樣無限迴圈。為了避免遞迴函式無限執行,遞迴函式必須具備兩個屬性:
基本條件 − 必須至少有一個基本條件或條件,使得當滿足此條件時,函式停止遞迴呼叫自身。
漸進式方法 − 遞迴呼叫應該以這樣一種方式進行,即每次進行遞迴呼叫時,它都更接近基本條件。
實現
許多程式語言使用堆疊來實現遞迴。通常,每當一個函式(呼叫方)呼叫另一個函式(被呼叫方)或自身作為被呼叫方時,呼叫方函式都會將執行控制權轉移到被呼叫方。此轉移過程可能還涉及一些資料從呼叫方傳遞到被呼叫方。
這意味著,呼叫方函式必須暫時掛起其執行,並在執行控制權從被呼叫方函式返回時恢復。在這裡,呼叫方函式需要從其掛起執行的確切位置開始。它還需要它正在處理的完全相同的資料值。為此,將為呼叫方函式建立一個啟用記錄(或堆疊幀)。
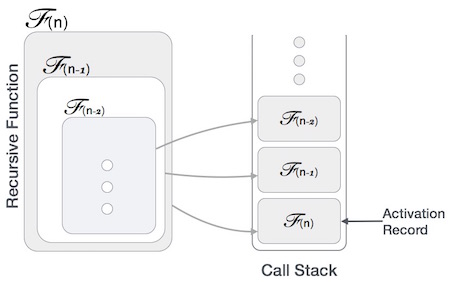
此啟用記錄儲存有關區域性變數、形式引數、返回地址以及傳遞給呼叫方函式的所有資訊的資訊。
遞迴分析
有人可能會爭論為什麼要使用遞迴,因為相同的任務可以用迭代來完成。第一個原因是,遞迴使程式更易讀,並且由於最新的增強型 CPU 系統,遞迴比迭代更有效。
時間複雜度
在迭代的情況下,我們使用迭代次數來計算時間複雜度。同樣,在遞迴的情況下,假設所有內容都是常數,我們嘗試找出進行遞迴呼叫的次數。對函式的呼叫為 Ο(1),因此遞迴呼叫次數為 (n) 使遞迴函式為 Ο(n)。
空間複雜度
空間複雜度計算為模組執行需要多少額外空間。在迭代的情況下,編譯器幾乎不需要任何額外的空間。編譯器會不斷更新迭代中使用的變數的值。但在遞迴的情況下,系統需要在每次進行遞迴呼叫時儲存啟用記錄。因此,認為遞迴函式的空間複雜度可能會高於具有迭代的函式的空間複雜度。
示例
// C program for Recursion Data Structure
#include <stdio.h>
int factorial(int n) {
// Base case: factorial of 0 is 1
if (n == 0)
return 1;
// Recursive case: multiply n with factorial of (n-1)
return n * factorial(n - 1);
}
int main() {
// case 1
int number = 6;
printf("Number is: %d\n" , 6);
//case 2
if (number < 0) {
printf("Error: Factorial is undefined for negative numbers.\n");
return 1;
}
int result = factorial(number);
//print the output
printf("Factorial of %d is: %d\n", number, result);
return 0;
}
輸出
Number is: 6 Factorial of 6 is: 720
// CPP program for Recursion Data Structure
#include <iostream>
int factorial(int n) {
// Base case: factorial of 0 is 1
if (n == 0)
return 1;
// Recursive case: multiply n with factorial of (n-1)
return n * factorial(n - 1);
}
int main() {
// case 1
int number = 6;
std::cout<<"Number is: "<<number<<"\n";
//case 2
if (number < 0) {
std::cout << "Error: Factorial is undefined for negative numbers.\n";
return 1;
}
int result = factorial(number);
//print the output
std::cout << "Factorial of " << number << " is: " << result << std::endl;
return 0;
}
輸出
Number is: 6 Factorial of 6 is: 720
// Java program for Recursion Data Structure
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static int factorial(int n) {
// Base case: factorial of 0 is 1
if (n == 0)
return 1;
// Recursive case: multiply n with factorial of (n-1)
return n * factorial(n - 1);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Case 1
int number = 6;
System.out.println("Number is: " + number);
//Case 2
if (number < 0) {
System.out.println("Error: Factorial is undefined for negative numbers.");
System.exit(1);
}
int result = factorial(number);
//print the output
System.out.println("Factorial of " + number + " is: " + result);
}
}
輸出
Number is: 6 Factorial of 6 is: 720
# Python program for Recursion Data Structure
def factorial(n):
#Base Case: factorial of 0 is 1
if n == 0:
return 1
# Recursive case: multiply n with factorial of (n-1)
return n * factorial(n - 1)
#Case 1:
number = 6;
print("Number is: ", number);
#Case 2:
if number < 0:
print("Error: Factorial is undefined for negative numbers.")
else:
result = factorial(number)
# print the output
print("Factorial of", number, "is: ", result)
輸出
Number is: 6 Factorial of 6 is: 720
漢諾塔問題使用遞迴
漢諾塔問題是一個數學謎題,它包含三個塔(樁)和多個環,如下圖所示:
這些環大小不同,並且按升序堆疊,即較小的環位於較大的環之上。還有其他版本的謎題,其中圓盤的數量增加,但塔的數量保持不變。
規則
任務是將所有圓盤移動到另一個塔,而不會違反排列順序。漢諾塔問題需要遵循以下規則:
- 在任何給定時間,只能在一個塔之間移動一個圓盤。
- 只能移除“頂部”圓盤。
- 較大的圓盤不能放在較小的圓盤上。
以下是使用三個圓盤解決漢諾塔問題的動畫演示。

具有 n 個圓盤的漢諾塔問題可以在最少 2n−1 步內解決。此演示表明,具有 3 個圓盤的謎題已執行 23 - 1 = 7 步。
演算法
要為漢諾塔編寫演算法,首先我們需要學習如何使用較少數量的圓盤(例如 → 1 或 2)來解決此問題。我們用名稱標記三個塔,源、目標和輔助(僅用於幫助移動圓盤)。如果我們只有一個圓盤,則可以輕鬆地將其從源樁移動到目標樁。
如果我們有 2 個圓盤:
- 首先,我們將較小的(頂部)圓盤移動到輔助樁。
- 然後,我們將較大的(底部)圓盤移動到目標樁。
- 最後,我們將較小的圓盤從輔助樁移動到目標樁。
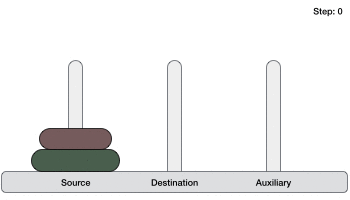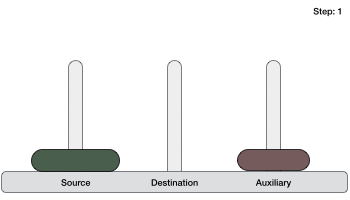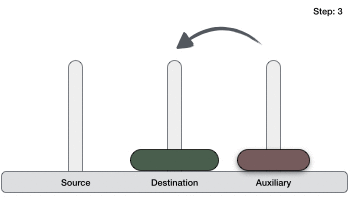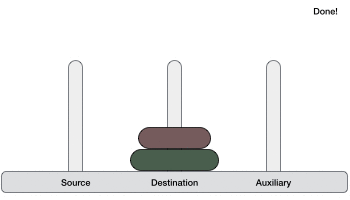
因此,現在我們可以為具有兩個以上圓盤的漢諾塔設計算法了。我們將圓盤堆疊分成兩部分。最大的圓盤(第 n 個圓盤)在一部分,所有其他 (n-1) 個圓盤在第二部分。
我們的最終目標是將圓盤 n 從源移動到目標,然後將所有其他 (n1) 個圓盤放在它上面。我們可以想象以遞迴的方式對所有給定的圓盤集應用相同的操作。
需要遵循的步驟如下:
Step 1 − Move n-1 disks fromsourcetoauxStep 2 − Move nth disk fromsourcetodestStep 3 − Move n-1 disks fromauxtodest
漢諾塔的遞迴演算法可以如下驅動:
START
Procedure Hanoi(disk, source, dest, aux)
IF disk == 1, THEN
move disk from source to dest
ELSE
Hanoi(disk - 1, source, aux, dest) // Step 1
move disk from source to dest // Step 2
Hanoi(disk - 1, aux, dest, source) // Step 3
END IF
END Procedure
STOP
示例
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAX 10
int list[MAX] = {1,8,4,6,0,3,5,2,7,9};
void display(){
int i;
printf("[");
// navigate through all items
for(i = 0; i < MAX; i++) {
printf("%d ",list[i]);
}
printf("]\n");
}
void bubbleSort() {
int temp;
int i,j;
bool swapped = false;
// loop through all numbers
for(i = 0; i < MAX-1; i++) {
swapped = false;
// loop through numbers falling ahead
for(j = 0; j < MAX-1-i; j++) {
printf("Items compared: [ %d, %d ] ", list[j],list[j+1]);
// check if next number is lesser than current no
// swap the numbers.
// (Bubble up the highest number)
if(list[j] > list[j+1]) {
temp = list[j];
list[j] = list[j+1];
list[j+1] = temp;
swapped = true;
printf(" => swapped [%d, %d]\n",list[j],list[j+1]);
} else {
printf(" => not swapped\n");
}
}
// if no number was swapped that means
// array is sorted now, break the loop.
if(!swapped) {
break;
}
printf("Iteration %d#: ",(i+1));
display();
}
}
int main() {
printf("Input Array: ");
display();
printf("\n");
bubbleSort();
printf("\nOutput Array: ");
display();
}
輸出
Input Array: [1 8 4 6 0 3 5 2 7 9 ] Items compared: [ 1, 8 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 8, 4 ] => swapped [4, 8] Items compared: [ 8, 6 ] => swapped [6, 8] Items compared: [ 8, 0 ] => swapped [0, 8] Items compared: [ 8, 3 ] => swapped [3, 8] Items compared: [ 8, 5 ] => swapped [5, 8] Items compared: [ 8, 2 ] => swapped [2, 8] Items compared: [ 8, 7 ] => swapped [7, 8] Items compared: [ 8, 9 ] => not swapped Iteration 1#: [1 4 6 0 3 5 2 7 8 9 ] Items compared: [ 1, 4 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 4, 6 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 6, 0 ] => swapped [0, 6] Items compared: [ 6, 3 ] => swapped [3, 6] Items compared: [ 6, 5 ] => swapped [5, 6] Items compared: [ 6, 2 ] => swapped [2, 6] Items compared: [ 6, 7 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 7, 8 ] => not swapped Iteration 2#: [1 4 0 3 5 2 6 7 8 9 ] Items compared: [ 1, 4 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 4, 0 ] => swapped [0, 4] Items compared: [ 4, 3 ] => swapped [3, 4] Items compared: [ 4, 5 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 5, 2 ] => swapped [2, 5] Items compared: [ 5, 6 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 6, 7 ] => not swapped Iteration 3#: [1 0 3 4 2 5 6 7 8 9 ] Items compared: [ 1, 0 ] => swapped [0, 1] Items compared: [ 1, 3 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 3, 4 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 4, 2 ] => swapped [2, 4] Items compared: [ 4, 5 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 5, 6 ] => not swapped Iteration 4#: [0 1 3 2 4 5 6 7 8 9 ] Items compared: [ 0, 1 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 1, 3 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 3, 2 ] => swapped [2, 3] Items compared: [ 3, 4 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 4, 5 ] => not swapped Iteration 5#: [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ] Items compared: [ 0, 1 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 1, 2 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 2, 3 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 3, 4 ] => not swapped Output Array: [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ]
// C++ Code for Tower of Hanoi
#include <iostream>
#include <array>
#include <algorithm>
const int MAX = 10;
std::array<int, MAX> list = {1, 8, 4, 6, 0, 3, 5, 2, 7, 9};
void display() {
std::cout << "[";
// navigate through all items
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++) {
std::cout << list[i] << " ";
}
std::cout << "]\n";
}
void bubbleSort() {
int temp;
bool swapped = false;
// loop through all numbers
for (int i = 0; i < MAX - 1; i++) {
swapped = false;
// loop through numbers falling ahead
for (int j = 0; j < MAX - 1 - i; j++) {
std::cout << "Items compared: [" << list[j] << ", " << list[j+1] << "] ";
// check if next number is lesser than current no
// swap the numbers.
// (Bubble up the highest number)
if (list[j] > list[j+1]) {
std::swap(list[j], list[j+1]);
swapped = true;
std::cout << "=> swapped [" << list[j] << ", " << list[j+1] << "]\n";
} else {
std::cout << "=> not swapped\n";
}
}
// if no number was swapped that means
// array is sorted now, break the loop.
if (!swapped) {
break;
}
std::cout << "Iteration " << (i+1) << "#: ";
display();
}
}
int main() {
std::cout << "Input Array: ";
display();
std::cout << "\n";
bubbleSort();
std::cout << "\nOutput Array: ";
display();
return 0;
}
輸出
Input Array: [1 8 4 6 0 3 5 2 7 9 ] Items compared: [1, 8] => not swapped Items compared: [8, 4] => swapped [4, 8] Items compared: [8, 6] => swapped [6, 8] Items compared: [8, 0] => swapped [0, 8] Items compared: [8, 3] => swapped [3, 8] Items compared: [8, 5] => swapped [5, 8] Items compared: [8, 2] => swapped [2, 8] Items compared: [8, 7] => swapped [7, 8] Items compared: [8, 9] => not swapped Iteration 1#: [1 4 6 0 3 5 2 7 8 9 ] Items compared: [1, 4] => not swapped Items compared: [4, 6] => not swapped Items compared: [6, 0] => swapped [0, 6] Items compared: [6, 3] => swapped [3, 6] Items compared: [6, 5] => swapped [5, 6] Items compared: [6, 2] => swapped [2, 6] Items compared: [6, 7] => not swapped Items compared: [7, 8] => not swapped Iteration 2#: [1 4 0 3 5 2 6 7 8 9 ] Items compared: [1, 4] => not swapped Items compared: [4, 0] => swapped [0, 4] Items compared: [4, 3] => swapped [3, 4] Items compared: [4, 5] => not swapped Items compared: [5, 2] => swapped [2, 5] Items compared: [5, 6] => not swapped Items compared: [6, 7] => not swapped Iteration 3#: [1 0 3 4 2 5 6 7 8 9 ] Items compared: [1, 0] => swapped [0, 1] Items compared: [1, 3] => not swapped Items compared: [3, 4] => not swapped Items compared: [4, 2] => swapped [2, 4] Items compared: [4, 5] => not swapped Items compared: [5, 6] => not swapped Iteration 4#: [0 1 3 2 4 5 6 7 8 9 ] Items compared: [0, 1] => not swapped Items compared: [1, 3] => not swapped Items compared: [3, 2] => swapped [2, 3] Items compared: [3, 4] => not swapped Items compared: [4, 5] => not swapped Iteration 5#: [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ] Items compared: [0, 1] => not swapped Items compared: [1, 2] => not swapped Items compared: [2, 3] => not swapped Items compared: [3, 4] => not swapped Output Array: [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ]
//Java Code for Tower of Hanoi
import java.util.Arrays;
public class BubbleSort {
public static final int MAX = 10;
public static int[] list = {1, 8, 4, 6, 0, 3, 5, 2, 7, 9};
public static void display() {
System.out.print("[");
// navigate through all items
for (int i = 0; i < MAX; i++) {
System.out.print(list[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println("]");
}
public static void bubbleSort() {
boolean swapped;
// loop through all numbers
for (int i = 0; i < MAX - 1; i++) {
swapped = false;
// loop through numbers falling ahead
for (int j = 0; j < MAX - 1 - i; j++) {
System.out.print("Items compared: [" + list[j] + ", " + list[j + 1] + "] ");
// check if next number is lesser than current no
// swap the numbers.
// (Bubble up the highest number)
if (list[j] > list[j + 1]) {
int temp = list[j];
list[j] = list[j + 1];
list[j + 1] = temp;
swapped = true;
System.out.println("=> swapped [" + list[j] + ", " + list[j + 1] + "]");
} else {
System.out.println("=> not swapped");
}
}
// if no number was swapped that means
// array is sorted now, break the loop.
if (!swapped) {
break;
}
System.out.print("Iteration " + (i + 1) + "#: ");
display();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.print("Input Array: ");
display();
System.out.println();
bubbleSort();
System.out.print("\nOutput Array: ");
display();
}
}
輸出
Input Array: [1 8 4 6 0 3 5 2 7 9 ] Items compared: [1, 8] => not swapped Items compared: [8, 4] => swapped [4, 8] Items compared: [8, 6] => swapped [6, 8] Items compared: [8, 0] => swapped [0, 8] Items compared: [8, 3] => swapped [3, 8] Items compared: [8, 5] => swapped [5, 8] Items compared: [8, 2] => swapped [2, 8] Items compared: [8, 7] => swapped [7, 8] Items compared: [8, 9] => not swapped Iteration 1#: [1 4 6 0 3 5 2 7 8 9 ] Items compared: [1, 4] => not swapped Items compared: [4, 6] => not swapped Items compared: [6, 0] => swapped [0, 6] Items compared: [6, 3] => swapped [3, 6] Items compared: [6, 5] => swapped [5, 6] Items compared: [6, 2] => swapped [2, 6] Items compared: [6, 7] => not swapped Items compared: [7, 8] => not swapped Iteration 2#: [1 4 0 3 5 2 6 7 8 9 ] Items compared: [1, 4] => not swapped Items compared: [4, 0] => swapped [0, 4] Items compared: [4, 3] => swapped [3, 4] Items compared: [4, 5] => not swapped Items compared: [5, 2] => swapped [2, 5] Items compared: [5, 6] => not swapped Items compared: [6, 7] => not swapped Iteration 3#: [1 0 3 4 2 5 6 7 8 9 ] Items compared: [1, 0] => swapped [0, 1] Items compared: [1, 3] => not swapped Items compared: [3, 4] => not swapped Items compared: [4, 2] => swapped [2, 4] Items compared: [4, 5] => not swapped Items compared: [5, 6] => not swapped Iteration 4#: [0 1 3 2 4 5 6 7 8 9 ] Items compared: [0, 1] => not swapped Items compared: [1, 3] => not swapped Items compared: [3, 2] => swapped [2, 3] Items compared: [3, 4] => not swapped Items compared: [4, 5] => not swapped Iteration 5#: [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ] Items compared: [0, 1] => not swapped Items compared: [1, 2] => not swapped Items compared: [2, 3] => not swapped Items compared: [3, 4] => not swapped Output Array: [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ]
#Python Code for Tower of Hanoi
MAX = 10
list = [1, 8, 4, 6, 0, 3, 5, 2, 7, 9]
def display():
print("[", end="")
# navigate through all items
for i in range(MAX):
print(list[i], end=" ")
print("]")
def bubbleSort():
swapped = False
# loop through all numbers
for i in range(MAX - 1):
swapped = False
# loop through numbers falling ahead
for j in range(MAX - 1 - i):
print("Items compared: [",
list[j],
", ",
list[j + 1],
"] ",
end="")
# check if next number is lesser than the current number
# swap the numbers.
# (Bubble up the highest number)
if list[j] > list[j + 1]:
temp = list[j]
list[j] = list[j + 1]
list[j + 1] = temp
swapped = True
print("=> swapped [", list[j], ", ", list[j + 1], "]")
else:
print("=> not swapped")
# if no number was swapped, the array is sorted now, break the loop
if not swapped:
break
print("Iteration", (i + 1), "#: ", end="")
display()
print("Input Array: ", end="")
display()
print()
bubbleSort()
print("\nOutput Array: ", end="")
display()
輸出
Input Array: [1 8 4 6 0 3 5 2 7 9 ] Items compared: [ 1 , 8 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 8 , 4 ] => swapped [ 4 , 8 ] Items compared: [ 8 , 6 ] => swapped [ 6 , 8 ] Items compared: [ 8 , 0 ] => swapped [ 0 , 8 ] Items compared: [ 8 , 3 ] => swapped [ 3 , 8 ] Items compared: [ 8 , 5 ] => swapped [ 5 , 8 ] Items compared: [ 8 , 2 ] => swapped [ 2 , 8 ] Items compared: [ 8 , 7 ] => swapped [ 7 , 8 ] Items compared: [ 8 , 9 ] => not swapped Iteration 1 #: [1 4 6 0 3 5 2 7 8 9 ] Items compared: [ 1 , 4 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 4 , 6 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 6 , 0 ] => swapped [ 0 , 6 ] Items compared: [ 6 , 3 ] => swapped [ 3 , 6 ] Items compared: [ 6 , 5 ] => swapped [ 5 , 6 ] Items compared: [ 6 , 2 ] => swapped [ 2 , 6 ] Items compared: [ 6 , 7 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 7 , 8 ] => not swapped Iteration 2 #: [1 4 0 3 5 2 6 7 8 9 ] Items compared: [ 1 , 4 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 4 , 0 ] => swapped [ 0 , 4 ] Items compared: [ 4 , 3 ] => swapped [ 3 , 4 ] Items compared: [ 4 , 5 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 5 , 2 ] => swapped [ 2 , 5 ] Items compared: [ 5 , 6 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 6 , 7 ] => not swapped Iteration 3 #: [1 0 3 4 2 5 6 7 8 9 ] Items compared: [ 1 , 0 ] => swapped [ 0 , 1 ] Items compared: [ 1 , 3 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 3 , 4 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 4 , 2 ] => swapped [ 2 , 4 ] Items compared: [ 4 , 5 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 5 , 6 ] => not swapped Iteration 4 #: [0 1 3 2 4 5 6 7 8 9 ] Items compared: [ 0 , 1 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 1 , 3 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 3 , 2 ] => swapped [ 2 , 3 ] Items compared: [ 3 , 4 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 4 , 5 ] => not swapped Iteration 5 #: [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ] Items compared: [ 0 , 1 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 1 , 2 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 2 , 3 ] => not swapped Items compared: [ 3 , 4 ] => not swapped Output Array: [0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ]
使用遞迴的斐波那契數列
斐波那契數列透過將前兩個數字相加來生成後續數字。斐波那契數列從兩個數字開始 − F0 & F1。F0 & F1 的初始值可以分別取 0、1 或 1、1。
斐波那契數列滿足以下條件:
Fn = Fn-1 + Fn-2
因此,斐波那契數列可能如下所示:
F8 = 0 1 1 2 3 5 8 13
或者,這樣:
F8 = 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21
為了說明目的,F8 的斐波那契數列顯示為:

斐波那契迭代演算法
首先,我們嘗試為斐波那契數列起草迭代演算法。
Procedure Fibonacci(n)
declare f0, f1, fib, loop
set f0 to 0
set f1 to 1
<b>display f0, f1</b>
for loop ← 1 to n
fib ← f0 + f1
f0 ← f1
f1 ← fib
<b>display fib</b>
end for
end procedure
斐波那契遞迴演算法
讓我們學習如何建立斐波那契數列的遞迴演算法。遞迴的基本條件。
START
Procedure Fibonacci(n)
declare f0, f1, fib, loop
set f0 to 0
set f1 to 1
display f0, f1
for loop ← 1 to n
fib ← f0 + f1
f0 ← f1
f1 ← fib
display fib
end for
END
示例
#include <stdio.h>
int factorial(int n) {
//base case
if(n == 0) {
return 1;
} else {
return n * factorial(n-1);
}
}
int fibbonacci(int n) {
if(n == 0){
return 0;
} else if(n == 1) {
return 1;
} else {
return (fibbonacci(n-1) + fibbonacci(n-2));
}
}
int main() {
int n = 5;
int i;
printf("Factorial of %d: %d\n" , n , factorial(n));
printf("Fibbonacci of %d: " , n);
for(i = 0;i<n;i++) {
printf("%d ",fibbonacci(i));
}
}
輸出
Factorial of 5: 120 Fibbonacci of 5: 0 1 1 2 3
// C++ Code for Fibonacci series
#include <iostream>
int factorial(int n) {
//base case
if(n == 0) {
return 1;
} else {
return n * factorial(n-1);
}
}
int fibbonacci(int n) {
if(n == 0){
return 0;
} else if(n == 1) {
return 1;
} else {
return (fibbonacci(n-1) + fibbonacci(n-2));
}
}
int main() {
int n = 5;
int i;
std::cout << "Factorial of " << n << ": " << factorial(n) << std::endl;
std::cout << "Fibbonacci of " << n << ": ";
for(i = 0;i<n;i++) {
std::cout << fibbonacci(i) << " ";
}
}
輸出
Factorial of 5: 120 Fibbonacci of 5: 0 1 1 2 3
// Java Code for Fibonacci series
public class Fibonacci {
public static int factorial(int n) {
// base case
if (n == 0) {
return 1;
} else {
return n * factorial(n - 1);
}
}
public static int fibonacci(int n) {
if (n == 0) {
return 0;
} else if (n == 1) {
return 1;
} else {
return fibonacci(n - 1) + fibonacci(n - 2);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 5;
int i;
System.out.println("Factorial of " + n + ": " + factorial(n));
System.out.print("Fibonacci of " + n + ": ");
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
System.out.print(fibonacci(i) + " ");
}
}
輸出
Factorial of 5: 120 Fibonacci of 5: 0 1 1 2 3
#Python code for fibonacci Series
def factorial(n):
# base case
if n == 0:
return 1
else:
return n * factorial(n-1)
def fibonacci(n):
if n == 0:
return 0
elif n == 1:
return 1
else:
return fibonacci(n-1) + fibonacci(n-2)
if __name__ == "__main__":
n = 5
print("Factorial of", n, ":", factorial(n))
print("Fibonacci of", n, ": ")
for i in range(n):
print(fibonacci(i))
輸出
Factorial of 5 : 120 Fibonacci of 5 : 0 1 1 2 3