
- 資料結構與演算法
- DSA - 首頁
- DSA - 概述
- DSA - 環境搭建
- DSA - 演算法基礎
- DSA - 漸近分析
- 資料結構
- DSA - 資料結構基礎
- DSA - 資料結構和型別
- DSA - 陣列資料結構
- 連結串列
- DSA - 連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 雙向連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 迴圈連結串列資料結構
- 棧與佇列
- DSA - 棧資料結構
- DSA - 表示式解析
- DSA - 佇列資料結構
- 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 線性搜尋演算法
- DSA - 二分搜尋演算法
- DSA - 插值搜尋
- DSA - 跳躍搜尋演算法
- DSA - 指數搜尋
- DSA - 斐波那契搜尋
- DSA - 子列表搜尋
- DSA - 雜湊表
- 排序演算法
- DSA - 排序演算法
- DSA - 氣泡排序演算法
- DSA - 插入排序演算法
- DSA - 選擇排序演算法
- DSA - 歸併排序演算法
- DSA - 希爾排序演算法
- DSA - 堆排序
- DSA - 桶排序演算法
- DSA - 計數排序演算法
- DSA - 基數排序演算法
- DSA - 快速排序演算法
- 圖資料結構
- DSA - 圖資料結構
- DSA - 深度優先遍歷
- DSA - 廣度優先遍歷
- DSA - 生成樹
- 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹的遍歷
- DSA - 二叉搜尋樹
- DSA - AVL樹
- DSA - 紅黑樹
- DSA - B樹
- DSA - B+樹
- DSA - 伸展樹
- DSA - Trie樹
- DSA - 堆資料結構
- 遞迴
- DSA - 遞迴演算法
- DSA - 使用遞迴的漢諾塔
- DSA - 使用遞迴的斐波那契數列
- 分治法
- DSA - 分治法
- DSA - 最大最小問題
- DSA - Strassen矩陣乘法
- DSA - Karatsuba演算法
- 貪心演算法
- DSA - 貪心演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(貪心法)
- DSA - Prim最小生成樹
- DSA - Kruskal最小生成樹
- DSA - Dijkstra最短路徑演算法
- DSA - 地圖著色演算法
- DSA - 分數揹包問題
- DSA - 帶截止日期的作業排序
- DSA - 最優合併模式演算法
- 動態規劃
- DSA - 動態規劃
- DSA - 矩陣鏈乘法
- DSA - Floyd-Warshall演算法
- DSA - 0-1揹包問題
- DSA - 最長公共子序列演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(動態規劃法)
- 近似演算法
- DSA - 近似演算法
- DSA - 頂點覆蓋演算法
- DSA - 集合覆蓋問題
- DSA - 旅行商問題(近似演算法)
- 隨機演算法
- DSA - 隨機演算法
- DSA - 隨機快速排序演算法
- DSA - Karger最小割演算法
- DSA - Fisher-Yates洗牌演算法
- DSA有用資源
- DSA - 問答
- DSA - 快速指南
- DSA - 有用資源
- DSA - 討論
迴圈連結串列資料結構
什麼是迴圈連結串列?
迴圈連結串列是連結串列的一種變體,其中第一個元素指向最後一個元素,最後一個元素指向第一個元素。單鏈表和雙鏈表都可以轉換為迴圈連結串列。
單鏈表作為迴圈連結串列
在單鏈表中,最後一個節點的next指標指向第一個節點。

雙鏈表作為迴圈連結串列
在雙鏈表中,最後一個節點的next指標指向第一個節點,第一個節點的prev指標指向最後一個節點,從而構成雙向迴圈。
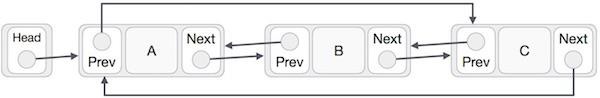
根據以上說明,需要考慮以下幾點:
在單鏈表和雙鏈表的情況下,最後一個連結的next指標都指向列表的第一個連結。
在雙鏈表的情況下,第一個連結的prev指標指向列表的最後一個連結。
迴圈連結串列的基本操作
以下是迴圈連結串列支援的重要操作:
插入 - 在列表的開頭插入一個元素。
刪除 - 從列表的開頭刪除一個元素。
顯示 - 顯示列表。
迴圈連結串列 - 插入操作
迴圈連結串列的插入操作只在列表的開頭插入元素。這與普通的單鏈表和雙鏈表不同,因為此列表沒有特定的起點和終點。插入操作可以在開頭進行,也可以在特定節點(或給定位置)之後進行。
演算法
1. START 2. Check if the list is empty 3. If the list is empty, add the node and point the head to this node 4. If the list is not empty, link the existing head as the next node to the new node. 5. Make the new node as the new head. 6. END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
bool isEmpty(){
return head == NULL;
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if (isEmpty()) {
head = link;
head->next = head;
} else {
//point it to old first node
link->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
}
//display the list
void printList(){
struct node *ptr = head;
printf("\n[ ");
//start from the beginning
if(head != NULL) {
while(ptr->next != ptr) {
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
printf(" ]");
}
void main(){
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertFirst(5,40);
insertFirst(6,56);
printf("Circular Linked List: ");
//print list
printList();
}
輸出
Circular Linked List: [ (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) ]
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdbool>
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
bool isEmpty(){
return head == NULL;
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if (isEmpty()) {
head = link;
head->next = head;
} else {
//point it to old first node
link->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
}
//display the list
void printList(){
struct node *ptr = head;
printf("\n[ ");
//start from the beginning
if(head != NULL) {
while(ptr->next != ptr) {
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
printf(" ]");
}
int main(){
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertFirst(5,40);
insertFirst(6,56);
printf("Circular Linked List: ");
//print list
printList();
return 0;
}
輸出
Circular Linked List: [ (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) ]
//Java program for circular link list
import java.util.*;
class Node {
int data;
int key;
Node next;
}
public class Main {
static Node head = null;
static Node current = null;
static boolean isEmpty() {
return head == null;
}
//insert link at the first location
static void insertFirst(int key, int data) {
//create a link
Node link = new Node();
link.key = key;
link.data = data;
if (isEmpty()) {
head = link;
head.next = head;
} else {
//point it to old first node
link.next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
}
//display the list
static void printList() {
Node ptr = head;
System.out.print("\n[ ");
//start from the beginning
if (head != null) {
while (ptr.next != ptr) {
System.out.print("(" + ptr.key + "," + ptr.data + ") ");
ptr = ptr.next;
}
}
System.out.print(" ]");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
insertFirst(1, 10);
insertFirst(2, 20);
insertFirst(3, 30);
insertFirst(4, 1);
insertFirst(5, 40);
insertFirst(6, 56);
System.out.print("Circular Linked List: ");
//print list
printList();
}
}
輸出
Circular Linked List: [ (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) ]
#python program for circular linked list
class Node:
def __init__(self, key, data):
self.key = key
self.data = data
self.next = None
head = None
current = None
def is_empty():
return head is None
#insert link at the first location
def insert_first(key, data):
#create a link
global head
new_node = Node(key, data)
if is_empty():
head = new_node
head.next = head
else:
#point it to old first node
new_node.next = head
#point first to the new first node
head = new_node
#display the list
def print_list():
global head
ptr = head
print("[", end=" ")
#start from the beginning
if head is not None:
while ptr.next != ptr:
print("({}, {})".format(ptr.key, ptr.data), end=" ")
ptr = ptr.next
print("]")
insert_first(1, 10)
insert_first(2, 20)
insert_first(3, 30)
insert_first(4, 1)
insert_first(5, 40)
insert_first(6, 56)
#printlist
print("Circular Linked List: ")
print_list()
輸出
Circular Linked List: [ (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) ]
迴圈連結串列 - 刪除操作
迴圈連結串列的刪除操作是從列表中刪除某個節點。此類列表中的刪除操作可以在開頭、給定位置或結尾進行。
演算法
1. START 2. If the list is empty, then the program is returned. 3. If the list is not empty, we traverse the list using a current pointer that is set to the head pointer and create another pointer previous that points to the last node. 4. Suppose the list has only one node, the node is deleted by setting the head pointer to NULL. 5. If the list has more than one node and the first node is to be deleted, the head is set to the next node and the previous is linked to the new head. 6. If the node to be deleted is the last node, link the preceding node of the last node to head node. 7. If the node is neither first nor last, remove the node by linking its preceding node to its succeeding node. 8. END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
bool isEmpty(){
return head == NULL;
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if (isEmpty()) {
head = link;
head->next = head;
} else {
//point it to old first node
link->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
}
//delete first item
struct node * deleteFirst(){
//save reference to first link
struct node *tempLink = head;
if(head->next == head) {
head = NULL;
return tempLink;
}
//mark next to first link as first
head = head->next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
//display the list
void printList(){
struct node *ptr = head;
//start from the beginning
if(head != NULL) {
while(ptr->next != ptr) {
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
}
void main(){
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertFirst(5,40);
insertFirst(6,56);
printf("Circular Linked List: ");
//print list
printList();
deleteFirst();
printf("\nList after deleting the first item: ");
printList();
}
輸出
Circular Linked List: (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) List after deleting the first item: (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdbool>
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
bool isEmpty(){
return head == NULL;
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if (isEmpty()) {
head = link;
head->next = head;
} else {
//point it to old first node
link->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
}
//delete first item
struct node * deleteFirst(){
//save reference to first link
struct node *tempLink = head;
if(head->next == head) {
head = NULL;
return tempLink;
}
//mark next to first link as first
head = head->next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
//display the list
void printList(){
struct node *ptr = head;
//start from the beginning
if(head != NULL) {
while(ptr->next != ptr) {
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
}
int main(){
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertFirst(5,40);
insertFirst(6,56);
printf("Circular Linked List: ");
//print list
printList();
deleteFirst();
printf("\nList after deleting the first item: ");
printList();
return 0;
}
輸出
Circular Linked List: (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) List after deleting the first item: (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20)
//Java program for circular linked list
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static class Node {
int data;
int key;
Node next;
}
static Node head = null;
static Node current = null;
static boolean isEmpty() {
return head == null;
}
//insert link at the first location
static void insertFirst(int key, int data) {
//create a link
Node link = new Node();
link.key = key;
link.data = data;
if (isEmpty()) {
head = link;
head.next = head;
} else {
//point it to old first node
link.next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
}
//delete first item
static Node deleteFirst() {
//save reference to first link
Node tempLink = head;
if (head.next == head) {
head = null;
return tempLink;
}
//mark next to first link as first
head = head.next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
//display the list
static void printList() {
Node ptr = head;
//start from the beginning
if (head != null) {
while (ptr.next != ptr) {
System.out.printf("(%d,%d) ", ptr.key, ptr.data);
ptr = ptr.next;
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
insertFirst(1, 10);
insertFirst(2, 20);
insertFirst(3, 30);
insertFirst(4, 1);
insertFirst(5, 40);
insertFirst(6, 56);
System.out.print("Circular Linked List: ");
//print list
printList();
deleteFirst();
System.out.print("\nList after deleting the first item: ");
printList();
}
}
輸出
Circular Linked List: (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) List after deleting the first item: (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20)
#python program for circular linked list
class Node:
def __init__(self, key, data):
self.key = key
self.data = data
self.next = None
head = None
current = None
def is_empty():
return head is None
#insert link at the first location
def insert_first(key, data):
#create a link
global head
new_node = Node(key, data)
if is_empty():
head = new_node
head.next = head
else:
#point it to old first node
new_node.next = head
#point first to the new first node
head = new_node
def print_list():
global head
ptr = head
print("[", end=" ")
#start from the beginning
if head is not None:
while ptr.next != ptr:
print("({}, {})".format(ptr.key, ptr.data), end=" ")
ptr = ptr.next
print("]")
def delete_first():
global head
temp_link = head
if head.next == head:
head = None
return temp_link
head = head.next
return temp_link
insert_first(1, 10)
insert_first(2, 20)
insert_first(3, 30)
insert_first(4, 1)
insert_first(5, 40)
insert_first(6, 56)
#printlist
print("Circular Linked List: ")
print_list()
delete_first()
print("\nList after deleting the first item: ")
print_list();
輸出
Circular Linked List: [ (6, 56) (5, 40) (4, 1) (3, 30) (2, 20) ] List after deleting the first item: [ (5, 40) (4, 1) (3, 30) (2, 20) ]
迴圈連結串列 - 顯示列表
顯示列表操作訪問列表中的每個節點,並將它們全部列印到輸出中。
演算法
1. START 2. Walk through all the nodes of the list and print them 3. END
示例
以下是此操作在各種程式語言中的實現:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
bool isEmpty(){
return head == NULL;
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if (isEmpty()) {
head = link;
head->next = head;
} else {
//point it to old first node
link->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
}
//display the list
void printList(){
struct node *ptr = head;
printf("\n[ ");
//start from the beginning
if(head != NULL) {
while(ptr->next != ptr) {
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
printf(" ]");
}
void main(){
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertFirst(5,40);
insertFirst(6,56);
printf("Circular Linked List: ");
//print list
printList();
}
輸出
Circular Linked List: [ (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) ]
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdbool>
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
bool isEmpty(){
return head == NULL;
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if (isEmpty()) {
head = link;
head->next = head;
} else {
//point it to old first node
link->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
}
//display the list
void printList(){
struct node *ptr = head;
printf("\n[ ");
//start from the beginning
if(head != NULL) {
while(ptr->next != ptr) {
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
printf(" ]");
}
int main(){
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertFirst(5,40);
insertFirst(6,56);
printf("Circular Linked List: ");
//print list
printList();
return 0;
}
輸出
Circular Linked List: [ (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) ]
//Java program for circular link list
import java.util.*;
class Node {
int data;
int key;
Node next;
}
public class Main {
static Node head = null;
static Node current = null;
static boolean isEmpty() {
return head == null;
}
//insert link at the first location
static void insertFirst(int key, int data) {
//create a link
Node link = new Node();
link.key = key;
link.data = data;
if (isEmpty()) {
head = link;
head.next = head;
} else {
//point it to old first node
link.next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
}
//display the list
static void printList() {
Node ptr = head;
System.out.print("\n[ ");
//start from the beginning
if (head != null) {
while (ptr.next != ptr) {
System.out.print("(" + ptr.key + "," + ptr.data + ") ");
ptr = ptr.next;
}
}
System.out.print(" ]");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
insertFirst(1, 10);
insertFirst(2, 20);
insertFirst(3, 30);
insertFirst(4, 1);
insertFirst(5, 40);
insertFirst(6, 56);
System.out.print("Circular Linked List: ");
//print list
printList();
}
}
輸出
Circular Linked List: [ (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) ]
#python program for circular linked list
class Node:
def __init__(self, key, data):
self.key = key
self.data = data
self.next = None
head = None
current = None
def is_empty():
return head is None
#insert link at the first location
def insert_first(key, data):
#create a link
global head
new_node = Node(key, data)
if is_empty():
head = new_node
head.next = head
else:
#point it to old first node
new_node.next = head
#point first to the new first node
head = new_node
#display the list
def print_list():
global head
ptr = head
print("[", end=" ")
#start from the beginning
if head is not None:
while ptr.next != ptr:
print("({}, {})".format(ptr.key, ptr.data), end=" ")
ptr = ptr.next
print("]")
insert_first(1, 10)
insert_first(2, 20)
insert_first(3, 30)
insert_first(4, 1)
insert_first(5, 40)
insert_first(6, 56)
#printlist
print("Circular Linked List: ")
print_list()
輸出
Circular Linked List: [ (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) ]
迴圈連結串列 - 完整實現
以下是迴圈連結串列在各種程式語言中的完整實現:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
bool isEmpty(){
return head == NULL;
}
int length(){
int length = 0;
//if list is empty
if(head == NULL) {
return 0;
}
current = head->next;
while(current != head) {
length++;
current = current->next;
}
return length;
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if (isEmpty()) {
head = link;
head->next = head;
} else {
//point it to old first node
link->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
}
//delete first item
struct node * deleteFirst(){
//save reference to first link
struct node *tempLink = head;
if(head->next == head) {
head = NULL;
return tempLink;
}
//mark next to first link as first
head = head->next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
//display the list
void printList(){
struct node *ptr = head;
printf("\n[ ");
//start from the beginning
if(head != NULL) {
while(ptr->next != ptr) {
printf("(%d,%d) ",ptr->key,ptr->data);
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
printf(" ]");
}
int main(){
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertFirst(5,40);
insertFirst(6,56);
printf("Original List: ");
//print list
printList();
while(!isEmpty()) {
struct node *temp = deleteFirst();
printf("\nDeleted value:");
printf("(%d,%d) ",temp->key,temp->data);
}
printf("\nList after deleting all items: ");
printList();
}
輸出
Original List: [ (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) ] Deleted value:(6,56) Deleted value:(5,40) Deleted value:(4,1) Deleted value:(3,30) Deleted value:(2,20) Deleted value:(1,10) List after deleting all items: [ ]
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdbool>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
int key;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
bool isEmpty(){
return head == NULL;
}
int length(){
int length = 0;
//if list is empty
if(head == NULL) {
return 0;
}
current = head->next;
while(current != head) {
length++;
current = current->next;
}
return length;
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data){
//create a link
struct node *link = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
link->key = key;
link->data = data;
if (isEmpty()) {
head = link;
head->next = head;
} else {
//point it to old first node
link->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
}
//delete first item
struct node * deleteFirst(){
//save reference to first link
struct node *tempLink = head;
if(head->next == head) {
head = NULL;
return tempLink;
}
//mark next to first link as first
head = head->next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
//display the list
void printList(){
struct node *ptr = head;
cout << "\n[ ";
//start from the beginning
if(head != NULL) {
while(ptr->next != ptr) {
cout << "(" << ptr->key << "," << ptr->data << ") ";
ptr = ptr->next;
}
}
cout << " ]";
}
int main(){
insertFirst(1,10);
insertFirst(2,20);
insertFirst(3,30);
insertFirst(4,1);
insertFirst(5,40);
insertFirst(6,56);
cout << "Original List: ";
//print list
printList();
while(!isEmpty()) {
struct node *temp = deleteFirst();
cout << "\n Deleted value:";
cout << "(" << temp->key << "," << temp->data << ") ";
}
cout << "\n List after deleting all items: ";
printList();
return 0;
}
輸出
Original List: [ (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) ] Deleted value:(6,56) Deleted value:(5,40) Deleted value:(4,1) Deleted value:(3,30) Deleted value:(2,20) Deleted value:(1,10) List after deleting all items: [ ]
class Node {
int data;
int key;
Node next;
Node(int key, int data) {
this.key = key;
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
public class LinkedList {
private Node head;
private Node current;
boolean isEmpty() {
return head == null;
}
int length() {
int length = 0;
//if list is empty
if (head == null) {
return 0;
}
current = head.next;
while (current != head) {
length++;
current = current.next;
}
return length;
}
//insert link at the first location
void insertFirst(int key, int data) {
//create a link
Node link = new Node(key, data);
if (isEmpty()) {
head = link;
head.next = head;
} else {
//point it to old first node
link.next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = link;
}
}
//delete first item
Node deleteFirst() {
if (head.next == head) {
//save reference to first link
Node tempLink = head;
head = null;
return tempLink;
}
Node tempLink = head;
//mark next to first link as first
head = head.next;
//return the deleted link
return tempLink;
}
//display the list
void printList() {
Node ptr = head;
System.out.print("\n[ ");
//start from the beginning
if (head != null) {
while (ptr.next != ptr) {
System.out.print("(" + ptr.key + "," + ptr.data + ") ");
ptr = ptr.next;
}
}
System.out.print(" ]");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedList linkedList = new LinkedList();
linkedList.insertFirst(1, 10);
linkedList.insertFirst(2, 20);
linkedList.insertFirst(3, 30);
linkedList.insertFirst(4, 1);
linkedList.insertFirst(5, 40);
linkedList.insertFirst(6, 56);
System.out.print("Original List: ");
linkedList.printList();
//print list
while (!linkedList.isEmpty()) {
Node temp = linkedList.deleteFirst();
System.out.println("\nDeleted value: (" + temp.key + "," + temp.data + ")");
}
System.out.print("\nList after deleting all items: ");
linkedList.printList();
}
}
輸出
Original List: [ (6,56) (5,40) (4,1) (3,30) (2,20) ] Deleted value: (6,56) Deleted value: (5,40) Deleted value: (4,1) Deleted value: (3,30) Deleted value: (2,20) Deleted value: (1,10) List after deleting all items: [ ]
class Node:
def __init__(self, key, data):
self.key = key
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
self.current = None
def is_empty(self):
return self.head is None
def length(self):
length = 0
# If list is empty
if self.head is None:
return 0
self.current = self.head.next
while self.current != self.head:
length += 1
self.current = self.current.next
return length
# insert link at the first location
def insert_first(self, key, data):
# create a link
new_node = Node(key, data)
if self.is_empty():
self.head = new_node
self.head.next = self.head
else:
# point it to old first node
new_node.next = self.head
# point first to new first node
self.head = new_node
# delete first item
def delete_first(self):
# save reference to first link
if self.head.next == self.head:
temp_link = self.head
self.head = None
return temp_link
# mark next to first link as first
temp_link = self.head
self.head = self.head.next
# return the deleted link
return temp_link
# Diplay the list
def print_list(self):
ptr = self.head
print("[", end=" ")
# start from the beginning
if self.head is not None:
while ptr.next != ptr:
print("({}, {})".format(ptr.key, ptr.data), end=" ")
ptr = ptr.next
print("]")
# Main function
if __name__ == '__main__':
linked_list = LinkedList()
linked_list.insert_first(1, 10)
linked_list.insert_first(2, 20)
linked_list.insert_first(3, 30)
linked_list.insert_first(4, 1)
linked_list.insert_first(5, 40)
linked_list.insert_first(6, 56)
print("Original List: ", end="")
linked_list.print_list()
while not linked_list.is_empty():
temp = linked_list.delete_first()
print("\nDeleted value: ({}, {})".format(temp.key, temp.data))
# print list
print("List after deleting all items: ", end="")
linked_list.print_list()
輸出
Original List: [ (6, 56) (5, 40) (4, 1) (3, 30) (2, 20) ] Deleted value: (6, 56) Deleted value: (5, 40) Deleted value: (4, 1) Deleted value: (3, 30) Deleted value: (2, 20)Deleted value: (1, 10) List after deleting all items: [ ]
廣告