
- 資料結構與演算法
- DSA - 首頁
- DSA - 概述
- DSA - 環境設定
- DSA - 演算法基礎
- DSA - 漸進分析
- 資料結構
- DSA - 資料結構基礎
- DSA - 資料結構和型別
- DSA - 陣列資料結構
- 連結串列
- DSA - 連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 雙向連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 迴圈連結串列資料結構
- 棧與佇列
- DSA - 棧資料結構
- DSA - 表示式解析
- DSA - 佇列資料結構
- 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 線性搜尋演算法
- DSA - 二分搜尋演算法
- DSA - 插值搜尋
- DSA - 跳躍搜尋演算法
- DSA - 指數搜尋
- DSA - 斐波那契搜尋
- DSA - 子列表搜尋
- DSA - 雜湊表
- 排序演算法
- DSA - 排序演算法
- DSA - 氣泡排序演算法
- DSA - 插入排序演算法
- DSA - 選擇排序演算法
- DSA - 歸併排序演算法
- DSA - 希爾排序演算法
- DSA - 堆排序
- DSA - 桶排序演算法
- DSA - 計數排序演算法
- DSA - 基數排序演算法
- DSA - 快速排序演算法
- 圖資料結構
- DSA - 圖資料結構
- DSA - 深度優先遍歷
- DSA - 廣度優先遍歷
- DSA - 生成樹
- 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹的遍歷
- DSA - 二叉搜尋樹
- DSA - AVL樹
- DSA - 紅黑樹
- DSA - B樹
- DSA - B+樹
- DSA - 伸展樹
- DSA - 字典樹
- DSA - 堆資料結構
- 遞迴
- DSA - 遞迴演算法
- DSA - 使用遞迴的漢諾塔問題
- DSA - 使用遞迴的斐波那契數列
- 分治法
- DSA - 分治法
- DSA - 最大-最小問題
- DSA - Strassen矩陣乘法
- DSA - Karatsuba演算法
- 貪心演算法
- DSA - 貪心演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(貪心演算法)
- DSA - Prim最小生成樹
- DSA - Kruskal最小生成樹
- DSA - Dijkstra最短路徑演算法
- DSA - 地圖著色演算法
- DSA - 分數揹包問題
- DSA - 帶截止日期的作業排序
- DSA - 最佳合併模式演算法
- 動態規劃
- DSA - 動態規劃
- DSA - 矩陣鏈乘法
- DSA - Floyd-Warshall演算法
- DSA - 0-1揹包問題
- DSA - 最長公共子序列演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(動態規劃)
- 近似演算法
- DSA - 近似演算法
- DSA - 頂點覆蓋演算法
- DSA - 集合覆蓋問題
- DSA - 旅行商問題(近似演算法)
- 隨機演算法
- DSA - 隨機演算法
- DSA - 隨機快速排序演算法
- DSA - Karger最小割演算法
- DSA - Fisher-Yates洗牌演算法
- DSA有用資源
- DSA - 問答
- DSA - 快速指南
- DSA - 有用資源
- DSA - 討論
子列表搜尋演算法
到目前為止,在本教程中,我們只看到瞭如何在元素的順序序列中搜索一個元素。但是子列表搜尋演算法提供了一個在另一個連結串列中搜索連結串列的過程。它的工作原理與任何簡單的模式匹配演算法類似,其目的是確定一個列表是否存在於另一個列表中。
該演算法遍歷連結串列,其中一個列表的第一個元素與第二個列表的第一個元素進行比較;如果未找到匹配項,則第一個列表的第二個元素與第二個列表的第一個元素進行比較。此過程持續進行,直到找到匹配項或到達列表的末尾。
例如,考慮兩個值為 {4, 6, 7, 3, 8, 2, 6} 和 {3, 8, 2} 的連結串列。子列表搜尋檢查第二個列表的值是否出現在第一個連結串列中。輸出以布林值 {True, False} 獲得。它不能返回子列表的位置,因為連結串列不是有序的資料結構。
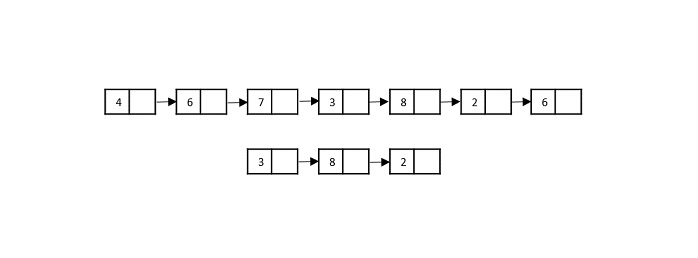
注意 - 只有當第二個連結串列以完全相同的順序出現在第一個列表中時,才會返回 true。
子列表搜尋演算法
該演算法的主要目的是證明一個連結串列是另一個列表的子列表。在此過程中,搜尋是線性進行的,逐個檢查連結串列的每個元素;如果輸出返回 true,則證明第二個列表是第一個連結串列的子列表。
子列表搜尋演算法的過程如下:
步驟 1 - 保持兩個指標,每個指標指向一個列表。這些指標用於遍歷連結串列。
步驟 2 - 檢查連結串列的基本情況:
如果兩個連結串列都為空,則輸出返回 true。
如果第二個列表不為空但第一個列表為空,則我們返回 false。
如果第一個列表不為空但第二個列表為空,則我們返回 false。
步驟 3 - 一旦確定兩個列表都不為空,就使用指標逐個元素遍歷列表。
步驟 4 - 比較第一個連結串列的第一個元素和第二個連結串列的第一個元素;如果匹配,則兩個指標分別指向兩個列表中的下一個值。
步驟 5 - 如果不匹配,則將第二個列表中的指標保持在第一個元素,但將第一個列表中的指標向前移動。再次比較元素。
步驟 6 - 重複步驟 4 和 5,直到到達列表的末尾。
步驟 7 - 如果找到輸出,則返回 TRUE;否則返回 FALSE。
虛擬碼
Begin Sublist Search
list_ptr -> points to the first list
sub_ptr -> points to the second list
ptr1 = list_ptr
ptr2 = sub_ptr
if list_ptr := NULL and sub_ptr := NULL then:
return TRUE
end
else if sub_ptr := NULL or sub_ptr != NULL and list_ptr := NULL then:
return FALSE
end
while list_ptr != NULL do:
ptr1 = list_ptr
while ptr2 != NULL do:
if ptr1 := NULL then:
return false
else if ptr2->data := ptr1->data then:
ptr2 = ptr2->next
ptr1 = ptr1->next
else break
done
if ptr2 := NULL
return TRUE
ptr2 := sub_ptr
list_ptr := list.ptr->next
done
return FALSE
end
分析
子列表搜尋的時間複雜度取決於所涉及的兩個連結串列中存在的元素數量。演算法執行的最壞情況時間為 O(m*n),其中 m 是第一個連結串列中存在的元素數量,n 是第二個連結串列中存在的元素數量。
示例
假設我們有兩個連結串列,其元素如下:
List 1 = {2, 5, 3, 3, 6, 7, 0}
List 2 = {6, 7, 0}
使用子列表搜尋,我們需要找出列表 2 是否存在於列表 1 中。
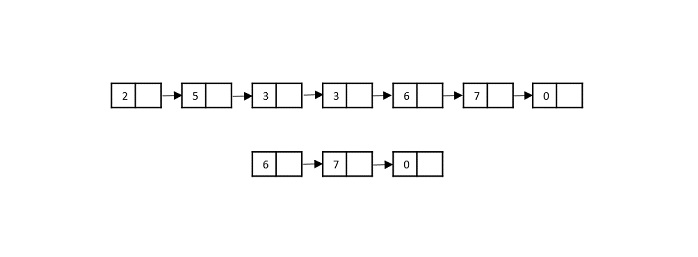
步驟 1
將列表 2 的第一個元素與列表 1 的第一個元素進行比較。它不匹配,因此列表 1 中的指標移動到它的下一個記憶體地址。

步驟 2
在此步驟中,將列表 1 的第二個元素與列表 2 的第一個元素進行比較。它不匹配,因此列表 1 中的指標移動到下一個記憶體地址。

步驟 3
現在,將列表 1 中的第三個元素與列表 2 中的第一個元素進行比較。由於它不匹配,因此列表 1 中的指標向前移動。
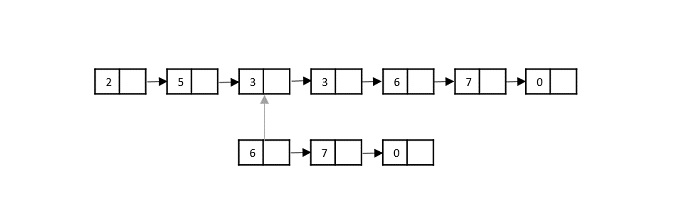
步驟 4
現在,將列表 1 中的第四個元素與列表 2 中的第一個元素進行比較。由於它不匹配,因此列表 1 中的指標向前移動。
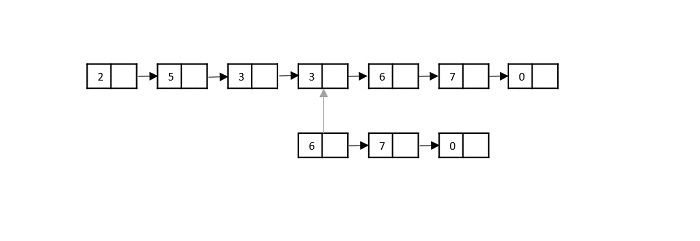
步驟 5
現在,將列表 1 中的第五個元素與列表 2 中的第一個元素進行比較。由於它匹配,因此列表 1 和列表 2 中的指標都向前移動。
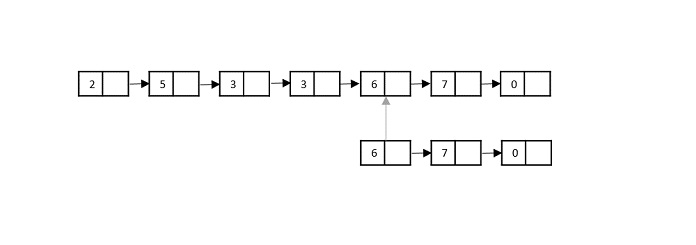
步驟 6
將列表 1 中的第六個元素與列表 2 中的第二個元素進行比較。由於它也匹配,因此列表 1 和列表 2 中的指標都向前移動。

步驟 7
將列表 1 中的第七個元素與列表 2 中的第三個元素進行比較。由於它也匹配,因此證明列表 2 是列表 1 的子列表。
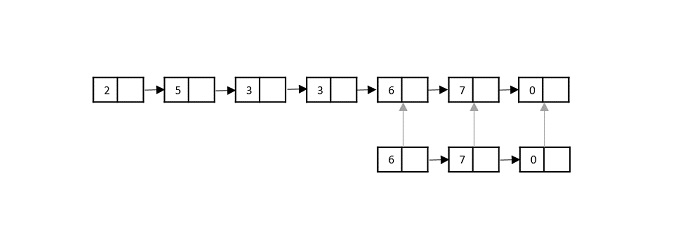
輸出返回 TRUE。
實現
在子列表搜尋實現中,首先使用 C 語言中的 struct 關鍵字以及 C++、JAVA 和 Python 語言中的物件建立連結串列。檢查這些連結串列是否為空;然後逐個線性比較元素以查詢匹配項。如果第二個連結串列以相同的順序出現在第一個連結串列中,則輸出返回 TRUE;否則輸出列印 FALSE。
在本教程中,子列表搜尋在四種不同的程式語言中執行 - C、C++、JAVA 和 Python。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
struct Node {
int data;
struct Node* next;
};
struct Node *newNode(int key){
struct Node *val = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));;
val-> data= key;
val->next = NULL;
return val;
}
bool sublist_search(struct Node* list_ptr, struct Node* sub_ptr){
struct Node* ptr1 = list_ptr, *ptr2 = sub_ptr;
if (list_ptr == NULL && sub_ptr == NULL)
return true;
if ( sub_ptr == NULL || (sub_ptr != NULL && list_ptr == NULL))
return false;
while (list_ptr != NULL) {
ptr1 = list_ptr;
while (ptr2 != NULL) {
if (ptr1 == NULL)
return false;
else if (ptr2->data == ptr1->data) {
ptr2 = ptr2->next;
ptr1 = ptr1->next;
} else
break;
}
if (ptr2 == NULL)
return true;
ptr2 = sub_ptr;
list_ptr = list_ptr->next;
}
return false;
}
int main(){
struct Node *list = newNode(2);
list->next = newNode(5);
list->next->next = newNode(3);
list->next->next->next = newNode(3);
list->next->next->next->next = newNode(6);
list->next->next->next->next->next = newNode(7);
list->next->next->next->next->next->next = newNode(0);
struct Node *sub_list = newNode(3);
sub_list->next = newNode(6);
sub_list->next->next = newNode(7);
bool res = sublist_search(list, sub_list);
if (res)
printf("Is the sublist present in the list? %d" , res);
}
輸出
Is the sublist present in the list? 1
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Node {
int data;
Node* next;
};
Node *newNode(int key){
Node *val = new Node;
val-> data= key;
val->next = NULL;
return val;
}
bool sublist_search(Node* list_ptr, Node* sub_ptr){
Node* ptr1 = list_ptr, *ptr2 = sub_ptr;
if (list_ptr == NULL && sub_ptr == NULL)
return true;
if ( sub_ptr == NULL || (sub_ptr != NULL && list_ptr == NULL))
return false;
while (list_ptr != NULL) {
ptr1 = list_ptr;
while (ptr2 != NULL) {
if (ptr1 == NULL)
return false;
else if (ptr2->data == ptr1->data) {
ptr2 = ptr2->next;
ptr1 = ptr1->next;
} else
break;
}
if (ptr2 == NULL)
return true;
ptr2 = sub_ptr;
list_ptr = list_ptr->next;
}
return false;
}
int main(){
Node *list = newNode(2);
list->next = newNode(5);
list->next->next = newNode(3);
list->next->next->next = newNode(3);
list->next->next->next->next = newNode(6);
list->next->next->next->next->next = newNode(7);
list->next->next->next->next->next->next = newNode(0);
Node *sub_list = newNode(3);
sub_list->next = newNode(6);
sub_list->next->next = newNode(7);
bool res = sublist_search(list, sub_list);
if (res)
cout << "Is the sublist present in the list? "<<res;
}
輸出
Is the sublist present in the list? 1
import java.io.*;
public class SublistSearch {
public static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
}
public static Node newNode(int key) {
Node val = new Node();
val.data= key;
val.next = null;
return val;
}
public static boolean sublist_search(Node list_ptr, Node sub_ptr) {
Node ptr1 = list_ptr, ptr2 = sub_ptr;
if (list_ptr == null && sub_ptr == null)
return true;
if ( sub_ptr == null || (sub_ptr != null && list_ptr == null))
return false;
while (list_ptr != null) {
ptr1 = list_ptr;
while (ptr2 != null) {
if (ptr1 == null)
return false;
else if (ptr2.data == ptr1.data) {
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
ptr1 = ptr1.next;
} else
break;
}
if (ptr2 == null)
return true;
ptr2 = sub_ptr;
list_ptr = list_ptr.next;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Node list = newNode(2);
list.next = newNode(5);
list.next.next = newNode(3);
list.next.next.next = newNode(3);
list.next.next.next.next = newNode(6);
list.next.next.next.next.next = newNode(7);
list.next.next.next.next.next.next = newNode(0);
Node sub_list = newNode(3);
sub_list.next = newNode(6);
sub_list.next.next = newNode(7);
boolean res = sublist_search(list, sub_list);
if (res){
System.out.print("Is the sublist present in the list? " + res);
}
}
}
輸出
Is the sublist present in the list? true
class Node:
def __init__(self, val = 0):
self.val = val
self.next = None
def sublist_search(sub_ptr, list_ptr):
if not sub_ptr and not list_ptr:
return True
if not sub_ptr or not list_ptr:
return False
ptr1 = sub_ptr
ptr2 = list_ptr
while ptr2:
ptr2 = list_ptr
while ptr1:
if not ptr2:
return False
elif ptr1.val == ptr2.val:
ptr1 = ptr1.next
ptr2 = ptr2.next
else:
break
if not ptr1:
return True
ptr1 = sub_ptr
list_ptr = list_ptr.next
return False
node_sublist = Node(3)
node_sublist.next = Node(3)
node_sublist.next.next = Node(6)
node_list = Node(2)
node_list.next = Node(5)
node_list.next.next = Node(3)
node_list.next.next.next = Node(3)
node_list.next.next.next.next = Node(6)
node_list.next.next.next.next.next = Node(7)
node_list.next.next.next.next.next.next = Node(0)
res = sublist_search(node_sublist, node_list)
if res == True:
print("Is the sublist present in the list? ", res)
輸出
Is the sublist present in the list? True
