
- 資料結構與演算法
- DSA - 首頁
- DSA - 概述
- DSA - 環境搭建
- DSA - 演算法基礎
- DSA - 漸進分析
- 資料結構
- DSA - 資料結構基礎
- DSA - 資料結構和型別
- DSA - 陣列資料結構
- 連結串列
- DSA - 連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 雙向連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 迴圈連結串列資料結構
- 棧與佇列
- DSA - 棧資料結構
- DSA - 表示式解析
- DSA - 佇列資料結構
- 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 線性搜尋演算法
- DSA - 二分搜尋演算法
- DSA - 插值搜尋
- DSA - 跳躍搜尋演算法
- DSA - 指數搜尋
- DSA - 斐波那契搜尋
- DSA - 子列表搜尋
- DSA - 雜湊表
- 排序演算法
- DSA - 排序演算法
- DSA - 氣泡排序演算法
- DSA - 插入排序演算法
- DSA - 選擇排序演算法
- DSA - 歸併排序演算法
- DSA - 希爾排序演算法
- DSA - 堆排序
- DSA - 桶排序演算法
- DSA - 計數排序演算法
- DSA - 基數排序演算法
- DSA - 快速排序演算法
- 圖資料結構
- DSA - 圖資料結構
- DSA - 深度優先遍歷
- DSA - 廣度優先遍歷
- DSA - 生成樹
- 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹的遍歷
- DSA - 二叉搜尋樹
- DSA - AVL樹
- DSA - 紅黑樹
- DSA - B樹
- DSA - B+樹
- DSA - 伸展樹
- DSA - 字典樹
- DSA - 堆資料結構
- 遞迴
- DSA - 遞迴演算法
- DSA - 使用遞迴實現漢諾塔
- DSA - 使用遞迴實現斐波那契數列
- 分治法
- DSA - 分治法
- DSA - 最大最小問題
- DSA - Strassen矩陣乘法
- DSA - Karatsuba演算法
- 貪心演算法
- DSA - 貪心演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(貪心法)
- DSA - Prim最小生成樹
- DSA - Kruskal最小生成樹
- DSA - Dijkstra最短路徑演算法
- DSA - 地圖著色演算法
- DSA - 分數揹包問題
- DSA - 帶截止時間的作業排序
- DSA - 最優合併模式演算法
- 動態規劃
- DSA - 動態規劃
- DSA - 矩陣鏈乘法
- DSA - Floyd-Warshall演算法
- DSA - 0-1揹包問題
- DSA - 最長公共子序列演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(動態規劃法)
- 近似演算法
- DSA - 近似演算法
- DSA - 頂點覆蓋演算法
- DSA - 集合覆蓋問題
- DSA - 旅行商問題(近似演算法)
- 隨機演算法
- DSA - 隨機演算法
- DSA - 隨機快速排序演算法
- DSA - Karger最小割演算法
- DSA - Fisher-Yates洗牌演算法
- DSA 有用資源
- DSA - 問答
- DSA - 快速指南
- DSA - 有用資源
- DSA - 討論
連結串列資料結構
什麼是連結串列?
連結串列是一種線性資料結構,可以儲存透過連結(即指標)連線在一起的“節點”集合。連結串列節點並非儲存在連續的位置,而是使用指標連結到不同的記憶體位置。一個節點由資料值和指向連結串列中下一個節點地址的指標組成。
連結串列是一種動態線性資料結構,其記憶體大小可以在執行時根據插入或刪除操作進行分配或釋放,這有助於有效利用系統記憶體。連結串列可以用來實現各種資料結構,例如棧、佇列、圖、雜湊對映等。
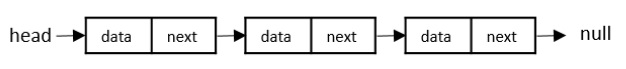
連結串列以一個頭節點開始,它指向第一個節點。每個節點都包含一個儲存與節點相關聯的實際資料(值)的資料部分和一個指向連結串列中下一個節點的記憶體地址的 next 指標。最後一個節點稱為連結串列的尾節點,它指向null,表示連結串列的結尾。
連結串列與陣列
對於陣列,大小是在建立時給定的,因此陣列是固定長度的,而連結串列的大小是動態的,可以動態地在連結串列中新增任意數量的節點。陣列可以容納類似型別的資料型別,而連結串列可以儲存不同資料型別的各種節點。
連結串列型別
以下是各種型別的連結串列。
單鏈表
單鏈表在一個節點中包含兩個“桶”;一個桶儲存資料,另一個桶儲存連結串列中下一個節點的地址。遍歷只能在一個方向上進行,因為同一連結串列的兩個節點之間只有一個單向連結。

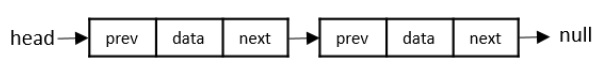
雙向連結串列
雙向連結串列在一個節點中包含三個“桶”;一個桶儲存資料,其他桶儲存列表中前一個和下一個節點的地址。由於列表中的節點從兩側相互連線,因此列表會被遍歷兩次。
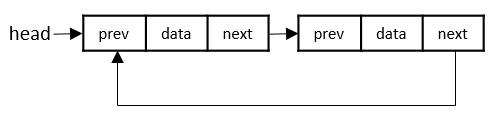
迴圈連結串列
迴圈連結串列可以存在於單鏈表和雙向連結串列中。
由於迴圈連結串列的最後一個節點和第一個節點連線在一起,因此在這個連結串列中的遍歷將永遠持續下去,直到它被中斷。
連結串列的基本操作
連結串列的基本操作包括插入、刪除、搜尋、顯示和刪除給定鍵的元素。這些操作在單鏈表上執行,如下所示:
插入 - 在列表的開頭新增一個元素。
刪除 - 刪除列表開頭的一個元素。
顯示 - 顯示整個列表。
搜尋 - 使用給定的鍵搜尋元素。
刪除 - 使用給定的鍵刪除元素。
連結串列 - 插入操作
在連結串列中新增一個新節點是一個多步驟的操作。我們將在此處用圖表學習它。首先,使用相同的結構建立一個節點,並找到它必須插入的位置。
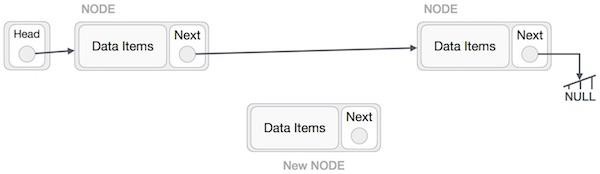
假設我們在節點 A (LeftNode) 和 C (RightNode) 之間插入節點 B (NewNode)。然後將 B.next 指向 C:
NewNode.next -> RightNode;
它應該看起來像這樣:
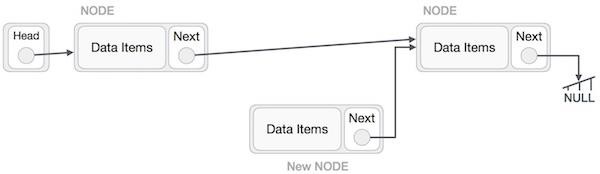
現在,左側的下一個節點應該指向新節點。
LeftNode.next -> NewNode;
這將把新節點放在這兩個節點的中間。新的列表應該如下所示:
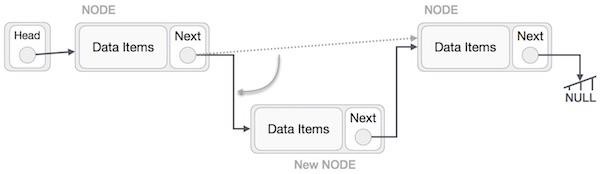
連結串列中的插入可以以三種不同的方式進行。解釋如下:
頭部插入
在此操作中,我們在列表的開頭新增一個元素。
演算法1. START 2. Create a node to store the data 3. Check if the list is empty 4. If the list is empty, add the data to the node and assign the head pointer to it. 5. If the list is not empty, add the data to a node and link to the current head. Assign the head to the newly added node. 6. END示例
以下是各種程式語言中此操作的實現:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
printf("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
printf(" %d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void main(){
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertatbegin(50);
printf("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 50 44 30 22 12 ]
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
cout << "\n[";
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
cout << " " << p->data << " ";
p = p->next;
}
cout << "]";
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
int main(){
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertatbegin(50);
cout << "Linked List: ";
// print list
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 50 44 30 22 12 ]
public class Linked_List {
static class node {
int data;
node next;
node (int value) {
data = value;
next = null;
}
}
static node head;
// display the list
static void printList() {
node p = head;
System.out.print("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != null) {
System.out.print(" " + p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
}
System.out.print("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
static void insertatbegin(int data) {
//create a link
node lk = new node(data);;
// point it to old first node
lk.next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertatbegin(50);
System.out.print("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
}
}
輸出
Linked List: [50 44 30 22 12 ]
class Node:
def __init__(self, data=None):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class SLL:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Print the linked list
def listprint(self):
printval = self.head
print("Linked List: ")
while printval is not None:
print (printval.data)
printval = printval.next
def AddAtBeginning(self,newdata):
NewNode = Node(newdata)
# Update the new nodes next val to existing node
NewNode.next = self.head
self.head = NewNode
l1 = SLL()
l1.head = Node("731")
e2 = Node("672")
e3 = Node("63")
l1.head.next = e2
e2.next = e3
l1.AddAtBeginning("122")
l1.listprint()
輸出
Linked List: 122 731 672 63
尾部插入
在此操作中,我們在列表的結尾新增一個元素。
演算法1. START 2. Create a new node and assign the data 3. Find the last node 4. Point the last node to new node 5. END示例
以下是各種程式語言中此操作的實現:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
printf("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
printf(" %d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void insertatend(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
struct node *linkedlist = head;
// point it to old first node
while(linkedlist->next != NULL)
linkedlist = linkedlist->next;
//point first to new first node
linkedlist->next = lk;
}
void main(){
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatend(22);
insertatend(30);
insertatend(44);
insertatend(50);
printf("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 12 22 30 44 50 ]
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
cout << "\n[";
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
cout << " " << p->data << " ";
p = p->next;
}
cout << "]";
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void insertatend(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
struct node *linkedlist = head;
// point it to old first node
while(linkedlist->next != NULL)
linkedlist = linkedlist->next;
//point first to new first node
linkedlist->next = lk;
}
int main(){
insertatbegin(12);
insertatend(22);
insertatend(30);
insertatend(44);
insertatend(50);
cout << "Linked List: ";
// print list
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 12 22 30 44 50 ]
public class Linked_List {
static class node {
int data;
node next;
node (int value) {
data = value;
next = null;
}
}
static node head;
// display the list
static void printList() {
node p = head;
System.out.print("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != null) {
System.out.print(" " + p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
}
System.out.print("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
static void insertatbegin(int data) {
//create a link
node lk = new node(data);;
// point it to old first node
lk.next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
static void insertatend(int data) {
//create a link
node lk = new node(data);
node linkedlist = head;
// point it to old first node
while(linkedlist.next != null)
linkedlist = linkedlist.next;
//point first to new first node
linkedlist.next = lk;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatend(22);
insertatend(30);
insertatend(44);
insertatend(50);
System.out.print("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
}
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 12 22 30 44 50 ]
class Node:
def __init__(self, data=None):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LL:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def listprint(self):
val = self.head
print("Linked List:")
while val is not None:
print(val.data)
val = val.next
l1 = LL()
l1.head = Node("23")
l2 = Node("12")
l3 = Node("7")
l4 = Node("14")
l5 = Node("61")
# Linking the first Node to second node
l1.head.next = l2
# Linking the second Node to third node
l2.next = l3
l3.next = l4
l4.next = l5
l1.listprint()
輸出
Linked List: 23 12 7 14 61
指定位置插入
在此操作中,我們在列表中的任何位置新增一個元素。
演算法1. START 2. Create a new node and assign data to it 3. Iterate until the node at position is found 4. Point first to new first node 5. END示例
以下是各種程式語言中此操作的實現:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
printf("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
printf(" %d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void insertafternode(struct node *list, int data){
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
lk->next = list->next;
list->next = lk;
}
void main(){
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertafternode(head->next, 30);
printf("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 22 12 30 ]
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
cout << "\n[";
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
cout << " " << p->data << " ";
p = p->next;
}
cout << "]";
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void insertafternode(struct node *list, int data){
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
lk->next = list->next;
list->next = lk;
}
int main(){
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertafternode(head->next,44);
insertafternode(head->next->next, 50);
cout << "Linked List: ";
// print list
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 30 22 44 50 12 ]
public class Linked_List {
static class node {
int data;
node next;
node (int value) {
data = value;
next = null;
}
}
static node head;
// display the list
static void printList() {
node p = head;
System.out.print("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != null) {
System.out.print(" " + p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
}
System.out.print("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
static void insertatbegin(int data) {
//create a link
node lk = new node(data);;
// point it to old first node
lk.next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
static void insertafternode(node list, int data) {
node lk = new node(data);
lk.next = list.next;
list.next = lk;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertafternode(head.next, 50);
insertafternode(head.next.next, 33);
System.out.println("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
}
}
輸出
Linked List: [44 30 50 33 22 12 ]
class Node:
def __init__(self, data=None):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class SLL:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Print the linked list
def listprint(self):
printval = self.head
print("Linked List: ")
while printval is not None:
print (printval.data)
printval = printval.next
# Function to add node
def InsertAtPos(self,nodeatpos,newdata):
if nodeatpos is None:
print("The mentioned node is absent")
return
NewNode = Node(newdata)
NewNode.next = nodeatpos.next
nodeatpos.next = NewNode
l1 = SLL()
l1.head = Node("731")
e2 = Node("672")
e3 = Node("63")
l1.head.next = e2
e2.next = e3
l1.InsertAtPos(l1.head.next, "122")
l1.listprint()
輸出
Linked List: 731 672 122 63
連結串列 - 刪除操作
刪除也是一個多步驟的過程。我們將用圖解來學習。首先,使用搜索演算法找到要刪除的目標節點。

目標節點的左(前一個)節點現在應該指向目標節點的下一個節點:
LeftNode.next -> TargetNode.next;

這將刪除指向目標節點的連結。現在,使用以下程式碼,我們將刪除目標節點指向的內容。
TargetNode.next -> NULL;

我們需要使用已刪除的節點。我們可以將其儲存在記憶體中,否則我們可以簡單地釋放記憶體並完全清除目標節點。


如果在列表的開頭插入節點,則應採取類似的步驟。在結尾插入時,列表的倒數第二個節點應指向新節點,新節點將指向 NULL。
連結串列中的刪除也以三種不同的方式執行。如下所示:
頭部刪除
在此連結串列的刪除操作中,我們從列表的開頭刪除一個元素。為此,我們將頭指標指向第二個節點。
演算法1. START 2. Assign the head pointer to the next node in the list 3. END示例
以下是各種程式語言中此操作的實現:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
printf("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
printf(" %d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void deleteatbegin(){
head = head->next;
}
int main(){
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(40);
insertatbegin(55);
printf("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
deleteatbegin();
printf("\nLinked List after deletion: ");
// print list
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 55 40 30 22 12 ] Linked List after deletion: [ 40 30 22 12 ]
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
cout << "\n[";
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
cout << " " << p->data << " ";
p = p->next;
}
cout << "]";
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void deleteatbegin(){
head = head->next;
}
int main(){
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertatbegin(50);
cout << "Linked List: ";
// print list
printList();
deleteatbegin();
cout << "\nLinked List after deletion: ";
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 50 44 30 22 12 ] Linked List after deletion: [ 44 30 22 12 ]
public class Linked_List {
static class node {
int data;
node next;
node (int value) {
data = value;
next = null;
}
}
static node head;
// display the list
static void printList() {
node p = head;
System.out.print("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != null) {
System.out.print(" " + p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
}
System.out.print("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
static void insertatbegin(int data) {
//create a link
node lk = new node(data);;
// point it to old first node
lk.next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
static void deleteatbegin() {
head = head.next;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertatbegin(50);
insertatbegin(33);
System.out.print("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
deleteatbegin();
System.out.print("\nLinked List after deletion: ");
// print list
printList();
}
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 33 50 44 30 22 12 ] Linked List after deletion: [ 50 44 30 22 12 ]
#python code for deletion at beginning using linked list.
from typing import Optional
class Node:
def __init__(self, data: int, next: Optional['Node'] = None):
self.data = data
self.next = next
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
#display the list
def print_list(self):
p = self.head
print("\n[", end="")
while p:
print(f" {p.data} ", end="")
p = p.next
print("]")
#Insertion at the beginning
def insert_at_begin(self, data: int):
lk = Node(data)
#point it to old first node
lk.next = self.head
#point firt to new first node
self.head = lk
def delete_at_begin(self):
self.head = self.head.next
if __name__ == "__main__":
linked_list = LinkedList()
linked_list.insert_at_begin(12)
linked_list.insert_at_begin(22)
linked_list.insert_at_begin(30)
linked_list.insert_at_begin(44)
linked_list.insert_at_begin(50)
#print list
print("Linked List: ", end="")
linked_list.print_list()
linked_list.delete_at_begin()
print("Linked List after deletion: ", end="")
linked_list.print_list()
輸出
Linked List: [ 50 44 30 22 12 ] Linked List after deletion: [ 44 30 22 12 ]
尾部刪除
在此連結串列的刪除操作中,我們從列表的結尾刪除一個元素。
演算法1. START 2. Iterate until you find the second last element in the list. 3. Assign NULL to the second last element in the list. 4. END示例
以下是各種程式語言中此操作的實現:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
printf("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
printf(" %d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void deleteatend(){
struct node *linkedlist = head;
while (linkedlist->next->next != NULL)
linkedlist = linkedlist->next;
linkedlist->next = NULL;
}
void main(){
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(40);
insertatbegin(55);
printf("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
deleteatend();
printf("\nLinked List after deletion: ");
// print list
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 55 40 30 22 12 ] Linked List after deletion: [ 55 40 30 22 ]
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// Displaying the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
while(p != NULL) {
cout << " " << p->data << " ";
p = p->next;
}
}
// Insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void deleteatend(){
struct node *linkedlist = head;
while (linkedlist->next->next != NULL)
linkedlist = linkedlist->next;
linkedlist->next = NULL;
}
int main(){
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertatbegin(50);
cout << "Linked List: ";
// print list
printList();
deleteatend();
cout << "\nLinked List after deletion: ";
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: 50 44 30 22 12 Linked List after deletion: 50 44 30 22
public class Linked_List {
static class node {
int data;
node next;
node (int value) {
data = value;
next = null;
}
}
static node head;
// display the list
static void printList() {
node p = head;
System.out.print("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != null) {
System.out.print(" " + p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
}
System.out.print("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
static void insertatbegin(int data) {
//create a link
node lk = new node(data);;
// point it to old first node
lk.next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
static void deleteatend() {
node linkedlist = head;
while (linkedlist.next.next != null)
linkedlist = linkedlist.next;
linkedlist.next = null;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertatbegin(50);
insertatbegin(33);
System.out.print("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
//deleteatbegin();
deleteatend();
System.out.print("\nLinked List after deletion: ");
// print list
printList();
}
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 33 50 44 30 22 12 ] Linked List after deletion: [ 33 50 44 30 22 ]
#python code for deletion at beginning using linked list.
class Node:
def __init__(self, data=None):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
#Displaying the list
def printList(self):
p = self.head
print("\n[", end="")
while p != None:
print(" " + str(p.data) + " ", end="")
p = p.next
print("]")
#Insertion at the beginning
def insertatbegin(self, data):
#create a link
lk = Node(data)
#point it to old first node
lk.next = self.head
#point first to new first node
self.head = lk
def deleteatend(self):
linkedlist = self.head
while linkedlist.next.next != None:
linkedlist = linkedlist.next
linkedlist.next = None
if __name__ == "__main__":
linked_list = LinkedList()
linked_list.insertatbegin(12)
linked_list.insertatbegin(22)
linked_list.insertatbegin(30)
linked_list.insertatbegin(40)
linked_list.insertatbegin(55)
#print list
print("Linked List: ", end="")
linked_list.printList()
linked_list.deleteatend()
print("Linked List after deletion: ", end="")
linked_list.printList()
輸出
Linked List: [ 55 40 30 22 12 ] Linked List after deletion: [ 55 40 30 22 ]
指定位置刪除
在此連結串列的刪除操作中,我們刪除列表中任何位置的一個元素。
演算法1. START 2. Iterate until find the current node at position in the list. 3. Assign the adjacent node of current node in the list to its previous node. 4. END示例
以下是各種程式語言中此操作的實現:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
printf("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
printf(" %d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void deletenode(int key){
struct node *temp = head, *prev;
if (temp != NULL && temp->data == key) {
head = temp->next;
return;
}
// Find the key to be deleted
while (temp != NULL && temp->data != key) {
prev = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
// If the key is not present
if (temp == NULL) return;
// Remove the node
prev->next = temp->next;
}
void main(){
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(40);
insertatbegin(55);
printf("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
deletenode(30);
printf("\nLinked List after deletion: ");
// print list
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 55 40 30 22 12 ] Linked List after deletion: [ 55 40 22 12 ]
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
cout << "\n[";
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
cout << " " << p->data << " ";
p = p->next;
}
cout << "]";
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void deletenode(int key){
struct node *temp = head, *prev;
if (temp != NULL && temp->data == key) {
head = temp->next;
return;
}
// Find the key to be deleted
while (temp != NULL && temp->data != key) {
prev = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
// If the key is not present
if (temp == NULL) return;
// Remove the node
prev->next = temp->next;
}
int main(){
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertatbegin(50);
cout << "Linked List: ";
// print list
printList();
deletenode(30);
cout << "\nLinked List after deletion: ";
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 50 44 30 22 12 ] Linked List after deletion: [ 50 44 22 12 ]
public class Linked_List {
static class node {
int data;
node next;
node (int value) {
data = value;
next = null;
}
}
static node head;
// display the list
static void printList() {
node p = head;
System.out.print("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != null) {
System.out.print(" " + p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
}
System.out.print("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
static void insertatbegin(int data) {
//create a link
node lk = new node(data);;
// point it to old first node
lk.next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
static void deletenode(int key) {
node temp = head;
node prev = null;
if (temp != null && temp.data == key) {
head = temp.next;
return;
}
// Find the key to be deleted
while (temp != null && temp.data != key) {
prev = temp;
temp = temp.next;
}
// If the key is not present
if (temp == null) return;
// Remove the node
prev.next = temp.next;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertatbegin(50);
insertatbegin(33);
System.out.print("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
//deleteatbegin();
//deleteatend();
deletenode(12);
System.out.print("\nLinked List after deletion: ");
// print list
printList();
}
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 33 50 44 30 22 12 ] Linked List after deletion: [ 33 50 44 30 22 ]
#python code for deletion at given position using linked list.
class Node:
def __init__(self, data=None):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LinkedList:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# display the list
def printList(self):
p = self.head
print("\n[", end="")
#start from the beginning
while(p != None):
print(" ", p.data, " ", end="")
p = p.next
print("]")
#insertion at the beginning
def insertatbegin(self, data):
#create a link
lk = Node(data)
# point it to old first node
lk.next = self.head
#point first to new first node
self.head = lk
def deletenode(self, key):
temp = self.head
if (temp != None and temp.data == key):
self.head = temp.next
return
# Find the key to be deleted
while (temp != None and temp.data != key):
prev = temp
temp = temp.next
# If the key is not present
if (temp == None):
return
# Remove the node
prev.next = temp.next
llist = LinkedList()
llist.insertatbegin(12)
llist.insertatbegin(22)
llist.insertatbegin(30)
llist.insertatbegin(40)
llist.insertatbegin(55)
print("Original Linked List: ", end="")
# print list
llist.printList()
llist.deletenode(30)
print("Linked List after deletion: ", end="")
# print list
llist.printList()
輸出
Original Linked List: [ 55 40 30 22 12 ] Linked List after deletion: [ 55 40 22 12 ]
連結串列 - 反轉操作
此操作是一個徹底的操作。我們需要使頭節點指向最後一個節點並反轉整個連結串列。

首先,我們遍歷到列表的末尾。它應該指向 NULL。現在,我們將使其指向其前一個節點:

我們必須確保最後一個節點不是最後一個節點。因此,我們將有一些臨時節點,它看起來像頭節點指向最後一個節點。現在,我們將一個接一個地使所有左側節點指向它們的前一個節點。

除了頭節點指向的節點(第一個節點)之外,所有節點都應該指向它們的前驅節點,使其成為它們新的後繼節點。第一個節點將指向 NULL。
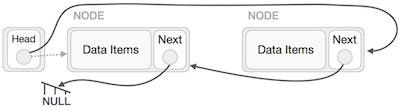
我們將使用臨時節點使頭節點指向新的第一個節點。

演算法
反轉連結串列的逐步過程如下:
1. START 2. We use three pointers to perform the reversing: prev, next, head. 3. Point the current node to head and assign its next value to the prev node. 4. Iteratively repeat the step 3 for all the nodes in the list. 5. Assign head to the prev node.
示例
以下是各種程式語言中此操作的實現:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
printf("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
printf(" %d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void reverseList(struct node** head){
struct node *prev = NULL, *cur=*head, *tmp;
while(cur!= NULL) {
tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
*head = prev;
}
void main(){
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(40);
insertatbegin(55);
printf("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
reverseList(&head);
printf("\nReversed Linked List: ");
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 55 40 30 22 12 ] Reversed Linked List: [ 12 22 30 40 55 ]
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
printf("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
printf(" %d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void reverseList(struct node** head){
struct node *prev = NULL, *cur=*head, *tmp;
while(cur!= NULL) {
tmp = cur->next;
cur->next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
*head = prev;
}
int main(){
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(40);
insertatbegin(55);
printf("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
reverseList(&head);
printf("\nReversed Linked List: ");
printList();
return 0;
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 55 40 30 22 12 ] Reversed Linked List: [ 12 22 30 40 55 ]
public class Linked_List {
static Node head;
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node (int value) {
data = value;
next = null;
}
}
// display the list
static void printList(Node node) {
System.out.print("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(node != null) {
System.out.print(" " + node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
System.out.print("]");
}
static Node reverseList(Node head) {
Node prev = null;
Node cur = head;
Node temp = null;
while (cur != null) {
temp = cur.next;
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = temp;
}
head = prev;
return head;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Linked_List list = new Linked_List();
list.head = new Node(33);
list.head.next = new Node(50);
list.head.next.next = new Node(44);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(22);
list.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(12);
System.out.print("Linked List: ");
// print list
list.printList(head);
head = list.reverseList(head);
System.out.print("\nReversed linked list ");
list.printList(head);
}
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 33 50 44 22 12 ] Reversed linked list [ 12 22 44 50 33 ]
class Node:
def __init__(self, data=None):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class SLL:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Print the linked list
def listprint(self):
printval = self.head
print("Linked List: ")
while printval is not None:
print (printval.data)
printval = printval.next
def reverse(self):
prev = None
curr = self.head
while(curr is not None):
next = curr.next
curr.next = prev
prev = curr
curr = next
self.head = prev
l1 = SLL()
l1.head = Node("731")
e2 = Node("672")
e3 = Node("63")
l1.head.next = e2
e2.next = e3
l1.listprint()
l1.reverse()
print("After reversing: ")
l1.listprint()
輸出
Linked List: 731 672 63 After reversing: Linked List: 63 672 731
連結串列 - 搜尋操作
使用關鍵元素在列表中搜索元素。此操作與陣列搜尋方式相同;將列表中的每個元素與給定的關鍵元素進行比較。
演算法
1 START 2 If the list is not empty, iteratively check if the list contains the key 3 If the key element is not present in the list, unsuccessful search 4 END
示例
以下是各種程式語言中此操作的實現:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
printf("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
printf(" %d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
int searchlist(int key){
struct node *temp = head;
while(temp != NULL) {
if (temp->data == key) {
return 1;
}
temp=temp->next;
}
return 0;
}
void main(){
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(40);
insertatbegin(55);
printf("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
int ele = 30;
printf("\nElement to be searched is: %d", ele);
k = searchlist(30);
if (k == 1)
printf("\nElement is found");
else
printf("\nElement is not found in the list");
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 55 40 30 22 12 ] Element to be searched is: 30 Element is found
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
cout << "\n[";
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
cout << " " << p->data << " ";
p = p->next;
}
cout << "]";
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
int searchlist(int key){
struct node *temp = head;
while(temp != NULL) {
if (temp->data == key) {
return 1;
}
temp=temp->next;
}
return 0;
}
int main(){
int k = 0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertatbegin(50);
cout << "Linked List: ";
// print list
printList();
int ele = 16;
cout<<"\nElement to be searched is: "<<ele;
k = searchlist(ele);
if (k == 1)
cout << "\nElement is found";
else
cout << "\nElement is not found in the list";
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 50 44 30 22 12 ] Element to be searched is: 16 Element is not found in the list
public class Linked_List {
static class node {
int data;
node next;
node (int value) {
data = value;
next = null;
}
}
static node head;
// display the list
static void printList() {
node p = head;
System.out.print("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != null) {
System.out.print(" " + p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
}
System.out.print("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
static void insertatbegin(int data) {
//create a link
node lk = new node(data);;
// point it to old first node
lk.next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
static int searchlist(int key) {
node temp = head;
while(temp != null) {
if (temp.data == key) {
return 1;
}
temp=temp.next;
}
return 0;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertatbegin(50);
insertatbegin(33);
System.out.print("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
int ele = 44;
System.out.print("\nElement to be searched is: " + ele);
k = searchlist(ele);
if (k == 1)
System.out.println("\nElement is found");
else
System.out.println("\nElement is not found in the list");
}
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 33 50 44 30 22 12 ] Element to be searched is: 44 Element is found
class Node:
def __init__(self, data=None):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class SLL:
def listprint(self):
printval = self.head
print("Linked List: ")
while printval is not None:
print (printval.data)
printval = printval.next
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def search(self, x):
count = 0
# Initialize current to head
current = self.head
# loop till current not equal to None
while current != None:
if current.data == x:
print("Element is found")
count = count + 1
current = current.next
if count == 0:
print("Element is not found in the list")
l1 = SLL()
l1.head = Node("731")
e2 = Node("672")
e3 = Node("63")
l1.head.next = e2
e2.next = e3
l1.listprint()
ele = "63"
print("Element to be searched is: ", ele);
l1.search(ele)
輸出
Linked List: 731 672 63 Element to be searched is: 63 Element is found
連結串列 - 遍歷操作
遍歷操作按順序遍歷列表中的所有元素,並按該順序顯示這些元素。
演算法
1. START 2. While the list is not empty and did not reach the end of the list, print the data in each node 3. END
示例
以下是各種程式語言中此操作的實現:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
printf("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
printf(" %d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void main(){
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
printf("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 30 22 12 ]
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// Displaying the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
while(p != NULL) {
cout << " " << p->data << " ";
p = p->next;
}
}
// Insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
int main(){
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertatbegin(50);
cout << "Linked List: ";
// print list
printList();
}
輸出
Linked List: 50 44 30 22 12
public class Linked_List {
static class node {
int data;
node next;
node (int value) {
data = value;
next = null;
}
}
static node head;
// display the list
static void printList() {
node p = head;
System.out.print("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != null) {
System.out.print(" " + p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
}
System.out.print("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
static void insertatbegin(int data) {
//create a link
node lk = new node(data);;
// point it to old first node
lk.next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatbegin(30);
insertatbegin(44);
insertatbegin(50);
insertatbegin(33);
System.out.print("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
}
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 33 50 44 30 22 12 ]
class Node:
def __init__(self, data=None):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class SLL:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
# Print the linked list
def listprint(self):
printval = self.head
print("Linked List: ")
while printval is not None:
print (printval.data)
printval = printval.next
l1 = SLL()
l1.head = Node("731")
e2 = Node("672")
e3 = Node("63")
l1.head.next = e2
e2.next = e3
l1.listprint()
輸出
Linked List: 731 672 63
連結串列 -完整實現
以下是各種程式語言中連結串列的完整實現:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
printf("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
printf(" %d ",p->data);
p = p->next;
}
printf("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void insertatend(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
struct node *linkedlist = head;
// point it to old first node
while(linkedlist->next != NULL)
linkedlist = linkedlist->next;
//point first to new first node
linkedlist->next = lk;
}
void insertafternode(struct node *list, int data){
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
lk->next = list->next;
list->next = lk;
}
void deleteatbegin(){
head = head->next;
}
void deleteatend(){
struct node *linkedlist = head;
while (linkedlist->next->next != NULL)
linkedlist = linkedlist->next;
linkedlist->next = NULL;
}
void deletenode(int key){
struct node *temp = head, *prev;
if (temp != NULL && temp->data == key) {
head = temp->next;
return;
}
// Find the key to be deleted
while (temp != NULL && temp->data != key) {
prev = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
// If the key is not present
if (temp == NULL) return;
// Remove the node
prev->next = temp->next;
}
int searchlist(int key){
struct node *temp = head;
while(temp != NULL) {
if (temp->data == key) {
return 1;
}
temp=temp->next;
}
return 0;
}
void main(){
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatend(30);
insertatend(44);
insertatbegin(50);
insertafternode(head->next->next, 33);
printf("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
deleteatbegin();
deleteatend();
deletenode(12);
printf("\nLinked List after deletion: ");
// print list
printList();
insertatbegin(4);
insertatbegin(16);
printf("\nUpdated Linked List: ");
printList();
k = searchlist(16);
if (k == 1)
printf("\nElement is found");
else
printf("\nElement is not present in the list");
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 50 22 12 33 30 44 ] Linked List after deletion: [ 22 33 30 ] Updated Linked List: [ 16 4 22 33 30 ] Element is found
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int data;
struct node *next;
};
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *current = NULL;
// display the list
void printList(){
struct node *p = head;
cout << "\n[";
//start from the beginning
while(p != NULL) {
cout << " " << p->data << " ";
p = p->next;
}
cout << "]";
}
//insertion at the beginning
void insertatbegin(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
// point it to old first node
lk->next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
void insertatend(int data){
//create a link
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
struct node *linkedlist = head;
// point it to old first node
while(linkedlist->next != NULL)
linkedlist = linkedlist->next;
//point first to new first node
linkedlist->next = lk;
}
void insertafternode(struct node *list, int data){
struct node *lk = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
lk->data = data;
lk->next = list->next;
list->next = lk;
}
void deleteatbegin(){
head = head->next;
}
void deleteatend(){
struct node *linkedlist = head;
while (linkedlist->next->next != NULL)
linkedlist = linkedlist->next;
linkedlist->next = NULL;
}
void deletenode(int key){
struct node *temp = head, *prev;
if (temp != NULL && temp->data == key) {
head = temp->next;
return;
}
// Find the key to be deleted
while (temp != NULL && temp->data != key) {
prev = temp;
temp = temp->next;
}
// If the key is not present
if (temp == NULL) return;
// Remove the node
prev->next = temp->next;
}
int searchlist(int key){
struct node *temp = head;
while(temp != NULL) {
if (temp->data == key) {
temp=temp->next;
return 1;
} else
return 0;
}
return key;
}
int main(){
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatend(30);
insertatend(44);
insertatbegin(50);
insertafternode(head->next->next, 33);
cout << "Linked List: ";
// print list
printList();
deleteatbegin();
deleteatend();
deletenode(12);
cout << "\nLinked List after deletion: ";
// print list
printList();
insertatbegin(4);
insertatbegin(16);
cout << "\nUpdated Linked List: ";
printList();
k = searchlist(16);
if (k == 1)
cout << "\nElement is found";
else
cout << "\nElement is not present in the list";
return 0;
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 50 22 12 33 30 44 ] Linked List after deletion: [ 22 33 30 ] Updated Linked List: [ 16 4 22 33 30 ] Element is found
public class Linked_List {
static class node {
int data;
node next;
node (int value) {
data = value;
next = null;
}
}
static node head;
// display the list
static void printList() {
node p = head;
System.out.print("\n[");
//start from the beginning
while(p != null) {
System.out.print(" " + p.data + " ");
p = p.next;
}
System.out.print("]");
}
//insertion at the beginning
static void insertatbegin(int data) {
//create a link
node lk = new node(data);;
// point it to old first node
lk.next = head;
//point first to new first node
head = lk;
}
static void insertatend(int data) {
//create a link
node lk = new node(data);
node linkedlist = head;
// point it to old first node
while(linkedlist.next != null)
linkedlist = linkedlist.next;
//point first to new first node
linkedlist.next = lk;
}
static void insertafternode(node list, int data) {
node lk = new node(data);
lk.next = list.next;
list.next = lk;
}
static void deleteatbegin() {
head = head.next;
}
static void deleteatend() {
node linkedlist = head;
while (linkedlist.next.next != null)
linkedlist = linkedlist.next;
linkedlist.next = null;
}
static void deletenode(int key) {
node temp = head;
node prev = null;
if (temp != null && temp.data == key) {
head = temp.next;
return;
}
// Find the key to be deleted
while (temp != null && temp.data != key) {
prev = temp;
temp = temp.next;
}
// If the key is not present
if (temp == null) return;
// Remove the node
prev.next = temp.next;
}
static int searchlist(int key) {
node temp = head;
while(temp != null) {
if (temp.data == key) {
temp=temp.next;
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
int k=0;
insertatbegin(12);
insertatbegin(22);
insertatend(30);
insertatend(44);
insertatbegin(50);
insertafternode(head.next.next, 33);
System.out.print("Linked List: ");
// print list
printList();
deleteatbegin();
deleteatend();
deletenode(12);
System.out.print("\nLinked List after deletion: ");
// print list
printList();
insertatbegin(4);
insertatbegin(16);
System.out.print("\nUpdated Linked List: ");
printList();
k = searchlist(16);
if (k == 1)
System.out.print("\nElement is found");
else
System.out.print("\nElement is not present in the list");
}
}
輸出
Linked List: [ 50 22 12 33 30 44 ] Linked List after deletion: [ 22 33 30 ] Updated Linked List: [ 16 4 22 33 30 ] Element is found
class LLNode:
def __init__(self, data=None):
self.data = data
self.next = None
class LL:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def listprint(self):
printval = self.head
while printval is not None:
print(printval.data)
printval = printval.next
def AddAtBeginning(self,newdata):
NewNode = LLNode(newdata)
# Update the new nodes next val to existing node
NewNode.next = self.head
self.head = NewNode
# Function to add node at a position
def InsertAtPos(self,nodeatpos,newdata):
if nodeatpos is None:
print("The mentioned node is absent")
return
NewNode = LLNode(newdata)
NewNode.next = nodeatpos.next
nodeatpos.next = NewNode
def reverse(self):
prev = None
curr = self.head
while(curr is not None):
next = curr.next
curr.next = prev
prev = curr
curr = next
self.head = prev
def search(self, x):
count = 0
# Initialize current to head
current = self.head
# loop till current not equal to None
while current != None:
if current.data == x:
print("Element is found")
count = count + 1
current = current.next
if count == 0:
print("Element is not found in the list")
l1 = LL()
l1.head = LLNode("23")
l2 = LLNode("12")
l3 = LLNode("7")
l4 = LLNode("14")
l5 = LLNode("61")
# Linking the first Node to second node
l1.head.next = l2
# Linking the second Node to third node
l2.next = l3
l3.next = l4
l4.next = l5
print("Original Linked List: ")
l1.listprint()
l1.AddAtBeginning("45")
l1.InsertAtPos(l1.head.next.next, "4")
print("Updated Linked List:")
l1.listprint()
l1.reverse()
print("Reversed Linked List:")
l1.listprint()
l1.search("7")
輸出
Original Linked List: 23 12 7 14 61 Updated Linked List: 45 23 12 4 7 14 61 Reversed Linked List: 61 14 7 4 12 23 45 Element is found