
- 資料結構與演算法
- DSA - 首頁
- DSA - 概述
- DSA - 環境設定
- DSA - 演算法基礎
- DSA - 漸進分析
- 資料結構
- DSA - 資料結構基礎
- DSA - 資料結構和型別
- DSA - 陣列資料結構
- 連結串列
- DSA - 連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 雙向連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 迴圈連結串列資料結構
- 棧和佇列
- DSA - 棧資料結構
- DSA - 表示式解析
- DSA - 佇列資料結構
- 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 線性搜尋演算法
- DSA - 二分搜尋演算法
- DSA - 插值搜尋
- DSA - 跳躍搜尋演算法
- DSA - 指數搜尋
- DSA - 斐波那契搜尋
- DSA - 子列表搜尋
- DSA - 雜湊表
- 排序演算法
- DSA - 排序演算法
- DSA - 氣泡排序演算法
- DSA - 插入排序演算法
- DSA - 選擇排序演算法
- DSA - 歸併排序演算法
- DSA - 希爾排序演算法
- DSA - 堆排序
- DSA - 桶排序演算法
- DSA - 計數排序演算法
- DSA - 基數排序演算法
- DSA - 快速排序演算法
- 圖資料結構
- DSA - 圖資料結構
- DSA - 深度優先遍歷
- DSA - 廣度優先遍歷
- DSA - 生成樹
- 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹的遍歷
- DSA - 二叉搜尋樹
- DSA - AVL樹
- DSA - 紅黑樹
- DSA - B樹
- DSA - B+樹
- DSA - 伸展樹
- DSA - 字典樹
- DSA - 堆資料結構
- 遞迴
- DSA - 遞迴演算法
- DSA - 使用遞迴實現漢諾塔
- DSA - 使用遞迴實現斐波那契數列
- 分治法
- DSA - 分治法
- DSA - 最大最小問題
- DSA - Strassen矩陣乘法
- DSA - Karatsuba演算法
- 貪心演算法
- DSA - 貪心演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(貪心演算法)
- DSA - Prim最小生成樹
- DSA - Kruskal最小生成樹
- DSA - Dijkstra最短路徑演算法
- DSA - 地圖著色演算法
- DSA - 分數揹包問題
- DSA - 帶截止日期的作業排序
- DSA - 最佳合併模式演算法
- 動態規劃
- DSA - 動態規劃
- DSA - 矩陣鏈乘法
- DSA - Floyd-Warshall演算法
- DSA - 0-1揹包問題
- DSA - 最長公共子序列演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(動態規劃)
- 近似演算法
- DSA - 近似演算法
- DSA - 頂點覆蓋演算法
- DSA - 集合覆蓋問題
- DSA - 旅行商問題(近似演算法)
- 隨機化演算法
- DSA - 隨機化演算法
- DSA - 隨機化快速排序演算法
- DSA - Karger最小割演算法
- DSA - Fisher-Yates洗牌演算法
- DSA 有用資源
- DSA - 問答
- DSA - 快速指南
- DSA - 有用資源
- DSA - 討論
快速排序演算法
快速排序是一種高效的排序演算法,基於將資料陣列劃分為較小的陣列。一個大的陣列被劃分為兩個陣列,其中一個數組包含小於指定值(例如,樞軸)的值,根據該值進行分割槽,另一個數組包含大於樞軸值的值。
快速排序會對陣列進行分割槽,然後遞迴呼叫自身兩次來對兩個生成的子陣列進行排序。對於大型資料集,此演算法非常有效,因為它的平均和最壞情況複雜度分別為 O(n log n) 和 O(n2)。
快速排序中的分割槽
以下動畫表示說明了如何在陣列中找到樞軸值。
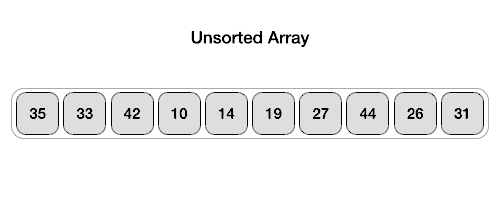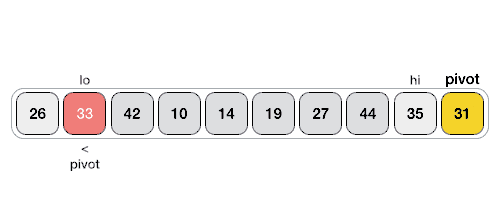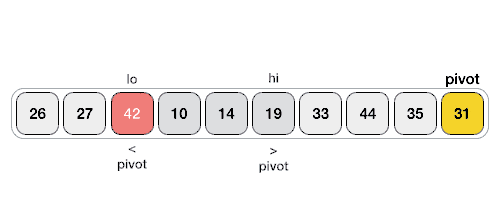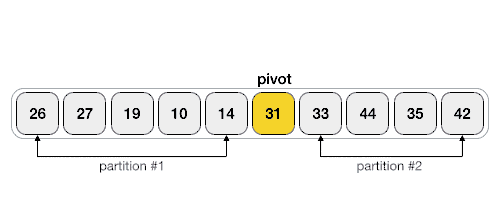
樞軸值將列表分成兩部分。然後,我們遞迴地為每個子列表查詢樞軸,直到所有列表僅包含一個元素。
快速排序樞軸演算法
基於我們對快速排序中分割槽的理解,我們現在將嘗試為其編寫一個演算法,如下所示。
1. Choose the highest index value has pivot 2. Take two variables to point left and right of the list excluding pivot 3. Left points to the low index 4. Right points to the high 5. While value at left is less than pivot move right 6. While value at right is greater than pivot move left 7. If both step 5 and step 6 does not match swap left and right 8. If left ≥ right, the point where they met is new pivot
快速排序樞軸虛擬碼
上述演算法的虛擬碼可以匯出為:
function partitionFunc(left, right, pivot)
leftPointer = left
rightPointer = right - 1
while True do
while A[++leftPointer] < pivot do
//do-nothing
end while
while rightPointer > 0 && A[--rightPointer] > pivot do
//do-nothing
end while
if leftPointer >= rightPointer
break
else
swap leftPointer,rightPointer
end if
end while
swap leftPointer,right
return leftPointer
end function
快速排序演算法
使用樞軸演算法遞迴地,我們最終得到儘可能小的分割槽。然後,每個分割槽都會被處理以進行快速排序。我們定義快速排序的遞迴演算法如下:
1. Make the right-most index value pivot 2. Partition the array using pivot value 3. Quicksort left partition recursively 4. Quicksort right partition recursively
快速排序虛擬碼
為了更深入地瞭解,讓我們看看快速排序演算法的虛擬碼:
procedure quickSort(left, right)
if right-left <= 0
return
else
pivot = A[right]
partition = partitionFunc(left, right, pivot)
quickSort(left,partition-1)
quickSort(partition+1,right)
end if
end procedure
分析
快速排序演算法的最壞情況複雜度為 O(n2)。但是,使用這種技術,在一般情況下,我們通常可以在 O(n log n) 時間內獲得輸出。
實現
以下是各種程式語言中快速排序演算法的實現:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#define MAX 7
int intArray[MAX] = {
4,6,3,2,1,9,7
};
void printline(int count) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < count - 1; i++) {
printf("=");
}
printf("=\n");
}
void display() {
int i;
printf("[");
// navigate through all items
for (i = 0; i < MAX; i++) {
printf("%d ", intArray[i]);
}
printf("]\n");
}
void swap(int num1, int num2) {
int temp = intArray[num1];
intArray[num1] = intArray[num2];
intArray[num2] = temp;
}
int partition(int left, int right, int pivot) {
int leftPointer = left - 1;
int rightPointer = right;
while (true) {
while (intArray[++leftPointer] < pivot) {
//do nothing
}
while (rightPointer > 0 && intArray[--rightPointer] > pivot) {
//do nothing
}
if (leftPointer >= rightPointer) {
break;
} else {
printf(" item swapped :%d,%d\n", intArray[leftPointer], intArray[rightPointer]);
swap(leftPointer, rightPointer);
}
}
printf(" pivot swapped :%d,%d\n", intArray[leftPointer], intArray[right]);
swap(leftPointer, right);
printf("Updated Array: ");
display();
return leftPointer;
}
void quickSort(int left, int right) {
if (right - left <= 0) {
return;
} else {
int pivot = intArray[right];
int partitionPoint = partition(left, right, pivot);
quickSort(left, partitionPoint - 1);
quickSort(partitionPoint + 1, right);
}
}
int main() {
printf("Input Array: ");
display();
printline(50);
quickSort(0, MAX - 1);
printf("Output Array: ");
display();
printline(50);
}
輸出
Input Array: [4 6 3 2 1 9 7 ] ================================================== pivot swapped :9,7 Updated Array: [4 6 3 2 1 7 9 ] pivot swapped :4,1 Updated Array: [1 6 3 2 4 7 9 ] item swapped :6,2 pivot swapped :6,4 Updated Array: [1 2 3 4 6 7 9 ] pivot swapped :3,3 Updated Array: [1 2 3 4 6 7 9 ] Output Array: [1 2 3 4 6 7 9 ] ==================================================
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 7
int intArray[MAX] = {4,6,3,2,1,9,7};
void display() {
int i;
cout << "[";
// navigate through all items
for(i = 0;i < MAX;i++) {
cout << intArray[i] << " ";
}
cout << "]\n";
}
void swap(int num1, int num2) {
int temp = intArray[num1];
intArray[num1] = intArray[num2];
intArray[num2] = temp;
}
int partition(int left, int right, int pivot) {
int leftPointer = left -1;
int rightPointer = right;
while(true) {
while(intArray[++leftPointer] < pivot) {
//do nothing
}
while(rightPointer > 0 && intArray[--rightPointer] > pivot) {
//do nothing
}
if(leftPointer >= rightPointer) {
break;
} else {
cout << "item swapped : " << intArray[leftPointer] << "," << intArray[rightPointer] << endl;
swap(leftPointer, rightPointer);
}
}
cout << "\npivot swapped : " << intArray[leftPointer] << "," << intArray[right] << endl;
swap(leftPointer,right);
cout << "Updated Array: ";
display();
return leftPointer;
}
void quickSort(int left, int right) {
if(right-left <= 0) {
return;
} else {
int pivot = intArray[right];
int partitionPoint = partition(left, right, pivot);
quickSort(left, partitionPoint - 1);
quickSort(partitionPoint + 1,right);
}
}
int main() {
cout << "Input Array: ";
display();
quickSort(0, MAX-1);
cout << "\nOutput Array: ";
display();
}
輸出
Input Array: [4 6 3 2 1 9 7 ] pivot swapped : 9,7 Updated Array: [4 6 3 2 1 7 9 ] pivot swapped : 4,1 Updated Array: [1 6 3 2 4 7 9 ] item swapped : 6,2 pivot swapped : 6,4 Updated Array: [1 2 3 4 6 7 9 ] pivot swapped : 3,3 Updated Array: [1 2 3 4 6 7 9 ] Output Array: [1 2 3 4 6 7 9 ]
import java.util.Arrays;
public class QuickSortExample {
int[] intArray = {4,6,3,2,1,9,7};
void swap(int num1, int num2) {
int temp = intArray[num1];
intArray[num1] = intArray[num2];
intArray[num2] = temp;
}
int partition(int left, int right, int pivot) {
int leftPointer = left - 1;
int rightPointer = right;
while (true) {
while (intArray[++leftPointer] < pivot) {
// do nothing
}
while (rightPointer > 0 && intArray[--rightPointer] > pivot) {
// do nothing
}
if (leftPointer >= rightPointer) {
break;
} else {
swap(leftPointer, rightPointer);
}
}
swap(leftPointer, right);
// System.out.println("Updated Array: ");
return leftPointer;
}
void quickSort(int left, int right) {
if (right - left <= 0) {
return;
} else {
int pivot = intArray[right];
int partitionPoint = partition(left, right, pivot);
quickSort(left, partitionPoint - 1);
quickSort(partitionPoint + 1, right);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
QuickSortExample sort = new QuickSortExample();
int max = sort.intArray.length;
System.out.println("Contents of the array :");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sort.intArray));
sort.quickSort(0, max - 1);
System.out.println("Contents of the array after sorting :");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sort.intArray));
}
}
輸出
Contents of the array : [4, 6, 3, 2, 1, 9, 7] Contents of the array after sorting : [1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 9]
def partition(arr, low, high):
i = low - 1
pivot = arr[high] # pivot element
for j in range(low, high):
if arr[j] <= pivot:
# increment
i = i + 1
arr[i], arr[j] = arr[j], arr[i]
arr[i + 1], arr[high] = arr[high], arr[i + 1]
return i + 1
def quickSort(arr, low, high):
if low < high:
pi = partition(arr, low, high)
quickSort(arr, low, pi - 1)
quickSort(arr, pi + 1, high)
arr = [2, 5, 3, 8, 6, 5, 4, 7]
n = len(arr)
print("Contents of the array: ")
for i in range(n):
print(arr[i], end=" ")
quickSort(arr, 0, n - 1)
print("\nContents of the array after sorting: ")
for i in range(n):
print(arr[i], end=" ")
輸出
Contents of the array: 2 5 3 8 6 5 4 7 Contents of the array after sorting: 2 3 4 5 5 6 7 8
廣告
