
- 資料結構與演算法
- DSA - 首頁
- DSA - 概述
- DSA - 環境設定
- DSA - 演算法基礎
- DSA - 漸近分析
- 資料結構
- DSA - 資料結構基礎
- DSA - 資料結構和型別
- DSA - 陣列資料結構
- 連結串列
- DSA - 連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 雙向連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 迴圈連結串列資料結構
- 棧與佇列
- DSA - 棧資料結構
- DSA - 表示式解析
- DSA - 佇列資料結構
- 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 線性搜尋演算法
- DSA - 二分搜尋演算法
- DSA - 插值搜尋
- DSA - 跳躍搜尋演算法
- DSA - 指數搜尋
- DSA - 斐波那契搜尋
- DSA - 子列表搜尋
- DSA - 雜湊表
- 排序演算法
- DSA - 排序演算法
- DSA - 氣泡排序演算法
- DSA - 插入排序演算法
- DSA - 選擇排序演算法
- DSA - 歸併排序演算法
- DSA - 希爾排序演算法
- DSA - 堆排序
- DSA - 桶排序演算法
- DSA - 計數排序演算法
- DSA - 基數排序演算法
- DSA - 快速排序演算法
- 圖資料結構
- DSA - 圖資料結構
- DSA - 深度優先遍歷
- DSA - 廣度優先遍歷
- DSA - 生成樹
- 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹遍歷
- DSA - 二叉搜尋樹
- DSA - AVL樹
- DSA - 紅黑樹
- DSA - B樹
- DSA - B+樹
- DSA - 伸展樹
- DSA - 字典樹
- DSA - 堆資料結構
- 遞迴
- DSA - 遞迴演算法
- DSA - 使用遞迴的漢諾塔
- DSA - 使用遞迴的斐波那契數列
- 分治法
- DSA - 分治法
- DSA - 最大最小問題
- DSA - Strassen矩陣乘法
- DSA - Karatsuba演算法
- 貪心演算法
- DSA - 貪心演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(貪心法)
- DSA - Prim最小生成樹
- DSA - Kruskal最小生成樹
- DSA - Dijkstra最短路徑演算法
- DSA - 地圖著色演算法
- DSA - 分數揹包問題
- DSA - 帶截止期限的作業排序
- DSA - 最優合併模式演算法
- 動態規劃
- DSA - 動態規劃
- DSA - 矩陣鏈乘法
- DSA - Floyd-Warshall演算法
- DSA - 0-1揹包問題
- DSA - 最長公共子序列演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(動態規劃法)
- 近似演算法
- DSA - 近似演算法
- DSA - 頂點覆蓋演算法
- DSA - 集合覆蓋問題
- DSA - 旅行商問題(近似演算法)
- 隨機化演算法
- DSA - 隨機化演算法
- DSA - 隨機化快速排序演算法
- DSA - Karger最小割演算法
- DSA - Fisher-Yates洗牌演算法
- DSA有用資源
- DSA - 問答
- DSA - 快速指南
- DSA - 有用資源
- DSA - 討論
跳躍搜尋演算法
跳躍搜尋演算法是對線性搜尋演算法略微修改的版本。該演算法的主要思想是透過比較比線性搜尋演算法更少的元素來減少時間複雜度。因此,輸入陣列被排序並分成塊,以便在跳過這些塊時執行搜尋。
例如,讓我們看看下面的例子;排序的輸入陣列在每個3個元素的塊中進行搜尋。所需的鍵僅在2次比較後找到,而不是線性搜尋的6次比較。
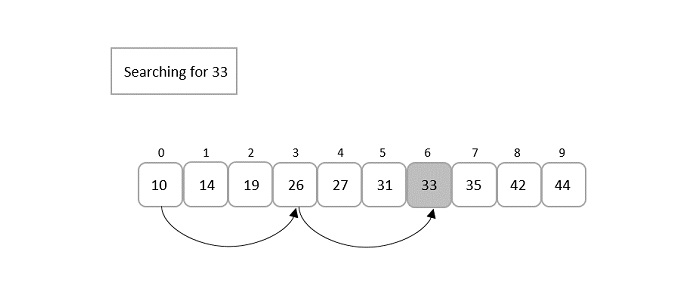
這裡出現了一個關於如何劃分這些塊的問題。為了回答這個問題,如果輸入陣列的大小為“n”,則塊被劃分為√n的區間。每個塊的第一個元素都與鍵元素進行比較,直到鍵元素的值小於塊元素。由於輸入已排序,因此僅對之前的塊執行線性搜尋。如果找到元素,則表示搜尋成功;否則,返回搜尋失敗。
本章將詳細討論跳躍搜尋演算法。
跳躍搜尋演算法
跳躍搜尋演算法將排序陣列作為輸入,該陣列被分成較小的塊以簡化搜尋。演算法如下:
步驟1 - 如果輸入陣列的大小為“n”,則塊的大小為√n。設定i = 0。
步驟2 - 將要搜尋的鍵與陣列的第i個元素進行比較。如果匹配,則返回元素的位置;否則,將i增加塊大小。
步驟3 - 重複步驟2,直到第i個元素大於鍵元素。
步驟4 - 現在,由於輸入陣列已排序,因此可以確定元素位於前一個塊中。因此,線性搜尋應用於該塊以查詢元素。
步驟5 - 如果找到元素,則返回其位置。如果未找到元素,則提示搜尋失敗。
虛擬碼
Begin
blockSize := √size
start := 0
end := blockSize
while array[end] <= key AND end < size do
start := end
end := end + blockSize
if end > size – 1 then
end := size
done
for i := start to end -1 do
if array[i] = key then
return i
done
return invalid location
End
分析
跳躍搜尋技術的時間複雜度為O(√n),空間複雜度為O(1)。
示例
讓我們透過從下面的排序陣列A中搜索元素66來理解跳躍搜尋演算法:

步驟1
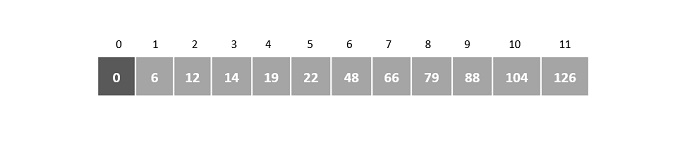
初始化 i = 0,輸入陣列大小 ‘n’ = 12
假設塊大小表示為 ‘m’。那麼,m = √n = √12 = 3
步驟2
將A[0]與鍵元素進行比較,並檢查是否匹配,
A[0] = 0 ≠ 66
因此,i 增加塊大小 3。現在與鍵元素比較的元素是 A[3]。
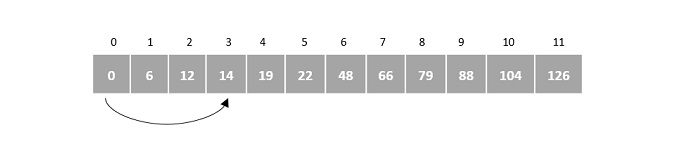
步驟3
A[3] = 14 ≠ 66
由於它不匹配,i 再次增加 3。
步驟4
A[6] = 48 ≠ 66
i 再次增加 3。將 A[9] 與鍵元素進行比較。

步驟5
A[9] = 88 ≠ 66
然而,88 大於 66,因此線性搜尋應用於當前塊。
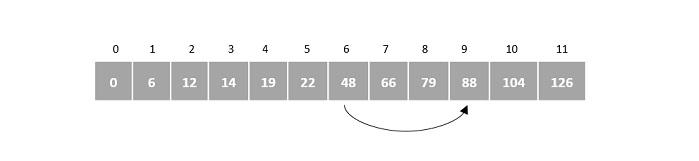
步驟6
應用線性搜尋後,指標從第6個索引增加到第7個。因此,將 A[7] 與鍵元素進行比較。
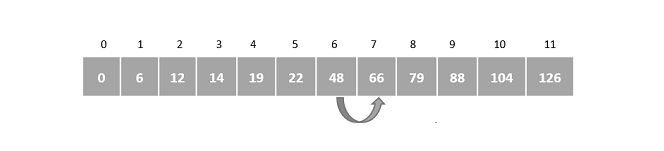
我們發現 A[7] 是所需元素,因此程式返回第7個索引作為輸出。
實現
跳躍搜尋演算法是線性搜尋的擴充套件變體。該演算法將輸入陣列劃分為多個較小的塊,並在假設包含該元素的單個塊上執行線性搜尋。如果在假設的塊中未找到該元素,則返回搜尋失敗。
輸出列印陣列中元素的位置而不是其索引。索引是指從 0 開始的陣列索引號,而位置是儲存元素的位置。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
int jump_search(int[], int, int);
int main(){
int i, n, key, index;
int arr[12] = {0, 6, 12, 14, 19, 22, 48, 66, 79, 88, 104, 126};
int len = sizeof(arr)/sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("Array elements are:");
for(int j = 0; j<len; j++){
printf(" %d", arr[j]);
}
n = 12;
key = 66;
printf("\nThe element to be searched: %d\n", key);
index = jump_search(arr, n, key);
if(index >= 0)
printf("The element is found at position %d", index+1);
else
printf("Unsuccessful Search");
return 0;
}
int jump_search(int arr[], int n, int key){
int i, j, m, k;
i = 0;
m = sqrt(n);
k = m;
while(arr[m] <= key && m < n) {
i = m;
m += k;
if(m > n - 1)
return -1;
}
// linear search on the block
for(j = i; j<m; j++) {
if(arr[j] == key)
return j;
}
return -1;
}
輸出
Array elements are: 0 6 12 14 19 22 48 66 79 88 104 126 The element to be searched: 66 The element is found at position 8
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int jump_search(int[], int, int);
int main(){
int i, n, key, index;
int arr[12] = {0, 6, 12, 14, 19, 22, 48, 66, 79, 88, 104, 126};
printf("Array elements are: ");
for (auto j : arr){
cout<<j<<" ";
}
n = 12;
key = 66;
cout<<"\nThe element to be searched: "<<key<<endl;
index = jump_search(arr, n, key);
if(index >= 0)
cout << "The element is found at position " << index+1;
else
cout << "Unsuccessful Search";
return 0;
}
int jump_search(int arr[], int n, int key){
int i, j, m, k;
i = 0;
m = sqrt(n);
k = m;
while(arr[m] <= key && m < n) {
i = m;
m += k;
if(m > n - 1)
return -1;
}
// linear search on the block
for(j = i; j<m; j++) {
if(arr[j] == key)
return j;
}
return -1;
}
輸出
Array elements are: 0 6 12 14 19 22 48 66 79 88 104 126 The element to be searched: 66 The element is found at position 8
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.lang.Math;
public class JumpSearch {
public static void main(String args[]) {
int i, n, key, index;
int arr[] = {0, 6, 12, 14, 19, 22, 48, 66, 79, 88, 104, 126};
System.out.println("Array elements are: ");
for(int j = 0; j<arr.length; j++){
System.out.print(arr[j] + " ");
}
n = 12;
key = 66;
System.out.println("\nThe element to be searched: "+ key);
index = jump_search(arr, n, key);
if(index >= 0)
System.out.print("The element is found at position " + (index+1));
else
System.out.print("Unsuccessful Search");
}
static int jump_search(int arr[], int n, int key) {
int i, j, m, k;
i = 0;
m = (int)Math.sqrt(n);
k = m;
while(arr[m] <= key && m < n) {
i = m;
m += k;
if(m > n - 1)
return -1;
}
// linear search on the block
for(j = i; j<m; j++) {
if(arr[j] == key)
return j;
}
return -1;
}
}
輸出
Array elements are: 0 6 12 14 19 22 48 66 79 88 104 126 The element to be searched: 66 The element is found at position 8
import math
def jump_search(a, n, key):
i = 0
m = int(math.sqrt(n))
k = m
while(a[m] <= key and m < n):
i = m
m += k
if(m > n - 1):
return -1
for j in range(m):
if(arr[j] == key):
return j
return -1
arr = [0, 6, 12, 14, 19, 22, 48, 66, 79, 88, 104, 126]
n = len(arr);
print("Array elements are: ")
for i in range(n):
print(arr[i], end = " ")
key = 66
print("\nThe element to be searched: ", key)
index = jump_search(arr, n, key)
if(index >= 0):
print("The element is found at position: ", (index+1))
else:
print("\nUnsuccessful Search")
輸出
Array elements are: 0 6 12 14 19 22 48 66 79 88 104 126 The element to be searched: 66 The element is found at position: 8
