
- 資料結構與演算法
- DSA - 首頁
- DSA - 概述
- DSA - 環境設定
- DSA - 演算法基礎
- DSA - 漸近分析
- 資料結構
- DSA - 資料結構基礎
- DSA - 資料結構和型別
- DSA - 陣列資料結構
- 連結串列
- DSA - 連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 雙向連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 迴圈連結串列資料結構
- 棧與佇列
- DSA - 棧資料結構
- DSA - 表示式解析
- DSA - 佇列資料結構
- 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 線性搜尋演算法
- DSA - 二分搜尋演算法
- DSA - 插值搜尋
- DSA - 跳躍搜尋演算法
- DSA - 指數搜尋
- DSA - 斐波那契搜尋
- DSA - 子列表搜尋
- DSA - 雜湊表
- 排序演算法
- DSA - 排序演算法
- DSA - 氣泡排序演算法
- DSA - 插入排序演算法
- DSA - 選擇排序演算法
- DSA - 歸併排序演算法
- DSA - 希爾排序演算法
- DSA - 堆排序
- DSA - 桶排序演算法
- DSA - 計數排序演算法
- DSA - 基數排序演算法
- DSA - 快速排序演算法
- 圖資料結構
- DSA - 圖資料結構
- DSA - 深度優先遍歷
- DSA - 廣度優先遍歷
- DSA - 生成樹
- 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹的遍歷
- DSA - 二叉搜尋樹
- DSA - AVL樹
- DSA - 紅黑樹
- DSA - B樹
- DSA - B+樹
- DSA - 伸展樹
- DSA - 字典樹 (Trie)
- DSA - 堆資料結構
- 遞迴
- DSA - 遞迴演算法
- DSA - 使用遞迴實現漢諾塔
- DSA - 使用遞迴實現斐波那契數列
- 分治法
- DSA - 分治法
- DSA - 最大最小問題
- DSA - Strassen矩陣乘法
- DSA - Karatsuba演算法
- 貪心演算法
- DSA - 貪心演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(貪心法)
- DSA - Prim最小生成樹
- DSA - Kruskal最小生成樹
- DSA - Dijkstra最短路徑演算法
- DSA - 地圖著色演算法
- DSA - 分數揹包問題
- DSA - 帶截止期限的作業排序
- DSA - 最優合併模式演算法
- 動態規劃
- DSA - 動態規劃
- DSA - 矩陣鏈乘法
- DSA - Floyd-Warshall演算法
- DSA - 0-1揹包問題
- DSA - 最長公共子序列演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(動態規劃法)
- 近似演算法
- DSA - 近似演算法
- DSA - 頂點覆蓋演算法
- DSA - 集合覆蓋問題
- DSA - 旅行商問題(近似演算法)
- 隨機化演算法
- DSA - 隨機化演算法
- DSA - 隨機化快速排序演算法
- DSA - Karger最小割演算法
- DSA - Fisher-Yates洗牌演算法
- DSA有用資源
- DSA - 問答
- DSA - 快速指南
- DSA - 有用資源
- DSA - 討論
集合覆蓋問題
集合覆蓋演算法為許多現實世界中的資源分配問題提供瞭解決方案。例如,考慮一家航空公司為每架飛機分配機組人員,以確保他們有足夠的人員來滿足旅程的要求。他們會考慮航班時間、持續時間、中途停留以及機組人員的可用性,以便將他們分配到航班。這就是集合覆蓋演算法發揮作用的地方。
給定一個包含一些元素的全集 U,所有這些元素都被分成子集。將這些子集的集合視為 S = {S1, S2, S3, S4... Sn},集合覆蓋演算法找到最少的子集數量,使得它們覆蓋全集中的所有元素。
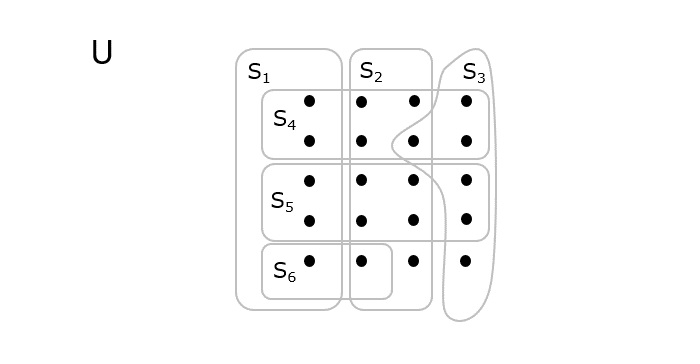
如上圖所示,點表示存在於全集 U 中的元素,這些元素被分成不同的集合 S = {S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6}。為了覆蓋所有元素,需要選擇的最小集合數將是最優輸出 = {S1, S2, S3}。
集合覆蓋演算法
集合覆蓋演算法將集合的集合作為輸入,並返回包含所有全集元素所需的最小集合數。
集合覆蓋問題是一個 NP-Hard 問題,並且是一個 2-逼近貪心演算法。
演算法
步驟 1 - 初始化 Output = {},其中 Output 表示輸出元素集。
步驟 2 - 當 Output 集不包含全集中的所有元素時,執行以下操作:
使用公式 $\frac{Cost\left ( S_{i} \right )}{S_{i}-Output}$ 查詢全集中的每個子集的成本效益。
找到每次迭代中成本效益最低的子集。將子集新增到 Output 集。
步驟 3 - 重複步驟 2,直到宇宙中沒有剩餘元素。達到的輸出是最終的 Output 集。
虛擬碼
APPROX-GREEDY-SET_COVER(X, S)
U = X
OUTPUT = ф
while U ≠ ф
select Si Є S which has maximum |Si∩U|
U = U – S
OUTPUT = OUTPUT∪ {Si}
return OUTPUT
分析
假設元素總數等於集合總數(|X| = |S|),則程式碼執行時間為 O(|X|3)
示例

讓我們來看一個更詳細地描述集合覆蓋問題近似演算法的例子
S1 = {1, 2, 3, 4} cost(S1) = 5
S2 = {2, 4, 5, 8, 10} cost(S2) = 10
S3 = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13} cost(S3) = 20
S4 = {4, 8, 12, 16, 20} cost(S4) = 12
S5 = {5, 6, 7, 8, 9} cost(S5) = 15
步驟 1
輸出集 Output = ф
找到輸出集中沒有元素時每個集合的成本效益,
S1 = cost(S1) / (S1 – Output) = 5 / (4 – 0) S2 = cost(S2) / (S2 – Output) = 10 / (5 – 0) S3 = cost(S3) / (S3 – Output) = 20 / (7 – 0) S4 = cost(S4) / (S4 – Output) = 12 / (5 – 0) S5 = cost(S5) / (S5 – Output) = 15 / (5 – 0)
本次迭代中,S1 的成本效益最低,因此,新增到輸出集的子集 Output = {S1},其元素為 {1, 2, 3, 4}。
步驟 2
找到輸出集中新元素的每個集合的成本效益,
S2 = cost(S2) / (S2 – Output) = 10 / (5 – 4) S3 = cost(S3) / (S3 – Output) = 20 / (7 – 4) S4 = cost(S4) / (S4 – Output) = 12 / (5 – 4) S5 = cost(S5) / (S5 – Output) = 15 / (5 – 4)
本次迭代中,S3 的成本效益最低,因此,新增到輸出集的子集 Output = {S1, S3},其元素為 {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13}。
步驟 3
找到輸出集中新元素的每個集合的成本效益,
S2 = cost(S2) / (S2 – Output) = 10 / |(5 – 9)| S4 = cost(S4) / (S4 – Output) = 12 / |(5 – 9)| S5 = cost(S5) / (S5 – Output) = 15 / |(5 – 9)|
本次迭代中,S2 的成本效益最低,因此,新增到輸出集的子集 Output = {S1, S3, S2},其元素為 {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13}。
步驟 4
找到輸出集中新元素的每個集合的成本效益,
S4 = cost(S4) / (S4 – Output) = 12 / |(5 – 11)| S5 = cost(S5) / (S5 – Output) = 15 / |(5 – 11)|
本次迭代中,S4 的成本效益最低,因此,新增到輸出集的子集 Output = {S1, S3, S2, S4},其元素為 {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 16, 20}。
步驟 5
找到輸出集中新元素的每個集合的成本效益,
S5 = cost(S5) / (S5 – Output) = 15 / |(5 – 14)|
本次迭代中,S5 的成本效益最低,因此,新增到輸出集的子集 Output = {S1, S3, S2, S4, S5},其元素為 {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 16, 20}。
最終覆蓋有限全集中的所有元素的輸出為 Output = {S1, S3, S2, S4, S5}。
實現
以下是上述方法在各種程式語言中的實現:
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX_SETS 100
#define MAX_ELEMENTS 1000
int setCover(int X[], int S[][MAX_ELEMENTS], int numSets, int numElements, int output[]) {
int U[MAX_ELEMENTS];
for (int i = 0; i < numElements; i++) {
U[i] = X[i];
}
int selectedSets[MAX_SETS];
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_SETS; i++) {
selectedSets[i] = 0; // Initialize all to 0 (not selected)
}
int outputIdx = 0;
while (outputIdx < numSets) { // Ensure we don't exceed the maximum number of sets
int maxIntersectionSize = 0;
int selectedSetIdx = -1;
// Find the set Si with the maximum intersection with U
for (int i = 0; i < numSets; i++) {
if (selectedSets[i] == 0) { // Check if the set is not already selected
int intersectionSize = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < numElements; j++) {
if (U[j] && S[i][j]) {
intersectionSize++;
}
}
if (intersectionSize > maxIntersectionSize) {
maxIntersectionSize = intersectionSize;
selectedSetIdx = i;
}
}
}
// If no set found, break from the loop
if (selectedSetIdx == -1) {
break;
}
// Mark the selected set as "selected" in the array
selectedSets[selectedSetIdx] = 1;
// Remove the elements covered by the selected set from U
for (int j = 0; j < numElements; j++) {
U[j] = U[j] - S[selectedSetIdx][j];
}
// Add the selected set to the output
output[outputIdx++] = selectedSetIdx;
}
return outputIdx;
}
int main() {
int X[MAX_ELEMENTS] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
int S[MAX_SETS][MAX_ELEMENTS] = {
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1}
};
int numSets = 5;
int numElements = 10;
int output[MAX_SETS];
int numSelectedSets = setCover(X, S, numSets, numElements, output);
printf("Selected Sets: ");
for (int i = 0; i < numSelectedSets; i++) {
printf("%d ", output[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return 0;
}
輸出
Selected Sets: 1 2 3 4 0
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_SETS 100
#define MAX_ELEMENTS 1000
// Function to find the set cover using the Approximate Greedy Set Cover algorithm
int setCover(int X[], int S[][MAX_ELEMENTS], int numSets, int numElements, int output[])
{
int U[MAX_ELEMENTS];
for (int i = 0; i < numElements; i++) {
U[i] = X[i];
}
int selectedSets[MAX_SETS];
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_SETS; i++) {
selectedSets[i] = 0; // Initialize all to 0 (not selected)
}
int outputIdx = 0;
while (outputIdx < numSets) { // Ensure we don't exceed the maximum number of sets
int maxIntersectionSize = 0;
int selectedSetIdx = -1;
// Find the set Si with maximum intersection with U
for (int i = 0; i < numSets; i++) {
if (selectedSets[i] == 0) { // Check if the set is not already selected
int intersectionSize = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < numElements; j++) {
if (U[j] && S[i][j]) {
intersectionSize++;
}
}
if (intersectionSize > maxIntersectionSize) {
maxIntersectionSize = intersectionSize;
selectedSetIdx = i;
}
}
}
// If no set found, break from the loop
if (selectedSetIdx == -1) {
break;
}
// Mark the selected set as "selected" in the array
selectedSets[selectedSetIdx] = 1;
// Remove the elements covered by the selected set from U
for (int j = 0; j < numElements; j++) {
U[j] = U[j] - S[selectedSetIdx][j];
}
// Add the selected set to the output
output[outputIdx++] = selectedSetIdx;
}
return outputIdx;
}
int main()
{
int X[MAX_ELEMENTS] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
int S[MAX_SETS][MAX_ELEMENTS] = {
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1}
};
int numSets = 5;
int numElements = 10;
int output[MAX_SETS];
int numSelectedSets = setCover(X, S, numSets, numElements, output);
cout << "Selected Sets: ";
for (int i = 0; i < numSelectedSets; i++) {
cout << output[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
輸出
Selected Sets: 1 2 3 4 0
import java.util.*;
public class SetCover {
public static List<Integer> setCover(int[] X, int[][] S) {
Set<Integer> U = new HashSet<>();
for (int x : X) {
U.add(x);
}
List<Integer> output = new ArrayList<>();
while (!U.isEmpty()) {
int maxIntersectionSize = 0;
int selectedSetIdx = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < S.length; i++) {
int intersectionSize = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < S[i].length; j++) {
if (U.contains(S[i][j])) {
intersectionSize++;
}
}
if (intersectionSize > maxIntersectionSize) {
maxIntersectionSize = intersectionSize;
selectedSetIdx = i;
}
}
if (selectedSetIdx == -1) {
break;
}
for (int j = 0; j < S[selectedSetIdx].length; j++) {
U.remove(S[selectedSetIdx][j]);
}
output.add(selectedSetIdx);
}
return output;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] X = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
int[][] S = {
{1, 2},
{2, 3, 4},
{4, 5, 6},
{6, 7, 8},
{8, 9, 10}
};
List<Integer> selectedSets = setCover(X, S);
System.out.print("Selected Sets: ");
for (int idx : selectedSets) {
System.out.print(idx + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
輸出
Selected Sets: 1 3 4 0 2
def set_cover(X, S):
U = set(X)
output = []
while U:
max_intersection_size = 0
selected_set_idx = -1
for i, s in enumerate(S):
intersection_size = len(U.intersection(s))
if intersection_size > max_intersection_size:
max_intersection_size = intersection_size
selected_set_idx = i
if selected_set_idx == -1:
break
U = U - set(S[selected_set_idx])
output.append(selected_set_idx)
return output
if __name__ == "__main__":
X = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
S = [
{1, 2},
{2, 3, 4},
{4, 5, 6},
{6, 7, 8},
{8, 9, 10}
]
selected_sets = set_cover(X, S)
print("Selected Sets:", selected_sets)
輸出
Selected Sets: 1 3 4 0 2
