
- 資料結構與演算法
- DSA - 首頁
- DSA - 概述
- DSA - 環境設定
- DSA - 演算法基礎
- DSA - 漸進分析
- 資料結構
- DSA - 資料結構基礎
- DSA - 資料結構和型別
- DSA - 陣列資料結構
- 連結串列
- DSA - 連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 雙向連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 迴圈連結串列資料結構
- 棧和佇列
- DSA - 棧資料結構
- DSA - 表示式解析
- DSA - 佇列資料結構
- 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 線性搜尋演算法
- DSA - 二分搜尋演算法
- DSA - 插值搜尋
- DSA - 跳躍搜尋演算法
- DSA - 指數搜尋
- DSA - 斐波那契搜尋
- DSA - 子列表搜尋
- DSA - 雜湊表
- 排序演算法
- DSA - 排序演算法
- DSA - 氣泡排序演算法
- DSA - 插入排序演算法
- DSA - 選擇排序演算法
- DSA - 歸併排序演算法
- DSA - 希爾排序演算法
- DSA - 堆排序
- DSA - 桶排序演算法
- DSA - 計數排序演算法
- DSA - 基數排序演算法
- DSA - 快速排序演算法
- 圖資料結構
- DSA - 圖資料結構
- DSA - 深度優先遍歷
- DSA - 廣度優先遍歷
- DSA - 生成樹
- 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹的遍歷
- DSA - 二叉搜尋樹
- DSA - AVL樹
- DSA - 紅黑樹
- DSA - B樹
- DSA - B+樹
- DSA - 伸展樹
- DSA - 字典樹
- DSA - 堆資料結構
- 遞迴
- DSA - 遞迴演算法
- DSA - 使用遞迴的漢諾塔
- DSA - 使用遞迴的斐波那契數列
- 分治法
- DSA - 分治法
- DSA - 最大-最小問題
- DSA - Strassen矩陣乘法
- DSA - Karatsuba演算法
- 貪心演算法
- DSA - 貪心演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(貪心法)
- DSA - Prim最小生成樹
- DSA - Kruskal最小生成樹
- DSA - Dijkstra最短路徑演算法
- DSA - 地圖著色演算法
- DSA - 分數揹包問題
- DSA - 帶截止日期的作業排序
- DSA - 最佳合併模式演算法
- 動態規劃
- DSA - 動態規劃
- DSA - 矩陣鏈乘法
- DSA - Floyd Warshall演算法
- DSA - 0-1揹包問題
- DSA - 最長公共子序列演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(動態規劃法)
- 近似演算法
- DSA - 近似演算法
- DSA - 頂點覆蓋演算法
- DSA - 集合覆蓋問題
- DSA - 旅行商問題(近似法)
- 隨機化演算法
- DSA - 隨機化演算法
- DSA - 隨機化快速排序演算法
- DSA - Karger最小割演算法
- DSA - Fisher-Yates洗牌演算法
- DSA有用資源
- DSA - 問答
- DSA - 快速指南
- DSA - 有用資源
- DSA - 討論
矩陣或網格資料結構
什麼是矩陣資料結構?
矩陣,也稱為網格,是一種特殊的二維陣列,其中元素按行和列排列。我們也可以說它是在另一個數組中巢狀的陣列。矩陣的每個元素都可以透過行和列索引來識別。
通常,矩陣資料結構用於儲存和操作二維結構,例如圖形、地圖、表格等。它還可以用於表示線性方程、變換、旋轉和其他數學概念。
矩陣的宣告和初始化
要宣告一個矩陣,我們只需要指定矩陣的資料型別和名稱,後跟兩個方括號。這些方括號指定矩陣的行和列。
在所有程式語言中,矩陣的宣告和初始化過程都非常相似。讓我們看看在各種程式語言中建立矩陣的語法:
data_type array_name[rows][cols] = {elements separated by commas};
在 Python 程式語言中,不需要指定資料型別:
array_name[rows][cols] = {elements separated by commas};
矩陣的必要性
矩陣在各個領域都非常有用,包括數學、計算機科學、圖形、機器人技術等等。全球各地的公司都以矩陣的形式儲存其使用者的資訊,這有助於進行推薦和目標營銷。
無論是我們最喜歡的電影還是遊戲,都是藉助矩陣計算構建的。許多科學創新和研究直接或間接地需要這些計算。
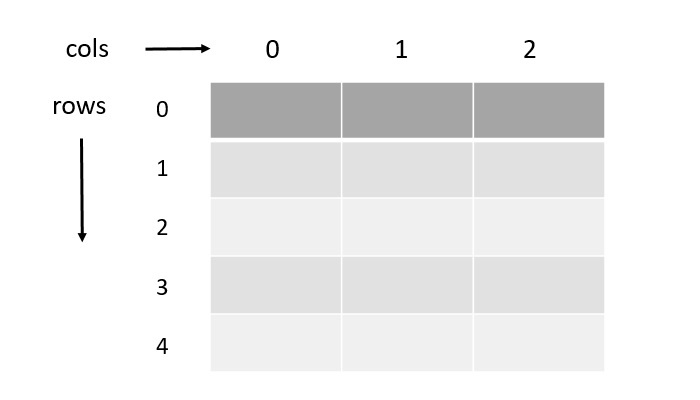
矩陣表示
我們可以將矩陣資料結構表示為一個表格,其中每個元素都儲存在一個單元格中。下圖說明了矩陣是如何表示的:
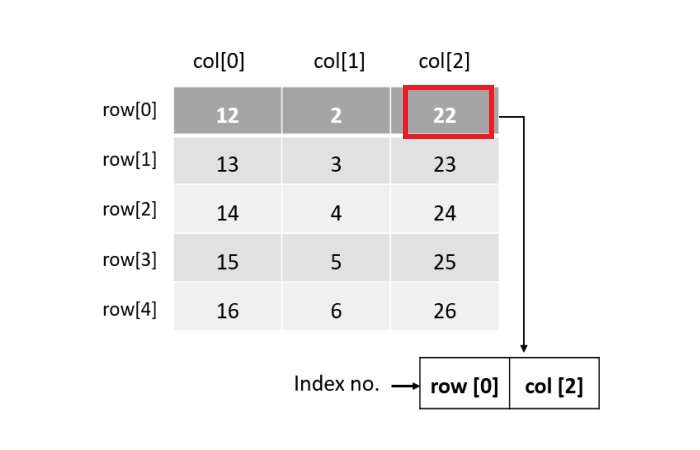

從上面的說明中,我們可以得出以下重要結論:
索引從 0 開始。
一個 5x3 維度的矩陣將有 15 個元素。
我們可以藉助其行和列索引訪問或定位任何元素。
矩陣的基本操作
我們可以透過對給定矩陣資料結構執行各種操作來操作它,例如旋轉、加法、乘法等等。
以下是可以在給定矩陣上執行的基本操作:
- 訪問 - 訪問矩陣的特定行或列。
- 搜尋 - 定位矩陣的特定元素。
- 排序 - 按特定順序排列矩陣元素。
- 插入 - 在指定的索引處新增一行。
- 刪除 - 從矩陣中刪除一行。
矩陣 - 訪問操作
在訪問操作中,我們列印特定行或列的元素。
演算法
以下是訪問矩陣元素的演算法:
1. Start 2. Declare and initialize a matrix. 3. Access the required row. 4. Print the result. 5. Stop
示例
在這裡,我們看到了訪問操作的實際實現,我們嘗試列印一行的元素:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
// declaration and initialization of a 3x3 matrix
int matrix[3][3] = {{1, 2, 1}, {4, 5, 4}, {7, 8, 7}};
// accessing the second row
int* rowScnd = matrix[1];
// loop to print the result
printf("Accessing a row: ");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
printf("%d ", rowScnd[i]);
}
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// declaration and initialization of a 3x3 matrix
int matrix[3][3] = {{1, 2, 1}, {4, 5, 4}, {7, 8, 7}};
// accessing the second row
int* rowScnd = matrix[1];
// loop to print the result
cout<< "Accessing a row: ";
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
cout << rowScnd[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// declaration and initialization of a 3x3 matrix
int matrix[][] = {{1, 2, 1}, {4, 5, 4}, {7, 8, 7}};
// accessing the second row
int rowScnd[] = matrix[1];
// printing the result
System.out.println("Accessing a row: " + Arrays.toString(rowScnd));
}
}
# declaration and initialization of a 3x3 matrix
matrix = [[1, 2, 1], [4, 5, 4], [7, 8, 7]]
# accessing the second row
rowScnd = matrix[1]
# printing the result
print("Accessing a row:" )
print(rowScnd)
輸出
Accessing a row: 4 5 4
矩陣 - 搜尋操作
要搜尋給定矩陣中指定的元素,我們需要遍歷每一行和每一列,並將元素與我們要查詢的值進行比較。
演算法
以下演算法演示瞭如何在給定矩陣中搜索元素:
1. Start 2. Declare and initialize a matrix. 3. Define the target element. 4. Use a for loop to search elements in the row. 5. Define another for loop to search elements in the column. 6. If found return the indices, otherwise return [-1, -1]. 7. Stop
示例
讓我們看看在各種程式語言中搜索操作的實際示例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
// Function to search element
int* srchmatrix(int matrix[3][3], int target) {
// array to hold the result
static int indX[2];
// Looping through each row
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
// Looping through each column
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
// Comparing the element with the targeted element
if (matrix[i][j] == target) {
// to return the row and column indices
int* indX = malloc(2 * sizeof(int));
indX[0] = i;
indX[1] = j;
return indX;
}
}
}
// return negative value if element not found
indX[0] = -1;
indX[1] = -1;
return indX;
}
int main() {
// declaration and initialization of a 3x3 matrix
int matrix[3][3] = {{1, 2, 1}, {4, 5, 4}, {7, 8, 7}};
// calling the function
int* indX = srchmatrix(matrix, 5);
// to print the result
printf("The specified element is at index: [%d, %d]\n", indX[0], indX[1]);
free(indX);
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Function to search element
int* srchmatrix(int matrix[3][3], int targtElem) {
// array to hold the result
static int indX[2];
// Looping through each row
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
// Looping through each column
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
// Comparing the element with the targeted element
if (matrix[i][j] == targtElem) {
// to return the row and column indices
indX[0] = i;
indX[1] = j;
return indX;
}
}
}
// return negative value if element not found
indX[0] = -1;
indX[1] = -1;
return indX;
}
int main() {
// declaration and initialization of a 3x3 matrix
int matrix[3][3] = {{1, 2, 1}, {4, 5, 4}, {7, 8, 7}};
// calling the function
int* indX = srchmatrix(matrix, 5);
// to print the result
cout << "The specified element is at index: [" << indX[0] << ", " << indX[1] << "]" << endl;
return 0;
}
public class Main {
// method to search element
public static int[] srchmatrix(int[][] matrix, int targtElem) {
// Looping through each row
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
// Looping through each column
for (int j = 0; j < matrix[i].length; j++) {
// Comparing the element with the desired element
if (matrix[i][j] == targtElem) {
// to return the row and column indices
return new int[]{i, j};
}
}
}
// return negative value if element not found
return new int[]{-1, -1};
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// declaration and initialization of a 3x3 matrix
int[][] matrix = {{1, 2, 1}, {4, 5, 4}, {7, 8, 7}};
// desired element we are looking for
int targtElem = 5;
// calling the method
int[] indX = srchmatrix(matrix, targtElem);
// printing the result
System.out.println("The specified element is at index: [" + indX[0] + ", " + indX[1] + "]");
}
}
# declaration and initialization of a 3x3 matrix
matrix = [[1, 2, 1], [4, 5, 4], [7, 8, 7]]
# method to search element
def searchMatrix(matrix, targtElem):
# Looping through each row
for i in range(len(matrix)):
# Looping through each column
for j in range(len(matrix[i])):
# Comparing the element with the desired element
if matrix[i][j] == targtElem:
# to return the row and column indices
return (i, j)
# Return negative value if element not found
return (-1, -1)
# desired element we are looking for
targtElem = 5
# calling the method
indX = searchMatrix(matrix, targtElem)
# printing the result
print(f"The specified element is at index: {indX}")
輸出
The specified element is at index: [1, 1]
矩陣 - 排序操作
在排序操作中,我們按指定的順序(例如升序或降序)排列給定矩陣的元素。
演算法
按升序排列矩陣元素的演算法如下:
1. Start 2. Declare and initialize a matrix. 3. Compare and sort each element of the specified row. 4. Print the result. 5. Stop
示例
在以下示例中,我們看到了排序操作的實際實現:
#include <stdio.h>
// function to sort the array
void araySort(int mat[], int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n-1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n-i-1; j++) {
if (mat[j] > mat[j+1]) {
// swapping mat[j] and mat[j+1]
int temp = mat[j];
mat[j] = mat[j+1];
mat[j+1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
// declaration and initialization of 3x4 matrix
int matrix[3][4] = {{12, 10, 7, 36}, {20, 9, 8, 4}, {15, 73, 83, 13}};
// Sorting the first row
araySort(matrix[0], 4);
// Printing the result
printf("The matrix after sorting first row: \n");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
printf("%d ", matrix[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// declaration and initialization of 3x4 matrix
int matrix[3][4] = {{12, 10, 7, 36}, {20, 9, 8, 4}, {15, 73, 83, 13}};
// Sorting the first row
sort(matrix[0], matrix[0] + 4);
// Printing the result
cout << "The matrix after sorting first row: " << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
cout << matrix[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
public static void main(String []args) {
// declaration and initialization of 3x4 matrix
int[][] matrix = {{12, 10, 7, 36}, {20, 9, 8, 4}, {15, 73, 83, 13}};
// Sorting the first row
Arrays.sort(matrix[0]);
// Printing the result
System.out.println("The matrix after sorting first row: " );
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < matrix[i].length; j++) {
System.out.print(matrix[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
# declaration and initialization of 3x4 matrix
matrix = [[12, 10, 7, 36], [20, 9, 8, 4], [15, 73, 83, 13]]
# Sorting the first row
matrix[0].sort()
# Printing the result
print("The matrix after sorting first row: ")
for row in matrix:
print(' '.join(map(str, row)))
輸出
The matrix after sorting first row: 7 10 12 36 20 9 8 4 15 73 83 13
矩陣 - 插入操作
在插入操作中,我們在矩陣的指定位置插入一行。
演算法
以下是將一行插入給定矩陣的第二個位置的演算法:
1. Start 2. Declare and initialize a matrix. 3. Define another matrix. 4. Copy the first row of original matrix to new matrix. 5. Insert the required row at second index. 6. Copy the remaining rows. 7. Print the result. 8. Stop
示例
下面的示例在不同的程式語言中實際說明了插入操作:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
// The original matrix
int matrix[2][3] = {{19, 14, 21}, {22, 91, 81}};
// Create a new matrix with an extra row
int newmatrix[3][3];
// Copy the first row of the original matrix to the new matrix
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
newmatrix[0][j] = matrix[0][j];
}
// Adding second row to the new matrix
int newRow[3] = {53, 63, 73};
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
newmatrix[1][j] = newRow[j];
}
// Copying the remaining rows of the original matrix to the new matrix
for (int i = 2; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
newmatrix[i][j] = matrix[i - 1][j];
}
}
// Printing the new matrix
printf("The new Matrix after adding a row: \n");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
printf("%d ", newmatrix[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main() {
// The original matrix
int matrix[2][3] = {{19, 14, 21}, {22, 91, 81}};
// Create a new matrix with an extra row
int newmatrix[3][3];
// Copy the first row of the original matrix to the new matrix
copy(begin(matrix[0]), end(matrix[0]), begin(newmatrix[0]));
// Adding second row to the new matrix
int newRow[3] = {53, 63, 73};
copy(begin(newRow), end(newRow), begin(newmatrix[1]));
// Copying the remaining rows of the original matrix to the new matrix
copy(begin(matrix[1]), end(matrix[1]), begin(newmatrix[2]));
// Printing the new matrix
cout << "The new Matrix after adding a row: " << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
cout << newmatrix[i][j] << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
}
return 0;
}
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// the original matrix
int[][] matrix = {{19, 14, 21}, {22, 91, 81}};
// Create a new matrix with an extra row
int[][] newmatrix = new int[matrix.length + 1][matrix[0].length];
// Copy the first row of the original matrix to the new matrix
for (int j = 0; j < matrix[0].length; j++) {
newmatrix[0][j] = matrix[0][j];
}
// adding second row to the new matrix
int[] newRow = {53, 63, 73};
for (int j = 0; j < newRow.length; j++) {
newmatrix[1][j] = newRow[j];
}
// Copying the remaining rows of the original matrix to the new matrix
for (int i = 2; i < newmatrix.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < matrix[0].length; j++) {
newmatrix[i][j] = matrix[i - 1][j];
}
}
// Printing the new matrix
System.out.println("The new Matrix after adding a row: ");
for (int i = 0; i < newmatrix.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < newmatrix[0].length; j++) {
System.out.print(newmatrix[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
# The original matrix
matrix = [[19, 14, 21], [22, 91, 81]]
# Create a new matrix with an extra row
newmatrix = matrix.copy()
# Adding second row to the new matrix
newRow = [53, 63, 73]
newmatrix.insert(1, newRow)
# Printing the new matrix
print("The new Matrix after adding a row: ")
for row in newmatrix:
print(' '.join(map(str, row)))
輸出
The new Matrix after adding a row: 19 14 21 53 63 73 22 91 81
矩陣 - 刪除操作
刪除操作從矩陣中刪除特定行。
演算法
以下是對給定矩陣執行刪除操作的演算法:
1. Start 2. Declare and initialize a matrix. 3. Define another matrix. 4. Copy all elements except the row to be deleted. 5. Print the new matrix. 6. Stop
示例
在這裡,我們看到了刪除操作的實際實現:
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to delete a row from the matrix
void deleteRow(int mat[3][3], int rowIndex, int rows, int cols) {
// Create a new matrix with one less row
int newMat[2][3];
// Copy the elements except the row to be deleted
int newRow = 0;
// Loop through the rows of original matrix
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
// Skip the row to be deleted
if (i != rowIndex) {
// Loop through the cols of original matrix
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
// Copy the element from mat to newMat
newMat[newRow][j] = mat[i][j];
}
newRow++; // Increment the row index
}
}
// Print the new matrix
printf("The new Matrix after deleting a row: \n");
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
printf("%d ", newMat[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int main() {
// The original matrix
int matrix[3][3] = {{19, 14, 21}, {53, 63, 73}, {22, 91, 81}};
// Delete the first row
deleteRow(matrix, 0, 3, 3);
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// Function to delete a row from the matrix
void deleteRow(int mat[3][3], int rowIndex, int rows, int cols) {
// Create a new matrix with one less row
int newMat[2][3];
// Copy the elements except the row to be deleted
int newRow = 0;
// Loop through the rows of original matrix
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
// Skip the row to be deleted
if (i != rowIndex) {
// Loop through the cols of original matrix
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
// Copy the element from mat to newMat
newMat[newRow][j] = mat[i][j];
}
newRow++; // Increment the row index
}
}
// Print the new matrix
cout << "The new Matrix after deleting a row: \n";
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
cout << newMat[i][j] << ' ';
}
cout << '\n';
}
}
int main() {
// The original matrix
int matrix[3][3] = {{19, 14, 21}, {53, 63, 73}, {22, 91, 81}};
// Delete the first row
deleteRow(matrix, 0, 3, 3);
return 0;
}
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
// method to delete row
public static int[][] deleteRow(int[][] mat, int rowIndex) {
// get the number of rows and columns
int rows = mat.length;
int cols = mat[0].length;
// create a new matrix with one less row
int[][] newMat = new int[rows - 1][cols];
// copy the elements except the row to be deleted
int newRow = 0;
// loop through the rows of original matrix
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
// skip the row to be deleted
if (i != rowIndex) {
// loop through the cols of original matrix
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
// copy the element from mat to newMat
newMat[newRow][j] = mat[i][j];
}
newRow++; // increment the row index
}
}
// return the new matrix
return newMat;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// the original matrix
int[][] matrix = {{19, 14, 21}, {53, 63, 73}, {22, 91, 81}};
// delete the first row
int[][] newmatrix = deleteRow(matrix, 0);
// Printing the new matrix
System.out.println("The new Matrix after deleting a row: ");
for (int i = 0; i < newmatrix.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < newmatrix[0].length; j++) {
System.out.print(newmatrix[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
# The original matrix
matrix = [[19, 14, 21], [53, 63, 73], [22, 91, 81]]
# Delete the first row
newmatrix = matrix[1:]
# Printing the new matrix
print("The new Matrix after deleting a row: ")
for row in newmatrix:
print(' '.join(map(str, row)))
輸出
The new Matrix after deleting a row: 53 63 73 22 91 81