
- 資料結構與演算法
- DSA - 首頁
- DSA - 概述
- DSA - 環境搭建
- DSA - 演算法基礎
- DSA - 漸進分析
- 資料結構
- DSA - 資料結構基礎
- DSA - 資料結構和型別
- DSA - 陣列資料結構
- 連結串列
- DSA - 連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 雙向連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 迴圈連結串列資料結構
- 棧與佇列
- DSA - 棧資料結構
- DSA - 表示式解析
- DSA - 佇列資料結構
- 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 線性搜尋演算法
- DSA - 二分搜尋演算法
- DSA - 插值搜尋
- DSA - 跳躍搜尋演算法
- DSA - 指數搜尋
- DSA - 斐波那契搜尋
- DSA - 子列表搜尋
- DSA - 雜湊表
- 排序演算法
- DSA - 排序演算法
- DSA - 氣泡排序演算法
- DSA - 插入排序演算法
- DSA - 選擇排序演算法
- DSA - 歸併排序演算法
- DSA - 希爾排序演算法
- DSA - 堆排序
- DSA - 桶排序演算法
- DSA - 計數排序演算法
- DSA - 基數排序演算法
- DSA - 快速排序演算法
- 圖資料結構
- DSA - 圖資料結構
- DSA - 深度優先遍歷
- DSA - 廣度優先遍歷
- DSA - 生成樹
- 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹的遍歷
- DSA - 二叉搜尋樹
- DSA - AVL樹
- DSA - 紅黑樹
- DSA - B樹
- DSA - B+樹
- DSA - 伸展樹
- DSA - Trie樹
- DSA - 堆資料結構
- 遞迴
- DSA - 遞迴演算法
- DSA - 使用遞迴實現漢諾塔
- DSA - 使用遞迴實現斐波那契數列
- 分治法
- DSA - 分治法
- DSA - 最大最小值問題
- DSA - Strassen矩陣乘法
- DSA - Karatsuba演算法
- 貪心演算法
- DSA - 貪心演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(貪心法)
- DSA - Prim最小生成樹
- DSA - Kruskal最小生成樹
- DSA - Dijkstra最短路徑演算法
- DSA - 地圖著色演算法
- DSA - 分數揹包問題
- DSA - 帶截止日期的作業排序
- DSA - 最優合併模式演算法
- 動態規劃
- DSA - 動態規劃
- DSA - 矩陣鏈乘法
- DSA - Floyd-Warshall演算法
- DSA - 0-1揹包問題
- DSA - 最長公共子序列演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(動態規劃法)
- 近似演算法
- DSA - 近似演算法
- DSA - 頂點覆蓋演算法
- DSA - 集合覆蓋問題
- DSA - 旅行商問題(近似演算法)
- 隨機化演算法
- DSA - 隨機化演算法
- DSA - 隨機化快速排序演算法
- DSA - Karger最小割演算法
- DSA - Fisher-Yates洗牌演算法
- DSA有用資源
- DSA - 問答
- DSA - 快速指南
- DSA - 有用資源
- DSA - 討論
DSA - 位運算演算法
位運算演算法介紹
位運算演算法是指控制資料個體位操作的演算法。這些演算法主要用於提高運算速度和記憶體效率,尤其是在處理大型資料集時。
什麼是位?
計算機無法理解人類語言,需要使用位編碼的資料。這裡,位是計算機中最小的資訊單位。它由二進位制數字表示,只有兩個值,即0和1。它的其他表示形式為是或否,真或假,以及開或關。
位操作(運算子)
位操作是一種技術,它涉及對資料的個體位執行低階操作,例如加密、切換、移位或遮蔽它們。對位執行的操作稱為位運算。此操作需要一個或兩個運算元,它們首先被轉換為二進位制,然後將運算子應用於每對相應的位。此操作的結果也是一個二進位制數。
位操作可用於各種目的,例如:
它可用於實現需要直接訪問資料二進位制表示的低階演算法或資料結構,例如加密、壓縮、雜湊或密碼學。
它可以透過減少執行給定任務(例如算術、邏輯或位計數)所需的指令或位元組數來最佳化效能或記憶體使用。
位操作還用於操作使用特定位來控制裝置行為或狀態的硬體暫存器或裝置驅動程式。
為了執行位操作,我們使用各種位運算子。它們解釋如下:
按位與運算子 (&)
單個“與”符號(&)表示按位與運算子。它接受兩個運算元,如果兩個位都是1,則返回1,否則返回0。
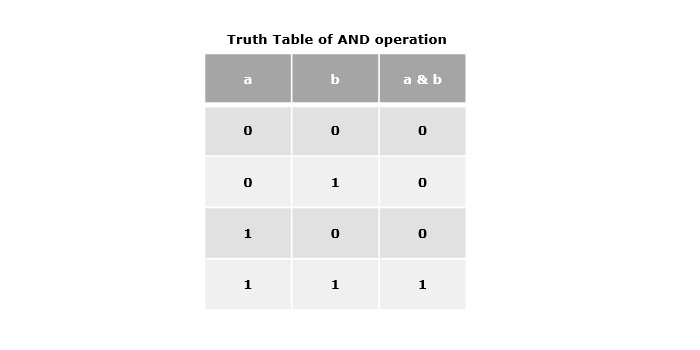
示例
在以下示例中,我們將說明各種程式語言中的與運算。
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int valOne = 8;
int valTwo = 9;
int output = valOne & valTwo;
printf("Result of AND operation: %d\n", output);
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int valOne = 8;
int valTwo = 9;
int output = valOne & valTwo;
cout << "Result of AND operation: " << output << endl;
return 0;
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int valOne = 8;
int valTwo = 9;
int output = valOne & valTwo;
System.out.println("Result of AND operation: " + output);
}
}
valOne = 8
valTwo = 9
output = valOne & valTwo
print("Result of AND operation:", output)
輸出
Result of AND operation: 8
按位或運算子 (|)
單個管道符號(|)表示按位或運算子。它接受兩個運算元作為引數值,如果任一位為1,則返回1,否則返回0。
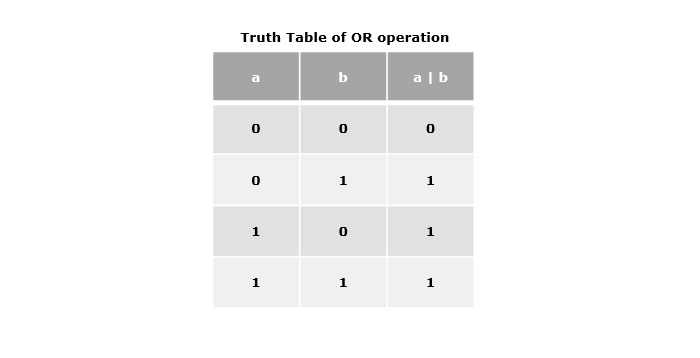
示例
以下示例演示了不同程式語言中按位或運算子的工作原理。
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int valOne = 8;
int valTwo = 9;
int output = valOne | valTwo;
printf("Result of OR operation: %d\n", output);
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int valOne = 8;
int valTwo = 9;
int output = valOne | valTwo;
cout << "Result of OR operation: " << output << endl;
return 0;
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int valOne = 8;
int valTwo = 9;
int output = valOne | valTwo;
System.out.println("Result of OR operation: " + output);
}
}
valOne = 8
valTwo = 9
output = valOne | valTwo
print("Result of OR operation:", output)
輸出
Result of OR operation: 9
按位異或運算子 (^)
按位異或運算子由插入符號(^)表示。它也接受兩個運算元,如果位不同,則返回1,否則返回0。
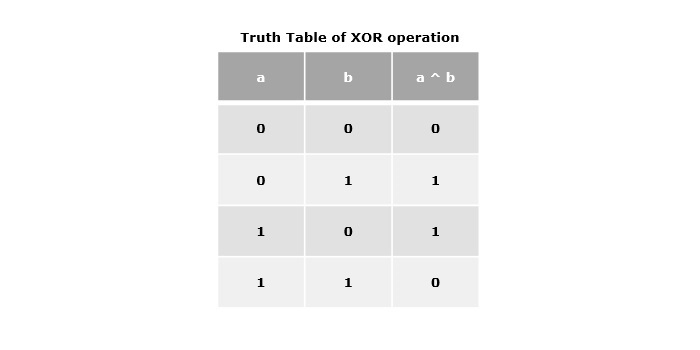
示例
以下示例顯示了按位異或運算子的工作原理。
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int valOne = 8;
int valTwo = 9;
int output = valOne ^ valTwo;
printf("Result of XOR operation: %d\n", output);
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int valOne = 8;
int valTwo = 9;
int output = valOne ^ valTwo;
cout << "Result of XOR operation: " << output << endl;
return 0;
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int valOne = 8;
int valTwo = 9;
int output = valOne ^ valTwo;
System.out.println("Result of XOR operation: " + output);
}
}
valOne = 8
valTwo = 9
output = valOne ^ valTwo
print("Result of XOR operation:", output)
輸出
Result of XOR operation: 1
按位非運算子 (~)
按位非運算子由單個波浪號(~)表示。它接受1或0作為運算元,並返回該運算元的補碼,這意味著它將每個位從0翻轉到1,從1翻轉到0。
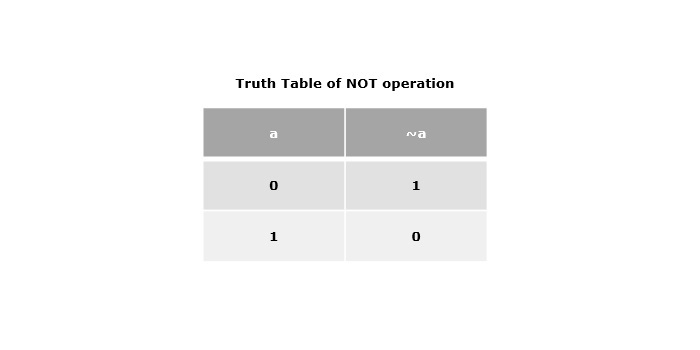
示例
以下示例說明了各種程式語言中非運算子的工作原理。
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int value = 0;
int output = ~value;
printf("Result of NOT operation: %d\n", output);
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int value = 0;
int output = ~value;
cout << "Result of NOT operation: " << output << endl;
return 0;
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int value = 0;
int output = ~value;
System.out.println("Result of NOT operation: " + output);
}
}
value = 0
output = ~value
print("Result of NOT operation:", output)
輸出
Result of NOT operation: -1
左移運算子 (<<)
雙左箭頭符號(<<)表示左移運算子。它用於將運算元的指定位向左移動給定數量的位置。它用零填充空缺的位。
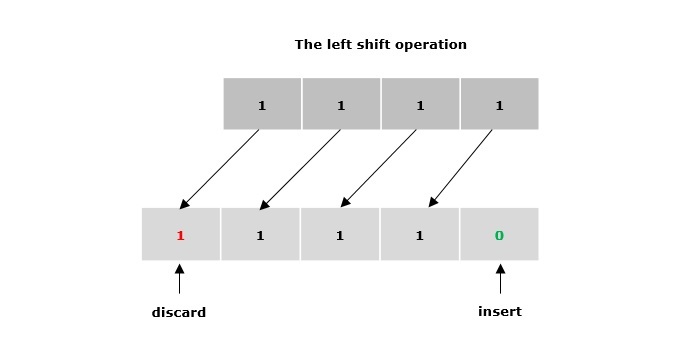
示例
在以下示例中,我們將說明各種程式語言中的左移操作。
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int value = 11;
// int to binary conversion
char newVal[5];
for(int i = 3; i >= 0; i--) {
newVal[3-i] = ((value >> i) & 1) ? '1' : '0';
}
newVal[4] = '\0';
int output = value << 2;
printf("Binary representation of value: %s\n", newVal);
printf("Result of Left-Shift operation: %d\n", output);
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int value = 11;
// int to binary conversion
string newVal = bitset<4>(value).to_string();
int output = value << 2;
cout << "Binary representation of value: " << newVal << endl;
cout << "Result of Left-Shift operation: " << output << endl;
return 0;
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int value = 11;
// int to binary conversion
String newVal = Integer.toBinaryString(value);
int output = value << 2;
System.out.println("Binary representation of value: " + newVal);
System.out.println("Result of Left-Shift operation: " + output);
}
}
value = 11
# int to binary conversion
newVal = format(value, '04b')
output = value << 2
print("Binary representation of value:", newVal)
print("Result of Left-Shift operation:", output)
輸出
Binary representation of value: 1011 Result of Left-Shift operation: 44
右移運算子 (>>)
雙右箭頭符號(>>)表示右移運算子。它用於將運算元的指定位向右移動給定數量的位置。它用零或符號位填充空缺的位(取決於運算元是有符號的還是無符號的)。
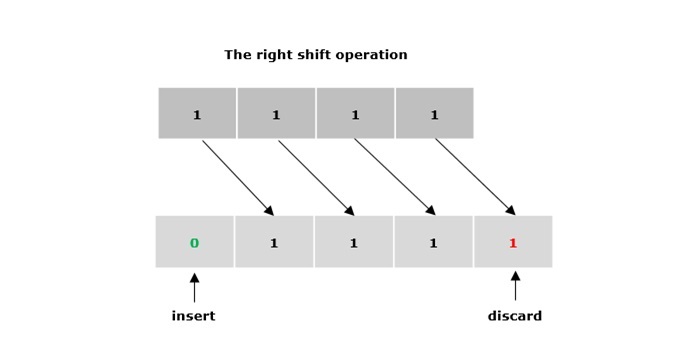
示例
以下示例演示了各種程式語言中右移操作的工作原理。
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int value = 11;
// int to binary conversion
char newVal[5];
for(int i = 3; i >= 0; i--) {
newVal[3-i] = ((value >> i) & 1) ? '1' : '0';
}
newVal[4] = '\0';
int output = value >> 2;
printf("Binary representation of value: %s\n", newVal);
printf("Result of Right-Shift operation: %d\n", output);
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <bitset>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int value = 11;
// int to binary conversion
string newVal = bitset<4>(value).to_string();
int output = value >> 2;
cout << "Binary representation of value: " << newVal << endl;
cout << "Result of Right-Shift operation: " << output << endl;
return 0;
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int value = 11;
// int to binary conversion
String newVal = Integer.toBinaryString(value);
int output = value >> 2;
System.out.println("Binary representation of value: " + newVal);
System.out.println("Result of Right-Shift operation: " + output);
}
}
value = 11
# int to binary conversion
newVal = format(value, '04b')
output = value >> 2
print("Binary representation of value:", newVal)
print("Result of Right-Shift operation:", output)
輸出
Binary representation of value: 1011 Result of Right-Shift operation: 2