
- 資料結構與演算法
- DSA - 首頁
- DSA - 概述
- DSA - 環境搭建
- DSA - 演算法基礎
- DSA - 漸近分析
- 資料結構
- DSA - 資料結構基礎
- DSA - 資料結構和型別
- DSA - 陣列資料結構
- 連結串列
- DSA - 連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 雙向連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 迴圈連結串列資料結構
- 棧與佇列
- DSA - 棧資料結構
- DSA - 表示式解析
- DSA - 佇列資料結構
- 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 線性搜尋演算法
- DSA - 二分搜尋演算法
- DSA - 插值搜尋
- DSA - 跳躍搜尋演算法
- DSA - 指數搜尋
- DSA - 斐波那契搜尋
- DSA - 子列表搜尋
- DSA - 雜湊表
- 排序演算法
- DSA - 排序演算法
- DSA - 氣泡排序演算法
- DSA - 插入排序演算法
- DSA - 選擇排序演算法
- DSA - 歸併排序演算法
- DSA - 希爾排序演算法
- DSA - 堆排序
- DSA - 桶排序演算法
- DSA - 計數排序演算法
- DSA - 基數排序演算法
- DSA - 快速排序演算法
- 圖資料結構
- DSA - 圖資料結構
- DSA - 深度優先遍歷
- DSA - 廣度優先遍歷
- DSA - 生成樹
- 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹的遍歷
- DSA - 二叉搜尋樹
- DSA - AVL樹
- DSA - 紅黑樹
- DSA - B樹
- DSA - B+樹
- DSA - 伸展樹
- DSA - Trie樹
- DSA - 堆資料結構
- 遞迴
- DSA - 遞迴演算法
- DSA - 使用遞迴實現漢諾塔
- DSA - 使用遞迴實現斐波那契數列
- 分治法
- DSA - 分治法
- DSA - 最大-最小問題
- DSA - Strassen矩陣乘法
- DSA - Karatsuba演算法
- 貪心演算法
- DSA - 貪心演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(貪心法)
- DSA - Prim最小生成樹
- DSA - Kruskal最小生成樹
- DSA - Dijkstra最短路徑演算法
- DSA - 地圖著色演算法
- DSA - 分數揹包問題
- DSA - 帶截止時間的作業排序
- DSA - 最優合併模式演算法
- 動態規劃
- DSA - 動態規劃
- DSA - 矩陣鏈乘法
- DSA - Floyd-Warshall演算法
- DSA - 0-1揹包問題
- DSA - 最長公共子序列演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(動態規劃法)
- 近似演算法
- DSA - 近似演算法
- DSA - 頂點覆蓋演算法
- DSA - 集合覆蓋問題
- DSA - 旅行商問題(近似演算法)
- 隨機化演算法
- DSA - 隨機化演算法
- DSA - 隨機化快速排序演算法
- DSA - Karger最小割演算法
- DSA - Fisher-Yates洗牌演算法
- DSA有用資源
- DSA - 問答
- DSA - 快速指南
- DSA - 有用資源
- DSA - 討論
Boyer-Moore 演算法
用於模式匹配的Boyer-Moore演算法
Boyer-Moore演算法用於確定給定模式是否存在於指定文字中。它採用了一種反向的模式搜尋/匹配方法。在一個給定字串中搜索特定模式的任務被稱為模式搜尋問題。例如,如果文字是“THIS IS A SAMPLE TEXT”,模式是“TEXT”,則輸出應為10,這是模式在給定文字中第一次出現的索引。
該演算法由Robert Boyer和J Strother Moore於1977年開發。它被認為是最有效和最廣泛使用的模式匹配演算法。
Boyer-Moore演算法是如何工作的?
在前面的章節中,我們已經看到了解決這個問題的簡單方法,它涉及到逐個滑動模式覆蓋文字,並比較每個字元。然而,這種方法非常慢,因為它需要O(n*m)時間,其中'n'是文字的長度,'m'是模式的長度。Boyer-Moore演算法透過預處理模式並使用兩種啟發式方法來跳過一些不可能匹配的比較來改進這一點。
這兩種啟發式方法如下:
壞字元啟發式 - 此啟發式方法使用一個表來儲存模式中每個字元的最後出現位置。當文字中某個字元(壞字元)發生不匹配時,演算法會檢查此字元是否出現在模式中。如果出現,則它會移動模式,使模式中該字元的最後出現位置與文字中的壞字元對齊。如果沒有,則它會將模式移過壞字元。
好字尾啟發式 - 此啟發式方法使用另一個表來儲存當壞字元啟發式方法失敗時的移位資訊。在這種情況下,我們會在模式內查詢,直到壞字元變成文字的好字尾。然後我們繼續移動以查詢給定的模式。
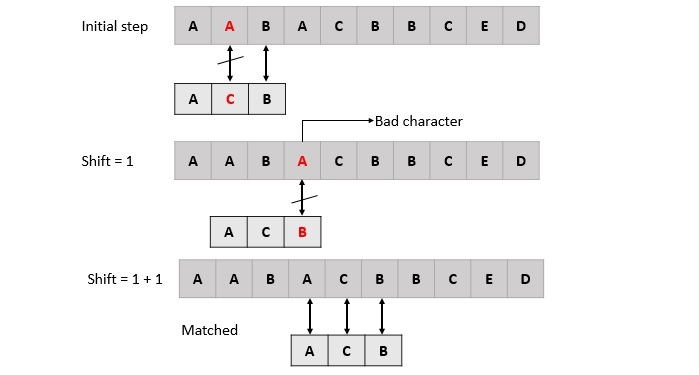
Boyer-Moore演算法透過在每一步選擇它們建議的最大位移來組合這兩種啟發式方法。在這個過程中,子串或模式是從模式的最後一個字元開始搜尋的。當主字串的子串與模式的子串匹配時,它會移動以查詢匹配子串的其他出現位置。如果發生不匹配,它會應用啟發式方法並相應地移動模式。當找到完全匹配或到達文字末尾時,演算法停止。
Boyer-Moore演算法的最壞情況時間複雜度為O(nm),但是,它的效能可能遠高於此。事實上,在某些情況下,它可以達到O(n/m)的亞線性時間複雜度,這意味著它可以在不比較文字中某些字元的情況下跳過這些字元。當模式沒有重複字元或具有較大的字母表大小時,就會發生這種情況。
為了說明Boyer-Moore演算法是如何工作的,讓我們考慮一個例子:
Input: main String: "AABAAABCEDBABCDDEBC" pattern: "ABC" Output: Pattern found at position: 5 Pattern found at position: 11
示例
在下面的示例中,我們將演示Boyer-Moore演算法在各種程式語言中的工作方式。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
// Function for full suffix match
void computeFullShift(int shiftArr[], int longSuffArr[], char patrn[], int n) {
int i = n;
int j = n+1;
longSuffArr[i] = j;
while(i > 0) {
// Searching right if (i-1)th and (j-1)th item are not the same
while(j <= n && patrn[i-1] != patrn[j-1] ) {
// to shift pattern from i to j
if(shiftArr[j] == 0) {
shiftArr[j] = j-i;
}
// Updating long suffix value
j = longSuffArr[j];
}
i--;
j--;
longSuffArr[i] = j;
}
}
// Function for good suffix match
void computeGoodSuffix(int shiftArr[], int longSuffArr[], char patrn[], int n) {
int j;
j = longSuffArr[0];
// Looping through the pattern
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++) {
// setting shift to long suffix value
if(shiftArr[i] == 0) {
shiftArr[i] = j;
if(i == j) {
// Updating long suffix value
j = longSuffArr[j];
}
}
}
}
// Function for searching the pattern
void searchPattern(char orgnStr[], char patrn[], int array[], int *index) {
// length of the pattern
int patLen = strlen(patrn);
// length of main string
int strLen = strlen(orgnStr);
int longerSuffArray[patLen+1];
int shiftArr[patLen + 1];
// Initializing shift array elements to 0
for(int i = 0; i<=patLen; i++) {
shiftArr[i] = 0;
}
// Calling computeFullShift function
computeFullShift(shiftArr, longerSuffArray, patrn, patLen);
// Calling computeGoodSuffix function
computeGoodSuffix(shiftArr, longerSuffArray, patrn, patLen);
int shift = 0;
while(shift <= (strLen - patLen)) {
int j = patLen - 1;
// decrement j when pattern and main string character is matching
while(j >= 0 && patrn[j] == orgnStr[shift+j]) {
j--;
}
if(j < 0) {
(*index)++;
// to store the position where pattern is found
array[(*index)] = shift;
shift += shiftArr[0];
}else {
shift += shiftArr[j+1];
}
}
}
int main() {
// original string
char orgnStr[] = "AABAAABCEDBABCDDEBC";
// Pattern to be searched
char patrn[] = "ABC";
// Array to store the positions where pattern is found
int locArray[strlen(orgnStr)];
int index = -1;
// Calling the searchPattern function
searchPattern(orgnStr, patrn, locArray, &index);
// Printing the positions where pattern is found
for(int i = 0; i <= index; i++) {
printf("Pattern found at position: %d\n", locArray[i]);
}
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
// Function for full suffix match
void computeFullShift(int shiftArr[], int longSuffArr[], string patrn) {
// length of pattern
int n = patrn.size();
int i = n;
int j = n+1;
longSuffArr[i] = j;
while(i > 0) {
// Searching right if (i-1)th and (j-1)th item are not the same
while(j <= n && patrn[i-1] != patrn[j-1] ) {
// to shift pattern from i to j
if(shiftArr[j] == 0) {
shiftArr[j] = j-i;
}
// Updating long suffix value
j = longSuffArr[j];
}
i--;
j--;
longSuffArr[i] = j;
}
}
// Function for good suffix match
void computeGoodSuffix(int shiftArr[], int longSuffArr[], string patrn) {
// length of the pattern
int n = patrn.size();
int j;
j = longSuffArr[0];
// Looping through the pattern
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++) {
// setting shift to long suffix value
if(shiftArr[i] == 0) {
shiftArr[i] = j;
if(i == j) {
// Updating long suffix value
j = longSuffArr[j];
}
}
}
}
// Function for searching the pattern
void searchPattern(string orgnStr, string patrn, int array[], int *index) {
// length of the pattern
int patLen = patrn.size();
// length of main string
int strLen = orgnStr.size();
int longerSuffArray[patLen+1];
int shiftArr[patLen + 1];
// Initializing shift array elements to 0
for(int i = 0; i<=patLen; i++) {
shiftArr[i] = 0;
}
// Calling computeFullShift function
computeFullShift(shiftArr, longerSuffArray, patrn);
// Calling computeGoodSuffix function
computeGoodSuffix(shiftArr, longerSuffArray, patrn);
int shift = 0;
while(shift <= (strLen - patLen)) {
int j = patLen - 1;
// decrement j when pattern and main string character is matching
while(j >= 0 && patrn[j] == orgnStr[shift+j]) {
j--;
}
if(j < 0) {
(*index)++;
// to store the position where pattern is found
array[(*index)] = shift;
shift += shiftArr[0];
}else {
shift += shiftArr[j+1];
}
}
}
int main() {
// original string
string orgnStr = "AABAAABCEDBABCDDEBC";
// Pattern to be searched
string patrn = "ABC";
// Array to store the positions where pattern is found
int locArray[orgnStr.size()];
int index = -1;
// Calling the searchPattern function
searchPattern(orgnStr, patrn, locArray, &index);
// Printing the positions where pattern is found
for(int i = 0; i <= index; i++) {
cout << "Pattern found at position: " << locArray[i]<<endl;
}
}
public class BMalgo {
// method for full suffix match
static void computeFullShift(int[] shiftArr, int[] longSuffArr, String patrn) {
// length of pattern
int n = patrn.length();
int i = n;
int j = n+1;
longSuffArr[i] = j;
while(i > 0) {
// Searching right if (i-1)th and (j-1)th item are not the same
while(j <= n && patrn.charAt(i-1) != patrn.charAt(j-1)) {
// to shift pattern from i to j
if(shiftArr[j] == 0) {
shiftArr[j] = j-i;
}
// Updating long suffix value
j = longSuffArr[j];
}
i--;
j--;
longSuffArr[i] = j;
}
}
// method for good suffix match
static void computeGoodSuffix(int[] shiftArr, int[] longSuffArr, String patrn) {
// length of the pattern
int n = patrn.length();
int j;
j = longSuffArr[0];
// Looping through the pattern
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++) {
// setting shift to long suffix value
if(shiftArr[i] == 0) {
shiftArr[i] = j;
if(i == j) {
// Updating long suffix value
j = longSuffArr[j];
}
}
}
}
// method for searching the pattern
static void searchPattern(String orgnStr, String patrn, int[] array, int[] index) {
// length of the pattern
int patLen = patrn.length();
// length of main string
int strLen = orgnStr.length();
int[] longerSuffArray = new int[patLen+1];
int[] shiftArr = new int[patLen + 1];
// Initializing shift array elements to 0
for(int i = 0; i<=patLen; i++) {
shiftArr[i] = 0;
}
// Calling computeFullShift method
computeFullShift(shiftArr, longerSuffArray, patrn);
// Calling computeGoodSuffix method
computeGoodSuffix(shiftArr, longerSuffArray, patrn);
int shift = 0;
while(shift <= (strLen - patLen)) {
int j = patLen - 1;
// decrement j when pattern and main string character is matching
while(j >= 0 && patrn.charAt(j) == orgnStr.charAt(shift+j)) {
j--;
}
if(j < 0) {
index[0]++;
// to store the position where pattern is found
array[index[0]] = shift;
shift += shiftArr[0];
}else {
shift += shiftArr[j+1];
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// original string
String orgnStr = "AABAAABCEDBABCDDEBC";
// Pattern to be searched
String patrn = "ABC";
// Array to store the positions where pattern is found
int[] locArray = new int[orgnStr.length()];
int[] index = {-1};
// Calling the searchPattern method
searchPattern(orgnStr, patrn, locArray, index);
// Printing the positions where pattern is found
for(int i = 0; i <= index[0]; i++) {
System.out.println("Pattern found at position: " + locArray[i]);
}
}
}
# Function for full suffix match
def compute_full_shift(shift_arr, long_suff_arr, patrn):
# length of pattern
n = len(patrn)
i = n
j = n+1
long_suff_arr[i] = j
while i > 0:
# Searching right if (i-1)th and (j-1)th item are not the same
while j <= n and patrn[i-1] != patrn[j-1]:
# to shift pattern from i to j
if shift_arr[j] == 0:
shift_arr[j] = j-i
# Updating long suffix value
j = long_suff_arr[j]
i -= 1
j -= 1
long_suff_arr[i] = j
# Function for good suffix match
def compute_good_suffix(shift_arr, long_suff_arr, patrn):
# length of the pattern
n = len(patrn)
j = long_suff_arr[0]
# Looping through the pattern
for i in range(n):
# setting shift to long suffix value
if shift_arr[i] == 0:
shift_arr[i] = j
if i == j:
# Updating long suffix value
j = long_suff_arr[j]
# Function for searching the pattern
def search_pattern(orgn_str, patrn, array, index):
# length of the pattern
pat_len = len(patrn)
# length of main string
str_len = len(orgn_str)
longer_suff_array = [0]*(pat_len+1)
shift_arr = [0]*(pat_len + 1)
# Initializing shift array elements to 0
for i in range(pat_len+1):
shift_arr[i] = 0
# Calling compute_full_shift function
compute_full_shift(shift_arr, longer_suff_array, patrn)
# Calling compute_good_suffix function
compute_good_suffix(shift_arr, longer_suff_array, patrn)
shift = 0
while shift <= (str_len - pat_len):
j = pat_len - 1
# decrement j when pattern and main string character is matching
while j >= 0 and patrn[j] == orgn_str[shift+j]:
j -= 1
if j < 0:
index[0] += 1
# to store the position where pattern is found
array[index[0]] = shift
shift += shift_arr[0]
else:
shift += shift_arr[j+1]
# original string
orgn_str = "AABAAABCEDBABCDDEBC"
# Pattern to be searched
patrn = "ABC"
# Array to store the positions where pattern is found
loc_array = [0]*len(orgn_str)
index = [-1]
# Calling the search_pattern function
search_pattern(orgn_str, patrn, loc_array, index)
# Printing the positions where pattern is found
for i in range(index[0]+1):
print("Pattern found at position: ", loc_array[i])
輸出
Pattern found at position: 5 Pattern found at position: 11