
- 資料結構與演算法
- DSA - 首頁
- DSA - 概述
- DSA - 環境搭建
- DSA - 演算法基礎
- DSA - 漸進分析
- 資料結構
- DSA - 資料結構基礎
- DSA - 資料結構和型別
- DSA - 陣列資料結構
- 連結串列
- DSA - 連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 雙向連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 迴圈連結串列資料結構
- 棧與佇列
- DSA - 棧資料結構
- DSA - 表示式解析
- DSA - 佇列資料結構
- 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 線性搜尋演算法
- DSA - 二分搜尋演算法
- DSA - 插值搜尋
- DSA - 跳躍搜尋演算法
- DSA - 指數搜尋
- DSA - 斐波那契搜尋
- DSA - 子列表搜尋
- DSA - 雜湊表
- 排序演算法
- DSA - 排序演算法
- DSA - 氣泡排序演算法
- DSA - 插入排序演算法
- DSA - 選擇排序演算法
- DSA - 歸併排序演算法
- DSA - 希爾排序演算法
- DSA - 堆排序
- DSA - 桶排序演算法
- DSA - 計數排序演算法
- DSA - 基數排序演算法
- DSA - 快速排序演算法
- 圖資料結構
- DSA - 圖資料結構
- DSA - 深度優先遍歷
- DSA - 廣度優先遍歷
- DSA - 生成樹
- 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹的遍歷
- DSA - 二叉搜尋樹
- DSA - AVL樹
- DSA - 紅黑樹
- DSA - B樹
- DSA - B+樹
- DSA - 伸展樹
- DSA - 字典樹
- DSA - 堆資料結構
- 遞迴
- DSA - 遞迴演算法
- DSA - 使用遞迴實現漢諾塔問題
- DSA - 使用遞迴實現斐波那契數列
- 分治法
- DSA - 分治法
- DSA - 最大最小問題
- DSA - Strassen矩陣乘法
- DSA - Karatsuba演算法
- 貪心演算法
- DSA - 貪心演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(貪心演算法)
- DSA - Prim最小生成樹演算法
- DSA - Kruskal最小生成樹演算法
- DSA - Dijkstra最短路徑演算法
- DSA - 地圖著色演算法
- DSA - 分數揹包問題
- DSA - 帶截止日期的作業排序
- DSA - 最優合併模式演算法
- 動態規劃
- DSA - 動態規劃
- DSA - 矩陣鏈乘法
- DSA - Floyd-Warshall演算法
- DSA - 0-1揹包問題
- DSA - 最長公共子序列演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(動態規劃)
- 近似演算法
- DSA - 近似演算法
- DSA - 頂點覆蓋演算法
- DSA - 集合覆蓋問題
- DSA - 旅行商問題(近似演算法)
- 隨機化演算法
- DSA - 隨機化演算法
- DSA - 隨機化快速排序演算法
- DSA - Karger最小割演算法
- DSA - Fisher-Yates洗牌演算法
- DSA有用資源
- DSA - 問答
- DSA - 快速指南
- DSA - 有用資源
- DSA - 討論
騎士巡遊問題
什麼是騎士巡遊問題?
在騎士巡遊問題中,我們得到一個大小為NxN的空棋盤和一個騎士。在國際象棋中,騎士是一個看起來像馬的棋子。假設它可以從棋盤上的任何位置開始。現在,我們的任務是檢查騎士是否可以訪問棋盤上的所有方格。當它可以訪問所有方格時,列印從起始位置到達該位置所需的跳躍次數。
騎士可以有兩種方式完成它的巡遊。在第一種方式中,騎士移動一步並返回到起始位置形成一個迴圈,這稱為閉合巡遊。在第二種方式即開放巡遊中,它在棋盤上的任何位置結束。
對於不熟悉國際象棋的人,請注意騎士的移動方式很特殊。它可以在每個方向上水平移動兩個方格和垂直移動一個方格,或者垂直移動兩個方格和水平移動一個方格。因此,完整的移動看起來像英文字母'L'。
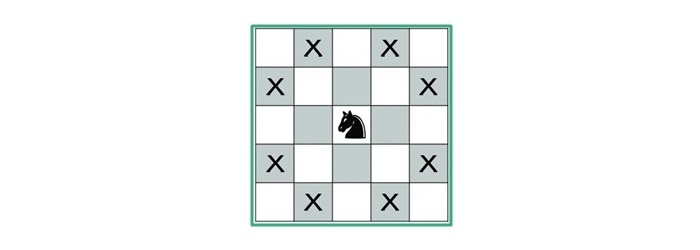
假設給定棋盤的大小為8,並且騎士位於棋盤的左上角位置。接下來的可能的移動如下所示:
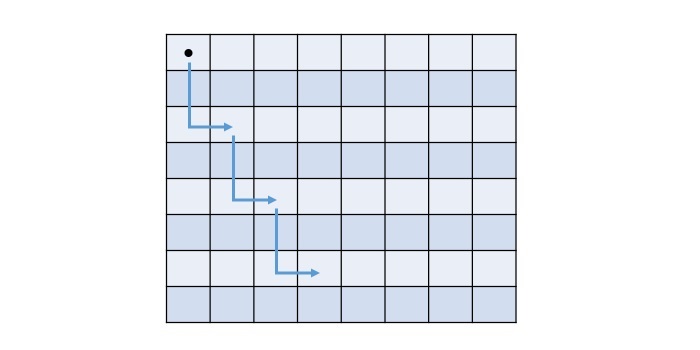
上面棋盤中的每個單元格都包含一個數字,表示從哪裡開始以及騎士需要多少步才能到達一個單元格。單元格的最終值將由以下矩陣表示:
0 59 38 33 30 17 8 63 37 34 31 60 9 62 29 16 58 1 36 39 32 27 18 7 35 48 41 26 61 10 15 28 42 57 2 49 40 23 6 19 47 50 45 54 25 20 11 14 56 43 52 3 22 13 24 5 51 46 55 44 53 4 21 12
請記住,此問題可能有多個解決方案,上面的矩陣是一個可能的解決方案。
解決騎士巡遊問題的一種方法是逐一生成所有巡遊,然後檢查它們是否滿足指定的約束條件。但是,這很耗時,不是一種有效的方法。
回溯法解決騎士巡遊問題
解決此問題的另一種方法是使用回溯法。這是一種嘗試不同可能性直到找到解決方案或嘗試所有選項的技術。它包括選擇一個移動,執行它,然後遞迴地嘗試解決問題的其餘部分。如果當前移動導致死衚衕,我們回溯並撤消該移動,然後嘗試另一個移動。
要使用回溯法解決騎士巡遊問題,請按照以下步驟操作:
從棋盤上的任何一個單元格開始,並將其標記為騎士已訪問。
將騎士移動到一個有效的未訪問單元格,並將其標記為已訪問。從任何一個單元格,騎士最多可以進行8次移動。
如果當前單元格無效或沒有通往解決方案的路徑,則回溯並嘗試其他可能通往解決方案的移動。
重複此過程,直到騎士的移動次數等於8 x 8 = 64。
示例
在下面的示例中,我們將實際演示如何解決騎士巡遊問題。
#include <stdio.h>
#define N 8
int sol[N][N];
//check place is in range and not assigned yet
int isValid(int x, int y) {
return ( x >= 0 && x < N && y >= 0 && y < N && sol[x][y] == -1);
}
void displaySolution() {
printf("The possible solution: \n");
for (int x = 0; x < N; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < N; y++)
printf("%3d ", sol[x][y]);
printf("\n");
}
}
int knightTour(int x, int y, int move, int xMove[N], int yMove[N]) {
int xNext, yNext;
//when the total board is covered
if (move == N*N)
return 1;
for (int k = 0; k < 8; k++) {
xNext = x + xMove[k];
yNext = y + yMove[k];
//check room is preoccupied or not
if (isValid(xNext, yNext)) {
sol[xNext][yNext] = move;
if (knightTour(xNext, yNext, move+1, xMove, yMove) == 1)
return 1;
else
// backtracking
sol[xNext][yNext] = -1;
}
}
return 0;
}
int findKnightTourSol() {
//initially set all values to -1 of solution matrix
for (int x = 0; x < N; x++)
for (int y = 0; y < N; y++)
sol[x][y] = -1;
//all possible moves for knight
int xMove[8] = { 2, 1, -1, -2, -2, -1, 1, 2 };
int yMove[8] = { 1, 2, 2, 1, -1, -2, -2, -1 };
//starting from room (0, 0)
sol[0][0] = 0;
if (knightTour(0, 0, 1, xMove, yMove) == 0) {
printf("Solution does not exist");
return 0;
} else
displaySolution();
return 1;
}
int main() {
findKnightTourSol();
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#define N 8
using namespace std;
int sol[N][N];
//check place is in range and not assigned yet
bool isValid(int x, int y, int sol[N][N]) {
return ( x >= 0 && x < N && y >= 0 && y < N && sol[x][y] == -1);
}
void displaySolution() {
cout << "The possible solution: " << endl;
for (int x = 0; x < N; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < N; y++)
cout << setw(3) << sol[x][y] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
int knightTour(int x, int y, int move, int sol[N][N], int xMove[N], int yMove[N]) {
int xNext, yNext;
//when the total board is covered
if (move == N*N)
return true;
for (int k = 0; k < 8; k++) {
xNext = x + xMove[k];
yNext = y + yMove[k];
//check room is preoccupied or not
if (isValid(xNext, yNext, sol)) {
sol[xNext][yNext] = move;
if (knightTour(xNext, yNext, move+1, sol, xMove, yMove) == true)
return true;
else
// backtracking
sol[xNext][yNext] = -1;
}
}
return false;
}
bool findKnightTourSol() {
//initially set all values to -1 of solution matrix
for (int x = 0; x < N; x++)
for (int y = 0; y < N; y++)
sol[x][y] = -1;
//all possible moves for knight
int xMove[8] = { 2, 1, -1, -2, -2, -1, 1, 2 };
int yMove[8] = { 1, 2, 2, 1, -1, -2, -2, -1 };
//starting from room (0, 0)
sol[0][0] = 0;
if (knightTour(0, 0, 1, sol, xMove, yMove) == false) {
cout << "Solution does not exist";
return false;
} else
displaySolution();
return true;
}
int main() {
findKnightTourSol();
}
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Main {
static final int N = 8;
static int[][] sol = new int[N][N];
//check place is in range and not assigned yet
static boolean isValid(int x, int y) {
return (x >= 0 && x < N && y >= 0 && y < N && sol[x][y] == -1);
}
static void displaySolution() {
System.out.println("The possible solution: ");
for (int x = 0; x < N; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < N; y++)
System.out.printf("%3d ", sol[x][y]);
System.out.println();
}
}
static boolean knightTour(int x, int y, int move, int[] xMove, int[] yMove) {
int xNext, yNext;
//when the total board is covered
if (move == N*N)
return true;
for (int k = 0; k < 8; k++) {
xNext = x + xMove[k];
yNext = y + yMove[k];
//check room is preoccupied or not
if (isValid(xNext, yNext)) {
sol[xNext][yNext] = move;
if (knightTour(xNext, yNext, move+1, xMove, yMove))
return true;
else
// backtracking
sol[xNext][yNext] = -1;
}
}
return false;
}
static boolean findKnightTourSol() {
//initially set all values to -1 of solution matrix
for (int[] row : sol)
Arrays.fill(row, -1);
//all possible moves for knight
int[] xMove = {2, 1, -1, -2, -2, -1, 1, 2};
int[] yMove = {1, 2, 2, 1, -1, -2, -2, -1};
//starting from room (0, 0)
sol[0][0] = 0;
if (!knightTour(0, 0, 1, xMove, yMove)) {
System.out.println("Solution does not exist");
return false;
} else
displaySolution();
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
findKnightTourSol();
}
}
N = 8
# The solution matrix
sol = [[-1 for _ in range(N)] for _ in range(N)]
# Check if place is in range and not assigned yet
def isValid(x, y):
return (x >= 0 and x < N and y >= 0 and y < N and sol[x][y] == -1)
# Function to print the solution
def displaySolution():
print("The possible solution: ")
for x in range(N):
for y in range(N):
print(f"{sol[x][y]:3}", end=" ")
print()
# Recursive function to solve the problem
def knightTour(x, y, move, xMove, yMove):
if move == N*N:
return True
for k in range(8):
xNext = x + xMove[k]
yNext = y + yMove[k]
if isValid(xNext, yNext):
sol[xNext][yNext] = move
if knightTour(xNext, yNext, move+1, xMove, yMove):
return True
else:
# Backtracking
sol[xNext][yNext] = -1
return False
def findKnightTourSol():
# All possible moves for knight
xMove = [2, 1, -1, -2, -2, -1, 1, 2]
yMove = [1, 2, 2, 1, -1, -2, -2, -1]
# Starting from room (0, 0)
sol[0][0] = 0
if not knightTour(0, 0, 1, xMove, yMove):
print("Solution does not exist")
return False
else:
displaySolution()
return True
if __name__ == "__main__":
findKnightTourSol()
輸出
The possible solution: 0 59 38 33 30 17 8 63 37 34 31 60 9 62 29 16 58 1 36 39 32 27 18 7 35 48 41 26 61 10 15 28 42 57 2 49 40 23 6 19 47 50 45 54 25 20 11 14 56 43 52 3 22 13 24 5 51 46 55 44 53 4 21 12