
- 資料結構與演算法
- DSA - 首頁
- DSA - 概述
- DSA - 環境設定
- DSA - 演算法基礎
- DSA - 漸進分析
- 資料結構
- DSA - 資料結構基礎
- DSA - 資料結構和型別
- DSA - 陣列資料結構
- 連結串列
- DSA - 連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 雙向連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 迴圈連結串列資料結構
- 棧和佇列
- DSA - 棧資料結構
- DSA - 表示式解析
- DSA - 佇列資料結構
- 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 線性搜尋演算法
- DSA - 二分搜尋演算法
- DSA - 插值搜尋
- DSA - 跳躍搜尋演算法
- DSA - 指數搜尋
- DSA - 斐波那契搜尋
- DSA - 子列表搜尋
- DSA - 雜湊表
- 排序演算法
- DSA - 排序演算法
- DSA - 氣泡排序演算法
- DSA - 插入排序演算法
- DSA - 選擇排序演算法
- DSA - 歸併排序演算法
- DSA - 希爾排序演算法
- DSA - 堆排序
- DSA - 桶排序演算法
- DSA - 計數排序演算法
- DSA - 基數排序演算法
- DSA - 快速排序演算法
- 圖資料結構
- DSA - 圖資料結構
- DSA - 深度優先遍歷
- DSA - 廣度優先遍歷
- DSA - 生成樹
- 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹的遍歷
- DSA - 二叉搜尋樹
- DSA - AVL樹
- DSA - 紅黑樹
- DSA - B樹
- DSA - B+樹
- DSA - 伸展樹
- DSA - 字典樹
- DSA - 堆資料結構
- 遞迴
- DSA - 遞迴演算法
- DSA - 使用遞迴實現漢諾塔
- DSA - 使用遞迴實現斐波那契數列
- 分治法
- DSA - 分治法
- DSA - 最大-最小問題
- DSA - Strassen矩陣乘法
- DSA - Karatsuba演算法
- 貪心演算法
- DSA - 貪心演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(貪心演算法)
- DSA - Prim最小生成樹
- DSA - Kruskal最小生成樹
- DSA - Dijkstra最短路徑演算法
- DSA - 地圖著色演算法
- DSA - 分數揹包問題
- DSA - 帶截止日期的作業排序
- DSA - 最佳合併模式演算法
- 動態規劃
- DSA - 動態規劃
- DSA - 矩陣鏈乘法
- DSA - Floyd-Warshall演算法
- DSA - 0-1揹包問題
- DSA - 最長公共子序列演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(動態規劃)
- 近似演算法
- DSA - 近似演算法
- DSA - 頂點覆蓋演算法
- DSA - 集合覆蓋問題
- DSA - 旅行商問題(近似演算法)
- 隨機化演算法
- DSA - 隨機化演算法
- DSA - 隨機化快速排序演算法
- DSA - Karger最小割演算法
- DSA - Fisher-Yates洗牌演算法
- DSA有用資源
- DSA - 問答
- DSA - 快速指南
- DSA - 有用資源
- DSA - 討論
迷宮中的老鼠問題
迷宮中的老鼠問題是一個尋路謎題,我們的目標是從起點找到一條到達出口的最佳路徑。在這個謎題中,有一隻老鼠被困在一個由方形矩陣表示的迷宮中。迷宮包含不同的單元格,老鼠可以透過這些單元格到達迷宮的出口。
使用回溯法解決迷宮中的老鼠問題
假設迷宮的大小為NxN,其中單元格可以標記為1或0。標記為1的單元格表示有效路徑,而標記為0的單元格表示牆壁或障礙物。請記住,老鼠可以向上、下、左、右移動,但每個單元格只能訪問一次。源位置和目標位置分別是左上角和右下角單元格。
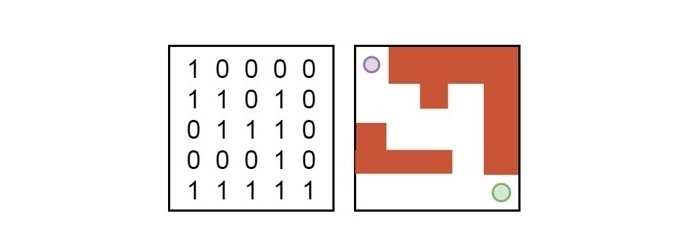
目標是找到老鼠從起始單元格(0,0)到達目標單元格(N-1,N-1)的所有可能的路徑。該演算法將顯示一個矩陣,從中我們可以找到老鼠到達目標點的路徑。下圖說明了路徑 -
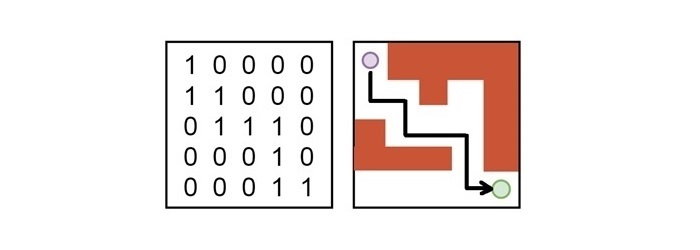
回溯過程透過標記已訪問的單元格並從死衚衕回溯來系統地探索所有可能的路徑。這種方法保證瞭如果給定問題存在解決方案,則會找到所有可能的解決方案。
要使用回溯法解決迷宮中的老鼠問題,請遵循以下步驟 -
首先,將起始單元格標記為已訪問。
接下來,探索所有方向以檢查是否存在有效單元格。
如果存在有效的未訪問單元格,則移動到該單元格並將其標記為已訪問。
如果沒有找到有效的單元格,則回溯並檢查其他單元格,直到到達出口點。
示例
以下示例說明了如何在各種程式語言中解決迷宮中的老鼠問題。
#include <stdio.h>
#define N 5
// Original maze
int maze[N][N] = {
{1, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{1, 1, 1, 1, 1}
};
// To store the final solution of the maze path
int sol[N][N];
void showPath() {
printf("The solution maze:\n");
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
printf("%d ", sol[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
}
// Function to check if a place is inside the maze and has value 1
int isValidPlace(int x, int y) {
if (x >= 0 && x < N && y >= 0 && y < N && maze[x][y] == 1)
return 1;
return 0;
}
int solveRatMaze(int x, int y) {
// When (x,y) is the bottom right room
if (x == N - 1 && y == N - 1) {
sol[x][y] = 1;
return 1;
}
// Check whether (x,y) is valid or not
if (isValidPlace(x, y)) {
// Set 1 when it is a valid place
sol[x][y] = 1;
// Find path by moving in the right direction
if (solveRatMaze(x + 1, y))
return 1;
// When the x direction is blocked, go for the bottom direction
if (solveRatMaze(x, y + 1))
return 1;
// If both directions are closed, there is no path
sol[x][y] = 0;
return 0;
}
return 0;
}
int findSolution() {
if (solveRatMaze(0, 0) == 0) {
printf("There is no path\n");
return 0;
}
showPath();
return 1;
}
int main() {
findSolution();
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
#define N 5
using namespace std;
// original maze
int maze[N][N] = {
{1, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{1, 1, 1, 1, 1}
};
// to store the final solution of the maze path
int sol[N][N];
void showPath() {
cout << "The solution maze: " << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++)
cout << sol[i][j] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
// function to check place is inside the maze and have value 1
bool isValidPlace(int x, int y) {
if(x >= 0 && x < N && y >= 0 && y < N && maze[x][y] == 1)
return true;
return false;
}
bool solveRatMaze(int x, int y) {
// when (x,y) is the bottom right room
if(x == N-1 && y == N-1) {
sol[x][y] = 1;
return true;
}
//check whether (x,y) is valid or not
if(isValidPlace(x, y) == true) {
//set 1, when it is valid place
sol[x][y] = 1;
//find path by moving right direction
if (solveRatMaze(x+1, y) == true)
return true;
//when x direction is blocked, go for bottom direction
if (solveRatMaze(x, y+1) == true)
return true;
//if both are closed, there is no path
sol[x][y] = 0;
return false;
}
return false;
}
bool findSolution() {
if(solveRatMaze(0, 0) == false) {
cout << "There is no path";
return false;
}
showPath();
return true;
}
int main() {
findSolution();
}
import java.util.Arrays;
public class MazeSolverClass {
private static final int N = 5;
// Original maze
private static int[][] maze = {
{1, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 1, 0},
{0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 0},
{1, 1, 1, 1, 1}
};
// To store the final solution of the maze path
private static int[][] sol = new int[N][N];
// to display path
private static void showPath() {
System.out.println("The solution maze:");
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(sol[i]));
}
}
// Function to check if a place is inside the maze and has value 1
private static boolean isValidPlace(int x, int y) {
return x >= 0 && x < N && y >= 0 && y < N && maze[x][y] == 1;
}
private static boolean solveRatMaze(int x, int y) {
// When (x,y) is the bottom right room
if (x == N - 1 && y == N - 1) {
sol[x][y] = 1;
return true;
}
// Check whether (x,y) is valid or not
if (isValidPlace(x, y)) {
// Set 1 when it is a valid place
sol[x][y] = 1;
// Find path by moving in the right direction
if (solveRatMaze(x + 1, y)) {
return true;
}
// When the x direction is blocked, go for the bottom direction
if (solveRatMaze(x, y + 1)) {
return true;
}
// If both directions are closed, there is no path
sol[x][y] = 0;
return false;
}
return false;
}
private static boolean findSolution() {
return solveRatMaze(0, 0);
}
// main method
public static void main(String[] args) {
if (findSolution()) {
showPath();
} else {
System.out.println("There is no path");
}
}
}
N = 5
# Original maze
maze = [
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 1, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 1, 1, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[1, 1, 1, 1, 1]
]
# To store the final solution of the maze path
sol = [[0] * N for _ in range(N)]
def showPath():
print("The solution maze:")
for row in sol:
print(*row)
def isValidPlace(x, y):
return 0 <= x < N and 0 <= y < N and maze[x][y] == 1
def solveRatMaze(x, y):
# When (x,y) is the bottom right room
if x == N - 1 and y == N - 1:
sol[x][y] = 1
return True
# Check whether (x,y) is valid or not
if isValidPlace(x, y):
# Set 1 when it is a valid place
sol[x][y] = 1
# Find path by moving in the right direction
if solveRatMaze(x + 1, y):
return True
# When the x direction is blocked, go for the bottom direction
if solveRatMaze(x, y + 1):
return True
# If both directions are closed, there is no path
sol[x][y] = 0
return False
return False
def findSolution():
if not solveRatMaze(0, 0):
print("There is no path")
return False
showPath()
return True
if __name__ == "__main__":
findSolution()
輸出
The solution maze: 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1
廣告