
- 資料結構與演算法
- DSA - 首頁
- DSA - 概述
- DSA - 環境設定
- DSA - 演算法基礎
- DSA - 漸近分析
- 資料結構
- DSA - 資料結構基礎
- DSA - 資料結構和型別
- DSA - 陣列資料結構
- 連結串列
- DSA - 連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 雙向連結串列資料結構
- DSA - 迴圈連結串列資料結構
- 棧與佇列
- DSA - 棧資料結構
- DSA - 表示式解析
- DSA - 佇列資料結構
- 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 搜尋演算法
- DSA - 線性搜尋演算法
- DSA - 二分搜尋演算法
- DSA - 插值搜尋
- DSA - 跳躍搜尋演算法
- DSA - 指數搜尋
- DSA - 斐波那契搜尋
- DSA - 子列表搜尋
- DSA - 雜湊表
- 排序演算法
- DSA - 排序演算法
- DSA - 氣泡排序演算法
- DSA - 插入排序演算法
- DSA - 選擇排序演算法
- DSA - 歸併排序演算法
- DSA - 希爾排序演算法
- DSA - 堆排序
- DSA - 桶排序演算法
- DSA - 計數排序演算法
- DSA - 基數排序演算法
- DSA - 快速排序演算法
- 圖資料結構
- DSA - 圖資料結構
- DSA - 深度優先遍歷
- DSA - 廣度優先遍歷
- DSA - 生成樹
- 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹資料結構
- DSA - 樹遍歷
- DSA - 二叉搜尋樹
- DSA - AVL 樹
- DSA - 紅黑樹
- DSA - B 樹
- DSA - B+ 樹
- DSA - 伸展樹
- DSA - Trie 樹
- DSA - 堆資料結構
- 遞迴
- DSA - 遞迴演算法
- DSA - 使用遞迴實現漢諾塔
- DSA - 使用遞迴實現斐波那契數列
- 分治法
- DSA - 分治法
- DSA - 最大最小問題
- DSA - Strassen 矩陣乘法
- DSA - Karatsuba 演算法
- 貪心演算法
- DSA - 貪心演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(貪心法)
- DSA - Prim 最小生成樹
- DSA - Kruskal 最小生成樹
- DSA - Dijkstra 最短路徑演算法
- DSA - 地圖著色演算法
- DSA - 分數揹包問題
- DSA - 帶截止日期的作業排序
- DSA - 最優合併模式演算法
- 動態規劃
- DSA - 動態規劃
- DSA - 矩陣鏈乘法
- DSA - Floyd-Warshall 演算法
- DSA - 0-1 揹包問題
- DSA - 最長公共子序列演算法
- DSA - 旅行商問題(動態規劃法)
- 近似演算法
- DSA - 近似演算法
- DSA - 頂點覆蓋演算法
- DSA - 集合覆蓋問題
- DSA - 旅行商問題(近似演算法)
- 隨機化演算法
- DSA - 隨機化演算法
- DSA - 隨機化快速排序演算法
- DSA - Karger 最小割演算法
- DSA - Fisher-Yates 洗牌演算法
- DSA 有用資源
- DSA - 問答
- DSA - 快速指南
- DSA - 有用資源
- DSA - 討論
Rabin-Karp 演算法
Rabin-Karp 演算法是一種模式匹配演算法,它使用雜湊來比較模式和文字。這裡,雜湊指的是將較大的輸入值對映到較小的輸出值(稱為雜湊值)的過程。此過程有助於避免不必要的比較,從而最佳化該演算法的複雜度。因此,Rabin-Karp 演算法的時間複雜度為O(n + m),其中 n 是文字的長度,m 是模式的長度。
Rabin-Karp 演算法是如何工作的?
Rabin-Karp 演算法透過逐個移動視窗來檢查文字中是否存在給定的模式,但它不會在所有情況下都檢查所有字元,而是查詢雜湊值。然後,將此雜湊值與文字中所有與模式長度相同的子串的雜湊值進行比較。
如果雜湊值匹配,則模式和子串可能相等,我們可以透過逐個字元比較來驗證。如果雜湊值不匹配,則可以跳過子串並繼續下一個子串。在下一節中,我們將瞭解如何計算雜湊值。
在 Rabin-Karp 演算法中計算雜湊值
計算雜湊值的步驟如下:
步驟 1:分配模數和基值
假設我們有一個文字Txt = "DAACABCDBA"和一個模式Ptrn = "CAB"。我們將首先根據字元的排名為文字的字元分配數值。最左邊的字元排名為 1,最右邊的字元排名為 10。此外,對於我們的雜湊函式,我們將使用基數b = 10(文字中字元的數量)和模數m = 11。需要注意的是,模數m需要是一個素數,因為它有助於避免溢位問題。
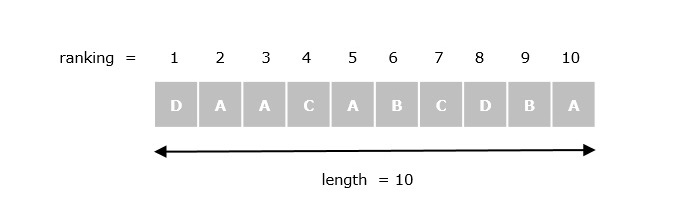
步驟 2:計算模式的雜湊值
計算模式雜湊值的公式如下:
hash value(Ptrn) = Σ(r * bl-i-1) mod 11
where, r: ranking of character
l: length of Pattern
i: index of character within the pattern
因此,Patrn的雜湊值為:
h(Ptrn) = ((4 * 102) + (5 * 101) + (6 * 100)) mod 11
= 456 mod 11
= 5
步驟 3:計算第一個文字視窗的雜湊值
開始透過滑動文字中的字元來計算所有字元的雜湊值。我們將從第一個子串開始,如下所示:
h(DAA) = ((1 * 102) + (2 * 101) + (3 * 100)) mod 11
= 123 mod 11
= 6
現在,比較模式和子串的雜湊值。如果它們匹配,則檢查字元是否匹配。如果匹配,則找到匹配項,否則,移動到下一個字元。
在上面的示例中,雜湊值不匹配。因此,我們移動到下一個字元。
步驟 4:更新雜湊值
現在,我們需要刪除前一個字元並移動到下一個字元。在此過程中,也應該更新雜湊值,直到找到匹配項。
示例
以下示例實際上演示了 Rabin-Karp 演算法的工作原理。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#define MAXCHAR 256
// Function to perform Rabin-Karp algorithm
void rabinKSearch(char orgnlString[], char pattern[], int prime, int array[], int *index) {
int patLen = strlen(pattern);
int strLen = strlen(orgnlString);
int charIndex, pattHash = 0, strHash = 0, h = 1;
// Calculate the value of helper variable
for(int i = 0; i<patLen-1; i++) {
h = (h*MAXCHAR) % prime;
}
// Calculating initial hash values and first window
for(int i = 0; i<patLen; i++) {
pattHash = (MAXCHAR*pattHash + pattern[i]) % prime;
strHash = (MAXCHAR*strHash + orgnlString[i]) % prime;
}
// Slide the pattern over the text one by one
for(int i = 0; i<=(strLen-patLen); i++) {
// Check the hash values of current window of text and pattern
if(pattHash == strHash) {
for(charIndex = 0; charIndex < patLen; charIndex++) {
if(orgnlString[i+charIndex] != pattern[charIndex])
break;
}
if(charIndex == patLen) {
(*index)++;
array[(*index)] = i;
}
}
// Calculating hash value for next window of text
if(i < (strLen-patLen)) {
strHash = (MAXCHAR*(strHash - orgnlString[i]*h) + orgnlString[i+patLen])%prime;
// If strHash is negative, convert it to positive
if(strHash < 0) {
strHash += prime;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
char orgnlString[] = "AAAABCAEAAABCBDDAAAABC";
char pattern[] = "AABC";
int locArray[strlen(orgnlString)];
int prime = 101;
int index = -1;
// Calling Rabin-Karp search function
rabinKSearch(orgnlString, pattern, prime, locArray, &index);
for(int i = 0; i <= index; i++) {
printf("Pattern found at position: %d\n", locArray[i]);
}
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
#define MAXCHAR 256
using namespace std;
// Function to perform Rabin-Karp algorithm
void rabinKSearch(string orgnlString, string pattern, int prime, int array[], int *index) {
int patLen = pattern.size();
int strLen = orgnlString.size();
int charIndex, pattHash = 0, strHash = 0, h = 1;
// Calculate the value of helper variable
for(int i = 0; i<patLen-1; i++) {
h = (h*MAXCHAR) % prime;
}
// Calculating initial hash values and first window
for(int i = 0; i<patLen; i++) {
pattHash = (MAXCHAR*pattHash + pattern[i]) % prime;
strHash = (MAXCHAR*strHash + orgnlString[i]) % prime;
}
// Slide the pattern over the text one by one
for(int i = 0; i<=(strLen-patLen); i++) {
// Check the hash values of current window of text and pattern
if(pattHash == strHash) {
for(charIndex = 0; charIndex < patLen; charIndex++) {
if(orgnlString[i+charIndex] != pattern[charIndex])
break;
}
if(charIndex == patLen) {
(*index)++;
array[(*index)] = i;
}
}
// Calculating hash value for next window of text
if(i < (strLen-patLen)) {
strHash = (MAXCHAR*(strHash - orgnlString[i]*h) + orgnlString[i+patLen])%prime;
// If strHash is negative, convert it to positive
if(strHash < 0) {
strHash += prime;
}
}
}
}
int main() {
string orgnlString = "AAAABCAEAAABCBDDAAAABC";
// Pattern to be searched
string pattern = "AABC";
// Array to store the locations of the pattern
int locArray[orgnlString.size()];
int prime = 101;
int index = -1;
// Calling Rabin-Karp search function
rabinKSearch(orgnlString, pattern, prime, locArray, &index);
// print the result
for(int i = 0; i <= index; i++) {
cout << "Pattern found at position: " << locArray[i]<<endl;
}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
static final int MAXCHAR = 256;
// method to perform Rabin-Karp algorithm
static void rabinKSearch(String orgnlString, String pattern, int prime, ArrayList<Integer> locArray) {
int patLen = pattern.length();
int strLen = orgnlString.length();
int charIndex, pattHash = 0, strHash = 0, h = 1;
// Calculating value of helper variable
for (int i = 0; i < patLen - 1; i++) {
h = (h * MAXCHAR) % prime;
}
// Calculating initial hash values and first window
for (int i = 0; i < patLen; i++) {
pattHash = (MAXCHAR * pattHash + pattern.charAt(i)) % prime;
strHash = (MAXCHAR * strHash + orgnlString.charAt(i)) % prime;
}
// Slide the pattern over the text one by one
for (int i = 0; i <= (strLen - patLen); i++) {
// Check the hash values of current window of text and pattern
if (pattHash == strHash) {
for (charIndex = 0; charIndex < patLen; charIndex++) {
if (orgnlString.charAt(i + charIndex) != pattern.charAt(charIndex))
break;
}
if (charIndex == patLen) {
locArray.add(i);
}
}
// Calculating hash value for next window of text
if (i < (strLen - patLen)) {
strHash = (MAXCHAR * (strHash - orgnlString.charAt(i) * h) + orgnlString.charAt(i + patLen)) % prime;
// If strHash is negative, convert it to positive
if (strHash < 0) {
strHash += prime;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
String orgnlString = "AAAABCAEAAABCBDDAAAABC";
// Pattern to be searched
String pattern = "AABC";
// Array to store the locations of the pattern
ArrayList<Integer> locArray = new ArrayList<>();
int prime = 101;
// Calling Rabin-Karp method
rabinKSearch(orgnlString, pattern, prime, locArray);
// print the result
for (int i = 0; i < locArray.size(); i++) {
System.out.println("Pattern found at position: " + locArray.get(i));
}
}
}
MAXCHAR = 256
# method to perform Rabin-Karp algorithm
def rabinKSearch(orgnlString, pattern, prime):
patLen = len(pattern)
strLen = len(orgnlString)
pattHash = 0
strHash = 0
h = 1
locArray = []
# Calculating value of helper variable
for i in range(patLen-1):
h = (h*MAXCHAR) % prime
# Calculating initial hash values and first window
for i in range(patLen):
pattHash = (MAXCHAR*pattHash + ord(pattern[i])) % prime
strHash = (MAXCHAR*strHash + ord(orgnlString[i])) % prime
# Slide the pattern over the text one by one
for i in range(strLen-patLen+1):
if pattHash == strHash:
for charIndex in range(patLen):
if orgnlString[i+charIndex] != pattern[charIndex]:
break
else:
locArray.append(i)
# Calculating hash value for next window of text
if i < strLen-patLen:
strHash = (MAXCHAR*(strHash - ord(orgnlString[i])*h) + ord(orgnlString[i+patLen])) % prime
if strHash < 0:
strHash += prime
return locArray
def main():
orgnlString = "AAAABCAEAAABCBDDAAAABC"
pattern = "AABC"
prime = 101
locArray = rabinKSearch(orgnlString, pattern, prime)
for i in locArray:
print(f"Pattern found at position: {i}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
輸出
Pattern found at position: 2 Pattern found at position: 9 Pattern found at position: 18
廣告