- Mahotas 教程
- Mahotas - 首頁
- Mahotas - 簡介
- Mahotas - 計算機視覺
- Mahotas - 歷史
- Mahotas - 特性
- Mahotas - 安裝
- Mahotas 影像處理
- Mahotas - 影像處理
- Mahotas - 載入影像
- Mahotas - 載入灰度影像
- Mahotas - 顯示影像
- Mahotas - 顯示影像形狀
- Mahotas - 儲存影像
- Mahotas - 影像質心
- Mahotas - 影像卷積
- Mahotas - 建立RGB影像
- Mahotas - 影像尤拉數
- Mahotas - 影像中零的比例
- Mahotas - 獲取影像矩
- Mahotas - 影像區域性最大值
- Mahotas - 影像橢圓軸
- Mahotas - 影像RGB拉伸
- Mahotas 顏色空間轉換
- Mahotas - 顏色空間轉換
- Mahotas - RGB轉灰度轉換
- Mahotas - RGB轉LAB轉換
- Mahotas - RGB轉棕褐色
- Mahotas - RGB轉XYZ轉換
- Mahotas - XYZ轉LAB轉換
- Mahotas - XYZ轉RGB轉換
- Mahotas - 增加伽馬校正
- Mahotas - 拉伸伽馬校正
- Mahotas 標記影像函式
- Mahotas - 標記影像函式
- Mahotas - 標記影像
- Mahotas - 過濾區域
- Mahotas - 邊界畫素
- Mahotas - 形態學運算
- Mahotas - 形態學運算元
- Mahotas - 求影像平均值
- Mahotas - 裁剪影像
- Mahotas - 影像離心率
- Mahotas - 影像疊加
- Mahotas - 影像圓度
- Mahotas - 調整影像大小
- Mahotas - 影像直方圖
- Mahotas - 影像膨脹
- Mahotas - 影像腐蝕
- Mahotas - 分水嶺演算法
- Mahotas - 影像開運算
- Mahotas - 影像閉運算
- Mahotas - 填充影像空洞
- Mahotas - 條件膨脹影像
- Mahotas - 條件腐蝕影像
- Mahotas - 影像條件分水嶺
- Mahotas - 影像區域性最小值
- Mahotas - 影像區域最大值
- Mahotas - 影像區域最小值
- Mahotas - 高階概念
- Mahotas - 影像閾值化
- Mahotas - 設定閾值
- Mahotas - 軟閾值
- Mahotas - Bernsen區域性閾值化
- Mahotas - 小波變換
- 建立小波中心影像
- Mahotas - 距離變換
- Mahotas - 多邊形工具
- Mahotas - 區域性二值模式
- 閾值鄰域統計
- Mahotas - Haralick特徵
- 標記區域的權重
- Mahotas - Zernike特徵
- Mahotas - Zernike矩
- Mahotas - 排序濾波器
- Mahotas - 二維拉普拉斯濾波器
- Mahotas - 多數濾波器
- Mahotas - 均值濾波器
- Mahotas - 中值濾波器
- Mahotas - Otsu方法
- Mahotas - 高斯濾波
- Mahotas - 擊中與錯過變換
- Mahotas - 標記最大值陣列
- Mahotas - 影像平均值
- Mahotas - SURF密集點
- Mahotas - SURF積分影像
- Mahotas - Haar變換
- 突出顯示影像最大值
- 計算線性二值模式
- 獲取標籤邊界
- 反轉Haar變換
- Riddler-Calvard 方法
- 標記區域的大小
- Mahotas - 模板匹配
- 加速魯棒特徵
- 去除邊界標記
- Mahotas - Daubechies小波
- Mahotas - Sobel邊緣檢測
Mahotas - 影像條件分水嶺
“分水嶺”一詞源於物理分水嶺的概念,它是分隔不同流域的界線。類似地,分水嶺演算法旨在尋找影像中的邊界或分離區域。
分水嶺演算法是一種常用的影像分割方法,它是將影像分割成不同區域的過程。
因此,在影像處理中,分水嶺影像指的是經過分水嶺分割處理的影像。
分水嶺分割技術將影像中的畫素強度視為地形表面,其中明亮區域代表高海拔,黑暗區域代表低海拔。
Mahotas中的分水嶺演算法
Mahotas 提供條件分水嶺函式,而不是傳統的分割演算法。
Mahotas中的條件分水嶺是分水嶺演算法的增強版本,它允許我們透過提供特定的標記來指導分割過程。
讓我們看看Mahotas中條件分水嶺演算法的逐步過程:
步驟1 - 想象一下我們有一張影像,我們想把它分成不同的區域。使用條件分水嶺,我們可以將影像中的某些區域標記為標記,這些標記代表我們感興趣的區域。
步驟2 - 然後,演算法從填充這些標記區域開始注水。水只會在每個標記區域內流動,不會越過其他標記的邊界。
步驟3 - 結果是一個分割後的影像,其中每個區域都由您提供的標記定義的邊界劃分。
mahotas.cwatershed() 函式
Mahotas中的cwatershed()函式有兩個輸入:輸入影像和標記影像,並返回一個被分割成不同區域的輸出影像。
標記影像是一個二值影像,其中前景畫素(布林值1)代表不同區域的邊界。
語法
以下是Mahotas中cwatershed()函式的基本語法:
mahotas.cwatershed(surface, markers, Bc=None, return_lines=False) W, WL = cwatershed(surface, markers, Bc=None, return_lines=True)
引數
cwatershed()函式接受的引數如下:
surface - 它表示將進行分水嶺分割的輸入影像。它通常是灰度影像。
markers - 它表示分水嶺分割的標記。標記指示影像中感興趣的區域。
Bc (可選) - 它表示用於鄰域運算的結構元素。如果設定為None,則使用預設連線性。
return_lines - 它是一個布林標誌,用於指定是否除了標記影像外還要返回分水嶺線。如果為True,則函式返回標記影像和分水嶺線。
如果為False,則只返回標記影像。預設設定為False。
返回值
W 或 WL - 它表示從分水嶺分割獲得的標記影像,其中每個區域都分配了一個唯一的標籤。標記影像的形狀與輸入影像相同。
WL (可選) - 只有當return_lines引數設定為True時才會返回。它表示分水嶺線,即影像中分割區域之間的邊界。
示例
在下面的示例中,我們嘗試顯示影像的基本條件分水嶺分割:
import mahotas as mh
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Loading the input image
image = mh.imread('sea.bmp')
# Creating markers or seeds
markers = mh.imread('tree.tiff')
# Perform conditional watershed segmentation
segmented_image = mh.cwatershed(image, markers)
# Display all three images in one plot
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
# Display image1
plt.subplot(1, 3, 1)
plt.imshow(image)
plt.title('Sea')
plt.axis('off')
# Display image2
plt.subplot(1, 3, 2)
plt.imshow(markers)
plt.title('Tree')
plt.axis('off')
# Display the segmented image
plt.subplot(1, 3, 3)
plt.imshow(segmented_image, cmap='gray')
plt.title('Segmented Image')
plt.axis('off')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
輸出
生成的輸出如下:

使用自定義結構元素的條件分水嶺
結構元素是一個小的二值影像,通常表示為矩陣。它用於分析參考畫素的區域性鄰域。
在條件分水嶺的上下文中,自定義結構元素允許我們在分水嶺過程中定義畫素之間的連線性。
透過自定義結構元素,我們可以控制每個畫素的鄰域如何影響影像的分割。
示例
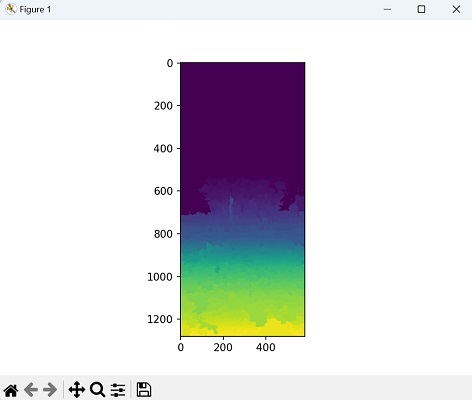
import mahotas as mh
import numpy as np
from pylab import imshow, show
# Load the image
image = mh.imread('nature.jpeg')
# Convert the image to grayscale
image_gray = mh.colors.rgb2grey(image).astype(np.uint8)
# Threshold the image
threshold = mh.thresholding.otsu(image_gray)
image_thresholded = image_gray > threshold
# Perform conditional watershed with custom structuring element
struct_element = np.array([[0, 1, 0], [1, 1, 1], [0, 1, 0]])
labels, _ = mh.label(image_thresholded, struct_element)
watershed = mh.cwatershed(image_gray.max() - image_gray, labels)
# Show the result
imshow(watershed)
show()
輸出
上述程式碼的輸出如下: