- Mahotas 教程
- Mahotas - 首頁
- Mahotas - 簡介
- Mahotas - 計算機視覺
- Mahotas - 歷史
- Mahotas - 特性
- Mahotas - 安裝
- Mahotas 處理影像
- Mahotas - 處理影像
- Mahotas - 載入影像
- Mahotas - 載入影像為灰度
- Mahotas - 顯示影像
- Mahotas - 顯示影像形狀
- Mahotas - 儲存影像
- Mahotas - 影像的質心
- Mahotas - 影像卷積
- Mahotas - 建立 RGB 影像
- Mahotas - 影像的尤拉數
- Mahotas - 影像中零的比例
- Mahotas - 獲取影像矩
- Mahotas - 影像中的區域性最大值
- Mahotas - 影像橢圓軸
- Mahotas - 影像拉伸 RGB
- Mahotas 顏色空間轉換
- Mahotas - 顏色空間轉換
- Mahotas - RGB 到灰度轉換
- Mahotas - RGB 到 LAB 轉換
- Mahotas - RGB 到棕褐色轉換
- Mahotas - RGB 到 XYZ 轉換
- Mahotas - XYZ 到 LAB 轉換
- Mahotas - XYZ 到 RGB 轉換
- Mahotas - 增加伽馬校正
- Mahotas - 拉伸伽馬校正
- Mahotas 標記影像函式
- Mahotas - 標記影像函式
- Mahotas - 標記影像
- Mahotas - 過濾區域
- Mahotas - 邊界畫素
- Mahotas - 形態學操作
- Mahotas - 形態學運算元
- Mahotas - 查詢影像均值
- Mahotas - 裁剪影像
- Mahotas - 影像的偏心率
- Mahotas - 疊加影像
- Mahotas - 影像的圓度
- Mahotas - 調整影像大小
- Mahotas - 影像直方圖
- Mahotas - 膨脹影像
- Mahotas - 腐蝕影像
- Mahotas - 分水嶺
- Mahotas - 影像上的開運算
- Mahotas - 影像上的閉運算
- Mahotas - 填充影像中的孔洞
- Mahotas - 條件膨脹影像
- Mahotas - 條件腐蝕影像
- Mahotas - 影像的條件分水嶺
- Mahotas - 影像中的區域性最小值
- Mahotas - 影像的區域最大值
- Mahotas - 影像的區域最小值
- Mahotas - 高階概念
- Mahotas - 影像閾值化
- Mahotas - 設定閾值
- Mahotas - 軟閾值
- Mahotas - Bernsen 區域性閾值化
- Mahotas - 小波變換
- 製作影像小波中心
- Mahotas - 距離變換
- Mahotas - 多邊形實用程式
- Mahotas - 區域性二值模式
- 閾值鄰域統計
- Mahotas - Haralic 特徵
- 標記區域的權重
- Mahotas - Zernike 特徵
- Mahotas - Zernike 矩
- Mahotas - 排序濾波器
- Mahotas - 2D 拉普拉斯濾波器
- Mahotas - 多數濾波器
- Mahotas - 均值濾波器
- Mahotas - 中值濾波器
- Mahotas - Otsu 方法
- Mahotas - 高斯濾波
- Mahotas - 擊中與不擊中變換
- Mahotas - 標記最大陣列
- Mahotas - 影像的平均值
- Mahotas - SURF 密集點
- Mahotas - SURF 積分
- Mahotas - Haar 變換
- 突出顯示影像最大值
- 計算線性二值模式
- 獲取標籤的邊界
- 反轉 Haar 變換
- Riddler-Calvard 方法
- 標記區域的大小
- Mahotas - 模板匹配
- 加速魯棒特徵
- 移除帶邊框的標記
- Mahotas - Daubechies 小波
- Mahotas - Sobel 邊緣檢測
Mahotas - 條件腐蝕影像
在我們上一章中,我們探討了影像腐蝕的概念,這是一種用於將所有畫素縮小到影像中區域邊界的操作。另一方面,條件腐蝕基於某些條件,縮小(移除)某些特定區域的畫素。
條件可以基於影像畫素的強度值或影像中的一些特定模式。
例如,讓我們考慮一個灰度影像。您可以有條件地僅腐蝕滿足特定強度閾值的畫素,而不是腐蝕所有前景畫素。
如果畫素的強度低於預定義的閾值,則應用腐蝕;否則,畫素保持不變。
在 Mahotas 中條件腐蝕影像
在 mahotas 中,條件腐蝕是傳統腐蝕操作的擴充套件,它包含基於第二張影像(通常稱為“標記影像”)的條件。
它允許您控制腐蝕過程,以便腐蝕僅在標記影像具有特定畫素值的位置發生。
我們可以使用 **cerode()** 函式在 mahotas 中對影像執行條件腐蝕。此函式根據標記影像的畫素值將腐蝕過程限制在特定區域。
mahotas.cerode() 函式
Mahotas 中的 cerode() 函式接受兩個輸入 - 輸入影像和掩碼(條件)陣列。它根據提供的條件對輸入影像執行條件腐蝕,並返回生成的腐蝕影像。
掩碼用於識別影像內的特定區域。它們充當過濾器,突出顯示某些區域,同時忽略其他區域。
語法
以下是 mahotas 中 cerode() 函式的基本語法:
mahotas.cerode(f, g, Bc={3x3 cross}, out={np.empty_as(A)})
其中,
**f** - 它是要執行條件腐蝕的輸入影像。
**g** - 它是條件腐蝕期間要應用的掩碼。
**Bc={3×3 十字} (可選)** - 它是用於膨脹的結構元素。預設為 {3×3 十字}。
**out={np.empty_as(A)} (可選)** - 它提供一個輸出陣列來儲存腐蝕操作的結果
示例
在以下示例中,我們透過縮減其畫素強度來對影像執行條件腐蝕:
import mahotas as mh
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
image= mh.imread('nature.jpeg')
# Define the scaling factor
scale_factor = 0.5
# Scale down the intensity by multiplying with the scale factor
scaled_image = image * scale_factor
# Convert the scaled image to the appropriate data type
scaled_image = scaled_image.astype(np.uint8)
conditional_eroded_image = mh.cerode(image, scaled_image)
# Create a figure with subplots
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(7,5 ))
# Display the original image
axes[0].imshow(image)
axes[0].set_title('Original Image')
axes[0].axis('off')
# Display the conditional eroded image
axes[1].imshow(conditional_eroded_image, cmap='gray')
axes[1].set_title('Conditional Eroded Image')
axes[1].axis('off')
# Adjust the layout and display the plot
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
輸出
執行上述程式碼後,我們將獲得以下輸出:

使用結構元素
要在 Mahotas 中使用結構元素執行條件腐蝕,首先,我們需要定義基於其應用腐蝕的條件。例如,您可以根據畫素強度指定條件或提供二值掩碼。
接下來,選擇一個結構元素來定義腐蝕的鄰域。Mahotas 提供了幾個預定義的結構元素,例如圓盤和正方形,您可以根據所需的形狀和大小進行選擇。
最後,檢索生成的影像,該影像將僅包含滿足條件的位置的腐蝕效果。
示例
在這裡,我們嘗試使用結構元素對影像執行條件腐蝕:
import mahotas as mh
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
image= mh.imread('nature.jpeg', as_grey = True).astype(np.uint8)
# Define the condition based on pixel intensity
condition = image > 0.5
# Define a structuring element for erosion
structuring_element = mh.disk(5)
conditional_eroded_image = mh.cerode(image, condition, structuring_element)
# Create a figure with subplots
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(7,5 ))
# Display the original image
axes[0].imshow(image)
axes[0].set_title('Original Image')
axes[0].axis('off')
# Display the conditional eroded image
axes[1].imshow(conditional_eroded_image, cmap='gray')
axes[1].set_title('Conditional Eroded Image')
axes[1].axis('off')
# Adjust the layout and display the plot
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
輸出
獲得的輸出如下所示:

使用自定義條件函式
我們還可以使用自定義條件函式對影像執行條件腐蝕。
為此,我們首先定義一個自定義條件函式,該函式確定哪些畫素應該進行腐蝕。
接下來,選擇一個結構元素來定義腐蝕操作的形狀和大小。最後,執行條件腐蝕並檢索腐蝕影像。
示例
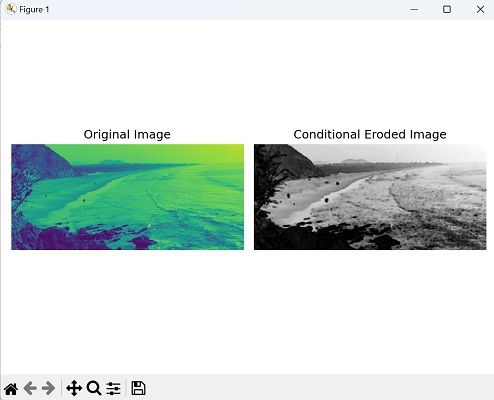
現在,我們使用自定義條件函式膨脹影像:
import mahotas as mh
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Load image
image = mh.imread('sea.bmp', as_grey=True).astype(np.uint8)
# Define a custom condition function
def custom_condition(pixel_value):
return pixel_value > 0.5
# Define a structuring element
structuring_element = mh.disk(5)
# Create a binary mask based on the custom condition function
condition = custom_condition(image)
# Perform conditional erosion
conditional_eroded_image = mh.cerode(image, condition, structuring_element)
# Create a figure with subplots
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize=(7,5 ))
# Display the original image
axes[0].imshow(image)
axes[0].set_title('Original Image')
axes[0].axis('off')
# Display the conditional eroded image
axes[1].imshow(conditional_eroded_image, cmap='gray')
axes[1].set_title('Conditional Eroded Image')
axes[1].axis('off')
# Adjust the layout and display the plot
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
輸出
以下是上述程式碼的輸出: