
- 密碼學教程
- 密碼學 - 首頁
- 密碼學 - 起源
- 密碼學 - 歷史
- 密碼學 - 原理
- 密碼學 - 應用
- 密碼學 - 優點與缺點
- 密碼學 - 現代
- 密碼學 - 傳統密碼
- 密碼學 - 加密需求
- 密碼學 - 雙重強度加密
- 密碼系統
- 密碼系統
- 密碼系統 - 組成部分
- 密碼系統攻擊
- 密碼系統 - 彩虹表攻擊
- 密碼系統 - 字典攻擊
- 密碼系統 - 暴力破解攻擊
- 密碼系統 - 密碼分析技術
- 密碼學型別
- 密碼系統 - 型別
- 公鑰加密
- 現代對稱金鑰加密
- 密碼學雜湊函式
- 金鑰管理
- 密碼系統 - 金鑰生成
- 密碼系統 - 金鑰儲存
- 密碼系統 - 金鑰分發
- 密碼系統 - 金鑰撤銷
- 分組密碼
- 密碼系統 - 流密碼
- 密碼學 - 分組密碼
- 密碼學 - Feistel 分組密碼
- 分組密碼的工作模式
- 分組密碼的工作模式
- 電子密碼本 (ECB) 模式
- 密碼分組連結 (CBC) 模式
- 密碼反饋 (CFB) 模式
- 輸出反饋 (OFB) 模式
- 計數器 (CTR) 模式
- 古典密碼
- 密碼學 - 反向密碼
- 密碼學 - 凱撒密碼
- 密碼學 - ROT13 演算法
- 密碼學 - 置換密碼
- 密碼學 - 加密置換密碼
- 密碼學 - 解密置換密碼
- 密碼學 - 乘法密碼
- 密碼學 - 仿射密碼
- 密碼學 - 簡單替換密碼
- 密碼學 - 簡單替換密碼加密
- 密碼學 - 簡單替換密碼解密
- 密碼學 - 維吉尼亞密碼
- 密碼學 - 維吉尼亞密碼實現
- 現代密碼
- Base64 編碼與解碼
- 密碼學 - XOR 加密
- 替換技術
- 密碼學 - 單表代換密碼
- 密碼學 - 單表代換密碼破解
- 密碼學 - 多表代換密碼
- 密碼學 - Playfair 密碼
- 密碼學 - Hill 密碼
- 多表代換密碼
- 密碼學 - 一次性密碼本
- 一次性密碼本的實現
- 密碼學 - 置換技術
- 密碼學 - 柵欄密碼
- 密碼學 - 列置換
- 密碼學 -隱寫術
- 對稱演算法
- 密碼學 - 資料加密
- 密碼學 - 加密演算法
- 密碼學 - 資料加密標準 (DES)
- 密碼學 - 三重 DES
- 密碼學 - 雙重 DES
- 高階加密標準 (AES)
- 密碼學 - AES 結構
- 密碼學 - AES 變換函式
- 密碼學 - 位元組替換變換
- 密碼學 - 行移位變換
- 密碼學 - 列混淆變換
- 密碼學 - 輪金鑰加變換
- 密碼學 - AES 金鑰擴充套件演算法
- 密碼學 - Blowfish 演算法
- 密碼學 - SHA 演算法
- 密碼學 - RC4 演算法
- 密碼學 - Camellia 加密演算法
- 密碼學 - ChaCha20 加密演算法
- 密碼學 - CAST5 加密演算法
- 密碼學 - SEED 加密演算法
- 密碼學 - SM4 加密演算法
- IDEA - 國際資料加密演算法
- 公鑰(非對稱)密碼演算法
- 密碼學 - RSA 演算法
- 密碼學 - RSA 加密
- 密碼學 - RSA 解密
- 密碼學 - 建立 RSA 金鑰
- 密碼學 - 破解 RSA 密碼
- 密碼學 - ECDSA 演算法
- 密碼學 - DSA 演算法
- 密碼學 - Diffie-Hellman 演算法
- 密碼學中的資料完整性
- 密碼學中的資料完整性
- 訊息認證
- 密碼學數字簽名
- 公鑰基礎設施 (PKI)
- 雜湊
- MD5(訊息摘要演算法 5)
- SHA-1(安全雜湊演算法 1)
- SHA-256(安全雜湊演算法 256 位)
- SHA-512(安全雜湊演算法 512 位)
- SHA-3(安全雜湊演算法 3)
- 密碼雜湊
- Bcrypt 雜湊模組
- 現代密碼學
- 量子密碼學
- 後量子密碼學
- 密碼協議
- 密碼學 - SSL/TLS 協議
- 密碼學 - SSH 協議
- 密碼學 - IPsec 協議
- 密碼學 - PGP 協議
- 影像與檔案加密
- 密碼學 - 影像
- 密碼學 - 檔案
- 隱寫術 - 影像
- 檔案加密和解密
- 密碼學 - 檔案加密
- 密碼學 - 檔案解密
- 物聯網中的密碼學
- 物聯網安全挑戰、威脅和攻擊
- 物聯網安全的加密技術
- 物聯網裝置的通訊協議
- 常用密碼技術
- 自定義構建密碼演算法(混合密碼學)
- 雲密碼學
- 量子密碼學
- 密碼學中的影像隱寫術
- DNA 密碼學
- 密碼學中的一次性密碼 (OTP) 演算法
- 區別
- 密碼學 - MD5 與 SHA1
- 密碼學 - RSA 與 DSA
- 密碼學 - RSA 與 Diffie-Hellman
- 密碼學與密碼學
- 密碼學 - 密碼學與密碼分析
- 密碼學 - 經典與量子
- 密碼學與隱寫術
- 密碼學與加密
- 密碼學與網路安全
- 密碼學 - 流密碼與分組密碼
- 密碼學 - AES 與 DES 密碼
- 密碼學 - 對稱與非對稱
- 密碼學有用資源
- 密碼學 - 快速指南
- 密碼學 - 討論
密碼學 - 柵欄密碼
柵欄法是一種基本的換位密碼。它是一種加密過程,其中訊息中的字母被重新排列以形成新的、看似無關的訊息。這種方法的名稱來自我們書寫訊息的方式。當使用柵欄法建立文字時,結果是一個之字形圖案,其中每個字母在轉到下一行之前都會被拼寫出來。
為了使用柵欄法加密訊息,必須將訊息寫入表格的第一行。此外,訊息的第二個字母需要寫在第二行。這個過程必須繼續進行,直到所有訊息的字母都被寫入。最後,我們按行讀取資料庫以建立加密的訊息。
現在讓我們開始討論如何解碼訊息。解密的第一步是根據加密訊息的長度找到表格的行數。此外,我們必須將加密訊息的第一個字母寫在第一行,第二個字母寫在第二行,依此類推。這個過程必須遵循,直到所有訊息的字母都被寫入。
總而言之,柵欄法的加密非常簡單。它不能提供非常強的安全性。即使是具有基本密碼學知識的人也可以輕鬆破解它。但是,在不需要高安全性的時候,它仍然可以用於簡單的通訊。
柵欄密碼的工作原理?
本節將詳細解釋柵欄密碼使用的加密和解密過程。
加密
為了使用柵欄密碼解密訊息,我們應該首先選擇軌道數,使用該數字以之字形圖案對角線寫入訊息,然後從左到右組合每條軌道上的字母。我們將在下面的示例中逐步講解每個步驟。
讓我們以“RAILFENCE”作為明文為例。現在假設有三個軌道或柵欄,也稱為金鑰。之字形圖案的高度將由金鑰決定。然後可以以之字形圖案對角線從左到右寫入訊息:
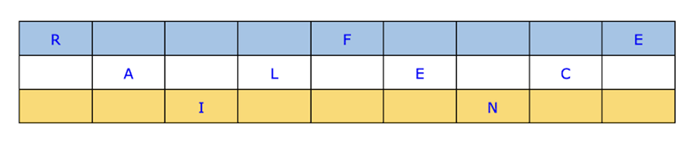
為了建立密文,我們將合併不同的行,在本例中為“RFEALECIN”。
解密
在我們開始解密過程之前,需要確定密文中行和列的數量。密文的長度等於列數。之後,我們需要確定加密了多少行——充當金鑰。
現在我們知道了有多少行和列,我們可以構建表格並弄清楚字母應該放在哪裡,因為柵欄密碼以之字形圖案從左到右對角線加密文字:
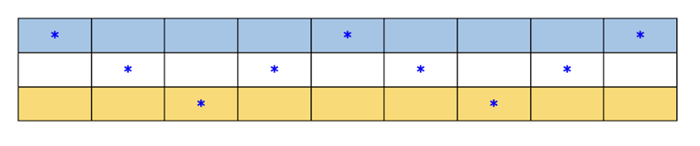
星號 (*) 表示插入密文中的字母以建立明文的位置。從頂行(即第一“軌道”)開始,我們從左到右填寫字母。直到所有星號位置都用密文中的字母填充,然後我們在下一軌道上繼續此模式,依此類推:
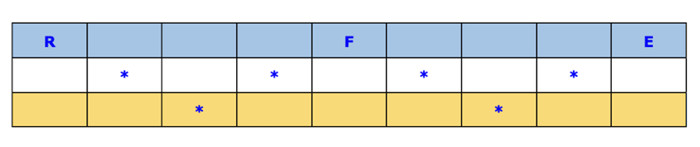
讓我們完成上面的表格:

最後,我們能夠從左到右和從上到下組合字元以獲得明文“RAILFENCE”。
實現
現在我們將使用 Python、Java、C++ 和 Javascript 實現柵欄密碼。
使用 Python 實現
首先,我們將使用 Python 建立程式碼並實現柵欄密碼。我們將建立兩個不同的函式,一個用於加密,另一個用於解密。請看下面的程式碼:
示例
# Function to encrypt a message
def encrypt_rail_fence(plaintext, rails):
# Create the matrix for cipher
rail_matrix = [['\n' for i in range(len(plaintext))]
for j in range(rails)]
# Find the direction
down_direction = False
row, col = 0, 0
for i in range(len(plaintext)):
# Check the direction of flow
# Reverse the direction if just filled the top or bottom rail
if (row == 0) or (row == rails - 1):
down_direction = not down_direction
# Fill the corresponding alphabet
rail_matrix[row][col] = plaintext[i]
col += 1
# Find the next row using direction flag
if down_direction:
row += 1
else:
row -= 1
# Construct the cipher using the rail matrix
cipher_text = []
for i in range(rails):
for j in range(len(plaintext)):
if rail_matrix[i][j] != '\n':
cipher_text.append(rail_matrix[i][j])
return("" . join(cipher_text))
# Function to decrypt the cipher-text
# Function to decrypt the cipher-text
def decrypt_rail_fence(cipher, rails):
# Create the matrix to cipher
# plaintext - rows, length(cipher) - columns
# Fill the rail matrix to distinguish filled spaces from blank ones
rail_matrix = [['\n' for i in range(len(cipher))]
for j in range(rails)]
# Find the direction
down_direction = None
row, col = 0, 0
for i in range(len(cipher)):
# Check the direction of flow
if row == 0:
down_direction = True
if row == rails - 1:
down_direction = False
# Place the cipher text in the rail matrix
rail_matrix[row][col] = '*'
col += 1
# Find the next row using direction flag
if down_direction:
row += 1
else:
row -= 1
# Reconstruct the rail matrix with cipher text
index = 0
for i in range(rails):
for j in range(len(cipher)):
if rail_matrix[i][j] == '*' and index < len(cipher):
rail_matrix[i][j] = cipher[index]
index += 1
# Read the rail matrix in zig-zag manner to construct the resultant text
result = []
row, col = 0, 0
for i in range(len(cipher)):
# Check the direction of flow
if row == 0:
down_direction = True
if row == rails - 1:
down_direction = False
# Add characters from the rail matrix to the result
if rail_matrix[row][col] != '*':
result.append(rail_matrix[row][col])
col += 1
# Find the next row using direction flag
if down_direction:
row += 1
else:
row -= 1
return ''.join(result)
# Driver code
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("First Encrypted Text: ", encrypt_rail_fence("Hello Tutorialspoint", 2))
print("Second Encrypted Text: ", encrypt_rail_fence("Simple Text", 3))
print("Third Encrypted Text: ", encrypt_rail_fence("I am great Cipher", 5))
# Decryption of the cipher-text
print("First Decrypted Text: ", decrypt_rail_fence("HloTtrasonel uoilpit", 2))
print("Second Decrypted Text: ", decrypt_rail_fence("SleipeTxm t", 3))
print("Third Decrypted Text: ", decrypt_rail_fence("Iar etear hmgCp i", 5))
以下是上述示例的輸出:
輸入/輸出
First Encrypted Text: HloTtrason Second Encrypted Text: S Third Encrypted Text: I First Decrypted Text: H Second Decrypted Text: S Third Decrypted Text: I
使用 Java 實現
現在我們將使用 Java 程式語言實現柵欄密碼。我們將使用與 Python 中相同的 approach。在這裡,我們將使用 Java 的 Arrays 庫來實現柵欄矩陣。程式碼如下:
示例
import java.util.Arrays;
public class CustomRailFence {
//Encrypt a message
public static String encryptMessage(String plaintext, int rails) {
// Create the matrix
char[][] railMatrix = new char[rails][plaintext.length()];
// Filling the rail matrix
for (int i = 0; i < rails; i++)
Arrays.fill(railMatrix[i], '\n');
boolean dirDown = false;
int row = 0, col = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < plaintext.length(); i++) {
// Check the direction of flow
if (row == 0 || row == rails - 1)
dirDown = !dirDown;
// Fill the corresponding alphabet
railMatrix[row][col++] = plaintext.charAt(i);
// Find the next row using direction flag
if (dirDown)
row++;
else
row--;
}
// Now we can create the cipher
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < rails; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < plaintext.length(); j++)
if (railMatrix[i][j] != '\n')
result.append(railMatrix[i][j]);
return result.toString();
}
//Decrypt the ciphertext
public static String decryptMessage(String cipher, int rails) {
// Create the matrix
char[][] railMatrix = new char[rails][cipher.length()];
// Filling the rail matrix
for (int i = 0; i < rails; i++)
Arrays.fill(railMatrix[i], '\n');
// Find the direction
boolean dirDown = true;
int row = 0, col = 0;
// Mark the places with '*'
for (int i = 0; i < cipher.length(); i++) {
// Check the direction of flow
if (row == 0)
dirDown = true;
if (row == rails - 1)
dirDown = false;
// Place the marker
railMatrix[row][col++] = '*';
// Find the next row
if (dirDown)
row++;
else
row--;
}
// Now we can produce the fill the rail matrix
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < rails; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < cipher.length(); j++)
if (railMatrix[i][j] == '*' && index < cipher.length())
railMatrix[i][j] = cipher.charAt(index++);
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
row = 0;
col = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < cipher.length(); i++) {
// Check the direction of flow
if (row == 0)
dirDown = true;
if (row == rails - 1)
dirDown = false;
// Place the marker
if (railMatrix[row][col] != '*')
result.append(railMatrix[row][col++]);
// Find the next row using direction flag
if (dirDown)
row++;
else
row--;
}
return result.toString();
}
// Driver function
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Encryption
System.out.println("The Encrypted Messages: ");
System.out.println(encryptMessage("hello world", 2));
System.out.println(encryptMessage("Simple Text", 4));
System.out.println(encryptMessage("Java is great", 5));
// Now decryption of the same cipher-text
System.out.println("\nThe Decrypted Messages: ");
System.out.println(decryptMessage("hlowrdel ol", 2));
System.out.println(decryptMessage("S ieTmletpx", 4));
System.out.println(decryptMessage("Jga rvseaia t", 5));
}
}
以下是上述示例的輸出:
輸入/輸出
The Encrypted Message: hlowrdel ol S ieTmletpx Jga rvseaia t The Decrypted Messages: hello world Simple Text Java is great
使用 C++ 實現
在本節中,我們將構建C++程式碼來展示柵欄密碼的過程。它將使用必要的庫,如iostream和string。程式定義了兩個主要函式,encryptMessage和decryptMessage,用於使用柵欄密碼加密和解密訊息。這些函式使用矩陣表示來建立柵欄密碼演算法,根據給定的軌數以鋸齒形圖案填充矩陣。以下是帶有柵欄密碼加密和解密函式的C++程式:
示例
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
// Function to encrypt a message using Rail Fence Cipher
string encryptMessage(string plaintext, int rails) {
// Create a matrix to represent the rail fence
char rail[rails][plaintext.length()];
// Fill the rail matrix with newline characters
for (int i = 0; i < rails; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < plaintext.length(); j++) {
rail[i][j] = '\n';
}
}
// Determine the direction of movement
bool moveDown = false;
int row = 0, col = 0;
// Traverse the plaintext and fill the rail matrix
for (int i = 0; i < plaintext.length(); i++) {
if (row == 0 || row == rails - 1) {
moveDown = !moveDown;
}
rail[row][col++] = plaintext[i];
moveDown ? row++ : row--;
}
// Construct the cipher text from the rail matrix
string ciphertext;
for (int i = 0; i < rails; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < plaintext.length(); j++) {
if (rail[i][j] != '\n') {
ciphertext.push_back(rail[i][j]);
}
}
}
return ciphertext;
}
// Function to decrypt the cipher text using Rail Fence Cipher
string decryptMessage(string ciphertext, int rails) {
char rail[rails][ciphertext.length()];
// Fill the rail matrix with newline characters
for (int i = 0; i < rails; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < ciphertext.length(); j++) {
rail[i][j] = '\n';
}
}
// Determine the direction of movement
bool moveDown = true;
int row = 0, col = 0;
// Mark the places with '*'
for (int i = 0; i < ciphertext.length(); i++) {
if (row == 0) {
moveDown = true;
}
if (row == rails - 1) {
moveDown = false;
}
rail[row][col++] = '*';
moveDown ? row++ : row--;
}
// Reconstruct the rail matrix with cipher text
int index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < rails; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < ciphertext.length(); j++) {
if (rail[i][j] == '*' && index < ciphertext.length()) {
rail[i][j] = ciphertext[index++];
}
}
}
// Construct the plaintext from the rail matrix
string plaintext;
row = 0, col = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < ciphertext.length(); i++) {
if (row == 0) {
moveDown = true;
}
if (row == rails - 1) {
moveDown = false;
}
if (rail[row][col] != '*') {
plaintext.push_back(rail[row][col++]);
}
moveDown ? row++ : row--;
}
return plaintext;
}
int main() {
cout << "The Encrypted Messages: " << endl;
cout << encryptMessage("hello Tutorialspoint", 2) << endl;
cout << encryptMessage("Simple Text", 4) << endl;
cout << encryptMessage("Cplusplus is great", 5) << endl;
// Now decryption of the same cipher-text
cout << "\nThe Decrypted Messages: " << endl;
cout << decryptMessage("hloTtrasonel uoilpit", 2) << endl;
cout << decryptMessage("S ieTmletpx", 4) << endl;
cout << decryptMessage("Csapu etllirupsgs", 5) << endl;
return 0;
}
以下是上述示例的輸出:
輸入/輸出
The Encrypted Messages: hloTtrasonel uoilpit S ieTmletpx Csapu etllirupsgs The Decrypted Messages: hello Tutorialspoint Simple Text Cptrgulus lpssiea
複雜性和應用
建立訊息所需的行的數量決定了柵欄技術的複雜程度。使用的行數越多,加密就越複雜。此外,如果行數更多,攻擊者可能更難以找出訊息中字元的初始位置。
然而,即使有多行,柵欄技術仍然不是一種非常安全的加密形式。它始終容易受到某些型別的攻擊,攻擊者可以快速破解它。
在現代通訊中,柵欄技術並不常用。它是各種基本低安全通訊協議的組成部分。但是,現在有更安全、更適合保護私人資料的解決方案。
柵欄方法的一個用途是用於兒童的教育遊戲或活動。它可以是一種快速而有趣的方法來講解密碼學的 fundamentals。但是,它不應用於任何重要的安全應用。
優點
現在我們瞭解了柵欄方法背後的基本概念。讓我們討論一下它的優點:
柵欄方法具有許多優點,包括多功能性、簡單性和易用性。
柵欄技術相對易於理解和應用,因此在不需要更高安全級別的情況下,它是基本通訊的有用選擇。柵欄技術可以在無需專用工具或軟體的情況下手動執行。
最後,柵欄系統可以使用任意數量的行。它允許使用者選擇最符合其需求的複雜程度。
缺點
現在讓我們討論柵欄密碼的缺點:
該技術的主要缺點是其容易受到攻擊、缺乏安全性以及有效性有限。
由於任何具有基本密碼學知識的人都可以輕鬆破解柵欄技術,因此它不是一種安全的加密形式。對於較長的訊息,這種方法也不太成功。
此外,某些型別的攻擊,例如已知明文攻擊,可以針對柵欄方法。因此,攻擊者可以簡單地發起攻擊來解密資料。
限制
使用頻率分析,柵欄密碼的加密很容易被破解。小於或等於密文長度的數字充當加密金鑰。因此它非常容易受到暴力攻擊。