
- 密碼學教程
- 密碼學 - 首頁
- 密碼學 - 起源
- 密碼學 - 歷史
- 密碼學 - 原理
- 密碼學 - 應用
- 密碼學 - 優點與缺點
- 密碼學 - 現代
- 密碼學 - 傳統密碼
- 密碼學 - 加密需求
- 密碼學 - 雙重強度加密
- 密碼系統
- 密碼系統
- 密碼系統 - 元件
- 密碼系統攻擊
- 密碼系統 - 彩虹表攻擊
- 密碼系統 - 字典攻擊
- 密碼系統 - 暴力破解攻擊
- 密碼系統 - 密碼分析技術
- 密碼學型別
- 密碼系統 - 型別
- 公鑰加密
- 現代對稱金鑰加密
- 密碼學雜湊函式
- 金鑰管理
- 密碼系統 - 金鑰生成
- 密碼系統 - 金鑰儲存
- 密碼系統 - 金鑰分發
- 密碼系統 - 金鑰吊銷
- 分組密碼
- 密碼系統 - 流密碼
- 密碼學 - 分組密碼
- 密碼學 - Feistel 分組密碼
- 分組密碼操作模式
- 分組密碼操作模式
- 電子密碼本 (ECB) 模式
- 密碼分組連結 (CBC) 模式
- 密碼反饋 (CFB) 模式
- 輸出反饋 (OFB) 模式
- 計數器 (CTR) 模式
- 經典密碼
- 密碼學 - 反向密碼
- 密碼學 - 凱撒密碼
- 密碼學 - ROT13 演算法
- 密碼學 - 換位密碼
- 密碼學 - 加密換位密碼
- 密碼學 - 解密換位密碼
- 密碼學 - 乘法密碼
- 密碼學 - 仿射密碼
- 密碼學 - 簡單替換密碼
- 密碼學 - 簡單替換密碼加密
- 密碼學 - 簡單替換密碼解密
- 密碼學 - 維吉尼亞密碼
- 密碼學 - 實現維吉尼亞密碼
- 現代密碼
- Base64 編碼和解碼
- 密碼學 - XOR 加密
- 替換技術
- 密碼學 - 單表代換密碼
- 密碼學 - 破解單表代換密碼
- 密碼學 - 多表代換密碼
- 密碼學 - Playfair 密碼
- 密碼學 - 希爾密碼
- 多表代換密碼
- 密碼學 - 一次性密碼本密碼
- 一次性密碼本密碼的實現
- 密碼學 - 換位技術
- 密碼學 - 柵欄密碼
- 密碼學 - 列移位密碼
- 密碼學 - 隱寫術
- 對稱演算法
- 密碼學 - 資料加密
- 密碼學 - 加密演算法
- 密碼學 - 資料加密標準
- 密碼學 - 三重DES
- 密碼學 - 雙重DES
- 高階加密標準
- 密碼學 - AES 結構
- 密碼學 - AES 變換函式
- 密碼學 - 位元組替換變換
- 密碼學 - 行移位變換
- 密碼學 - 列混合變換
- 密碼學 - 輪金鑰加變換
- 密碼學 - AES 金鑰擴充套件演算法
- 密碼學 - Blowfish 演算法
- 密碼學 - SHA 演算法
- 密碼學 - RC4 演算法
- 密碼學 - Camellia 加密演算法
- 密碼學 - ChaCha20 加密演算法
- 密碼學 - CAST5 加密演算法
- 密碼學 - SEED 加密演算法
- 密碼學 - SM4 加密演算法
- IDEA - 國際資料加密演算法
- 公鑰(非對稱)密碼學演算法
- 密碼學 - RSA 演算法
- 密碼學 - RSA 加密
- 密碼學 - RSA 解密
- 密碼學 - 建立 RSA 金鑰
- 密碼學 - 破解 RSA 密碼
- 密碼學 - ECDSA 演算法
- 密碼學 - DSA 演算法
- 密碼學 - Diffie-Hellman 演算法
- 密碼學中的資料完整性
- 密碼學中的資料完整性
- 訊息認證
- 密碼學數字簽名
- 公鑰基礎設施
- 雜湊
- MD5(訊息摘要演算法 5)
- SHA-1(安全雜湊演算法 1)
- SHA-256(安全雜湊演算法 256 位)
- SHA-512(安全雜湊演算法 512 位)
- SHA-3(安全雜湊演算法 3)
- 雜湊密碼
- Bcrypt 雜湊模組
- 現代密碼學
- 量子密碼學
- 後量子密碼學
- 密碼學協議
- 密碼學 - SSL/TLS 協議
- 密碼學 - SSH 協議
- 密碼學 - IPsec 協議
- 密碼學 - PGP 協議
- 影像和檔案加密
- 密碼學 - 影像
- 密碼學 - 檔案
- 隱寫術 - 影像
- 檔案加密和解密
- 密碼學 - 檔案加密
- 密碼學 - 檔案解密
- 物聯網中的密碼學
- 物聯網安全挑戰、威脅和攻擊
- 物聯網安全的加密技術
- 物聯網裝置的通訊協議
- 常用密碼學技術
- 自定義構建密碼學演算法(混合密碼學)
- 雲密碼學
- 量子密碼學
- 密碼學中的影像隱寫術
- DNA 密碼學
- 密碼學中的一次性密碼 (OTP) 演算法
- 區別
- 密碼學 - MD5 與 SHA1
- 密碼學 - RSA 與 DSA
- 密碼學 - RSA 與 Diffie-Hellman
- 密碼學與密碼學
- 密碼學 - 密碼學與密碼分析
- 密碼學 - 經典與量子
- 密碼學與隱寫術
- 密碼學與加密
- 密碼學與網路安全
- 密碼學 - 流密碼與分組密碼
- 密碼學 - AES 與 DES 密碼
- 密碼學 - 對稱與非對稱
- 密碼學有用資源
- 密碼學 - 快速指南
- 密碼學 - 討論
密碼學 - 乘法密碼
在本章中,我們將深入探討乘法密碼演算法及其工作原理!讓我們在下面的章節中看看它。
乘法密碼屬於單表代換密碼的範疇。在乘法密碼中,明文中的每個字母都根據預先確定的乘法金鑰替換為密文中相應的字母。
乘法密碼背後的主要思想是使用模算術對明文進行編碼和解碼,模算術使用一個大的素數作為乘法金鑰。在整個加密過程中,明文中每個字母的數值都乘以金鑰,然後計算結果對金鑰取模。例如,如果明文字母是“s”並且金鑰是 7,則密文字母是 (18*7) mod 26 = 22,因為“s”的數值是 18。因此,在這種情況下,字母“a”的密文符號將是“w”。
解密只是反向執行加密過程:密文中每個字母都賦予一個數值,該數值除以金鑰,然後結果對金鑰取模。乘法密碼的一個主要優點是它的簡單性——即易於實現、理解和處理能力要求低。
但是這種方法雖然易於使用和理解,但安全性不高。它類似於一個簡單的秘密程式碼,很容易被別人破解。對於小事情來說,它是合適的,但對於需要強力保護的重要事情來說,它是不合適的。
乘法密碼是如何工作的?
你的金鑰是一個你選擇的大的素數。然後你使用數學運算修改訊息中的每個字母。例如,如果你的金鑰是 7,並且你的訊息包含字母“s”,它是數字 18,你執行 (18 乘以 7) 除以 26 並取餘數。這將給你 22,它對應於字母“w”。因此,“s”在秘密訊息中變為“w”。
你只需反轉數學運算即可讀取秘密訊息。你可以用金鑰除以每個字母的數字,並取餘數。
如果使用乘法轉換為密文,則稱為環繞情況。請考慮如下所示的字母和關聯的數字−
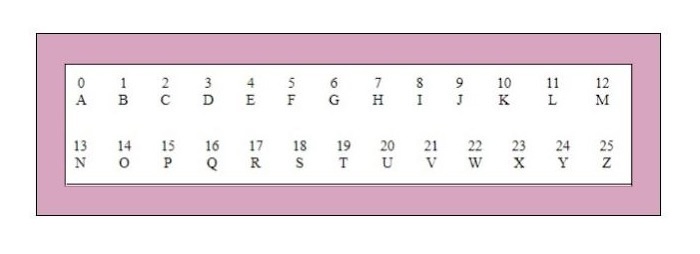
這些數字將被乘以,相應的金鑰是 7。在這種情況下,要建立乘法密碼,基本公式如下−

現在使用上述公式將“hello”轉換為密文,使用金鑰 K。假設我們的金鑰 K 是 3。以下是我們將如何將給定公式應用於“hello”中的每個字母−
對於“h”:P(“h”的明文值)= 7(假設“a”是 0,“b”是 1,…,“h”是 7)
密文 = (7 + 3) Mod 26 = 10 Mod 26 = 10
對於“e”:P(“e”的明文值)= 4
密文 = (4 + 3) Mod 26 = 7 Mod 26 = 7
對於“l”:P(“l”的明文值)= 11
密文 = (11 + 3) Mod 26 = 14 Mod 26 = 14
對於“l”:P(“l”的明文值)= 11
密文 = (11 + 3) Mod 26 = 14 Mod 26 = 14
對於“o”:P(“o”的明文值)= 14
密文 = (14 + 3) Mod 26 = 17 Mod 26 = 17
因此,關於數字 10、7、14、14、17 的值分別是 k、h、o、o、r。
因此,金鑰為 3 的“hello”的密文將是“khoor”。
乘法密碼演算法
加密演算法
首先,你需要選擇一個素數作為加密金鑰。
為明文訊息中的每個字母分配數值。
將每個數值乘以加密金鑰。
取結果模 26,即英語字母表中字母的數量,以確保結果應保持在字母表的範圍內。
將結果數值轉換回字母以獲取密文訊息。
解密演算法
選擇與解密金鑰相同的素數。
為密文訊息中的每個字母分配數值。
將每個數值除以解密金鑰。
取結果模 26。
將結果數值轉換回字母以獲取原始明文訊息。
使用 Python 實現
因此,我們可以透過不同的方式實現此演算法−
使用基本算術
在本例中,我們將使用基本的算術運算來進行乘法密碼的加密和解密。因此,在加密過程中,我們將使用ASCII值將明文訊息轉換為數字(0-25)。每個數字將乘以加密金鑰。然後,對結果取模26,以確保它落在字母範圍(0-25)內。最後,我們將使用ASCII值將數字轉換回字元。
在解密過程中,我們將使用ASCII值將密文訊息轉換為數字(0-25)。每個數字乘以加密金鑰的模逆元。然後對結果取模26。最後,將得到的數字使用ASCII值轉換回字元。
示例
下面是乘法密碼演算法的簡單Python程式碼。請檢視下面的程式 -
def multiplicative_encrypt(message, key):
cipher_text = ''
for char in message:
if char.isalpha():
# Change char to number (0-25)
num = ord(char.lower()) - ord('a')
# Encrypt with the help of (P * K) % 26
encrypted_num = (num * key) % 26
# change back to character
cipher_text += chr(encrypted_num + ord('a'))
else:
cipher_text += char
return cipher_text
def multiplicative_decrypt(ciphertext, key):
plain_text = ''
# get the modular multiplicative inverse of the key
inverse_key = pow(key, -1, 26)
for char in ciphertext:
if char.isalpha():
# change char to number (0-25)
num = ord(char.lower()) - ord('a')
# Decrypt using the formula (C * K_inverse) % 26
decrypted_num = (num * inverse_key) % 26
# change back to character
plain_text += chr(decrypted_num + ord('a'))
else:
plain_text += char
return plain_text
plaintext = "hello tutorialspoint"
key = 7
encrypted_message = multiplicative_encrypt(plaintext, key)
print("Encrypted message:", encrypted_message)
decrypted_message = multiplicative_decrypt(encrypted_message, key)
print("Decrypted message:", decrypted_message)
以下是上述示例的輸出 -
輸入/輸出
Encrypted message: xczzu dkdupeazwbuend Decrypted message: hello tutorialspoint
使用sympy和math庫
在下面的示例中,我們將使用Python的sympy和math庫來實現不同的目的 -
Sympy庫 - 從sympy庫中,我們將匯入mod_inverse函式。此函式將用於計算一個數的模逆元。在乘法密碼中,此函式用於查詢加密/解密金鑰模26的逆元。
Math庫 - 我們將匯入整個math庫。我們將使用math庫中的math.gcd()函式來計算26和加密/解密金鑰的最大公約數(GCD)。GCD用於檢查金鑰是否與26互質。此檢查對於確保金鑰對加密有效非常重要。
簡單來說,我們可以說sympy庫用於計算模逆元,而math庫用於計算金鑰驗證的最大公約數。這兩個庫都提供了在實現乘法密碼演算法中很有用的數學函式。
示例
以下是乘法密碼演算法的簡單Python程式碼。請檢視下面的程式碼 -
from sympy import mod_inverse
import math
def multiplicative_cipher(text, mode, key):
char_to_num = {}
result_message = ''
# dictionary mapping characters to their numerical values
for i in range(26):
char_to_num[chr(ord('a') + i)] = i
# List of characters
char_list = list(char_to_num.keys())
# Dictionary mapping numerical values to characters
num_to_char = dict(zip(char_to_num.values(), char_to_num.keys()))
if mode == 'encrypt':
if math.gcd(26, key) == 1:
# Encryption
for char in text:
if char in char_list:
# Encrypt each character
new_num = (char_to_num[char] * key) % 26
result_message += num_to_char[new_num]
else:
# Leave non-alphabetic characters unchanged
result_message += char
else:
print('Invalid key selected')
elif mode == 'decrypt':
# Calculate the multiplicative inverse of the key
inv_key = mod_inverse(key, 26)
# Decryption
for char in text:
if char in char_list:
# Decrypt each character
new_num = (char_to_num[char] * inv_key) % 26
result_message += num_to_char[new_num]
else:
# Leave non-alphabetic characters unchanged
result_message += char
return result_message
encrypted_text = multiplicative_cipher('hello world', 'encrypt', 7)
print("Encrypted message:", encrypted_text)
decrypted_text = multiplicative_cipher('xczzu yupzv', 'decrypt', 7)
print("Decrypted message:", decrypted_text)
以下是上述示例的輸出 -
輸入/輸出
Encrypted message: xczzu yupzv Decrypted message: hello world
使用Java實現
現在,我們將使用Java程式語言建立一個乘法密碼程式。其中,我們將有一個類,以及兩個函式,透過它們我們可以加密和解密給定的明文訊息。
示例
因此,使用Java程式語言的實現如下 -
public class MultiplicativeCipher {
private int key;
public MultiplicativeCipher(int k) {
key = k;
}
public String encrypt(String plaintext) {
StringBuilder ciphertext = new StringBuilder();
for (char c : plaintext.toCharArray()) {
if (Character.isLetter(c)) {
if (Character.isUpperCase(c))
ciphertext.append((char)(((c - 'A') * key) % 26 + 'A'));
else
ciphertext.append((char)(((c - 'a') * key) % 26 + 'a'));
} else {
ciphertext.append(c);
}
}
return ciphertext.toString();
}
public String decrypt(String ciphertext) {
StringBuilder plaintext = new StringBuilder();
int modInverse = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if ((key * i) % 26 == 1) {
modInverse = i;
break;
}
}
for (char c : ciphertext.toCharArray()) {
if (Character.isLetter(c)) {
if (Character.isUpperCase(c))
plaintext.append((char)(((c - 'A') * modInverse) % 26 + 'A'));
else
plaintext.append((char)(((c - 'a') * modInverse) % 26 + 'a'));
} else {
plaintext.append(c);
}
}
return plaintext.toString();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MultiplicativeCipher cipher = new MultiplicativeCipher(3); // Set the key to 3
String plaintext = "Hello world, How are you";
String ciphertext = cipher.encrypt(plaintext);
System.out.println("The Encrypted text: " + ciphertext);
System.out.println("The Decrypted text: " + cipher.decrypt(ciphertext));
}
}
以下是上述示例的輸出 -
輸入/輸出
The Encrypted text: Vmhhq oqzhj, Vqo azm uqi The Decrypted text: Hello world, How are you
使用C++實現
我們將使用C++程式語言來實現乘法密碼。我們將有一個名為MultiplicativeCipher的類。它提供了訊息加密和解密的工具。encrypt()方法將使用提供的金鑰加密輸入的文字字串並返回結果。而decrypt()方法將使用給定的金鑰解密密文字串並返回明文。
示例
因此,使用C++實現乘法密碼如下 -
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class MultiplicativeCipher {
private:
int key;
public:
MultiplicativeCipher(int k) {
key = k;
}
string encrypt(string plaintext) {
string ciphertext = "";
for (char& c : plaintext) {
if (isalpha(c)) {
if (isupper(c))
ciphertext += char(((c - 'A') * key) % 26 + 'A');
else
ciphertext += char(((c - 'a') * key) % 26 + 'a');
} else {
ciphertext += c;
}
}
return ciphertext;
}
string decrypt(string ciphertext) {
string plaintext = "";
int modInverse = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
if ((key * i) % 26 == 1) {
modInverse = i;
break;
}
}
for (char& c : ciphertext) {
if (isalpha(c)) {
if (isupper(c))
plaintext += char(((c - 'A') * modInverse) % 26 + 'A');
else
plaintext += char(((c - 'a') * modInverse) % 26 + 'a');
} else {
plaintext += c;
}
}
return plaintext;
}
};
int main() {
MultiplicativeCipher cipher(3); // Set the key to 3
string plaintext = "hello this world is awesome!";
string ciphertext = cipher.encrypt(plaintext);
cout << "The Encrypted text: " << ciphertext << endl;
cout << "The Decrypted text: " << cipher.decrypt(ciphertext) << endl;
return 0;
}
以下是上述示例的輸出 -
輸入/輸出
The Encrypted text: vmhhq fvyc oqzhj yc aomcqkm! The Decrypted text: hello this world is awesome!
乘法密碼的特徵
以下是乘法密碼的一些主要特徵 -
乘法密碼易於理解和使用。它遵循一種簡單的替換訊息中字母的方法。
它依賴於素數作為加密和解密的金鑰。
該密碼使用模運算,其中我們在除法後取餘數。此方法幫助我們將加密值保持在一定範圍內,在乘法密碼的情況下,它是字母表的長度。
由於它非常易於實現,因此不適用於傳輸敏感資訊。它可以使用基本技術輕鬆破解。
它不需要大量的計算能力來加密或解密訊息。
乘法密碼適用於小型應用或安全要求不高的場景。
總結
在本章中,我們學習了乘法密碼及其實現。乘法密碼是一種將訊息轉換為秘密程式碼的方法,方法是使用乘以一個特殊數字(稱為金鑰)的方式替換每個字母。有不同的方法來實現這種密碼技術,我們使用了不同的程式語言,例如Python、C++和Java。您可以使用基本的算術運算或sympy和math之類的庫。程式碼示例展示瞭如何使用這些方法加密和解密訊息。您可以根據您的理解和使用情況使用它們。