
- Matlab 教程
- MATLAB - 首頁
- MATLAB - 概述
- MATLAB - 特性
- MATLAB - 環境設定
- MATLAB - 編輯器
- MATLAB - 線上版
- MATLAB - 工作區
- MATLAB - 語法
- MATLAB - 變數
- MATLAB - 命令
- MATLAB - 資料型別
- MATLAB - 運算子
- MATLAB - 日期和時間
- MATLAB - 數字
- MATLAB - 隨機數
- MATLAB - 字串和字元
- MATLAB - 文字格式化
- MATLAB - 時間表
- MATLAB - M 檔案
- MATLAB - 冒號表示法
- MATLAB - 資料匯入
- MATLAB - 資料匯出
- MATLAB - 資料歸一化
- MATLAB - 預定義變數
- MATLAB - 決策
- MATLAB - 決策語句
- MATLAB - if 語句
- MATLAB - if else 語句
- MATLAB - if…elseif else 語句
- MATLAB - 巢狀 if 語句
- MATLAB - switch 語句
- MATLAB - 巢狀 switch
- MATLAB - 迴圈
- MATLAB - 迴圈
- MATLAB - for 迴圈
- MATLAB - while 迴圈
- MATLAB - 巢狀迴圈
- MATLAB - break 語句
- MATLAB - continue 語句
- MATLAB - end 語句
- MATLAB - 陣列
- MATLAB - 陣列
- MATLAB - 向量
- MATLAB - 轉置運算子
- MATLAB - 陣列索引
- MATLAB - 多維陣列
- MATLAB - 相容陣列
- MATLAB - 分類陣列
- MATLAB - 元胞陣列
- MATLAB - 矩陣
- MATLAB - 稀疏矩陣
- MATLAB - 表格
- MATLAB - 結構體
- MATLAB - 陣列乘法
- MATLAB - 陣列除法
- MATLAB - 陣列函式
- MATLAB - 函式
- MATLAB - 函式
- MATLAB - 函式引數
- MATLAB - 匿名函式
- MATLAB - 巢狀函式
- MATLAB - 返回語句
- MATLAB - 空函式
- MATLAB - 區域性函式
- MATLAB - 全域性變數
- MATLAB - 函式控制代碼
- MATLAB - 濾波函式
- MATLAB - 階乘
- MATLAB - 私有函式
- MATLAB - 子函式
- MATLAB - 遞迴函式
- MATLAB - 函式優先順序順序
- MATLAB - map 函式
- MATLAB - mean 函式
- MATLAB - end 函式
- MATLAB - 錯誤處理
- MATLAB - 錯誤處理
- MATLAB - try…catch 語句
- MATLAB - 除錯
- MATLAB - 繪圖
- MATLAB - 繪圖
- MATLAB - 繪製陣列
- MATLAB - 繪製向量
- MATLAB - 條形圖
- MATLAB - 直方圖
- MATLAB - 圖形
- MATLAB - 二維線圖
- MATLAB - 三維圖
- MATLAB - 圖表格式化
- MATLAB - 對數座標軸圖
- MATLAB - 繪製誤差條
- MATLAB - 繪製三維等值線圖
- MATLAB - 極座標圖
- MATLAB - 散點圖
- MATLAB - 繪製表示式或函式
- MATLAB - 繪製矩形
- MATLAB - 繪製頻譜圖
- MATLAB - 繪製網格曲面
- MATLAB - 繪製正弦波
- MATLAB - 插值
- MATLAB - 插值
- MATLAB - 線性插值
- MATLAB - 二維陣列插值
- MATLAB - 三維陣列插值
- MATLAB - 多項式
- MATLAB - 多項式
- MATLAB - 多項式加法
- MATLAB - 多項式乘法
- MATLAB - 多項式除法
- MATLAB - 多項式的導數
- MATLAB - 變換
- MATLAB - 變換函式
- MATLAB - 拉普拉斯變換
- MATLAB - 拉普拉斯濾波器
- MATLAB - 高斯-拉普拉斯濾波器
- MATLAB - 逆傅立葉變換
- MATLAB - 傅立葉變換
- MATLAB - 快速傅立葉變換
- MATLAB - 二維逆餘弦變換
- MATLAB - 向座標軸新增圖例
- MATLAB - 面向物件
- MATLAB - 面向物件程式設計
- MATLAB - 類和物件
- MATLAB - 函式過載
- MATLAB - 運算子過載
- MATLAB - 使用者自定義類
- MATLAB - 複製物件
- MATLAB - 代數
- MATLAB - 線性代數
- MATLAB - 高斯消元法
- MATLAB - 高斯-約旦消元法
- MATLAB - 簡化行階梯形式
- MATLAB - 特徵值和特徵向量
- MATLAB - 積分
- MATLAB - 積分
- MATLAB - 二重積分
- MATLAB - 梯形法則
- MATLAB - 辛普森法則
- MATLAB - 其他
- MATLAB - 微積分
- MATLAB - 微分
- MATLAB - 矩陣的逆
- MATLAB - GNU Octave
- MATLAB - Simulink
- MATLAB - 有用資源
- MATLAB - 快速指南
- MATLAB - 有用資源
- MATLAB - 討論
MATLAB - 類和物件
在 MATLAB 中,使用類和物件可以更有效地組織和管理複雜的程式。MATLAB 中的面向物件程式設計 (OOP) 使您可以建立封裝資料和函式的物件,從而提高模組化、可重用性和清晰度。
理解類和物件
- 類 − 類是建立物件的藍圖。它定義了物件將具有的屬性(資料)和方法(函式)。
- 物件 − 物件是類的例項。它包含類中定義的資料和函式。
使用類和物件的益處
- 模組化 − 將您的程式分解成更小、更易於管理的部分(物件),每個部分都有特定作用。
- 可重用性 − 透過定義可在不同專案中使用的類來建立可重用程式碼。
- 可維護性 − 更易於維護和更新程式碼,因為對類的更改會自動應用於由此類建立的所有物件。
- 封裝 − 透過限制對資料的直接訪問並僅允許透過定義的方法進行修改來保護資料安全。
關鍵概念
- 屬性 − 儲存特定於物件的變數。例如,BankAccount 類可能具有 AccountNumber 和 Balance 等屬性。
- 方法:對物件資料進行操作的函式。例如,BankAccount 類可能具有 deposit 和 withdraw 等方法。
在 Matlab 中建立類
在 MATLAB 中建立簡單的類涉及定義類定義檔案,指定屬性(資料成員)和類將具有的方法(函式)。以下是如何建立簡單的 MATLAB 類的分步方法。
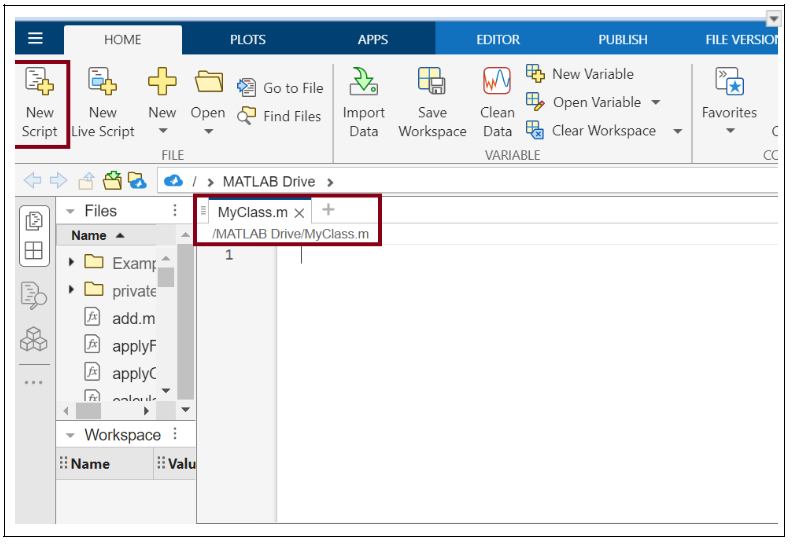
首先要做的是建立一個檔案,為此請按照以下步驟操作:
- 開啟 Matlab
- 轉到“主頁”選項卡,然後單擊“新建指令碼”以建立新檔案。
- 使用“.m”副檔名儲存檔案,並將類檔案命名為 MyClass.m。請記住,檔名必須與類名匹配。
如何在 matlab 中完成此操作的螢幕截圖如下所示:
接下來將開始定義類
開啟 MyClass.m 檔案並使用 classdef 關鍵字,這是一個類的基本框架。
classdef MyClass
properties
% Define properties (data members) here
Property1
Property2
end
methods
% Define methods (functions) here
function obj = MyClass(inputArg1, inputArg2)
% Constructor method
obj.Property1 = inputArg1;
obj.Property2 = inputArg2;
end
function result = myMethod(obj, inputArg)
% Example method
result = obj.Property1 + inputArg;
end
end
end
現在讓我們進入類細節。首先讓我們討論屬性。
定義屬性
屬性是類的成員資料。在 properties 塊內定義它們。例如,假設我有兩個屬性,Property1 和 Property2。
在我的類 MyClass.m 中的屬性定義如下。
properties
Property1
Property2
end
完成屬性定義後,我們將繼續定義方法。
定義類的函式
方法是對類中的資料進行操作的函式。它們在 methods 塊中定義。
我們有兩種方法:建構函式和常規方法。
讓我們首先了解建構函式
建構函式 − 建立類的例項時呼叫此方法。使用與類相同的名稱定義它。
function obj = MyClass(inputArg1, inputArg2)
% Constructor method
obj.Property1 = inputArg1;
obj.Property2 = inputArg2;
end
常規方法 − 這些是對類屬性進行操作的常規函式。使用任何您喜歡的名稱定義它們。
function result = myMethod(obj, inputArg)
% Example method
result = obj.Property1 + inputArg;
end
現在我們已將類儲存為 MyClass.m,您現在可以建立 MyClass 的例項並從 MATLAB 命令視窗呼叫其方法,如下所示。
obj = MyClass(10, 20); disp(obj.Property1) disp(obj.Property2) result = obj.myMethod(5) disp(result)
在 matlab 命令視窗中執行後,輸出為:
>> obj = MyClass(10, 20);
disp(obj.Property1)
disp(obj.Property2)
result = obj.myMethod(5)
disp(result)
10
20
result =
15
15
MATLAB 中的 classdef 關鍵字
MATLAB 中的 classdef 關鍵字用於定義一個新類。
語法
classdef (Attributes) ClassName < SuperclassNames
properties (Attributes) ... end
methods (Attributes) ... end
events (Attributes) ... end
enumeration ... end
end
讓我們詳細瞭解語法。
classdef (屬性) 類名 < 超類名
- classdef − 用於定義類的關鍵字。
- 屬性 − 指定類的某些屬性的可選屬性(例如,Sealed、Abstract、HandleCompatible)。
- 類名 − 類的名稱。
- 超類名 − 此類繼承自的一個或多個類的列表(即其超類或超類)。
屬性塊
屬性 (屬性) − 定義類的成員資料屬性。屬性儲存特定於物件的資料。
properties (Attributes)
PropertyName
end
屬性 − 指定類屬性的某些屬性的可選屬性(例如,Constant、Dependent、Access)。
方法塊
方法 (屬性) − 定義類的函式(方法)。方法對類的物件執行操作。
methods (Attributes)
function obj = MethodName(obj, args)
end
end
屬性 − 指定方法的某些屬性的可選屬性(例如,Static、Abstract、Access)。
事件塊
事件 (屬性) − 定義類可以觸發的事件。事件允許物件將更改或操作傳達給其他物件。
events (Attributes)
EventName
end
屬性 − 指定事件的某些屬性的可選屬性。
列舉塊
列舉 − 使用一組固定的命名值定義列舉類。列舉類可用於定義一組相關的常量。
enumeration
EnumMember
end
這是一個簡單的類定義示例。
classdef (Sealed) MyClass < SuperClass
properties (Access = private)
Property1
end
methods
function obj = MyClass(inputArg)
obj.Property1 = inputArg;
end
function output = myMethod(obj, inputArg)
output = obj.Property1 + inputArg;
end
end
events
Event1
end
enumeration
EnumMember1, EnumMember2
end
end
在這個例子中。
- MyClass 是一個繼承自 SuperClass 的類。
- 該類被標記為 Sealed,這意味著它不能被子類化。
- 它有一個私有屬性 Property1。
- 它有一個建構函式 MyClass 和另一個方法 myMethod。
- 它定義了一個事件 Event1。
- 它有兩個列舉成員 EnumMember1 和 EnumMember2。
MATLAB 中的 class(obj)
MATLAB 中的 class 函式用於確定物件的類(型別)。此函式返回一個字元向量,該向量指定輸入物件的類名。它對於內省特別有用,在內省中,您需要在執行時知道物件的型別。
語法
className = class(obj)
在上述語法中
- obj − 您要確定其類型別的物件。這可以是任何 MATLAB 變數,包括陣列、結構體、函式控制代碼或自定義類的物件。
- className:表示輸入物件 obj 的類的名稱的字元向量。
請注意
- 當您將內建型別(例如,double、char、cell)傳遞給 class 函式時,它會返回該型別的名稱。
- 當您傳遞自定義類的物件時,它會返回該類的名稱。
- 此函式可用於除錯以及編寫需要根據其輸入的類而不同地執行的函式。
讓我們看幾個例子。
示例 1:內建型別
% Determine the class of a numeric array
a = [1, 2, 3];
className = class(a)
% Determine the class of a string
str = 'Hello, World!';
className = class(str)
% Determine the class of a cell array
c = {1, 2, 3};
className = class(c)
在 matlab 命令視窗中執行後,輸出為:
>> % Determine the class of a numeric array
a = [1, 2, 3];
className = class(a)
% Determine the class of a string
str = 'Hello, World!';
className = class(str)
% Determine the class of a cell array
c = {1, 2, 3};
className = class(c)
className = double
className = char
className = cell
示例 2:自定義類
假設您有一個如下定義的自定義類 MyClass。
classdef MyClass
properties
Property1
Property2
end
methods
function obj = MyClass(inputArg1, inputArg2)
% Constructor method
obj.Property1 = inputArg1;
obj.Property2 = inputArg2;
end
function result = myMethod(obj, inputArg)
% Example method
result = obj.Property1 + inputArg;
end
end
end
您可以建立此類的物件並使用 class 函式來確定其型別。
% Create an instance of MyClass obj = MyClass(10, 20) % Determine the class of the object className = class(obj)
在 matlab 命令視窗中執行後,輸出為:
>> % Create an instance of MyClass
obj = MyClass(10, 20)
% Determine the class of the object
className = class(obj)
obj =
MyClass with properties:
Property1: 10
Property2: 20
className =
'MyClass'
>>
MATLAB 中的 isobject() 函式
MATLAB 中的 isobject() 函式用於確定變數是否為使用者定義類的物件。當您需要在執行特定於物件的運算之前檢查變數的型別時,這將特別有用。
在MATLAB中,變數可以屬於不同的資料型別,包括數值陣列、字元陣列、結構體、元胞陣列和物件。MATLAB中的物件是類的例項,該類可以是內建類或使用者定義類。`isobject`函式有助於識別給定變數是否為物件。
語法
tf = isobject(A)
在上文的語法中:
- A − 要測試的變數。
- tf − 一個邏輯值(真或假)。如果A是物件,則返回真;否則返回假。
讓我們看幾個例子
示例1:檢查數值陣列
A = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; tf = isobject(A); disp(['Is A an object? ', num2str(tf)]);
在上例中,`tf = isobject(A);` 檢查A是否為物件。
在 matlab 命令視窗中執行後,輸出為:
>> A = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]; tf = isobject(A); disp(['Is A an object? ', num2str(tf)]); Is A an object? 0 >>
示例2:檢查結構體
我們的程式碼是
B = struct('field1', 10, 'field2', 20);
tf = isobject(B);
disp(['Is B an object? ', num2str(tf)]);
這裡`tf = isobject(B);` 檢查B是否為物件。
在 matlab 命令視窗中執行後,輸出為:
>> B = struct('field1', 10, 'field2', 20);
tf = isobject(B);
disp(['Is B an object? ', num2str(tf)]);
Is B an object? 0
>>
示例3:檢查使用者自定義物件
首先,在一個名為MyClass.m的檔案中定義一個自定義類MyClass
我們的程式碼是。
% MyClass.m
classdef MyClass
properties
Property1
Property2
end
methods
function obj = MyClass(val1, val2)
obj.Property1 = val1;
obj.Property2 = val2;
end
end
end
現在,建立一個此類的例項並檢查它是否為物件。
C = MyClass(10, 20); tf = isobject(C); disp(['Is C an object? ', num2str(tf)]);
在上例程式碼中,`tf = isobject(C);` 檢查C是否為物件。
在MATLAB命令視窗中執行後的輸出是。
>> C = MyClass(10, 20); tf = isobject(C); disp(['Is C an object? ', num2str(tf)]); Is C an object? 1 >>