
- Android 基礎
- Android - 首頁
- Android - 概述
- Android - 環境設定
- Android - 架構
- Android - 應用元件
- Android - Hello World 示例
- Android - 資源
- Android - 活動
- Android - 服務
- Android - 廣播接收器
- Android - 內容提供器
- Android - 碎片
- Android - 意圖/過濾器
- Android - 使用者介面
- Android - UI 佈局
- Android - UI 控制元件
- Android - 事件處理
- Android - 樣式和主題
- Android - 自定義元件
- Android 高階概念
- Android - 拖放
- Android - 通知
- 基於位置的服務
- Android - 傳送郵件
- Android - 傳送簡訊
- Android - 電話呼叫
- 釋出 Android 應用
- Android 有用示例
- Android - 警報對話方塊
- Android - 動畫
- Android - 音訊捕獲
- Android - 音訊管理器
- Android - 自動完成
- Android - 最佳實踐
- Android - 藍牙
- Android - 相機
- Android - 剪貼簿
- Android - 自定義字型
- Android - 資料備份
- Android - 開發者工具
- Android - 模擬器
- Android - Facebook 整合
- Android - 手勢
- Android - Google 地圖
- Android - 影像效果
- Android - ImageSwitcher
- Android - 內部儲存
- Android - JetPlayer
- Android - JSON 解析器
- Android - Linkedin 整合
- Android - 載入微調器
- Android - 本地化
- Android - 登入螢幕
- Android - MediaPlayer
- Android - 多點觸控
- Android - 導航
- Android - 網路連線
- Android - NFC 指南
- Android - PHP/MySQL
- Android - 進度圓圈
- Android - 進度條
- Android - 推送通知
- Android - RenderScript
- Android - RSS 閱讀器
- Android - 螢幕錄製
- Android - SDK 管理器
- Android - 感測器
- Android - 會話管理
- Android - 共享首選項
- Android - SIP 協議
- Android - 拼寫檢查器
- Android - SQLite 資料庫
- Android - 支援庫
- Android - 測試
- Android - 文字轉語音
- Android - TextureView
- Android - Twitter 整合
- Android - UI 設計
- Android - UI 模式
- Android - UI 測試
- Android - WebView 佈局
- Android - Wi-Fi
- Android - 小部件
- Android - XML 解析器
- Android 有用資源
- Android - 問答
- Android - 有用資源
- Android - 討論
Android - 服務
服務是一個在後臺執行以執行長時間執行的操作的元件,而無需與使用者互動,即使應用程式被銷燬,它也能工作。服務基本上可以處於兩種狀態:
| 序號 | 狀態和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
已啟動 當應用程式元件(例如活動)透過呼叫startService()啟動服務時,服務就會啟動。啟動後,服務可以在後臺無限期執行,即使啟動它的元件被銷燬也是如此。 |
| 2 |
繫結 當應用程式元件透過呼叫bindService()繫結到服務時,服務就會繫結。繫結服務提供了一個客戶端-伺服器介面,允許元件與服務互動,傳送請求,獲取結果,甚至透過程序間通訊 (IPC) 在程序之間進行互動。 |
服務具有生命週期回撥方法,您可以實現這些方法來監視服務狀態的變化,並且可以在適當的階段執行工作。左側的以下圖表顯示了使用startService()建立服務時的生命週期,右側的圖表顯示了使用bindService()建立服務時的生命週期:(圖片來自:android.com)
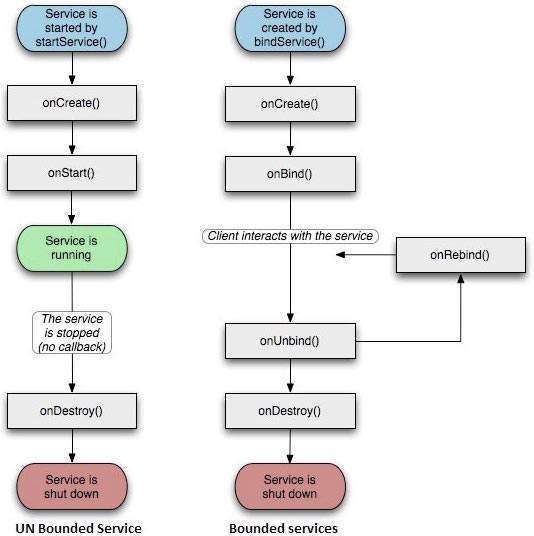
要建立服務,您可以建立一個擴充套件Service基類或其現有子類的Java類。Service基類定義了各種回撥方法,其中最重要的列在下面。您不需要實現所有回撥方法。但是,瞭解每個方法並實現確保您的應用按使用者預期的方式執行的方法非常重要。
| 序號 | 回撥和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | onStartCommand() 當另一個元件(例如活動)透過呼叫startService()請求啟動服務時,系統會呼叫此方法。如果您實現了此方法,則有責任在服務完成工作時透過呼叫stopSelf()或stopService()方法停止服務。 |
| 2 |
onBind() 當另一個元件想要透過呼叫bindService()與服務繫結時,系統會呼叫此方法。如果您實現了此方法,則必須提供客戶端用來與服務通訊的介面,方法是返回一個IBinder物件。您必須始終實現此方法,但如果您不想允許繫結,則應返回null。 |
| 3 |
onUnbind() 當所有客戶端都已斷開與服務釋出的特定介面的連線時,系統會呼叫此方法。 |
| 4 |
onRebind() 當新的客戶端在之前已在onUnbind(Intent)中收到所有客戶端都已斷開連線的通知後連線到服務時,系統會呼叫此方法。 |
| 5 |
onCreate() 當服務首次使用onStartCommand()或onBind()建立時,系統會呼叫此方法。此呼叫是執行一次性設定所必需的。 |
| 6 |
onDestroy() 當服務不再使用且正在被銷燬時,系統會呼叫此方法。您的服務應實現此方法以清理任何資源,例如執行緒、已註冊的偵聽器、接收器等。 |
以下骨架服務演示了每個生命週期方法:
package com.tutorialspoint;
import android.app.Service;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class HelloService extends Service {
/** indicates how to behave if the service is killed */
int mStartMode;
/** interface for clients that bind */
IBinder mBinder;
/** indicates whether onRebind should be used */
boolean mAllowRebind;
/** Called when the service is being created. */
@Override
public void onCreate() {
}
/** The service is starting, due to a call to startService() */
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
return mStartMode;
}
/** A client is binding to the service with bindService() */
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return mBinder;
}
/** Called when all clients have unbound with unbindService() */
@Override
public boolean onUnbind(Intent intent) {
return mAllowRebind;
}
/** Called when a client is binding to the service with bindService()*/
@Override
public void onRebind(Intent intent) {
}
/** Called when The service is no longer used and is being destroyed */
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
}
}
示例
此示例將引導您完成簡單的步驟,以展示如何建立您自己的 Android 服務。按照以下步驟修改我們在Hello World 示例章節中建立的 Android 應用程式:
| 步驟 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 您將使用 Android Studio IDE 建立一個 Android 應用程式,並在包com.example.tutorialspoint7.myapplication下將其命名為我的應用程式,如Hello World 示例章節中所述。 |
| 2 | 修改主活動檔案MainActivity.java以新增startService()和stopService()方法。 |
| 3 | 在包com.example.My Application下建立一個新的 Java 檔案MyService.java。此檔案將包含與 Android 服務相關的方法的實現。 |
| 4 | 使用<service.../>標籤在AndroidManifest.xml檔案中定義您的服務。應用程式可以擁有一個或多個服務,沒有任何限制。 |
| 5 | 修改res/layout/activity_main.xml檔案的預設內容,以線上性佈局中包含兩個按鈕。 |
| 6 | 無需更改res/values/strings.xml檔案中的任何常量。Android Studio 會處理字串值 |
| 7 | 執行應用程式以啟動 Android 模擬器並驗證對應用程式所做的更改的結果。 |
以下是修改後的主活動檔案MainActivity.java的內容。此檔案可以包含每個基本生命週期方法。我們添加了startService()和stopService()方法來啟動和停止服務。
package com.example.tutorialspoint7.myapplication;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
String msg = "Android : ";
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
Log.d(msg, "The onCreate() event");
}
public void startService(View view) {
startService(new Intent(getBaseContext(), MyService.class));
}
// Method to stop the service
public void stopService(View view) {
stopService(new Intent(getBaseContext(), MyService.class));
}
}
以下是MyService.java的內容。此檔案可以根據需要包含一個或多個與服務關聯的方法的實現。目前,我們將僅實現onStartCommand()和onDestroy()兩個方法:
package com.example.tutorialspoint7.myapplication;
import android.app.Service;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.IBinder;
import android.support.annotation.Nullable;
import android.widget.Toast;
/**
* Created by TutorialsPoint7 on 8/23/2016.
*/
public class MyService extends Service {
@Nullable
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return null;
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
// Let it continue running until it is stopped.
Toast.makeText(this, "Service Started", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
return START_STICKY;
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
Toast.makeText(this, "Service Destroyed", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
}
以下是AndroidManifest.xml檔案的修改內容。在這裡,我們添加了<service.../>標籤以包含我們的服務:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.tutorialspoint7.myapplication">
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<service android:name=".MyService" />
</application>
</manifest>
以下是res/layout/activity_main.xml檔案的內容,其中包含兩個按鈕:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin" tools:context=".MainActivity">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Example of services"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:textSize="30dp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView2"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Tutorials point "
android:textColor="#ff87ff09"
android:textSize="30dp"
android:layout_above="@+id/imageButton"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginBottom="40dp" />
<ImageButton
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/imageButton"
android:src="@drawable/abc"
android:layout_centerVertical="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:id="@+id/button2"
android:text="Start Services"
android:onClick="startService"
android:layout_below="@+id/imageButton"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" />
<Button
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Stop Services"
android:id="@+id/button"
android:onClick="stopService"
android:layout_below="@+id/button2"
android:layout_alignLeft="@+id/button2"
android:layout_alignStart="@+id/button2"
android:layout_alignRight="@+id/button2"
android:layout_alignEnd="@+id/button2" />
</RelativeLayout>
讓我們嘗試執行我們剛剛修改的Hello World!應用程式。我假設您在進行環境設定時建立了您的AVD。要從 Android Studio 執行應用程式,請開啟專案的某個活動檔案,然後單擊工具欄中的執行 圖示。Android Studio 將應用程式安裝到您的 AVD 並啟動它,如果您的設定和應用程式一切正常,它將顯示以下模擬器視窗:
圖示。Android Studio 將應用程式安裝到您的 AVD 並啟動它,如果您的設定和應用程式一切正常,它將顯示以下模擬器視窗:

現在要啟動您的服務,讓我們單擊啟動服務按鈕,這將啟動服務,並且根據我們在onStartCommand()方法中的程式設計,訊息服務已啟動將出現在模擬器的底部,如下所示:

要停止服務,您可以單擊停止服務按鈕。
