
- Android 基礎
- Android - 首頁
- Android - 概述
- Android - 環境設定
- Android - 架構
- Android - 應用元件
- Android - Hello World 例子
- Android - 資源
- Android - 活動 (Activities)
- Android - 服務 (Services)
- Android - 廣播接收器 (Broadcast Receivers)
- Android - 內容提供器 (Content Providers)
- Android - 片段 (Fragments)
- Android - 意圖/過濾器 (Intents/Filters)
- Android - 使用者介面
- Android - UI 佈局
- Android - UI 控制元件
- Android - 事件處理
- Android - 樣式和主題
- Android - 自定義元件
- Android 高階概念
- Android - 拖放
- Android - 通知
- 基於位置的服務
- Android - 傳送郵件
- Android - 傳送簡訊
- Android - 電話呼叫
- 釋出 Android 應用
- Android 有用示例
- Android - 警報對話方塊
- Android - 動畫
- Android - 音訊捕捉
- Android - AudioManager
- Android - 自動完成
- Android - 最佳實踐
- Android - 藍牙
- Android - 相機
- Android - 剪貼簿
- Android - 自定義字型
- Android - 資料備份
- Android - 開發者工具
- Android - 模擬器
- Android - Facebook 整合
- Android - 手勢
- Android - Google 地圖
- Android - 圖片效果
- Android - ImageSwitcher
- Android - 內部儲存
- Android - JetPlayer
- Android - JSON 解析器
- Android - LinkedIn 整合
- Android - 載入 Spinne
- Android - 本地化
- Android - 登入螢幕
- Android - MediaPlayer
- Android - 多點觸控
- Android - 導航
- Android - 網路連線
- Android - NFC 指南
- Android - PHP/MySQL
- Android - 進度圓圈
- Android - ProgressBar
- Android - 推送通知
- Android - RenderScript
- Android - RSS 閱讀器
- Android - 螢幕錄製
- Android - SDK 管理器
- Android - 感測器
- Android - 會話管理
- Android - Shared Preferences
- Android - SIP 協議
- Android - 拼寫檢查器
- Android - SQLite 資料庫
- Android - 支援庫
- Android - 測試
- Android - 文字轉語音
- Android - TextureView
- Android - Twitter 整合
- Android - UI 設計
- Android - UI 模式
- Android - UI 測試
- Android - WebView 佈局
- Android - Wi-Fi
- Android - 小部件 (Widgets)
- Android - XML 解析器
- Android 有用資源
- Android - 問答
- Android - 有用資源
- Android - 討論
Android - JSON 解析器
JSON 代表 JavaScript 物件表示法 (JavaScript Object Notation)。它是一種獨立的資料交換格式,是 XML 的最佳替代方案。本章解釋如何解析 JSON 檔案並從中提取必要資訊。
Android 提供四個不同的類來操作 JSON 資料。這些類是 **JSONArray、JSONObject、JSONStringer 和 JSONTokenizer**。
第一步是確定您感興趣的 JSON 資料中的欄位。例如,在下面的 JSON 中,我們只對獲取溫度感興趣。
{
"sys":
{
"country":"GB",
"sunrise":1381107633,
"sunset":1381149604
},
"weather":[
{
"id":711,
"main":"Smoke",
"description":"smoke",
"icon":"50n"
}
],
"main":
{
"temp":304.15,
"pressure":1009,
}
}
JSON - 元素
JSON 檔案包含許多元件。以下是定義 JSON 檔案元件及其描述的表格:
| 序號 | 元件及描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 陣列([]) 在 JSON 檔案中,方括號([])表示 JSON 陣列。 |
| 2 | 物件({}) 在 JSON 檔案中,花括號({})表示 JSON 物件。 |
| 3 | 鍵 (Key) JSON 物件包含一個鍵,它只是一個字串。鍵/值對構成一個 JSON 物件。 |
| 4 | 值 (Value) 每個鍵都有一個值,可以是字串、整數或雙精度數等。 |
JSON - 解析
為了解析 JSON 物件,我們將建立一個 JSONObject 類的物件,並向其指定包含 JSON 資料的字串。其語法如下:
String in; JSONObject reader = new JSONObject(in);
最後一步是解析 JSON。JSON 檔案由不同的物件組成,這些物件具有不同的鍵/值對等。因此,JSONObject 具有一個單獨的函式來解析 JSON 檔案的每個元件。其語法如下:
JSONObject sys = reader.getJSONObject("sys");
country = sys.getString("country");
JSONObject main = reader.getJSONObject("main");
temperature = main.getString("temp");
方法 **getJSONObject** 返回 JSON 物件。方法 **getString** 返回指定鍵的字串值。
除了這些方法外,此類還提供了其他方法以更好地解析 JSON 檔案。這些方法列在下面:
| 序號 | 方法及描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | get(String name) 此方法只返回物件型別的值。 |
| 2 | getBoolean(String name) 此方法返回鍵指定的布林值。 |
| 3 | getDouble(String name) 此方法返回鍵指定的雙精度值。 |
| 4 |
getInt(String name)
此方法返回鍵指定的整數值。 |
| 5 | getLong(String name) 此方法返回鍵指定的長整數值。 |
| 6 | length() 此方法返回此物件中名稱/值對映的數量。 |
| 7 | names() 此方法返回一個包含此物件中字串名稱的陣列。 |
示例
要試驗此示例,您可以在實際裝置或模擬器上執行它。
| 步驟 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 您將使用 Android Studio 建立一個 Android 應用。 |
| 2 | 修改 src/MainActivity.java 檔案以新增必要的程式碼。 |
| 3 | 修改 res/layout/activity_main 以新增相應的 XML 元件。 |
| 4 | 修改 res/values/strings.xml 以新增必要的字串元件。 |
| 5 | 執行應用程式,選擇正在執行的 Android 裝置,將應用程式安裝到該裝置上,並驗證結果。 |
以下是修改後的主活動檔案 **src/MainActivity.java** 的內容。
package com.example.tutorialspoint7.myapplication;
import android.os.AsyncTask;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.util.Log;
import android.widget.ListAdapter;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.SimpleAdapter;
import android.widget.Toast;
import org.json.JSONArray;
import org.json.JSONException;
import org.json.JSONObject;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private String TAG = MainActivity.class.getSimpleName();
private ListView lv;
ArrayList<HashMap<String, String>> contactList;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
contactList = new ArrayList<>();
lv = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.list);
new GetContacts().execute();
}
private class GetContacts extends AsyncTask<Void, Void, Void> {
@Override
protected void onPreExecute() {
super.onPreExecute();
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"Json Data is
downloading",Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
@Override
protected Void doInBackground(Void... arg0) {
HttpHandler sh = new HttpHandler();
// Making a request to url and getting response
String url = "http://api.androidhive.info/contacts/";
String jsonStr = sh.makeServiceCall(url);
Log.e(TAG, "Response from url: " + jsonStr);
if (jsonStr != null) {
try {
JSONObject jsonObj = new JSONObject(jsonStr);
// Getting JSON Array node
JSONArray contacts = jsonObj.getJSONArray("contacts");
// looping through All Contacts
for (int i = 0; i < contacts.length(); i++) {
JSONObject c = contacts.getJSONObject(i);
String id = c.getString("id");
String name = c.getString("name");
String email = c.getString("email");
String address = c.getString("address");
String gender = c.getString("gender");
// Phone node is JSON Object
JSONObject phone = c.getJSONObject("phone");
String mobile = phone.getString("mobile");
String home = phone.getString("home");
String office = phone.getString("office");
// tmp hash map for single contact
HashMap<String, String> contact = new HashMap<>();
// adding each child node to HashMap key => value
contact.put("id", id);
contact.put("name", name);
contact.put("email", email);
contact.put("mobile", mobile);
// adding contact to contact list
contactList.add(contact);
}
} catch (final JSONException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Json parsing error: " + e.getMessage());
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),
"Json parsing error: " + e.getMessage(),
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
});
}
} else {
Log.e(TAG, "Couldn't get json from server.");
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
Toast.makeText(getApplicationContext(),
"Couldn't get json from server. Check LogCat for possible errors!",
Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
}
});
}
return null;
}
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(Void result) {
super.onPostExecute(result);
ListAdapter adapter = new SimpleAdapter(MainActivity.this, contactList,
R.layout.list_item, new String[]{ "email","mobile"},
new int[]{R.id.email, R.id.mobile});
lv.setAdapter(adapter);
}
}
}
以下是修改後的 xml 檔案 **HttpHandler.java** 的內容。
package com.example.tutorialspoint7.myapplication;
import android.util.Log;
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.ProtocolException;
import java.net.URL;
public class HttpHandler {
private static final String TAG = HttpHandler.class.getSimpleName();
public HttpHandler() {
}
public String makeServiceCall(String reqUrl) {
String response = null;
try {
URL url = new URL(reqUrl);
HttpURLConnection conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setRequestMethod("GET");
// read the response
InputStream in = new BufferedInputStream(conn.getInputStream());
response = convertStreamToString(in);
} catch (MalformedURLException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "MalformedURLException: " + e.getMessage());
} catch (ProtocolException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "ProtocolException: " + e.getMessage());
} catch (IOException e) {
Log.e(TAG, "IOException: " + e.getMessage());
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.e(TAG, "Exception: " + e.getMessage());
}
return response;
}
private String convertStreamToString(InputStream is) {
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(is));
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
String line;
try {
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
sb.append(line).append('\n');
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
以下是修改後的 xml 檔案 **res/layout/activity_main.xml** 的內容。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.example.tutorialspoint7.myapplication.MainActivity">
<ListView
android:id="@+id/list"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" />
</RelativeLayout>
以下是修改後的 xml 檔案 **res/layout/list_item.xml** 的內容。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/email"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:paddingBottom="2dip"
android:textColor="@color/colorAccent" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/mobile"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textColor="#5d5d5d"
android:textStyle="bold" />
</LinearLayout>
以下是 **AndroidManifest.xml** 檔案的內容。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.tutorialspoint7.myapplication">
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
讓我們嘗試執行我們剛剛修改的應用程式。我假設您在進行環境設定時已經建立了您的 **AVD**。要從 Android Studio 執行該應用,請開啟專案中的一個活動檔案,然後點選工具欄中的執行  圖示。Android Studio 將應用安裝到您的 AVD 並啟動它,如果您的設定和應用程式一切正常,它將顯示以下模擬器視窗:
圖示。Android Studio 將應用安裝到您的 AVD 並啟動它,如果您的設定和應用程式一切正常,它將顯示以下模擬器視窗:
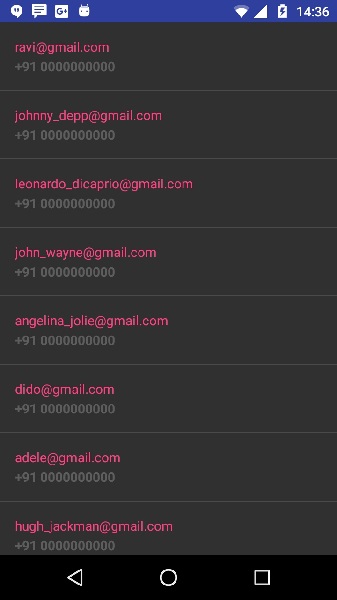
上面的示例顯示了來自字串 json 的資料,資料包含僱員詳細資訊以及薪資資訊。
