
- ReactJS 教程
- ReactJS - 首頁
- ReactJS - 簡介
- ReactJS - 路線圖
- ReactJS - 安裝
- ReactJS - 特性
- ReactJS - 優點與缺點
- ReactJS - 架構
- ReactJS - 建立 React 應用
- ReactJS - JSX
- ReactJS - 元件
- ReactJS - 巢狀元件
- ReactJS - 使用新建立的元件
- ReactJS - 元件集合
- ReactJS - 樣式
- ReactJS - 屬性 (props)
- ReactJS - 使用屬性建立元件
- ReactJS - props 驗證
- ReactJS - 建構函式
- ReactJS - 元件生命週期
- ReactJS - 事件管理
- ReactJS - 建立一個事件感知元件
- ReactJS - 在 Expense Manager APP 中引入事件
- ReactJS - 狀態管理
- ReactJS - 狀態管理 API
- ReactJS - 無狀態元件
- ReactJS - 使用 React Hooks 進行狀態管理
- ReactJS - 使用 React Hooks 進行元件生命週期管理
- ReactJS - 佈局元件
- ReactJS - 分頁
- ReactJS - Material UI
- ReactJS - Http 客戶端程式設計
- ReactJS - 表單程式設計
- ReactJS - 受控元件
- ReactJS - 非受控元件
- ReactJS - Formik
- ReactJS - 條件渲染
- ReactJS - 列表
- ReactJS - Keys
- ReactJS - 路由
- ReactJS - Redux
- ReactJS - 動畫
- ReactJS - Bootstrap
- ReactJS - Map
- ReactJS - 表格
- ReactJS - 使用 Flux 管理狀態
- ReactJS - 測試
- ReactJS - CLI 命令
- ReactJS - 構建和部署
- ReactJS - 示例
- Hooks
- ReactJS - Hooks 簡介
- ReactJS - 使用 useState
- ReactJS - 使用 useEffect
- ReactJS - 使用 useContext
- ReactJS - 使用 useRef
- ReactJS - 使用 useReducer
- ReactJS - 使用 useCallback
- ReactJS - 使用 useMemo
- ReactJS - 自定義 Hooks
- ReactJS 高階
- ReactJS - 可訪問性
- ReactJS - 程式碼分割
- ReactJS - Context
- ReactJS - 錯誤邊界
- ReactJS - 轉發 Refs
- ReactJS - Fragments
- ReactJS - 高階元件
- ReactJS - 與其他庫整合
- ReactJS - 效能最佳化
- ReactJS - Profiler API
- ReactJS - Portals
- ReactJS - 無 ES6 ECMAScript 的 React
- ReactJS - 無 JSX 的 React
- ReactJS - 調和
- ReactJS - Refs 和 DOM
- ReactJS - Render Props
- ReactJS - 靜態型別檢查
- ReactJS - Strict Mode
- ReactJS - Web Components
- 其他概念
- ReactJS - 日期選擇器
- ReactJS - Helmet
- ReactJS - 內聯樣式
- ReactJS - PropTypes
- ReactJS - BrowserRouter
- ReactJS - DOM
- ReactJS - 輪播圖
- ReactJS - 圖示
- ReactJS - 表單元件
- ReactJS - 參考 API
- ReactJS 有用資源
- ReactJS - 快速指南
- ReactJS - 有用資源
- ReactJS - 討論
ReactJS - testInstance.parent 屬性
在程式設計中,尤其是在測試的上下文中,testInstance.parent 屬性是一種引用更高級別或包含特定測試例項的封閉結構的方法。可以把它想象成查詢特定程式碼段的“容器”。
例如,如果我們有一個包含多個測試用例的測試套件,每個測試用例就像一個子項,而測試套件就是父項。因此,如果我們說 testInstance.parent,我們實際上是在問:“這個特定測試用例屬於哪個組或集合!”
此屬性對於組織和理解測試的層次結構很有用。它有助於以組為單位管理和執行測試,從而更輕鬆地處理和分析結果。
這就像把我們的物品放在不同的盒子裡。每個盒子(測試用例)都有自己的內容,但更大的盒子(測試套件)將它們全部放在一起。因此,testInstance.parent 幫助我們找出哪個大盒子包含我們感興趣的特定小盒子。
語法
testInstance.parent
返回值
testInstance.parent 通常返回特定測試例項的父項或更高級別的容器。它告訴我們當前測試例項屬於哪個組或集合。
示例
示例 - 基本的父子關係
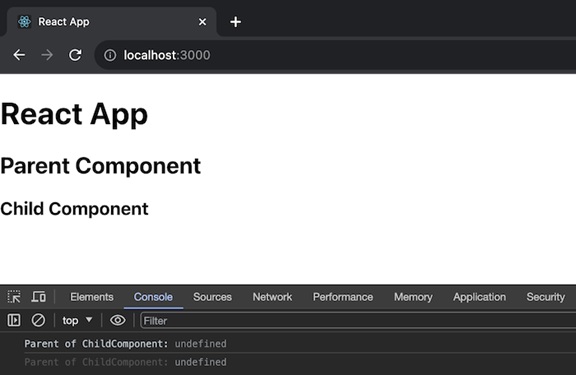
在這個 React 應用中,我們將有三個元件:ParentComponent、ChildComponent 和主 App 元件。ParentComponent 渲染一個帶有 <h2> 標題的 div,並將 ChildComponent 包裝在 ParentContext.Provider 中,為上下文提供值為“Parent”的值。ChildComponent 使用 React.useContext 從 ParentContext 訪問該值並將其記錄。它渲染一個帶有 <h3> 標題的 div。最後,主 App 元件渲染一個帶有 <h1> 標題的 div,幷包含 ParentComponent。因此,此完整應用程式的程式碼如下:
ParentComponent.js
import React from 'react';
import ChildComponent from './ChildComponent';
// Create a context
const ParentContext = React.createContext();
const ParentComponent = () => {
return (
<ParentContext.Provider value={'Parent'}>
<div>
<h2>Parent Component</h2>
<ChildComponent />
</div>
</ParentContext.Provider>
);
};
export default ParentComponent;
ChildComponent.js
import React from 'react';
// Import the context
import ParentContext from './ParentComponent';
const ChildComponent = () => {
// Use the context
const parent = React.useContext(ParentContext);
console.log('Parent of ChildComponent:', parent);
return (
<div>
<h3>Child Component</h3>
</div>
);
};
export default ChildComponent;
App.js
import React from 'react';
import ParentComponent from './ParentComponent';
const App = () => {
return (
<div>
<h1>React App</h1>
<ParentComponent />
</div>
);
};
export default App;
輸出
示例 - 巢狀元件
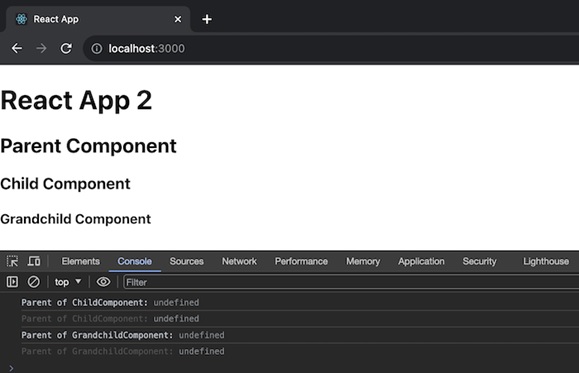
在這個應用中,我們將看到元件之間的父子孫關係,每個元件都記錄其父級上下文。渲染輸出將顯示具有自身標題的元件層次結構,在控制檯中,我們將看到每個子元件和孫元件的已記錄父級上下文。完整的應用程式如下所示:
ParentComponent.js
import React from 'react';
import ChildComponent from './ChildComponent';
const ParentComponent = () => {
return (
<div>
<h2>Parent Component</h2>
<ChildComponent />
</div>
);
};
export default ParentComponent;
ChildComponent.js
import React from 'react';
import GrandchildComponent from './GrandchildComponent';
const ChildComponent = () => {
const parent = React.useContext(ParentContext);
console.log('Parent of ChildComponent:', parent);
return (
<div>
<h3>Child Component</h3>
<GrandchildComponent />
</div>
);
};
export default ChildComponent;
GrandchildComponent.js
import React from 'react';
const GrandchildComponent = () => {
const parent = React.useContext(ParentContext);
console.log('Parent of GrandchildComponent:', parent);
return (
<div>
<h4>Grandchild Component</h4>
</div>
);
};
export default GrandchildComponent;
App.js
import React from 'react';
import ParentComponent from './ParentComponent';
const App = () => {
return (
<div>
<h1>React App 2</h1>
<ParentComponent />
</div>
);
};
export default App;
輸出
示例 - 動態元件渲染
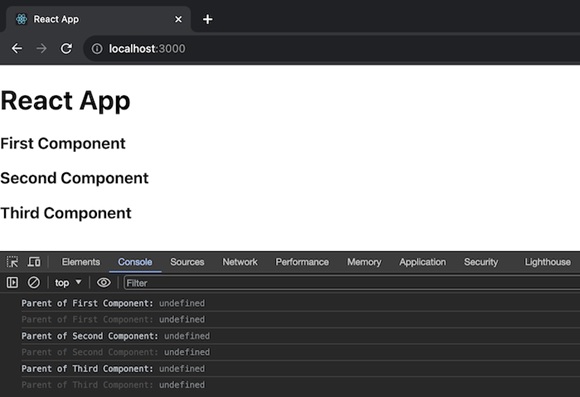
這個 React 應用具有動態元件結構,它使用上下文來共享資料。ParentComponent 建立一個名為 ParentContext 的上下文,其值為“Parent”,並充當其子元件的提供者。DynamicComponent 使用 useContext hook 獲取並記錄上下文值。此應用程式將動態渲染具有名稱的元件。程式碼如下:
ParentComponent.js
import React from 'react';
// Create a context
const ParentContext = React.createContext();
const ParentComponent = ({ children }) => {
return (
<ParentContext.Provider value={'Parent'}>
<div>
<h2>Parent Component</h2>
{children}
</div>
</ParentContext.Provider>
);
};
export { ParentComponent, ParentContext };
DynamicComponent.js
import React from 'react';
import { ParentContext } from './ParentComponent';
const DynamicComponent = ({ name }) => {
const parent = React.useContext(ParentContext);
console.log(`Parent of ${name} Component:`, parent);
return (
<div>
<h3>{name} Component</h3>
</div>
);
};
export default DynamicComponent;
App.js
import React from 'react';
import DynamicComponent from './DynamicComponent';
const App = () => {
const componentsToRender = ['First', 'Second', 'Third'];
return (
<div>
<h1>React App</h1>
{componentsToRender.map((component, index) => (
<DynamicComponent key={index} name={component} />
))}
</div>
);
};
export default App;
輸出
總結
在程式設計中,主要是在測試中,testInstance.parent 屬性指的是圍繞單個測試的結構。這就像查詢程式碼段的“容器”。因此,使用 testInstance.parent 可以幫助我們找出哪個大盒子包含我們感興趣的特定小盒子。正如我們已經看到了此屬性的不同示例以獲得它的實踐經驗。