
- ReactJS 教程
- ReactJS - 首頁
- ReactJS - 簡介
- ReactJS - 路線圖
- ReactJS - 安裝
- ReactJS - 特性
- ReactJS - 優點與缺點
- ReactJS - 架構
- ReactJS - 建立 React 應用
- ReactJS - JSX
- ReactJS - 元件
- ReactJS - 巢狀元件
- ReactJS - 使用新建立的元件
- ReactJS - 元件集合
- ReactJS - 樣式
- ReactJS - 屬性 (props)
- ReactJS - 使用屬性建立元件
- ReactJS - props 驗證
- ReactJS - 建構函式
- ReactJS - 元件生命週期
- ReactJS - 事件管理
- ReactJS - 建立一個事件感知元件
- ReactJS - 在 Expense Manager 應用中引入事件
- ReactJS - 狀態管理
- ReactJS - 狀態管理 API
- ReactJS - 無狀態元件
- ReactJS - 使用 React Hooks 進行狀態管理
- ReactJS - 使用 React Hooks 進行元件生命週期管理
- ReactJS - 佈局元件
- ReactJS - 分頁
- ReactJS - Material UI
- ReactJS - Http 客戶端程式設計
- ReactJS - 表單程式設計
- ReactJS - 受控元件
- ReactJS - 非受控元件
- ReactJS - Formik
- ReactJS - 條件渲染
- ReactJS - 列表
- ReactJS - Keys
- ReactJS - 路由
- ReactJS - Redux
- ReactJS - 動畫
- ReactJS - Bootstrap
- ReactJS - 地圖
- ReactJS - 表格
- ReactJS - 使用 Flux 管理狀態
- ReactJS - 測試
- ReactJS - CLI 命令
- ReactJS - 構建和部署
- ReactJS - 示例
- Hooks
- ReactJS - Hooks 簡介
- ReactJS - 使用 useState
- ReactJS - 使用 useEffect
- ReactJS - 使用 useContext
- ReactJS - 使用 useRef
- ReactJS - 使用 useReducer
- ReactJS - 使用 useCallback
- ReactJS - 使用 useMemo
- ReactJS - 自定義 Hooks
- ReactJS 高階
- ReactJS - 可訪問性
- ReactJS - 程式碼分割
- ReactJS - 上下文
- ReactJS - 錯誤邊界
- ReactJS - 轉發 Refs
- ReactJS - 碎片
- ReactJS - 高階元件
- ReactJS - 整合其他庫
- ReactJS - 最佳化效能
- ReactJS - Profiler API
- ReactJS - 埠
- ReactJS - 無 ES6 ECMAScript 的 React
- ReactJS - 無 JSX 的 React
- ReactJS - 調和
- ReactJS - Refs 和 DOM
- ReactJS - 渲染 Props
- ReactJS - 靜態型別檢查
- ReactJS - 嚴格模式
- ReactJS - Web Components
- 其他概念
- ReactJS - 日期選擇器
- ReactJS - Helmet
- ReactJS - 內聯樣式
- ReactJS - PropTypes
- ReactJS - BrowserRouter
- ReactJS - DOM
- ReactJS - 走馬燈
- ReactJS - 圖示
- ReactJS - 表單元件
- ReactJS - 參考 API
- ReactJS 有用資源
- ReactJS - 快速指南
- ReactJS - 有用資源
- ReactJS - 討論
ReactJS - PropTypes
JavaScript 是一種動態型別的語言。這意味著 JavaScript 不需要宣告或指定變數的型別。在程式執行(執行時)期間,JavaScript 檢查分配給變數的值,然後推斷變數的型別。例如,如果變數 num 被賦值為 John,則它推斷 num 的型別為字串。如果同一個變數 num 被賦值為 10,則它推斷 num 的型別為數字。
var num = 'John' // The type of `num` is string var num = 10 // The type of `num` is number
動態型別對於指令碼語言來說很好,因為它可以加快開發速度。動態型別的另一方面是 JavaScript 引擎在開始執行程式之前不知道變數的型別。這阻止了 JavaScript 引擎查詢或識別某些錯誤。例如,下面提到的程式碼不會執行並停止程式。
var num = 10 var name = 'John' var result = num + name // throws error during runtime
React 和型別
在 React 中,每個元件將有多個 props,並且每個 props 都應分配給具有正確型別的 value。具有錯誤型別的元件 props 將引發意外行為。為了更好地理解這個問題,讓我們建立一個新的應用程式並建立一個元件 Sum,它將彙總其屬性並顯示結果。
要建立一個新的 React 應用,請執行以下命令:
create-react-app myapp
建立應用程式後,在元件資料夾下建立一個新的元件 Sum(src/components/PropTypes/Sum.js)
import React from 'react'
class Sum extends React.Component {
render() {
return <p>The sum of {this.props.num1} and {this.props.num2}
is {parseInt(this.props.num1) + parseInt(this.props.num2)}</p>
}
}
export default Sum
這裡,Sum 元件接受兩個數字 num1 和 num2,並列印這兩個數字的總和。如果為 props 提供了數字值,則元件將工作。但是,如果 sum 元件提供了字串,則它將顯示 NaN 作為這兩個屬性的總和。
無法找到 num1 和 num2 props 的給定值是否格式不正確。讓我們在根元件 (src/App.js) 中使用 Sum 元件,看看它是如何渲染的。
import Sum from "./components/PropTypes/Sum";
function App() {
var num1 = 10
var num2 = 200
var name1 = "John"
var name2 = "Peter"
return (
<div>
<Sum num1={num1} num2={num2} />
<Sum num1={name1} num2={name2} />
</div>
);
}
export default App;
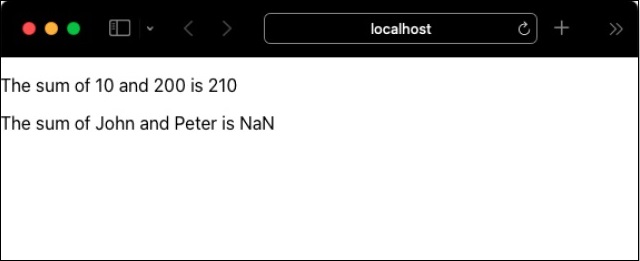
PropTypes
React 社群提供了一個特殊的包 prop-types 來解決屬性型別不匹配的問題。prop-types 允許透過元件內部的自定義設定 (propTypes) 指定元件屬性的型別。例如,可以使用 PropTypes.number 選項指定數字型別的屬性,如下所示。
Sum.propTypes = {
num1: PropTypes.number,
num2: PropTypes.number
}
一旦指定了屬性的型別,React 就會在應用程式的開發階段發出警告。讓我們在我們的示例應用程式中包含 propTypes,看看它如何幫助捕獲屬性型別不匹配的問題。
使用節點包管理器 (npm) 安裝 prop-types 包,如下所示:
npm i prop-types --save
現在,指定 **Sum** 元件屬性的型別,如下所示:
import React from 'react'
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
class Sum extends React.Component {
render() {
return <p>The sum of {this.props.num1} and {this.props.num2}
is {parseInt(this.props.num1) + parseInt(this.props.num2)}</p>
}
}
Sum.propTypes = {
num1: PropTypes.number,
num2: PropTypes.number
}
export default Sum
最後,使用以下命令執行應用程式:
npm start
在您喜歡的瀏覽器中開啟應用程式,並透過開發者工具開啟 JavaScript 控制檯。JavaScript 會發出警告,表明提供了意外的型別,如下所示:
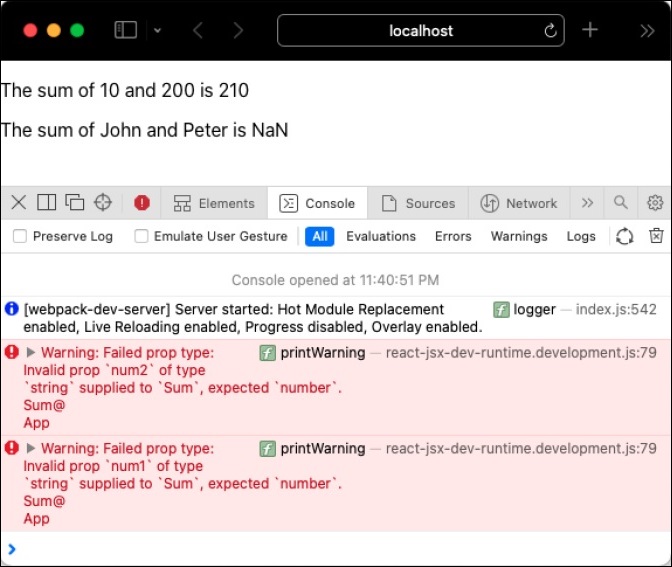
propTypes 僅在開發階段有效,以消除由於額外檢查 props 型別而導致的應用程式效能下降。這不會影響生產/即時環境中應用程式的效能。
可用驗證器
prop-types 提供了大量現成的驗證器。它們如下所示:
PropTypes.array
PropTypes.bigint
PropTypes.bool
PropTypes.func
PropTypes.number
PropTypes.object
PropTypes.string
PropTypes.symbol
PropTypes.node - 任何可以渲染的內容
PropTypes.element - React 元件
PropTypes.elementType - React 元件的型別
PropTypes.instanceOf() - 指定類的例項
propTypes.oneOf(['Value1', 'valueN']) - Value 和 ValueN 之一
PropTypes.oneOfType([]) - 例如,PropTypes.oneOfType([PropTypes.number, PropTypes.bigint])
PropTypes.arrayOf() - 例如,PropTypes.arrayOf(PropTypes.number)
PropTypes.objectOf() - 例如,PropTypes.objectOf(PropTypes.number)
PropTypes.func.isRequired
propTypes.element.isRequired
PropTypes.any.isRequired
還可以建立自定義驗證器並用於驗證屬性的值。假設元件有一個 email 屬性,並且值應為有效的電子郵件地址。然後,可以編寫一個驗證函式並將其附加到 email 屬性,如下所示:

Sum.propTypes = {
num1: PropTypes.number,
num2: PropTypes.number,
email: function(myProps, myPropName, myComponentName) {
if (!/^[^\s@]+@[^\s@]+\.[^\s@]+$/.test(myProps[myPropName])) {
return new Error(
'Invalid prop value `' + myProps[myPropName] + '` supplied to' +
' `' + myComponentName + '/' + myPropName + '`. Validation failed.'
);
}
}
}
這裡,
/^[^\s@]+@[^\s@]+\.[^\s@]+$/ 是一個簡單的正則表示式電子郵件模式。
myProps 表示所有屬性。
myPropName 表示當前正在驗證的屬性。
myComponentName 表示正在驗證的元件的名稱。
類似地,可以使用以下函式簽名為陣列和物件屬性建立和使用自定義驗證器
PropTypes.arrayOf(function(propValue, key, componentName, location, propFullName) { ... })