
- ReactJS 教程
- ReactJS - 首頁
- ReactJS - 簡介
- ReactJS - 路線圖
- ReactJS - 安裝
- ReactJS - 特性
- ReactJS - 優點與缺點
- ReactJS - 架構
- ReactJS - 建立 React 應用
- ReactJS - JSX
- ReactJS - 元件
- ReactJS - 巢狀元件
- ReactJS - 使用新建立的元件
- ReactJS - 元件集合
- ReactJS - 樣式
- ReactJS - 屬性 (props)
- ReactJS - 使用屬性建立元件
- ReactJS - props 驗證
- ReactJS - 建構函式
- ReactJS - 元件生命週期
- ReactJS - 事件管理
- ReactJS - 建立一個事件感知元件
- ReactJS - 在 Expense Manager 應用中引入事件
- ReactJS - 狀態管理
- ReactJS - 狀態管理 API
- ReactJS - 無狀態元件
- ReactJS - 使用 React Hooks 進行狀態管理
- ReactJS - 使用 React Hooks 進行元件生命週期管理
- ReactJS - 佈局元件
- ReactJS - 分頁
- ReactJS - Material UI
- ReactJS - Http 客戶端程式設計
- ReactJS - 表單程式設計
- ReactJS - 受控元件
- ReactJS - 非受控元件
- ReactJS - Formik
- ReactJS - 條件渲染
- ReactJS - 列表
- ReactJS - Keys
- ReactJS - 路由
- ReactJS - Redux
- ReactJS - 動畫
- ReactJS - Bootstrap
- ReactJS - 地圖
- ReactJS - 表格
- ReactJS - 使用 Flux 管理狀態
- ReactJS - 測試
- ReactJS - CLI 命令
- ReactJS - 構建和部署
- ReactJS - 示例
- Hooks
- ReactJS - Hooks 簡介
- ReactJS - 使用 useState
- ReactJS - 使用 useEffect
- ReactJS - 使用 useContext
- ReactJS - 使用 useRef
- ReactJS - 使用 useReducer
- ReactJS - 使用 useCallback
- ReactJS - 使用 useMemo
- ReactJS - 自定義 Hooks
- ReactJS 高階
- ReactJS - 可訪問性
- ReactJS - 程式碼分割
- ReactJS - 上下文
- ReactJS - 錯誤邊界
- ReactJS - 轉發 Refs
- ReactJS - 片段
- ReactJS - 高階元件
- ReactJS - 整合其他庫
- ReactJS - 最佳化效能
- ReactJS - Profiler API
- ReactJS - 埠
- ReactJS - 無 ES6 ECMAScript 的 React
- ReactJS - 無 JSX 的 React
- ReactJS - 調和
- ReactJS - Refs 和 DOM
- ReactJS - 渲染 Props
- ReactJS - 靜態型別檢查
- ReactJS - 嚴格模式
- ReactJS - Web Components
- 其他概念
- ReactJS - 日期選擇器
- ReactJS - Helmet
- ReactJS - 內聯樣式
- ReactJS - PropTypes
- ReactJS - BrowserRouter
- ReactJS - DOM
- ReactJS - 走馬燈
- ReactJS - 圖示
- ReactJS - 表單元件
- ReactJS - 參考 API
- ReactJS 有用資源
- ReactJS - 快速指南
- ReactJS - 有用資源
- ReactJS - 討論
ReactJS - act() 測試工具
當我們使用 React 構建 Web 應用時,測試我們的元件非常重要。這就像檢查所有內容是否按預期工作。為了幫助我們做到這一點,React 中有一個名為 act() 的工具。它模擬 Web 瀏覽器,並確保我們的元件能夠正確地相互通訊。
因此,act() 就像一個幫助程式,它確保在測試元件時它們的行為符合預期。它就像一個小助手,幫助你正確地進行測試。
act() 是一個函式,它幫助我們在測試 React 元件時驗證其行為是否如同在真實的 Web 瀏覽器中執行一樣。對於執行非同步任務(例如資料提取、更新或使用者互動)的元件,這一點尤其重要。
語法
import { act } from 'react-dom/test-utils';
act(() => {
// The code to interact with React components
});
引數
act() 函式接受單個輸入,該輸入是一個包含我們要測試的程式碼的函式。任何與 React 元件的互動,例如渲染、點選或表單提交,都應包含在此程式碼中。
返回值
React 中的 act() 方法不返回任何內容。
示例
示例 - 狀態更改應用
提供的程式碼是一個名為 MyComponent 的簡單 React 元件及其相應的測試,使用 @testing-library/react 和 @testing-library/user-event 庫。元件的初始狀態設定為“初始狀態”。測試渲染 MyComponent。它使用 userEvent.click 模擬按鈕點選。當點選按鈕時,元件的狀態更新為“新狀態”。測試斷言渲染輸出中存在文字“新狀態”。
// MyComponent.js
import React, { useState } from 'react';
const MyComponent = () => {
const [currentState, setCurrentState] = useState('Initial State');
const handleButtonClick = () => {
setCurrentState('New State');
};
return (
<div>
<p>{currentState}</p>
<button onClick={handleButtonClick}>Click me</button>
</div>
);
};
export default MyComponent;
MyComponent.test.js
import { render, screen, act } from '@testing-library/react';
import userEvent from '@testing-library/user-event';
import MyComponent from './MyComponent';
test('updates state on button click', () => {
// Render the component
render(<MyComponent />);
// Use act() to interact with the component
act(() => {
userEvent.click(screen.getByRole('button'));
});
// Assert the expected state
expect(screen.getByText('New State')).toBeInTheDocument();
});
輸出
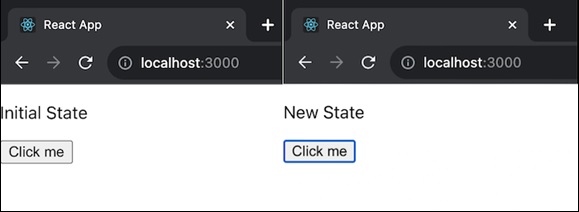
示例 - 非同步元件
在這個應用中,我們將有一個名為 MyAsyncComponent 的 React 元件,它使用 fetchData 函式模擬非同步資料獲取。此外,還有一個使用 @testing-library/react 庫和 act 函式處理非同步操作的元件測試程式碼。因此,應用及其相應的測試檔案的程式碼如下所示:
// MyAsyncComponent.js
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
const fetchData = () => {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
// asynchronous data fetching
setTimeout(() => {
resolve('Fetched Data');
}, 1000);
});
};
const MyAsyncComponent = () => {
const [data, setData] = useState(null);
useEffect(() => {
const fetchDataAsync = async () => {
const result = await fetchData();
setData(result);
};
fetchDataAsync();
}, []);
return (
<div>
<p>{data ? data : 'Loading...'}</p>
</div>
);
};
export default MyAsyncComponent;
MyAsyncComponent.test.js
import { render, screen, act } from '@testing-library/react';
import MyAsyncComponent from './MyAsyncComponent';
test('renders data after fetching', async () => {
// Render the component
render(<MyAsyncComponent />);
// Use act() to wait for the asynchronous data fetching
await act(async () => {
});
expect(screen.getByText('Fetched Data')).toBeInTheDocument();
});
輸出
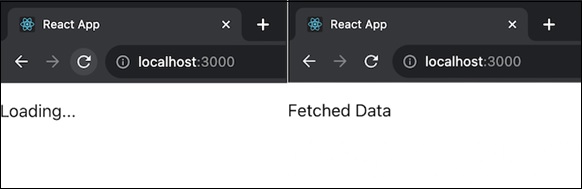
示例 - 計數器應用
讓我們看一個例子。我們有一個帶有一個按鈕的 Counter 元件。因此,當我們按下按鈕時,它會遞增一個計數器並更新標題。為了建立此應用,我們將按照以下步驟操作:
設定測試環境
在每個測試之前建立一個容器元素。
在每個測試之後移除容器。
元件測試
我們將使用 act() 函式包裝元件的渲染。這確保 React 在瀏覽器中正確執行。
act() 函式可用於提供使用者互動(例如點選按鈕)。
// Code for Counter component
// Set up a container for rendering the component
let container;
beforeEach(() => {
container = document.createElement('div');
document.body.appendChild(container);
});
afterEach(() => {
document.body.removeChild(container);
container = null;
});
it('can render and update a counter', () => {
// Test first render and componentDidMount
act(() => {
ReactDOM.createRoot(container).render(<Counter />);
});
// A click event
act(() => {
button.dispatchEvent(new MouseEvent('click', {bubbles: true}));
});
});
總結
act() 是一個允許我們測試 React 元件的工具,尤其是在處理非同步操作或 DOM 互動時。透過使用 act(),我們可以確保我們的測試正確地遵循元件在真實 Web 瀏覽器中的行為方式。測試是建立可靠且無錯誤程式的重要組成部分,而 act() 是此過程中一個有用的函式。