
- Windows 10 開發教程
- Windows 10 - 首頁
- Windows 10 - 簡介
- Windows 10 – UWP
- Windows 10 – 第一個應用
- Windows 10 - 應用商店
- Windows 10 - XAML 控制元件
- Windows 10 - 資料繫結
- Windows 10 - XAML 效能
- Windows 10 - 自適應設計
- Windows 10 - 自適應 UI
- Windows 10 - 自適應程式碼
- Windows 10 - 檔案管理
- Windows 10 - SQLite 資料庫
- Windows 10 – 通訊
- Windows 10 - 應用本地化
- Windows 10 - 應用生命週期
- Windows 10 - 後臺執行
- Windows 10 - 應用服務
- Windows 10 - Web 平臺
- Windows 10 - 連線體驗
- Windows 10 - 導航
- Windows 10 - 網路
- Windows 10 - 雲服務
- Windows 10 - 動態磁貼
- Windows 10 - 共享契約
- Windows 10 - 移植到 Windows
- Windows 10 有用資源
- Windows 10 - 快速指南
- Windows 10 - 有用資源
- Windows 10 - 討論
Windows 10 開發 - 生命週期
歷史上,Windows 擁有一個使用者可以同時執行多個應用程式的環境。使用者可以輕鬆地在不同的應用程式之間切換。這種模式對於通常專注於單一應用程式使用的手機或平板電腦裝置並不適用。
Windows 8 應用商店應用程式程式設計師面臨的最大挑戰之一是管理和理解應用程式生命週期。如果您一直在構建 Windows 手機應用程式,那麼其中很多內容您都會很熟悉。
在 Windows 8 下,作業系統管理應用程式的生命週期,雖然使用者可以終止應用程式,但通常使用者會開啟新的應用程式,而不會有意識地終止正在執行的應用程式。
Windows 10 的通用 Windows 平臺 (UWP) 解決了這些問題,為桌面使用者提供了一些很酷的功能,以便可以以多視窗體驗執行多個應用程式。
Windows 應用程式在基本級別可以存在三種狀態,如下所示。
執行中
掛起
終止
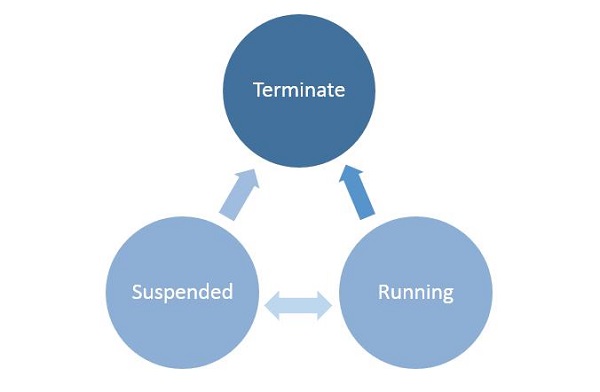
當用戶啟動/啟用任何應用程式時,它將進入執行中狀態。
如果使用者不使用應用程式並且它不再處於前臺,則可以掛起應用程式。
從掛起狀態,應用程式可以恢復該應用程式或終止作業系統以回收系統資源。
程序狀態轉換
瞭解正在執行的應用程式中的程序狀態轉換非常重要。當用戶首次啟動應用程式時,將顯示啟動畫面,然後應用程式開始執行。
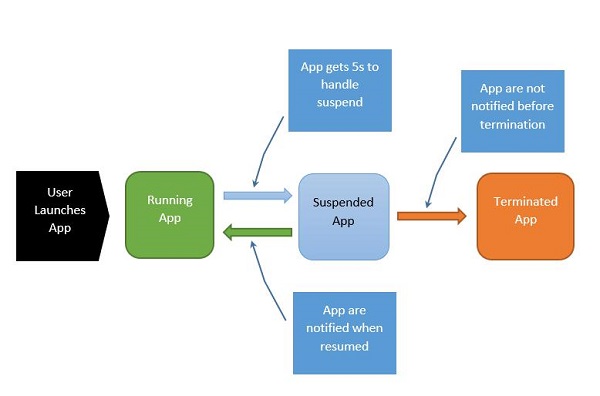
該過程可以解釋如下:
當應用程式掛起時,您的應用程式有五秒鐘的時間來處理該掛起事件。
當應用程式掛起時,絕對不會執行任何程式碼,也不會分配任何資源。
恢復時,應用程式會收到已恢復的通知。如果您是從掛起狀態恢復的,則無需執行任何操作。
在記憶體壓力下,您的應用程式可能會被終止。
請記住,您不會在該點收到通知,因此您必須在進入掛起應用程式狀態時執行任何儲存操作。
當應用程式在執行中和掛起狀態之間來回轉換時,分別觸發掛起和恢復事件。
有時,您需要儲存資料。然後,您必須呼叫非同步方法,如下所示。
Application.Current.Suspending += new SuspendingEventHandler(App_Suspending);
async void App_Suspending(Object sender, Windows.ApplicationModel.SuspendingEventArgs e){
// Create a simple setting
localSettings.Values["FirstName"] = fName.Text;
localSettings.Values["LastName"] = lName.Text;
localSettings.Values["Email"] = email.Text;
}
Application.Current.Resuming += new EventHandler<Object>(App_Resuming);
private void App_Resuming(Object sender, Object e){
fName.Text = localSettings.Values["FirstName"];
lName.Text = localSettings.Values["LastName"];
email.Text = localSettings.Values["Email"];
}
讓我們研究一個示例,其中添加了控制元件,如下面的 XAML 檔案所示。
<Page
x:Class = "UWPLifeCycleDemo.MainPage"
xmlns = "http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x = "http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:local = "using:UWPLifeCycleDemo"
xmlns:d = "http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc = "http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
mc:Ignorable = "d">
<Grid Background = "{ThemeResource ApplicationPageBackgroundThemeBrush}">
<Hub Header = "Details" />
<StackPanel VerticalAlignment = "Top" HorizontalAlignment = "Left"
Margin = "12,64,0,0">
<TextBox Header = "First Name" Text = "{Binding FirstName,
Mode = TwoWay, UpdateSourceTrigger = PropertyChanged}"
Width = "200" />
<TextBox Header = "Last Name" Text = "{Binding LastName, Mode = TwoWay,
UpdateSourceTrigger = PropertyChanged}" Width = "200" />
<TextBox Header = "Email" Text = "{Binding Email, Mode = TwoWay,
UpdateSourceTrigger = PropertyChanged}" Width = "200" />
<Button Margin = "0,12">Submit</Button>
</StackPanel>
</Grid>
</Page>
以下是實現了掛起和恢復事件的 C# 程式碼。當前資料將儲存在本地設定中的掛起事件中,然後從本地設定中的恢復事件中檢索資料,如下所示。
using System;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Runtime.CompilerServices;
using Windows.UI.Xaml;
using Windows.UI.Xaml.Controls;
namespace UWPLifeCycleDemo {
/// <summary>
/// An empty page that can be used on its own or navigated to within a Frame.
/// </summary>
public sealed partial class MainPage : Page{
var localSettings = Windows.Storage.ApplicationData.Current.LocalSettings;
public MainPage() {
this.InitializeComponent();
Application.Current.Suspending += new SuspendingEventHandler(App_Suspending);
Application.Current.Resuming += new EventHandler<Object>(App_Resuming);
}
async void App_Suspending(Object sender, Windows.ApplicationModel.SuspendingEventArgs e){
// Create a simple setting
localSettings.Values["FirstName"] = fName.Text;
localSettings.Values["LastName"] = lName.Text;
localSettings.Values["Email"] = email.Text;
}
private void App_Resuming(Object sender, Object e){
fName.Text = localSettings.Values["FirstName"];
lName.Text = localSettings.Values["LastName"];
email.Text = localSettings.Values["Email"];
}
}
public abstract class BindableBase : INotifyPropertyChanged {
private string _FirstName = default(string);
public string FirstName {
get { return _FirstName; }
set { Set(ref _FirstName, value); }
}
private string _LastName = default(string);
public string LastName {
get { return _LastName; }
set { Set(ref _LastName, value); }
}
private string _Email = default(string);
public string Email {
get { return _Email; }
set { Set(ref _Email, value); }
}
public event PropertyChangedEventHandler PropertyChanged;
public void RaisePropertyChanged([CallerMemberName]string propertyName = null) {
PropertyChanged?.Invoke(this, new PropertyChangedEventArgs(propertyName));
}
public void Set<T>(ref T storage, T value,
[CallerMemberName()]string propertyName = null){
if (!object.Equals(storage, value)){
storage = value;
RaisePropertyChanged(propertyName);
}
}
}
}
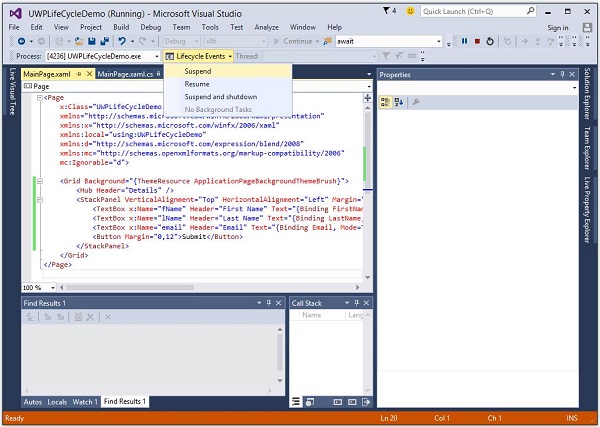
編譯並執行上述程式碼後,您將看到以下視窗。現在編寫所需的資訊。

讓我們轉到生命週期事件下拉選單並選擇掛起。現在,您的應用程式將被掛起,所需資訊將儲存在本地設定中。請參見下圖所示的螢幕截圖。
現在,當您想要恢復應用程式時,請從生命週期事件選單中選擇恢復選項。
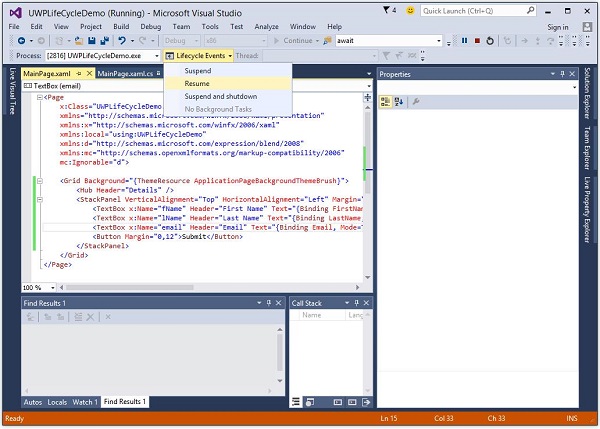
現在您將看到從本地設定中檢索到的儲存資訊,並且應用程式將從掛起時的相同狀態恢復。
