- Windows 10 開發教程
- Windows 10 - 首頁
- Windows 10 - 簡介
- Windows 10 – UWP
- Windows 10 – 第一個應用
- Windows 10 - 應用商店
- Windows 10 - XAML 控制元件
- Windows 10 - 資料繫結
- Windows 10 - XAML 效能
- Windows 10 - 自適應設計
- Windows 10 - 自適應 UI
- Windows 10 - 自適應程式碼
- Windows 10 - 檔案管理
- Windows 10 - SQLite 資料庫
- Windows 10 – 通訊
- Windows 10 - 應用本地化
- Windows 10 - 應用生命週期
- Windows 10 - 後臺執行
- Windows 10 - 應用服務
- Windows 10 - Web 平臺
- Windows 10 - 連線體驗
- Windows 10 - 導航
- Windows 10 - 網路
- Windows 10 - 雲服務
- Windows 10 - 動態磁貼
- Windows 10 - 共享契約
- Windows 10 - 移植到 Windows
- Windows 10 有用資源
- Windows 10 - 快速指南
- Windows 10 - 有用資源
- Windows 10 - 討論
Windows 10 開發 - 檔案管理
在任何應用程式中,資料都是最重要的內容之一。如果您是.net 開發人員,您可能瞭解隔離儲存,並且同樣的概念也適用於通用 Windows 平臺 (UWP) 應用程式。
檔案位置
這些是您的應用程式可以訪問資料的區域。應用程式包含一些對特定應用程式私有的區域,其他應用程式無法訪問,但還有許多其他區域,您可以在其中將資料儲存和儲存到檔案中。
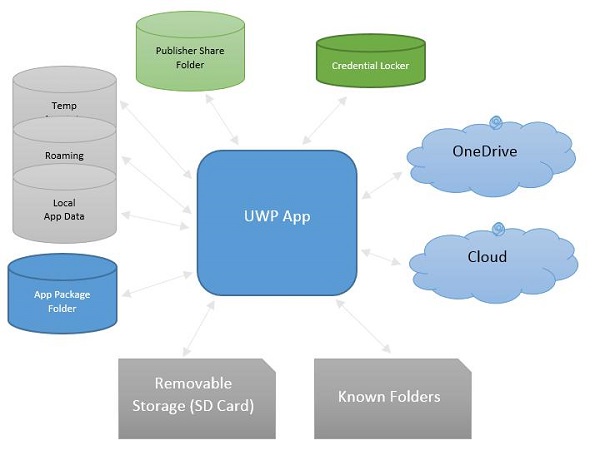
以下是每個資料夾的簡要說明。
| 序號 | 資料夾及說明 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 應用包資料夾 包管理器將所有與應用相關的檔案安裝到應用包資料夾中,應用只能從此資料夾讀取資料。 |
| 2 | 本地資料夾 應用程式將本地資料儲存到本地資料夾中。它可以儲存的資料量取決於儲存裝置上的限制。 |
| 3 | 漫遊資料夾 與應用程式相關的設定和屬性儲存在漫遊資料夾中。其他裝置也可以從此資料夾訪問資料。每個應用程式的大小限制為 100KB。 |
| 4 | 臨時資料夾 用於臨時儲存,不能保證在應用程式再次執行時仍然可用。 |
| 5 | 釋出者共享 來自同一釋出者的所有應用的共享儲存。它在應用清單中宣告。 |
| 6 | 憑據保管箱 用於安全儲存密碼憑據物件。 |
| 7 | OneDrive OneDrive 是您 Microsoft 帳戶附帶的免費線上儲存。 |
| 8 | 雲 將資料儲存在雲中。 |
| 9 | 已知資料夾 這些資料夾是已知的資料夾,例如“我的圖片”、“影片”和“音樂”。 |
| 10 | 可移動儲存 USB 儲存裝置或外部硬碟驅動器等。 |
檔案處理 API
在 Windows 8 中,引入了新的檔案處理 API。這些 API 位於Windows.Storage 和Windows.Storage.Streams 名稱空間中。您可以使用這些 API 來代替System.IO.IsolatedStorage 名稱空間。使用這些 API,可以更輕鬆地將 Windows Phone 應用移植到 Windows 應用商店,並且可以輕鬆地將您的應用程序升級到 Windows 的未來版本。
要訪問本地、漫遊或臨時資料夾,您需要呼叫這些 API:
StorageFolder localFolder = ApplicationData.Current.LocalFolder; StorageFolder roamingFolder = ApplicationData.Current.RoamingFolder; StorageFolder tempFolder = ApplicationData.Current.TemporaryFolder;
要在本地資料夾中建立新檔案,請使用以下程式碼:
StorageFolder localFolder = ApplicationData.Current.LocalFolder; StorageFile textFile = await localFolder.CreateFileAsync(filename, CreationCollisionOption.ReplaceExisting);
以下是開啟新建立的檔案並在該檔案中寫入一些內容的程式碼。
using (IRandomAccessStream textStream = await textFile.OpenAsync(FileAccessMode.ReadWrite)) {
using (DataWriter textWriter = new DataWriter(textStream)){
textWriter.WriteString(contents);
await textWriter.StoreAsync();
}
}
您可以再次從本地資料夾開啟同一個檔案,如下面的程式碼所示。
using (IRandomAccessStream textStream = await textFile.OpenReadAsync()) {
using (DataReader textReader = new DataReader(textStream)){
uint textLength = (uint)textStream.Size;
await textReader.LoadAsync(textLength);
contents = textReader.ReadString(textLength);
}
}
為了瞭解資料的讀寫是如何工作的,讓我們來看一個簡單的例子。以下是新增不同控制元件的 XAML 程式碼。
<Page
x:Class = "UWPFileHandling.MainPage"
xmlns = "http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x = "http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:local = "using:UWPFileHandling"
xmlns:d = "http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc = "http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
mc:Ignorable = "d">
<Grid Background = "{ThemeResource ApplicationPageBackgroundThemeBrush}">
<Button x:Name = "readFile" Content = "Read Data From File"
HorizontalAlignment = "Left" Margin = "62,518,0,0"
VerticalAlignment = "Top" Height = "37" Width = "174"
Click = "readFile_Click"/>
<TextBox x:FieldModifier = "public" x:Name = "textBox"
HorizontalAlignment = "Left" Margin = "58,145,0,0" TextWrapping = "Wrap"
VerticalAlignment = "Top" Height = "276" Width = "245"/>.
<Button x:Name = "writeFile" Content = "Write Data to File"
HorizontalAlignment = "Left" Margin = "64,459,0,0"
VerticalAlignment = "Top" Click = "writeFile_Click"/>
<TextBlock x:Name = "textBlock" HorizontalAlignment = "Left"
Margin = "386,149,0,0" TextWrapping = "Wrap"
VerticalAlignment = "Top" Height = "266" Width = "250"
Foreground = "#FF6231CD"/>
</Grid>
</Page>
以下是不同事件的 C# 實現,以及用於讀取和寫入文字檔案資料的FileHelper 類的實現。
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Windows.Storage;
using Windows.Storage.Streams;
using Windows.UI.Xaml;
using Windows.UI.Xaml.Controls;
// The Blank Page item template is documented at
http://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=402352&clcid=0x409
namespace UWPFileHandling {
/// <summary>
/// An empty page that can be used on its own or navigated to within a Frame.
/// </summary>
public partial class MainPage : Page {
const string TEXT_FILE_NAME = "SampleTextFile.txt";
public MainPage(){
this.InitializeComponent();
}
private async void readFile_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) {
string str = await FileHelper.ReadTextFile(TEXT_FILE_NAME);
textBlock.Text = str;
}
private async void writeFile_Click(object sender, RoutedEventArgs e) {
string textFilePath = await FileHelper.WriteTextFile(TEXT_FILE_NAME, textBox.Text);
}
}
public static class FileHelper {
// Write a text file to the app's local folder.
public static async Task<string>
WriteTextFile(string filename, string contents) {
StorageFolder localFolder = ApplicationData.Current.LocalFolder;
StorageFile textFile = await localFolder.CreateFileAsync(filename,
CreationCollisionOption.ReplaceExisting);
using (IRandomAccessStream textStream = await
textFile.OpenAsync(FileAccessMode.ReadWrite)){
using (DataWriter textWriter = new DataWriter(textStream)){
textWriter.WriteString(contents);
await textWriter.StoreAsync();
}
}
return textFile.Path;
}
// Read the contents of a text file from the app's local folder.
public static async Task<string> ReadTextFile(string filename) {
string contents;
StorageFolder localFolder = ApplicationData.Current.LocalFolder;
StorageFile textFile = await localFolder.GetFileAsync(filename);
using (IRandomAccessStream textStream = await textFile.OpenReadAsync()){
using (DataReader textReader = new DataReader(textStream)){
uint textLength = (uint)textStream.Size;
await textReader.LoadAsync(textLength);
contents = textReader.ReadString(textLength);
}
}
return contents;
}
}
}
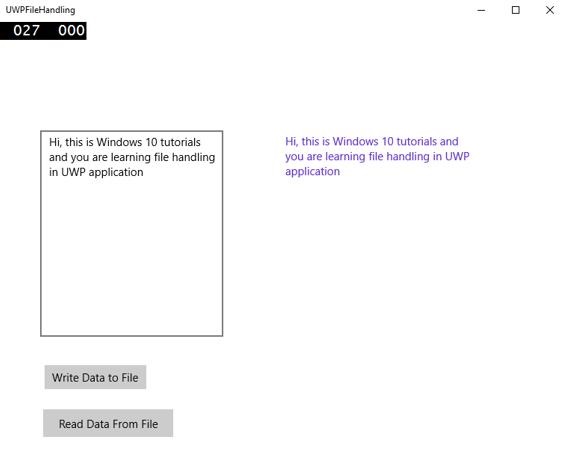
編譯並執行上述程式碼後,您將看到以下視窗。
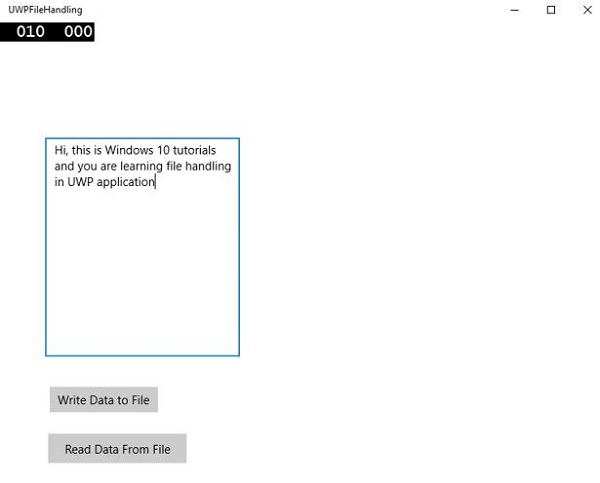
現在,您在文字框中寫入內容,然後單擊“將資料寫入檔案”按鈕。程式將資料寫入本地資料夾中的文字檔案。如果您單擊“從檔案讀取資料”按鈕,程式將從位於本地資料夾中的同一文字檔案讀取資料,並將其顯示在文字塊上。