
- Python基礎
- Python - 首頁
- Python - 概述
- Python - 歷史
- Python - 特性
- Python vs C++
- Python - Hello World程式
- Python - 應用領域
- Python - 直譯器
- Python - 環境搭建
- Python - 虛擬環境
- Python - 基本語法
- Python - 變數
- Python - 資料型別
- Python - 型別轉換
- Python - Unicode系統
- Python - 字面量
- Python - 運算子
- Python - 算術運算子
- Python - 比較運算子
- Python - 賦值運算子
- Python - 邏輯運算子
- Python - 位運算子
- Python - 成員運算子
- Python - 身份運算子
- Python - 運算子優先順序
- Python - 註釋
- Python - 使用者輸入
- Python - 數字
- Python - 布林值
- Python控制語句
- Python - 控制流
- Python - 決策制定
- Python - if語句
- Python - if else語句
- Python - 巢狀if語句
- Python - match-case語句
- Python - 迴圈
- Python - for迴圈
- Python - for-else迴圈
- Python - while迴圈
- Python - break語句
- Python - continue語句
- Python - pass語句
- Python - 巢狀迴圈
- Python函式與模組
- Python - 函式
- Python - 預設引數
- Python - 關鍵字引數
- Python - 僅關鍵字引數
- Python - 位置引數
- Python - 僅位置引數
- Python - 可變引數
- Python - 變數作用域
- Python - 函式註解
- Python - 模組
- Python - 內建函式
- Python字串
- Python - 字串
- Python - 字串切片
- Python - 修改字串
- Python - 字串連線
- Python - 字串格式化
- Python - 跳脫字元
- Python - 字串方法
- Python - 字串練習
- Python列表
- Python - 列表
- Python - 訪問列表元素
- Python - 修改列表元素
- Python - 新增列表元素
- Python - 刪除列表元素
- Python - 遍歷列表
- Python - 列表推導式
- Python - 排序列表
- Python - 複製列表
- Python - 合併列表
- Python - 列表方法
- Python - 列表練習
- Python元組
- Python - 元組
- Python - 訪問元組元素
- Python - 更新元組
- Python - 解包元組
- Python - 遍歷元組
- Python - 合併元組
- Python - 元組方法
- Python - 元組練習
- Python集合
- Python - 集合
- Python - 訪問集合元素
- Python - 新增集合元素
- Python - 刪除集合元素
- Python - 遍歷集合
- Python - 合併集合
- Python - 複製集合
- Python - 集合運算子
- Python - 集合方法
- Python - 集合練習
- Python字典
- Python - 字典
- Python - 訪問字典元素
- Python - 修改字典元素
- Python - 新增字典元素
- Python - 刪除字典元素
- Python - 字典檢視物件
- Python - 遍歷字典
- Python - 複製字典
- Python - 巢狀字典
- Python - 字典方法
- Python - 字典練習
- Python陣列
- Python - 陣列
- Python - 訪問陣列元素
- Python - 新增陣列元素
- Python - 刪除陣列元素
- Python - 遍歷陣列
- Python - 複製陣列
- Python - 反轉陣列
- Python - 排序陣列
- Python - 合併陣列
- Python - 陣列方法
- Python - 陣列練習
- Python檔案處理
- Python - 檔案處理
- Python - 寫入檔案
- Python - 讀取檔案
- Python - 重新命名和刪除檔案
- Python - 目錄
- Python - 檔案方法
- Python - OS檔案/目錄方法
- Python - OS路徑方法
- 面向物件程式設計
- Python - OOPs概念
- Python - 類與物件
- Python - 類屬性
- Python - 類方法
- Python - 靜態方法
- Python - 建構函式
- Python - 訪問修飾符
- Python - 繼承
- Python - 多型
- Python - 方法重寫
- Python - 方法過載
- Python - 動態繫結
- Python - 動態型別
- Python - 抽象
- Python - 封裝
- Python - 介面
- Python - 包
- Python - 內部類
- Python - 匿名類和物件
- Python - 單例類
- Python - 包裝器類
- Python - 列舉
- Python - 反射
- Python錯誤與異常
- Python - 語法錯誤
- Python - 異常
- Python - try-except塊
- Python - try-finally塊
- Python - 丟擲異常
- Python - 異常鏈
- Python - 巢狀try塊
- Python - 使用者自定義異常
- Python - 日誌記錄
- Python - 斷言
- Python - 內建異常
- Python多執行緒
- Python - 多執行緒
- Python - 執行緒生命週期
- Python - 建立執行緒
- Python - 啟動執行緒
- Python - 加入執行緒
- Python - 執行緒命名
- Python - 執行緒排程
- Python - 執行緒池
- Python - 主執行緒
- Python - 執行緒優先順序
- Python - 守護執行緒
- Python - 執行緒同步
- Python同步
- Python - 執行緒間通訊
- Python - 執行緒死鎖
- Python - 中斷執行緒
- Python網路程式設計
- Python - 網路程式設計
- Python - Socket程式設計
- Python - URL處理
- Python - 泛型
- Python庫
- NumPy教程
- Pandas教程
- SciPy教程
- Matplotlib教程
- Django教程
- OpenCV教程
- Python雜項
- Python - 日期與時間
- Python - 數學
- Python - 迭代器
- Python - 生成器
- Python - 閉包
- Python - 裝飾器
- Python - 遞迴
- Python - 正則表示式
- Python - PIP
- Python - 資料庫訪問
- Python - 弱引用
- Python - 序列化
- Python - 模板
- Python - 輸出格式化
- Python - 效能測量
- Python - 資料壓縮
- Python - CGI程式設計
- Python - XML處理
- Python - GUI程式設計
- Python - 命令列引數
- Python - 文件字串
- Python - JSON
- Python - 傳送郵件
- Python - 擴充套件
- Python - 工具/實用程式
- Python - GUIs
- Python高階概念
- Python - 抽象基類
- Python - 自定義異常
- Python - 高階函式
- Python - 物件內部結構
- Python - 記憶體管理
- Python - 元類
- Python - 使用元類進行超程式設計
- Python - 模擬和存根
- Python - 猴子補丁
- Python - 訊號處理
- Python - 型別提示
- Python - 自動化教程
- Python - Humanize包
- Python - 上下文管理器
- Python - 協程
- Python - 描述符
- Python - 診斷和修復記憶體洩漏
- Python - 不可變資料結構
- Python有用資源
- Python - 問答
- Python - 線上測驗
- Python - 快速指南
- Python - 參考
- Python - 速查表
- Python - 專案
- Python - 有用資源
- Python - 討論
- Python編譯器
- NumPy編譯器
- Matplotlib編譯器
- SciPy編譯器
使用Pygame製作的太空侵略者遊戲
太空侵略者遊戲是一款使用著名的Python框架Pygame開發的基本二維遊戲。遊戲中玩家操控一艘宇宙飛船,向其他宇宙飛船射擊,同時躲避其他宇宙飛船射來的子彈。隨著玩家得分增加,遊戲難度也會提升,敵人的速度和射擊頻率會加快。
如何玩太空侵略者遊戲?
1. 開始遊戲
首先,按鍵盤上的ENTER鍵開始遊戲。

2. 移動
使用A和D鍵控制飛船左右移動。使用W鍵向上移動,S鍵向下移動。
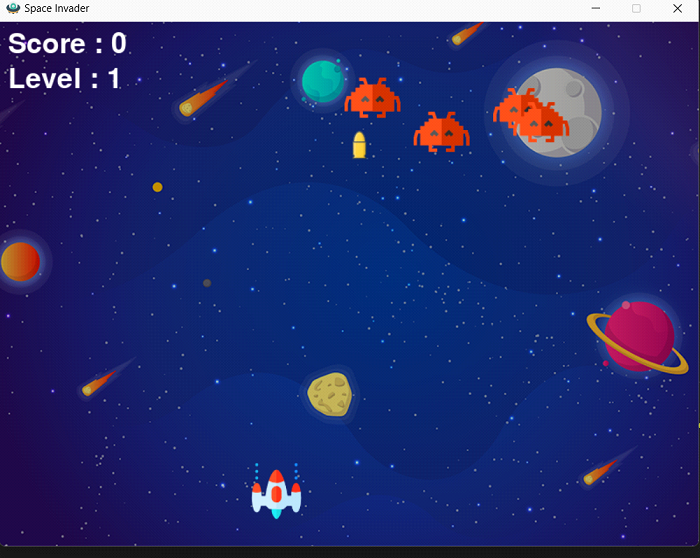
3. 射擊
按空格鍵向敵人射擊。
4. 目標
儘可能擊落更多的敵方宇宙飛船,同時躲避它們的子彈。
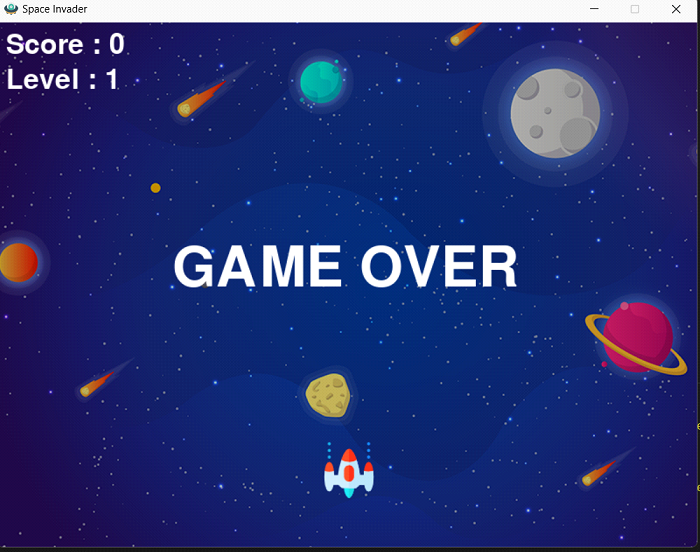
5. 遊戲結束
如果敵人的子彈擊中你的飛船,或者敵人到達螢幕底部,遊戲結束。
注意
請確保下載敵方宇宙飛船和背景的圖片,否則遊戲無法正常執行。
最終遊戲

使用Pygame實現太空侵略者遊戲
1. 所需庫
要實現此遊戲,您需要安裝以下庫:
- math - 用於計算距離以檢測子彈和敵人之間的碰撞。
- random - 用於生成隨機的敵人位置和子彈射擊時間。
- Pygame − 用於計算距離,檢測子彈與敵機之間的碰撞。
2. 遊戲初始化
啟動 Pygame 並設定顯示
此部分初始化 Pygame 庫並設定遊戲視窗的寬度和高度。還會載入遊戲的背景音樂和影像。
玩家設定
載入玩家的宇宙飛船,並設定初始位置和移動變數。
敵機設定
初始化敵機,包括它們各自的位置、速度和移動變化。
開始選單
顯示開始選單,包含標題和提示玩家開始遊戲的提示。
3. 主遊戲迴圈
處理事件、更新玩家和敵機移動的主迴圈。它還處理碰撞檢測、子彈移動和更新遊戲顯示。
使用 Pygame 實現太空侵略者遊戲的程式碼
以下是實現該遊戲的完整程式碼:
import math
import random
import pygame
from pygame import mixer
# Initialize pygame
pygame.init()
# Screen dimensions
display_width, display_height = 800, 600
display = pygame.display.set_mode((display_width, display_height))
# Background image
space_bg = pygame.image.load(r"C:\Users\souvi\OneDrive\Desktop\koko\Space-Invaders-Pygame\space_background.png")
# Background music
mixer.music.load(r"C:\Users\souvi\OneDrive\Desktop\koko\Space-Invaders-Pygame\space_music.wav")
mixer.music.play(-1)
# Title and Icon
pygame.display.set_caption("Space Guardian")
game_icon = pygame.image.load(r"C:\Users\souvi\OneDrive\Desktop\koko\Space-Invaders-Pygame\alien_ship.png")
pygame.display.set_icon(game_icon)
# Fonts
text_font = pygame.font.Font('freesansbold.ttf', 32)
header_font = pygame.font.Font('freesansbold.ttf', 64)
# Player spaceship
hero_image = pygame.image.load(r"C:\Users\souvi\OneDrive\Desktop\koko\Space-Invaders-Pygame\spaceship_hero.png")
hero_x = 370
hero_y = 500
hero_x_change = 0
hero_y_change = 0
# Enemy ships
enemy_sprites = []
enemy_x_pos = []
enemy_y_pos = []
enemy_x_change = []
enemy_y_change = []
number_of_enemies = 5
base_enemy_velocity = 0.4
i = 0
while i < number_of_enemies:
enemy_sprites.append(pygame.image.load(r"C:\Users\souvi\OneDrive\Desktop\koko\Space-Invaders-Pygame\alien_enemy.png"))
enemy_x_pos.append(random.randint(0, 736))
enemy_y_pos.append(random.randint(50, 150))
enemy_x_change.append(base_enemy_velocity)
enemy_y_change.append(20)
i += 1
# Player bullets
bullet_sprite = pygame.image.load(r"C:\Users\souvi\OneDrive\Desktop\koko\Space-Invaders-Pygame\laser_bullet.png")
bullet_x = 0
bullet_y = 500
bullet_x_change = 0
bullet_y_change = 10
bullet_state = "ready"
# Enemy bullets
enemy_bullet_sprite = []
enemy_bullet_x = []
enemy_bullet_y = []
enemy_bullet_y_change = []
enemy_bullet_state = []
j = 0
while j < number_of_enemies:
enemy_bullet_sprite.append(pygame.image.load(r"C:\Users\souvi\OneDrive\Desktop\koko\Space-Invaders-Pygame\laser_bullet.png"))
enemy_bullet_x.append(0)
enemy_bullet_y.append(enemy_y_pos[j])
enemy_bullet_y_change.append(2)
enemy_bullet_state.append("ready")
j += 1
# Score and level
score = 0
game_level = 1
text_x = 10
text_y = 10
# Game Over font
game_over_font = pygame.font.Font('freesansbold.ttf', 64)
# Start Menu
def start_menu():
display.fill((0, 0, 0))
title_text = header_font.render("Space Guardian", True, (255, 255, 255))
display.blit(title_text, (200, 200))
instructions = text_font.render("Press ENTER to Start", True, (255, 255, 255))
display.blit(instructions, (250, 300))
pygame.display.update()
start = False
while not start:
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
pygame.quit()
quit()
if event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN and event.key == pygame.K_RETURN:
start = True
# Display score
def display_score(x, y):
score_text = text_font.render("Score: " + str(score), True, (255, 255, 255))
display.blit(score_text, (x, y))
# Display level
def display_level(x, y):
level_text = text_font.render("Level: " + str(game_level), True, (255, 255, 255))
display.blit(level_text, (x, y + 40))
# Game Over text
def game_over():
over_text = game_over_font.render("GAME OVER", True, (255, 255, 255))
display.blit(over_text, (200, 250))
# Player sprite
def player(x, y):
display.blit(hero_image, (x, y))
# Enemy sprite
def enemy(x, y, index):
display.blit(enemy_sprites[index], (x, y))
# Fire player bullet
def fire_hero_bullet(x, y):
global bullet_state
bullet_state = "fire"
display.blit(bullet_sprite, (x + 16, y + 10))
# Fire enemy bullet
def fire_enemy_bullet(x, y, index):
global enemy_bullet_state
enemy_bullet_state[index] = "fire"
display.blit(enemy_bullet_sprite[index], (x + 16, y + 10))
# Collision detection (player bullet with enemy)
def collision_detected(enemy_x, enemy_y, bullet_x, bullet_y):
distance = math.sqrt(math.pow(enemy_x - bullet_x, 2) + (math.pow(enemy_y - bullet_y, 2)))
return distance < 27
# Collision detection (enemy bullet with player)
def player_hit(player_x, player_y, bullet_x, bullet_y):
distance = math.sqrt(math.pow(player_x - bullet_x, 2) + (math.pow(player_y - bullet_y, 2)))
return distance < 30
def game_loop():
global bullet_x, bullet_y, bullet_state, score, game_level
global hero_x, hero_y, hero_x_change, hero_y_change
global enemy_x_pos, enemy_y_pos, enemy_x_change, enemy_y_change
global enemy_bullet_x, enemy_bullet_y, enemy_bullet_state, enemy_bullet_y_change
try:
# Initialize variables
hero_x = 368 # Example starting position
hero_y = 480 # Example starting position
hero_x_change = 0
hero_y_change = 0
bullet_x = 0
bullet_y = 500
bullet_state = "ready"
score = 0
game_level = 1
# Example initialization for enemies and their bullets
number_of_enemies = 5
enemy_x_pos = [random.randint(0, 736) for _ in range(number_of_enemies)]
enemy_y_pos = [random.randint(50, 150) for _ in range(number_of_enemies)]
enemy_x_change = [base_enemy_velocity for _ in range(number_of_enemies)]
enemy_y_change = [40 for _ in range(number_of_enemies)]
enemy_bullet_x = [0 for _ in range(number_of_enemies)]
enemy_bullet_y = [0 for _ in range(number_of_enemies)]
enemy_bullet_state = ["ready" for _ in range(number_of_enemies)]
enemy_bullet_y_change = [10 for _ in range(number_of_enemies)]
running = True
start_menu() # Call start menu
while running:
display.fill((0, 0, 0))
display.blit(space_bg, (0, 0))
# Event handling
for event in pygame.event.get():
if event.type == pygame.QUIT:
running = False
# Key press detection
if event.type == pygame.KEYDOWN:
if event.key == pygame.K_a or event.key == pygame.K_LEFT:
hero_x_change = -5
if event.key == pygame.K_d or event.key == pygame.K_RIGHT:
hero_x_change = 5
if event.key == pygame.K_w or event.key == pygame.K_UP:
hero_y_change = -5
if event.key == pygame.K_s or event.key == pygame.K_DOWN:
hero_y_change = 5
if event.key == pygame.K_SPACE and bullet_state == "ready":
bullet_sound = mixer.Sound(r"C:\Users\souvi\OneDrive\Desktop\koko\Space-Invaders-Pygame\laser_sound.wav")
bullet_sound.play()
bullet_x = hero_x
bullet_y = hero_y # Initialize bullet_y when firing
bullet_state = "fire"
# Key release detection
if event.type == pygame.KEYUP:
if event.key == pygame.K_a or event.key == pygame.K_d:
hero_x_change = 0
if event.key == pygame.K_w or event.key == pygame.K_s:
hero_y_change = 0
# Move player
hero_x += hero_x_change
hero_y += hero_y_change
# Boundary for player
if hero_x <= 0:
hero_x = 0
elif hero_x >= 736:
hero_x = 736
if hero_y <= 0:
hero_y = 0
elif hero_y >= 536:
hero_y = 536
# Enemy movement and collision logic
e = 0
while e < number_of_enemies:
if enemy_y_pos[e] > 440 or player_hit(hero_x, hero_y, enemy_bullet_x[e], enemy_bullet_y[e]):
for j in range(number_of_enemies):
enemy_y_pos[j] = 2000
game_over()
break
enemy_x_pos[e] += enemy_x_change[e]
if enemy_x_pos[e] <= 0:
enemy_x_change[e] = base_enemy_velocity + (game_level - 1) / 4
enemy_y_pos[e] += enemy_y_change[e]
elif enemy_x_pos[e] >= 736:
enemy_x_change[e] = -(base_enemy_velocity + (game_level - 1) / 4)
enemy_y_pos[e] += enemy_y_change[e]
# Enemy bullet firing
if enemy_bullet_state[e] == "ready" and random.random() < 0.008:
enemy_bullet_x[e] = enemy_x_pos[e]
fire_enemy_bullet(enemy_bullet_x[e], enemy_bullet_y[e], e)
if enemy_bullet_state[e] == "fire":
fire_enemy_bullet(enemy_bullet_x[e], enemy_bullet_y[e], e)
enemy_bullet_y[e] += enemy_bullet_y_change[e]
if enemy_bullet_y[e] >= 600:
enemy_bullet_y[e] = enemy_y_pos[e]
enemy_bullet_state[e] = "ready"
# Check for collisions
if bullet_state == "fire":
collision = collision_detected(enemy_x_pos[e], enemy_y_pos[e], bullet_x, bullet_y)
if collision:
explosion_sound = mixer.Sound(r"C:\Users\souvi\OneDrive\Desktop\koko\Space-Invaders-Pygame\explosion.wav")
explosion_sound.play()
bullet_y = 500
bullet_state = "ready"
score += 1
enemy_x_pos[e] = random.randint(0, 736)
enemy_y_pos[e] = random.randint(50, 150)
enemy(enemy_x_pos[e], enemy_y_pos[e], e)
e += 1
# Bullet movement
if bullet_state == "fire":
fire_hero_bullet(bullet_x, bullet_y)
bullet_y -= bullet_y_change
if bullet_y <= 0:
bullet_y = 500
bullet_state = "ready"
# Update score and level
display_score(text_x, text_y)
display_level(text_x, text_y)
# Display player
player(hero_x, hero_y)
# Update the screen
pygame.display.update()
except Exception as e:
print(f"An error occurred: {e}")
finally:
pygame.quit()
# Call game_loop() in a try-except block
if __name__ == "__main__":
game_loop()
程式碼分解
匯入所需的庫:這些是遊戲功能所需的必要庫,包括數學庫、隨機數生成庫、Pygame 庫和 pygame.mixer 庫(用於遊戲音樂)。
- 初始化 pygame − Pygame 中的 init() 函式呼叫並初始化運行遊戲所需的許多模組。
- 設定螢幕尺寸 − 定義變數 display_width 為遊戲螢幕寬度,display_height 為遊戲螢幕高度。
- 建立遊戲視窗 − 使用 display.set_mode() 開發螢幕上顯示的圖形。
- 載入背景影像 − 使用 image.load() 中的 image 模組將背景影像載入到遊戲中。
- 載入並播放背景音樂 − 預先錄製好的音樂預設並在混音器上使用特定的 music.load() 和 mixer.music.play() 播放。
- 設定標題和圖示 − Pygame 用於設定遊戲的標題和視窗圖示,使用 display.set_caption() 和 pygame.display.set_icon()。
- 載入字型 − 分數字體、遊戲結束訊息字型和標題螢幕字型都是使用 font.Font() 載入的資源。
- 載入玩家影像 − 載入玩家的宇宙飛船影像,並設定宇宙飛船的初始 x 和 y 座標。
- 載入敵機 − 建立多個目標飛船,並將其隨機放置在戰場上。玩家需要載入子彈影像。還需要載入玩家可以看到的宇宙飛船的子彈影像。
- 載入敵機子彈 為每艘敵機建立敵機發射的子彈影像。
- 設定分數和關卡佔位符 − 玩家的分數以及當前的遊戲關卡是需要定義的變數。
- 遊戲結束字型 − 也建立了顯示“遊戲結束”訊息的字型。
- 定義開始選單 − 第一個選單建立遊戲標題並顯示遊戲玩法。
- 定義分數顯示 − 為在螢幕上顯示玩家分數,定義了一個特殊的函式。
- 定義關卡顯示 − 使用一個函式在玩家可見的螢幕上顯示遊戲關卡。
- 定義遊戲結束函式 − 開發另一個函式來顯示遊戲結束和玩家輸掉遊戲的訊息。
- 定義玩家函式 − 使用函式呈現玩家的宇宙飛船。
- 定義敵機函式 − 資源透過螢幕上的座標來描繪敵機。
- 發射玩家子彈函式 − 開發一個函式來處理玩家宇宙飛船發射子彈。
- 發射敵機子彈函式 − 同樣,為敵機定義了一個類似的函式,用於發射子彈。
- 使用碰撞檢測來檢測玩家子彈 − 一個函式透過計算距離來確定玩家的子彈是否會擊中敵人。
- 敵機子彈的碰撞解決 − 另一個函式檢查敵機子彈是否擊中了玩家的宇宙飛船。
- 定義遊戲迴圈 − 所有遊戲邏輯都放在一個迴圈中;這意味著遊戲會持續執行,直到玩家決定停止遊戲。
- 處理玩家移動 − 監督重要事件以管理玩家擁有的宇宙飛船的導航運動。
- 玩家邊界 − 準確地說,玩家的移動僅限於螢幕定義的區域,無論是水平還是垂直,可以是自由移動或橫向卷軸。
- 處理敵機移動 − 目標是中性的,會在水平和垂直方向移動,並在撞擊螢幕邊緣後下降。
- 敵機子彈移動 − 敵機子彈會隨機發射,並向下移動朝向玩家。
- 更新顯示 − 可以隨時在持續進行的過程中使用 **pygame** 更新螢幕。**display.update()** 用於遊戲迴圈中發生的所有更改。
python_reference.htm
廣告