
- Python 基礎
- Python - 首頁
- Python - 概述
- Python - 歷史
- Python - 特性
- Python vs C++
- Python - Hello World 程式
- Python - 應用領域
- Python - 直譯器
- Python - 環境搭建
- Python - 虛擬環境
- Python - 基本語法
- Python - 變數
- Python - 資料型別
- Python - 型別轉換
- Python - Unicode 系統
- Python - 字面量
- Python - 運算子
- Python - 算術運算子
- Python - 比較運算子
- Python - 賦值運算子
- Python - 邏輯運算子
- Python - 位運算子
- Python - 成員運算子
- Python - 身份運算子
- Python - 運算子優先順序
- Python - 註釋
- Python - 使用者輸入
- Python - 數字
- Python - 布林值
- Python 控制語句
- Python - 控制流
- Python - 決策
- Python - if 語句
- Python - if else
- Python - 巢狀 if
- Python - match-case 語句
- Python - 迴圈
- Python - for 迴圈
- Python - for-else 迴圈
- Python - while迴圈
- Python - break 語句
- Python - continue 語句
- Python - pass 語句
- Python - 巢狀迴圈
- Python 函式 & 模組
- Python - 函式
- Python - 預設引數
- Python - 關鍵字引數
- Python - 僅限關鍵字引數
- Python - 位置引數
- Python - 僅限位置引數
- Python - 可變引數
- Python - 變數作用域
- Python - 函式註解
- Python - 模組
- Python - 內建函式
- Python 字串
- Python - 字串
- Python - 字串切片
- Python - 修改字串
- Python - 字串連線
- Python - 字串格式化
- Python - 跳脫字元
- Python - 字串方法
- Python - 字串練習
- Python 列表
- Python - 列表
- Python - 訪問列表元素
- Python - 修改列表元素
- Python - 新增列表元素
- Python - 刪除列表元素
- Python - 迴圈遍歷列表
- Python - 列表推導式
- Python - 排序列表
- Python - 複製列表
- Python - 合併列表
- Python - 列表方法
- Python - 列表練習
- Python 元組
- Python - 元組
- Python - 訪問元組元素
- Python - 更新元組
- Python - 解包元組
- Python - 迴圈遍歷元組
- Python - 合併元組
- Python - 元組方法
- Python - 元組練習
- Python 集合
- Python - 集合
- Python - 訪問集合元素
- Python - 新增集合元素
- Python - 刪除集合元素
- Python - 迴圈遍歷集合
- Python - 合併集合
- Python - 複製集合
- Python - 集合運算子
- Python - 集合方法
- Python - 集合練習
- Python 字典
- Python - 字典
- Python - 訪問字典元素
- Python - 修改字典元素
- Python - 新增字典元素
- Python - 刪除字典元素
- Python - 字典檢視物件
- Python - 迴圈遍歷字典
- Python - 複製字典
- Python - 巢狀字典
- Python - 字典方法
- Python - 字典練習
- Python 陣列
- Python - 陣列
- Python - 訪問陣列元素
- Python - 新增陣列元素
- Python - 刪除陣列元素
- Python - 迴圈遍歷陣列
- Python - 複製陣列
- Python - 反轉陣列
- Python - 排序陣列
- Python - 合併陣列
- Python - 陣列方法
- Python - 陣列練習
- Python 檔案處理
- Python - 檔案處理
- Python - 寫入檔案
- Python - 讀取檔案
- Python - 重新命名和刪除檔案
- Python - 目錄
- Python - 檔案方法
- Python - OS 檔案/目錄方法
- Python - OS 路徑方法
- 面向物件程式設計
- Python - OOPs 概念
- Python - 類 & 物件
- Python - 類屬性
- Python - 類方法
- Python - 靜態方法
- Python - 建構函式
- Python - 訪問修飾符
- Python - 繼承
- Python - 多型
- Python - 方法重寫
- Python - 方法過載
- Python - 動態繫結
- Python - 動態型別
- Python - 抽象
- Python - 封裝
- Python - 介面
- Python - 包
- Python - 內部類
- Python - 匿名類和物件
- Python - 單例類
- Python - 包裝類
- Python - 列舉
- Python - 反射
- Python 錯誤 & 異常
- Python - 語法錯誤
- Python - 異常
- Python - try-except 塊
- Python - try-finally 塊
- Python - 丟擲異常
- Python - 異常鏈
- Python - 巢狀 try 塊
- Python - 使用者自定義異常
- Python - 日誌
- Python - 斷言
- Python - 內建異常
- Python 多執行緒
- Python - 多執行緒
- Python - 執行緒生命週期
- Python - 建立執行緒
- Python - 啟動執行緒
- Python - 加入執行緒
- Python - 執行緒命名
- Python - 執行緒排程
- Python - 執行緒池
- Python - 主執行緒
- Python - 執行緒優先順序
- Python - 守護執行緒
- Python - 執行緒同步
- Python 同步
- Python - 執行緒間通訊
- Python - 執行緒死鎖
- Python - 中斷執行緒
- Python 網路程式設計
- Python - 網路程式設計
- Python - 套接字程式設計
- Python - URL 處理
- Python - 泛型
- Python 庫
- NumPy 教程
- Pandas 教程
- SciPy 教程
- Matplotlib 教程
- Django 教程
- OpenCV 教程
- Python 其他
- Python - 日期 & 時間
- Python - 數學
- Python - 迭代器
- Python - 生成器
- Python - 閉包
- Python - 裝飾器
- Python - 遞迴
- Python - 正則表示式
- Python - PIP
- Python - 資料庫訪問
- Python - 弱引用
- Python - 序列化
- Python - 模板
- Python - 輸出格式化
- Python - 效能測量
- Python - 資料壓縮
- Python - CGI 程式設計
- Python - XML 處理
- Python - GUI 程式設計
- Python - 命令列引數
- Python - 文件字串
- Python - JSON
- Python - 傳送郵件
- Python - 擴充套件
- Python - 工具/實用程式
- Python - GUIs
- Python 高階概念
- Python - 抽象基類
- Python - 自定義異常
- Python - 高階函式
- Python - 物件內部
- Python - 記憶體管理
- Python - 元類
- Python - 使用元類進行超程式設計
- Python - 模擬和存根
- Python - Monkey Patching
- Python - 訊號處理
- Python - 型別提示
- Python - 自動化教程
- Python - Humanize 包
- Python - 上下文管理器
- Python - 協程
- Python - 描述符
- Python - 診斷和修復記憶體洩漏
- Python - 不可變資料結構
- Python 有用資源
- Python - 問答
- Python - 線上測驗
- Python - 快速指南
- Python - 參考
- Python - 速查表
- Python - 專案
- Python - 有用資源
- Python - 討論
- Python 編譯器
- NumPy 編譯器
- Matplotlib 編譯器
- SciPy 編譯器
Python - while迴圈
Python while 迴圈
在 Python 程式語言中,while 迴圈會重複執行目標語句,直到指定的布林表示式為假。此迴圈以while 關鍵字開頭,後跟布林表示式和冒號符號 (:)。然後,縮排的語句塊開始。
此處,語句可以是單個語句或具有統一縮排的語句塊。條件可以是任何表示式,真值為任何非零值。一旦表示式變為假,程式控制就會轉移到迴圈後緊跟的行。
如果它未能變為假,迴圈將繼續執行,除非強制停止否則不會停止。這種迴圈稱為無限迴圈,在計算機程式中是不希望看到的。
while 迴圈的語法
Python 程式語言中 while 迴圈的語法如下:
while expression: statement(s)
在Python中,所有在程式設計結構之後以相同數量的字元空格縮排的語句都被視為單個程式碼塊的一部分。Python 使用縮排作為其語句分組的方法。
while 迴圈的流程圖
下圖說明了 while 迴圈:
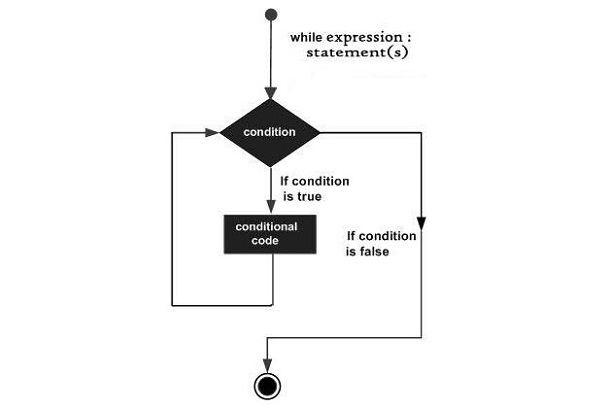
示例 1
以下示例說明了 while 迴圈的工作原理。此處,迭代執行直到 count 的值變為 5。
count=0
while count<5:
count+=1
print ("Iteration no. {}".format(count))
print ("End of while loop")
執行此程式碼後,將產生以下輸出:
Iteration no. 1 Iteration no. 2 Iteration no. 3 Iteration no. 4 Iteration no. 5 End of while loop
示例 2
這是一個使用while迴圈的另一個例子。每次迭代,程式都會請求使用者輸入,並持續重複,直到使用者輸入一個非數字字串。isnumeric()函式如果輸入是整數則返回true,否則返回false。
var = '0'
while var.isnumeric() == True:
var = "test"
if var.isnumeric() == True:
print ("Your input", var)
print ("End of while loop")
執行程式碼後,將產生以下輸出:
enter a number..10 Your input 10 enter a number..100 Your input 100 enter a number..543 Your input 543 enter a number..qwer End of while loop
Python無限while迴圈
如果條件永遠不會變成FALSE,迴圈就會變成無限迴圈。使用while迴圈時必須謹慎,因為此條件可能永遠不會解析為FALSE值。這將導致一個永不結束的迴圈。這樣的迴圈稱為無限迴圈。
無限迴圈可能在客戶端/伺服器程式設計中很有用,其中伺服器需要持續執行,以便客戶端程式可以根據需要與之通訊。
示例
讓我們來看一個例子,瞭解Python中的無限迴圈是如何工作的:
var = 1
while var == 1 : # This constructs an infinite loop
num = int(input("Enter a number :"))
print ("You entered: ", num)
print ("Good bye!")
執行此程式碼後,將產生以下輸出:
Enter a number :20
You entered: 20
Enter a number :29
You entered: 29
Enter a number :3
You entered: 3
Enter a number :11
You entered: 11
Enter a number :22
You entered: 22
Enter a number :Traceback (most recent call last):
File "examples\test.py", line 5, in
num = int(input("Enter a number :"))
KeyboardInterrupt
上面的例子進入無限迴圈,您需要使用CTRL+C來退出程式。
Python while-else迴圈
Python支援將else語句與while迴圈關聯起來。如果else語句與while迴圈一起使用,則當條件在控制轉移到主執行行之前變為false時,將執行else語句。
帶有else語句的While迴圈流程圖
下面的流程圖顯示瞭如何將else語句與while迴圈一起使用:
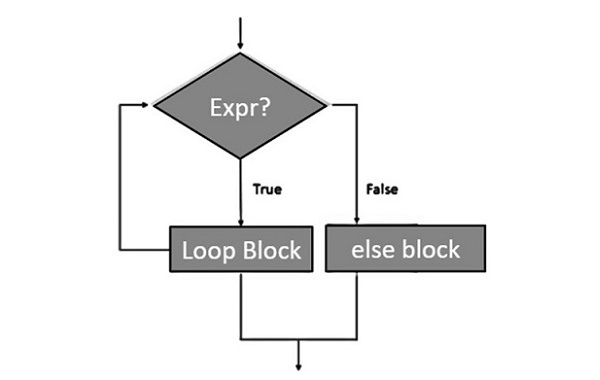
示例
下面的例子說明了else語句與while語句的組合。只要計數小於5,就會列印迭代計數。當它變成5時,else塊中的print語句會在控制傳遞到主程式中的下一條語句之前執行。
count=0
while count<5:
count+=1
print ("Iteration no. {}".format(count))
else:
print ("While loop over. Now in else block")
print ("End of while loop")
執行上面的程式碼後,它將列印以下輸出:
Iteration no. 1 Iteration no. 2 Iteration no. 3 Iteration no. 4 Iteration no. 5 While loop over. Now in else block End of while loop
單語句塊
類似於if語句語法,如果您的while子句只包含一個語句,則可以將其放在與while標題相同的行上。
示例
以下示例顯示瞭如何使用單行while子句。
flag = 0
while (flag): print ("Given flag is really true!")
print ("Good bye!")
執行此程式碼時,它將顯示以下輸出:
Good bye!
將標誌值更改為“1”並嘗試上述程式。如果您這樣做,它將進入無限迴圈,您需要按CTRL+C鍵退出。