
- Python 基礎
- Python - 首頁
- Python - 概述
- Python - 歷史
- Python - 特性
- Python vs C++
- Python - Hello World 程式
- Python - 應用領域
- Python - 直譯器
- Python - 環境搭建
- Python - 虛擬環境
- Python - 基本語法
- Python - 變數
- Python - 資料型別
- Python - 型別轉換
- Python - Unicode 系統
- Python - 字面量
- Python - 運算子
- Python - 算術運算子
- Python - 比較運算子
- Python - 賦值運算子
- Python - 邏輯運算子
- Python - 位運算子
- Python - 成員運算子
- Python - 身份運算子
- Python - 運算子優先順序
- Python - 註釋
- Python - 使用者輸入
- Python - 數字
- Python - 布林值
- Python 控制語句
- Python - 控制流
- Python - 決策
- Python - if 語句
- Python - if else
- Python - 巢狀 if
- Python - Match-Case 語句
- Python - 迴圈
- Python - for 迴圈
- Python - for-else 迴圈
- Python - while 迴圈
- Python - break 語句
- Python - continue 語句
- Python - pass 語句
- Python - 巢狀迴圈
- Python 函式與模組
- Python - 函式
- Python - 預設引數
- Python - 關鍵字引數
- Python - 僅限關鍵字引數
- Python - 位置引數
- Python - 僅限位置引數
- Python - 可變引數
- Python - 變數作用域
- Python - 函式註解
- Python - 模組
- Python - 內建函式
- Python 字串
- Python - 字串
- Python - 字串切片
- Python - 修改字串
- Python - 字串連線
- Python - 字串格式化
- Python - 跳脫字元
- Python - 字串方法
- Python - 字串練習
- Python 列表
- Python - 列表
- Python - 訪問列表元素
- Python - 修改列表元素
- Python - 新增列表元素
- Python - 刪除列表元素
- Python - 遍歷列表
- Python - 列表推導式
- Python - 排序列表
- Python - 複製列表
- Python - 合併列表
- Python - 列表方法
- Python - 列表練習
- Python 元組
- Python - 元組
- Python - 訪問元組元素
- Python - 更新元組
- Python - 解包元組
- Python - 遍歷元組
- Python - 合併元組
- Python - 元組方法
- Python - 元組練習
- Python 集合
- Python - 集合
- Python - 訪問集合元素
- Python - 新增集合元素
- Python - 刪除集合元素
- Python - 遍歷集合
- Python - 合併集合
- Python - 複製集合
- Python - 集合運算子
- Python - 集合方法
- Python - 集合練習
- Python 字典
- Python - 字典
- Python - 訪問字典元素
- Python - 修改字典元素
- Python - 新增字典元素
- Python - 刪除字典元素
- Python - 字典檢視物件
- Python - 遍歷字典
- Python - 複製字典
- Python - 巢狀字典
- Python - 字典方法
- Python - 字典練習
- Python 陣列
- Python - 陣列
- Python - 訪問陣列元素
- Python - 新增陣列元素
- Python - 刪除陣列元素
- Python - 遍歷陣列
- Python - 複製陣列
- Python - 反轉陣列
- Python - 排序陣列
- Python - 合併陣列
- Python - 陣列方法
- Python - 陣列練習
- Python 檔案處理
- Python - 檔案處理
- Python - 寫入檔案
- Python - 讀取檔案
- Python - 重新命名和刪除檔案
- Python - 目錄
- Python - 檔案方法
- Python - OS 檔案/目錄方法
- Python - OS 路徑方法
- 面向物件程式設計
- Python - OOPs 概念
- Python - 類與物件
- Python - 類屬性
- Python - 類方法
- Python - 靜態方法
- Python - 建構函式
- Python - 訪問修飾符
- Python - 繼承
- Python - 多型
- Python - 方法重寫
- Python - 方法過載
- Python - 動態繫結
- Python - 動態型別
- Python - 抽象
- Python - 封裝
- Python - 介面
- Python - 包
- Python - 內部類
- Python - 匿名類和物件
- Python - 單例類
- Python - 包裝器類
- Python - 列舉
- Python - 反射
- Python 錯誤與異常
- Python - 語法錯誤
- Python - 異常
- Python - try-except 塊
- Python - try-finally 塊
- Python - 丟擲異常
- Python - 異常鏈
- Python - 巢狀 try 塊
- Python - 使用者自定義異常
- Python - 日誌
- Python - 斷言
- Python - 內建異常
- Python 多執行緒
- Python - 多執行緒
- Python - 執行緒生命週期
- Python - 建立執行緒
- Python - 啟動執行緒
- Python - 連線執行緒
- Python - 執行緒命名
- Python - 執行緒排程
- Python - 執行緒池
- Python - 主執行緒
- Python - 執行緒優先順序
- Python - 守護執行緒
- Python - 同步執行緒
- Python 同步
- Python - 執行緒間通訊
- Python - 執行緒死鎖
- Python - 中斷執行緒
- Python 網路程式設計
- Python - 網路程式設計
- Python - Socket 程式設計
- Python - URL 處理
- Python - 泛型
- Python 庫
- NumPy 教程
- Pandas 教程
- SciPy 教程
- Matplotlib 教程
- Django 教程
- OpenCV 教程
- Python 雜項
- Python - 日期與時間
- Python - 數學
- Python - 迭代器
- Python - 生成器
- Python - 閉包
- Python - 裝飾器
- Python - 遞迴
- Python - 正則表示式
- Python - PIP
- Python - 資料庫訪問
- Python - 弱引用
- Python - 序列化
- Python - 模板
- Python - 輸出格式化
- Python - 效能測量
- Python - 資料壓縮
- Python - CGI 程式設計
- Python - XML 處理
- Python - GUI 程式設計
- Python - 命令列引數
- Python - 文件字串
- Python - JSON
- Python - 傳送郵件
- Python - 擴充套件
- Python - 工具/實用程式
- Python - GUIs
- Python 高階概念
- Python - 抽象基類
- Python - 自定義異常
- Python - 高階函式
- Python - 物件內部
- Python - 記憶體管理
- Python - 元類
- Python - 使用元類進行超程式設計
- Python - 模擬和存根
- Python - 猴子補丁
- Python - 訊號處理
- Python - 型別提示
- Python - 自動化教程
- Python - Humanize 包
- Python - 上下文管理器
- Python - 協程
- Python - 描述符
- Python - 診斷和修復記憶體洩漏
- Python - 不可變資料結構
- Python 有用資源
- Python - 問答
- Python - 線上測驗
- Python - 快速指南
- Python - 參考
- Python - 速查表
- Python - 專案
- Python - 有用資源
- Python - 討論
- Python 編譯器
- NumPy 編譯器
- Matplotlib 編譯器
- SciPy 編譯器
Python math.hypot() 方法
Python 的 math.hypot() 方法用於計算直角三角形的斜邊長度。
在 Python 3.8 之前的版本中,此方法僅用於查詢直角三角形的斜邊長度;但在 Python 3.8 及之後的版本中,它也用於查詢歐幾里得範數。
歐幾里得範數定義為笛卡爾平面上原點與座標之間的距離。因此,它實際上就是斜邊,其中座標軸充當直角三角形的底邊和高。
為了更好地理解這一點,讓我們來看下面的圖示 -
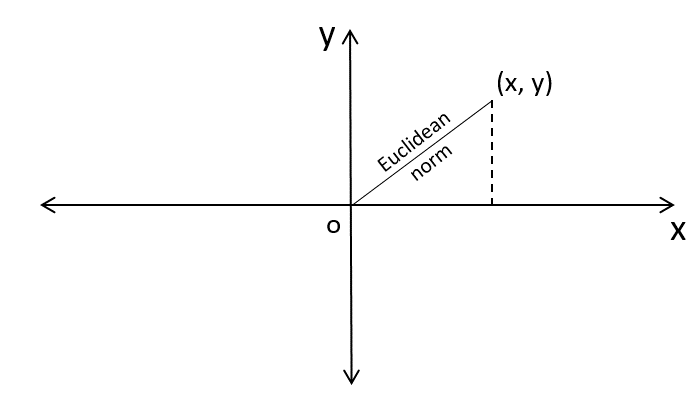
注意 - 此函式不能直接訪問,因此我們需要匯入 math 模組,然後需要使用 math 靜態物件呼叫此函式。
語法
以下是 Python math.hypot() 方法的語法 -
math.hypot(x, y)
引數
x, y - 必須是數值。
返回值
此方法返回歐幾里得範數,sqrt(x*x + y*y)。
示例
以下示例演示了 Python math.hypot() 方法的用法。這裡,我們建立兩個包含正浮點值的數字物件。這些物件作為引數傳遞給此方法,並計算歐幾里得範數。
import math # This will import the math module
# Create two numeric objects
x = 12.98
y = 44.06
# Calculate the euclidean norm
hyp = math.hypot(x, y)
# Display the length of the euclidean norm
print("The length of Euclidean norm is:", hyp)
執行以上程式時,會產生以下結果 -
The length of Euclidean norm is: 45.93216737755797
示例
即使我們將負座標 x 和 y 作為引數傳遞給此方法,歐幾里得範數也會作為正值獲得(因為它是距離)。
在以下示例中,我們建立兩個包含負值的數字物件。這些物件作為引數傳遞給該方法,並計算歐幾里得範數的長度。
import math # This will import the math module
# Create two numeric objects with negative values
x = -10.66
y = -15.12
# Calculate the euclidean norm
hyp = math.hypot(x, y)
# Display the length of the euclidean norm
print("The length of Euclidean norm is:", hyp)
讓我們編譯並執行給定的程式,輸出如下 -
The length of Euclidean norm is: 18.5
示例
假設 x 和 y 座標分別作為正無窮大和負無窮大值傳遞,歐幾里得範數的長度將是正無窮大。
import math # This will import the math module
# Create two numeric objects with infinity
x = float("inf")
y = float("-inf")
# Calculate the Euclidean norm
hyp = math.hypot(x, y)
# Display the length of the Euclidean norm
print("The length of Euclidean norm is:", hyp)
執行上面的程式後,輸出如下 -
The length of Euclidean norm is: inf
示例
當我們將NaN值作為引數傳遞給此方法時,返回值也將是NaN值。
import math # This will import the math module
# Create two numeric objects with NaN values
x = float("nan")
y = float("nan")
# Calculate the euclidean norm
hyp = math.hypot(x, y)
# Display the length of the euclidean norm
print("The length of Euclidean norm is:", hyp)
編譯並執行程式,結果如下:
The length of Euclidean norm is: nan
python_maths.htm
廣告