
- Python基礎
- Python - 首頁
- Python - 概述
- Python - 歷史
- Python - 特性
- Python vs C++
- Python - Hello World程式
- Python - 應用領域
- Python - 直譯器
- Python - 環境搭建
- Python - 虛擬環境
- Python - 基本語法
- Python - 變數
- Python - 資料型別
- Python - 型別轉換
- Python - Unicode系統
- Python - 字面量
- Python - 運算子
- Python - 算術運算子
- Python - 比較運算子
- Python - 賦值運算子
- Python - 邏輯運算子
- Python - 位運算子
- Python - 成員運算子
- Python - 身份運算子
- Python - 運算子優先順序
- Python - 註釋
- Python - 使用者輸入
- Python - 數字
- Python - 布林值
- Python控制語句
- Python - 控制流
- Python - 決策制定
- Python - if語句
- Python - if else
- Python - 巢狀if
- Python - match-case語句
- Python - 迴圈
- Python - for迴圈
- Python - for-else迴圈
- Python - while迴圈
- Python - break語句
- Python - continue語句
- Python - pass語句
- Python - 巢狀迴圈
- Python函式與模組
- Python - 函式
- Python - 預設引數
- Python - 關鍵字引數
- Python - 僅關鍵字引數
- Python - 位置引數
- Python - 僅位置引數
- Python - 可變引數
- Python - 變數作用域
- Python - 函式註解
- Python - 模組
- Python - 內建函式
- Python字串
- Python - 字串
- Python - 字串切片
- Python - 修改字串
- Python - 字串連線
- Python - 字串格式化
- Python - 跳脫字元
- Python - 字串方法
- Python - 字串練習
- Python列表
- Python - 列表
- Python - 訪問列表元素
- Python - 修改列表元素
- Python - 新增列表元素
- Python - 刪除列表元素
- Python - 迴圈遍歷列表
- Python - 列表推導式
- Python - 排序列表
- Python - 複製列表
- Python - 合併列表
- Python - 列表方法
- Python - 列表練習
- Python元組
- Python - 元組
- Python - 訪問元組元素
- Python - 更新元組
- Python - 解包元組
- Python - 迴圈遍歷元組
- Python - 合併元組
- Python - 元組方法
- Python - 元組練習
- Python集合
- Python - 集合
- Python - 訪問集合元素
- Python - 新增集合元素
- Python - 刪除集合元素
- Python - 迴圈遍歷集合
- Python - 合併集合
- Python - 複製集合
- Python - 集合運算子
- Python - 集合方法
- Python - 集合練習
- Python字典
- Python - 字典
- Python - 訪問字典元素
- Python - 修改字典元素
- Python - 新增字典元素
- Python - 刪除字典元素
- Python - 字典檢視物件
- Python - 迴圈遍歷字典
- Python - 複製字典
- Python - 巢狀字典
- Python - 字典方法
- Python - 字典練習
- Python陣列
- Python - 陣列
- Python - 訪問陣列元素
- Python - 新增陣列元素
- Python - 刪除陣列元素
- Python - 迴圈遍歷陣列
- Python - 複製陣列
- Python - 反轉陣列
- Python - 排序陣列
- Python - 合併陣列
- Python - 陣列方法
- Python - 陣列練習
- Python檔案處理
- Python - 檔案處理
- Python - 寫入檔案
- Python - 讀取檔案
- Python - 重新命名和刪除檔案
- Python - 目錄
- Python - 檔案方法
- Python - OS檔案/目錄方法
- Python - OS路徑方法
- 面向物件程式設計
- Python - OOPs概念
- Python - 類與物件
- Python - 類屬性
- Python - 類方法
- Python - 靜態方法
- Python - 建構函式
- Python - 訪問修飾符
- Python - 繼承
- Python - 多型
- Python - 方法重寫
- Python - 方法過載
- Python - 動態繫結
- Python - 動態型別
- Python - 抽象
- Python - 封裝
- Python - 介面
- Python - 包
- Python - 內部類
- Python - 匿名類和物件
- Python - 單例類
- Python - 包裝器類
- Python - 列舉
- Python - 反射
- Python錯誤與異常
- Python - 語法錯誤
- Python - 異常
- Python - try-except塊
- Python - try-finally塊
- Python - 丟擲異常
- Python - 異常鏈
- Python - 巢狀try塊
- Python - 使用者自定義異常
- Python - 日誌記錄
- Python - 斷言
- Python - 內建異常
- Python多執行緒
- Python - 多執行緒
- Python - 執行緒生命週期
- Python - 建立執行緒
- Python - 啟動執行緒
- Python - 加入執行緒
- Python - 執行緒命名
- Python - 執行緒排程
- Python - 執行緒池
- Python - 主執行緒
- Python - 執行緒優先順序
- Python - 守護執行緒
- Python - 同步執行緒
- Python同步
- Python - 執行緒間通訊
- Python - 執行緒死鎖
- Python - 中斷執行緒
- Python網路程式設計
- Python - 網路程式設計
- Python - 套接字程式設計
- Python - URL處理
- Python - 泛型
- Python庫
- NumPy教程
- Pandas教程
- SciPy教程
- Matplotlib教程
- Django教程
- OpenCV教程
- Python雜項
- Python - 日期與時間
- Python - 數學
- Python - 迭代器
- Python - 生成器
- Python - 閉包
- Python - 裝飾器
- Python - 遞迴
- Python - 正則表示式
- Python - PIP
- Python - 資料庫訪問
- Python - 弱引用
- Python - 序列化
- Python - 模板
- Python - 輸出格式化
- Python - 效能測量
- Python - 資料壓縮
- Python - CGI程式設計
- Python - XML處理
- Python - GUI程式設計
- Python - 命令列引數
- Python - 文件字串
- Python - JSON
- Python - 傳送郵件
- Python - 擴充套件功能
- Python - 工具/實用程式
- Python - GUIs
- Python高階概念
- Python - 抽象基類
- Python - 自定義異常
- Python - 高階函式
- Python - 物件內部結構
- Python - 記憶體管理
- Python - 元類
- Python - 使用元類進行超程式設計
- Python - 模擬和存根
- Python - 猴子補丁
- Python - 訊號處理
- Python - 型別提示
- Python - 自動化教程
- Python - Humanize包
- Python - 上下文管理器
- Python - 協程
- Python - 描述符
- Python - 診斷和修復記憶體洩漏
- Python - 不可變資料結構
- Python有用資源
- Python - 問答
- Python - 線上測驗
- Python - 快速指南
- Python - 參考
- Python - 速查表
- Python - 專案
- Python - 有用資源
- Python - 討論
- Python編譯器
- NumPy編譯器
- Matplotlib編譯器
- SciPy編譯器
如何用Python構建密碼管理器
這個密碼管理器應用程式將透過以組織的方式加密密碼來實現密碼的儲存和保護。
這個密碼管理器是用Python建立的,使用者介面是用Tkinter建立的,同時使用**cryptography**庫確保密碼安全。應用程式的一個特性是藉助強大的加密技術安全地儲存和顯示密碼。
安裝
首先按照以下安裝步驟操作:
1. 安裝Python
確保您已安裝Python 3.11或更高版本。下載並安裝它。閱讀更多內容 - Python環境搭建。
2. 安裝所需的庫
開啟終端或命令提示符,並使用pip安裝庫:
pip install cryptography
密碼管理器元件說明
密碼管理器應用程式包含幾個關鍵元件:密碼管理器應用程式包含幾個關鍵元件:
1. 金鑰生成和管理
最後一個是**generate_key()**函式,它會生成一個新的加密金鑰。
此函式**load_key()**作為預設函式,如果可用,則從檔案中載入現有金鑰,否則建立一個新金鑰。
2. 加密和解密
密碼使用Fernet加密演算法進行加密,這是由**encrypt_message()**函式完成的,而解密是在呈現之前使用**decrypt_message()**函式完成的。
3. 儲存密碼
**save_password()**函式從使用者那裡獲取服務、使用者名稱和密碼的字串輸入,然後在將其放入JSON檔案之前對其進行加密。它處理檔案操作並修改已存在的資料。
4. 檢視密碼
**view_passwords()**函式從JSON檔案中讀取加密的密碼,然後對其進行解密,並將其顯示給使用者。
5. 圖形使用者介面 (GUI)
Tkinter庫用於實現一個基本的使用者介面,其中包含用於服務、使用者名稱和密碼的輸入小部件以及用於儲存和顯示密碼的按鈕。
**閱讀更多**:Python GUI程式設計
構建密碼管理器的Python程式碼
import tkinter as tk
from tkinter import messagebox
from cryptography.fernet import Fernet
import os
import json
# Key generation and encryption setup
def generate_key():
return Fernet.generate_key()
def load_key():
if os.path.exists("secret.key"):
with open("secret.key", "rb") as key_file:
return key_file.read()
else:
key = generate_key()
with open("secret.key", "wb") as key_file:
key_file.write(key)
return key
def encrypt_message(message, key):
f = Fernet(key)
encrypted_message = f.encrypt(message.encode())
return encrypted_message
def decrypt_message(encrypted_message, key):
f = Fernet(key)
decrypted_message = f.decrypt(encrypted_message).decode()
return decrypted_message
# Initialize the key
key = load_key()
# Application functions
def save_password():
service = service_entry.get()
username = username_entry.get()
password = password_entry.get()
if not service or not username or not password:
messagebox.showwarning("Input Error", "Please fill all fields.")
return
encrypted_password = encrypt_message(password, key)
new_data = {service: {"username": username, "password": encrypted_password}}
if os.path.exists("passwords.json"):
with open("passwords.json", "r") as file:
try:
existing_data = json.load(file)
except (json.JSONDecodeError, TypeError):
existing_data = {}
existing_data.update(new_data)
else:
existing_data = new_data
# Ensure all values in existing_data are serializable
for service, info in existing_data.items():
if isinstance(info.get("password"), bytes):
info["password"] = info["password"].decode() # Convert bytes to string for serialization
with open("passwords.json", "w") as file:
try:
json.dump(existing_data, file, indent=4)
except TypeError as e:
messagebox.showerror("Serialization Error", f"Error serializing data: {e}")
service_entry.delete(0, tk.END)
username_entry.delete(0, tk.END)
password_entry.delete(0, tk.END)
messagebox.showinfo("Success", "Password saved successfully!")
def view_passwords():
if os.path.exists("passwords.json"):
with open("passwords.json", "r") as file:
try:
data = json.load(file)
except json.JSONDecodeError:
data = {}
result = ""
if data:
for service, info in data.items():
username = info.get("username", "N/A")
password = info.get("password", b"")
decrypted_password = decrypt_message(password.encode(), key)
result += f"Service: {service}\nUsername: {username}\nPassword: {decrypted_password}\n\n"
else:
result = "No passwords stored yet."
messagebox.showinfo("Stored Passwords", result)
else:
messagebox.showinfo("No Data", "No passwords stored yet.")
# GUI setup
root = tk.Tk()
root.title("Password Manager")
tk.Label(root, text="Service").grid(row=0, column=0, padx=10, pady=10)
tk.Label(root, text="Username").grid(row=1, column=0, padx=10, pady=10)
tk.Label(root, text="Password").grid(row=2, column=0, padx=10, pady=10)
service_entry = tk.Entry(root, width=50)
service_entry.grid(row=0, column=1, padx=10, pady=10)
username_entry = tk.Entry(root, width=50)
username_entry.grid(row=1, column=1, padx=10, pady=10)
password_entry = tk.Entry(root, width=50, show="*")
password_entry.grid(row=2, column=1, padx=10, pady=10)
tk.Button(root, text="Save Password", command=save_password).grid(row=3, column=0, columnspan=2, pady=10)
tk.Button(root, text="View Passwords", command=view_passwords).grid(row=4, column=0, columnspan=2, pady=10)
root.mainloop()
輸出
首先,您必須輸入您的服務、使用者名稱和密碼。
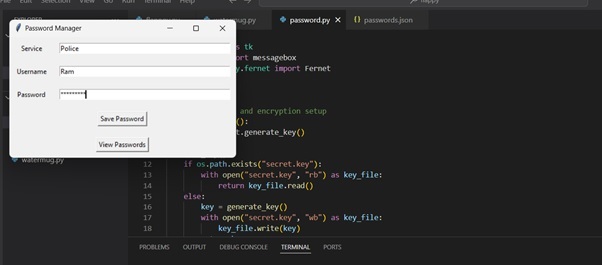
然後,您必須單擊儲存按鈕進行儲存:
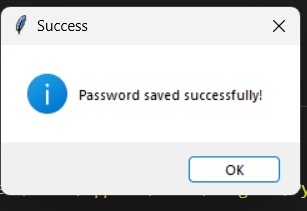
之後,您可以檢視您儲存的密碼:
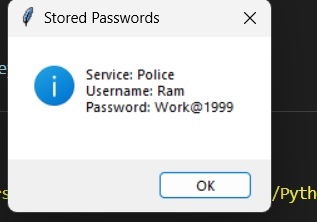
您可以再次建立密碼、使用者名稱和服務:
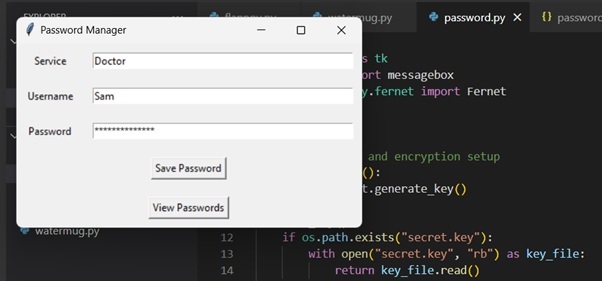
儲存密碼後,單擊“檢視密碼”,您將看到之前建立的兩個使用者名稱:
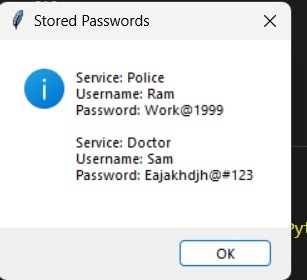
所有密碼都將儲存在JSON檔案中:
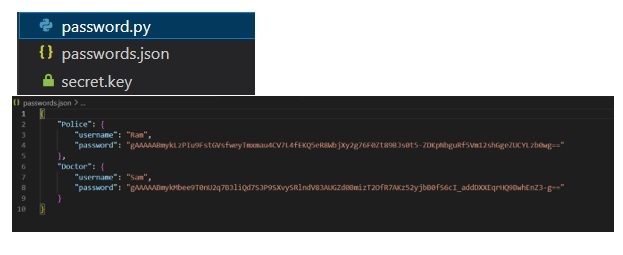
結論
這個用Python建立的密碼管理器可以作為處理密碼安全問題的有用工具。使用簡單的加密和友好的圖形使用者介面,它只允許授權使用者訪問,同時保持資料安全。從安裝說明和原始碼可以看出,使用者可以執行自己的密碼管理器並提高他們的線上安全性。