
- FastAPI 教程
- FastAPI - 首頁
- FastAPI - 簡介
- FastAPI - Hello World
- FastAPI - OpenAPI
- FastAPI - Uvicorn
- FastAPI - 型別提示
- FastAPI - IDE 支援
- FastAPI - REST 架構
- FastAPI - 路徑引數
- FastAPI - 查詢引數
- FastAPI - 引數驗證
- FastAPI - Pydantic
- FastAPI - 請求體
- FastAPI - 模板
- FastAPI - 靜態檔案
- FastAPI - HTML 表單模板
- FastAPI - 訪問表單資料
- FastAPI - 上傳檔案
- FastAPI - Cookie 引數
- FastAPI - 頭部引數
- FastAPI - 響應模型
- FastAPI - 巢狀模型
- FastAPI - 依賴項
- FastAPI - CORS
- FastAPI - CRUD 操作
- FastAPI - SQL 資料庫
- FastAPI - 使用 MongoDB
- FastAPI - 使用 GraphQL
- FastAPI - Websockets
- FastAPI - FastAPI 事件處理器
- FastAPI - 掛載子應用
- FastAPI - 中介軟體
- FastAPI - 掛載 Flask 應用
- FastAPI - 部署
- FastAPI 有用資源
- FastAPI - 快速指南
- FastAPI - 有用資源
- FastAPI - 討論
FastAPI - SQL 資料庫
在上一章中,我們使用了 Python 列表作為記憶體資料庫來使用 FastAPI 執行 CRUD 操作。相反,我們可以使用任何關係資料庫(例如 MySQL、Oracle 等)來執行儲存、檢索、更新和刪除操作。
我們不使用符合 **DB-API** 的資料庫驅動程式,而是使用 **SQLAlchemy** 作為 Python 程式碼和資料庫之間的介面(我們將使用 SQLite 資料庫,因為 Python 對其有內建支援)。SQLAlchemy 是一個流行的 SQL 工具包和 **物件關係對映器**。
物件關係對映 (ORM) 是一種程式設計技術,用於在面向物件程式語言中轉換不相容型別系統之間的資料。通常,面嚮物件語言(如 Python)中使用的型別系統包含非標量型別。但是,大多數資料庫產品(如 Oracle、MySQL 等)中的資料型別是原始型別,例如整數和字串。
在 ORM 系統中,每個類都對映到底層資料庫中的一個表。ORM 代替您編寫繁瑣的資料庫介面程式碼,讓您可以專注於系統邏輯的程式設計。
為了使用 SQLAlchemy,我們需要首先使用 PIP 安裝程式安裝該庫。
pip install sqlalchemy
SQLAlchemy 旨在與為特定資料庫構建的 DBAPI 實現一起工作。它使用方言系統與各種型別的 DBAPI 實現和資料庫進行通訊。所有方言都需要安裝相應的 DBAPI 驅動程式。
包含以下方言:
Firebird
Microsoft SQL Server
MySQL
Oracle
PostgreSQL
SQLite
Sybase
由於我們將使用 SQLite 資料庫,因此我們需要為名為 test.db 的資料庫建立一個數據庫引擎。從 sqlalchemy 模組匯入 **create_engine()** 函式。
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy.dialects.sqlite import *
SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URL = "sqlite:///./test.db"
engine = create_engine(SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URL, connect_args = {"check_same_thread": False})
為了與資料庫互動,我們需要獲取其控制代碼。會話物件是資料庫的控制代碼。會話類使用 **sessionmaker()** 定義 - 一個可配置的會話工廠方法,它繫結到引擎物件。
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker, Session session = sessionmaker(autocommit=False, autoflush=False, bind=engine)
接下來,我們需要一個宣告性基類,用於在宣告性系統中儲存類和對映表的目錄。
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base Base = declarative_base()
**Books**(**Base** 的子類)對映到資料庫中的 **book** 表。**Books** 類中的屬性對應於目標表中列的資料型別。請注意,id 屬性對應於 book 表中的主鍵。
from sqlalchemy import Column, Integer, String class Books(Base): __tablename__ = 'book' id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True, nullable=False) title = Column(String(50), unique=True) author = Column(String(50)) publisher = Column(String(50)) Base.metadata.create_all(bind=engine)
**create_all()** 方法在資料庫中建立相應的表。
現在,我們必須宣告一個與宣告性基類子類(上面定義的 Books 類)對應的 Pydantic 模型。
from typing import List
from pydantic import BaseModel, constr
class Book(BaseModel):
id: int
title: str
author:str
publisher: str
class Config:
orm_mode = True
請注意 config 類中 **orm_mode=True** 的使用,這表示它與 SQLAlchemy 的 ORM 類對映。
其餘程式碼與記憶體 CRUD 操作類似,不同之處在於操作函式透過 SQLalchemy 介面與資料庫互動。FastAPI 應用物件的 POST 操作定義如下:
from fastapi import FastAPI, Depends
app=FastAPI()
def get_db():
db = session()
try:
yield db
finally:
db.close()
@app.post('/add_new', response_model=Book)
def add_book(b1: Book, db: Session = Depends(get_db)):
bk=Books(id=b1.id, title=b1.title, author=b1.author,
publisher=b1.publisher)
db.add(bk)
db.commit()
db.refresh(bk)
return Books(**b1.dict())
首先建立資料庫會話。來自 POST 請求體的資料作為新行新增到 book 表中。執行 **add_book()** 操作函式以將示例資料新增到 books 表中。要進行驗證,您可以使用 SQLiteStudio(SQLite 資料庫的 GUI 工具)。
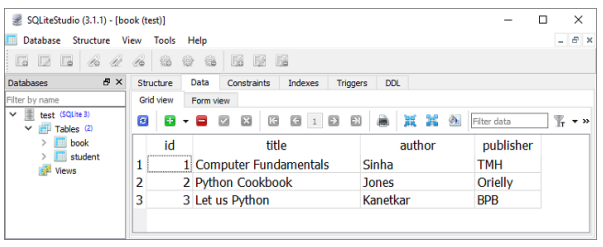
定義了兩個用於 GET 操作的操作函式,一個用於獲取所有記錄,另一個用於匹配路徑引數的記錄。
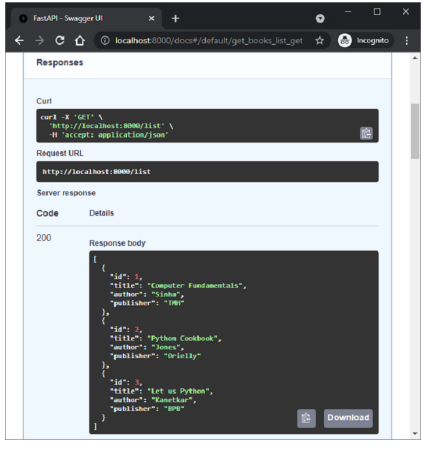
以下是繫結到 /list 路由的 **get_books()** 函式。執行時,其伺服器響應是所有記錄的列表。
@app.get('/list', response_model=List[Book])
def get_books(db: Session = Depends(get_db)):
recs = db.query(Books).all()
return recs
** /book/{id}** 路由呼叫 **get_book()** 函式,其中 id 作為路徑引數。SQLAlchemy 的查詢返回與給定 id 對應的物件。
@app.get('/book/{id}', response_model=Book)
def get_book(id:int, db: Session = Depends(get_db)):
return db.query(Books).filter(Books.id == id).first()
下圖顯示了從 Swagger UI 執行 **get_books()** 函式的結果。
更新和刪除操作由 **update_book()** 函式(訪問 ** /update/{id}** 路由時執行)和訪問 ** /delete/{id}** 路由時呼叫的 **del_book()** 函式執行。
@app.put('/update/{id}', response_model=Book)
def update_book(id:int, book:Book, db: Session = Depends(get_db)):
b1 = db.query(Books).filter(Books.id == id).first()
b1.id=book.id
b1.title=book.title
b1.author=book.author
b1.publisher=book.publisher
db.commit()
return db.query(Books).filter(Books.id == id).first()
@app.delete('/delete/{id}')
def del_book(id:int, db: Session = Depends(get_db)):
try:
db.query(Books).filter(Books.id == id).delete()
db.commit()
except Exception as e:
raise Exception(e)
return {"delete status": "success"}
如果您打算使用 SQLite 之外的任何其他資料庫,則只需相應地更改方言定義。例如,要使用 MySQL 資料庫和 **pymysql** 驅動程式,請將引擎物件的語句更改為以下內容:
engine = create_engine('mysql+pymysql://user:password@localhost/test')