
- 設計模式教程
- 設計模式 - 首頁
- 設計模式 - 概述
- 設計模式 - 工廠模式
- 抽象工廠模式
- 設計模式 - 單例模式
- 設計模式 - 建造者模式
- 設計模式 - 原型模式
- 設計模式 - 介面卡模式
- 設計模式 - 橋接模式
- 設計模式 - 過濾器模式
- 設計模式 - 組合模式
- 設計模式 - 裝飾器模式
- 設計模式 - 外觀模式
- 設計模式 - 享元模式
- 設計模式 - 代理模式
- 責任鏈模式
- 設計模式 - 命令模式
- 設計模式 - 直譯器模式
- 設計模式 - 迭代器模式
- 設計模式 - 中介者模式
- 設計模式 - 備忘錄模式
- 設計模式 - 觀察者模式
- 設計模式 - 狀態模式
- 設計模式 - 空物件模式
- 設計模式 - 策略模式
- 設計模式 - 模板模式
- 設計模式 - 訪問者模式
- 設計模式 - MVC 模式
- 業務代表模式
- 複合實體模式
- 資料訪問物件模式
- 前端控制器模式
- 攔截過濾器模式
- 服務定位器模式
- 傳輸物件模式
- 設計模式資源
- 設計模式 - 問答
- 設計模式 - 快速指南
- 設計模式 - 有用資源
- 設計模式 - 討論
設計模式 - 服務定位器模式
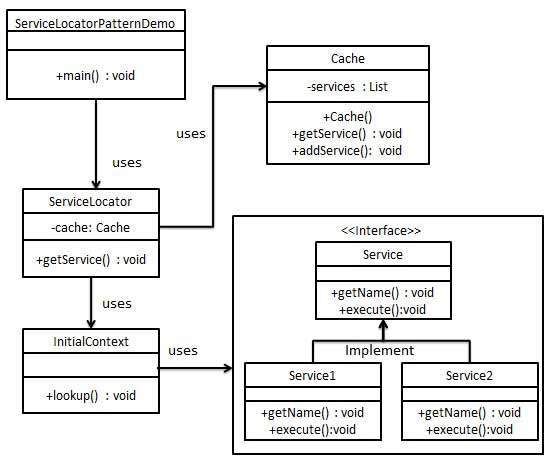
當我們希望使用 JNDI 查詢來定位各種服務時,就會使用服務定位器設計模式。考慮到查詢 JNDI 服務的高成本,服務定位器模式利用了快取技術。首次需要服務時,服務定位器會在 JNDI 中查詢並快取服務物件。之後透過服務定位器查詢相同服務時,將在其快取中進行查詢,這在很大程度上提高了應用程式的效能。以下是這種設計模式的實體。
服務 - 處理請求的實際服務。此類服務的引用需要在 JNDI 伺服器中查詢。
上下文/初始上下文 - JNDI 上下文包含用於查詢目的的服務引用。
服務定位器 - 服務定位器是透過 JNDI 查詢獲取服務的單一聯絡點,並快取服務。
快取 - 用於儲存服務引用以重複使用它們。
客戶端 - 客戶端是透過 ServiceLocator 呼叫服務的物件。
實現
我們將建立ServiceLocator、InitialContext、Cache、Service作為表示我們實體的各種物件。Service1和Service2表示具體服務。
我們的演示類ServiceLocatorPatternDemo在這裡充當客戶端,並將使用ServiceLocator來演示服務定位器設計模式。
步驟 1
建立 Service 介面。
Service.java
public interface Service {
public String getName();
public void execute();
}
步驟 2
建立具體服務。
Service1.java
public class Service1 implements Service {
public void execute(){
System.out.println("Executing Service1");
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return "Service1";
}
}
Service2.java
public class Service2 implements Service {
public void execute(){
System.out.println("Executing Service2");
}
@Override
public String getName() {
return "Service2";
}
}
步驟 3
建立用於 JNDI 查詢的 InitialContext。
InitialContext.java
public class InitialContext {
public Object lookup(String jndiName){
if(jndiName.equalsIgnoreCase("SERVICE1")){
System.out.println("Looking up and creating a new Service1 object");
return new Service1();
}
else if (jndiName.equalsIgnoreCase("SERVICE2")){
System.out.println("Looking up and creating a new Service2 object");
return new Service2();
}
return null;
}
}
步驟 4
建立快取。
Cache.java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Cache {
private List<Service> services;
public Cache(){
services = new ArrayList<Service>();
}
public Service getService(String serviceName){
for (Service service : services) {
if(service.getName().equalsIgnoreCase(serviceName)){
System.out.println("Returning cached " + serviceName + " object");
return service;
}
}
return null;
}
public void addService(Service newService){
boolean exists = false;
for (Service service : services) {
if(service.getName().equalsIgnoreCase(newService.getName())){
exists = true;
}
}
if(!exists){
services.add(newService);
}
}
}
步驟 5
建立服務定位器。
ServiceLocator.java
public class ServiceLocator {
private static Cache cache;
static {
cache = new Cache();
}
public static Service getService(String jndiName){
Service service = cache.getService(jndiName);
if(service != null){
return service;
}
InitialContext context = new InitialContext();
Service service1 = (Service)context.lookup(jndiName);
cache.addService(service1);
return service1;
}
}
步驟 6
使用ServiceLocator來演示服務定位器設計模式。
ServiceLocatorPatternDemo.java
public class ServiceLocatorPatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Service service = ServiceLocator.getService("Service1");
service.execute();
service = ServiceLocator.getService("Service2");
service.execute();
service = ServiceLocator.getService("Service1");
service.execute();
service = ServiceLocator.getService("Service2");
service.execute();
}
}
步驟 7
驗證輸出。
Looking up and creating a new Service1 object Executing Service1 Looking up and creating a new Service2 object Executing Service2 Returning cached Service1 object Executing Service1 Returning cached Service2 object Executing Service2
廣告