
- 設計模式教程
- 設計模式 - 首頁
- 設計模式 - 概述
- 設計模式 - 工廠模式
- 抽象工廠模式
- 設計模式 - 單例模式
- 設計模式 - 建造者模式
- 設計模式 - 原型模式
- 設計模式 - 介面卡模式
- 設計模式 - 橋接模式
- 設計模式 - 過濾器模式
- 設計模式 - 組合模式
- 設計模式 - 裝飾器模式
- 設計模式 - 外觀模式
- 設計模式 - 享元模式
- 設計模式 - 代理模式
- 責任鏈模式
- 設計模式 - 命令模式
- 設計模式 - 直譯器模式
- 設計模式 - 迭代器模式
- 設計模式 - 中介者模式
- 設計模式 - 備忘錄模式
- 設計模式 - 觀察者模式
- 設計模式 - 狀態模式
- 設計模式 - 空物件模式
- 設計模式 - 策略模式
- 設計模式 - 模板模式
- 設計模式 - 訪問者模式
- 設計模式 - MVC 模式
- 業務代表模式
- 複合實體模式
- 資料訪問物件模式
- 前端控制器模式
- 攔截過濾器模式
- 服務定位器模式
- 傳輸物件模式
- 設計模式資源
- 設計模式 - 問答
- 設計模式 - 快速指南
- 設計模式 - 有用資源
- 設計模式 - 討論
設計模式 - 享元模式
享元模式主要用於減少建立的物件數量,從而減少記憶體佔用並提高效能。這種設計模式屬於結構型模式,因為它提供了一種減少物件數量從而改進應用程式物件結構的方法。
享元模式嘗試透過儲存已存在的相似物件來重用它們,並在找不到匹配物件時建立新物件。我們將透過繪製 20 個不同位置的圓圈來演示此模式,但我們只建立 5 個物件。只有 5 種顏色可用,因此顏色屬性用於檢查已存在的 Circle 物件。
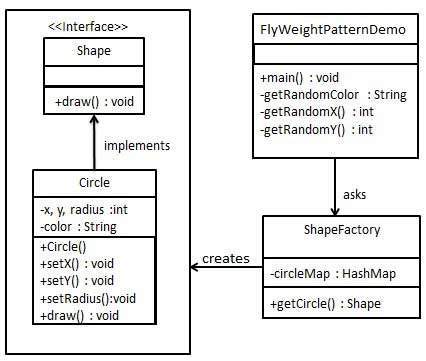
實現
我們將建立一個 Shape 介面和一個實現 Shape 介面的具體類 Circle。下一步定義一個工廠類 ShapeFactory。
ShapeFactory 包含一個 Circle 的 HashMap,其鍵為 Circle 物件的顏色。每當有請求建立特定顏色的圓圈到 ShapeFactory 時,它都會檢查其 HashMap 中是否存在圓圈物件,如果找到 Circle 物件,則返回該物件,否則建立新物件,將其儲存在 hashmap 中以備將來使用,並返回給客戶端。
FlyWeightPatternDemo,我們的演示類,將使用 ShapeFactory 獲取 Shape 物件。它將資訊(紅色/綠色/藍色/黑色/白色)傳遞給 ShapeFactory 以獲取其所需的所需顏色的圓圈。
步驟 1
建立一個介面。
Shape.java
public interface Shape {
void draw();
}
步驟 2
建立實現相同介面的具體類。
Circle.java
public class Circle implements Shape {
private String color;
private int x;
private int y;
private int radius;
public Circle(String color){
this.color = color;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
public void setRadius(int radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("Circle: Draw() [Color : " + color + ", x : " + x + ", y :" + y + ", radius :" + radius);
}
}
步驟 3
建立一個工廠,根據給定的資訊生成具體類的物件。
ShapeFactory.java
import java.util.HashMap;
public class ShapeFactory {
// Uncomment the compiler directive line and
// javac *.java will compile properly.
// @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private static final HashMap circleMap = new HashMap();
public static Shape getCircle(String color) {
Circle circle = (Circle)circleMap.get(color);
if(circle == null) {
circle = new Circle(color);
circleMap.put(color, circle);
System.out.println("Creating circle of color : " + color);
}
return circle;
}
}
步驟 4
使用工廠透過傳遞資訊(如顏色)來獲取具體類的物件。
FlyweightPatternDemo.java
public class FlyweightPatternDemo {
private static final String colors[] = { "Red", "Green", "Blue", "White", "Black" };
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=0; i < 20; ++i) {
Circle circle = (Circle)ShapeFactory.getCircle(getRandomColor());
circle.setX(getRandomX());
circle.setY(getRandomY());
circle.setRadius(100);
circle.draw();
}
}
private static String getRandomColor() {
return colors[(int)(Math.random()*colors.length)];
}
private static int getRandomX() {
return (int)(Math.random()*100 );
}
private static int getRandomY() {
return (int)(Math.random()*100);
}
}
步驟 5
驗證輸出。
Creating circle of color : Black Circle: Draw() [Color : Black, x : 36, y :71, radius :100 Creating circle of color : Green Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 27, y :27, radius :100 Creating circle of color : White Circle: Draw() [Color : White, x : 64, y :10, radius :100 Creating circle of color : Red Circle: Draw() [Color : Red, x : 15, y :44, radius :100 Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 19, y :10, radius :100 Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 94, y :32, radius :100 Circle: Draw() [Color : White, x : 69, y :98, radius :100 Creating circle of color : Blue Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 13, y :4, radius :100 Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 21, y :21, radius :100 Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 55, y :86, radius :100 Circle: Draw() [Color : White, x : 90, y :70, radius :100 Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 78, y :3, radius :100 Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 64, y :89, radius :100 Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 3, y :91, radius :100 Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 62, y :82, radius :100 Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 97, y :61, radius :100 Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 86, y :12, radius :100 Circle: Draw() [Color : Green, x : 38, y :93, radius :100 Circle: Draw() [Color : Red, x : 76, y :82, radius :100 Circle: Draw() [Color : Blue, x : 95, y :82, radius :100
廣告