
- TensorFlow 教程
- TensorFlow - 首頁
- TensorFlow - 簡介
- TensorFlow - 安裝
- 理解人工智慧
- 數學基礎
- 機器學習與深度學習
- TensorFlow - 基礎
- 卷積神經網路
- 迴圈神經網路
- TensorBoard 視覺化
- TensorFlow - 詞嵌入
- 單層感知器
- TensorFlow - 線性迴歸
- TFLearn 及其安裝
- CNN 和 RNN 的區別
- TensorFlow - Keras
- TensorFlow - 分散式計算
- TensorFlow - 匯出
- 多層感知器學習
- 感知器的隱藏層
- TensorFlow - 最佳化器
- TensorFlow - XOR 實現
- 梯度下降最佳化
- TensorFlow - 形成圖
- 使用 TensorFlow 進行影像識別
- 神經網路訓練建議
- TensorFlow 有用資源
- TensorFlow - 快速指南
- TensorFlow - 有用資源
- TensorFlow - 討論
TensorFlow - 迴圈神經網路
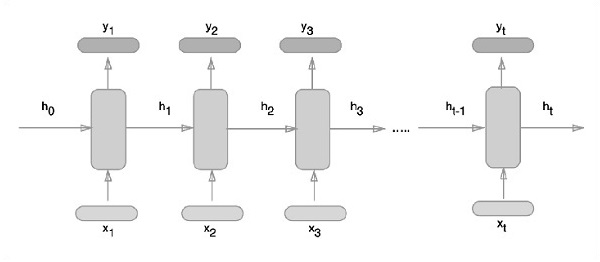
迴圈神經網路是一種面向深度學習的演算法,它遵循順序方法。在神經網路中,我們總是假設每個輸入和輸出都獨立於所有其他層。這些型別的神經網路被稱為迴圈神經網路,因為它們以順序方式執行數學計算。
考慮以下訓練迴圈神經網路的步驟:
步驟 1 - 從資料集中輸入一個特定的示例。
步驟 2 - 網路將獲取一個示例並使用隨機初始化的變數進行一些計算。
步驟 3 - 然後計算預測結果。
步驟 4 - 生成的實際結果與預期值的比較將產生誤差。
步驟 5 - 為了追蹤誤差,它會透過相同的路徑傳播,其中變數也會被調整。
步驟 6 - 重複步驟 1 到 5,直到我們確信宣告以獲取輸出的變數已正確定義。
步驟 7 - 透過應用這些變數來獲取新的未見輸入,從而進行系統預測。
下面描述了表示迴圈神經網路的示意圖方法:
使用 TensorFlow 實現迴圈神經網路
在本節中,我們將學習如何使用 TensorFlow 實現迴圈神經網路。
步驟 1 - TensorFlow 包含用於迴圈神經網路模組的特定實現的各種庫。
#Import necessary modules
from __future__ import print_function
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.contrib import rnn
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("/tmp/data/", one_hot = True)
如上所述,這些庫有助於定義輸入資料,這是迴圈神經網路實現的主要部分。
步驟 2 - 我們的主要目的是使用迴圈神經網路對影像進行分類,其中我們將每個影像行視為畫素序列。MNIST 影像形狀被專門定義為 28*28 px。現在我們將處理每個樣本的 28 個 28 步序列。我們將定義輸入引數以完成順序模式。
n_input = 28 # MNIST data input with img shape 28*28
n_steps = 28
n_hidden = 128
n_classes = 10
# tf Graph input
x = tf.placeholder("float", [None, n_steps, n_input])
y = tf.placeholder("float", [None, n_classes]
weights = {
'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_hidden, n_classes]))
}
biases = {
'out': tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([n_classes]))
}
步驟 3 - 使用 RNN 中定義的函式計算結果以獲得最佳結果。在這裡,每個資料形狀都與當前輸入形狀進行比較,並計算結果以保持準確率。
def RNN(x, weights, biases): x = tf.unstack(x, n_steps, 1) # Define a lstm cell with tensorflow lstm_cell = rnn.BasicLSTMCell(n_hidden, forget_bias=1.0) # Get lstm cell output outputs, states = rnn.static_rnn(lstm_cell, x, dtype = tf.float32) # Linear activation, using rnn inner loop last output return tf.matmul(outputs[-1], weights['out']) + biases['out'] pred = RNN(x, weights, biases) # Define loss and optimizer cost = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits = pred, labels = y)) optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate = learning_rate).minimize(cost) # Evaluate model correct_pred = tf.equal(tf.argmax(pred,1), tf.argmax(y,1)) accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_pred, tf.float32)) # Initializing the variables init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
步驟 4 - 在此步驟中,我們將啟動圖形以獲取計算結果。這也有助於計算測試結果的準確性。
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
step = 1
# Keep training until reach max iterations
while step * batch_size < training_iters:
batch_x, batch_y = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
batch_x = batch_x.reshape((batch_size, n_steps, n_input))
sess.run(optimizer, feed_dict={x: batch_x, y: batch_y})
if step % display_step == 0:
# Calculate batch accuracy
acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: batch_x, y: batch_y})
# Calculate batch loss
loss = sess.run(cost, feed_dict={x: batch_x, y: batch_y})
print("Iter " + str(step*batch_size) + ", Minibatch Loss= " + \
"{:.6f}".format(loss) + ", Training Accuracy= " + \
"{:.5f}".format(acc))
step += 1
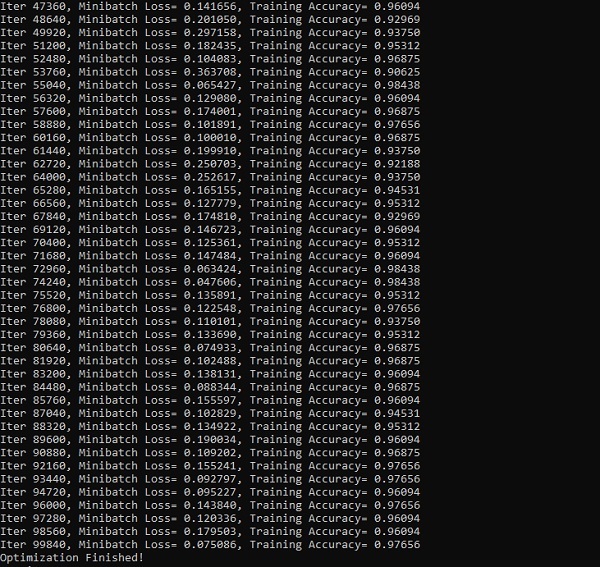
print("Optimization Finished!")
test_len = 128
test_data = mnist.test.images[:test_len].reshape((-1, n_steps, n_input))
test_label = mnist.test.labels[:test_len]
print("Testing Accuracy:", \
sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: test_data, y: test_label}))
下面的螢幕截圖顯示了生成的輸出:
廣告