
- TensorFlow 教程
- TensorFlow - 首頁
- TensorFlow - 簡介
- TensorFlow - 安裝指南
- 瞭解人工智慧
- 數學基礎
- 機器學習與深度學習
- TensorFlow - 基礎知識
- 卷積神經網路
- 迴圈神經網路
- TensorBoard 視覺化
- TensorFlow - 詞嵌入
- 單層感知器
- TensorFlow - 線性迴歸
- TFLearn 及其安裝指南
- CNN 和 RNN 的區別
- TensorFlow - Keras
- TensorFlow - 分散式計算
- TensorFlow - 匯出
- 多層感知器學習
- 感知器隱含層
- TensorFlow - 最佳化器
- TensorFlow - XOR 實現
- 梯度下降最佳化
- TensorFlow - 繪製圖
- 使用 TensorFlow 進行影像識別
- 神經網路訓練建議
- TensorFlow 有用資源
- TensorFlow - 快速指南
- TensorFlow - 有用資源
- TensorFlow - 討論
TensorFlow - 繪製圖
偏微分方程 (PDE) 是一種涉及具有多個自變數未知函式偏導數的微分方程。針對偏微分方程,我們將重點關注建立新圖。
我們假設有一個面積為 500*500 平方的池塘 −
N = 500
現在,我們將計算偏微分方程並使用它繪製相應的圖。按照下面給出的步驟計算圖。
步驟 1 − 匯入庫以進行模擬。
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
步驟 2 − 包含將 2D 陣列轉換為卷積核的轉換函式和簡化的 2D 卷積運算。
def make_kernel(a): a = np.asarray(a) a = a.reshape(list(a.shape) + [1,1]) return tf.constant(a, dtype=1) def simple_conv(x, k): """A simplified 2D convolution operation""" x = tf.expand_dims(tf.expand_dims(x, 0), -1) y = tf.nn.depthwise_conv2d(x, k, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding = 'SAME') return y[0, :, :, 0] def laplace(x): """Compute the 2D laplacian of an array""" laplace_k = make_kernel([[0.5, 1.0, 0.5], [1.0, -6., 1.0], [0.5, 1.0, 0.5]]) return simple_conv(x, laplace_k) sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
步驟 3 − 包含迭代次數和計算圖以相應顯示記錄。
N = 500
# Initial Conditions -- some rain drops hit a pond
# Set everything to zero
u_init = np.zeros([N, N], dtype = np.float32)
ut_init = np.zeros([N, N], dtype = np.float32)
# Some rain drops hit a pond at random points
for n in range(100):
a,b = np.random.randint(0, N, 2)
u_init[a,b] = np.random.uniform()
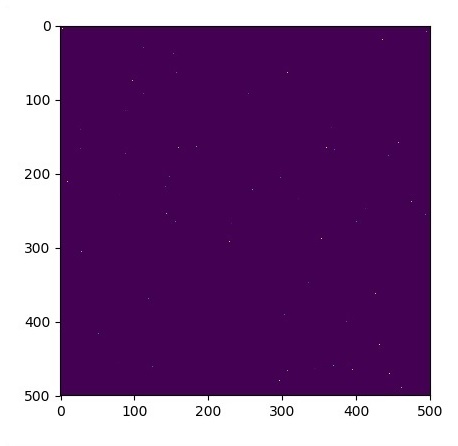
plt.imshow(u_init)
plt.show()
# Parameters:
# eps -- time resolution
# damping -- wave damping
eps = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape = ())
damping = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape = ())
# Create variables for simulation state
U = tf.Variable(u_init)
Ut = tf.Variable(ut_init)
# Discretized PDE update rules
U_ = U + eps * Ut
Ut_ = Ut + eps * (laplace(U) - damping * Ut)
# Operation to update the state
step = tf.group(U.assign(U_), Ut.assign(Ut_))
# Initialize state to initial conditions
tf.initialize_all_variables().run()
# Run 1000 steps of PDE
for i in range(1000):
# Step simulation
step.run({eps: 0.03, damping: 0.04})
# Visualize every 50 steps
if i % 500 == 0:
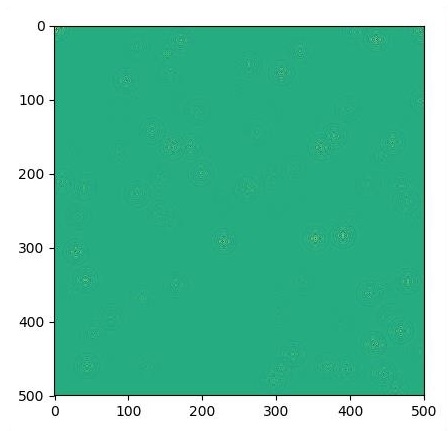
plt.imshow(U.eval())
plt.show()
繪製的圖如下所示 −
廣告