
- TensorFlow 教程
- TensorFlow - 首頁
- TensorFlow - 簡介
- TensorFlow - 安裝
- 理解人工智慧
- 數學基礎
- 機器學習與深度學習
- TensorFlow - 基礎
- 卷積神經網路
- 迴圈神經網路
- TensorBoard 視覺化
- TensorFlow - 詞嵌入
- 單層感知器
- TensorFlow - 線性迴歸
- TFLearn 及其安裝
- CNN 和 RNN 的區別
- TensorFlow - Keras
- TensorFlow - 分散式計算
- TensorFlow - 匯出
- 多層感知器學習
- 感知器的隱藏層
- TensorFlow - 最佳化器
- TensorFlow - XOR 實現
- 梯度下降最佳化
- TensorFlow - 構建圖
- 使用 TensorFlow 進行影像識別
- 神經網路訓練建議
- TensorFlow 有用資源
- TensorFlow - 快速指南
- TensorFlow - 有用資源
- TensorFlow - 討論
TensorFlow - 卷積神經網路
在理解機器學習概念之後,我們現在可以將重點轉向深度學習概念。深度學習是機器學習的一個分支,被認為是近幾十年來研究人員取得的一個關鍵步驟。深度學習實現的例子包括影像識別和語音識別等應用。
以下是兩種重要的深度神經網路型別:
- 卷積神經網路
- 迴圈神經網路
在本章中,我們將重點介紹卷積神經網路 (CNN)。
卷積神經網路
卷積神經網路旨在透過多層陣列處理資料。這種型別的神經網路用於影像識別或人臉識別等應用。CNN 與任何其他普通神經網路的主要區別在於,CNN 將輸入作為二維陣列,並直接對影像進行操作,而不是像其他神經網路那樣關注特徵提取。
CNN 的主要方法包括針對識別問題的解決方案。谷歌和Facebook 等頂級公司已投資於識別專案的研發,以更快地完成活動。
卷積神經網路使用三個基本思想:
- 區域性感受野
- 卷積
- 池化
讓我們詳細瞭解這些思想。
CNN 利用輸入資料中存在的空間相關性。神經網路的每一層都連線一些輸入神經元。這個特定區域稱為區域性感受野。區域性感受野關注隱藏神經元。隱藏神經元處理上述區域內的輸入資料,而不會意識到特定邊界外的變化。
以下是生成區域性感受野的示意圖:
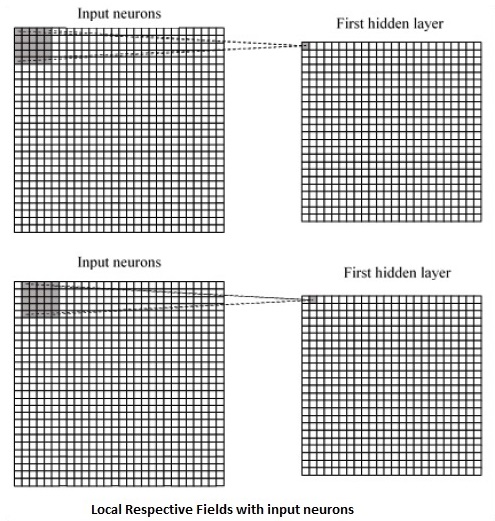
如果我們觀察上面的表示,每個連線都會學習隱藏神經元與其相關的連線的權重,並從一層移動到另一層。在這裡,單個神經元會不時地發生轉移。這個過程稱為“卷積”。
從輸入層到隱藏特徵圖的連線對映定義為“共享權重”,包含的偏差稱為“共享偏差”。
CNN 或卷積神經網路使用池化層,這些層位於 CNN 宣告之後。它將使用者的輸入作為來自卷積網路的特徵圖,並準備一個壓縮的特徵圖。池化層有助於建立具有先前層神經元的層。
TensorFlow 中 CNN 的實現
在本節中,我們將學習 CNN 的 TensorFlow 實現。執行和正確確定整個網路維度所需的步驟如下所示:
步驟 1 - 包含 TensorFlow 和資料集合模組所需的必要模組,這些模組需要計算 CNN 模型。
import tensorflow as tf import numpy as np from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
步驟 2 - 宣告一個名為 run_cnn() 的函式,其中包括各種引數和最佳化變數以及資料佔位符的宣告。這些最佳化變數將宣告訓練模式。
def run_cnn():
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets("MNIST_data/", one_hot = True)
learning_rate = 0.0001
epochs = 10
batch_size = 50
步驟 3 - 在此步驟中,我們將宣告訓練資料佔位符以及輸入引數 - 對於 28 x 28 畫素 = 784。這是從 mnist.train.nextbatch() 中提取的展平的影像資料。
我們可以根據需要重新調整張量的形狀。第一個值 (-1) 告訴函式根據傳遞給它的資料量動態地塑造該維度。兩個中間維度設定為影像大小(即 28 x 28)。
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784]) x_shaped = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28, 28, 1]) y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10])
步驟 4 - 現在重要的是建立一些卷積層:
layer1 = create_new_conv_layer(x_shaped, 1, 32, [5, 5], [2, 2], name = 'layer1') layer2 = create_new_conv_layer(layer1, 32, 64, [5, 5], [2, 2], name = 'layer2')
步驟 5 - 讓我們展平輸出,準備用於全連線輸出階段 - 在兩層步長為 2 的池化之後,維度為 28 x 28,降為 14 x 14 或最小 7 x 7 x,y 座標,但具有 64 個輸出通道。要使用“密集”層建立全連線層,新的形狀需要是 [-1, 7 x 7 x 64]。我們可以為此層設定一些權重和偏差值,然後使用 ReLU 啟用。
flattened = tf.reshape(layer2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64]) wd1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([7 * 7 * 64, 1000], stddev = 0.03), name = 'wd1') bd1 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([1000], stddev = 0.01), name = 'bd1') dense_layer1 = tf.matmul(flattened, wd1) + bd1 dense_layer1 = tf.nn.relu(dense_layer1)
步驟 6 - 另一個具有特定 softmax 啟用函式和所需最佳化器的層定義了精度評估,這使得初始化運算子的設定成為可能。
wd2 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([1000, 10], stddev = 0.03), name = 'wd2') bd2 = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([10], stddev = 0.01), name = 'bd2') dense_layer2 = tf.matmul(dense_layer1, wd2) + bd2 y_ = tf.nn.softmax(dense_layer2) cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean( tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits = dense_layer2, labels = y)) optimiser = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate = learning_rate).minimize(cross_entropy) correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1)) accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32)) init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer()
步驟 7 - 我們應該設定記錄變數。這會新增一個摘要來儲存資料的精度。
tf.summary.scalar('accuracy', accuracy)
merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter('E:\TensorFlowProject')
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init_op)
total_batch = int(len(mnist.train.labels) / batch_size)
for epoch in range(epochs):
avg_cost = 0
for i in range(total_batch):
batch_x, batch_y = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size = batch_size)
_, c = sess.run([optimiser, cross_entropy], feed_dict = {
x:batch_x, y: batch_y})
avg_cost += c / total_batch
test_acc = sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict = {x: mnist.test.images, y:
mnist.test.labels})
summary = sess.run(merged, feed_dict = {x: mnist.test.images, y:
mnist.test.labels})
writer.add_summary(summary, epoch)
print("\nTraining complete!")
writer.add_graph(sess.graph)
print(sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict = {x: mnist.test.images, y:
mnist.test.labels}))
def create_new_conv_layer(
input_data, num_input_channels, num_filters,filter_shape, pool_shape, name):
conv_filt_shape = [
filter_shape[0], filter_shape[1], num_input_channels, num_filters]
weights = tf.Variable(
tf.truncated_normal(conv_filt_shape, stddev = 0.03), name = name+'_W')
bias = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([num_filters]), name = name+'_b')
#Out layer defines the output
out_layer =
tf.nn.conv2d(input_data, weights, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding = 'SAME')
out_layer += bias
out_layer = tf.nn.relu(out_layer)
ksize = [1, pool_shape[0], pool_shape[1], 1]
strides = [1, 2, 2, 1]
out_layer = tf.nn.max_pool(
out_layer, ksize = ksize, strides = strides, padding = 'SAME')
return out_layer
if __name__ == "__main__":
run_cnn()
以下是上述程式碼生成的輸出:
See @{tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2}.
2018-09-19 17:22:58.802268: I
T:\src\github\tensorflow\tensorflow\core\platform\cpu_feature_guard.cc:140]
Your CPU supports instructions that this TensorFlow binary was not compiled to
use: AVX2
2018-09-19 17:25:41.522845: W
T:\src\github\tensorflow\tensorflow\core\framework\allocator.cc:101] Allocation
of 1003520000 exceeds 10% of system memory.
2018-09-19 17:25:44.630941: W
T:\src\github\tensorflow\tensorflow\core\framework\allocator.cc:101] Allocation
of 501760000 exceeds 10% of system memory.
Epoch: 1 cost = 0.676 test accuracy: 0.940
2018-09-19 17:26:51.987554: W
T:\src\github\tensorflow\tensorflow\core\framework\allocator.cc:101] Allocation
of 1003520000 exceeds 10% of system memory.