
- Selenium 教程
- Selenium - 首頁
- Selenium - 概述
- Selenium - 元件
- Selenium - 自動化測試
- Selenium - 環境設定
- Selenium - 遠端控制
- Selenium IDE 教程
- Selenium - IDE 簡介
- Selenium - 特性
- Selenium - 限制
- Selenium - 安裝
- Selenium - 建立測試
- Selenium - 建立指令碼
- Selenium - 控制流
- Selenium - 儲存變數
- Selenium - 警報和彈出視窗
- Selenium - Selenese 命令
- Selenium - Actions 命令
- Selenium - Accessors 命令
- Selenium - Assertions 命令
- Selenium - Assert/Verify 方法
- Selenium - 定位策略
- Selenium - 指令碼除錯
- Selenium - 驗證點
- Selenium - 模式匹配
- Selenium - JSON 資料檔案
- Selenium - 瀏覽器執行
- Selenium - 使用者擴充套件
- Selenium - 程式碼匯出
- Selenium - 程式碼輸出
- Selenium - JavaScript 函式
- Selenium - 外掛
- Selenium WebDriver 教程
- Selenium - 簡介
- Selenium WebDriver vs RC
- Selenium - 安裝
- Selenium - 第一個測試指令碼
- Selenium - 驅動程式會話
- Selenium - 瀏覽器選項
- Selenium - Chrome 選項
- Selenium - Edge 選項
- Selenium - Firefox 選項
- Selenium - Safari 選項
- Selenium - 雙擊
- Selenium - 右鍵單擊
- Python 中的 HTML 報告
- 處理編輯框
- Selenium - 單個元素
- Selenium - 多個元素
- Selenium Web 元素
- Selenium - 檔案上傳
- Selenium - 定位器策略
- Selenium - 相對定位器
- Selenium - 查詢器
- Selenium - 查詢所有連結
- Selenium - 使用者互動
- Selenium - WebElement 命令
- Selenium - 瀏覽器互動
- Selenium - 瀏覽器命令
- Selenium - 瀏覽器導航
- Selenium - 警報和彈出視窗
- Selenium - 處理表單
- Selenium - 視窗和標籤頁
- Selenium - 處理連結
- Selenium - 輸入框
- Selenium - 單選按鈕
- Selenium - 複選框
- Selenium - 下拉框
- Selenium - 處理 IFrame
- Selenium - 處理 Cookie
- Selenium - 日期時間選擇器
- Selenium - 動態 Web 表格
- Selenium - Actions 類
- Selenium - Action 類
- Selenium - 鍵盤事件
- Selenium - 鍵上/下
- Selenium - 複製和貼上
- Selenium - 處理特殊鍵
- Selenium - 滑鼠事件
- Selenium - 拖放
- Selenium - 筆事件
- Selenium - 滾動操作
- Selenium - 等待策略
- Selenium - 顯式/隱式等待
- Selenium - 支援特性
- Selenium - 多選
- Selenium - 等待支援
- Selenium - 選擇支援
- Selenium - 顏色支援
- Selenium - ThreadGuard
- Selenium - 錯誤和日誌記錄
- Selenium - 異常處理
- Selenium - 其他
- Selenium - 處理 Ajax 呼叫
- Selenium - JSON 資料檔案
- Selenium - CSV 資料檔案
- Selenium - Excel 資料檔案
- Selenium - 跨瀏覽器測試
- Selenium - 多瀏覽器測試
- Selenium - 多視窗測試
- Selenium - JavaScript 執行器
- Selenium - 無頭執行
- Selenium - 捕獲螢幕截圖
- Selenium - 捕獲影片
- Selenium - 頁面物件模型
- Selenium - 頁面工廠
- Selenium - 記錄和回放
- Selenium - 框架
- Selenium - 瀏覽上下文
- Selenium - DevTools
- Selenium Grid 教程
- Selenium - 概述
- Selenium - 架構
- Selenium - 元件
- Selenium - 配置
- Selenium - 建立測試指令碼
- Selenium - 測試執行
- Selenium - 端點
- Selenium - 自定義節點
- Selenium 報告工具
- Selenium - 報告工具
- Selenium - TestNG
- Selenium - JUnit
- Selenium - Allure
- Selenium & 其他技術
- Selenium - Java 教程
- Selenium - Python 教程
- Selenium - C# 教程
- Selenium - Javascript 教程
- Selenium - Kotlin 教程
- Selenium - Ruby 教程
- Selenium - Maven & Jenkins
- Selenium - 資料庫測試
- Selenium - LogExpert 日誌記錄
- Selenium - Log4j 日誌記錄
- Selenium - Robot Framework
- Selenium - AutoIT
- Selenium - Flash 測試
- Selenium - Apache Ant
- Selenium - Github 教程
- Selenium - SoapUI
- Selenium - Cucumber
- Selenium - IntelliJ
- Selenium - XPath
- Selenium 其他概念
- Selenium - IE 驅動程式
- Selenium - 自動化框架
- Selenium - 關鍵字驅動框架
- Selenium - 資料驅動框架
- Selenium - 混合驅動框架
- Selenium - SSL 證書錯誤
- Selenium - 替代方案
- Selenium 有用資源
- Selenium - 問答
- Selenium - 快速指南
- Selenium - 有用資源
- Selenium - 自動化實踐
- Selenium - 討論
Selenium - 遠端控制 (RC)
Selenium 是一款開源且可移植的自動化軟體測試工具,用於測試 Web 應用程式。它能夠跨不同的瀏覽器和作業系統執行。Selenium 不僅僅是一個工具,而是一套工具,可以幫助測試人員更有效地自動化基於 Web 的應用程式。Selenium 通常被稱為 Selenium 工具套件。總共有四個工具,它們統稱為 Selenium 元件。它們是:
Selenium IDE
Selenium RC
Selenium WebDriver
Selenium Grid
什麼是 Selenium 遠端控制?
Selenium 遠端控制是 Selenium 套件的一部分,包含客戶端庫和一個預設情況下開啟和關閉瀏覽器的伺服器。它是一個用 Java 實現的伺服器。它可以使用 HTTP 接受瀏覽器的命令。在當前版本的 Selenium 中,Selenium 遠端控制已過時,已被 Selenium 棄用。
Selenium 遠端控制中的自動化測試可以用任何程式語言開發,例如 Java、Python、C# 等。Selenium 遠端控制可用於編寫自動化測試來測試 Web 應用程式。Selenium 遠端控制包含一個代理伺服器,它允許瀏覽器像被測應用程式在代理伺服器域中可用一樣工作。要啟動測試執行,我們首先必須建立一個 Selenium 遠端控制伺服器例項。
Selenium 遠端控制 (RC) 是 Selenium 的主要專案,在 Selenium WebDriver (Selenium 2.0) 出現之前已經持續很長時間了。現在,Selenium 遠端控制幾乎不再使用,因為 WebDriver 提供了更強大的功能,但是使用者仍然可以使用 Selenium 遠端控制繼續開發指令碼。
它允許我們藉助 Java、C#、Perl、Python 和 PHP 等程式語言的強大功能編寫自動化的 Web 應用程式 UI 測試,以建立更復雜的測試,例如讀取和寫入檔案、查詢資料庫以及傳送電子郵件測試結果。
Selenium 遠端控制的架構
Selenium 遠端控制的架構如下圖所示:
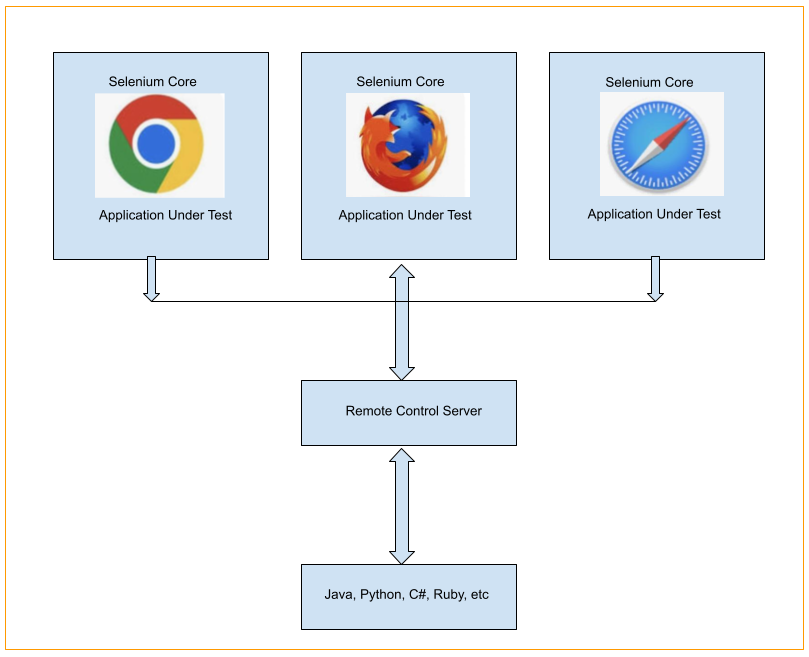
Selenium 遠端控制的架構並不簡單。為了在 Selenium 遠端控制中觸發測試,我們需要在系統中安裝和設定遠端控制伺服器。它類似於 Web 瀏覽器和命令之間的橋樑。Selenium 遠端控制伺服器將 Selenium Core(一個 JavaScript 程式)放入瀏覽器中。之後,Selenium Core 根據測試以 JavaScript 命令的形式從 Selenium 遠端控制伺服器接收訊息。瀏覽器執行從 Selenium Core 收到的命令,並將測試響應傳送回伺服器。
Selenium 伺服器充當整個應用程式的中央處理器。它接收要執行的測試用例的指令碼,解釋命令並報告測試執行結果。RC 伺服器繫結 Selenium Core 並自動將指令碼注入瀏覽器。所有這些操作只有在測試程式使用客戶端庫 API 執行瀏覽器後才會執行。伺服器透過接收透過 HTTP 網路以 GET 和 POST 操作型別傳輸的 Selenese 命令來工作,這使得我們可以使用任何程式語言將這些命令傳遞給伺服器。
客戶端庫是程式語言特定的庫,測試人員使用它們來建立測試指令碼。這些庫因語言而異。它們提供執行 Selenium 命令的函式。每個 Selenese 命令都有對應的函式已經定義。
Selenium 遠端控制的侷限性
Selenium 遠端控制的侷限性是由於其複雜的架構。此外,測試執行需要大量時間,效能也不盡如人意。這是因為 Selenium RC 將 JavaScript 命令作為瀏覽器的指令。無法使用 Selenium RC 實現無頭執行,並且其 API 缺乏面向物件特性。
使用 Java 安裝 Selenium 遠端控制
安裝 Selenium 遠端控制之前的先決條件:
步驟 1 - 從以下連結下載並安裝 Java:
https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/downloads/.
要更詳細地瞭解如何設定 Java,請參考以下連結:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bxIZ1GVWYkQ.
成功安裝 Java 後,我們可以透過執行命令:java(在命令提示符中)來確認其安裝。
C:\java
它將在螢幕上顯示以下資訊:
Usage: java [options] <mainclass> [args...]
(to execute a class)
or java [options] -jar <jarfile> [args...]
(to execute a jar file)
or java [options] -m <module>[/<mainclass>] [args...]
java [options] --module <module>[/<mainclass>] [args...]
(to execute the main class in a module)
or java [options] <sourcefile> [args]
(to execute a single source-file program)
Arguments following the main class, source file, -jar <jarfile>,
-m or --module <module>/<mainclass> are passed as the arguments to
main class.
where options include:
-cp <class search path of directories and zip/jar files>
-classpath <class search path of directories and zip/jar files>
--class-path <class search path of directories and zip/jar files>
A ; separated list of directories, JAR archives,
and ZIP archives to search for class files.
-p <module path>
--module-path <module path>...
A ; separated list of directories, each directory
is a directory of modules.
--upgrade-module-path <module path>...
A ; separated list of directories, each directory
is a directory of modules that replace upgradeable
modules in the runtime image
--add-modules <module name>[,<module name>...]
root modules to resolve in addition to the initial module.
<module name> can also be ALL-DEFAULT, ALL-SYSTEM,
ALL-MODULE-PATH.
--enable-native-access <module name>[,<module name>...]
modules that are permitted to perform restricted native operations.
<module name> can also be ALL-UNNAMED.
--list-modules
list observable modules and exit
-d <module name>
--describe-module <module name>
describe a module and exit
--dry-run create VM and load main class but do not execute main method.
The --dry-run option may be useful for validating the
command-line options such as the module system configuration.
--validate-modules
validate all modules and exit
The --validate-modules option may be useful for finding
conflicts and other errors with modules on the module path.
-D<name>=<value>
set a system property
-verbose:[class|module|gc|jni]
enable verbose output for the given subsystem
-version print product version to the error stream and exit
--version print product version to the output stream and exit
-showversion print product version to the error stream and continue
--show-version
print product version to the output stream and continue
--show-module-resolution
show module resolution output during startup
-? -h -help
print this help message to the error stream
--help print this help message to the output stream
-X print help on extra options to the error stream
--help-extra print help on extra options to the output stream
-ea[:<packagename>...|:<classname>]
-enableassertions[:<packagename>...|:<classname>]
enable assertions with specified granularity
-da[:<packagename>...|:<classname>]
-disableassertions[:<packagename>...|:<classname>]
disable assertions with specified granularity
-esa | -enablesystemassertions
enable system assertions
-dsa | -disablesystemassertions
disable system assertions
-agentlib:<libname>[=<options>]
load native agent library <libname>, e.g. -agentlib:jdwp
see also -agentlib:jdwp=help
-agentpath:<pathname>[=<options>]
load native agent library by full pathname
-javaagent:<jarpath>[=<options>]
load Java programming language agent, see java.lang.instrument
-splash:<imagepath>
show splash screen with specified image
HiDPI scaled images are automatically supported and used
if available. The unscaled image filename, e.g. image.ext,
should always be passed as the argument to the -splash option.
The most appropriate scaled image provided will be picked up
automatically.
See the SplashScreen API documentation for more information
@argument files
one or more argument files containing options
--disable-@files
prevent further argument file expansion
--enable-preview
allow classes to depend on preview features of this release
To specify an argument for a long option, you can use --<name>=<value> or
--<name> <value>.
步驟 2 - 接下來,我們將透過執行以下命令來確認已安裝的 Java 版本:
java –version
它將顯示以下輸出:
openjdk version "17.0.9" 2023-10-17 OpenJDK Runtime Environment Homebrew (build 17.0.9+0) OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM Homebrew (build 17.0.9+0, mixed mode, sharing)
執行的命令的輸出表示系統中安裝的 Java 版本為 17.0.9。
使用 Java 安裝 Selenium 遠端控制的方法如下:
步驟 1 - 從以下連結下載 Selenium Java 客戶端:
https://selenium.programming.tw/downloads/.
步驟 2 - 解壓 selenium-java 的 jar 檔案。
步驟 3 - 安裝任何程式碼編輯器,如 IntelliJ、Eclipse 等,來編寫和執行 Selenium 測試。市場上有多種編輯器可用,例如:Eclipse、IntelliJ、Atom 等。使用這些編輯器,我們可以開始使用 Java 專案來啟動我們的測試自動化。
要更詳細地瞭解如何設定 IntelliJ,請參考以下連結:
https://tutorialspoint.tw/selenium/intellij_selenium.htm.
步驟 4 - 在已安裝的編輯器中建立一個 Java 專案。
步驟 5 − 將 selenium-java.jar 檔案新增到類路徑和引用中。
步驟 6 − 在 Java 中建立一個 Selenium 測試。
步驟 7 − 下載並解壓 Java jar 檔案 - selenium-server-standalone.jar 到某個位置。
步驟 8 − 導航到已解壓 Java jar 檔案 - selenium-server-standalone.jar 的位置。
步驟 9 − 在命令列中執行以下命令:
java -jar selenium-server-standalone-<version-number>.jar.
步驟 10 − 從編輯器或命令列執行在步驟 6 中開發的 Selenium 測試。
本教程全面介紹了 Selenium 遠端控制 (RC)。我們首先介紹了什麼是 Selenium 遠端控制,Selenium 遠端控制的架構是什麼,Selenium 遠端控制的侷限性是什麼,以及如何使用 Java 安裝 Selenium 遠端控制。
這使您能夠深入瞭解 Selenium 遠端控制 (RC)。建議您繼續練習所學內容,並探索與 Selenium 相關的其他知識,以加深您的理解並拓寬您的視野。
