
- 生成式 AI 教程
- 生成式 AI - 首頁
- 生成式 AI 基礎
- 生成式 AI 基礎
- 生成式 AI 的演變
- 機器學習和生成式 AI
- 生成式 AI 模型
- 判別式模型與生成式模型
- 生成式 AI 模型的型別
- 機率分佈
- 機率密度函式
- 最大似然估計
- 生成式 AI 網路
- GAN 如何工作?
- GAN - 架構
- 條件 GAN
- StyleGAN 和 CycleGAN
- 訓練 GAN
- GAN 應用
- 生成式 AI Transformer
- 生成式 AI 中的 Transformer
- 生成式 AI 中 Transformer 的架構
- Transformer 中的輸入嵌入
- 多頭注意力機制
- 位置編碼
- 前饋神經網路
- Transformer 中的殘差連線
- 生成式 AI 自編碼器
- 生成式 AI 中的自編碼器
- 自編碼器的型別和應用
- 使用 Python 實現自編碼器
- 變分自編碼器
- 生成式 AI 和 ChatGPT
- 一個生成式 AI 模型
- 生成式 AI 雜項
- 生成式 AI 用於製造業
- 生成式 AI 用於開發者
- 生成式 AI 用於網路安全
- 生成式 AI 用於軟體測試
- 生成式 AI 用於營銷
- 生成式 AI 用於教育工作者
- 生成式 AI 用於醫療保健
- 生成式 AI 用於學生
- 生成式 AI 用於行業
- 生成式 AI 用於電影
- 生成式 AI 用於音樂
- 生成式 AI 用於烹飪
- 生成式 AI 用於媒體
- 生成式 AI 用於通訊
- 生成式 AI 用於攝影
- 生成式 AI 資源
- 生成式 AI - 有用資源
- 生成式 AI - 討論
Transformer 模型中的位置編碼
藉助輸入嵌入,Transformer 可以獲得離散標記(如單詞、子詞或字元)的向量表示。但是,這些向量表示不提供這些標記在序列中位置的資訊。這就是為什麼在 Transformer 的架構中,在輸入嵌入子層之後,使用了名為“位置編碼”的關鍵元件。
位置編碼使模型能夠透過為輸入序列中的每個標記提供其位置資訊來理解序列順序。在本章中,我們將瞭解什麼是位置編碼,為什麼需要它,它的工作原理以及它在 Python 程式語言中的實現。
什麼是位置編碼?
位置編碼是 Transformer 中用於提供輸入序列中標記順序資訊的一種機制。在 Transformer 架構中,位置編碼元件新增在輸入嵌入子層之後。
請檢視下圖;它是原始 Transformer 架構的一部分,表示位置編碼元件的結構 -
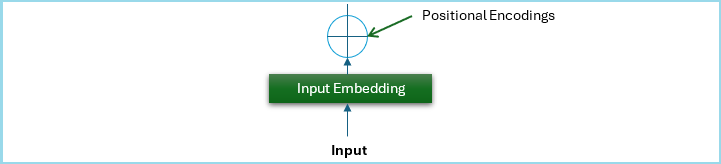
為什麼 Transformer 模型需要位置編碼?
Transformer 儘管擁有強大的自注意力機制,但缺乏固有的順序感。與按特定順序處理序列的迴圈神經網路 (RNN) 和長短期記憶網路 (LSTM) 不同,Transformer 的並行處理不提供輸入序列中標記位置的資訊。因此,模型無法理解上下文,尤其是在單詞順序很重要的任務中。
為了克服這一限制,引入了位置編碼,它為輸入序列中的每個標記提供其位置資訊。然後將這些編碼新增到輸入嵌入中,確保 Transformer 能夠連同其位置上下文一起處理標記。
位置編碼如何工作?
我們在上一章中討論過,Transformer 期望位置編碼函式的輸出的每個向量表示都位於固定大小的維度空間中(可能是 dmodel = 512 或任何其他常數值)。
例如,讓我們看下面給出的句子 -
I am playing with the brown ball and my brother is playing with the red ball.
單詞“brown”和“red”可能相似,但在本句中,它們相距甚遠。單詞“brown”位於位置 6 (pos = 6),單詞“red”位於位置 15 (pos = 15)。
這裡,問題是我們需要找到一種方法,為輸入句子中每個單詞的詞嵌入新增一個值,以便它包含有關其序列的資訊。但是,對於每個詞嵌入,我們需要找到一種方法,在 (0, 512) 的範圍內提供資訊。
位置編碼可以透過多種方式實現,但在原始 Transformer 模型中,Vashwani 等人 (2017) 使用了一種基於正弦函式的特定方法來為序列中的每個位置生成唯一的位置編碼。
下面的等式顯示瞭如何定義給定位置 pos 和維度 i 的位置編碼 -
$$\mathrm{PE_{pos \: 2i} \: = \: sin\left(\frac{pos}{10000^{\frac{2i}{d_{model}}}}\right)}$$
$$\mathrm{PE_{pos \: 2i+1} \: = \: cos\left(\frac{pos}{10000^{\frac{2i}{d_{model}}}}\right)}$$
這裡,dmodel 是嵌入的維度。
使用正弦函式建立位置編碼
下面是一個使用正弦函式建立位置編碼的 Python 指令碼 -
def positional_encoding(max_len, d_model):
pe = np.zeros((max_len, d_model))
position = np.arange(0, max_len).reshape(-1, 1)
div_term = np.exp(np.arange(0, d_model, 2) * -(np.log(10000.0) / d_model))
pe[:, 0::2] = np.sin(position * div_term)
pe[:, 1::2] = np.cos(position * div_term)
return pe
# Parameters
max_len = len(tokens)
# Generate positional encodings
pos_encodings = positional_encoding(max_len, embed_dim)
# Adjust the length of the positional encodings to match the input
input_embeddings_with_pos = input_embeddings + pos_encodings[:len(tokens)]
print("Positional Encodings:\n", pos_encodings)
print("Input Embeddings with Positional Encoding:\n", input_embeddings_with_pos)
現在,讓我們看看如何將它們新增到我們在上一章中實現的輸入嵌入中 -
import numpy as np
# Example text and tokenization
text = "Transformers revolutionized the field of NLP"
tokens = text.split()
# Creating a vocabulary
vocab = {word: idx for idx, word in enumerate(tokens)}
# Example input (sequence of token indices)
input_indices = np.array([vocab[word] for word in tokens])
print("Vocabulary:", vocab)
print("Input Indices:", input_indices)
# Parameters
vocab_size = len(vocab)
embed_dim = 512 # Dimension of the embeddings
# Initialize the embedding matrix with random values
embedding_matrix = np.random.rand(vocab_size, embed_dim)
# Get the embeddings for the input indices
input_embeddings = embedding_matrix[input_indices]
print("Embedding Matrix:\n", embedding_matrix)
print("Input Embeddings:\n", input_embeddings)
def positional_encoding(max_len, d_model):
pe = np.zeros((max_len, d_model))
position = np.arange(0, max_len).reshape(-1, 1)
div_term = np.exp(np.arange(0, d_model, 2) * -(np.log(10000.0) / d_model))
pe[:, 0::2] = np.sin(position * div_term)
pe[:, 1::2] = np.cos(position * div_term)
return pe
# Parameters
max_len = len(tokens)
# Generate positional encodings
pos_encodings = positional_encoding(max_len, embed_dim)
# Adjust the length of the positional encodings to match the input
input_embeddings_with_pos = input_embeddings + pos_encodings[:len(tokens)]
print("Positional Encodings:\n", pos_encodings)
print("Input Embeddings with Positional Encoding:\n", input_embeddings_with_pos)
輸出
執行上述指令碼後,我們將得到以下輸出 -
Vocabulary: {'Transformers': 0, 'revolutionized': 1, 'the': 2, 'field': 3, 'of': 4, 'NLP': 5}
Input Indices: [0 1 2 3 4 5]
Embedding Matrix:
[[0.71034683 0.08027048 0.89859858 ... 0.48071898 0.76495253 0.53869711]
[0.71247114 0.33418585 0.15329225 ... 0.61768814 0.32710687 0.89633072]
[0.11731439 0.97467007 0.66899319 ... 0.76157481 0.41975638 0.90980636]
[0.42299987 0.51534082 0.6459627 ... 0.58178494 0.13362482 0.13826352]
[0.2734792 0.80146145 0.75947837 ... 0.15180679 0.93250566 0.43946461]
[0.5750698 0.49106984 0.56273384 ... 0.77180581 0.18834177 0.6658962 ]]
Input Embeddings:
[[0.71034683 0.08027048 0.89859858 ... 0.48071898 0.76495253 0.53869711]
[0.71247114 0.33418585 0.15329225 ... 0.61768814 0.32710687 0.89633072]
[0.11731439 0.97467007 0.66899319 ... 0.76157481 0.41975638 0.90980636]
[0.42299987 0.51534082 0.6459627 ... 0.58178494 0.13362482 0.13826352]
[0.2734792 0.80146145 0.75947837 ... 0.15180679 0.93250566 0.43946461]
[0.5750698 0.49106984 0.56273384 ... 0.77180581 0.18834177 0.6658962 ]]
Positional Encodings:
[[ 0.00000000e+00 1.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 ... 1.00000000e+00
0.00000000e+00 1.00000000e+00]
[ 8.41470985e-01 5.40302306e-01 8.21856190e-01 ... 9.99999994e-01
1.03663293e-04 9.99999995e-01]
[ 9.09297427e-01 -4.16146837e-01 9.36414739e-01 ... 9.99999977e-01
2.07326584e-04 9.99999979e-01]
[ 1.41120008e-01 -9.89992497e-01 2.45085415e-01 ... 9.99999948e-01
3.10989874e-04 9.99999952e-01]
[-7.56802495e-01 -6.53643621e-01 -6.57166863e-01 ... 9.99999908e-01
4.14653159e-04 9.99999914e-01]
[-9.58924275e-01 2.83662185e-01 -9.93854779e-01 ... 9.99999856e-01
5.18316441e-04 9.99999866e-01]]
Input Embeddings with Positional Encoding:
[[0.71034683 1.08027048 0.89859858 ... 1.48071898 0.76495253 1.53869711]
[1.55394213 0.87448815 0.97514844 ... 1.61768813 0.32721053 1.89633072]
[1.02661182 0.55852323 1.60540793 ... 1.76157479 0.4199637 1.90980634]
[0.56411987 -0.47465167 0.89104811 ... 1.58178489 0.13393581 1.13826347]
[-0.4833233 0.14781783 0.1023115 ... 1.15180669 0.93292031 1.43946452]
[-0.38385447 0.77473203 -0.43112094 ... 1.77180567 0.18886009 1.66589607]]
結論
在本章中,我們介紹了位置編碼的基礎知識、其必要性、工作原理、Python 實現以及在 Transformer 模型中的整合。位置編碼是 Transformer 架構的一個基本組成部分,它使模型能夠捕獲序列中標記的順序。
瞭解和實現位置編碼的概念對於充分利用 Transformer 模型的潛力並將其有效地應用於解決複雜的 NLP 問題非常重要。