- GWT 教程
- GWT - 首頁
- GWT - 概述
- GWT - 環境設定
- GWT - 應用
- GWT - 建立應用
- GWT - 部署應用
- GWT - 使用 CSS 樣式
- GWT - 基本部件
- GWT - 表單部件
- GWT - 複雜部件
- GWT - 佈局面板
- GWT - 事件處理
- GWT - 自定義部件
- GWT - UIBinder
- GWT - RPC 通訊
- GWT - JUnit 整合
- GWT - 除錯應用
- GWT - 國際化
- GWT - History 類
- GWT - 書籤支援
- GWT - 日誌框架
- GWT 有用資源
- GWT - 問答
- GWT 快速指南
- GWT - 有用資源
- GWT - 討論
GWT 快速指南
GWT - 概述
什麼是 GWT?
Google Web Toolkit (GWT) 是一款用於建立富網際網路應用 (RIA)的開發工具包。以下是一些值得注意的功能:-
GWT 為開發人員提供了使用 JAVA 編寫客戶端應用程式的選項。
GWT 將用 JAVA 編寫的程式碼編譯成 JavaScript 程式碼。
用 GWT 編寫的應用程式與跨瀏覽器相容。GWT 自動生成適合每個瀏覽器的 javascript 程式碼。
GWT 是開源的,完全免費的,並且被全球數千名開發人員使用。它根據 Apache 許可證 2.0 版獲得許可。
總的來說,GWT 是一個框架,用於構建大規模、高效能的 Web 應用程式,同時保持易於維護。
為什麼要使用 GWT?
基於 Java,您可以使用 Eclipse 等 Java IDE 開發 GWT 應用程式。
開發人員可以使用程式碼自動完成/重構/導航/專案管理以及 IDE 的所有功能。GWT 提供了完整的除錯功能。開發人員可以像除錯 Java 應用程式一樣除錯客戶端應用程式。
GWT 提供了與 Junit 和 Maven 的輕鬆整合。
同樣基於 Java,GWT 對 Java 開發人員來說學習曲線較低。
GWT 生成最佳化的 javascript 程式碼,自行生成瀏覽器特定的 javascript 程式碼。
GWT 提供的部件庫提供了應用程式中所需的大多數任務。
GWT 是可擴充套件的,可以建立自定義部件來滿足應用程式的需求。
最重要的是,GWT 應用程式可以在所有主要的瀏覽器和智慧手機上執行,包括基於 Android 和 iOS 的手機/平板電腦。
GWT 的缺點
儘管 GWT 提供了許多優點,但它也存在以下缺點:-
不可索引 - 由 GWT 生成的網頁不會被搜尋引擎索引,因為這些應用程式是動態生成的。
不可降級 - 如果您的應用程式使用者停用了 Javascript,則使用者只會看到基本頁面,而不會看到更多內容。
對設計人員不友好 - GWT 不適合喜歡使用純 HTML 併為以後插入動態內容預留佔位符的網頁設計師。
GWT 元件
GWT 框架可以分為以下三個主要部分:-
GWT Java 到 JavaScript 編譯器 - 這是 GWT 最重要的部分,它使 GWT 成為構建 RIA 的強大工具。GWT 編譯器用於將用 Java 編寫的所有應用程式程式碼轉換為 JavaScript。
JRE 模擬庫 - Google Web Toolkit 包含一個模擬 Java 執行時庫子集的庫。該列表包括 java.lang、java.lang.annotation、java.math、java.io、java.sql、java.util 和 java.util.logging
GWT UI 構建庫 - GWT 的這部分包含許多子部分,包括實際的 UI 元件、RPC 支援、歷史管理等等。
GWT 還提供了一個 GWT 託管 Web 瀏覽器,它允許您在託管模式下執行和執行 GWT 應用程式,其中您的程式碼在 Java 虛擬機器中作為 Java 執行,而無需編譯為 JavaScript。
GWT - 環境設定
本教程將指導您如何準備開發環境以開始使用 GWT 框架的工作。本教程還將教您如何在設定 GWT 框架之前在您的機器上設定 JDK、Tomcat 和 Eclipse:-
系統需求
GWT 需要 JDK 1.6 或更高版本,因此首要要求是在您的機器上安裝 JDK。
| JDK | 1.6 或更高版本。 |
|---|---|
| 記憶體 | 沒有最低要求。 |
| 磁碟空間 | 沒有最低要求。 |
| 作業系統 | 沒有最低要求。 |
按照以下步驟設定您的環境以開始 GWT 應用程式開發。
步驟 1 - 驗證您的機器上是否安裝了 Java
現在開啟控制檯並執行以下 java 命令。
| 作業系統 | 任務 | 命令 |
|---|---|---|
| Windows | 開啟命令控制檯 | c:\> java -version |
| Linux | 開啟命令終端 | $ java -version |
| Mac | 開啟終端 | machine:~ joseph$ java -version |
讓我們驗證所有作業系統的輸出
| 序號 | 作業系統和生成的輸出 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Windows java version "1.6.0_21" Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.6.0_21-b07) Java HotSpot(TM) Client VM (build 17.0-b17, mixed mode, sharing) |
| 2 |
Linux java version "1.6.0_21" Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.6.0_21-b07) ava HotSpot(TM) Client VM (build 17.0-b17, mixed mode, sharing) |
| 3 |
Mac java version "1.6.0_21" Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.6.0_21-b07) Java HotSpot(TM)64-Bit Server VM (build 17.0-b17, mixed mode, sharing) |
步驟 2 - 設定 Java 開發工具包 (JDK)
如果您沒有安裝 Java,則可以從 Oracle 的 Java 網站安裝 Java 軟體開發工具包 (SDK):Java SE 下載。您將在下載的檔案中找到安裝 JDK 的說明,請按照給定的說明安裝和配置設定。最後設定 PATH 和 JAVA_HOME 環境變數以引用包含 java 和 javac 的目錄,通常分別為 java_install_dir/bin 和 java_install_dir。
設定JAVA_HOME環境變數以指向 Java 安裝在您機器上的基本目錄位置。例如
| 序號 | 作業系統和輸出 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Windows 將 JAVA_HOME 環境變數設定為 C:\Program Files\Java\jdk1.6.0_21 |
| 2 |
Linux export JAVA_HOME = /usr/local/java-current |
| 3 |
Mac export JAVA_HOME = /Library/Java/Home |
將 Java 編譯器位置新增到系統路徑。
| 序號 | 作業系統和輸出 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
Windows 將字串 ;%JAVA_HOME%\bin 附加到系統變數 Path 的末尾。 |
| 2 |
Linux export PATH=$PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin/ |
| 3 |
Mac 不需要 |
或者,如果您使用整合開發環境 (IDE),如 Borland JBuilder、Eclipse、IntelliJ IDEA 或 Sun ONE Studio,請編譯並執行一個簡單的程式以確認 IDE 知道您安裝 Java 的位置,否則請按照 IDE 給定的文件進行正確的設定。
步驟 3 - 設定 Eclipse IDE
本教程中的所有示例都是使用 Eclipse IDE 編寫的。因此,我建議您應該在您的機器上安裝最新版本的 Eclipse,具體取決於您的作業系統。
要安裝 Eclipse IDE,請從https://www.eclipse.org下載最新的 Eclipse 二進位制檔案。下載安裝後,將二進位制分發版解壓縮到方便的位置。例如在 Windows 上的 C:\eclipse,或在 Linux/Unix 上的 /usr/local/eclipse,最後適當地設定 PATH 變數。
可以透過在 Windows 機器上執行以下命令啟動 Eclipse,或者您可以簡單地雙擊 eclipse.exe
%C:\eclipse\eclipse.exe
可以透過在 Unix(Solaris、Linux 等)機器上執行以下命令啟動 Eclipse:-
$/usr/local/eclipse/eclipse
啟動成功後,如果一切正常,則應顯示以下結果:-

步驟 4 - 為 Eclipse 安裝 GWT SDK 和外掛
按照連結Eclipse 外掛(包括 SDK)中提供的說明,為安裝在您的機器上的 Eclipse 版本安裝 GWT SDK 和外掛。
GWT 外掛設定成功後,如果一切正常,則應顯示以下螢幕,其中Google 圖示用紅色矩形標記,如下所示:-
步驟 5:設定 Apache Tomcat
您可以從https://tomcat.apache.org/下載最新版本的 Tomcat。下載安裝後,將二進位制分發版解壓縮到方便的位置。例如在 Windows 上的 C:\apache-tomcat-6.0.33,或在 Linux/Unix 上的 /usr/local/apache-tomcat-6.0.33,並設定指向安裝位置的 CATALINA_HOME 環境變數。
可以透過在 Windows 機器上執行以下命令啟動 Tomcat,或者您可以簡單地雙擊 startup.bat
%CATALINA_HOME%\bin\startup.bat or /usr/local/apache-tomcat-6.0.33/bin/startup.sh
啟動成功後,可以透過訪問https://:8080/訪問 Tomcat 附帶的預設 Web 應用程式。如果一切正常,則應顯示以下結果:-
有關配置和執行 Tomcat 的更多資訊,可以在此處包含的文件以及 Tomcat 網站上找到:-https://tomcat.apache.org/
可以透過在 Windows 機器上執行以下命令停止 Tomcat:-
%CATALINA_HOME%\bin\shutdown or C:\apache-tomcat-5.5.29\bin\shutdown
可以透過在 Unix(Solaris、Linux 等)機器上執行以下命令停止 Tomcat:-
$CATALINA_HOME/bin/shutdown.sh or /usr/local/apache-tomcat-5.5.29/bin/shutdown.sh
GWT - 應用
在開始使用 GWT 建立實際的“HelloWorld”應用程式之前,讓我們看看 GWT 應用程式的實際組成部分是什麼:-
GWT 應用程式包含以下四個重要部分,其中最後一個部分是可選的,但前三個部分是必須的。
- 模組描述符
- 公共資源
- 客戶端程式碼
- 伺服器端程式碼
典型 gwt 應用程式HelloWord的不同部分的示例位置將如下所示:-
| 名稱 | 位置 |
|---|---|
| 專案根目錄 | HelloWorld/ |
| 模組描述符 | src/com/tutorialspoint/HelloWorld.gwt.xml |
| 公共資源 | src/com/tutorialspoint/war/ |
| 客戶端程式碼 | src/com/tutorialspoint/client/ |
| 伺服器端程式碼 | src/com/tutorialspoint/server/ |
模組描述符
模組描述符是以 XML 形式存在的配置檔案,用於配置 GWT 應用程式。
模組描述符副檔名為 *.gwt.xml,其中 * 是應用程式的名稱,此檔案應位於專案的根目錄中。
以下是 HelloWorld 應用程式的預設模組描述符 HelloWorld.gwt.xml:-
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "utf-8"?> <module rename-to = 'helloworld'> <!-- inherit the core web toolkit stuff. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.user'/> <!-- inherit the default gwt style sheet. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.theme.clean.Clean'/> <!-- specify the app entry point class. --> <entry-point class = 'com.tutorialspoint.client.HelloWorld'/> <!-- specify the paths for translatable code --> <source path = '...'/> <source path = '...'/> <!-- specify the paths for static files like html, css etc. --> <public path = '...'/> <public path = '...'/> <!-- specify the paths for external javascript files --> <script src = "js-url" /> <script src = "js-url" /> <!-- specify the paths for external style sheet files --> <stylesheet src = "css-url" /> <stylesheet src = "css-url" /> </module>
以下是關於模組描述符中使用的不同部分的簡要說明。
| 序號 | 節點和說明 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
<module rename-to = "helloworld"> 這提供了應用程式的名稱。 |
| 2 |
<inherits name = "logical-module-name" /> 這將其他 gwt 模組新增到應用程式中,就像 java 應用程式中的 import 一樣。可以以這種方式繼承任意數量的模組。 |
| 3 |
<entry-point class = "classname" /> 此項指定了將開始載入 GWT 應用程式的類的名稱。可以新增任意數量的入口點類,並且它們會按照在模組檔案中出現的順序依次呼叫。因此,當第一個入口點的 onModuleLoad() 完成時,下一個入口點將立即被呼叫。 |
| 4 |
<source path = "path" /> 此項指定了 GWT 編譯器將搜尋原始碼進行編譯的原始檔夾名稱。 |
| 5 |
<public path = "path" /> 公共路徑是專案中儲存 GWT 模組引用的靜態資源(如 CSS 或影像)的位置。預設公共路徑是模組 XML 檔案儲存位置下的 public 子目錄。 |
| 6 |
<script src="js-url" /> 自動注入位於 src 指定位置的外部 JavaScript 檔案。 |
| 7 |
<stylesheet src="css-url" /> 自動注入位於 src 指定位置的外部 CSS 檔案。 |
公共資源
這些都是 GWT 模組引用的所有檔案,例如主機 HTML 頁面、CSS 或影像。
這些資源的位置可以使用模組配置檔案中的 <public path = "path" /> 元素進行配置。預設情況下,它是模組 XML 檔案儲存位置下的 public 子目錄。
當您將應用程式編譯成 JavaScript 時,可以在公共路徑上找到的所有檔案都將複製到模組的輸出目錄。
最重要的公共資源是主機頁面,它用於呼叫實際的 GWT 應用程式。應用程式的典型 HTML 主機頁面可能根本不包含任何可見的 HTML body 內容,但始終預期透過如下所示的 <script.../> 標籤包含 GWT 應用程式
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello World</title>
<link rel = "stylesheet" href = "HelloWorld.css"/>
<script language = "javascript" src = "helloworld/helloworld.nocache.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World</h1>
<p>Welcome to first GWT application</p>
</body>
</html>
以下是我們包含在主機頁面中的示例樣式表 -
body {
text-align: center;
font-family: verdana, sans-serif;
}
h1 {
font-size: 2em;
font-weight: bold;
color: #777777;
margin: 40px 0px 70px;
text-align: center;
}
客戶端程式碼
這是實現應用程式業務邏輯的實際 Java 程式碼,GWT 編譯器會將其轉換為 JavaScript,最終在瀏覽器中執行。這些資源的位置可以使用模組配置檔案中的 <source path = "path" /> 元素進行配置。
例如,**入口點**程式碼將用作客戶端程式碼,其位置將使用 <source path = "path" /> 指定。
模組**入口點**是任何可分配給**EntryPoint**且無需引數即可構造的類。載入模組時,將例項化每個入口點類,並呼叫其**EntryPoint.onModuleLoad()**方法。一個 HelloWorld 入口點類的示例如下 -
public class HelloWorld implements EntryPoint {
public void onModuleLoad() {
Window.alert("Hello, World!");
}
}
伺服器端程式碼
這是應用程式的伺服器端部分,它是完全可選的。如果您沒有在應用程式中進行任何後端處理,則不需要此部分,但如果後端需要一些處理並且您的客戶端應用程式與伺服器互動,則您需要開發這些元件。
下一章將利用上述所有概念,使用 Eclipse IDE 建立 HelloWorld 應用程式。
GWT - 建立應用
由於 GWT 的強大功能在於**用 Java 編寫,在 JavaScript 中執行**,我們將使用 Java IDE Eclipse 來演示我們的示例。
讓我們從一個簡單的 _HelloWorld_ 應用程式開始 -
步驟 1 - 建立專案
第一步是使用 Eclipse IDE 建立一個簡單的 Web 應用程式專案。使用選項**Google 圖示 ![]() > 新建 Web 應用程式專案...** 啟動專案嚮導。現在使用嚮導視窗將您的專案命名為 _HelloWorld_,如下所示 -
> 新建 Web 應用程式專案...** 啟動專案嚮導。現在使用嚮導視窗將您的專案命名為 _HelloWorld_,如下所示 -
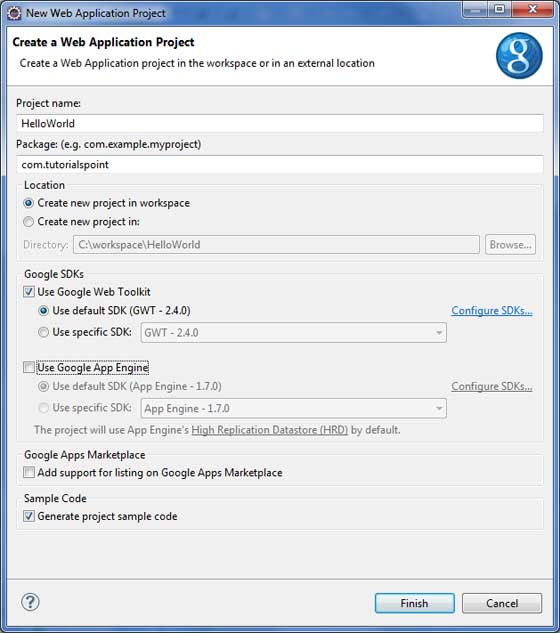
取消選中**使用 Google App Engine**,因為我們在此專案中不使用它,並保留其他預設值(保持**生成示例專案程式碼**選項選中),然後單擊完成按鈕。
專案成功建立後,您的專案資源管理器中將包含以下內容 -
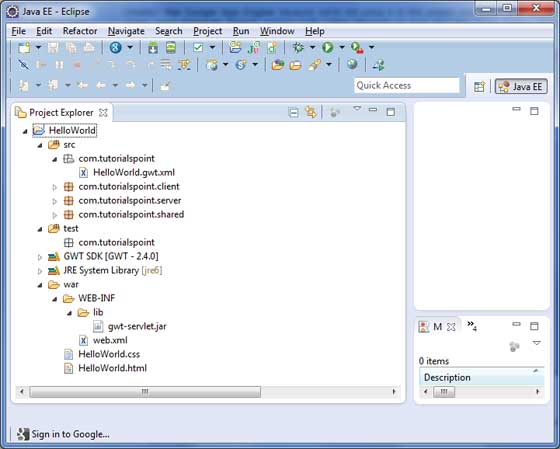
以下是所有重要資料夾的簡要說明
| 序號 | 資料夾 & 位置 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
src 原始碼(Java 類)檔案。 包含負責客戶端 UI 顯示的客戶端特定 Java 類的 Client 資料夾。 包含負責伺服器端處理的伺服器端 Java 類的 Server 資料夾。 包含用於在伺服器和客戶端之間傳輸資料的 Java 模型類的 Shared 資料夾。 HelloWorld.gwt.xml,GWT 編譯器編譯 HelloWorld 專案所需的模組描述符檔案。 |
| 2 |
test 測試程式碼(Java 類)原始檔。 包含負責測試 gwt 客戶端程式碼的 Java 類的 Client 資料夾。 |
| 3 |
war 這是最重要的部分,它代表了實際的可部署 Web 應用程式。 包含已編譯的類、gwt 庫、servlet 庫的 WEB-INF。 HelloWorld.css,專案樣式表。 HelloWorld.html,將呼叫 GWT UI 應用程式的主機 HTML。 |
步驟 2 - 修改模組描述符:HelloWorld.gwt.xml
GWT 外掛將建立一個預設的模組描述符檔案 _src/com.tutorialspoint/HelloWorld.gwt.xml_,如下所示。對於此示例,我們不會修改它,但您可以根據需要修改它。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <module rename-to = 'helloworld'> <!-- Inherit the core Web Toolkit stuff. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.User'/> <!-- Inherit the default GWT style sheet. You can change --> <!-- the theme of your GWT application by uncommenting --> <!-- any one of the following lines. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.theme.clean.Clean'/> <!-- <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.theme.chrome.Chrome'/> --> <!-- <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.theme.dark.Dark'/> --> <!-- Other module inherits --> <!-- Specify the app entry point class. --> <entry-point class = 'com.tutorialspoint.client.HelloWorld'/> <!-- Specify the paths for translatable code --> <source path = 'client'/> <source path = 'shared'/> </module>
步驟 3 - 修改樣式表:HelloWorld.css
GWT 外掛將建立一個預設的樣式表文件 _war/HelloWorld.css_。讓我們修改此檔案,以使我們的示例保持最簡單的理解級別 -
body {
text-align: center;
font-family: verdana, sans-serif;
}
h1 {
font-size: 2em;
font-weight: bold;
color: #777777;
margin: 40px 0px 70px;
text-align: center;
}
步驟 4 - 修改主機檔案:HelloWorld.html
GWT 外掛將建立一個預設的 HTML 主機檔案 _war/HelloWorld.html_。讓我們修改此檔案,以使我們的示例保持最簡單的理解級別 -
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello World</title>
<link rel = "stylesheet" href = "HelloWorld.css"/>
<script language = "javascript" src = "helloworld/helloworld.nocache.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World</h1>
<p>Welcome to first GWT application</p>
</body>
</html>
您可以在同一個源目錄中建立更多靜態檔案(如 HTML、CSS 或影像),或者可以建立更多子目錄並將檔案移動到這些子目錄中,並在應用程式的模組描述符中配置這些子目錄。
步驟 5 - 修改入口點:HelloWorld.java
GWT 外掛將建立一個預設的 Java 檔案 _src/com.tutorialspoint/HelloWorld.java_,它為應用程式提供了一個入口點。
讓我們修改此檔案以顯示“Hello,World!”
package com.tutorialspoint.client;
import com.google.gwt.core.client.EntryPoint;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.Window;
public class HelloWorld implements EntryPoint {
public void onModuleLoad() {
Window.alert("Hello, World!");
}
}
您可以在同一個源目錄中建立更多 Java 檔案以定義入口點或定義輔助例程。
步驟 6 - 編譯應用程式
完成所有更改後,就可以編譯專案了。使用選項**Google 圖示 ![]() > GWT 編譯專案...** 啟動 GWT 編譯對話方塊,如下所示 -
> GWT 編譯專案...** 啟動 GWT 編譯對話方塊,如下所示 -
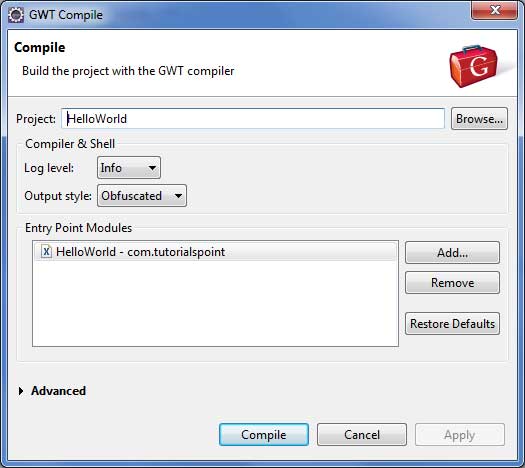
保持預設值不變,然後單擊編譯按鈕。如果一切順利,您將在 Eclipse 控制檯中看到以下輸出
Compiling module com.tutorialspoint.HelloWorld
Compiling 6 permutations
Compiling permutation 0...
Compiling permutation 1...
Compiling permutation 2...
Compiling permutation 3...
Compiling permutation 4...
Compiling permutation 5...
Compile of permutations succeeded
Linking into C:\workspace\HelloWorld\war\helloworld
Link succeeded
Compilation succeeded -- 33.029s
步驟 7 - 執行應用程式
現在單擊 ![]() 執行應用程式選單,然後選擇**HelloWorld**應用程式以執行該應用程式。
執行應用程式選單,然後選擇**HelloWorld**應用程式以執行該應用程式。
如果一切正常,您應該會看到 Eclipse 中啟用的 GWT 開發模式,其中包含一個 URL,如下所示。雙擊 URL 以開啟 GWT 應用程式。
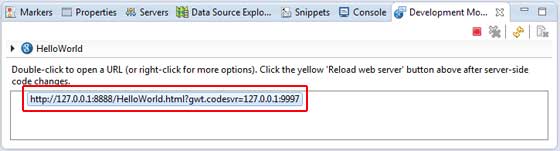
因為您是在開發模式下執行應用程式,所以需要為瀏覽器安裝 GWT 外掛。只需按照螢幕上的說明安裝外掛即可。
如果您已經為瀏覽器設定了 GWT 外掛,則應該能夠看到以下輸出
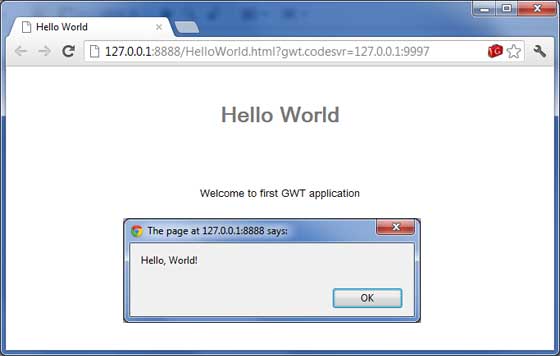
恭喜!您已經使用 Google Web Toolkit (GWT) 實現了自己的第一個應用程式。
GWT - 部署應用
本教程將向您解釋如何建立應用程式**“war”**檔案以及如何在 Apache Tomcat Web 伺服器根目錄中部署它。
如果您理解了這個簡單的示例,那麼您也可以按照相同的步驟部署複雜的 GWT 應用程式。
讓我們使用已安裝 GWT 外掛的 Eclipse IDE,並按照以下步驟建立一個 GWT 應用程式 -
| 步驟 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 在 _GWT - 建立應用程式_ 章節中說明的 _com.tutorialspoint_ 包下建立一個名為 _HelloWorld_ 的專案。 |
| 2 | 修改 _HelloWorld.gwt.xml_、_HelloWorld.css_、_HelloWorld.html_ 和 _HelloWorld.java_,如下所述。保持其餘檔案不變。 |
| 3 | 編譯並執行應用程式,以確保業務邏輯按要求工作。 |
| 4 | 最後,將應用程式 war 資料夾的內容壓縮成 war 檔案,並將其部署到 Apache Tomcat Web 伺服器中。 |
| 5 | 使用最後一步中說明的適當 URL 啟動您的 Web 應用程式。 |
以下是修改後的模組描述符 **src/com.tutorialspoint/HelloWorld.gwt.xml** 的內容。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <module rename-to = 'helloworld'> <!-- Inherit the core Web Toolkit stuff. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.User'/> <!-- Inherit the default GWT style sheet. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.theme.clean.Clean'/> <!-- Specify the app entry point class. --> <entry-point class = 'com.tutorialspoint.client.HelloWorld'/> <!-- Specify the paths for translatable code --> <source path = 'client'/> <source path = 'shared'/> </module>
以下是修改後的樣式表文件 **war/HelloWorld.css** 的內容。
body {
text-align: center;
font-family: verdana, sans-serif;
}
h1 {
font-size: 2em;
font-weight: bold;
color: #777777;
margin: 40px 0px 70px;
text-align: center;
}
以下是修改後的 HTML 主機檔案 **war/HelloWorld.html** 的內容。
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello World</title>
<link rel = "stylesheet" href = "HelloWorld.css"/>
<script language = "javascript" src = "helloworld/helloworld.nocache.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World</h1>
<div id = "gwtContainer"></div>
</body>
</html>
我稍微修改了一下上一個示例中的 HTML。在這裡,我建立了一個佔位符 <div>...</div>,我們將使用入口點 Java 類在此處插入一些內容。因此,讓我們看看 Java 檔案 **src/com.tutorialspoint/HelloWorld.java** 的以下內容。
package com.tutorialspoint.client;
import com.google.gwt.core.client.EntryPoint;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.HTML;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.RootPanel;
public class HelloWorld implements EntryPoint {
public void onModuleLoad() {
HTML html = new HTML("<p>Welcome to GWT application</p>");
RootPanel.get("gwtContainer").add(html);
}
}
在這裡,我們建立了一個基本的 widgest HTML 並將其新增到 id 為“gwtContainer”的 div 標籤中。我們將在接下來的章節中學習不同的 GWT 小部件。
完成所有更改後,讓我們像在 GWT - 建立應用程式 章節中所做的那樣,在開發模式下編譯並執行應用程式。如果您的應用程式一切正常,這將產生以下結果 -

建立 WAR 檔案
現在我們的應用程式執行良好,我們可以將其匯出為 war 檔案了。
請按照以下步驟操作 -
進入專案的 **war** 目錄 **C:\workspace\HelloWorld\war**
選擇 war 目錄中所有可用的檔案和資料夾。
將所有選定的檔案和資料夾壓縮到一個名為 _HelloWorld.zip_ 的檔案中。
將 _HelloWorld.zip_ 重新命名為 _HelloWorld.war_。
部署 WAR 檔案
停止 tomcat 伺服器。
將 _HelloWorld.war_ 檔案複製到 **tomcat 安裝目錄 > webapps 資料夾。**
啟動 tomcat 伺服器。
檢視 webapps 目錄,應該建立了一個名為 **helloworld** 的資料夾。
現在 HelloWorld.war 已成功部署到 Tomcat Web 伺服器根目錄。
執行應用程式
在 Web 瀏覽器中輸入 URL:**https://:8080/HelloWorld** 以啟動應用程式
伺服器名稱 (localhost) 和埠 (8080) 可能因您的 tomcat 配置而異。

GWT - 使用 CSS 樣式
GWT 小部件依賴於層疊樣式表 (CSS) 進行視覺樣式設定。預設情況下,每個元件的類名為 **gwt-<classname>**。
例如,Button 小部件的預設樣式為 _gwt-Button_,類似地,TextBox 小部件的預設樣式為 _gwt-TextBox_。
為了使所有按鈕和文字框都具有更大的字型,您可以在應用程式的 CSS 檔案中新增以下規則
.gwt-Button { font-size: 150%; }
.gwt-TextBox { font-size: 150%; }
預設情況下,瀏覽器和 GWT 都不會為小部件建立預設的 **id** 屬性。您必須為可以在 CSS 中使用的元素顯式建立唯一的 id。為了使 id 為 **my-button-id** 的特定按鈕具有更大的字型,您可以在應用程式的 CSS 檔案中新增以下規則 -
#my-button-id { font-size: 150%; }
要設定 GWT 小部件的 id,請檢索其 DOM 元素,然後設定 id 屬性,如下所示 -
Button b = new Button(); DOM.setElementAttribute(b.getElement(), "id", "my-button-id")
CSS 樣式 API
有許多 API 可用於處理任何 GWT 小部件的 CSS 設定。以下是一些重要的 API,將幫助您使用 GWT 進行日常 Web 程式設計 -
| 序號 | API & 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
public void setStyleName(java.lang.String style) 此方法將清除任何現有樣式,並將小部件樣式設定為使用 _style_ 提供的新 CSS 類。 |
| 2 |
public void addStyleName(java.lang.String style) 此方法將向小部件新增輔助或依賴樣式名稱。輔助樣式名稱是一個附加樣式名稱,因此,如果應用了任何先前的樣式名稱,則會保留它們。 |
| 3 |
public void removeStyleName(java.lang.String style) 此方法將從部件中移除給定的樣式,並保留與部件關聯的任何其他樣式。 |
| 4 |
public java.lang.String getStyleName() 此方法獲取物件的所有樣式名稱,以空格分隔的列表形式表示。 |
| 5 |
public void setStylePrimaryName(java.lang.String style) 此方法設定物件的樣式主名稱,並更新所有相關的樣式名稱。 |
例如,讓我們定義兩個我們將應用於文字的新樣式 -
.gwt-Big-Text {
font-size:150%;
}
.gwt-Small-Text {
font-size:75%;
}
.gwt-Red-Text {
color:red;
}
現在您可以使用setStyleName(Style)將預設設定更改為新設定。應用以下規則後,文字的字型將變大
txtWidget.setStyleName("gwt-Big-Text");
我們可以在同一個部件上應用一個輔助 CSS 規則來更改其顏色,如下所示 -
txtWidget.addStyleName("gwt-Red-Text");
使用上述方法,您可以新增任意數量的樣式以應用於部件。如果您從按鈕部件中刪除第一個樣式,則第二個樣式將仍然保留在文字中。
txtWidget.removeStyleName("gwt-Big-Text");
主樣式和輔助樣式
預設情況下,部件的主樣式名稱將是其部件類(例如,按鈕部件的gwt-Button)的預設樣式名稱。當我們使用 AddStyleName() 方法新增和刪除樣式名稱時,這些樣式稱為輔助樣式。
部件的最終外觀由新增到它的所有輔助樣式以及其主樣式的總和決定。您可以使用setStylePrimaryName(String)方法設定部件的主樣式。為了說明,假設我們有一個 Label 部件。在我們的 CSS 檔案中,我們定義了以下規則 -
.MyText {
color: blue;
}
.BigText {
font-size: large;
}
.LoudText {
font-weight: bold;
}
假設我們希望特定的標籤部件始終顯示藍色文字,並且在某些情況下,使用更大、更粗的字型來增強強調。
我們可以這樣做 -
// set up our primary style
Label someText = new Label();
someText.setStylePrimaryName("MyText");
...
// later on, to really grab the user's attention
someText.addStyleName("BigText");
someText.addStyleName("LoudText");
...
// after the crisis is over
someText.removeStyleName("BigText");
someText.removeStyleName("LoudText");
關聯 CSS 檔案
有多種方法可以將 CSS 檔案與您的模組關聯。現代 GWT 應用程式通常結合使用 CssResource 和 UiBinder。在我們的示例中,我們只使用第一種方法。
在主機 HTML 頁面中使用<link>標籤。
在模組 XML 檔案中使用<stylesheet>元素。
使用包含在ClientBundle中的CssResource。
在UiBinder模板中使用內聯<ui:style>元素。
GWT CSS 示例
此示例將指導您完成在 GWT 部件上應用不同 CSS 規則的簡單步驟。讓我們準備好包含 GWT 外掛的 Eclipse IDE,並按照以下步驟建立一個 GWT 應用程式 -
| 步驟 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 在 _GWT - 建立應用程式_ 章節中說明的 _com.tutorialspoint_ 包下建立一個名為 _HelloWorld_ 的專案。 |
| 2 | 修改 _HelloWorld.gwt.xml_、_HelloWorld.css_、_HelloWorld.html_ 和 _HelloWorld.java_,如下所述。保持其餘檔案不變。 |
| 3 | 編譯並執行應用程式以驗證實現邏輯的結果。 |
以下是修改後的模組描述符 **src/com.tutorialspoint/HelloWorld.gwt.xml** 的內容。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <module rename-to = 'helloworld'> <!-- Inherit the core Web Toolkit stuff. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.User'/> <!-- Inherit the default GWT style sheet. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.theme.clean.Clean'/> <!-- Specify the app entry point class. --> <entry-point class = 'com.tutorialspoint.client.HelloWorld'/> <!-- Specify the paths for translatable code --> <source path = 'client'/> <source path = 'shared'/> </module>
以下是修改後的樣式表文件 **war/HelloWorld.css** 的內容。
body {
text-align: center;
font-family: verdana, sans-serif;
}
h1 {
font-size: 2em;
font-weight: bold;
color: #777777;
margin: 40px 0px 70px;
text-align: center;
}
.gwt-Button {
font-size: 150%;
font-weight: bold;
width:100px;
height:100px;
}
.gwt-Big-Text {
font-size:150%;
}
.gwt-Small-Text {
font-size:75%;
}
以下是修改後的 HTML 主機檔案war/HelloWorld.html的內容,以容納兩個按鈕。
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello World</title>
<link rel = "stylesheet" href = "HelloWorld.css"/>
<script language = "javascript" src = "helloworld/helloworld.nocache.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id = "mytext"><h1>Hello, World!</h1></div>
<div id = "gwtGreenButton"></div>
<div id = "gwtRedButton"></div>
</body>
</html>
讓我們看看 Java 檔案src/com.tutorialspoint/HelloWorld.java的內容,它將負責在 HTML 中新增兩個按鈕並應用自定義 CSS 樣式。
package com.tutorialspoint.client;
import com.google.gwt.core.client.EntryPoint;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.ClickEvent;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.ClickHandler;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Button;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.HTML;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.RootPanel;
public class HelloWorld implements EntryPoint {
public void onModuleLoad() {
// add button to change font to big when clicked.
Button Btn1 = new Button("Big Text");
Btn1.addClickHandler(new ClickHandler() {
public void onClick(ClickEvent event) {
RootPanel.get("mytext").setStyleName("gwt-Big-Text");
}
});
// add button to change font to small when clicked.
Button Btn2 = new Button("Small Text");
Btn2.addClickHandler(new ClickHandler() {
public void onClick(ClickEvent event) {
RootPanel.get("mytext").setStyleName("gwt-Small-Text");
}
});
RootPanel.get("gwtGreenButton").add(Btn1);
RootPanel.get("gwtRedButton").add(Btn2);
}
}
完成所有更改後,讓我們像在 GWT - 建立應用程式 章節中所做的那樣,在開發模式下編譯並執行應用程式。如果您的應用程式一切正常,這將產生以下結果 -
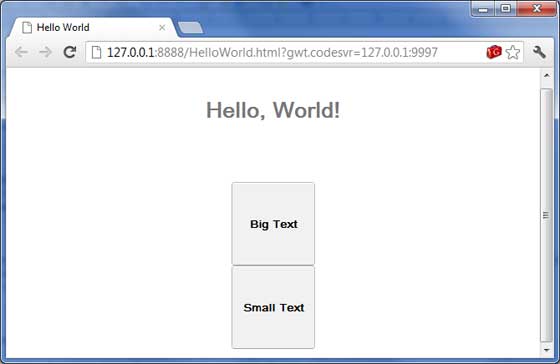
現在嘗試點選顯示的兩個按鈕,並觀察“Hello, World!”文字,該文字在點選兩個按鈕時會不斷更改其字型。
GWT - 基本部件
每個使用者介面都考慮以下三個主要方面 -
UI 元素 - 這些是使用者最終看到並與其互動的核心視覺元素。GWT 提供了大量廣泛使用和常見的元素,從基本到複雜,我們將在本教程中介紹。
佈局 - 它們定義了 UI 元素如何在螢幕上組織,併為 GUI(圖形使用者介面)提供最終的外觀和感覺。這部分將在佈局章節中介紹。
行為 - 這些是使用者與 UI 元素互動時發生的事件。這部分將在事件處理章節中介紹。
GWT UI 元素
GWT 庫在定義良好的類層次結構中提供類,以建立複雜的基於 Web 的使用者介面。此元件層次結構中的所有類都從UIObject基類派生,如下所示 -

每個基本 UI 部件都繼承 Widget 類的屬性,而 Widget 類又繼承 UIObject 的屬性。樹和選單將在複雜部件教程中介紹。
| 序號 | 部件和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
GWT UIObject 類
此部件包含文字,不解釋為使用<div>元素的 HTML,導致它以塊佈局顯示。 |
| 2 |
GWT Widget 類
此部件可以包含 HTML 文字,並使用<div>元素顯示 html 內容,導致它以塊佈局顯示。 |
基本部件
以下是一些重要的基本部件 -
| 序號 | 部件和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
標籤
此部件包含文字,不解釋為使用<div>元素的 HTML,導致它以塊佈局顯示。 |
| 2 |
HTML
此部件可以包含 HTML 文字,並使用<div>元素顯示 html 內容,導致它以塊佈局顯示。 |
| 3 |
影像
此部件在給定 URL 上顯示影像。 |
| 4 |
錨點
此部件表示一個簡單的<a>元素。 |
GWT - 表單部件
表單部件允許使用者輸入資料,併為他們提供與應用程式互動的功能。每個表單部件都繼承 Widget 類的屬性,而 Widget 類又繼承 UIObject 和 Wigdet 類。
| 序號 | 部件和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
GWT UIObject 類
此部件包含文字,不解釋為使用<div>元素的 HTML,導致它以塊佈局顯示。 |
| 2 |
GWT Widget 類
此部件可以包含 HTML 文字,並使用<div>元素顯示 html 內容,導致它以塊佈局顯示。 |
表單部件
以下是一些重要的表單部件 -
| 序號 | 部件和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
按鈕
此部件表示標準的按鈕。 |
| 2 |
PushButton
此部件表示具有自定義樣式的普通按鈕。 |
| 3 |
ToggleButton
此部件表示一個時尚的有狀態按鈕,允許使用者在向上和向下狀態之間切換。 |
| 4 |
複選框
此部件表示標準的複選框部件。此類也用作 RadioButton 的基類。 |
| 5 |
RadioButton
此部件表示互斥選擇的單選按鈕部件。 |
| 6 |
ListBox
此部件向用戶顯示一系列選擇,可以是列表框或下拉列表。 |
| 7 |
SuggestBox
此部件表示文字框或文字區域,顯示與使用者輸入匹配的預配置選擇集。每個 SuggestBox 都與單個 SuggestOracle 相關聯。SuggestOracle 用於根據特定查詢字串提供選擇集。 |
| 8 |
TextBox
此部件表示單行文字框。 |
| 9 |
PasswordTextBox
此部件表示一個文字框,它會視覺上遮蔽其輸入以防止竊聽。 |
| 10 |
TextArea
此部件表示允許輸入多行文字的文字框。 |
| 11 |
RichTextArea
此部件表示一個富文字編輯器,允許進行復雜的樣式設定和格式化。 |
| 12 |
FileUpload
此部件包裝 HTML <input type='file'>元素。 |
| 13 |
Hidden
此部件表示 HTML 表單中的隱藏欄位。 |
GWT - 複雜部件
“複雜部件”允許使用者與應用程式進行高階互動功能。每個複雜部件都繼承 Widget 類的屬性,而 Widget 類又繼承 UIObject 的屬性。
| 序號 | 部件和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
GWT UIObject 類
此部件包含文字,不解釋為使用<div>元素的 HTML,導致它以塊佈局顯示。 |
| 2 |
GWT Widget 類
此部件可以包含 HTML 文字,並使用<div>元素顯示 html 內容,導致它以塊佈局顯示。 |
複雜部件
以下是一些重要的複雜部件 -
| 序號 | 部件和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
樹
此部件表示標準的分層樹部件。樹包含使用者可以開啟、關閉和選擇的 TreeItems 層次結構。 |
| 2 |
MenuBar
此部件表示標準的選單欄部件。選單欄可以包含任意數量的選單項,每個選單項可以觸發命令或開啟級聯選單欄。 |
| 3 |
DatePicker
此部件表示標準的 GWT 日期選擇器。 |
| 4 |
CellTree
此部件表示樹的檢視。此部件僅在標準模式下工作,這要求執行它的 HTML 頁面具有明確的<!DOCTYPE>宣告。 |
| 5 |
CellList
此部件表示單元格的單列列表。 |
| 6 |
CellTable
此部件表示支援分頁和列的表格檢視。 |
| 7 |
CellBrowser
此部件表示樹的可瀏覽檢視,其中在任何時間只能開啟每個級別的單個節點。此部件僅在標準模式下工作,這要求執行它的 HTML 頁面具有明確的<!DOCTYPE>宣告。 |
GWT - 佈局面板
佈局面板可以包含其他部件。這些面板控制部件在使用者介面上的顯示方式。每個 Panel 部件都繼承 Panel 類的屬性,而 Panel 類又繼承 Widget 類,Widget 類又繼承 UIObject 類。
| 序號 | 部件和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
GWT UIObject 類
此部件包含文字,不解釋為使用<div>元素的 HTML,導致它以塊佈局顯示。 |
| 2 |
GWT Widget 類
此部件可以包含 HTML 文字,並使用<div>元素顯示 html 內容,導致它以塊佈局顯示。 |
| 3 |
GWT Panel 類
這是所有面板的抽象基類,面板是可以包含其他部件的部件。 |
佈局面板
以下是一些重要的佈局面板 -
| 序號 | 部件和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
FlowPanel
此部件表示一個面板,該面板使用預設的 HTML 佈局行為格式化其子部件。 |
| 2 |
HorizontalPanel
此部件表示一個面板,該面板將其所有部件都佈置在單個水平列中。 |
| 3 |
VerticalPanel
此部件表示一個面板,該面板將其所有部件都佈置在單個垂直列中。 |
| 4 |
HorizontalSplitPanel
此部件表示一個面板,該面板將兩個部件排列在單個水平行中,並允許使用者互動地更改分配給這兩個部件的寬度的比例。包含在 HorizontalSplitPanel 中的部件將在必要時自動裝飾有捲軸。 |
| 5 |
VerticalSplitPanel
此部件表示一個面板,該面板將兩個部件排列在單個垂直列中,並允許使用者互動地更改分配給這兩個部件的高度比例。包含在 VertialSplitPanel 中的部件將在必要時自動裝飾有捲軸。 |
| 6 |
FlexTable
此部件表示一個靈活的表格,該表格根據需要建立單元格。它可以是不規則的(即,每一行可以包含不同數量的單元格),並且可以將各個單元格設定為跨越多個行或列。 |
| 7 |
Grid
此部件表示一個矩形網格,可以在其單元格中包含文字、html 或子部件。必須將其顯式調整為所需的行列數。 |
| 8 |
DeckPanel
面板,它以“疊放”的方式顯示其所有子部件,其中一次只能顯示一個。它由 TabPanel 使用。 |
| 9 |
DockPanel
此部件表示一個面板,該面板將其子部件佈置在其外邊緣“停靠”,並允許其最後一個部件佔據其中心剩餘的空間。 |
| 10 |
HTMLPanel
此部件表示一個包含 HTML 的面板,並且可以將子部件附加到該 HTML 中的已識別元素。 |
| 11 |
TabPanel
此部件表示一個面板,該面板表示一組選項卡式頁面,每個頁面都包含另一個部件。當用戶選擇與其關聯的各種選項卡時,將顯示其子部件。選項卡可以包含任意 HTML。 |
| 12 |
Composite
此部件表示一種可以包裝另一個部件的部件型別,隱藏被包裝部件的方法。當新增到面板時,複合部件的行為就像已添加了它所包裝的部件一樣。 |
| 13 |
簡單面板
此部件表示僅包含一個部件的面板的基本類。 |
| 14 |
滾動面板
此部件表示一個簡單的面板,它將其內容包裝在可滾動區域中。 |
| 15 |
焦點面板
此部件表示一個簡單的面板,它使它的內容可聚焦,並增加了捕獲滑鼠和鍵盤事件的能力。 |
| 16 |
表單面板
此部件表示一個面板,它將其內容包裝在 HTML <FORM> 元素中。 |
| 17 |
彈出面板
此部件表示一個可以**彈出**到其他部件上方的面板。它覆蓋瀏覽器的客戶端區域(以及任何先前建立的彈出視窗)。 |
| 18 |
對話方塊
此部件表示一種彈出視窗的形式,頂部有一個標題區域,使用者可以拖動它。與 PopupPanel 不同,對 PopupPanel.setWidth(String) 和 PopupPanel.setHeight(String) 的呼叫將設定對話方塊本身的寬度和高度,即使尚未新增部件也是如此。 |
GWT - 事件處理
GWT 提供了一個類似於 Java AWT 或 SWING 使用者介面框架的事件處理程式模型。
監聽器介面定義了一個或多個方法,部件呼叫這些方法來宣佈事件。GWT 提供了一個與各種可能事件相對應的介面列表。
希望接收特定型別事件的類實現關聯的處理程式介面,然後將對自身的引用傳遞給部件以訂閱一組事件。
例如,**按鈕**類釋出**點選事件**,因此您必須編寫一個類來實現ClickHandler以處理**點選**事件。
事件處理程式介面
所有 GWT 事件處理程式都擴充套件自EventHandler介面,並且每個處理程式只有一個具有單個引數的方法。此引數始終是關聯事件型別的物件。每個**事件**物件都有一些方法來操作傳遞的事件物件。例如,對於點選事件,您必須按如下方式編寫處理程式:
/**
* create a custom click handler which will call
* onClick method when button is clicked.
*/
public class MyClickHandler implements ClickHandler {
@Override
public void onClick(ClickEvent event) {
Window.alert("Hello World!");
}
}
現在,任何希望接收點選事件的類都將呼叫addClickHandler()來註冊事件處理程式,如下所示:
/**
* create button and attach click handler
*/
Button button = new Button("Click Me!");
button.addClickHandler(new MyClickHandler());
每個支援事件型別的部件都將具有 HandlerRegistration addFooHandler(FooEvent) 形式的方法,其中Foo是實際事件,如 Click、Error、KeyPress 等。
以下是重要的 GWT 事件處理程式及其關聯事件和處理程式註冊方法的列表:
| 序號 | 事件介面 | 事件方法和描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 選擇前處理程式<I> |
void on Before Selection (Before Selection Event<I> event); 當觸發 BeforeSelectionEvent 時呼叫。 |
| 2 | 失焦處理程式 |
void on Blur(Blur Event event); 當觸發 Blur 事件時呼叫。 |
| 3 | 更改處理程式 |
void on Change(ChangeEvent event); 當觸發更改事件時呼叫。 |
| 4 | 點選處理程式 |
void on Click(ClickEvent event); 當觸發原生點選事件時呼叫。 |
| 5 | 關閉處理程式<T> |
void on Close(CloseEvent<T> event); 當觸發 CloseEvent 時呼叫。 |
| 6 | 上下文選單處理程式 |
void on Context Menu(Context Menu Event event); 當觸發原生上下文選單事件時呼叫。 |
| 7 | 雙擊處理程式 |
void on Double Click(Double Click Event event); 當觸發雙擊事件時呼叫。 |
| 8 | 錯誤處理程式 |
void on Error(Error Event event); 當觸發 Error 事件時呼叫。 |
| 9 | 聚焦處理程式 |
void on Focus(Focus Event event); 當觸發 Focus 事件時呼叫。 |
| 10 | 表單面板.提交完成處理程式 |
void on Submit Complete(Form Panel.Submit Complete Event event); 表單成功提交後觸發。 |
| 11 | FormPanel.SubmitHandler |
void on Submit(Form Panel.Submit Event event); 提交表單時觸發。 |
| 12 | 鍵盤按下處理程式 |
void on Key Down(Key Down Event event); 當觸發 KeyDownEvent 時呼叫。 |
| 13 | KeyPressHandler |
void on KeyPress(KeyPressEvent event); 當觸發 KeyPressEvent 時呼叫。 |
| 14 | KeyUpHandler |
void on KeyUp(KeyUpEvent event); 當觸發 KeyUpEvent 時呼叫。 |
| 15 | 載入處理程式 |
void on Load(LoadEvent event); 當觸發 LoadEvent 時呼叫。 |
| 16 | 滑鼠按下處理程式 |
void on MouseDown(MouseDownEvent event); 當觸發 MouseDown 時呼叫。 |
| 17 | 滑鼠移動處理程式 |
void on MouseMove(MouseMoveEvent event); 當觸發 MouseMoveEvent 時呼叫。 |
| 18 | 滑鼠移出處理程式 |
void on MouseOut(MouseOutEvent event); 當觸發 MouseOutEvent 時呼叫。 |
| 19 | 滑鼠懸停處理程式 |
void on MouseOver(MouseOverEvent event); 當觸發 MouseOverEvent 時呼叫。 |
| 20 | 滑鼠抬起處理程式 |
void on MouseUp(MouseUpEvent event); 當觸發 MouseUpEvent 時呼叫。 |
| 21 | 滑鼠滾輪處理程式 |
void on MouseWheel(MouseWheelEvent event); 當觸發 MouseWheelEvent 時呼叫。 |
| 22 | 調整大小處理程式 |
void on Resize(ResizeEvent event); 部件大小調整時觸發。 |
| 23 | 滾動處理程式 |
void on Scroll(ScrollEvent event); 當觸發 ScrollEvent 時呼叫。 |
| 24 | 選擇處理程式<I> |
void on Selection(SelectionEvent<I> event); 當觸發 SelectionEvent 時呼叫。 |
| 25 | 值更改處理程式<I> |
void on ValueChange(ValueChangeEvent<I> event); 當觸發 ValueChangeEvent 時呼叫。 |
| 26 | Window.ClosingHandler |
void on WindowClosing(Window.ClosingEvent event); 瀏覽器視窗關閉或導航到其他站點之前觸發。 |
| 27 | Window.ScrollHandler |
void on WindowScroll(Window.ScrollEvent event); 瀏覽器視窗滾動時觸發。 |
事件方法
如前所述,每個處理程式都只有一個具有單個引數的方法,該引數儲存事件物件,例如void onClick(ClickEvent event)或void onKeyDown(KeyDownEvent event)。事件物件如ClickEvent和KeyDownEvent有一些常見的方法,如下所示:
| 序號 | 方法和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
protected void dispatch(ClickHandler handler) 此方法應僅由 HandlerManager 呼叫。 |
| 2 |
DomEvent.Type <FooHandler> getAssociatedType() 此方法返回用於註冊Foo事件的型別。 |
| 3 |
static DomEvent.Type<FooHandler> getType() 此方法獲取與Foo事件關聯的事件型別。 |
| 4 |
public java.lang.Object getSource() 此方法返回最後觸發此事件的源。 |
| 5 |
protected final boolean isLive() 此方法返回事件是否處於活動狀態。 |
| 6 |
protected void kill() 此方法終止事件。 |
示例
此示例將引導您完成簡單的步驟,以展示如何在 GWT 中使用**點選**事件和**鍵盤按下**事件處理。按照以下步驟更新我們在GWT - 建立應用程式章節中建立的 GWT 應用程式:
| 步驟 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 在 _GWT - 建立應用程式_ 章節中說明的 _com.tutorialspoint_ 包下建立一個名為 _HelloWorld_ 的專案。 |
| 2 | 修改 _HelloWorld.gwt.xml_、_HelloWorld.css_、_HelloWorld.html_ 和 _HelloWorld.java_,如下所述。保持其餘檔案不變。 |
| 3 | 編譯並執行應用程式以驗證實現邏輯的結果。 |
以下是修改後的模組描述符 **src/com.tutorialspoint/HelloWorld.gwt.xml** 的內容。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <module rename-to = 'helloworld'> <!-- Inherit the core Web Toolkit stuff. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.User'/> <!-- Inherit the default GWT style sheet. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.theme.clean.Clean'/> <!-- Specify the app entry point class. --> <entry-point class = 'com.tutorialspoint.client.HelloWorld'/> <!-- Specify the paths for translatable code --> <source path = 'client'/> <source path = 'shared'/> </module>
以下是修改後的樣式表文件 **war/HelloWorld.css** 的內容。
body {
text-align: center;
font-family: verdana, sans-serif;
}
h1 {
font-size: 2em;
font-weight: bold;
color: #777777;
margin: 40px 0px 70px;
text-align: center;
}
以下是修改後的 HTML 主機檔案 **war/HelloWorld.html** 的內容。
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello World</title>
<link rel = "stylesheet" href = "HelloWorld.css"/>
<script language = "javascript" src = "helloworld/helloworld.nocache.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Event Handling Demonstration</h1>
<div id = "gwtContainer"></div>
</body>
</html>
讓我們在 Java 檔案src/com.tutorialspoint/HelloWorld.java中包含以下內容,它將演示在 GWT 中使用事件處理。
package com.tutorialspoint.client;
import com.google.gwt.core.client.EntryPoint;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.ClickEvent;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.ClickHandler;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.KeyCodes;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.KeyDownEvent;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.KeyDownHandler;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.Window;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Button;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.DecoratorPanel;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.HasHorizontalAlignment;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.RootPanel;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.TextBox;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.VerticalPanel;
public class HelloWorld implements EntryPoint {
public void onModuleLoad() {
/**
* create textbox and attach key down handler
*/
TextBox textBox = new TextBox();
textBox.addKeyDownHandler(new MyKeyDownHandler());
/*
* create button and attach click handler
*/
Button button = new Button("Click Me!");
button.addClickHandler(new MyClickHandler());
VerticalPanel panel = new VerticalPanel();
panel.setSpacing(10);
panel.setHorizontalAlignment(HasHorizontalAlignment.ALIGN_CENTER);
panel.setSize("300", "100");
panel.add(textBox);
panel.add(button);
DecoratorPanel decoratorPanel = new DecoratorPanel();
decoratorPanel.add(panel);
RootPanel.get("gwtContainer").add(decoratorPanel);
}
/**
* create a custom click handler which will call
* onClick method when button is clicked.
*/
private class MyClickHandler implements ClickHandler {
@Override
public void onClick(ClickEvent event) {
Window.alert("Hello World!");
}
}
/**
* create a custom key down handler which will call
* onKeyDown method when a key is down in textbox.
*/
private class MyKeyDownHandler implements KeyDownHandler {
@Override
public void onKeyDown(KeyDownEvent event) {
if(event.getNativeKeyCode() == KeyCodes.KEY_ENTER){
Window.alert(((TextBox)event.getSource()).getValue());
}
}
}
}
完成所有更改後,讓我們像在 GWT - 建立應用程式 章節中所做的那樣,在開發模式下編譯並執行應用程式。如果您的應用程式一切正常,這將產生以下結果 -

GWT - 自定義部件
GWT 提供三種建立自定義使用者介面元素的方式。有三種通用的策略可以遵循:
**透過擴充套件 Composite 類建立部件** - 這是建立自定義部件最常見和最簡單的方法。在這裡,您可以使用現有的部件來建立具有自定義屬性的複合檢視。
**使用 JAVA 中的 GWT DOM API 建立部件** - GWT 基本部件就是以這種方式建立的。但這仍然是建立自定義部件的一種非常複雜的方式,應謹慎使用。
**使用 JavaScript 並使用 JSNI 將其包裝在部件中** - 通常應僅在最後不得已時才這樣做。考慮到原生方法的跨瀏覽器影響,它變得非常複雜,並且也更難以除錯。
使用 Composite 類建立自定義部件
此示例將引導您完成簡單的步驟,以展示如何在 GWT 中建立自定義部件。按照以下步驟更新我們在GWT - 基本部件章節中建立的 GWT 應用程式:
在這裡,我們將透過擴充套件 Composite 類來建立一個自定義部件,這是構建自定義部件最簡單的方法。
| 步驟 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 在 _GWT - 建立應用程式_ 章節中說明的 _com.tutorialspoint_ 包下建立一個名為 _HelloWorld_ 的專案。 |
| 2 | 修改 _HelloWorld.gwt.xml_、_HelloWorld.css_、_HelloWorld.html_ 和 _HelloWorld.java_,如下所述。保持其餘檔案不變。 |
| 3 | 編譯並執行應用程式以驗證實現邏輯的結果。 |
以下是修改後的模組描述符 **src/com.tutorialspoint/HelloWorld.gwt.xml** 的內容。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <module rename-to = 'helloworld'> <!-- Inherit the core Web Toolkit stuff. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.User'/> <!-- Inherit the default GWT style sheet. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.theme.clean.Clean'/> <!-- Specify the app entry point class. --> <entry-point class = 'com.tutorialspoint.client.HelloWorld'/> <!-- Specify the paths for translatable code --> <source path = 'client'/> <source path = 'shared'/> </module>
以下是修改後的樣式表文件 **war/HelloWorld.css** 的內容。
body {
text-align: center;
font-family: verdana, sans-serif;
}
h1 {
font-size: 2em;
font-weight: bold;
color: #777777;
margin: 40px 0px 70px;
text-align: center;
}
以下是修改後的 HTML 主機檔案 **war/HelloWorld.html** 的內容。
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello World</title>
<link rel = "stylesheet" href = "HelloWorld.css"/>
<script language = "javascript" src = "helloworld/helloworld.nocache.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Custom Widget Demonstration</h1>
<div id = "gwtContainer"></div>
</body>
</html>
讓我們在 Java 檔案src/com.tutorialspoint/HelloWorld.java中包含以下內容,它將演示建立自定義部件。
package com.tutorialspoint.client;
import com.google.gwt.core.client.EntryPoint;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.ClickEvent;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.ClickHandler;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.CheckBox;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Composite;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.HorizontalPanel;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.RootPanel;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.TextBox;
public class HelloWorld implements EntryPoint {
/**
* A composite of a TextBox and a CheckBox that optionally enables it.
*/
private static class OptionalTextBox extends Composite implements
ClickHandler {
private TextBox textBox = new TextBox();
private CheckBox checkBox = new CheckBox();
private boolean enabled = true;
public boolean isEnabled() {
return enabled;
}
public void setEnabled(boolean enabled) {
this.enabled = enabled;
}
/**
* Style this widget using .optionalTextWidget CSS class.<br/>
* Style textbox using .optionalTextBox CSS class.<br/>
* Style checkbox using .optionalCheckBox CSS class.<br/>
* Constructs an OptionalTextBox with the given caption
* on the check.
* @param caption the caption to be displayed with the check box
*/
public OptionalTextBox(String caption) {
// place the check above the text box using a vertical panel.
HorizontalPanel panel = new HorizontalPanel();
// panel.setBorderWidth(1);
panel.setSpacing(10);
panel.add(checkBox);
panel.add(textBox);
// all composites must call initWidget() in their constructors.
initWidget(panel);
//set style name for entire widget
setStyleName("optionalTextWidget");
//set style name for text box
textBox.setStyleName("optionalTextBox");
//set style name for check box
checkBox.setStyleName("optionalCheckBox");
textBox.setWidth("200");
// Set the check box's caption, and check it by default.
checkBox.setText(caption);
checkBox.setValue(enabled);
checkBox.addClickHandler(this);
enableTextBox(enabled,checkBox.getValue());
}
public void onClick(ClickEvent event) {
if (event.getSource() == checkBox) {
// When the check box is clicked,
//update the text box's enabled state.
enableTextBox(enabled,checkBox.getValue());
}
}
private void enableTextBox(boolean enable,boolean isChecked){
enable = (enable && isChecked) || (!enable && !isChecked);
textBox.setStyleDependentName("disabled", !enable);
textBox.setEnabled(enable);
}
}
public void onModuleLoad() {
// Create an optional text box and add it to the root panel.
OptionalTextBox otb = new OptionalTextBox(
"Want to explain the solution?");
otb.setEnabled(true);
RootPanel.get().add(otb);
}
}
完成所有更改後,讓我們像在 GWT - 建立應用程式 章節中所做的那樣,在開發模式下編譯並執行應用程式。如果您的應用程式一切正常,這將產生以下結果 -
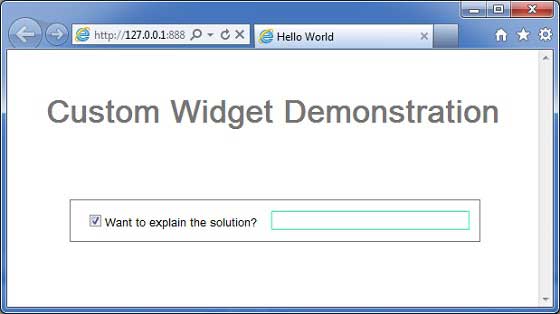
您可以注意到以下幾點
透過擴充套件 Composite 部件建立自定義部件非常簡單。
我們使用 GWT 內建部件 TextBox 和 CheckBox 建立了一個部件,從而使用了可重用性的概念。
TextBox 根據複選框的狀態停用/啟用。我們提供了一個 API 來啟用/停用控制元件。
我們透過記錄的 CSS 樣式公開了內部部件樣式。
GWT - UiBinder
簡介
UiBinder 是一個旨在分離使用者介面功能和檢視的框架。
UiBinder 框架允許開發人員將 gwt 應用程式構建為 HTML 頁面,並在其中配置 GWT 部件。
UiBinder 框架使與 UI 設計師的協作更加容易,因為 UI 設計師更熟悉 XML、HTML 和 CSS 而不是 Java 原始碼。
UIBinder 提供了一種宣告式的方式來定義使用者介面。
UIBinder 將程式邏輯與 UI 分離。
UIBinder 類似於 JSP 與 Servlet 的關係。
UiBinder 工作流程
步驟 1 - 建立 UI 宣告 XML 檔案
建立一個基於 XML/HTML 的使用者介面宣告檔案。在我們的示例中,我們建立了一個Login.ui.xml檔案。
<ui:UiBinder xmlns:ui = 'urn:ui:com.google.gwt.uibinder' xmlns:gwt = 'urn:import:com.google.gwt.user.client.ui' xmlns:res = 'urn:with:com.tutorialspoint.client.LoginResources'> <ui:with type = "com.tutorialspoint.client.LoginResources" field = "res"> </ui:with> <gwt:HTMLPanel> ... </gwt:HTMLPanel> </ui:UiBinder>
步驟 2 - 使用 ui:field 進行後期繫結
在 XML/HTML 元素中使用 ui:field 屬性將 XML 中的 UI 欄位與 JAVA 檔案中的 UI 欄位相關聯,以便進行後期繫結。
<gwt:Label ui:field = "completionLabel1" /> <gwt:Label ui:field = "completionLabel2" />
步驟 3 - 建立 UI XML 的 JAVA 對應部分
透過擴充套件 Composite 部件來建立基於 XML 佈局的 JAVA 對應部分。在我們的示例中,我們建立了一個Login.java檔案。
package com.tutorialspoint.client;
...
public class Login extends Composite {
...
}
步驟 4 - 使用 UiField 註解將 JAVA UI 欄位與之繫結
在Login.java中使用 @UiField 註解來指定對應類成員,以繫結到Login.ui.xml中基於 XML 的欄位。
public class Login extends Composite {
...
@UiField
Label completionLabel1;
@UiField
Label completionLabel2;
...
}
步驟 5 - 使用 UiTemplate 註解將 JAVA UI 與 UI XML 繫結
指示 GWT 使用 @UiTemplate 註解繫結基於 JAVA 的元件Login.java和基於 XML 的佈局Login.ui.xml。
public class Login extends Composite {
private static LoginUiBinder uiBinder = GWT.create(LoginUiBinder.class);
/*
* @UiTemplate is not mandatory but allows multiple XML templates
* to be used for the same widget.
* Default file loaded will be <class-name>.ui.xml
*/
@UiTemplate("Login.ui.xml")
interface LoginUiBinder extends UiBinder<Widget, Login> {
}
...
}
步驟 6 - 建立 CSS 檔案
建立一個外部 CSS 檔案Login.css和基於 JAVA 的資源LoginResources.java檔案,相當於 css 樣式。
.blackText {
font-family: Arial, Sans-serif;
color: #000000;
font-size: 11px;
text-align: left;
}
...
步驟 7 - 為 CSS 檔案建立基於 JAVA 的資原始檔
package com.tutorialspoint.client;
...
public interface LoginResources extends ClientBundle {
public interface MyCss extends CssResource {
String blackText();
...
}
@Source("Login.css")
MyCss style();
}
步驟 8 - 在基於 JAVA 的 UI 程式碼檔案中附加 CSS 資源。
使用基於 JAVA 的部件類Login.java的建構函式附加外部 CSS 檔案Login.css。
public Login() {
this.res = GWT.create(LoginResources.class);
res.style().ensureInjected();
initWidget(uiBinder.createAndBindUi(this));
}
UIBinder完整示例
此示例將引導您完成簡單的步驟,以展示如何在 GWT 中使用 UIBinder。按照以下步驟更新我們在GWT - 建立應用程式章節中建立的 GWT 應用程式:
| 步驟 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 在 _GWT - 建立應用程式_ 章節中說明的 _com.tutorialspoint_ 包下建立一個名為 _HelloWorld_ 的專案。 |
| 2 | 修改 _HelloWorld.gwt.xml_、_HelloWorld.css_、_HelloWorld.html_ 和 _HelloWorld.java_,如下所述。保持其餘檔案不變。 |
| 3 | 編譯並執行應用程式以驗證實現邏輯的結果。 |
以下是修改後的模組描述符 **src/com.tutorialspoint/HelloWorld.gwt.xml** 的內容。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <module rename-to = 'helloworld'> <!-- Inherit the core Web Toolkit stuff. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.User'/> <!-- Inherit the default GWT style sheet. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.theme.clean.Clean'/> <!-- Inherit the UiBinder module. --> <inherits name = "com.google.gwt.uibinder.UiBinder"/> <!-- Specify the app entry point class. --> <entry-point class = 'com.tutorialspoint.client.HelloWorld'/> <!-- Specify the paths for translatable code --> <source path ='client'/> <source path = 'shared'/> </module>
以下是修改後的樣式表文件 **war/HelloWorld.css** 的內容。
body {
text-align: center;
font-family: verdana, sans-serif;
}
h1 {
font-size: 2em;
font-weight: bold;
color: #777777;
margin: 40px 0px 70px;
text-align: center;
}
以下是修改後的 HTML 主機檔案 **war/HelloWorld.html** 的內容。
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello World</title>
<link rel = "stylesheet" href = "HelloWorld.css"/>
<script language = "javascript" src = "helloworld/helloworld.nocache.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>UiBinder Demonstration</h1>
<div id = "gwtContainer"></div>
</body>
</html>
現在建立一個新的 UiBinder 模板和所有者類(檔案→新建→UiBinder)。
為專案選擇客戶端包,然後將其命名為 Login。保留所有其他預設值。單擊“完成”按鈕,外掛將建立一個新的 UiBinder 模板和所有者類。
現在在src/com.tutorialspoint/client包中建立 Login.css 檔案,並在其中放置以下內容
.blackText {
font-family: Arial, Sans-serif;
color: #000000;
font-size: 11px;
text-align: left;
}
.redText {
font-family: Arial, Sans-serif;
color: #ff0000;
font-size: 11px;
text-align: left;
}
.loginButton {
border: 1px solid #3399DD;
color: #FFFFFF;
background: #555555;
font-size: 11px;
font-weight: bold;
margin: 0 5px 0 0;
padding: 4px 10px 5px;
text-shadow: 0 -1px 0 #3399DD;
}
.box {
border: 1px solid #AACCEE;
display: block;
font-size: 12px;
margin: 0 0 5px;
padding: 3px;
width: 203px;
}
.background {
background-color: #999999;
border: 1px none transparent;
color: #000000;
font-size: 11px;
margin-left: -8px;
margin-top: 5px;
padding: 6px;
}
現在在src/com.tutorialspoint/client包中建立 LoginResources.java 檔案,並在其中放置以下內容
package com.tutorialspoint.client;
import com.google.gwt.resources.client.ClientBundle;
import com.google.gwt.resources.client.CssResource;
public interface LoginResources extends ClientBundle {
/**
* Sample CssResource.
*/
public interface MyCss extends CssResource {
String blackText();
String redText();
String loginButton();
String box();
String background();
}
@Source("Login.css")
MyCss style();
}
將src/com.tutorialspoint/client包中 Login.ui.xml 的內容替換為以下內容
<ui:UiBinder xmlns:ui = 'urn:ui:com.google.gwt.uibinder'
xmlns:gwt = 'urn:import:com.google.gwt.user.client.ui'
xmlns:res = 'urn:with:com.tutorialspoint.client.LoginResources'>
<ui:with type = "com.tutorialspoint.client.LoginResources" field = "res">
</ui:with>
<gwt:HTMLPanel>
<div align = "center">
<gwt:VerticalPanel res:styleName = "style.background">
<gwt:Label text = "Login" res:styleName = "style.blackText" />
<gwt:TextBox ui:field="loginBox" res:styleName = "style.box" />
<gwt:Label text = "Password" res:styleName = "style.blackText" />
<gwt:PasswordTextBox ui:field = "passwordBox" res:styleName = "style.box" />
<gwt:HorizontalPanel verticalAlignment = "middle">
<gwt:Button ui:field = "buttonSubmit" text="Submit"
res:styleName = "style.loginButton" />
<gwt:CheckBox ui:field = "myCheckBox" />
<gwt:Label ui:field = "myLabel" text = "Remember me"
res:styleName = "style.blackText" />
</gwt:HorizontalPanel>
<gwt:Label ui:field = "completionLabel1" res:styleName = "style.blackText" />
<gwt:Label ui:field = "completionLabel2" res:styleName = "style.blackText" />
</gwt:VerticalPanel>
</div>
</gwt:HTMLPanel>
</ui:UiBinder>
將src/com.tutorialspoint/client包中 Login.java 的內容替換為以下內容
package com.tutorialspoint.client;
import com.google.gwt.core.client.GWT;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.ClickEvent;
import com.google.gwt.event.logical.shared.ValueChangeEvent;
import com.google.gwt.uibinder.client.UiBinder;
import com.google.gwt.uibinder.client.UiField;
import com.google.gwt.uibinder.client.UiHandler;
import com.google.gwt.uibinder.client.UiTemplate;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.Window;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Composite;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Label;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.TextBox;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Widget;
public class Login extends Composite {
private static LoginUiBinder uiBinder = GWT.create(LoginUiBinder.class);
/*
* @UiTemplate is not mandatory but allows multiple XML templates
* to be used for the same widget.
* Default file loaded will be <class-name>.ui.xml
*/
@UiTemplate("Login.ui.xml")
interface LoginUiBinder extends UiBinder<Widget, Login> {
}
@UiField(provided = true)
final LoginResources res;
public Login() {
this.res = GWT.create(LoginResources.class);
res.style().ensureInjected();
initWidget(uiBinder.createAndBindUi(this));
}
@UiField
TextBox loginBox;
@UiField
TextBox passwordBox;
@UiField
Label completionLabel1;
@UiField
Label completionLabel2;
private Boolean tooShort = false;
/*
* Method name is not relevant, the binding is done according to the class
* of the parameter.
*/
@UiHandler("buttonSubmit")
void doClickSubmit(ClickEvent event) {
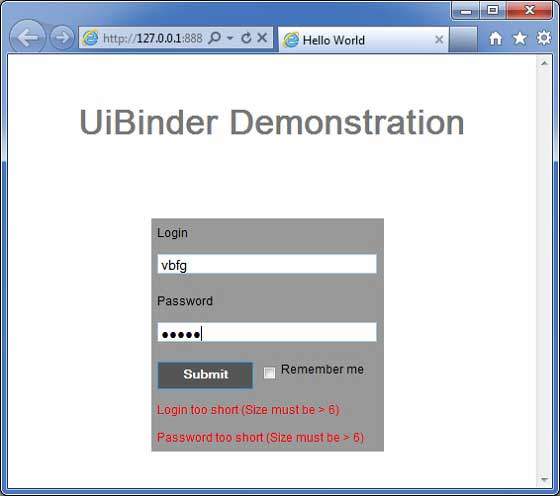
if (!tooShort) {
Window.alert("Login Successful!");
} else {
Window.alert("Login or Password is too short!");
}
}
@UiHandler("loginBox")
void handleLoginChange(ValueChangeEvent<String> event) {
if (event.getValue().length() < 6) {
completionLabel1.setText("Login too short (Size must be > 6)");
tooShort = true;
} else {
tooShort = false;
completionLabel1.setText("");
}
}
@UiHandler("passwordBox")
void handlePasswordChange(ValueChangeEvent<String> event) {
if (event.getValue().length() < 6) {
tooShort = true;
completionLabel2.setText("Password too short (Size must be > 6)");
} else {
tooShort = false;
completionLabel2.setText("");
}
}
}
讓我們在 Java 檔案src/com.tutorialspoint/HelloWorld.java中包含以下內容,它將演示 UiBinder 的用法。
package com.tutorialspoint.client;
import com.google.gwt.core.client.EntryPoint;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.RootPanel;
public class HelloWorld implements EntryPoint {
public void onModuleLoad() {
RootPanel.get().add(new Login());
}
}
完成所有更改後,讓我們像在 GWT - 建立應用程式 章節中所做的那樣,在開發模式下編譯並執行應用程式。如果您的應用程式一切正常,這將產生以下結果 -
GWT - RPC 通訊
基於 GWT 的應用程式通常由客戶端模組和伺服器端模組組成。客戶端程式碼在瀏覽器中執行,伺服器端程式碼在 Web 伺服器中執行。客戶端程式碼必須透過網路發出 HTTP 請求才能訪問伺服器端資料。
RPC,遠端過程呼叫是 GWT 使用的機制,客戶端程式碼可以直接執行伺服器端方法。
GWT RPC 基於 servlet。
GWT RPC 是非同步的,客戶端在通訊過程中永遠不會被阻塞。
使用 GWT RPC,Java 物件可以直接在客戶端和伺服器之間傳送(由 GWT 框架自動序列化)。
伺服器端 servlet 被稱為 **服務**。
從客戶端程式碼呼叫伺服器端 servlet 方法的遠端過程呼叫被稱為 **呼叫服務**。
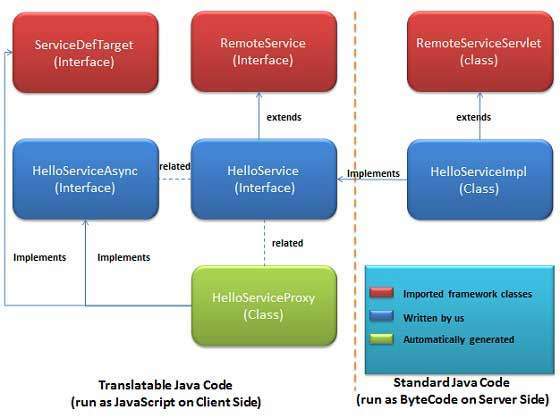
GWT RPC 元件
以下是 GWT RPC 通訊機制中使用的三個元件
- 在伺服器上執行的遠端服務(伺服器端 servlet)。
- 用於呼叫該服務的客戶端程式碼。
- 將在客戶端和伺服器之間傳遞的 Java 資料物件。
GWT 客戶端和伺服器都自動序列化和反序列化資料,因此開發人員無需序列化/反序列化物件,資料物件可以透過 HTTP 傳輸。
下圖顯示了 RPC 架構。
要開始使用 RPC,我們需要遵循 GWT 約定。
RPC 通訊工作流程
步驟 1 - 建立可序列化的模型類
在客戶端定義一個應該可序列化的 Java 模型物件。
public class Message implements Serializable {
...
private String message;
public Message(){};
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
...
}
步驟 2 - 建立服務介面
在客戶端為服務定義一個擴充套件 RemoteService 的介面,列出所有服務方法。
使用註釋 @RemoteServiceRelativePath 將服務對映到相對於模組基本 URL 的遠端 servlet 的預設路徑。
@RemoteServiceRelativePath("message")
public interface MessageService extends RemoteService {
Message getMessage(String input);
}
步驟 3 - 建立非同步服務介面
在客戶端(與上面提到的服務相同的位置)為服務定義一個非同步介面,這將在 GWT 客戶端程式碼中使用。
public interface MessageServiceAsync {
void getMessage(String input, AsyncCallback<Message> callback);
}
步驟 4 - 建立服務實現 Servlet 類
在伺服器端實現介面,並且該類應該擴充套件 RemoteServiceServlet 類。
public class MessageServiceImpl extends RemoteServiceServlet
implements MessageService{
...
public Message getMessage(String input) {
String messageString = "Hello " + input + "!";
Message message = new Message();
message.setMessage(messageString);
return message;
}
}
步驟 5 - 更新 Web.xml 以包含 Servlet 宣告
編輯 Web 應用程式部署描述符 (web.xml) 以包含 MessageServiceImpl Servlet 宣告。
<web-app>
...
<servlet>
<servlet-name>messageServiceImpl</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.tutorialspoint.server.MessageServiceImpl
</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>messageServiceImpl</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/helloworld/message</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
步驟 6 - 在應用程式程式碼中進行遠端過程呼叫
建立服務代理類。
MessageServiceAsync messageService = GWT.create(MessageService.class);
建立 AsyncCallback 處理程式來處理 RPC 回撥,其中伺服器將訊息返回給客戶端
class MessageCallBack implements AsyncCallback<Message> {
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable caught) {
Window.alert("Unable to obtain server response: "
+ caught.getMessage());
}
@Override
public void onSuccess(Message result) {
Window.alert(result.getMessage());
}
}
當用戶與 UI 互動時呼叫遠端服務
public class HelloWorld implements EntryPoint {
...
public void onModuleLoad() {
...
buttonMessage.addClickHandler(new ClickHandler() {
@Override
public void onClick(ClickEvent event) {
messageService.getMessage(txtName.getValue(),
new MessageCallBack());
}
});
...
}
}
RPC 通訊完整示例
此示例將引導您完成簡單的步驟,以展示 GWT 中 RPC 通訊的示例。請按照以下步驟更新我們在“GWT - 建立應用程式”章節中建立的 GWT 應用程式 -
| 步驟 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 在 _GWT - 建立應用程式_ 章節中說明的 _com.tutorialspoint_ 包下建立一個名為 _HelloWorld_ 的專案。 |
| 2 | 修改 _HelloWorld.gwt.xml_、_HelloWorld.css_、_HelloWorld.html_ 和 _HelloWorld.java_,如下所述。保持其餘檔案不變。 |
| 3 | 編譯並執行應用程式以驗證實現邏輯的結果。 |
以下是修改後的模組描述符 **src/com.tutorialspoint/HelloWorld.gwt.xml** 的內容。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <module rename-to = 'helloworld'> <!-- Inherit the core Web Toolkit stuff. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.User'/> <!-- Inherit the default GWT style sheet. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.theme.clean.Clean'/> <!-- Inherit the UiBinder module. --> <inherits name = "com.google.gwt.uibinder.UiBinder"/> <!-- Specify the app entry point class. --> <entry-point class = 'com.tutorialspoint.client.HelloWorld'/> <!-- Specify the paths for translatable code --> <source path = 'client'/> <source path = 'shared'/> </module>
以下是修改後的樣式表文件 **war/HelloWorld.css** 的內容。
body {
text-align: center;
font-family: verdana, sans-serif;
}
h1 {
font-size: 2em;
font-weight: bold;
color: #777777;
margin: 40px 0px 70px;
text-align: center;
}
以下是修改後的 HTML 主機檔案 **war/HelloWorld.html** 的內容。
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello World</title>
<link rel = "stylesheet" href = "HelloWorld.css"/>
<script language = "javascript" src = "helloworld/helloworld.nocache.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>RPC Communication Demonstration</h1>
<div id = "gwtContainer"></div>
</body>
</html>
現在在 **src/com.tutorialspoint/client** 包中建立 Message.java 檔案,並將以下內容放入其中
package com.tutorialspoint.client;
import java.io.Serializable;
public class Message implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
private String message;
public Message(){};
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
}
現在在 **src/com.tutorialspoint/client** 包中建立 MessageService.java 檔案,並將以下內容放入其中
package com.tutorialspoint.client;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.rpc.RemoteService;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.rpc.RemoteServiceRelativePath;
@RemoteServiceRelativePath("message")
public interface MessageService extends RemoteService {
Message getMessage(String input);
}
現在在 **src/com.tutorialspoint/client** 包中建立 MessageServiceAsync.java 檔案,並將以下內容放入其中
package com.tutorialspoint.client;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.rpc.AsyncCallback;
public interface MessageServiceAsync {
void getMessage(String input, AsyncCallback<Message> callback);
}
現在在 **src/com.tutorialspoint/server** 包中建立 MessageServiceImpl.java 檔案,並將以下內容放入其中
package com.tutorialspoint.server;
import com.google.gwt.user.server.rpc.RemoteServiceServlet;
import com.tutorialspoint.client.Message;
import com.tutorialspoint.client.MessageService;
public class MessageServiceImpl extends RemoteServiceServlet
implements MessageService{
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
public Message getMessage(String input) {
String messageString = "Hello " + input + "!";
Message message = new Message();
message.setMessage(messageString);
return message;
}
}
更新修改後的 Web 應用程式部署描述符 **war/WEB-INF/web.xml** 的內容,以包含 MessageServiceImpl Servlet 宣告。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE web-app
PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN"
"http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd">
<web-app>
<!-- Default page to serve -->
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>HelloWorld.html</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>messageServiceImpl</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.tutorialspoint.server.MessageServiceImpl
</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>messageServiceImpl</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/helloworld/message</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>
將 **src/com.tutorialspoint/client** 包中 HelloWorld.java 的內容替換為以下內容
package com.tutorialspoint.client;
import com.google.gwt.core.client.EntryPoint;
import com.google.gwt.core.client.GWT;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.ClickEvent;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.ClickHandler;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.KeyCodes;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.KeyUpEvent;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.KeyUpHandler;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.Window;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.rpc.AsyncCallback;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Button;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.DecoratorPanel;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.HasHorizontalAlignment;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.HorizontalPanel;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Label;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.RootPanel;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.TextBox;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.VerticalPanel;
public class HelloWorld implements EntryPoint {
private MessageServiceAsync messageService =
GWT.create(MessageService.class);
private class MessageCallBack implements AsyncCallback<Message> {
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable caught) {
/* server side error occured */
Window.alert("Unable to obtain server response: " + caught.getMessage());
}
@Override
public void onSuccess(Message result) {
/* server returned result, show user the message */
Window.alert(result.getMessage());
}
}
public void onModuleLoad() {
/*create UI */
final TextBox txtName = new TextBox();
txtName.setWidth("200");
txtName.addKeyUpHandler(new KeyUpHandler() {
@Override
public void onKeyUp(KeyUpEvent event) {
if(event.getNativeKeyCode() == KeyCodes.KEY_ENTER){
/* make remote call to server to get the message */
messageService.getMessage(txtName.getValue(),
new MessageCallBack());
}
}
});
Label lblName = new Label("Enter your name: ");
Button buttonMessage = new Button("Click Me!");
buttonMessage.addClickHandler(new ClickHandler() {
@Override
public void onClick(ClickEvent event) {
/* make remote call to server to get the message */
messageService.getMessage(txtName.getValue(),
new MessageCallBack());
}
});
HorizontalPanel hPanel = new HorizontalPanel();
hPanel.add(lblName);
hPanel.add(txtName);
hPanel.setCellWidth(lblName, "130");
VerticalPanel vPanel = new VerticalPanel();
vPanel.setSpacing(10);
vPanel.add(hPanel);
vPanel.add(buttonMessage);
vPanel.setCellHorizontalAlignment(buttonMessage,
HasHorizontalAlignment.ALIGN_RIGHT);
DecoratorPanel panel = new DecoratorPanel();
panel.add(vPanel);
// Add widgets to the root panel.
RootPanel.get("gwtContainer").add(panel);
}
}
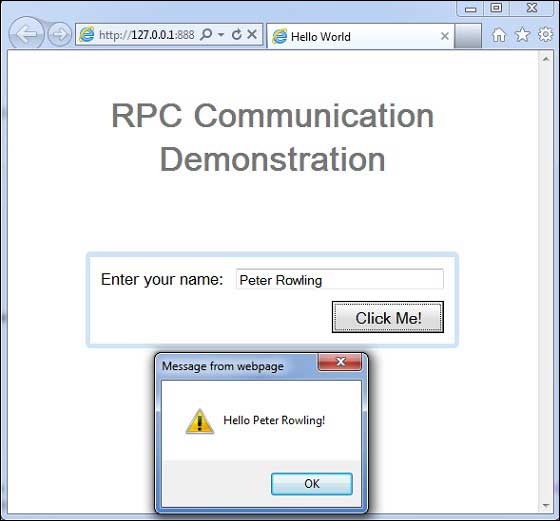
完成所有更改後,讓我們像在 GWT - 建立應用程式 章節中所做的那樣,在開發模式下編譯並執行應用程式。如果您的應用程式一切正常,這將產生以下結果 -
GWT - JUnit 整合
GWT 為使用 JUnit 測試框架自動測試客戶端程式碼提供了出色的支援。在本文中,我們將演示 GWT 和 JUNIT 的整合。
下載 Junit 歸檔檔案
JUnit 官方網站 - https://www.junit.org
下載 **Junit-4.10.jar**
| 作業系統 | 歸檔檔名 |
|---|---|
| Windows | junit4.10.jar |
| Linux | junit4.10.jar |
| Mac | junit4.10.jar |
將下載的 jar 檔案儲存到計算機上的某個位置。我們將其儲存在 **C:/ > JUNIT**
找到 GWT 安裝資料夾
| 作業系統 | GWT 安裝資料夾 |
|---|---|
| Windows | C:\GWT\gwt-2.1.0 |
| Linux | /usr/local/GWT/gwt-2.1.0 |
| Mac | /Library/GWT/gwt-2.1.0 |
GWTTestCase 類
GWT 提供了 **GWTTestCase** 基類,該基類提供了 JUnit 整合。執行擴充套件 GWTTestCase 的已編譯類在 JUnit 下會啟動 HtmlUnit 瀏覽器,該瀏覽器用於模擬測試執行期間的應用程式行為。
GWTTestCase 是從 JUnit 的 TestCase 派生的類,可以使用 JUnit TestRunner 執行它。
使用 webAppCreator
GWT 提供了一個特殊的命令列工具 **webAppCreator**,它可以為我們生成一個入門測試用例,以及用於在開發模式和生產模式下進行測試的 ant 目標和 eclipse 啟動配置。
開啟命令提示符並轉到 **C:\ > GWT_WORKSPACE >**,您希望在其中建立一個具有測試支援的新專案。執行以下命令
C:\GWT_WORKSPACE>C:\GWT\gwt-2.1.0\webAppCreator -out HelloWorld -junit C:\JUNIT\junit-4.10.jar com.tutorialspoint.HelloWorld
值得注意的要點
- 我們正在執行 webAppCreator 命令列實用程式。
- HelloWorld 是要建立的專案的名稱
- -junit 選項指示 webAppCreator 向專案新增 junit 支援
- com.tutorialspoint.HelloWorld 是模組的名稱
驗證輸出。
Created directory HelloWorld\src Created directory HelloWorld\war Created directory HelloWorld\war\WEB-INF Created directory HelloWorld\war\WEB-INF\lib Created directory HelloWorld\src\com\tutorialspoint Created directory HelloWorld\src\com\tutorialspoint\client Created directory HelloWorld\src\com\tutorialspoint\server Created directory HelloWorld\src\com\tutorialspoint\shared Created directory HelloWorld\test\com\tutorialspoint Created directory HelloWorld\test\com\tutorialspoint\client Created file HelloWorld\src\com\tutorialspoint\HelloWorld.gwt.xml Created file HelloWorld\war\HelloWorld.html Created file HelloWorld\war\HelloWorld.css Created file HelloWorld\war\WEB-INF\web.xml Created file HelloWorld\src\com\tutorialspoint\client\HelloWorld.java Created file HelloWorld\src\com\tutorialspoint\client\GreetingService.java Created file HelloWorld\src\com\tutorialspoint\client\GreetingServiceAsync.java Created file HelloWorld\src\com\tutorialspoint\server\GreetingServiceImpl.java Created file HelloWorld\src\com\tutorialspoint\shared\FieldVerifier.java Created file HelloWorld\build.xml Created file HelloWorld\README.txt Created file HelloWorld\test\com\tutorialspoint\HelloWorldJUnit.gwt.xml Created file HelloWorld\test\com\tutorialspoint\client\HelloWorldTest.java Created file HelloWorld\.project Created file HelloWorld\.classpath Created file HelloWorld\HelloWorld.launch Created file HelloWorld\HelloWorldTest-dev.launch Created file HelloWorld\HelloWorldTest-prod.launch
理解測試類:HelloWorldTest.java
package com.tutorialspoint.client;
import com.tutorialspoint.shared.FieldVerifier;
import com.google.gwt.core.client.GWT;
import com.google.gwt.junit.client.GWTTestCase;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.rpc.AsyncCallback;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.rpc.ServiceDefTarget;
/**
* GWT JUnit tests must extend GWTTestCase.
*/
public class HelloWorldTest extends GWTTestCase {
/**
* must refer to a valid module that sources this class.
*/
public String getModuleName() {
return "com.tutorialspoint.HelloWorldJUnit";
}
/**
* tests the FieldVerifier.
*/
public void testFieldVerifier() {
assertFalse(FieldVerifier.isValidName(null));
assertFalse(FieldVerifier.isValidName(""));
assertFalse(FieldVerifier.isValidName("a"));
assertFalse(FieldVerifier.isValidName("ab"));
assertFalse(FieldVerifier.isValidName("abc"));
assertTrue(FieldVerifier.isValidName("abcd"));
}
/**
* this test will send a request to the server using the greetServer
* method in GreetingService and verify the response.
*/
public void testGreetingService() {
/* create the service that we will test. */
GreetingServiceAsync greetingService =
GWT.create(GreetingService.class);
ServiceDefTarget target = (ServiceDefTarget) greetingService;
target.setServiceEntryPoint(GWT.getModuleBaseURL()
+ "helloworld/greet");
/* since RPC calls are asynchronous, we will need to wait
for a response after this test method returns. This line
tells the test runner to wait up to 10 seconds
before timing out. */
delayTestFinish(10000);
/* send a request to the server. */
greetingService.greetServer("GWT User",
new AsyncCallback<String>() {
public void onFailure(Throwable caught) {
/* The request resulted in an unexpected error. */
fail("Request failure: " + caught.getMessage());
}
public void onSuccess(String result) {
/* verify that the response is correct. */
assertTrue(result.startsWith("Hello, GWT User!"));
/* now that we have received a response, we need to
tell the test runner that the test is complete.
You must call finishTest() after an asynchronous test
finishes successfully, or the test will time out.*/
finishTest();
}
});
}
}
值得注意的要點
| 序號 | 注意 |
|---|---|
| 1 | HelloWorldTest 類是在 HelloWorld/test 目錄下的 com.tutorialspoint.client 包中生成的。 |
| 2 | HelloWorldTest 類將包含 HelloWorld 的單元測試用例。 |
| 3 | HelloWorldTest 類擴充套件了 com.google.gwt.junit.client 包中的 GWTTestCase 類。 |
| 4 | HelloWorldTest 類有一個抽象方法 (getModuleName),它必須返回 GWT 模組的名稱。對於 HelloWorld,它是 com.tutorialspoint.HelloWorldJUnit。 |
| 5 | HelloWorldTest 類生成了兩個示例測試用例 testFieldVerifier、testSimple。我們添加了 testGreetingService。 |
| 6 | 這些方法使用它從 JUnit Assert 類(GWTTestCase 的祖先)繼承的眾多 assert* 函式之一。 |
| 7 | assertTrue(boolean) 函式斷言傳入的布林引數計算結果為 true。如果不是,則在 JUnit 中執行時測試將失敗。 |
GWT - JUnit 整合完整示例
此示例將引導您完成簡單的步驟,以展示 JUnit 整合在 GWT 中的示例。
請按照以下步驟更新我們上面建立的 GWT 應用程式 -
| 步驟 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 使用匯入現有專案嚮導(檔案 → 匯入 → 常規 → 將現有專案匯入工作區)在 eclipse 中匯入名為 HelloWorld 的專案。 |
| 2 | 修改 _HelloWorld.gwt.xml_、_HelloWorld.css_、_HelloWorld.html_ 和 _HelloWorld.java_,如下所述。保持其餘檔案不變。 |
| 3 | 編譯並執行應用程式以驗證實現邏輯的結果。 |
以下是 eclipse 中的專案結構。

以下是修改後的模組描述符 **src/com.tutorialspoint/HelloWorld.gwt.xml** 的內容。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <module rename-to = 'helloworld'> <!-- Inherit the core Web Toolkit stuff. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.User'/> <!-- Inherit the default GWT style sheet. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.theme.clean.Clean'/> <!-- Inherit the UiBinder module. --> <inherits name = "com.google.gwt.uibinder.UiBinder"/> <!-- Specify the app entry point class. --> <entry-point class = 'com.tutorialspoint.client.HelloWorld'/> <!-- Specify the paths for translatable code --> <source path = 'client'/> <source path = 'shared'/> </module>
以下是修改後的樣式表文件 **war/HelloWorld.css** 的內容。
body {
text-align: center;
font-family: verdana, sans-serif;
}
h1 {
font-size: 2em;
font-weight: bold;
color: #777777;
margin: 40px 0px 70px;
text-align: center;
}
以下是修改後的 HTML 主機檔案 **war/HelloWorld.html** 的內容。
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello World</title>
<link rel = "stylesheet" href = "HelloWorld.css"/>
<script language = "javascript" src = "helloworld/helloworld.nocache.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>JUnit Integration Demonstration</h1>
<div id = "gwtContainer"></div>
</body>
</html>
將 **src/com.tutorialspoint/client** 包中 HelloWorld.java 的內容替換為以下內容
package com.tutorialspoint.client;
import com.google.gwt.core.client.EntryPoint;
import com.google.gwt.core.client.GWT;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.ClickEvent;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.ClickHandler;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.KeyCodes;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.KeyUpEvent;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.KeyUpHandler;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.Window;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.rpc.AsyncCallback;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Button;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.DecoratorPanel;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.HasHorizontalAlignment;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.HorizontalPanel;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Label;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.RootPanel;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.TextBox;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.VerticalPanel;
public class HelloWorld implements EntryPoint {
public void onModuleLoad() {
/*create UI */
final TextBox txtName = new TextBox();
txtName.setWidth("200");
txtName.addKeyUpHandler(new KeyUpHandler() {
@Override
public void onKeyUp(KeyUpEvent event) {
if(event.getNativeKeyCode() == KeyCodes.KEY_ENTER){
Window.alert(getGreeting(txtName.getValue()));
}
}
});
Label lblName = new Label("Enter your name: ");
Button buttonMessage = new Button("Click Me!");
buttonMessage.addClickHandler(new ClickHandler() {
@Override
public void onClick(ClickEvent event) {
Window.alert(getGreeting(txtName.getValue()));
}
});
HorizontalPanel hPanel = new HorizontalPanel();
hPanel.add(lblName);
hPanel.add(txtName);
hPanel.setCellWidth(lblName, "130");
VerticalPanel vPanel = new VerticalPanel();
vPanel.setSpacing(10);
vPanel.add(hPanel);
vPanel.add(buttonMessage);
vPanel.setCellHorizontalAlignment(buttonMessage,
HasHorizontalAlignment.ALIGN_RIGHT);
DecoratorPanel panel = new DecoratorPanel();
panel.add(vPanel);
// Add widgets to the root panel.
RootPanel.get("gwtContainer").add(panel);
}
public String getGreeting(String name){
return "Hello "+name+"!";
}
}
將 **test/com.tutorialspoint/client** 包中 HelloWorldTest.java 的內容替換為以下內容
package com.tutorialspoint.client;
import com.tutorialspoint.shared.FieldVerifier;
import com.google.gwt.core.client.GWT;
import com.google.gwt.junit.client.GWTTestCase;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.rpc.AsyncCallback;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.rpc.ServiceDefTarget;
/**
* GWT JUnit tests must extend GWTTestCase.
*/
public class HelloWorldTest extends GWTTestCase {
/**
* must refer to a valid module that sources this class.
*/
public String getModuleName() {
return "com.tutorialspoint.HelloWorldJUnit";
}
/**
* tests the FieldVerifier.
*/
public void testFieldVerifier() {
assertFalse(FieldVerifier.isValidName(null));
assertFalse(FieldVerifier.isValidName(""));
assertFalse(FieldVerifier.isValidName("a"));
assertFalse(FieldVerifier.isValidName("ab"));
assertFalse(FieldVerifier.isValidName("abc"));
assertTrue(FieldVerifier.isValidName("abcd"));
}
/**
* this test will send a request to the server using the greetServer
* method in GreetingService and verify the response.
*/
public void testGreetingService() {
/* create the service that we will test. */
GreetingServiceAsync greetingService =
GWT.create(GreetingService.class);
ServiceDefTarget target = (ServiceDefTarget) greetingService;
target.setServiceEntryPoint(GWT.getModuleBaseURL()
+ "helloworld/greet");
/* since RPC calls are asynchronous, we will need to wait
for a response after this test method returns. This line
tells the test runner to wait up to 10 seconds
before timing out. */
delayTestFinish(10000);
/* send a request to the server. */
greetingService.greetServer("GWT User",
new AsyncCallback<String>() {
public void onFailure(Throwable caught) {
/* The request resulted in an unexpected error. */
fail("Request failure: " + caught.getMessage());
}
public void onSuccess(String result) {
/* verify that the response is correct. */
assertTrue(result.startsWith("Hello, GWT User!"));
/* now that we have received a response, we need to
tell the test runner that the test is complete.
You must call finishTest() after an asynchronous test
finishes successfully, or the test will time out.*/
finishTest();
}
});
/**
* tests the getGreeting method.
*/
public void testGetGreeting() {
HelloWorld helloWorld = new HelloWorld();
String name = "Robert";
String expectedGreeting = "Hello "+name+"!";
assertEquals(expectedGreeting,helloWorld.getGreeting(name));
}
}
}
使用生成的啟動配置在 Eclipse 中執行測試用例
我們將使用 webAppCreator 為開發模式和生產模式生成的啟動配置在 Eclipse 中執行單元測試。
在開發模式下執行 JUnit 測試
- 從 Eclipse 選單欄中,選擇執行 → 執行配置...
- 在 JUnit 部分,選擇 HelloWorldTest-dev
- 要將更改儲存到引數,請按應用
- 要執行測試,請按執行
如果您的應用程式一切正常,這將產生以下結果 -

在生產模式下執行 JUnit 測試
- 從 Eclipse 選單欄中,選擇執行 → 執行配置...
- 在 JUnit 部分,選擇 HelloWorldTest-prod
- 要將更改儲存到引數,請按應用
- 要執行測試,請按執行
如果您的應用程式一切正常,這將產生以下結果 -

GWT - 除錯應用
GWT 提供了除錯客戶端和伺服器端程式碼的出色功能。
在開發模式下,GWT 應用程式基於 Java 程式碼,不會轉換為 JavaScript。
當應用程式在開發模式下執行時,Java 虛擬機器 (JVM) 實際上正在執行應用程式程式碼作為已編譯的 Java 位元組碼,使用 GWT 功能連線到瀏覽器視窗。
GWT 使用基於瀏覽器的外掛連線到 JVM。
因此,開發人員可以自由使用任何基於 Java 的 IDE 來除錯客戶端 GWT 程式碼以及伺服器端程式碼。
在本文中,我們將演示使用 Eclipse 除錯 GWT 客戶端程式碼的用法。我們將執行以下任務 -
- 在程式碼中設定斷點並在斷點資源管理器中檢視它們。
- 在除錯期間逐行單步執行程式碼。
- 檢視變數的值。
- 檢查所有變數的值。
- 檢查表示式的值。
- 顯示掛起執行緒的堆疊幀。
除錯示例
此示例將引導您完成簡單的步驟,以演示除錯 GWT 應用程式。請按照以下步驟更新我們在“GWT - 建立應用程式”章節中建立的 GWT 應用程式 -
| 步驟 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 在 _GWT - 建立應用程式_ 章節中說明的 _com.tutorialspoint_ 包下建立一個名為 _HelloWorld_ 的專案。 |
| 2 | 修改 _HelloWorld.gwt.xml_、_HelloWorld.css_、_HelloWorld.html_ 和 _HelloWorld.java_,如下所述。保持其餘檔案不變。 |
| 3 | 編譯並執行應用程式以驗證實現邏輯的結果。 |
以下是修改後的模組描述符 **src/com.tutorialspoint/HelloWorld.gwt.xml** 的內容。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <module rename-to = 'helloworld'> <!-- Inherit the core Web Toolkit stuff. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.User'/> <!-- Inherit the default GWT style sheet. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.theme.clean.Clean'/> <!-- Specify the app entry point class. --> <entry-point class = 'com.tutorialspoint.client.HelloWorld'/> <!-- Specify the paths for translatable code --> <source path = 'client'/> <source path = 'shared'/> </module>
以下是修改後的樣式表文件 **war/HelloWorld.css** 的內容。
body {
text-align: center;
font-family: verdana, sans-serif;
}
h1 {
font-size: 2em;
font-weight: bold;
color: #777777;
margin: 40px 0px 70px;
text-align: center;
}
.gwt-Label{
font-size: 150%;
font-weight: bold;
color:red;
padding:5px;
margin:5px;
}
以下是修改後的 HTML 主機檔案war/HelloWorld.html的內容,以容納兩個按鈕。
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello World</title>
<link rel = "stylesheet" href = "HelloWorld.css"/>
<script language = "javascript" src = "helloworld/helloworld.nocache.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Debugging Application Demonstration</h1>
<div id = "gwtContainer"></div>
</body>
</html>
讓我們使用以下 Java 檔案 **src/com.tutorialspoint/HelloWorld.java** 的內容,我們將使用它來演示 GWT 程式碼的除錯功能。
package com.tutorialspoint.client;
import com.google.gwt.core.client.EntryPoint;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.ClickEvent;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.ClickHandler;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.KeyCodes;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.KeyUpEvent;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.KeyUpHandler;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.Window;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Button;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.DecoratorPanel;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.HasHorizontalAlignment;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.HorizontalPanel;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Label;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.RootPanel;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.TextBox;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.VerticalPanel;
public class HelloWorld implements EntryPoint {
public void onModuleLoad() {
/*create UI */
final TextBox txtName = new TextBox();
txtName.setWidth("200");
txtName.addKeyUpHandler(new KeyUpHandler() {
@Override
public void onKeyUp(KeyUpEvent event) {
if(event.getNativeKeyCode() == KeyCodes.KEY_ENTER){
Window.alert(getGreeting(txtName.getValue()));
}
}
});
Label lblName = new Label("Enter your name: ");
Button buttonMessage = new Button("Click Me!");
buttonMessage.addClickHandler(new ClickHandler() {
@Override
public void onClick(ClickEvent event) {
Window.alert(getGreeting(txtName.getValue()));
}});
HorizontalPanel hPanel = new HorizontalPanel();
hPanel.add(lblName);
hPanel.add(txtName);
hPanel.setCellWidth(lblName, "130");
VerticalPanel vPanel = new VerticalPanel();
vPanel.setSpacing(10);
vPanel.add(hPanel);
vPanel.add(buttonMessage);
vPanel.setCellHorizontalAlignment(buttonMessage,
HasHorizontalAlignment.ALIGN_RIGHT);
DecoratorPanel panel = new DecoratorPanel();
panel.add(vPanel);
// Add widgets to the root panel.
RootPanel.get("gwtContainer").add(panel);
}
public String getGreeting(String name){
return "Hello "+name+"!";
}
}
步驟 1 - 放置斷點
在 HelloWorld.java 的 **onModuleLoad()** 的第一行放置一個斷點
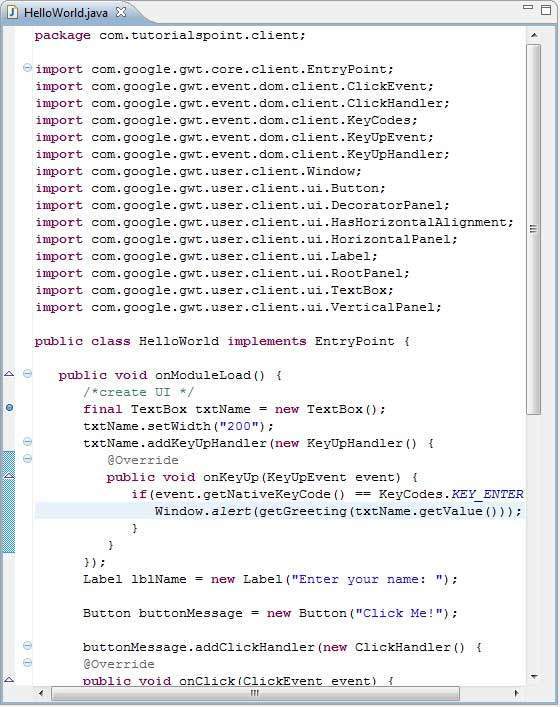
步驟 2 - 除錯應用程式
現在單擊 ![]() 除錯應用程式選單並選擇 **HelloWorld** 應用程式以除錯應用程式。
除錯應用程式選單並選擇 **HelloWorld** 應用程式以除錯應用程式。
如果一切正常,您應該會看到 Eclipse 中啟用的 GWT 開發模式,其中包含一個 URL,如下所示。雙擊 URL 以開啟 GWT 應用程式。

應用程式啟動後,您將在 Eclipse 斷點處看到焦點,因為我們在入口點方法的第一行放置了斷點。
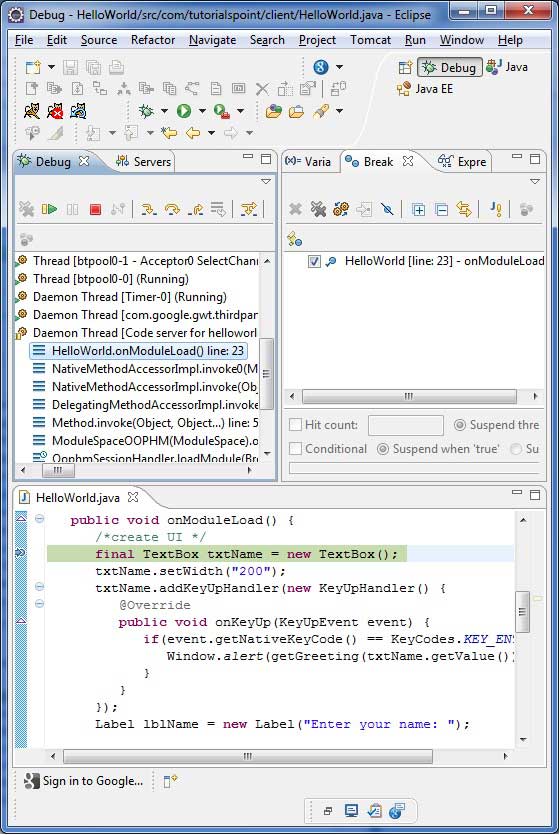
您可以看到掛起執行緒的堆疊跟蹤。
您可以看到表示式的值。
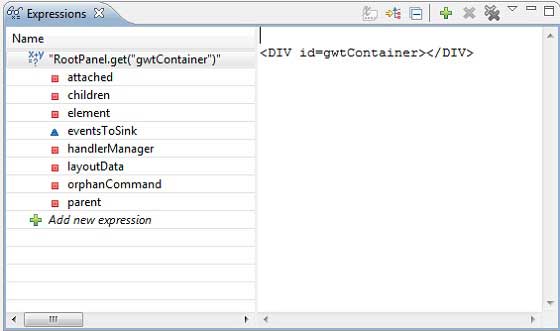
您可以看到已放置的斷點列表。
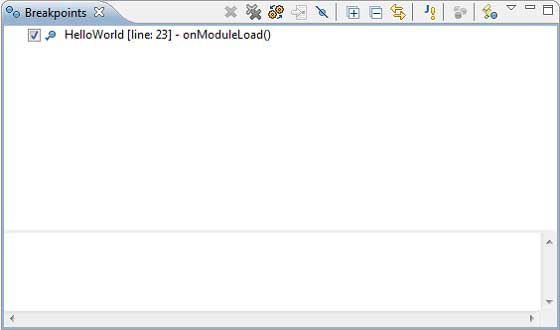
現在繼續按 F6 直到到達 onModuleLoad() 方法的最後一行。作為函式鍵的參考,F6 逐行檢查程式碼,F5 進一步深入,F8 將恢復應用程式。現在您可以看到 onModuleLoad() 方法的所有變數的值列表。
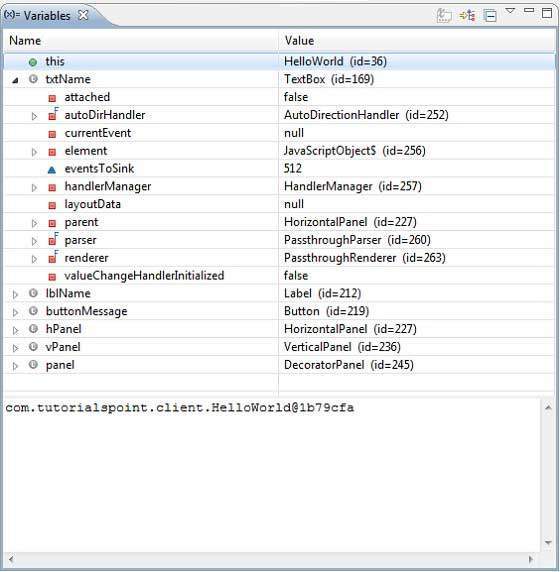
GWT 客戶端程式碼可以像除錯 Java 應用程式一樣除錯。在任何一行放置斷點並使用 GWT 的除錯功能。
GWT - 國際化
GWT 提供三種國際化 GWT 應用程式的方法,我們將演示靜態字串國際化的使用,這在專案中最常用。
| 序號 | 技術和描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 |
靜態字串國際化 此技術最為普遍,在執行時需要很少的開銷;是翻譯常量字串和引數化字串的非常有效的技術;最簡單易於實現。 靜態字串國際化使用標準 Java 屬性檔案儲存翻譯後的字串和引數化訊息,並建立強型別 Java 介面來檢索它們的值。 |
| 2 |
動態字串國際化 此技術非常靈活,但比靜態字串國際化慢。主機頁面包含本地化字串,因此當我們新增新的語言環境時,不需要重新編譯應用程式。如果 GWT 應用程式要與現有的伺服器端本地化系統整合,則應使用此技術。 |
| 3 |
可本地化介面 此技術是三種技術中最強大的。實現 Localizable 允許我們建立自定義型別的本地化版本。這是一種高階國際化技術。 |
國際化 GWT 應用程式的工作流程
步驟 1 - 建立屬性檔案
建立包含要在應用程式中使用的訊息的屬性檔案。我們在示例中建立了一個 **HelloWorldMessages.properties** 檔案。
enterName = Enter your name
clickMe = Click Me
applicationTitle = Application Internationalization Demonstration
greeting = Hello {0}
建立包含特定於語言環境的翻譯值的屬性檔案。我們在示例中建立了一個 **HelloWorldMessages_de.properties** 檔案。此檔案包含德語翻譯。_de 指定德語語言環境,我們將在應用程式中支援德語。
如果您使用 Eclipse 建立屬性檔案,則將檔案的編碼更改為 UTF-8。選擇檔案,然後在其上右鍵單擊以開啟其屬性視窗。將文字檔案編碼選擇為 **其他 UTF-8**。應用並儲存更改。
enterName = Geben Sie Ihren Namen
clickMe = Klick mich
applicationTitle = Anwendung Internationalisierung Demonstration
greeting = Hallo {0}
步驟 2 - 將 i18n 模組新增到模組描述符 XML 檔案
更新模組檔案 **HelloWorld.gwt.xml** 以包含對德語語言環境的支援
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <module rename-to = 'helloworld'> ... <extend-property name = "locale" values="de" /> ... </module>
步驟 3 - 建立等效於屬性檔案的介面
透過擴充套件 GWT 的 Messages 介面建立 HelloWorldMessages.java 介面以包含內部化的支援。它應該包含與屬性檔案中的鍵相同的的方法名。佔位符將替換為 String 引數。
public interface HelloWorldMessages extends Messages {
@DefaultMessage("Enter your name")
String enterName();
@DefaultMessage("Click Me")
String clickMe();
@DefaultMessage("Application Internalization Demonstration")
String applicationTitle();
@DefaultMessage("Hello {0}")
String greeting(String name);
}
步驟 4 - 在 UI 元件中使用訊息介面。
使用 **HelloWorld** 中的 **HelloWorldMessages** 物件獲取訊息。
public class HelloWorld implements EntryPoint {
/* create an object of HelloWorldMessages interface
using GWT.create() method */
private HelloWorldMessages messages =
GWT.create(HelloWorldMessages.class);
public void onModuleLoad() {
...
Label titleLabel = new Label(messages.applicationTitle());
//Add title to the application
RootPanel.get("gwtAppTitle").add(titleLabel);
...
}
}
國際化 - 完整示例
此示例將引導您完成簡單的步驟,演示 GWT 應用程式的國際化功能。
按照以下步驟更新我們在 *GWT - 建立應用程式* 章節中建立的 GWT 應用程式:
| 步驟 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 在 _GWT - 建立應用程式_ 章節中說明的 _com.tutorialspoint_ 包下建立一個名為 _HelloWorld_ 的專案。 |
| 2 | 修改 _HelloWorld.gwt.xml_、_HelloWorld.css_、_HelloWorld.html_ 和 _HelloWorld.java_,如下所述。保持其餘檔案不變。 |
| 3 | 編譯並執行應用程式以驗證實現邏輯的結果。 |
以下是修改後的模組描述符 **src/com.tutorialspoint/HelloWorld.gwt.xml** 的內容。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <module rename-to = 'helloworld'> <!-- Inherit the core Web Toolkit stuff. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.User'/> <!-- Inherit the default GWT style sheet. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.theme.clean.Clean'/> <!-- Specify the app entry point class. --> <entry-point class = 'com.tutorialspoint.client.HelloWorld'/> <extend-property name = "locale" values="de" /> <!-- Specify the paths for translatable code --> <source path = 'client'/> <source path = 'shared'/> </module>
以下是修改後的樣式表文件 **war/HelloWorld.css** 的內容。
body {
text-align: center;
font-family: verdana, sans-serif;
}
h1 {
font-size: 2em;
font-weight: bold;
color: #777777;
margin: 40px 0px 70px;
text-align: center;
}
以下是修改後的 HTML 主機檔案 **war/HelloWorld.html** 的內容。
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello World</title>
<link rel = "stylesheet" href = "HelloWorld.css"/>
<script language = "javascript" src = "helloworld/helloworld.nocache.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<h1 id = "gwtAppTitle"></h1>
<div id = "gwtContainer"></div>
</body>
</html>
現在在 **src/com.tutorialspoint/client** 包中建立 HelloWorldMessages.properties 檔案,並將以下內容放置其中
enterName = Enter your name
clickMe = Click Me
applicationTitle = Application Internationalization Demonstration
greeting = Hello {0}
現在在 **src/com.tutorialspoint/client** 包中建立 HelloWorldMessages_de.properties 檔案,並將以下內容放置其中
enterName = Geben Sie Ihren Namen
clickMe = Klick mich
applicationTitle = Anwendung Internationalisierung Demonstration
greeting = Hallo {0}
現在在 **src/com.tutorialspoint/client** 包中建立 HelloWorldMessages.java 類,並將以下內容放置其中
package com.tutorialspoint.client;
import com.google.gwt.i18n.client.Messages;
public interface HelloWorldMessages extends Messages {
@DefaultMessage("Enter your name")
String enterName();
@DefaultMessage("Click Me")
String clickMe();
@DefaultMessage("Application Internationalization Demonstration")
String applicationTitle();
@DefaultMessage("Hello {0}")
String greeting(String name);
}
讓我們使用以下 Java 檔案 **src/com.tutorialspoint/HelloWorld.java** 的內容,演示 GWT 程式碼的國際化功能。
package com.tutorialspoint.client;
import com.google.gwt.core.client.EntryPoint;
import com.google.gwt.core.client.GWT;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.ClickEvent;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.ClickHandler;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.KeyCodes;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.KeyUpEvent;
import com.google.gwt.event.dom.client.KeyUpHandler;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.Window;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Button;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.DecoratorPanel;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.HasHorizontalAlignment;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.HorizontalPanel;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Label;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.RootPanel;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.TextBox;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.VerticalPanel;
public class HelloWorld implements EntryPoint {
/* create an object of HelloWorldMessages interface
using GWT.create() method */
private HelloWorldMessages messages =
GWT.create(HelloWorldMessages.class);
public void onModuleLoad() {
/*create UI */
final TextBox txtName = new TextBox();
txtName.setWidth("200");
txtName.addKeyUpHandler(new KeyUpHandler() {
@Override
public void onKeyUp(KeyUpEvent event) {
if(event.getNativeKeyCode() == KeyCodes.KEY_ENTER){
Window.alert(getGreeting(txtName.getValue()));
}
}
});
Label lblName = new Label(messages.enterName() + ": ");
Button buttonMessage = new Button(messages.clickMe() + "!");
buttonMessage.addClickHandler(new ClickHandler() {
@Override
public void onClick(ClickEvent event) {
Window.alert(getGreeting(txtName.getValue()));
}
});
HorizontalPanel hPanel = new HorizontalPanel();
hPanel.add(lblName);
hPanel.add(txtName);
VerticalPanel vPanel = new VerticalPanel();
vPanel.setSpacing(10);
vPanel.add(hPanel);
vPanel.add(buttonMessage);
vPanel.setCellHorizontalAlignment(buttonMessage,
HasHorizontalAlignment.ALIGN_RIGHT);
DecoratorPanel panel = new DecoratorPanel();
panel.add(vPanel);
Label titleLabel = new Label(messages.applicationTitle());
//Add title to the application
RootPanel.get("gwtAppTitle").add(titleLabel);
// Add widgets to the root panel.
RootPanel.get("gwtContainer").add(panel);
}
public String getGreeting(String name){
return messages.greeting(name + "!");
}
}
完成所有更改後,讓我們像在 GWT - 建立應用程式 章節中所做的那樣,在開發模式下編譯並執行應用程式。如果您的應用程式一切正常,這將產生以下結果 -

現在更新 URL 以包含 locale=de。設定 URL:http://127.0.0.1:8888/HelloWorld.html?gwt.codesvr=127.0.0.1:9997&locale=de。如果您的應用程式一切正常,這將產生以下結果:
GWT - History 類
GWT 應用程式通常是執行 JavaScript 的單頁面應用程式,並且不包含很多頁面,因此瀏覽器不會跟蹤使用者與應用程式的互動。要使用瀏覽器的歷史記錄功能,應用程式應為每個可導航頁面生成唯一的 URL 片段。
GWT 提供 **歷史機制** 來處理這種情況。
GWT 使用術語 **標記**,它只是一個字串,應用程式可以解析它以返回到特定狀態。應用程式將此標記儲存在瀏覽器的歷史記錄中作為 URL 片段。
例如,名為“pageIndex1”的歷史標記將按如下方式新增到 URL 中:
https://tutorialspoint.tw/HelloWorld.html#pageIndex0
歷史管理工作流
步驟 1 - 啟用歷史記錄支援
為了使用 GWT 歷史記錄支援,我們必須首先將以下 iframe 嵌入到我們的主機 HTML 頁面中。
<iframe src = "javascript:''" id = "__gwt_historyFrame" style = "width:0;height:0;border:0"></iframe>
步驟 2 - 將標記新增到歷史記錄
以下示例說明如何將標記新增到瀏覽器歷史記錄
int index = 0;
History.newItem("pageIndex" + index);
步驟 3 - 從歷史記錄中檢索標記
當用戶使用瀏覽器的後退/前進按鈕時,我們將檢索標記並相應地更新我們的應用程式狀態。
History.addValueChangeHandler(new ValueChangeHandler<String>() {
@Override
public void onValueChange(ValueChangeEvent<String> event) {
String historyToken = event.getValue();
/* parse the history token */
try {
if (historyToken.substring(0, 9).equals("pageIndex")) {
String tabIndexToken = historyToken.substring(9, 10);
int tabIndex = Integer.parseInt(tabIndexToken);
/* select the specified tab panel */
tabPanel.selectTab(tabIndex);
} else {
tabPanel.selectTab(0);
}
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
tabPanel.selectTab(0);
}
}
});
現在讓我們看看 History 類的實際應用。
History 類 - 完整示例
此示例將引導您完成簡單的步驟,演示 GWT 應用程式的歷史記錄管理。按照以下步驟更新我們在 *GWT - 建立應用程式* 章節中建立的 GWT 應用程式:
| 步驟 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 在 _GWT - 建立應用程式_ 章節中說明的 _com.tutorialspoint_ 包下建立一個名為 _HelloWorld_ 的專案。 |
| 2 | 修改 _HelloWorld.gwt.xml_、_HelloWorld.css_、_HelloWorld.html_ 和 _HelloWorld.java_,如下所述。保持其餘檔案不變。 |
| 3 | 編譯並執行應用程式以驗證實現邏輯的結果。 |
以下是修改後的模組描述符 **src/com.tutorialspoint/HelloWorld.gwt.xml** 的內容。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <module rename-to = 'helloworld'> <!-- Inherit the core Web Toolkit stuff. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.User'/> <!-- Inherit the default GWT style sheet. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.theme.clean.Clean'/> <!-- Specify the app entry point class. --> <entry-point class = 'com.tutorialspoint.client.HelloWorld'/> <!-- Specify the paths for translatable code --> <source path = 'client'/> <source path = 'shared'/> </module>
以下是修改後的樣式表文件 **war/HelloWorld.css** 的內容。
body {
text-align: center;
font-family: verdana, sans-serif;
}
h1 {
font-size: 2em;
font-weight: bold;
color: #777777;
margin: 40px 0px 70px;
text-align: center;
}
以下是修改後的 HTML 主機檔案 **war/HelloWorld.html** 的內容
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello World</title>
<link rel = "stylesheet" href = "HelloWorld.css"/>
<script language = "javascript" src = "helloworld/helloworld.nocache.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<iframe src = "javascript:''"id = "__gwt_historyFrame"
style = "width:0;height:0;border:0"></iframe>
<h1> History Class Demonstration</h1>
<div id = "gwtContainer"></div>
</body>
</html>
讓我們使用以下 Java 檔案 **src/com.tutorialspoint/HelloWorld.java** 的內容,演示 GWT 程式碼中的歷史記錄管理。
package com.tutorialspoint.client;
import com.google.gwt.core.client.EntryPoint;
import com.google.gwt.event.logical.shared.SelectionEvent;
import com.google.gwt.event.logical.shared.SelectionHandler;
import com.google.gwt.event.logical.shared.ValueChangeEvent;
import com.google.gwt.event.logical.shared.ValueChangeHandler;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.History;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.HTML;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.RootPanel;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.TabPanel;
public class HelloWorld implements EntryPoint {
/**
* This is the entry point method.
*/
public void onModuleLoad() {
/* create a tab panel to carry multiple pages */
final TabPanel tabPanel = new TabPanel();
/* create pages */
HTML firstPage = new HTML("<h1>We are on first Page.</h1>");
HTML secondPage = new HTML("<h1>We are on second Page.</h1>");
HTML thirdPage = new HTML("<h1>We are on third Page.</h1>");
String firstPageTitle = "First Page";
String secondPageTitle = "Second Page";
String thirdPageTitle = "Third Page";
tabPanel.setWidth("400");
/* add pages to tabPanel*/
tabPanel.add(firstPage, firstPageTitle);
tabPanel.add(secondPage,secondPageTitle);
tabPanel.add(thirdPage, thirdPageTitle);
/* add tab selection handler */
tabPanel.addSelectionHandler(new SelectionHandler<Integer>() {
@Override
public void onSelection(SelectionEvent<Integer> event) {
/* add a token to history containing pageIndex
History class will change the URL of application
by appending the token to it.
*/
History.newItem("pageIndex" + event.getSelectedItem());
}
});
/* add value change handler to History
this method will be called, when browser's
Back button or Forward button are clicked
and URL of application changes.
*/
History.addValueChangeHandler(new ValueChangeHandler<String>() {
@Override
public void onValueChange(ValueChangeEvent<String> event) {
String historyToken = event.getValue();
/* parse the history token */
try {
if (historyToken.substring(0, 9).equals("pageIndex")) {
String tabIndexToken = historyToken.substring(9, 10);
int tabIndex = Integer.parseInt(tabIndexToken);
/* select the specified tab panel */
tabPanel.selectTab(tabIndex);
} else {
tabPanel.selectTab(0);
}
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
tabPanel.selectTab(0);
}
}
});
/* select the first tab by default */
tabPanel.selectTab(0);
/* add controls to RootPanel */
RootPanel.get().add(tabPanel);
}
}
完成所有更改後,讓我們像在 GWT - 建立應用程式 章節中所做的那樣,在開發模式下編譯並執行應用程式。如果您的應用程式一切正常,這將產生以下結果 -
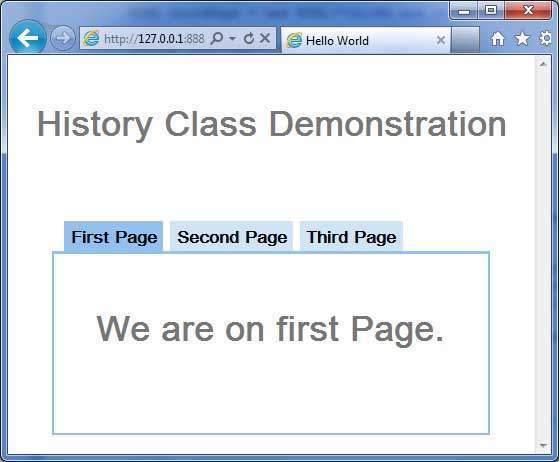
現在點選每個選項卡以選擇不同的頁面。
您應該注意到,當選擇每個選項卡時,應用程式 URL 會更改,並且 #pageIndex 會新增到 URL 中。
您還可以看到瀏覽器的後退和前進按鈕現在已啟用。
使用瀏覽器的後退和前進按鈕,您將看到不同的選項卡被相應地選中。
GWT - 書籤支援
GWT 使用 History 類支援瀏覽器歷史記錄管理,您可以參考 *GWT - History 類* 章節。
GWT 使用術語 **標記**,它只是一個字串,應用程式可以解析它以返回到特定狀態。應用程式將此標記儲存在瀏覽器的歷史記錄中作為 URL 片段。
在 *GWT - History 類* 章節中,我們透過編寫程式碼處理標記的建立和在歷史記錄中的設定。
在本文中,我們將討論一個特殊的部件 Hyperlink,它會自動為我們建立標記和管理歷史記錄,並使應用程式能夠新增書籤。
新增書籤示例
此示例將引導您完成簡單的步驟,演示 GWT 應用程式的新增書籤功能。
以下步驟更新我們在 *GWT - 建立應用程式* 章節中建立的 GWT 應用程式:
| 步驟 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 在 _GWT - 建立應用程式_ 章節中說明的 _com.tutorialspoint_ 包下建立一個名為 _HelloWorld_ 的專案。 |
| 2 | 修改 _HelloWorld.gwt.xml_、_HelloWorld.css_、_HelloWorld.html_ 和 _HelloWorld.java_,如下所述。保持其餘檔案不變。 |
| 3 | 編譯並執行應用程式以驗證實現邏輯的結果。 |
以下是修改後的模組描述符 **src/com.tutorialspoint/HelloWorld.gwt.xml** 的內容。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <module rename-to = 'helloworld'> <!-- Inherit the core Web Toolkit stuff. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.User'/> <!-- Inherit the default GWT style sheet. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.theme.clean.Clean'/> <!-- Specify the app entry point class. --> <entry-point class = 'com.tutorialspoint.client.HelloWorld'/> <!-- Specify the paths for translatable code --> <source path = 'client'/> <source path = 'shared'/> </module>
以下是修改後的樣式表文件 **war/HelloWorld.css** 的內容。
body {
text-align: center;
font-family: verdana, sans-serif;
}
h1 {
font-size: 2em;
font-weight: bold;
color: #777777;
margin: 40px 0px 70px;
text-align: center;
}
以下是修改後的 HTML 主機檔案 **war/HelloWorld.html** 的內容
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello World</title>
<link rel = "stylesheet" href = "HelloWorld.css"/>
<script language = "javascript" src = "helloworld/helloworld.nocache.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<iframe src = "javascript:''"id = "__gwt_historyFrame"
style = "width:0;height:0;border:0"></iframe>
<h1> Bookmarking Demonstration</h1>
<div id = "gwtContainer"></div>
</body>
</html>
讓我們使用以下 Java 檔案 **src/com.tutorialspoint/HelloWorld.java** 的內容,演示 GWT 程式碼中的新增書籤功能。
package com.tutorialspoint.client;
import com.google.gwt.core.client.EntryPoint;
import com.google.gwt.event.logical.shared.ValueChangeEvent;
import com.google.gwt.event.logical.shared.ValueChangeHandler;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.History;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.HTML;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.HorizontalPanel;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Hyperlink;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.RootPanel;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.TabPanel;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.VerticalPanel;
public class HelloWorld implements EntryPoint {
private TabPanel tabPanel;
private void selectTab(String historyToken){
/* parse the history token */
try {
if (historyToken.substring(0, 9).equals("pageIndex")) {
String tabIndexToken = historyToken.substring(9, 10);
int tabIndex = Integer.parseInt(tabIndexToken);
/* Select the specified tab panel */
tabPanel.selectTab(tabIndex);
} else {
tabPanel.selectTab(0);
}
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
tabPanel.selectTab(0);
}
}
/**
* This is the entry point method.
*/
public void onModuleLoad() {
/* create a tab panel to carry multiple pages */
tabPanel = new TabPanel();
/* create pages */
HTML firstPage = new HTML("<h1>We are on first Page.</h1>");
HTML secondPage = new HTML("<h1>We are on second Page.</h1>");
HTML thirdPage = new HTML("<h1>We are on third Page.</h1>");
String firstPageTitle = "First Page";
String secondPageTitle = "Second Page";
String thirdPageTitle = "Third Page";
Hyperlink firstPageLink = new Hyperlink("1", "pageIndex0");
Hyperlink secondPageLink = new Hyperlink("2", "pageIndex1");
Hyperlink thirdPageLink = new Hyperlink("3", "pageIndex2");
HorizontalPanel linksHPanel = new HorizontalPanel();
linksHPanel.setSpacing(10);
linksHPanel.add(firstPageLink);
linksHPanel.add(secondPageLink);
linksHPanel.add(thirdPageLink);
/* If the application starts with no history token,
redirect to a pageIndex0 */
String initToken = History.getToken();
if (initToken.length() == 0) {
History.newItem("pageIndex0");
initToken = "pageIndex0";
}
tabPanel.setWidth("400");
/* add pages to tabPanel*/
tabPanel.add(firstPage, firstPageTitle);
tabPanel.add(secondPage,secondPageTitle);
tabPanel.add(thirdPage, thirdPageTitle);
/* add value change handler to History
* this method will be called, when browser's Back button
* or Forward button are clicked.
* and URL of application changes.
* */
History.addValueChangeHandler(new ValueChangeHandler<String>() {
@Override
public void onValueChange(ValueChangeEvent<String> event) {
selectTab(event.getValue());
}
});
selectTab(initToken);
VerticalPanel vPanel = new VerticalPanel();
vPanel.setSpacing(10);
vPanel.add(tabPanel);
vPanel.add(linksHPanel);
/* add controls to RootPanel */
RootPanel.get().add(vPanel);
}
}
完成所有更改後,讓我們像在 GWT - 建立應用程式 章節中所做的那樣,在開發模式下編譯並執行應用程式。如果您的應用程式一切正常,這將產生以下結果 -
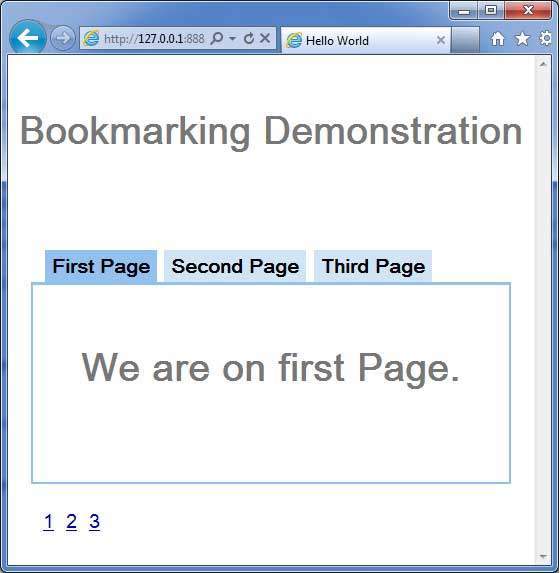
現在點選 1、2 或 3。您可以注意到選項卡會隨著索引更改。
您應該注意到,當您點選 1、2 或 3 時,應用程式 URL 會更改,並且 #pageIndex 會新增到 URL 中
您還可以看到瀏覽器的後退和前進按鈕現在已啟用。
使用瀏覽器的後退和前進按鈕,您將看到不同的選項卡被相應地選中。
右鍵點選 1、2 或 3。您可以看到諸如開啟、在新視窗中開啟、在新選項卡中開啟、新增到收藏夾等選項。
右鍵點選 3。選擇新增到收藏夾。將書籤儲存為頁面 3。
開啟收藏夾並選擇頁面 3。您將看到第三個選項卡被選中。
GWT - 日誌框架
日誌框架模擬 java.util.logging,因此它使用相同的語法並具有與伺服器端日誌程式碼相同的行為
GWT 日誌使用 .gwt.xml 檔案進行配置。
我們可以配置日誌的啟用/停用;我們可以啟用/停用特定的處理程式,並更改預設的日誌級別。
日誌記錄器的型別
日誌記錄器以樹狀結構組織,根日誌記錄器位於樹的根部。
日誌記錄器的名稱使用 **.** 分隔名稱的部分來確定父子關係。
例如,如果我們有兩個日誌記錄器 Hospital.room1 和 Hospital.room2,那麼它們是兄弟節點,它們的父節點是名為 Hospital 的日誌記錄器。Hospital 日誌記錄器(以及任何名稱不包含點“.”的日誌記錄器)的父節點是根日誌記錄器。
private static Logger room1Logger = Logger.getLogger("Hospital.room1");
private static Logger room2Logger = Logger.getLogger("Hospital.room2");
private static Logger hospitalLogger = Logger.getLogger("Hospital");
private static Logger rootLogger = Logger.getLogger("");
日誌處理程式
GWT 提供預設的處理程式,這些處理程式將顯示使用日誌記錄器生成的日誌條目。
| 處理程式 | 日誌輸出到 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| SystemLogHandler | 標準輸出 | 這些訊息只能在 DevMode 視窗的開發模式下看到。 |
| DevelopmentModeLogHandler | DevMode 視窗 | 透過呼叫方法 GWT.log 進行日誌記錄。這些訊息只能在 DevMode 視窗的開發模式下看到。 |
| ConsoleLogHandler | JavaScript 控制檯 | 日誌輸出到 JavaScript 控制檯,Firebug Lite(用於 IE)、Safari 和 Chrome 使用該控制檯。 |
| FirebugLogHandler | Firebug | 日誌輸出到 Firebug 控制檯。 |
| PopupLogHandler | 彈出視窗 | 日誌輸出到應用程式左上角的彈出視窗(當啟用此處理程式時)。 |
| SimpleRemoteLogHandler | 伺服器 | 此處理程式將日誌訊息傳送到伺服器,在那裡將使用伺服器端日誌記錄機制記錄它們。 |
在 GWT 應用程式中配置日誌記錄
需要配置 HelloWorld.gwt.xml 檔案以啟用 GWT 日誌記錄,如下所示:
# add logging module <inherits name = "com.google.gwt.logging.Logging"/> # To change the default logLevel <set-property name = "gwt.logging.logLevel" value = "SEVERE"/> # To enable logging <set-property name = "gwt.logging.enabled" value = "TRUE"/> # To disable a popup Handler <set-property name = "gwt.logging.popupHandler" value = "DISABLED" />
使用日誌記錄器記錄使用者操作
/* Create Root Logger */
private static Logger rootLogger = Logger.getLogger("");
...
rootLogger.log(Level.SEVERE, "pageIndex selected: " + event.getValue());
...
日誌框架示例
此示例將引導您完成簡單的步驟,演示 GWT 應用程式的日誌記錄功能。按照以下步驟更新我們在 *GWT - 建立應用程式* 章節中建立的 GWT 應用程式:
| 步驟 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | 在 _GWT - 建立應用程式_ 章節中說明的 _com.tutorialspoint_ 包下建立一個名為 _HelloWorld_ 的專案。 |
| 2 | 修改 _HelloWorld.gwt.xml_、_HelloWorld.css_、_HelloWorld.html_ 和 _HelloWorld.java_,如下所述。保持其餘檔案不變。 |
| 3 | 編譯並執行應用程式以驗證實現邏輯的結果。 |
以下是修改後的模組描述符 **src/com.tutorialspoint/HelloWorld.gwt.xml** 的內容。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <module rename-to = 'helloworld'> <!-- Inherit the core Web Toolkit stuff. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.User'/> <!-- Inherit the default GWT style sheet. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.theme.clean.Clean'/> <inherits name = "com.google.gwt.logging.Logging"/> <!-- Specify the app entry point class. --> <entry-point class = 'com.tutorialspoint.client.HelloWorld'/> <!-- Specify the paths for translatable code --> <source path = 'client'/> <source path = 'shared'/> <set-property name = "gwt.logging.logLevel" value="SEVERE"/> <set-property name = "gwt.logging.enabled" value = "TRUE"/> <set-property name = "gwt.logging.popupHandler" value= "DISABLED" /> </module>
以下是修改後的樣式表文件 **war/HelloWorld.css** 的內容。
body {
text-align: center;
font-family: verdana, sans-serif;
}
h1 {
font-size: 2em;
font-weight: bold;
color: #777777;
margin: 40px 0px 70px;
text-align: center;
}
以下是修改後的 HTML 主機檔案 **war/HelloWorld.html** 的內容
<html>
<head>
<title>Hello World</title>
<link rel = "stylesheet" href = "HelloWorld.css"/>
<script language = "javascript" src = "helloworld/helloworld.nocache.js">
</script>
</head>
<body>
<iframe src = "javascript:''"id = "__gwt_historyFrame"
style = "width:0;height:0;border:0"></iframe>
<h1> Logging Demonstration</h1>
<div id = "gwtContainer"></div>
</body>
</html>
讓我們使用以下 Java 檔案 **src/com.tutorialspoint/HelloWorld.java** 的內容,演示 GWT 程式碼中的新增書籤功能。
package com.tutorialspoint.client;
import java.util.logging.Level;
import java.util.logging.Logger;
import com.google.gwt.core.client.EntryPoint;
import com.google.gwt.event.logical.shared.ValueChangeEvent;
import com.google.gwt.event.logical.shared.ValueChangeHandler;
import com.google.gwt.logging.client.HasWidgetsLogHandler;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.History;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.HTML;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.HorizontalPanel;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.Hyperlink;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.RootPanel;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.TabPanel;
import com.google.gwt.user.client.ui.VerticalPanel;
public class HelloWorld implements EntryPoint {
private TabPanel tabPanel;
/* Create Root Logger */
private static Logger rootLogger = Logger.getLogger("");
private VerticalPanel customLogArea;
private void selectTab(String historyToken){
/* parse the history token */
try {
if (historyToken.substring(0, 9).equals("pageIndex")) {
String tabIndexToken = historyToken.substring(9, 10);
int tabIndex = Integer.parseInt(tabIndexToken);
/* Select the specified tab panel */
tabPanel.selectTab(tabIndex);
} else {
tabPanel.selectTab(0);
}
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
tabPanel.selectTab(0);
}
}
/**
* This is the entry point method.
*/
public void onModuleLoad() {
/* create a tab panel to carry multiple pages */
tabPanel = new TabPanel();
/* create pages */
HTML firstPage = new HTML("<h1>We are on first Page.</h1>");
HTML secondPage = new HTML("<h1>We are on second Page.</h1>");
HTML thirdPage = new HTML("<h1>We are on third Page.</h1>");
String firstPageTitle = "First Page";
String secondPageTitle = "Second Page";
String thirdPageTitle = "Third Page";
Hyperlink firstPageLink = new Hyperlink("1", "pageIndex0");
Hyperlink secondPageLink = new Hyperlink("2", "pageIndex1");
Hyperlink thirdPageLink = new Hyperlink("3", "pageIndex2");
HorizontalPanel linksHPanel = new HorizontalPanel();
linksHPanel.setSpacing(10);
linksHPanel.add(firstPageLink);
linksHPanel.add(secondPageLink);
linksHPanel.add(thirdPageLink);
/* If the application starts with no history token,
redirect to a pageIndex0 */
String initToken = History.getToken();
if (initToken.length() == 0) {
History.newItem("pageIndex0");
initToken = "pageIndex0";
}
tabPanel.setWidth("400");
/* add pages to tabPanel*/
tabPanel.add(firstPage, firstPageTitle);
tabPanel.add(secondPage,secondPageTitle);
tabPanel.add(thirdPage, thirdPageTitle);
/* add value change handler to History
* this method will be called, when browser's Back button
* or Forward button are clicked.
* and URL of application changes.
* */
History.addValueChangeHandler(new ValueChangeHandler<String>() {
@Override
public void onValueChange(ValueChangeEvent<String> event) {
selectTab(event.getValue());
rootLogger.log(Level.SEVERE, "pageIndex selected: "
+ event.getValue());
}
});
selectTab(initToken);
VerticalPanel vPanel = new VerticalPanel();
vPanel.setSpacing(10);
vPanel.add(tabPanel);
vPanel.add(linksHPanel);
customLogArea = new VerticalPanel();
vPanel.add(customLogArea);
/* an example of using own custom logging area. */
rootLogger.addHandler(new HasWidgetsLogHandler(customLogArea));
/* add controls to RootPanel */
RootPanel.get().add(vPanel);
}
}
完成所有更改後,讓我們像在 GWT - 建立應用程式 章節中所做的那樣,在開發模式下編譯並執行應用程式。如果您的應用程式一切正常,這將產生以下結果 -
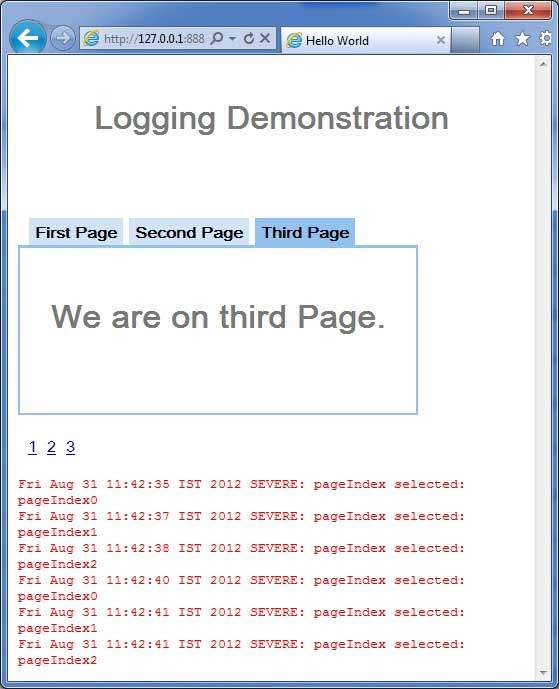
現在點選 1、2 或 3。您可以注意到,當您點選 1、2 或 3 時,您可以看到日誌正在列印,顯示 pageIndex。檢查 Eclipse 中的控制檯輸出。您可以在 Eclipse 控制檯中看到日誌正在列印。
Fri Aug 31 11:42:35 IST 2012 SEVERE: pageIndex selected: pageIndex0 Fri Aug 31 11:42:37 IST 2012 SEVERE: pageIndex selected: pageIndex1 Fri Aug 31 11:42:38 IST 2012 SEVERE: pageIndex selected: pageIndex2 Fri Aug 31 11:42:40 IST 2012 SEVERE: pageIndex selected: pageIndex0 Fri Aug 31 11:42:41 IST 2012 SEVERE: pageIndex selected: pageIndex1 Fri Aug 31 11:42:41 IST 2012 SEVERE: pageIndex selected: pageIndex2
現在更新模組描述符 **src/com.tutorialspoint/HelloWorld.gwt.xml** 以啟用 popupHandler。
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?> <module rename-to = 'helloworld'> <!-- Inherit the core Web Toolkit stuff. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.User'/> <!-- Inherit the default GWT style sheet. --> <inherits name = 'com.google.gwt.user.theme.clean.Clean'/> <inherits name = "com.google.gwt.logging.Logging"/> <!-- Specify the app entry point class. --> <entry-point class = 'com.tutorialspoint.client.HelloWorld'/> <!-- Specify the paths for translatable code --> <source path = 'client'/> <source path = 'shared'/> <set-property name = "gwt.logging.logLevel" value = "SEVERE"/> <set-property name = "gwt.logging.enabled" value = "TRUE"/> <set-property name="gwt.logging.popupHandler" value = "ENABLED" /> </module>
完成所有更改後,透過重新整理瀏覽器視窗重新載入應用程式(按 F5/瀏覽器的重新整理按鈕)。注意現在應用程式左上角出現了一個彈出視窗。
現在點選 1、2 或 3。您可以注意到,當您點選 1、2 或 3 時,您可以在彈出視窗中看到日誌正在列印,顯示 pageIndex。