
- 敏捷資料科學教程
- 敏捷資料科學 - 主頁
- 敏捷資料科學 - 簡介
- 方法論概念
- 敏捷資料科學 - 流程
- 敏捷工具和安裝
- 敏捷中的資料處理
- SQL 與 NoSQL
- NoSQL 和資料流程式設計
- 收集和顯示記錄
- 資料視覺化
- 資料增強
- 使用報告
- 預測的作用
- 使用 PySpark 提取特徵
- 構建迴歸模型
- 部署預測系統
- 敏捷資料科學 - SparkML
- 修復預測問題
- 提高預測效能
- 透過敏捷和資料科學創造更好的場景
- 敏捷的實施
- 敏捷資料科學有用資源
- 敏捷資料科學 - 快速指南
- 敏捷資料科學 - 資源
- 敏捷資料科學 - 討論
敏捷資料科學 - 資料增強
資料增強是指用於增強、改進和最佳化原始資料的一系列流程。它指有用的資料轉換(將原始資料轉換為有用的資訊)。資料增強流程專注於將資料變成現代業務或企業的寶貴資料資產。
最常見的資料增強流程包括使用特定的決策演算法來糾正資料庫中的拼寫錯誤或印刷錯誤。資料增強工具將有用的資訊新增到簡單的資料庫表中。
考慮以下單詞拼寫糾正程式碼 -
import re
from collections import Counter
def words(text): return re.findall(r'\w+', text.lower())
WORDS = Counter(words(open('big.txt').read()))
def P(word, N=sum(WORDS.values())):
"Probabilities of words"
return WORDS[word] / N
def correction(word):
"Spelling correction of word"
return max(candidates(word), key=P)
def candidates(word):
"Generate possible spelling corrections for word."
return (known([word]) or known(edits1(word)) or known(edits2(word)) or [word])
def known(words):
"The subset of `words` that appear in the dictionary of WORDS."
return set(w for w in words if w in WORDS)
def edits1(word):
"All edits that are one edit away from `word`."
letters = 'abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz'
splits = [(word[:i], word[i:]) for i in range(len(word) + 1)]
deletes = [L + R[1:] for L, R in splits if R]
transposes = [L + R[1] + R[0] + R[2:] for L, R in splits if len(R)>1]
replaces = [L + c + R[1:] for L, R in splits if R for c in letters]
inserts = [L + c + R for L, R in splits for c in letters]
return set(deletes + transposes + replaces + inserts)
def edits2(word):
"All edits that are two edits away from `word`."
return (e2 for e1 in edits1(word) for e2 in edits1(e1))
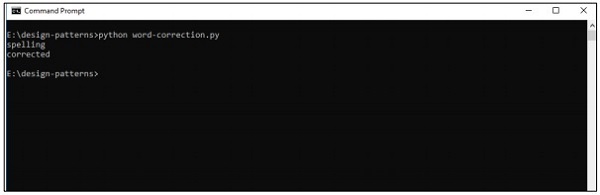
print(correction('speling'))
print(correction('korrectud'))
在該程式中,我們將在包含已更正單詞的“big.txt”中進行匹配。單詞與文字檔案中包含的單詞匹配,並相應地列印適當的結果。
輸出
上述程式碼將生成以下輸出 -
廣告