
- SciPy 教程
- SciPy - 主頁
- SciPy - 介紹
- SciPy - 環境設定
- SciPy - 基本功能
- SciPy - 叢集
- SciPy - 常量
- SciPy - FFTpack
- SciPy - 整合
- SciPy - 插值
- SciPy - 輸入和輸出
- SciPy - 線性代數
- SciPy - N維影像
- SciPy - 最佳化
- SciPy - 統計
- SciPy - 圖論
- SciPy - 空間
- SciPy - 正交距離迴歸
- SciPy - 特殊包
- SciPy 有用資源
- SciPy - 參考
- SciPy - 快速指南
- SciPy - 有用資源
- SciPy - 討論
SciPy - integrate.romb() 方法
SciPy integrate.romb() 方法用於執行數值積分或羅姆伯格積分任務。此方法還幫助我們根據樣本/座標點繪製圖形。
語法
以下為 SciPy integrate.romb() 方法的語法 -
romb(y, dx = int_val/float_val/1.0)
引數
此函式接受以下引數 -
- y: 此引數確定離散點上的陣列函式,並且這些點被認為是均勻間隔開的。
- dx: 此引數確定點之間的間隔,如果未指定,其預設值為 1.0。
返回值
此方法返回型別為浮點數的估計值。
示例 1
以下為展示簡單的積分函式 SciPy integrate.romb() 方法,即 f(x) = x2,其中積分割槽間在 0 到 1 之間。最終值基於五個離散點。
import numpy as np from scipy import integrate # define the function values at discrete points x = np.linspace(0, 1, 5) y = x**2 # calculate the integral res_integral = integrate.romb(y, dx=x[1] - x[0]) # display the result print(res_integral)
輸出
以上程式碼產生以下結果 -
0.3333333333333333
示例 2
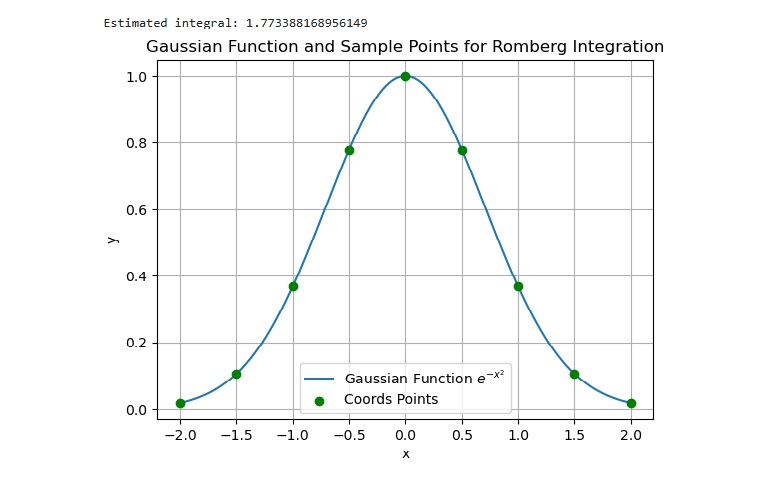
這個程式演示了高斯函式(即 e-x2)在 -2 到 2 之間區間的數值積分,並且該函式值被表示為九個點(x 軸)。
import numpy as np
from scipy.integrate import romb
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# define the function values at discrete points
x = np.linspace(-2, 2, 9)
y = np.exp(-x**2)
# calculate the integral
res_integral = romb(y, dx=x[1] - x[0])
# display the result
print(f"Estimated integral: {res_integral}")
# plot the Gaussian function and the points used in Romberg integration
x_fine = np.linspace(-2, 2, 1000)
y_fine = np.exp(-x_fine**2)
plt.plot(x_fine, y_fine, label='Gaussian Function $e^{-x^2}$')
plt.scatter(x, y, color='green', zorder=5, label='coords Points')
plt.title('Gaussian Function and Sample Points for Romberg Integration')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
輸出
以上程式碼產生以下結果 -
scipy_reference.htm
廣告