- Flutter 教程
- Flutter - 首頁
- Flutter - 簡介
- Flutter - 安裝
- 在 Android Studio 中建立簡單應用程式
- Flutter - 架構應用程式
- Dart 程式設計入門
- Flutter - Widget 入門
- Flutter - 佈局入門
- Flutter - 手勢入門
- Flutter - 狀態管理
- Flutter - 動畫
- Flutter - 編寫 Android 特定程式碼
- Flutter - 編寫 iOS 特定程式碼
- Flutter - 包入門
- Flutter - 訪問 REST API
- Flutter - 資料庫概念
- Flutter - 國際化
- Flutter - 測試
- Flutter - 部署
- Flutter - 開發工具
- Flutter - 編寫高階應用程式
- Flutter - 總結
- Flutter 有用資源
- Flutter - 快速指南
- Flutter - 有用資源
- Flutter - 討論
Flutter - 快速指南
Flutter - 簡介
通常,開發移動應用程式是一項複雜且具有挑戰性的任務。有很多框架可用於開發移動應用程式。Android 提供了一個基於 Java 語言的原生框架,而 iOS 提供了一個基於 Objective-C/Swift 語言的原生框架。
但是,要開發支援這兩個作業系統的應用程式,我們需要使用兩種不同的框架用兩種不同的語言進行編碼。為了幫助克服這種複雜性,存在支援這兩個作業系統的移動框架。這些框架從簡單的基於 HTML 的混合移動應用程式框架(使用 HTML 作為使用者介面和 JavaScript 作為應用程式邏輯)到複雜的特定語言框架(承擔將程式碼轉換為原生程式碼的繁重工作)不等。無論其簡單性或複雜性如何,這些框架總是有很多缺點,其中一個主要缺點是其效能緩慢。
在這種情況下,Flutter——一個基於 Dart 語言的簡單且高效能的框架,透過直接在作業系統的畫布上渲染 UI 而不是透過原生框架來提供高效能。
Flutter 還提供了許多現成的 Widget(UI)來建立現代應用程式。這些 Widget 已針對移動環境進行了最佳化,使用 Widget 設計應用程式就像設計 HTML 一樣簡單。
具體來說,Flutter 應用程式本身就是一個 Widget。Flutter Widget 也支援動畫和手勢。應用程式邏輯基於響應式程式設計。Widget 可以選擇具有狀態。透過更改 Widget 的狀態,Flutter 將自動(響應式程式設計)比較 Widget 的狀態(舊的和新的),並僅使用必要的更改渲染 Widget,而不是重新渲染整個 Widget。
我們將在接下來的章節中討論完整的架構。
Flutter 的特性
Flutter 框架為開發人員提供了以下特性:
現代且響應式的框架。
使用 Dart 程式語言,非常容易學習。
快速開發。
美觀流暢的使用者介面。
龐大的 Widget 目錄。
在多個平臺上執行相同的 UI。
高效能應用程式。
Flutter 的優勢
Flutter 配備了美觀且可自定義的 Widget,可實現高效能和出色的移動應用程式。它滿足所有自定義需求和要求。除此之外,Flutter 還提供了許多其他優勢,如下所述:
Dart 擁有大量的軟體包儲存庫,可讓您擴充套件應用程式的功能。
開發人員只需要為兩個應用程式(Android 和 iOS 平臺)編寫一個程式碼庫。Flutter 未來也可能擴充套件到其他平臺。
Flutter 需要較少的測試。由於其單一程式碼庫,如果我們為這兩個平臺編寫一次自動化測試就足夠了。
Flutter 的簡單性使其成為快速開發的理想選擇。其自定義能力和可擴充套件性使其更加強大。
使用 Flutter,開發人員可以完全控制 Widget 及其佈局。
Flutter 提供了很棒的開發者工具,以及令人驚歎的熱過載功能。
Flutter 的缺點
儘管 Flutter 擁有眾多優點,但它也存在以下缺點:
由於它是用 Dart 語言編寫的,因此開發人員需要學習新的語言(儘管它很容易學習)。
現代框架儘可能地將邏輯和 UI 分開,但在 Flutter 中,使用者介面和邏輯是混合在一起的。我們可以透過智慧編碼和使用高階模組來分離使用者介面和邏輯來克服這一點。
Flutter 只是另一個用於建立移動應用程式的框架。在使用者數量龐大的細分市場中,開發人員難以選擇合適的開發工具。
Flutter - 安裝
本章將詳細指導您在本地計算機上安裝 Flutter。
在 Windows 上安裝
在本節中,讓我們看看如何在 Windows 系統中安裝Flutter SDK及其要求。
步驟 1 - 訪問 URL,https://flutter.club.tw/docs/get-started/install/windows 並下載最新的 Flutter SDK。截至 2019 年 4 月,版本為 1.2.1,檔案為 flutter_windows_v1.2.1-stable.zip。
步驟 2 - 將 zip 壓縮檔案解壓縮到一個資料夾中,例如 C:\flutter\
步驟 3 - 更新系統路徑以包含 flutter bin 目錄。
步驟 4 - Flutter 提供了一個工具 flutter doctor,用於檢查是否滿足 Flutter 開發的所有要求。
flutter doctor
步驟 5 - 執行上述命令將分析系統並顯示其報告,如下所示:
Doctor summary (to see all details, run flutter doctor -v): [√] Flutter (Channel stable, v1.2.1, on Microsoft Windows [Version 10.0.17134.706], locale en-US) [√] Android toolchain - develop for Android devices (Android SDK version 28.0.3) [√] Android Studio (version 3.2) [√] VS Code, 64-bit edition (version 1.29.1) [!] Connected device ! No devices available ! Doctor found issues in 1 category.
該報告表明所有開發工具都可用,但裝置未連線。我們可以透過 USB 連線 Android 裝置或啟動 Android 模擬器來解決此問題。
步驟 6 - 安裝最新的 Android SDK(如果 flutter doctor 報告需要)。
步驟 7 - 安裝最新的 Android Studio(如果 flutter doctor 報告需要)。
步驟 8 - 啟動 Android 模擬器或將真實的 Android 裝置連線到系統。
步驟 9 - 為 Android Studio 安裝 Flutter 和 Dart 外掛。它提供了啟動模板以建立新的 Flutter 應用程式,以及在 Android Studio 本身中執行和除錯 Flutter 應用程式的選項等。
開啟 Android Studio。
單擊檔案 → 設定 → 外掛。
選擇 Flutter 外掛並單擊安裝。
當提示安裝 Dart 外掛時,單擊是。
重新啟動 Android Studio。
在 macOS 上安裝
要在 macOS 上安裝 Flutter,您需要執行以下步驟:
步驟 1 - 訪問 URL,https://flutter.club.tw/docs/get-started/install/macos 並下載最新的 Flutter SDK。截至 2019 年 4 月,版本為 1.2.1,檔案為 flutter_macos_v1.2.1-stable.zip。
步驟 2 - 將 zip 壓縮檔案解壓縮到一個資料夾中,例如 /path/to/flutter
步驟 3 - 更新系統路徑以包含 flutter bin 目錄(在 ~/.bashrc 檔案中)。
> export PATH = "$PATH:/path/to/flutter/bin"
步驟 4 - 使用以下命令在當前會話中啟用更新的路徑,然後對其進行驗證。
source ~/.bashrc source $HOME/.bash_profile echo $PATH
Flutter 提供了一個工具 flutter doctor,用於檢查是否滿足 Flutter 開發的所有要求。它類似於 Windows 版本。
步驟 5 - 安裝最新的 XCode(如果 flutter doctor 報告需要)。
步驟 6 - 安裝最新的 Android SDK(如果 flutter doctor 報告需要)。
步驟 7 - 安裝最新的 Android Studio(如果 flutter doctor 報告需要)。
步驟 8 - 啟動 Android 模擬器或將真實的 Android 裝置連線到系統以開發 Android 應用程式。
步驟 9 - 開啟 iOS 模擬器或將真實的 iPhone 裝置連線到系統以開發 iOS 應用程式。
步驟 10 - 為 Android Studio 安裝 Flutter 和 Dart 外掛。它提供了啟動模板以建立新的 Flutter 應用程式,以及在 Android Studio 本身中執行和除錯 Flutter 應用程式的選項等。
開啟 Android Studio
單擊首選項 → 外掛
選擇 Flutter 外掛並單擊安裝
當提示安裝 Dart 外掛時,單擊是。
重新啟動 Android Studio。
在 Android Studio 中建立簡單應用程式
在本章中,讓我們建立一個簡單的Flutter應用程式,以瞭解在 Android Studio 中建立 Flutter 應用程式的基本知識。
步驟 1 - 開啟 Android Studio
步驟 2 - 建立 Flutter 專案。為此,請單擊檔案 → 新建 → 新建 Flutter 專案
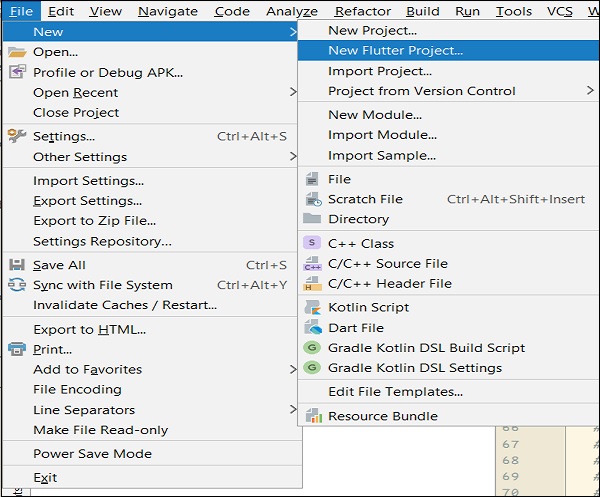
步驟 3 - 選擇 Flutter 應用程式。為此,請選擇Flutter 應用程式並單擊下一步。
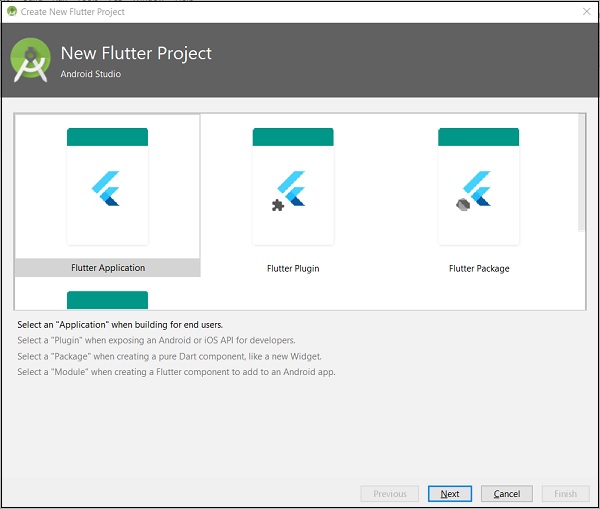
步驟 4 - 按如下所示配置應用程式,然後單擊下一步。
專案名稱:hello_app
Flutter SDK 路徑:<path_to_flutter_sdk>
專案位置:<path_to_project_folder>
描述:基於 Flutter 的 Hello World 應用程式
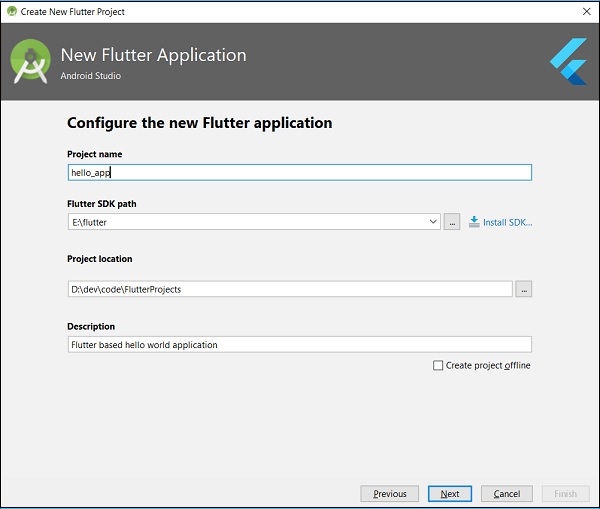
步驟 5 - 配置專案。
將公司域名設定為flutterapp.tutorialspoint.com,然後單擊完成。
步驟 6 - 輸入公司域名。
Android Studio 建立了一個功能最少的完全可用的 Flutter 應用程式。讓我們檢查一下應用程式的結構,然後更改程式碼以執行我們的任務。
應用程式的結構及其用途如下:
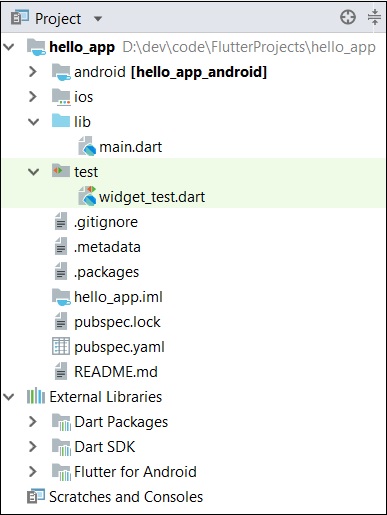
此處解釋了應用程式結構的各個元件:
android - 自動生成的原始碼以建立 Android 應用程式
ios - 自動生成的原始碼以建立 iOS 應用程式
lib - 包含使用 Flutter 框架編寫的 Dart 程式碼的主要資料夾
lib/main.dart - Flutter 應用程式的入口點
test - 包含用於測試 Flutter 應用程式的 Dart 程式碼的資料夾
test/widget_test.dart - 示例程式碼
.gitignore - Git 版本控制檔案
.metadata - 由 Flutter 工具自動生成
.packages - 自動生成以跟蹤 Flutter 包
.iml - Android Studio 使用的專案檔案
pubspec.yaml - 由Pub(Flutter 包管理器)使用
pubspec.lock - 由 Flutter 包管理器Pub自動生成
README.md - 用 Markdown 格式編寫的專案描述檔案
步驟 7 - 將lib/main.dart 檔案中的 Dart 程式碼替換為以下程式碼:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Hello World Demo Application',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: MyHomePage(title: 'Home page'),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatelessWidget {
MyHomePage({Key key, this.title}) : super(key: key);
final String title;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text(this.title),
),
body: Center(
child:
Text(
'Hello World',
)
),
);
}
}
讓我們逐行了解 Dart 程式碼。
第 1 行 - 匯入 Flutter 包material。material 是一個 Flutter 包,用於根據 Android 指定的材料設計指南建立使用者介面。
第 3 行 - 這是 Flutter 應用程式的入口點。呼叫runApp函式並向其傳遞MyApp類的物件。runApp函式的目的是將給定的 Widget 附加到螢幕上。
第 5-17 行 - Widget 用於在 Flutter 框架中建立 UI。StatelessWidget是一個 Widget,它不維護 Widget 的任何狀態。MyApp擴充套件了StatelessWidget並覆蓋了其build 方法。build方法的目的是建立應用程式 UI 的一部分。這裡,build方法使用MaterialApp,一個 Widget 來建立應用程式的根級 UI。它具有三個屬性 - title、theme和home。
title是應用程式的標題
theme是 Widget 的主題。在這裡,我們使用ThemeData類及其屬性primarySwatch將藍色設定為應用程式的整體顏色。
home 是應用程式的內部 UI,我們設定了另一個 Widget,MyHomePage
第 19 - 38 行 − MyHomePage 與 MyApp 相同,除了它返回 Scaffold 元件。Scaffold 是一個頂級元件,與 MaterialApp 元件並列使用,用於建立符合 Material Design 的 UI。它有兩個重要的屬性,appBar 用於顯示應用程式的標題,body 用於顯示應用程式的實際內容。AppBar 是另一個用於渲染應用程式標題的元件,我們已在 appBar 屬性中使用它。在 body 屬性中,我們使用了 Center 元件,它將它的子元件居中。Text 是最終的也是最內部的元件,用於顯示文字,它顯示在螢幕的中央。
步驟 8 − 現在,使用 執行 → 執行 main.dart 執行應用程式。
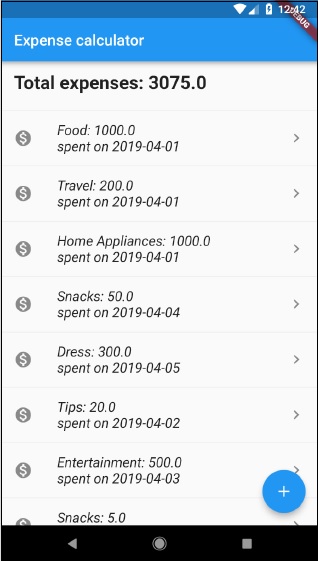
步驟 9 − 最後,應用程式的輸出如下所示 −

Flutter - 架構應用程式
在本章中,讓我們討論 Flutter 框架的架構。
元件
Flutter 框架的核心概念是 在 Flutter 中,一切皆為元件。元件基本上是用於建立應用程式使用者介面的使用者介面元件。
在 Flutter 中,應用程式本身就是一個元件。應用程式是頂級元件,其 UI 使用一個或多個子元件(元件)構建,這些子元件又使用其子元件構建。這種 組合性 特性幫助我們建立任何複雜度的使用者介面。
例如,Hello World 應用程式(在上一章中建立)的元件層次結構如下所示 −
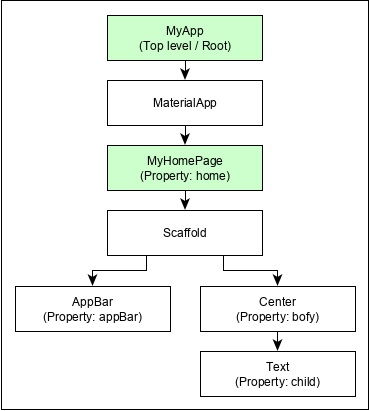
這裡以下幾點值得注意 −
MyApp 是使用者建立的元件,它使用 Flutter 原生元件 MaterialApp 構建。
MaterialApp 有一個 home 屬性來指定主頁的使用者介面,它又是一個使用者建立的元件 MyHomePage。
MyHomePage 使用另一個 Flutter 原生元件 Scaffold 構建
Scaffold 具有兩個屬性 – body 和 appBar
body 用於指定其主要使用者介面,appBar 用於指定其標題使用者介面
標題 UI 使用 Flutter 原生元件 AppBar 構建,主體 UI 使用 Center 元件構建。
Center 元件有一個屬性 Child,它引用實際內容,並且它使用 Text 元件構建
手勢
Flutter 元件透過一個特殊的元件 GestureDetector 支援互動。GestureDetector 是一個不可見的元件,能夠捕獲使用者互動,例如其子元件的點選、拖動等。Flutter 的許多原生元件都透過使用 GestureDetector 支援互動。我們還可以透過將 GestureDetector 元件與現有元件組合來將互動功能整合到現有元件中。我們將在後續章節中單獨學習手勢。
狀態的概念
Flutter 元件透過提供一個特殊的元件 StatefulWidget 來支援 狀態維護。元件需要從 StatefulWidget 元件派生才能支援狀態維護,所有其他元件都應該從 StatefulWidget 派生。Flutter 元件在原生中是 反應式 的。這類似於 reactjs,並且 StatefulWidget 只要其內部狀態發生變化就會自動重新渲染。重新渲染透過查詢舊元件 UI 和新元件 UI 之間的差異並僅渲染必要的更改來進行最佳化
層
Flutter 框架最重要的概念是,該框架根據複雜性被分為多個類別,並以複雜度遞減的順序清晰地排列在多層中。一層使用其緊鄰下一層構建。最頂層是特定於 Android 和 iOS 的元件。下一層包含所有 Flutter 原生元件。下一層是 渲染層,它是一個低階渲染器元件,渲染 Flutter 應用中的所有內容。層級一直延伸到核心平臺特定程式碼
Flutter 中層的概覽如下所示 −
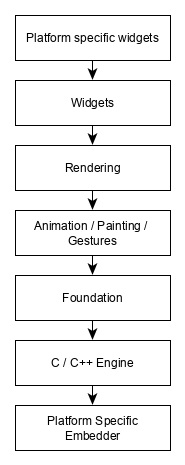
以下幾點總結了 Flutter 的架構 −
在 Flutter 中,一切皆為元件,一個複雜的元件是由已存在的元件組合而成的。
必要時可以使用 GestureDetector 元件整合互動功能。
必要時可以使用 StatefulWidget 元件維護元件的狀態。
Flutter 提供分層設計,以便可以根據任務的複雜性對任何層進行程式設計。
我們將在後續章節中詳細討論所有這些概念。
Flutter - Dart 程式設計入門
Dart 是一種開源通用程式語言。它最初由 Google 開發。Dart 是一種面向物件的語言,具有 C 風格的語法。它支援諸如介面、類等程式設計概念,與其他程式語言不同,Dart 不支援陣列。Dart 集合可用於複製資料結構,如陣列、泛型和可選型別。
以下程式碼顯示了一個簡單的 Dart 程式 −
void main() {
print("Dart language is easy to learn");
}
變數和資料型別
變數 是命名的儲存位置,資料型別 只是指與變數和函式關聯的資料的型別和大小。
Dart 使用 var 關鍵字宣告變數。var 的語法定義如下:
var name = 'Dart';
final 和 const 關鍵字用於宣告常量。它們定義如下 −
void main() {
final a = 12;
const pi = 3.14;
print(a);
print(pi);
}
Dart 語言支援以下資料型別 −
數字 − 用於表示數字字面量 - 整數和雙精度浮點數。
字串 − 表示一系列字元。字串值用單引號或雙引號指定。
布林值 − Dart 使用 bool 關鍵字表示布林值 - true 和 false。
列表和對映 − 用於表示物件的集合。一個簡單的列表可以定義如下 −。
void main() {
var list = [1,2,3,4,5];
print(list);
}
上面顯示的列表生成 [1,2,3,4,5] 列表。
對映可以定義如下 −
void main() {
var mapping = {'id': 1,'name':'Dart'};
print(mapping);
}
動態 − 如果未定義變數型別,則其預設型別為動態。以下示例說明了動態型別變數 −
void main() {
dynamic name = "Dart";
print(name);
}
決策和迴圈
決策塊在執行指令之前評估條件。Dart 支援 If、If..else 和 switch 語句。
迴圈用於重複執行程式碼塊,直到滿足特定條件。Dart 支援 for、for..in、while 和 do..while 迴圈。
讓我們瞭解一個關於控制語句和迴圈用法的簡單示例 −
void main() {
for( var i = 1 ; i <= 10; i++ ) {
if(i%2==0) {
print(i);
}
}
}
以上程式碼列印從 1 到 10 的偶數。
函式
函式是一組語句,它們一起執行特定的任務。讓我們看看這裡顯示的 Dart 中的一個簡單函式 −
void main() {
add(3,4);
}
void add(int a,int b) {
int c;
c = a+b;
print(c);
}
以上函式將兩個值相加,並生成 7 作為輸出。
面向物件程式設計
Dart 是一種面向物件的語言。它支援面向物件的程式設計特性,如類、介面等。
類是建立物件的藍圖。類定義包括以下內容 −
- 欄位
- Getter 和 Setter
- 建構函式
- 函式
現在,讓我們使用以上定義建立一個簡單的類 −
class Employee {
String name;
//getter method
String get emp_name {
return name;
}
//setter method
void set emp_name(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
//function definition
void result() {
print(name);
}
}
void main() {
//object creation
Employee emp = new Employee();
emp.name = "employee1";
emp.result(); //function call
}
Flutter - Widget 入門
正如我們在上一章中學到的,元件在 Flutter 框架中無處不在。我們已經在前面的章節中學習瞭如何在前面的章節中建立新的元件。
在本章中,讓我們瞭解建立元件背後的實際概念以及 Flutter 框架中提供的不同型別的元件。
讓我們檢查 Hello World 應用程式的 MyHomePage 元件。為此目的的程式碼如下所示 −
class MyHomePage extends StatelessWidget {
MyHomePage({Key key, this.title}) : super(key: key);
final String title;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text(this.title), ),
body: Center(child: Text( 'Hello World',)),
);
}
}
在這裡,我們透過擴充套件 StatelessWidget 建立了一個新的元件。
請注意,StatelessWidget 只需要在派生類中實現一個單一方法 build。build 方法獲取構建元件所需的上下文環境,透過 BuildContext 引數,並返回它構建的元件。
在程式碼中,我們使用了 title 作為建構函式引數之一,還使用了 Key 作為另一個引數。title 用於顯示標題,Key 用於在構建環境中識別元件。
在這裡,build 方法呼叫 Scaffold 的 build 方法,後者又呼叫 AppBar 和 Center 的 build 方法來構建其使用者介面。
最後,Center 的 build 方法呼叫 Text 的 build 方法。
為了更好地理解,下面給出了相同的視覺化表示 −
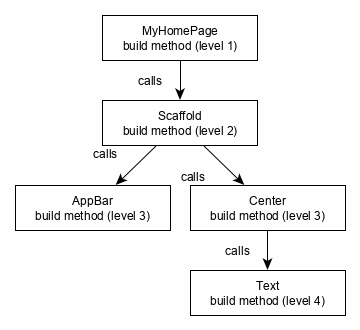
元件構建視覺化
在 Flutter 中,元件可以根據其功能分為多個類別,如下所示 −
- 平臺特定元件
- 佈局元件
- 狀態維護元件
- 平臺無關/基本元件
現在讓我們詳細討論每個元件。
平臺特定元件
Flutter 具有特定於特定平臺(Android 或 iOS)的元件。
Android 特定元件是根據 Android 作業系統的 Material Design 指南 設計的。Android 特定元件稱為 Material 元件。
iOS 特定元件是根據 Apple 的 Human Interface Guidelines 設計的,它們被稱為 Cupertino 元件。
一些最常用的 Material 元件如下 −
- Scaffold
- AppBar
- BottomNavigationBar
- TabBar
- TabBarView
- ListTile
- RaisedButton
- FloatingActionButton
- FlatButton
- IconButton
- DropdownButton
- PopupMenuButton
- ButtonBar
- TextField
- Checkbox
- Radio
- Switch
- Slider
- 日期和時間選擇器
- SimpleDialog
- AlertDialog
一些最常用的 Cupertino 元件如下 −
- CupertinoButton
- CupertinoPicker
- CupertinoDatePicker
- CupertinoTimerPicker
- CupertinoNavigationBar
- CupertinoTabBar
- CupertinoTabScaffold
- CupertinoTabView
- CupertinoTextField
- CupertinoDialog
- CupertinoDialogAction
- CupertinoFullscreenDialogTransition
- CupertinoPageScaffold
- CupertinoPageTransition
- CupertinoActionSheet
- CupertinoActivityIndicator
- CupertinoAlertDialog
- CupertinoPopupSurface
- CupertinoSlider
佈局元件
在 Flutter 中,可以透過組合一個或多個元件來建立元件。為了將多個元件組合成一個元件,Flutter 提供了大量具有佈局功能的元件。例如,可以使用 Center 元件將子元件居中。
一些流行的佈局元件如下 −
容器(Container) - 一個使用BoxDecoration部件裝飾的矩形框,包含背景、邊框和陰影。
居中(Center) - 將其子部件居中。
行(Row) - 將其子部件水平排列。
列(Column) - 將其子部件垂直排列。
堆疊(Stack) - 將一個部件疊加在另一個部件之上。
我們將在後續的佈局部件簡介章節中詳細介紹佈局部件。
狀態維護元件
在Flutter中,所有部件都派生自StatelessWidget或StatefulWidget。
派生自StatelessWidget的部件不包含任何狀態資訊,但它可能包含派生自StatefulWidget的部件。應用程式的動態特性來自於部件的互動行為以及互動過程中狀態的變化。例如,點選一個計數器按鈕將使計數器的內部狀態增加/減少1,並且Flutter部件的響應特性將使用新的狀態資訊自動重新渲染部件。
我們將在後續的狀態管理章節中詳細學習StatefulWidget部件的概念。
平臺無關/基本元件
Flutter提供了大量的基本部件,可以以平臺無關的方式建立簡單和複雜的使用者介面。讓我們在本節中瞭解一些基本部件。
文字(Text)
Text部件用於顯示一段字串。可以使用style屬性和TextStyle類設定字串的樣式。此目的的示例程式碼如下:
Text('Hello World!', style: TextStyle(fontWeight: FontWeight.bold))
Text部件有一個特殊的建構函式Text.rich,它接受型別為TextSpan的子部件來指定具有不同樣式的字串。TextSpan部件本質上是遞迴的,它接受TextSpan作為其子部件。此目的的示例程式碼如下:
Text.rich(
TextSpan(
children: <TextSpan>[
TextSpan(text: "Hello ", style:
TextStyle(fontStyle: FontStyle.italic)),
TextSpan(text: "World", style:
TextStyle(fontWeight: FontWeight.bold)),
],
),
)
Text部件最重要的屬性如下:
maxLines,int - 顯示的最大行數
overflow,TextOverFlow - 使用TextOverFlow類指定如何處理視覺溢位
style,TextStyle - 使用TextStyle類指定字串的樣式
textAlign,TextAlign - 使用TextAlign類指定文字的對齊方式,例如右對齊、左對齊、兩端對齊等。
textDirection,TextDirection - 文字流的方向,從左到右或從右到左。
影像(Image)
Image部件用於在應用程式中顯示影像。Image部件提供了不同的建構函式來從多個來源載入影像,如下所示:
Image - 使用ImageProvider的通用影像載入器
Image.asset - 從Flutter專案的資源載入影像
Image.file - 從系統資料夾載入影像
Image.memory - 從記憶體載入影像
Image.Network - 從網路載入影像
在Flutter中載入和顯示影像最簡單的選項是將影像作為應用程式的資源,並在需要時將其載入到部件中。
在專案資料夾中建立一個名為assets的資料夾,並將所需的影像放置其中。
在pubspec.yaml中指定資源,如下所示:
flutter:
assets:
- assets/smiley.png
現在,在應用程式中載入並顯示影像。
Image.asset('assets/smiley.png')
下面顯示了Hello World應用程式的MyHomePage部件的完整原始碼和結果。
class MyHomePage extends StatelessWidget {
MyHomePage({Key key, this.title}) : super(key: key);
final String title;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar( title: Text(this.title), ),
body: Center( child: Image.asset("assets/smiley.png")),
);
}
}
載入的影像如下所示:

Image部件最重要的屬性如下:
image,ImageProvider - 要載入的實際影像
width,double - 影像的寬度
height,double - 影像的高度
alignment,AlignmentGeometry - 如何在其邊界內對齊影像
圖示(Icon)
Icon部件用於顯示IconData類中描述的字型中的字形。載入簡單電子郵件圖示的程式碼如下:
Icon(Icons.email)
在Hello World應用程式中應用它的完整原始碼如下:
class MyHomePage extends StatelessWidget {
MyHomePage({Key key, this.title}) : super(key: key);
final String title;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text(this.title),),
body: Center( child: Icon(Icons.email)),
);
}
}
載入的圖示如下所示:
Flutter - 佈局入門
由於Flutter的核心概念是一切皆為部件,因此Flutter將使用者介面佈局功能整合到部件本身。Flutter提供了很多專門設計的部件,例如Container、Center、Align等,僅僅用於佈局使用者介面。透過組合其他部件構建的部件通常使用佈局部件。讓我們在本節中學習Flutter佈局的概念。
佈局部件的型別
根據其子部件,佈局部件可以分為兩類:
- 支援單個子部件的部件
- 支援多個子部件的部件
讓我們在接下來的部分中學習這兩種部件及其功能。
單子部件
在此類別中,部件只有一個部件作為其子部件,並且每個部件都具有特殊的佈局功能。
例如,Center部件只是將其子部件相對於其父部件居中,而Container部件提供了完全的靈活性,可以使用不同的選項(如填充、裝飾等)將其子部件放置在其內部的任何給定位置。
單子部件是建立具有單個功能的高質量部件(如按鈕、標籤等)的絕佳選擇。
使用Container部件建立簡單按鈕的程式碼如下:
class MyButton extends StatelessWidget {
MyButton({Key key}) : super(key: key);
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
decoration: const BoxDecoration(
border: Border(
top: BorderSide(width: 1.0, color: Color(0xFFFFFFFFFF)),
left: BorderSide(width: 1.0, color: Color(0xFFFFFFFFFF)),
right: BorderSide(width: 1.0, color: Color(0xFFFF000000)),
bottom: BorderSide(width: 1.0, color: Color(0xFFFF000000)),
),
),
child: Container(
padding: const
EdgeInsets.symmetric(horizontal: 20.0, vertical: 2.0),
decoration: const BoxDecoration(
border: Border(
top: BorderSide(width: 1.0, color: Color(0xFFFFDFDFDF)),
left: BorderSide(width: 1.0, color: Color(0xFFFFDFDFDF)),
right: BorderSide(width: 1.0, color: Color(0xFFFF7F7F7F)),
bottom: BorderSide(width: 1.0, color: Color(0xFFFF7F7F7F)),
),
color: Colors.grey,
),
child: const Text(
'OK',textAlign: TextAlign.center, style: TextStyle(color: Colors.black)
),
),
);
}
}
這裡,我們使用了兩個部件 - 一個Container部件和一個Text部件。部件的結果是一個自定義按鈕,如下所示:

讓我們檢查一下Flutter提供的一些最重要的單子佈局部件:
Padding - 用於透過給定的填充來排列其子部件。這裡,填充可以透過EdgeInsets類提供。
Align - 使用alignment屬性的值在其內部對齊其子部件。alignment屬性的值可以透過FractionalOffset類提供。FractionalOffset類以距左上角的距離來指定偏移量。
一些可能的偏移量值如下:
FractionalOffset(1.0, 0.0) 表示右上角。
FractionalOffset(0.0, 1.0) 表示左下角。
關於偏移量的示例程式碼如下:
Center(
child: Container(
height: 100.0,
width: 100.0,
color: Colors.yellow, child: Align(
alignment: FractionalOffset(0.2, 0.6),
child: Container( height: 40.0, width:
40.0, color: Colors.red,
),
),
),
)
FittedBox - 它縮放子部件,然後根據指定的適配方式對其進行定位。
AspectRatio - 它嘗試將子部件的大小調整為指定的縱橫比。
ConstrainedBox
Baseline
FractionalSizedBox
IntrinsicHeight
IntrinsicWidth
LimitedBox
OffStage
OverflowBox
SizedBox
SizedOverflowBox
Transform
CustomSingleChildLayout
我們的Hello World應用程式使用基於Material的佈局部件來設計主頁。讓我們修改我們的Hello World應用程式,使用如下指定的基本佈局部件來構建主頁:
Container - 通用、單子、基於框的容器部件,具有對齊、填充、邊框和邊距以及豐富的樣式功能。
Center - 簡單、單子容器部件,將子部件居中。
下面是MyHomePage和MyApp部件的修改後的程式碼:
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MyHomePage(title: "Hello World demo app");
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatelessWidget {
MyHomePage({Key key, this.title}) : super(key: key);
final String title;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
decoration: BoxDecoration(color: Colors.white,),
padding: EdgeInsets.all(25), child: Center(
child:Text(
'Hello World', style: TextStyle(
color: Colors.black, letterSpacing: 0.5, fontSize: 20,
),
textDirection: TextDirection.ltr,
),
)
);
}
}
這裡,
Container部件是頂級或根部件。Container使用decoration和padding屬性配置其內容佈局。
BoxDecoration具有許多屬性,如顏色、邊框等,用於裝飾Container部件,這裡使用color設定容器的顏色。
Container部件的padding透過使用EdgeInsets類設定,該類提供了指定填充值的選項。
Center是Container部件的子部件。同樣,Text是Center部件的子部件。Text用於顯示訊息,Center用於相對於父部件Container居中顯示文字訊息。
上面給出的程式碼的最終結果是一個佈局示例,如下所示:

多子部件
在此類別中,給定部件將有多個子部件,並且每個部件的佈局都是唯一的。
例如,Row部件允許將其子部件水平排列,而Column部件允許將其子部件垂直排列。透過組合Row和Column,可以構建任何複雜程度的部件。
讓我們在本節中學習一些常用的部件。
Row - 允許將其子部件水平排列。
Column - 允許將其子部件垂直排列。
ListView - 允許將其子部件作為列表排列。
GridView - 允許將其子部件作為畫廊排列。
Expanded - 用於使Row和Column部件的子部件佔用最大可能的區域。
Table - 基於表格的部件。
Flow - 基於流的部件。
Stack - 基於堆疊的部件。
高階佈局應用程式
在本節中,讓我們學習如何使用單子佈局部件和多子佈局部件建立具有自定義設計的複雜產品列表使用者介面。
為此,請按照以下順序操作:
在Android Studio中建立一個新的Flutter應用程式product_layout_app。
將main.dart程式碼替換為以下程式碼:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo', theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,),
home: MyHomePage(title: 'Product layout demo home page'),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatelessWidget {
MyHomePage({Key key, this.title}) : super(key: key);
final String title;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text(this.title),),
body: Center(child: Text( 'Hello World', )),
);
}
}
這裡,
我們透過擴充套件StatelessWidget而不是預設的StatefulWidget建立了MyHomePage部件,然後刪除了相關的程式碼。
現在,根據指定的如下所示的設計建立一個新的部件ProductBox:
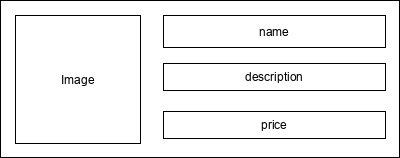
ProductBox的程式碼如下所示。
class ProductBox extends StatelessWidget {
ProductBox({Key key, this.name, this.description, this.price, this.image})
: super(key: key);
final String name;
final String description;
final int price;
final String image;
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(2), height: 120, child: Card(
child: Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly, children: <Widget>[
Image.asset("assets/appimages/" +image), Expanded(
child: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(5), child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: <Widget>[
Text(this.name, style: TextStyle(fontWeight:
FontWeight.bold)), Text(this.description),
Text("Price: " + this.price.toString()),
],
)
)
)
]
)
)
);
}
}
請注意程式碼中的以下內容:
ProductBox使用了四個引數,如下所示:
name - 產品名稱
description - 產品描述
price - 產品價格
image - 產品圖片
ProductBox使用了七個內建部件,如下所示:
- Container
- Expanded
- Row
- Column
- Card
- 文字(Text)
- 影像(Image)
ProductBox使用上述部件進行設計。部件的排列或層次結構在下面所示的圖中指定:
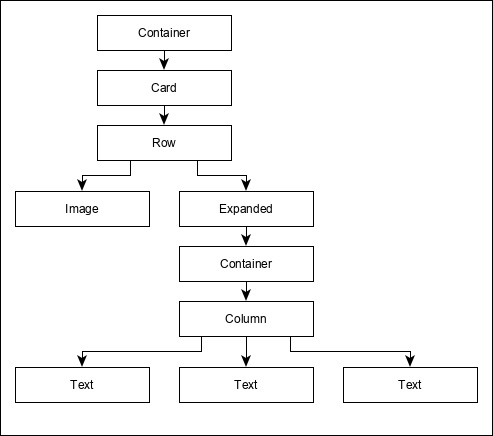
現在,將一些虛擬圖片(見下文)放置到應用程式的assets資料夾中,並在pubspec.yaml檔案中配置assets資料夾,如下所示:
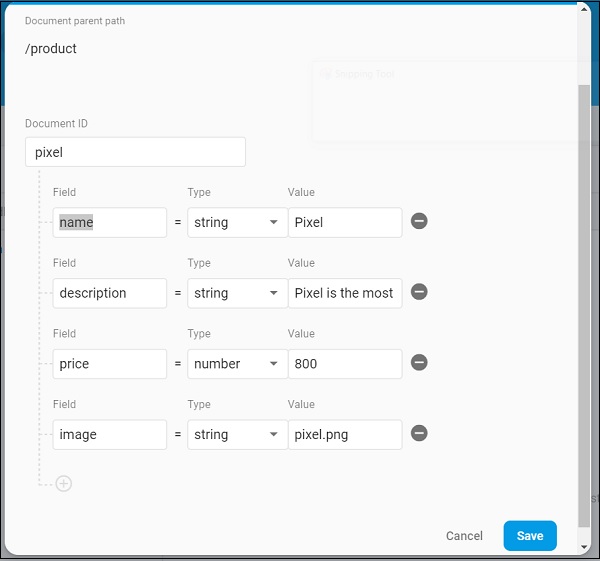
assets: - assets/appimages/floppy.png - assets/appimages/iphone.png - assets/appimages/laptop.png - assets/appimages/pendrive.png - assets/appimages/pixel.png - assets/appimages/tablet.png

iPhone.png
Pixel.png

Laptop.png

Tablet.png

Pendrive.png

Floppy.png
最後,在MyHomePage部件中使用ProductBox部件,如下所示:
class MyHomePage extends StatelessWidget {
MyHomePage({Key key, this.title}) : super(key: key);
final String title;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title:Text("Product Listing")),
body: ListView(
shrinkWrap: true, padding: const EdgeInsets.fromLTRB(2.0, 10.0, 2.0, 10.0),
children: <Widget> [
ProductBox(
name: "iPhone",
description: "iPhone is the stylist phone ever",
price: 1000,
image: "iphone.png"
),
ProductBox(
name: "Pixel",
description: "Pixel is the most featureful phone ever",
price: 800,
image: "pixel.png"
),
ProductBox(
name: "Laptop",
description: "Laptop is most productive development tool",
price: 2000,
image: "laptop.png"
),
ProductBox(
name: "Tablet",
description: "Tablet is the most useful device ever for meeting",
price: 1500,
image: "tablet.png"
),
ProductBox(
name: "Pendrive",
description: "Pendrive is useful storage medium",
price: 100,
image: "pendrive.png"
),
ProductBox(
name: "Floppy Drive",
description: "Floppy drive is useful rescue storage medium",
price: 20,
image: "floppy.png"
),
],
)
);
}
}
這裡,我們使用ProductBox作為ListView部件的子部件。
產品佈局應用程式(product_layout_app)的完整程式碼(main.dart)如下:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo', theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: MyHomePage(title: 'Product layout demo home page'),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatelessWidget {
MyHomePage({Key key, this.title}) : super(key: key);
final String title;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text("Product Listing")),
body: ListView(
shrinkWrap: true,
padding: const EdgeInsets.fromLTRB(2.0, 10.0, 2.0, 10.0),
children: <Widget>[
ProductBox(
name: "iPhone",
description: "iPhone is the stylist phone ever",
price: 1000,
image: "iphone.png"
),
ProductBox(
name: "Pixel",
description: "Pixel is the most featureful phone ever",
price: 800,
image: "pixel.png"
),
ProductBox(
name: "Laptop",
description: "Laptop is most productive development tool",
price: 2000,
image: "laptop.png"
),
ProductBox(
name: "Tablet",
description: "Tablet is the most useful device ever for meeting",
price: 1500,
image: "tablet.png"
),
ProductBox(
name: "Pendrive",
description: "Pendrive is useful storage medium",
price: 100,
image: "pendrive.png"
),
ProductBox(
name: "Floppy Drive",
description: "Floppy drive is useful rescue storage medium",
price: 20,
image: "floppy.png"
),
],
)
);
}
}
class ProductBox extends StatelessWidget {
ProductBox({Key key, this.name, this.description, this.price, this.image}) :
super(key: key);
final String name;
final String description;
final int price;
final String image;
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(2),
height: 120,
child: Card(
child: Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: <Widget>[
Image.asset("assets/appimages/" + image),
Expanded(
child: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(5),
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: <Widget>[
Text(
this.name, style: TextStyle(
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold
)
),
Text(this.description), Text(
"Price: " + this.price.toString()
),
],
)
)
)
]
)
)
);
}
}
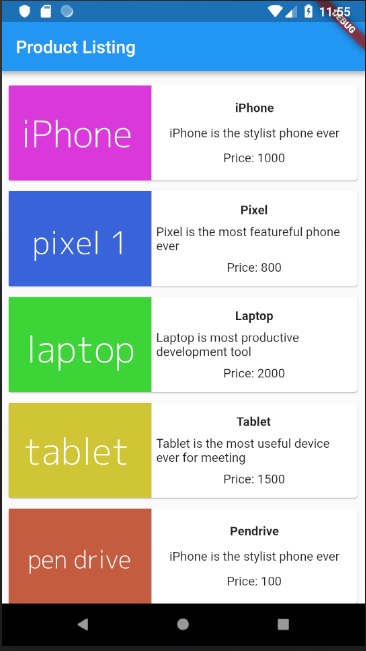
應用程式的最終輸出如下所示:
Flutter - 手勢入門
手勢主要是使用者與移動(或任何基於觸控的裝置)應用程式互動的方式。手勢通常定義為使用者為了啟用移動裝置的特定控制元件而進行的任何物理動作/移動。手勢可以像輕觸移動裝置螢幕一樣簡單,也可以像在遊戲應用程式中使用的更復雜的動作。
這裡提到了一些廣泛使用的手勢:
輕觸(Tap) - 用指尖短暫觸控裝置表面,然後鬆開指尖。
雙擊(Double Tap) - 在短時間內連續點選兩次。
拖動(Drag) - 用指尖觸控裝置表面,然後以穩定的方式移動指尖,最後鬆開指尖。
輕掃(Flick) - 類似於拖動,但以更快的速度進行。
捏合(Pinch) - 使用兩隻手指捏合裝置表面。
散開/縮放(Spread/Zoom) - 捏合的反向操作。
平移 - 用指尖觸碰裝置表面,並在任何方向移動,而不鬆開指尖。
Flutter 透過其獨有的 Widget,GestureDetector,為所有型別的手勢提供了極好的支援。GestureDetector 是一個非視覺 Widget,主要用於檢測使用者的手勢。要識別針對某個 Widget 的手勢,可以將該 Widget 放置在 GestureDetector Widget 內部。GestureDetector 將捕獲手勢並根據手勢分派多個事件。
下面列出了一些手勢及其對應的事件:
- 點選
- onTapDown
- onTapUp
- onTap
- onTapCancel
- 雙擊
- onDoubleTap
- 長按
- onLongPress
- 垂直拖動
- onVerticalDragStart
- onVerticalDragUpdate
- onVerticalDragEnd
- 水平拖動
- onHorizontalDragStart
- onHorizontalDragUpdate
- onHorizontalDragEnd
- 平移
- onPanStart
- onPanUpdate
- onPanEnd
現在,讓我們修改 hello world 應用以包含手勢檢測功能,並嘗試理解這個概念。
將MyHomePage Widget 的主體內容更改為如下所示:
body: Center(
child: GestureDetector(
onTap: () {
_showDialog(context);
},
child: Text( 'Hello World', )
)
),
請注意,在這裡,我們在 Widget 層次結構中將GestureDetector Widget 放置在 Text Widget 上方,捕獲了 onTap 事件,然後最終顯示了一個對話方塊視窗。
實現 *_showDialog* 函式,以便在使用者點選hello world 訊息時顯示對話方塊。它使用通用的showDialog 和AlertDialog Widget 建立一個新的對話方塊 Widget。程式碼如下所示:
// user defined function void _showDialog(BuildContext context) {
// flutter defined function
showDialog(
context: context, builder: (BuildContext context) {
// return object of type Dialog
return AlertDialog(
title: new Text("Message"),
content: new Text("Hello World"),
actions: <Widget>[
new FlatButton(
child: new Text("Close"),
onPressed: () {
Navigator.of(context).pop();
},
),
],
);
},
);
}
應用程式將使用熱過載功能在裝置中重新載入。現在,只需點選訊息“Hello World”,它將顯示如下所示的對話方塊:
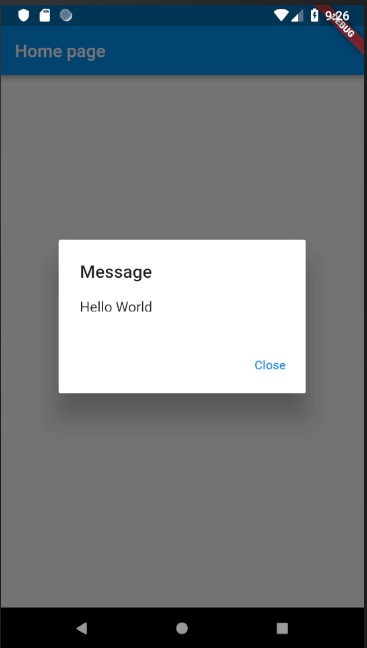
現在,透過點選對話方塊中的關閉選項關閉對話方塊。
完整程式碼(main.dart)如下:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Hello World Demo Application',
theme: ThemeData( primarySwatch: Colors.blue,),
home: MyHomePage(title: 'Home page'),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatelessWidget {
MyHomePage({Key key, this.title}) : super(key: key);
final String title;
// user defined function
void _showDialog(BuildContext context) {
// flutter defined function showDialog(
context: context, builder: (BuildContext context) {
// return object of type Dialog return AlertDialog(
title: new Text("Message"),
content: new Text("Hello World"),
actions: <Widget>[
new FlatButton(
child: new Text("Close"),
onPressed: () {
Navigator.of(context).pop();
},
),
],
);
},
);
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text(this.title),),
body: Center(
child: GestureDetector(
onTap: () {
_showDialog(context);
},
child: Text( 'Hello World', )
)
),
);
}
}
最後,Flutter 還透過Listener Widget 提供了一種低階的手勢檢測機制。它將檢測所有使用者互動,然後分派以下事件:
- PointerDownEvent
- PointerMoveEvent
- PointerUpEvent
- PointerCancelEvent
Flutter 還提供了一小組 Widget 來執行特定以及高階手勢。這些 Widget 列出如下:
Dismissible - 支援輕掃手勢來關閉 Widget。
Draggable - 支援拖動手勢來移動 Widget。
LongPressDraggable - 支援拖動手勢來移動 Widget,當其父 Widget 也可拖動時。
DragTarget - 接受任何Draggable Widget
IgnorePointer - 從手勢檢測過程中隱藏 Widget 及其子元素。
AbsorbPointer - 停止手勢檢測過程本身,因此任何重疊的 Widget 也無法參與手勢檢測過程,因此不會引發任何事件。
Scrollable - 支援滾動 Widget 內可用的內容。
Flutter - 狀態管理
在應用程式中管理狀態是應用程式生命週期中最重要和必要的流程之一。
讓我們考慮一個簡單的購物車應用程式。
使用者將使用其憑據登入應用程式。
使用者登入後,應用程式應在所有螢幕中保留已登入的使用者詳細資訊。
同樣,當用戶選擇產品並將其儲存到購物車中時,購物車資訊應在頁面之間保留,直到使用者結賬。
使用者及其購物車資訊在任何例項中都稱為該例項下應用程式的狀態。
狀態管理可以根據特定狀態在應用程式中持續的時間分為兩類。
短暫的 - 持續幾秒鐘,例如動畫的當前狀態或單個頁面,例如產品的當前評分。Flutter 透過 StatefulWidget 支援它。
應用程式狀態 - 持續整個應用程式,例如已登入的使用者詳細資訊、購物車資訊等。Flutter 透過 scoped_model 支援它。
導航和路由
在任何應用程式中,從一個頁面/螢幕導航到另一個頁面/螢幕定義了應用程式的工作流程。處理應用程式導航的方式稱為路由。Flutter 提供了一個基本的路由類 - MaterialPageRoute 和兩個方法 - Navigator.push 和 Navigator.pop,來定義應用程式的工作流程。
MaterialPageRoute
MaterialPageRoute 是一個 Widget,用於透過用特定於平臺的動畫替換整個螢幕來呈現其 UI。
MaterialPageRoute(builder: (context) => Widget())
在這裡,builder 將接受一個函式來構建其內容,方法是提供應用程式的當前上下文。
Navigation.push
Navigation.push 用於使用 MaterialPageRoute Widget 導航到新螢幕。
Navigator.push( context, MaterialPageRoute(builder: (context) => Widget()), );
Navigation.pop
Navigation.pop 用於導航到上一個螢幕。
Navigator.pop(context);
讓我們建立一個新的應用程式來更好地理解導航概念。
在 Android Studio 中建立一個新的 Flutter 應用程式,product_nav_app
將 assets 資料夾從 product_nav_app 複製到 product_state_app,並在 pubspec.yaml 檔案中新增 assets。
flutter: assets: - assets/appimages/floppy.png - assets/appimages/iphone.png - assets/appimages/laptop.png - assets/appimages/pendrive.png - assets/appimages/pixel.png - assets/appimages/tablet.png
將預設啟動程式碼(main.dart)替換為我們的啟動程式碼。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: MyHomePage(
title: 'Product state demo home page'
),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatelessWidget {
MyHomePage({Key key, this.title}) : super(key: key);
final String title;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text(this.title),
),
body: Center(
child: Text('Hello World',)
),
);
}
}
讓我們建立一個 Product 類來組織產品資訊。
class Product {
final String name;
final String description;
final int price;
final String image;
Product(this.name, this.description, this.price, this.image);
}
讓我們在 Product 類中編寫一個 getProducts 方法來生成我們的虛擬產品記錄。
static List<Product> getProducts() {
List<Product> items = <Product>[];
items.add(
Product(
"Pixel",
"Pixel is the most feature-full phone ever", 800,
"pixel.png"
)
);
items.add(
Product(
"Laptop",
"Laptop is most productive development tool",
2000, "
laptop.png"
)
);
items.add(
Product(
"Tablet",
"Tablet is the most useful device ever for meeting",
1500,
"tablet.png"
)
);
items.add(
Product(
"Pendrive",
"Pendrive is useful storage medium",
100,
"pendrive.png"
)
);
items.add(
Product(
"Floppy Drive",
"Floppy drive is useful rescue storage medium",
20,
"floppy.png"
)
);
return items;
}
import product.dart in main.dart
import 'Product.dart';
讓我們包含我們的新 Widget,RatingBox。
class RatingBox extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_RatingBoxState createState() =>_RatingBoxState();
}
class _RatingBoxState extends State<RatingBox> {
int _rating = 0;
void _setRatingAsOne() {
setState(() {
_rating = 1;
});
}
void _setRatingAsTwo() {
setState(() {
_rating = 2;
});
}
void _setRatingAsThree() {
setState(() {
_rating = 3;
});
}
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
double _size = 20;
print(_rating);
return Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.end,
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.end,
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.max,
children: <Widget>[
Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: IconButton(
icon: (
_rating >= 1?
Icon(
Icons.star,
size: _size,
)
: Icon(
Icons.star_border,
size: _size,
)
),
color: Colors.red[500],
onPressed: _setRatingAsOne,
iconSize: _size,
),
),
Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: IconButton(
icon: (
_rating >= 2?
Icon(
Icons.star,
size: _size,
)
: Icon(
Icons.star_border,
size: _size,
)
),
color: Colors.red[500],
onPressed: _setRatingAsTwo,
iconSize: _size,
),
),
Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: IconButton(
icon: (
_rating >= 3 ?
Icon(
Icons.star,
size: _size,
)
: Icon(
Icons.star_border,
size: _size,
)
),
color: Colors.red[500],
onPressed: _setRatingAsThree,
iconSize: _size,
),
),
],
);
}
}
讓我們修改我們的 ProductBox Widget 以與我們的新 Product 類一起使用。
class ProductBox extends StatelessWidget {
ProductBox({Key key, this.item}) : super(key: key);
final Product item;
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(2),
height: 140,
child: Card(
child: Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: <Widget>[
Image.asset("assets/appimages/" + this.item.image),
Expanded(
child: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(5),
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: <Widget>[
Text(this.item.name,
style: TextStyle(fontWeight: FontWeight.bold)),
Text(this.item.description),
Text("Price: " + this.item.price.toString()),
RatingBox(),
],
)
)
)
]
),
)
);
}
}
讓我們重寫我們的 MyHomePage Widget 以與 Product 模型一起使用,並使用 ListView 列出所有產品。
class MyHomePage extends StatelessWidget {
MyHomePage({Key key, this.title}) : super(key: key);
final String title;
final items = Product.getProducts();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold( appBar: AppBar(title: Text("Product Navigation")),
body: ListView.builder(
itemCount: items.length,
itemBuilder: (context, index) {
return GestureDetector(
child: ProductBox(item: items[index]),
onTap: () {
Navigator.push(
context, MaterialPageRoute(
builder: (context) => ProductPage(item: items[index]),
),
);
},
);
},
));
}
}
在這裡,我們使用了 MaterialPageRoute 導航到產品詳細資訊頁面。
現在,讓我們新增 ProductPage 來顯示產品詳細資訊。
class ProductPage extends StatelessWidget {
ProductPage({Key key, this.item}) : super(key: key);
final Product item;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text(this.item.name),
),
body: Center(
child: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.start,
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: <Widget>[
Image.asset("assets/appimages/" + this.item.image),
Expanded(
child: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(5),
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: <Widget>[
Text(
this.item.name, style: TextStyle(
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold
)
),
Text(this.item.description),
Text("Price: " + this.item.price.toString()),
RatingBox(),
],
)
)
)
]
),
),
),
);
}
}
應用程式的完整程式碼如下:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class Product {
final String name;
final String description;
final int price;
final String image;
Product(this.name, this.description, this.price, this.image);
static List<Product> getProducts() {
List<Product> items = <Product>[];
items.add(
Product(
"Pixel",
"Pixel is the most featureful phone ever",
800,
"pixel.png"
)
);
items.add(
Product(
"Laptop",
"Laptop is most productive development tool",
2000,
"laptop.png"
)
);
items.add(
Product(
"Tablet",
"Tablet is the most useful device ever for meeting",
1500,
"tablet.png"
)
);
items.add(
Product(
"Pendrive",
"iPhone is the stylist phone ever",
100,
"pendrive.png"
)
);
items.add(
Product(
"Floppy Drive",
"iPhone is the stylist phone ever",
20,
"floppy.png"
)
);
items.add(
Product(
"iPhone",
"iPhone is the stylist phone ever",
1000,
"iphone.png"
)
);
return items;
}
}
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: MyHomePage(title: 'Product Navigation demo home page'),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatelessWidget {
MyHomePage({Key key, this.title}) : super(key: key);
final String title;
final items = Product.getProducts();
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text("Product Navigation")),
body: ListView.builder(
itemCount: items.length,
itemBuilder: (context, index) {
return GestureDetector(
child: ProductBox(item: items[index]),
onTap: () {
Navigator.push(
context,
MaterialPageRoute(
builder: (context) => ProductPage(item: items[index]),
),
);
},
);
},
)
);
}
}
class ProductPage extends StatelessWidget {
ProductPage({Key key, this.item}) : super(key: key);
final Product item;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text(this.item.name),
),
body: Center(
child: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.start,
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.start,
children: <Widget>[
Image.asset("assets/appimages/" + this.item.image),
Expanded(
child: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(5),
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: <Widget>[
Text(this.item.name, style: TextStyle(fontWeight: FontWeight.bold)),
Text(this.item.description),
Text("Price: " + this.item.price.toString()),
RatingBox(),
],
)
)
)
]
),
),
),
);
}
}
class RatingBox extends StatefulWidget {
@override
_RatingBoxState createState() => _RatingBoxState();
}
class _RatingBoxState extends State<RatingBox> {
int _rating = 0;
void _setRatingAsOne() {
setState(() {
_rating = 1;
});
}
void _setRatingAsTwo() {
setState(() {
_rating = 2;
});
}
void _setRatingAsThree() {
setState(() {
_rating = 3;
});
}
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
double _size = 20;
print(_rating);
return Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.end,
crossAxisAlignment: CrossAxisAlignment.end,
mainAxisSize: MainAxisSize.max,
children: <Widget>[
Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: IconButton(
icon: (
_rating >= 1 ? Icon(
Icons.star,
size: _size,
)
: Icon(
Icons.star_border,
size: _size,
)
),
color: Colors.red[500],
onPressed: _setRatingAsOne,
iconSize: _size,
),
),
Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: IconButton(
icon: (
_rating >= 2 ?
Icon(
Icons.star,
size: _size,
)
: Icon(
Icons.star_border,
size: _size,
)
),
color: Colors.red[500],
onPressed: _setRatingAsTwo,
iconSize: _size,
),
),
Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(0),
child: IconButton(
icon: (
_rating >= 3 ?
Icon(
Icons.star,
size: _size,
)
: Icon(
Icons.star_border,
size: _size,
)
),
color: Colors.red[500],
onPressed: _setRatingAsThree,
iconSize: _size,
),
),
],
);
}
}
class ProductBox extends StatelessWidget {
ProductBox({Key key, this.item}) : super(key: key);
final Product item;
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(2),
height: 140,
child: Card(
child: Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: <Widget>[
Image.asset("assets/appimages/" + this.item.image),
Expanded(
child: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(5),
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: <Widget>[
Text(this.item.name, style: TextStyle(fontWeight: FontWeight.bold)), Text(this.item.description),
Text("Price: " + this.item.price.toString()),
RatingBox(),
],
)
)
)
]
),
)
);
}
}
執行應用程式並點選任意一個產品專案。它將顯示相關的詳細資訊頁面。我們可以透過點選後退按鈕移動到主頁。應用程式的產品列表頁面和產品詳細資訊頁面如下所示:

Flutter - 動畫
動畫是任何移動應用程式中一個複雜的流程。儘管其複雜性,動畫將使用者體驗提升到一個新的水平,並提供豐富的使用者互動。由於其豐富性,動畫成為現代移動應用程式不可或缺的一部分。Flutter 框架認識到動畫的重要性,並提供了一個簡單直觀的框架來開發所有型別的動畫。
簡介
動畫是在特定持續時間內按特定順序顯示一系列影像/圖片的過程,以產生運動的錯覺。動畫最重要的方面如下:
動畫有兩個不同的值:起始值和結束值。動畫從起始值開始,經過一系列中間值,最後以結束值結束。例如,要使 Widget 淡出,初始值將是完全不透明,最終值將是零不透明。
中間值可以是線性的或非線性的(曲線)的,並且可以進行配置。瞭解動畫按其配置方式工作。每個配置都會為動畫提供不同的感覺。例如,使 Widget 淡出將是線性的,而球的彈跳將是非線性的。
動畫過程的持續時間會影響動畫的速度(緩慢或快速)。
控制動畫過程的能力,例如啟動動畫、停止動畫、重複動畫特定次數、反轉動畫過程等。
在 Flutter 中,動畫系統不會執行任何真實的動畫。相反,它僅提供每幀渲染影像所需的 value。
基於動畫的類
Flutter 動畫系統基於 Animation 物件。核心動畫類及其用法如下:
Animation
在特定持續時間內生成兩個數字之間的插值 value。最常見的 Animation 類如下:
Animation<double> - 在兩個十進位制數字之間插值 value
Animation<Color> - 在兩種顏色之間插值顏色
Animation<Size> - 在兩種尺寸之間插值尺寸
AnimationController - 用於控制動畫本身的特殊 Animation 物件。每當應用程式準備好新幀時,它都會生成新的 value。它支援基於線性的動畫,並且 value 從 0.0 開始到 1.0 結束
controller = AnimationController(duration: const Duration(seconds: 2), vsync: this);
在這裡,controller 控制動畫,duration 選項控制動畫過程的持續時間。vsync 是一個用於最佳化動畫中使用的資源的特殊選項。
CurvedAnimation
類似於 AnimationController,但支援非線性動畫。CurvedAnimation 可以與 Animation 物件一起使用,如下所示:
controller = AnimationController(duration: const Duration(seconds: 2), vsync: this); animation = CurvedAnimation(parent: controller, curve: Curves.easeIn)
Tween<T>
派生自 Animatable<T>,用於生成除 0 和 1 之外的任何兩個數字之間的數字。它可以透過使用 animate 方法並將實際的 Animation 物件傳遞給它來與 Animation 物件一起使用。
AnimationController controller = AnimationController( duration: const Duration(milliseconds: 1000), vsync: this); Animation<int> customTween = IntTween( begin: 0, end: 255).animate(controller);
Tween 也可以與 CurvedAnimation 一起使用,如下所示:
AnimationController controller = AnimationController( duration: const Duration(milliseconds: 500), vsync: this); final Animation curve = CurvedAnimation(parent: controller, curve: Curves.easeOut); Animation<int> customTween = IntTween(begin: 0, end: 255).animate(curve);
在這裡,controller 是實際的動畫控制器。curve 提供非線性的型別,customTween 提供從 0 到 255 的自定義範圍。
Flutter 動畫的工作流程
動畫的工作流程如下:
在 StatefulWidget 的 initState 中定義並啟動動畫控制器。
AnimationController(duration: const Duration(seconds: 2), vsync: this); animation = Tween<double>(begin: 0, end: 300).animate(controller); controller.forward();
新增基於動畫的監聽器,addListener 來更改 Widget 的狀態。
animation = Tween<double>(begin: 0, end: 300).animate(controller) ..addListener(() {
setState(() {
// The state that has changed here is the animation object’s value.
});
});
內建 Widget,AnimatedWidget 和 AnimatedBuilder 可以用來跳過此過程。這兩個 Widget 都接受 Animation 物件並獲取動畫所需的當前 value。
在 Widget 的構建過程中獲取動畫 value,然後將其應用於寬度、高度或任何相關屬性,而不是原始 value。
child: Container( height: animation.value, width: animation.value, child: <Widget>, )
工作應用程式
讓我們編寫一個簡單的基於動畫的應用程式,以瞭解 Flutter 框架中動畫的概念。
在 Android Studio 中建立一個新的Flutter 應用程式,product_animation_app。
將 assets 資料夾從 product_nav_app 複製到 product_animation_app,並在 pubspec.yaml 檔案中新增 assets。
flutter: assets: - assets/appimages/floppy.png - assets/appimages/iphone.png - assets/appimages/laptop.png - assets/appimages/pendrive.png - assets/appimages/pixel.png - assets/appimages/tablet.png
刪除預設啟動程式碼(main.dart)。
新增匯入和基本 main 函式。
import 'package:flutter/material.dart'; void main() => runApp(MyApp());
建立從 StatefulWidgtet 派生的 MyApp Widget。
class MyApp extends StatefulWidget {
_MyAppState createState() => _MyAppState();
}
建立 _MyAppState Widget 並實現 initState 和 dispose,以及預設的 build 方法。
class _MyAppState extends State<MyApp> with SingleTickerProviderStateMixin {
Animation<double> animation;
AnimationController controller;
@override void initState() {
super.initState();
controller = AnimationController(
duration: const Duration(seconds: 10), vsync: this
);
animation = Tween<double>(begin: 0.0, end: 1.0).animate(controller);
controller.forward();
}
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
controller.forward();
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(primarySwatch: Colors.blue,),
home: MyHomePage(title: 'Product layout demo home page', animation: animation,)
);
}
@override
void dispose() {
controller.dispose();
super.dispose();
}
}
這裡,
在 initState 方法中,我們建立了一個動畫控制器物件(controller),一個動畫物件(animation)並使用 controller.forward 啟動了動畫。
在 dispose 方法中,我們處置了動畫控制器物件(controller)。
在 build 方法中,透過建構函式將動畫傳送到 MyHomePage Widget。現在,MyHomePage Widget 可以使用動畫物件來為其內容設定動畫。
現在,新增 ProductBox Widget
class ProductBox extends StatelessWidget {
ProductBox({Key key, this.name, this.description, this.price, this.image})
: super(key: key);
final String name;
final String description;
final int price;
final String image;
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(2),
height: 140,
child: Card(
child: Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: <Widget>[
Image.asset("assets/appimages/" + image),
Expanded(
child: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(5),
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: <Widget>[
Text(this.name, style:
TextStyle(fontWeight: FontWeight.bold)),
Text(this.description),
Text("Price: " + this.price.toString()),
],
)
)
)
]
)
)
);
}
}
建立一個新的 Widget,MyAnimatedWidget,使用不透明度執行簡單的淡入淡出動畫。
class MyAnimatedWidget extends StatelessWidget {
MyAnimatedWidget({this.child, this.animation});
final Widget child;
final Animation<double> animation;
Widget build(BuildContext context) => Center(
child: AnimatedBuilder(
animation: animation,
builder: (context, child) => Container(
child: Opacity(opacity: animation.value, child: child),
),
child: child),
);
}
在這裡,我們使用了 AniatedBuilder 來執行我們的動畫。AnimatedBuilder 是一個 Widget,它在執行動畫的同時構建其內容。它接受一個 animation 物件來獲取當前動畫 value。我們使用了動畫 value,animation.value 來設定子 Widget 的不透明度。實際上,Widget 將使用不透明度概念為子 Widget 設定動畫。
最後,建立 MyHomePage Widget 並使用動畫物件為其任何內容設定動畫。
class MyHomePage extends StatelessWidget {
MyHomePage({Key key, this.title, this.animation}) : super(key: key);
final String title;
final Animation<double>
animation;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text("Product Listing")),body: ListView(
shrinkWrap: true,
padding: const EdgeInsets.fromLTRB(2.0, 10.0, 2.0, 10.0),
children: <Widget>[
FadeTransition(
child: ProductBox(
name: "iPhone",
description: "iPhone is the stylist phone ever",
price: 1000,
image: "iphone.png"
), opacity: animation
),
MyAnimatedWidget(child: ProductBox(
name: "Pixel",
description: "Pixel is the most featureful phone ever",
price: 800,
image: "pixel.png"
), animation: animation),
ProductBox(
name: "Laptop",
description: "Laptop is most productive development tool",
price: 2000,
image: "laptop.png"
),
ProductBox(
name: "Tablet",
description: "Tablet is the most useful device ever for meeting",
price: 1500,
image: "tablet.png"
),
ProductBox(
name: "Pendrive",
description: "Pendrive is useful storage medium",
price: 100,
image: "pendrive.png"
),
ProductBox(
name: "Floppy Drive",
description: "Floppy drive is useful rescue storage medium",
price: 20,
image: "floppy.png"
),
],
)
);
}
}
在這裡,我們使用了 FadeAnimation 和 MyAnimationWidget 為列表中的前兩個專案設定動畫。FadeAnimation 是一個內建動畫類,我們使用它來使用不透明度概念為其子元素設定動畫。
完整程式碼如下:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatefulWidget {
_MyAppState createState() => _MyAppState();
}
class _MyAppState extends State<MyApp> with SingleTickerProviderStateMixin {
Animation<double> animation;
AnimationController controller;
@override
void initState() {
super.initState();
controller = AnimationController(
duration: const Duration(seconds: 10), vsync: this);
animation = Tween<double>(begin: 0.0, end: 1.0).animate(controller);
controller.forward();
}
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
controller.forward();
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo', theme: ThemeData(primarySwatch: Colors.blue,),
home: MyHomePage(title: 'Product layout demo home page', animation: animation,)
);
}
@override
void dispose() {
controller.dispose();
super.dispose();
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatelessWidget {
MyHomePage({Key key, this.title, this.animation}): super(key: key);
final String title;
final Animation<double> animation;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(title: Text("Product Listing")),
body: ListView(
shrinkWrap: true,
padding: const EdgeInsets.fromLTRB(2.0, 10.0, 2.0, 10.0),
children: <Widget>[
FadeTransition(
child: ProductBox(
name: "iPhone",
description: "iPhone is the stylist phone ever",
price: 1000,
image: "iphone.png"
),
opacity: animation
),
MyAnimatedWidget(
child: ProductBox(
name: "Pixel",
description: "Pixel is the most featureful phone ever",
price: 800,
image: "pixel.png"
),
animation: animation
),
ProductBox(
name: "Laptop",
description: "Laptop is most productive development tool",
price: 2000,
image: "laptop.png"
),
ProductBox(
name: "Tablet",
description: "Tablet is the most useful device ever for meeting",
price: 1500,
image: "tablet.png"
),
ProductBox(
name: "Pendrive",
description: "Pendrive is useful storage medium",
price: 100,
image: "pendrive.png"
),
ProductBox(
name: "Floppy Drive",
description: "Floppy drive is useful rescue storage medium",
price: 20,
image: "floppy.png"
),
],
)
);
}
}
class ProductBox extends StatelessWidget {
ProductBox({Key key, this.name, this.description, this.price, this.image}) :
super(key: key);
final String name;
final String description;
final int price;
final String image;
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(2),
height: 140,
child: Card(
child: Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: <Widget>[
Image.asset("assets/appimages/" + image),
Expanded(
child: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(5),
child: Column(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: <Widget>[
Text(
this.name, style: TextStyle(
fontWeight: FontWeight.bold
)
),
Text(this.description), Text(
"Price: " + this.price.toString()
),
],
)
)
)
]
)
)
);
}
}
class MyAnimatedWidget extends StatelessWidget {
MyAnimatedWidget({this.child, this.animation});
final Widget child;
final Animation<double> animation;
Widget build(BuildContext context) => Center(
child: AnimatedBuilder(
animation: animation,
builder: (context, child) => Container(
child: Opacity(opacity: animation.value, child: child),
),
child: child
),
);
}
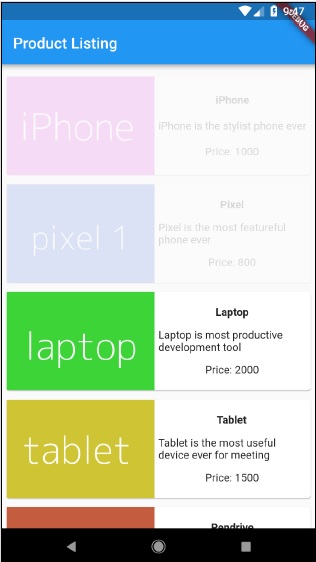
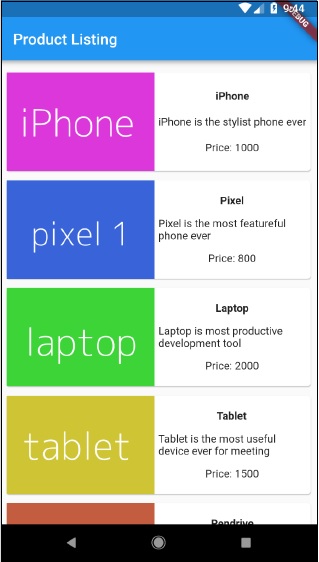
編譯並執行應用程式以檢視結果。應用程式的初始版本和最終版本如下所示:
Flutter - 編寫 Android 特定程式碼
Flutter 提供了一個通用框架來訪問平臺特定的功能。這使開發人員能夠使用平臺特定的程式碼擴充套件Flutter框架的功能。可以透過該框架輕鬆訪問平臺特定的功能,例如相機、電池電量、瀏覽器等。
訪問平臺特定程式碼的總體思路是透過簡單的訊息傳遞協議。Flutter 程式碼(客戶端)和平臺程式碼(主機)繫結到一個通用的訊息通道。客戶端透過訊息通道向主機發送訊息。主機監聽訊息通道,接收訊息並執行必要的功能,最後透過訊息通道將結果返回給客戶端。
平臺特定程式碼架構如下圖所示:
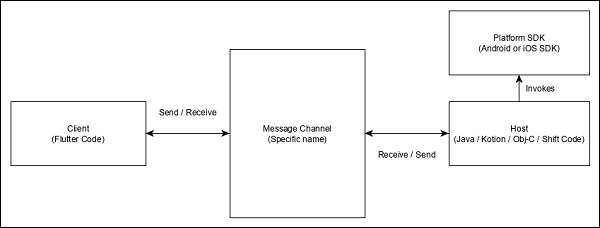
訊息傳遞協議使用標準訊息編解碼器(StandardMessageCodec 類),該編解碼器支援 JSON 類值的二進位制序列化,例如數字、字串、布林值等。序列化和反序列化在客戶端和主機之間透明地工作。
讓我們編寫一個簡單的應用程式,使用Android SDK開啟瀏覽器,並瞭解如何
在 Android Studio 中建立一個新的 Flutter 應用程式,flutter_browser_app
將 main.dart 程式碼替換為以下程式碼:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: MyHomePage(title: 'Flutter Demo Home Page'),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatelessWidget {
MyHomePage({Key key, this.title}) : super(key: key);
final String title;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text(this.title),
),
body: Center(
child: RaisedButton(
child: Text('Open Browser'),
onPressed: null,
),
),
);
}
}
在這裡,我們建立了一個新的按鈕來開啟瀏覽器,並將它的 onPressed 方法設定為 null。
現在,匯入以下包:
import 'dart:async'; import 'package:flutter/services.dart';
在這裡,services.dart 包含呼叫平臺特定程式碼的功能。
在 MyHomePage 小部件中建立一個新的訊息通道。
static const platform = const
MethodChannel('flutterapp.tutorialspoint.com/browser');
編寫一個方法 _openBrowser 來透過訊息通道呼叫平臺特定方法 openBrowser 方法。
Future<void> _openBrowser() async {
try {
final int result = await platform.invokeMethod(
'openBrowser', <String, String>{
'url': "https://flutter.club.tw"
}
);
}
on PlatformException catch (e) {
// Unable to open the browser
print(e);
}
}
在這裡,我們使用 platform.invokeMethod 呼叫 openBrowser(將在後續步驟中解釋)。openBrowser 有一個引數 url,用於開啟特定的 URL。
將 RaisedButton 的 onPressed 屬性的值從 null 更改為 _openBrowser。
onPressed: _openBrowser,
開啟 MainActivity.java(在 android 資料夾內)並匯入所需的庫:
import android.app.Activity; import android.content.Intent; import android.net.Uri; import android.os.Bundle; import io.flutter.app.FlutterActivity; import io.flutter.plugin.common.MethodCall; import io.flutter.plugin.common.MethodChannel; import io.flutter.plugin.common.MethodChannel.MethodCallHandler; import io.flutter.plugin.common.MethodChannel.Result; import io.flutter.plugins.GeneratedPluginRegistrant;
編寫一個方法 openBrowser 來開啟瀏覽器
private void openBrowser(MethodCall call, Result result, String url) {
Activity activity = this;
if (activity == null) {
result.error("ACTIVITY_NOT_AVAILABLE",
"Browser cannot be opened without foreground
activity", null);
return;
}
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
intent.setData(Uri.parse(url));
activity.startActivity(intent);
result.success((Object) true);
}
現在,在 MainActivity 類中設定通道名稱:
private static final String CHANNEL = "flutterapp.tutorialspoint.com/browser";
編寫 Android 特定的程式碼,在 onCreate 方法中設定訊息處理:
new MethodChannel(getFlutterView(), CHANNEL).setMethodCallHandler(
new MethodCallHandler() {
@Override
public void onMethodCall(MethodCall call, Result result) {
String url = call.argument("url");
if (call.method.equals("openBrowser")) {
openBrowser(call, result, url);
} else {
result.notImplemented();
}
}
});
在這裡,我們使用 MethodChannel 類建立了一個訊息通道,並使用 MethodCallHandler 類來處理訊息。onMethodCall 是實際負責透過檢查訊息來呼叫正確的平臺特定程式碼的方法。onMethodCall 方法從訊息中提取 url,然後僅當方法呼叫為 openBrowser 時才呼叫 openBrowser。否則,它返回 notImplemented 方法。
應用程式的完整原始碼如下:
main.dart
MainActivity.java
package com.tutorialspoint.flutterapp.flutter_browser_app;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Bundle;
import io.flutter.app.FlutterActivity;
import io.flutter.plugin.common.MethodCall;
import io.flutter.plugin.common.MethodChannel.Result;
import io.flutter.plugins.GeneratedPluginRegistrant;
public class MainActivity extends FlutterActivity {
private static final String CHANNEL = "flutterapp.tutorialspoint.com/browser";
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
GeneratedPluginRegistrant.registerWith(this);
new MethodChannel(getFlutterView(), CHANNEL).setMethodCallHandler(
new MethodCallHandler() {
@Override
public void onMethodCall(MethodCall call, Result result) {
String url = call.argument("url");
if (call.method.equals("openBrowser")) {
openBrowser(call, result, url);
} else {
result.notImplemented();
}
}
}
);
}
private void openBrowser(MethodCall call, Result result, String url) {
Activity activity = this; if (activity == null) {
result.error(
"ACTIVITY_NOT_AVAILABLE", "Browser cannot be opened without foreground activity", null
);
return;
}
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
intent.setData(Uri.parse(url));
activity.startActivity(intent);
result.success((Object) true);
}
}
main.dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'dart:async';
import 'package:flutter/services.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: MyHomePage(
title: 'Flutter Demo Home Page'
),
);
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatelessWidget {
MyHomePage({Key key, this.title}) : super(key: key);
final String title;
static const platform = const MethodChannel('flutterapp.tutorialspoint.com/browser');
Future<void> _openBrowser() async {
try {
final int result = await platform.invokeMethod('openBrowser', <String, String>{
'url': "https://flutter.club.tw"
});
}
on PlatformException catch (e) {
// Unable to open the browser print(e);
}
}
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text(this.title),
),
body: Center(
child: RaisedButton(
child: Text('Open Browser'),
onPressed: _openBrowser,
),
),
);
}
}
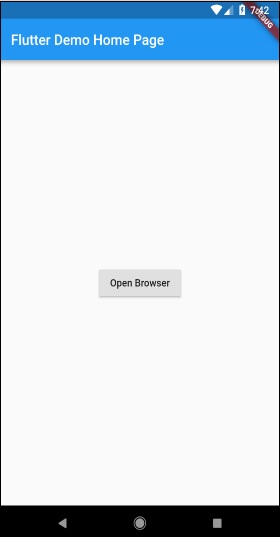
執行應用程式並點選“開啟瀏覽器”按鈕,您會看到瀏覽器已啟動。瀏覽器應用程式 - 首頁如下圖所示:

Flutter - 編寫 iOS 特定程式碼
訪問 iOS 特定程式碼與 Android 平臺類似,只是它使用 iOS 特定的語言 - Objective-C 或 Swift 以及 iOS SDK。否則,概念與 Android 平臺相同。
讓我們為 iOS 平臺編寫與上一章相同的應用程式。
讓我們在 Android Studio(macOS)中建立一個新的應用程式,flutter_browser_ios_app
按照上一章中的步驟 2-6 操作。
啟動 Xcode 並點選檔案 → 開啟
選擇 Flutter 專案 ios 目錄下的 Xcode 專案。
開啟Runner → Runner 路徑下的 AppDelegate.m。它包含以下程式碼:
#include "AppDelegate.h"
#include "GeneratedPluginRegistrant.h"
@implementation AppDelegate
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application
didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions {
// [GeneratedPluginRegistrant registerWithRegistry:self];
// Override point for customization after application launch.
return [super application:application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:launchOptions];
}
@end
我們添加了一個方法 openBrowser,用於使用指定的 url 開啟瀏覽器。它接受單個引數 url。
- (void)openBrowser:(NSString *)urlString {
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:urlString];
UIApplication *application = [UIApplication sharedApplication];
[application openURL:url];
}
在 didFinishLaunchingWithOptions 方法中,找到控制器並將其設定為 controller 變數。
FlutterViewController* controller = (FlutterViewController*)self.window.rootViewController;
在 didFinishLaunchingWithOptions 方法中,將瀏覽器通道設定為 flutterapp.tutorialspoint.com/browse:
FlutterMethodChannel* browserChannel = [ FlutterMethodChannel methodChannelWithName: @"flutterapp.tutorialspoint.com/browser" binaryMessenger:controller];
建立一個變數 weakSelf 並設定當前類:
__weak typeof(self) weakSelf = self;
現在,實現 setMethodCallHandler。透過匹配 call.method 呼叫 openBrowser。透過呼叫 call.arguments 獲取 url,並在呼叫 openBrowser 時傳遞它。
[browserChannel setMethodCallHandler:^(FlutterMethodCall* call, FlutterResult result) {
if ([@"openBrowser" isEqualToString:call.method]) {
NSString *url = call.arguments[@"url"];
[weakSelf openBrowser:url];
} else { result(FlutterMethodNotImplemented); }
}];
完整程式碼如下:
#include "AppDelegate.h"
#include "GeneratedPluginRegistrant.h"
@implementation AppDelegate
- (BOOL)application:(UIApplication *)application
didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:(NSDictionary *)launchOptions {
// custom code starts
FlutterViewController* controller = (FlutterViewController*)self.window.rootViewController;
FlutterMethodChannel* browserChannel = [
FlutterMethodChannel methodChannelWithName:
@"flutterapp.tutorialspoint.com /browser" binaryMessenger:controller];
__weak typeof(self) weakSelf = self;
[browserChannel setMethodCallHandler:^(
FlutterMethodCall* call, FlutterResult result) {
if ([@"openBrowser" isEqualToString:call.method]) {
NSString *url = call.arguments[@"url"];
[weakSelf openBrowser:url];
} else { result(FlutterMethodNotImplemented); }
}];
// custom code ends
[GeneratedPluginRegistrant registerWithRegistry:self];
// Override point for customization after application launch.
return [super application:application didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:launchOptions];
}
- (void)openBrowser:(NSString *)urlString {
NSURL *url = [NSURL URLWithString:urlString];
UIApplication *application = [UIApplication sharedApplication];
[application openURL:url];
}
@end
開啟專案設定。
轉到功能並啟用後臺模式。
新增*後臺獲取和遠端通知**。
現在,執行應用程式。它的工作原理與 Android 版本類似,但將開啟 Safari 瀏覽器而不是 Chrome 瀏覽器。
Flutter - 包入門
Dart 組織和共享一組功能的方式是透過包。Dart 包僅僅是可共享的庫或模組。通常,Dart 包與 Dart 應用程式相同,只是 Dart 包沒有應用程式入口點 main。
包的通用結構(考慮一個演示包 my_demo_package)如下所示:
lib/src/* - 私有 Dart 程式碼檔案。
lib/my_demo_package.dart - 主 Dart 程式碼檔案。它可以像這樣匯入到應用程式中:
import 'package:my_demo_package/my_demo_package.dart'
如果需要,其他私有程式碼檔案可以匯出到主程式碼檔案(my_demo_package.dart)中,如下所示:
export src/my_private_code.dart
lib/* - 任意數量的 Dart 程式碼檔案,以任何自定義資料夾結構排列。程式碼可以這樣訪問:
import 'package:my_demo_package/custom_folder/custom_file.dart'
pubspec.yaml - 專案規範,與應用程式相同。
包中的所有 Dart 程式碼檔案都只是 Dart 類,並且 Dart 程式碼沒有特殊要求才能將其包含在包中。
包的型別
由於 Dart 包基本上是相似功能的小集合,因此可以根據其功能進行分類。
Dart 包
通用 Dart 程式碼,可在 Web 和移動環境中使用。例如,english_words 就是這樣一個包,它包含大約 5000 個單詞,並具有諸如名詞(列出英語中的名詞)、音節(指定單詞中的音節數)等基本實用程式函式。
Flutter 包
通用 Dart 程式碼,依賴於 Flutter 框架,只能在移動環境中使用。例如,fluro 是 Flutter 的自定義路由器。它依賴於 Flutter 框架。
Flutter 外掛
通用 Dart 程式碼,依賴於 Flutter 框架以及底層平臺程式碼(Android SDK 或 iOS SDK)。例如,camera 是一個與裝置相機互動的外掛。它依賴於 Flutter 框架以及底層框架來訪問相機。
使用 Dart 包
Dart 包託管併發布到活動伺服器 https://pub.dartlang.org。此外,Flutter 提供了一個簡單的工具 pub 來管理應用程式中的 Dart 包。使用包所需的步驟如下:
將包名稱和所需的版本包含在 pubspec.yaml 中,如下所示:
dependencies: english_words: ^3.1.5
可以透過檢查線上伺服器找到最新的版本號。
使用以下命令將包安裝到應用程式中:
flutter packages get
在 Android Studio 中開發時,Android Studio 會檢測 pubspec.yaml 中的任何更改,並向開發人員顯示 Android Studio 包警報,如下所示:

可以使用選單選項在 Android Studio 中安裝或更新 Dart 包。
使用以下命令匯入必要的檔案並開始工作:
import 'package:english_words/english_words.dart';
使用包中提供的任何方法:
nouns.take(50).forEach(print);
在這裡,我們使用 nouns 函式獲取並列印前 50 個單詞。
開發 Flutter 外掛包
開發 Flutter 外掛類似於開發 Dart 應用程式或 Dart 包。唯一的例外是外掛將使用系統 API(Android 或 iOS)來獲取所需的平臺特定功能。
正如我們已經在前面的章節中學習瞭如何訪問平臺程式碼,讓我們開發一個簡單的外掛 my_browser 來理解外掛開發過程。my_browser 外掛的功能是允許應用程式在平臺特定的瀏覽器中開啟給定的網站。
啟動 Android Studio。
點選檔案 → 新建 Flutter 專案並選擇 Flutter 外掛選項。
您會看到一個 Flutter 外掛選擇視窗,如下所示:
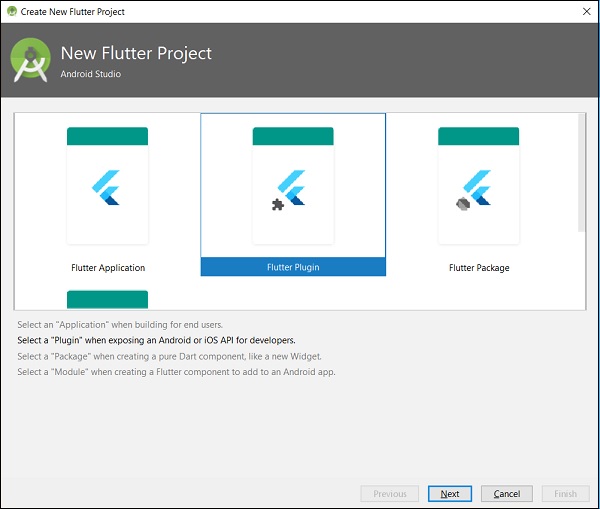
輸入 my_browser 作為專案名稱,然後點選下一步。
在視窗中輸入外掛名稱和其他詳細資訊,如下所示:
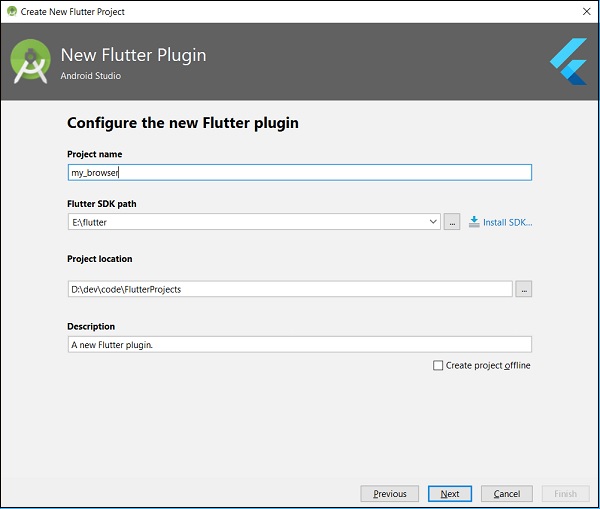
在下面顯示的視窗中輸入公司域名 flutterplugins.tutorialspoint.com,然後點選完成。它將生成一個啟動程式碼來開發我們的新外掛。
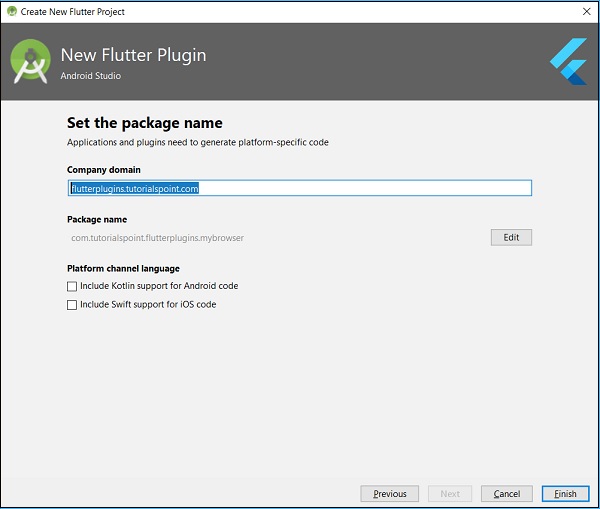
開啟 my_browser.dart 檔案並編寫一個方法 openBrowser 來呼叫平臺特定的 openBrowser 方法。
Future<void> openBrowser(String urlString) async {
try {
final int result = await _channel.invokeMethod(
'openBrowser', <String, String>{ 'url': urlString }
);
}
on PlatformException catch (e) {
// Unable to open the browser print(e);
}
}
開啟 MyBrowserPlugin.java 檔案並匯入以下類:
import android.app.Activity; import android.content.Intent; import android.net.Uri; import android.os.Bundle;
在這裡,我們必須匯入從 Android 開啟瀏覽器所需的庫。
在 MyBrowserPlugin 類中新增新的私有變數 mRegistrar,型別為 Registrar。
private final Registrar mRegistrar;
在這裡,Registrar 用於獲取呼叫程式碼的上下文資訊。
新增一個建構函式,在 MyBrowserPlugin 類中設定 Registrar。
private MyBrowserPlugin(Registrar registrar) {
this.mRegistrar = registrar;
}
更改 registerWith 以在 MyBrowserPlugin 類中包含我們的新建構函式。
public static void registerWith(Registrar registrar) {
final MethodChannel channel = new MethodChannel(registrar.messenger(), "my_browser");
MyBrowserPlugin instance = new MyBrowserPlugin(registrar);
channel.setMethodCallHandler(instance);
}
更改 onMethodCall 以在 MyBrowserPlugin 類中包含 openBrowser 方法。
@Override
public void onMethodCall(MethodCall call, Result result) {
String url = call.argument("url");
if (call.method.equals("getPlatformVersion")) {
result.success("Android " + android.os.Build.VERSION.RELEASE);
}
else if (call.method.equals("openBrowser")) {
openBrowser(call, result, url);
} else {
result.notImplemented();
}
}
編寫平臺特定的 openBrowser 方法以在 MyBrowserPlugin 類中訪問瀏覽器。
private void openBrowser(MethodCall call, Result result, String url) {
Activity activity = mRegistrar.activity();
if (activity == null) {
result.error("ACTIVITY_NOT_AVAILABLE",
"Browser cannot be opened without foreground activity", null);
return;
}
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
intent.setData(Uri.parse(url));
activity.startActivity(intent);
result.success((Object) true);
}
my_browser 外掛的完整原始碼如下:
my_browser.dart
import 'dart:async';
import 'package:flutter/services.dart';
class MyBrowser {
static const MethodChannel _channel = const MethodChannel('my_browser');
static Future<String> get platformVersion async {
final String version = await _channel.invokeMethod('getPlatformVersion'); return version;
}
Future<void> openBrowser(String urlString) async {
try {
final int result = await _channel.invokeMethod(
'openBrowser', <String, String>{'url': urlString});
}
on PlatformException catch (e) {
// Unable to open the browser print(e);
}
}
}
MyBrowserPlugin.java
package com.tutorialspoint.flutterplugins.my_browser;
import io.flutter.plugin.common.MethodCall;
import io.flutter.plugin.common.MethodChannel;
import io.flutter.plugin.common.MethodChannel.MethodCallHandler;
import io.flutter.plugin.common.MethodChannel.Result;
import io.flutter.plugin.common.PluginRegistry.Registrar;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Bundle;
/** MyBrowserPlugin */
public class MyBrowserPlugin implements MethodCallHandler {
private final Registrar mRegistrar;
private MyBrowserPlugin(Registrar registrar) {
this.mRegistrar = registrar;
}
/** Plugin registration. */
public static void registerWith(Registrar registrar) {
final MethodChannel channel = new MethodChannel(
registrar.messenger(), "my_browser");
MyBrowserPlugin instance = new MyBrowserPlugin(registrar);
channel.setMethodCallHandler(instance);
}
@Override
public void onMethodCall(MethodCall call, Result result) {
String url = call.argument("url");
if (call.method.equals("getPlatformVersion")) {
result.success("Android " + android.os.Build.VERSION.RELEASE);
}
else if (call.method.equals("openBrowser")) {
openBrowser(call, result, url);
} else {
result.notImplemented();
}
}
private void openBrowser(MethodCall call, Result result, String url) {
Activity activity = mRegistrar.activity();
if (activity == null) {
result.error("ACTIVITY_NOT_AVAILABLE",
"Browser cannot be opened without foreground activity", null);
return;
}
Intent intent = new Intent(Intent.ACTION_VIEW);
intent.setData(Uri.parse(url));
activity.startActivity(intent);
result.success((Object) true);
}
}
建立一個新專案 my_browser_plugin_test 來測試我們新建立的外掛。
開啟 pubspec.yaml 並將 my_browser 設定為外掛依賴項。
dependencies:
flutter:
sdk: flutter
my_browser:
path: ../my_browser
Android Studio 將提示 pubspec.yaml 已更新,如下面的 Android Studio 包警報所示:

點選獲取依賴項選項。Android Studio 將從 Internet 獲取包併為應用程式正確配置它。
開啟 main.dart 幷包含 my_browser 外掛,如下所示:
import 'package:my_browser/my_browser.dart';
從 my_browser 外掛呼叫 openBrowser 函式,如下所示:
onPressed: () => MyBrowser().openBrowser("https://flutter.club.tw"),
main.dart 的完整程式碼如下:
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:my_browser/my_browser.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: MyHomePage(
title: 'Flutter Demo Home Page'
),
);,
}
}
class MyHomePage extends StatelessWidget {
MyHomePage({Key key, this.title}) : super(key: key);
final String title;
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text(this.title),
),
body: Center(
child: RaisedButton(
child: Text('Open Browser'),
onPressed: () => MyBrowser().openBrowser("https://flutter.club.tw"),
),
),
);
}
}
執行應用程式並點選“開啟瀏覽器”按鈕,您會看到瀏覽器已啟動。您會看到瀏覽器應用程式 - 首頁,如下圖所示:
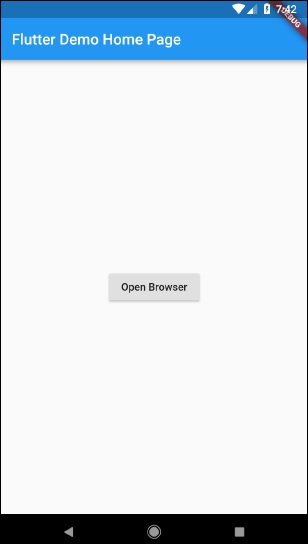
您會看到瀏覽器應用程式 - 瀏覽器螢幕,如下圖所示: