
- 演算法設計與分析
- 首頁
- 演算法基礎
- 演算法導論 - 演算法簡介
- 演算法導論 - 演算法分析
- 演算法導論 - 分析方法
- 演算法導論 - 漸近符號與先驗分析
- 演算法導論 - 時間複雜度
- 演算法導論 - 主定理
- 演算法導論 - 空間複雜度
- 分治法
- 演算法導論 - 分治演算法
- 演算法導論 - 最大最小問題
- 演算法導論 - 歸併排序演算法
- 演算法導論 - Strassen矩陣乘法
- 演算法導論 - Karatsuba演算法
- 演算法導論 - 漢諾塔
- 貪心演算法
- 演算法導論 - 貪心演算法
- 演算法導論 - 旅行商問題
- 演算法導論 - Prim最小生成樹演算法
- 演算法導論 - Kruskal最小生成樹演算法
- 演算法導論 - Dijkstra最短路徑演算法
- 演算法導論 - 地圖著色演算法
- 演算法導論 - 分數揹包問題
- 演算法導論 - 帶截止時間的作業排序
- 演算法導論 - 最優合併模式
- 動態規劃
- 演算法導論 - 動態規劃
- 演算法導論 - 矩陣鏈乘法
- 演算法導論 - Floyd-Warshall演算法
- 演算法導論 - 0-1揹包問題
- 演算法導論 - 最長公共子序列演算法
- 演算法導論 - 使用動態規劃的旅行商問題
- 隨機化演算法
- 演算法導論 - 隨機化演算法
- 演算法導論 - 隨機化快速排序演算法
- 演算法導論 - Karger最小割演算法
- 演算法導論 - Fisher-Yates洗牌演算法
- 近似演算法
- 演算法導論 - 近似演算法
- 演算法導論 - 頂點覆蓋問題
- 演算法導論 - 集合覆蓋問題
- 演算法導論 - 旅行商問題近似演算法
- 排序技術
- 演算法導論 - 氣泡排序演算法
- 演算法導論 - 插入排序演算法
- 演算法導論 - 選擇排序演算法
- 演算法導論 - 希爾排序演算法
- 演算法導論 - 堆排序演算法
- 演算法導論 - 桶排序演算法
- 演算法導論 - 計數排序演算法
- 演算法導論 - 基數排序演算法
- 演算法導論 - 快速排序演算法
- 查詢技術
- 演算法導論 - 查詢技術簡介
- 演算法導論 - 線性查詢
- 演算法導論 - 二分查詢
- 演算法導論 - 插值查詢
- 演算法導論 - 跳躍查詢
- 演算法導論 - 指數查詢
- 演算法導論 - 斐波那契查詢
- 演算法導論 - 子列表查詢
- 演算法導論 - 散列表
- 圖論
- 演算法導論 - 最短路徑
- 演算法導論 - 多階段圖
- 演算法導論 - 最優代價二叉搜尋樹
- 堆演算法
- 演算法導論 - 二叉堆
- 演算法導論 - 插入方法
- 演算法導論 - 堆化方法
- 演算法導論 - 提取方法
- 複雜性理論
- 演算法導論 - 確定性計算與非確定性計算
- 演算法導論 - 最大團
- 演算法導論 - 頂點覆蓋
- 演算法導論 - P類和NP類
- 演算法導論 - Cook定理
- 演算法導論 - NP難和NP完全類
- 演算法導論 - 爬山演算法
- 演算法導論有用資源
- 演算法導論 - 快速指南
- 演算法導論 - 有用資源
- 演算法導論 - 討論
最大團
在一個無向圖中,團是一個給定圖的完全子圖。完全子圖意味著這個子圖的所有頂點都連線到這個子圖的所有其他頂點。
最大團問題是尋找圖的最大團的計算問題。最大團用於許多現實世界的問題。
讓我們考慮一個社交網路應用程式,其中頂點代表人們的個人資料,邊代表圖中的相互認識。在這個圖中,團代表一群彼此都認識的人。
為了找到最大團,可以系統地檢查所有子集,但是這種蠻力搜尋對於包含幾十個以上頂點的網路來說過於耗時。
最大團演算法
尋找圖的最大團的演算法相對簡單。該過程的步驟如下:
步驟1:將一個圖作為演算法的輸入,該圖具有非空的頂點集和邊集。
步驟2:建立一個輸出集,如果邊構成圖的團,則將它們新增到輸出集中。
步驟3:迭代地重複步驟2,直到檢查圖的所有頂點,並且列表不再形成團。
步驟4:然後回溯輸出集以檢查哪個團具有最大邊數。
虛擬碼
Algorithm: Max-Clique (G, n, k)
S := ф
for i = 1 to k do
t := choice (1…n)
if t є S then
return failure
S := S U t
for all pairs (i, j) such that i є S and j є S and i ≠ j do
if (i, j) is not a edge of the graph then
return failure
return success
分析
最大團問題是一個非確定性演算法。在這個演算法中,我們首先嚐試確定一組k個不同的頂點,然後我們嘗試測試這些頂點是否構成一個完全圖。
沒有多項式時間確定性演算法可以解決這個問題。這個問題是NP完全的。
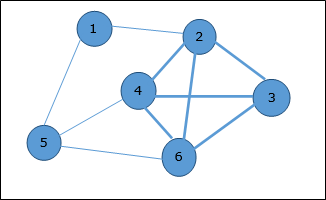
示例
看下面的圖。這裡,包含頂點2、3、4和6的子圖構成一個完全圖。因此,這個子圖是一個團。由於這是所提供圖的最大完全子圖,因此它是一個4-團。
實現
以下是上述方法在各種程式語言中的實現:
#include <stdio.h>
#define MAX 100
int store[MAX], n;
int graph[MAX][MAX];
int d[MAX];
int max(int a, int b){
if(a > b){
return a;
}
else{
return b;
}
}
int is_clique(int b)
{
for (int i = 1; i < b; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < b; j++) {
if (graph[store[i]][store[j]] == 0) {
return 0;
}
}
}
return 1;
}
int maxCliques(int i, int l)
{
int max_ = 0;
for (int j = i + 1; j <= n; j++) {
store[l] = j;
if (is_clique(l + 1)) {
max_ = max(max_, l);
max_ = max(max_, maxCliques(j, l + 1));
}
}
return max_;
}
int main()
{
int edges[][2] = { { 1, 4 }, { 4, 6 }, { 1, 6 },
{ 3, 3 }, { 4, 2 }, { 8, 12 } };
int size = sizeof(edges) / sizeof(edges[0]);
n = 6;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
graph[edges[i][0]][edges[i][1]] = 1;
graph[edges[i][1]][edges[i][0]] = 1;
d[edges[i][0]]++;
d[edges[i][1]]++;
}
printf("Max clique: %d\n", maxCliques(0, 1));
return 0;
}
輸出
Max clique: 3
using namespace std;
#include<iostream>
const int MAX = 100;
// Storing the vertices
int store[MAX], n;
// Graph
int graph[MAX][MAX];
// Degree of the vertices
int d[MAX];
// Function to check if the given set of vertices in store array is a clique or not
bool is_clique(int b)
{
// Run a loop for all set of edges
for (int i = 1; i < b; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < b; j++)
// If any edge is missing
if (graph[store[i]][store[j]] == 0)
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Function to find all the sizes of maximal cliques
int maxCliques(int i, int l)
{
// Maximal clique size
int max_ = 0;
// Check if any vertices from i+1 can be inserted
for (int j = i + 1; j <= n; j++) {
// Add the vertex to store
store[l] = j;
// If the graph is not a clique of size k then
// it cannot be a clique by adding another edge
if (is_clique(l + 1)) {
// Update max
max_ = max(max_, l);
// Check if another edge can be added
max_ = max(max_, maxCliques(j, l + 1));
}
}
return max_;
}
// Driver code
int main()
{
int edges[][2] = { { 1, 4 }, { 4, 6 }, { 1, 6 },
{ 3, 3 }, { 4, 2 }, { 8, 12 } };
int size = sizeof(edges) / sizeof(edges[0]);
n = 6;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
graph[edges[i][0]][edges[i][1]] = 1;
graph[edges[i][1]][edges[i][0]] = 1;
d[edges[i][0]]++;
d[edges[i][1]]++;
}
cout <<"Max clique: "<<maxCliques(0, 1);
return 0;
}
輸出
Max clique: 3
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class MaxCliques {
static final int MAX = 100;
static int[] store = new int[MAX];
static int[][] graph = new int[MAX][MAX];
static int[] d = new int[MAX];
static int n;
// Function to check if the given set of vertices in store array is a clique or not
static boolean isClique(int b) {
for (int i = 1; i < b; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < b; j++)
if (graph[store[i]][store[j]] == 0)
return false;
}
return true;
}
// Function to find all the sizes of maximal cliques
static int maxCliques(int i, int l) {
int max_ = 0;
for (int j = i + 1; j <= n; j++) {
store[l] = j;
if (isClique(l + 1)) {
max_ = Math.max(max_, l);
max_ = Math.max(max_, maxCliques(j, l + 1));
}
}
return max_;
}
// Driver code
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] edges = { { 1, 4 }, { 4, 6 }, { 1, 6 },
{ 3, 3 }, { 4, 2 }, { 8, 12 } };
int size = edges.length;
n = 6;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
graph[edges[i][0]][edges[i][1]] = 1;
graph[edges[i][1]][edges[i][0]] = 1;
d[edges[i][0]]++;
d[edges[i][1]]++;
}
System.out.println("Max cliques: " + maxCliques(0, 1));
}
}
輸出
Max cliques: 3
MAX = 100
# Storing the vertices
store = [0] * MAX
n = 0
# Graph
graph = [[0] * MAX for _ in range(MAX)]
# Degree of the vertices
d = [0] * MAX
# Function to check if the given set of vertices in store array is a clique or not
def is_clique(b):
# Run a loop for all set of edges
for i in range(1, b):
for j in range(i + 1, b):
# If any edge is missing
if graph[store[i]][store[j]] == 0:
return False
return True
# Function to find all the sizes of maximal cliques
def maxCliques(i, l):
# Maximal clique size
max_ = 0
# Check if any vertices from i+1 can be inserted
for j in range(i + 1, n + 1):
# Add the vertex to store
store[l] = j
# If the graph is not a clique of size k then
# it cannot be a clique by adding another edge
if is_clique(l + 1):
# Update max
max_ = max(max_, l)
# Check if another edge can be added
max_ = max(max_, maxCliques(j, l + 1))
return max_
# Driver code
def main():
global n
edges = [(1, 4), (4, 6), (1, 6),
(3, 3), (4, 2), (8, 12)]
size = len(edges)
n = 6
for i in range(size):
graph[edges[i][0]][edges[i][1]] = 1
graph[edges[i][1]][edges[i][0]] = 1
d[edges[i][0]] += 1
d[edges[i][1]] += 1
print("Max cliques:" ,maxCliques(0, 1))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
輸出
Max cliques: 3
廣告
