尤拉路徑與歐拉回路
尤拉路徑是一條路徑,我們可以透過它精確訪問每條邊一次。我們可以多次使用相同的頂點。歐拉回路是一種特殊的尤拉路徑。當尤拉路徑的起始頂點也與該路徑的結束頂點相連時,則稱為歐拉回路。
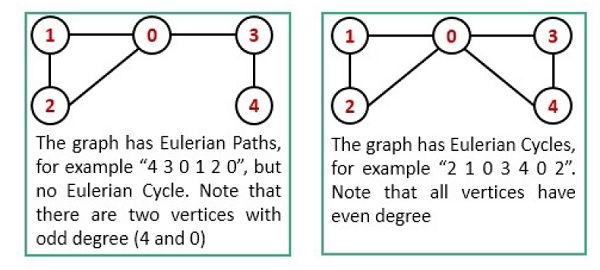
為了檢測路徑和迴路,我們必須遵循以下條件:
- 圖必須是連通的。
- 當恰好有兩個頂點具有奇數度時,它是一條尤拉路徑。
- 現在,當無向圖的任何頂點都沒有奇數度時,它就是一個歐拉回路。
輸入和輸出
Input: Adjacency matrix of a graph. 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 Output: The graph has an Eulerian path.
演算法
traverse(u, visited)
輸入:起始節點 u 和已訪問節點,用於標記哪個節點已被訪問。
輸出:遍歷所有連通頂點。
Begin mark u as visited for all vertex v, if it is adjacent with u, do if v is not visited, then traverse(v, visited) done End
isConnected(graph)
輸入:圖。
輸出:如果圖是連通的,則返回 True。
Begin define visited array for all vertices u in the graph, do make all nodes unvisited traverse(u, visited) if any unvisited node is still remaining, then return false done return true End
isEulerian(Graph)
輸入:給定的圖。
輸出:如果是非尤拉圖則返回 0,如果具有尤拉路徑則返回 1,如果找到歐拉回路則返回 2。
Begin if isConnected() is false, then return false define list of degree for each node oddDegree := 0 for all vertex i in the graph, do for all vertex j which are connected with i, do increase degree done if degree of vertex i is odd, then increase dooDegree done if oddDegree > 2, then return 0 if oddDegree = 0, then return 2 else return 1 End
示例
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#define NODE 5
using namespace std;
int graph[NODE][NODE] = {
{0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 0}
};
/* int graph[NODE][NODE] = {
{0, 1, 1, 1, 1},
{1, 0, 1, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 1},
{1, 0, 0, 1, 0}
};
*/ //uncomment to check Euler Circuit
/* int graph[NODE][NODE] = {
{0, 1, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 0, 1, 1, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 1, 0, 0, 1},
{0, 0, 0, 1, 0}
};
*/ //Uncomment to check Non Eulerian Graph
void traverse(int u, bool visited[]) {
visited[u] = true; //mark v as visited
for(int v = 0; v<NODE; v++) {
if(graph[u][v]) {
if(!visited[v])
traverse(v, visited);
}
}
}
bool isConnected() {
bool *vis = new bool[NODE];
//for all vertex u as start point, check whether all nodes are visible or not
for(int u; u < NODE; u++) {
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++)
vis[i] = false; //initialize as no node is visited
traverse(u, vis);
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++) {
if(!vis[i]) //if there is a node, not visited by traversal, graph is not connected
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
int isEulerian() {
if(isConnected() == false) //when graph is not connected
return 0;
vector<int> degree(NODE, 0);
int oddDegree = 0;
for(int i = 0; i<NODE; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j<NODE; j++) {
if(graph[i][j])
degree[i]++; //increase degree, when connected edge found
}
if(degree[i] % 2 != 0) //when degree of vertices are odd
oddDegree++; //count odd degree vertices
}
if(oddDegree > 2) //when vertices with odd degree greater than 2
return 0;
return (oddDegree)?1:2; //when oddDegree is 0, it is Euler circuit, and when 2, it is Euler path
}
int main() {
int check;
check = isEulerian();
switch(check) {
case 0: cout << "The graph is not an Eulerian graph.";
break;
case 1: cout << "The graph has an Eulerian path.";
break;
case 2: cout << "The graph has a Eulerian circuit.";
break;
}
}輸出
The graph has an Eulerian path.

廣告

 資料結構
資料結構 網路
網路 關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS)
關係資料庫管理系統 (RDBMS) 作業系統
作業系統 Java
Java iOS
iOS HTML
HTML CSS
CSS Android
Android Python
Python C語言程式設計
C語言程式設計 C++
C++ C#
C# MongoDB
MongoDB MySQL
MySQL Javascript
Javascript PHP
PHP